Predicting Mortality in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients Using Big Data and Machine Learning: A Nationwide Study in Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Feature Selection and Data Preprocessing
2.3. Machine Learning Techniques
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
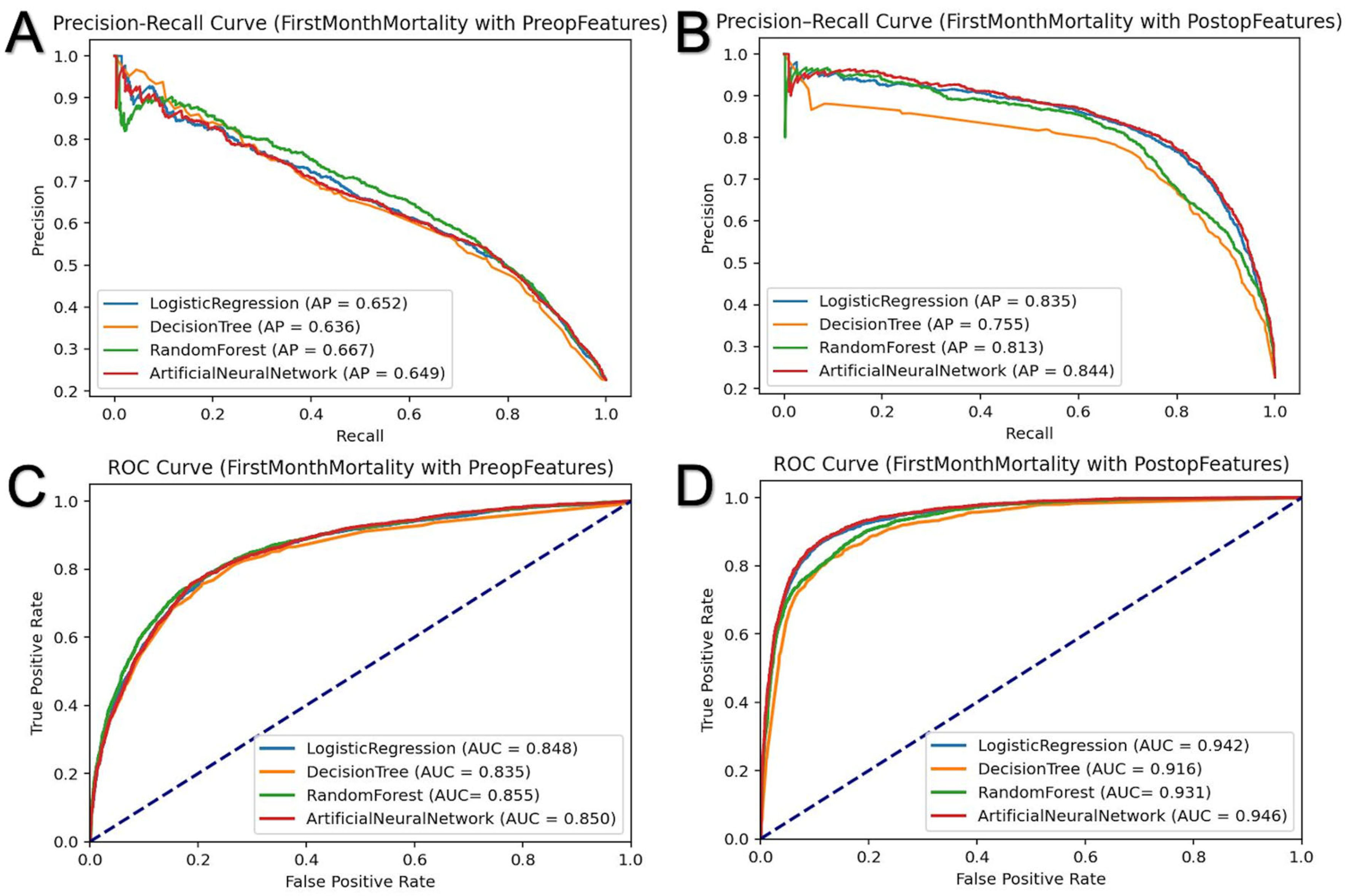
3.2. First-Month Mortality Prediction
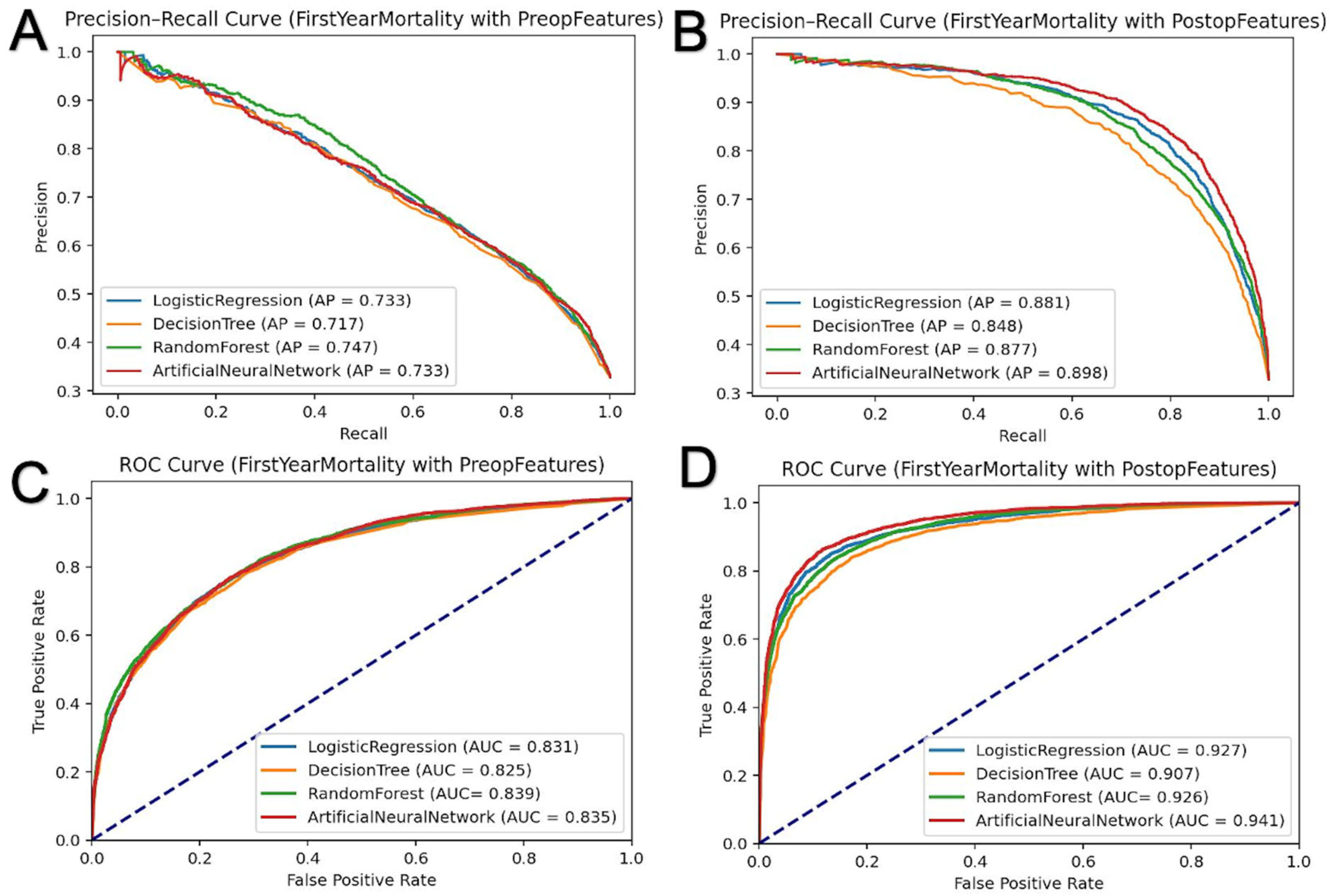
3.3. First-Year Mortality Prediction
3.4. Significance Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ota, N.; Morita, A.; Tominari, S.; Nakayama, T.; Nozaki, K.; Tominaga, T.; Noda, K.; Kamiyama, H.; Tanikawa, R.; on behalf of the Japan Neurosurgical Society for UCAS Japan Investigators. Differences Between Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Seen in Daily Practice and Aneurysms That Rupture During Follow-Up. Stroke 2021, 52, e491–e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, N.; Noda, K.; Chida, D.; Kiko, K.; Miyoshi, N.; Kondo, T.; Haraguchi, K.; Kamiyama, H.; Tokuda, S.; Tanikawa, R. Emergent Subarachnoid Clot Removal with Aneurysm Repair for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Might Improves Clinical Outcome. World Neurosurg. 2022, 167, e100–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanalioglu, S.; Sahin, B.; Sayyahmelli, S.; Ozaydin, B.; Erginoglu, U.; Aycan, A.; Baskaya, M.K. The role of microsurgery for poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhages in the endovascular era. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Q.; Liu, Y.; Leng, B.; Xu, B.; Gu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, W.; Mao, Y. A Prognostic Model for Early Post-Treatment Outcome of Elderly Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2016, 95, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, A.M.; Cwajna, M.; Elfil, M.; Derhab, M.; Desouki, M.T.; Kobeissi, H.; Ghozy, S.; Kallmes, D.F. Impact of frailty on post-operative outcomes following subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 244, 108413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Cai, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G. Predicting the Outcome of Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Machine-Learning-Guided Scorecard. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, G.; Aquarius, R.; Sanaan, B.; Bartels, R.H.M.A.; Grotenhuis, J.A.; Henssen, D.J.H.A.; Boogaarts, H.D. Prediction Models in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Forecasting Clinical Outcome with Artificial Intelligence. Neurosurgery 2021, 88, E427–E434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniyev, T.; Copenhaver, M.S.; Safavi, K.C.; Levi, R. A prescriptive optimization approach to identification of minimal barriers for surgical patients. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, K.C.; Khaniyev, T.; Copenhaver, M.; Seelen, M.; Zenteno Langle, A.C.; Zanger, J.; Daily, B.; Levi, R.; Dunn, P. Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model to Aid Discharge Processes for Inpatient Surgical Care. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1917221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, M.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Tan, X.; Zhao, B. Predicting Long-Term Outcomes After Poor-Grade Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Decision Tree Modeling. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldaner, N.; Zeitlberger, A.M.; Sosnova, M.; Goldberg, J.; Fung, C.; Bervini, D.; May, A.; Bijlenga, P.; Schaller, K.; Roethlisberger, M.; et al. Development of a Complication- and Treatment-Aware Prediction Model for Favorable Functional Outcome in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Based on Machine Learning. Neurosurgery 2021, 88, E150–E157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, D.; Seeberger, M.; Schwedhelm, E.; Czorlich, P.; Goetz, A.E.; Böger, R.H.; Hannemann, J. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginines are Markers of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia and Neurological Outcome in Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2018, 29, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Acharjee, A.; Ament, Z.; Schleicher, R.; Bevers, M.; Stapleton, C.; Patel, A.; Kimberly, W.T. Machine Learning-Driven Metabolomic Evaluation of Cerebrospinal Fluid: Insights into Poor Outcomes After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2021, 88, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, C.J.; Acharjee, A.; Irvine, H.J.; Wolcott, Z.C.; Patel, A.B.; Kimberly, W.T. High-throughput metabolite profiling: Identification of plasma taurine as a potential biomarker of functional outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 133, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Teng, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Tao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.; et al. Predicting who has delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage using machine learning approach: A multicenter, retrospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Souza, N.V.; Rouanet, C.; Solla, D.J.F.; de Lima, C.V.B.; de Souza, C.A.; Rezende, F.; Alves, M.M.; Manuel, A.L.d.O.; Neto, F.C.; Frudit, M.; et al. The Role of VASOGRADE as a Simple Grading Scale to Predict Delayed Cerebral Ischemia and Functional Outcome After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2023, 38, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamout, F.; Zhu, T.; Clifton, D.A. Machine Learning for Clinical Outcome Prediction. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 14, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senders, J.T.; Staples, P.C.; Karhade, A.V.; Zaki, M.M.; Gormley, W.B.; Broekman, M.L.D.; Smith, T.R.; Arnaout, O. Machine Learning and Neurosurgical Outcome Prediction: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, 476–486.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yuan, A.; Yu, D.; Zha, A.; Wu, H. Machine learning to predict mortality for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) using a large nationwide EHR database. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Janzen, I.; Devnath, L.; Khattra, S.; Myers, R.; Lam, S.; MacAulay, C. MA19.11 Predicting Future Lung Cancer Risk with Low-Dose Screening CT Using an Artificial Intelligence Model. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnath, L.; Summons, P.; Luo, S.; Wang, D.; Shaukat, K.; Hameed, I.A.; Aljuaid, H. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis in Chest X-ray Radiographs Using Machine Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichim, C.; Pavel, V.; Mester, P.; Schmid, S.; Todor, S.B.; Stoia, O.; Anderco, P.; Kandulski, A.; Müller, M.; Heumann, P.; et al. Assessing Key Factors Influencing Successful Resuscitation Outcomes in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA). J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warman, A.; Kalluri, A.L.; Azad, T.D. Machine learning predictive models in neurosurgery: An appraisal based on the TRIPOD guidelines. Systematic review. Neurosurg. Focus 2023, 54, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourelo-Fariña, M.; Pértega, S.; Galeiras, R. A Model for Prediction of In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2021, 34, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghistani, T.A.; Elshawi, R.; Sakr, S.; Ahmed, A.M.; Al-Thwayee, A.; Al-Mallah, M.H. Predictors of in-hospital length of stay among cardiac patients: A machine learning approach. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 288, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, J.; Hedberg, J.; Thuresson, M.; Aarskog, P.; Johannesen, K.M.; Oldgren, J. Low-Dose Aspirin Discontinuation and Risk of Cardiovascular Events. Circulation 2017, 136, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charehsaz, A.; Vayisoglu, T.; Uyaniker, Z.A.; Cekic, E.; Ozturk, E.; Isikay, A.I.; Hanalioglu, S. Relative Cortical Atrophy Index as a Strong Predictor of Recurrence After Surgery for Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Neurosurgery 2024, 95, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldeman, M.; Rossmann, T.; Weiss, M.; Conzen-Dilger, C.; Korja, M.; Hoellig, A.; Virta, J.J.; Satopää, J.; Luostarinen, T.; Clusmann, H.; et al. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Hospitalized Patients on Anticoagulants—A Two Center Matched Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbik, F.; Yang, C.; Howard, B.M.; Grossberg, J.A.; Danyluk, L.; Martin, K.S.; Alawieh, A.; Rindler, R.S.; Tong, F.C.; Barrow, D.L.; et al. Delayed Presentations and Worse Outcomes After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in the Early COVID-19 Era. Neurosurgery 2022, 91, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintas, K.; Rohde, S.; Ellrichmann, G.; El-Hamalawi, B.; Sarge, R.; Müller, O. Subarachnoid hemorrhages and aneurysms during the SARS-CoV2-pandemia at a tertiary medical center—Analysis of incidence and outcome. Brain Spine 2023, 3, 101757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Baskett, W.I.; Huang, W.; Shyu, D.; Myers, D.; Lobanova, I.; Ishfaq, M.F.; Naqvi, S.H.; French, B.R.; Siddiq, F.; et al. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and COVID-19: An Analysis of 282,718 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2021, 151, e615–e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.D.; Balabhadra, A.; Otite, F.; Patel, N.; Tunguturi, A.; Bruno, C.; Sussman, E.; Ollenschleger, M.; Alberts, M.J.; Mehta, T. Abstract TP34: Outcomes and Trends of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Stroke 2024, 55, ATP34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Sanchez, J.D.; Perez-Chadid, D.A.; Vargas-Urbina, J.; Zumaeta, J.; Rodriguez, R.R.; Palacios, F.; Flores-Castillo, J. Pandemic impact on aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in Peru’s high COVID-19 lethality setting: A public institutional experience. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2023, 14, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SVIN COVID-19 Global SAH Registry. Global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on subarachnoid haemorrhage hospitalisations, aneurysm treatment and in-hospital mortality: 1-year follow-up. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; He, Z. Characterizing Risk of In-Hospital Mortality Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Machine Learning: A Retrospective Study. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 891984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarraj, J.P.J.; Hergenroeder, G.W.; Zhu, L.; Chang, T.; Park, S.; Megjhani, M.; Vahidy, F.S.; Zhao, Z.; Kitagawa, R.S.; Choi, H.A. Machine Learning to Predict Delayed Cerebral Ischemia and Outcomes in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurology 2021, 96, e553–e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, G.; Su, Z.; Gao, X.; Chen, J.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yan, T.; et al. A Comparison of LASSO Regression and Tree-Based Models for Delayed Cerebral Ischemia in Elderly Patients With Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 791547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.A.; van der Steen, W.E.; Sales Barros, R.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van den Berg, R.; Verbaan, D.; Vandertop, W.P.; Zijlstra, I.J.A.J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Strijkers, G.J.; et al. Machine learning improves prediction of delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Toledo, P.; Rios, P.M.; Ledezma, A.; Sanchis, A.; Alen, J.F.; Lagares, A. Predicting the Outcome of Patients With Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Machine Learning Techniques. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Williams, G.W.; Aguilar, D.; Yamal, J.; Maroufy, V.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Talebi, Y.; et al. Machine learning prediction of the adverse outcome for nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage patients. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, H.A.; Safwan, Z.; Nabi, R. Advancing grading and outcome prediction in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Harnessing artificial intelligence and machine learning for precision healthcare. Neurosurg. Rev. 2024, 47, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Koziarz, A.; Badhiwala, J.H.; Almenawer, S.A. Predicting outcomes in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. BMJ 2018, 360, k102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.R.; Fitzgerald, E.; Delaney, A.; Finfer, S. A Systematic Review of Outcome Measures Employed in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (aSAH) Clinical Research. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 30, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaja, B.N.R.; Cusimano, M.D.; Etminan, N.; Hanggi, D.; Hasan, D.; Ilodigwe, D.; Lantigua, H.; Le Roux, P.; Lo, B.; Louffat-Olivares, A.; et al. Clinical Prediction Models for Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review. Neurocrit. Care 2013, 18, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Yan, T.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Liao, Q.; Yang, L.; Xiao, B.; et al. Explainable machine learning in outcome prediction of high-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Aging 2024, 16, 4654–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic, E.; Pinar, E.; Pinar, M.; Dagcinar, A. Deep Learning-Assisted Segmentation and Classification of Brain Tumor Types on Magnetic Resonance and Surgical Microscope Images. World Neurosurg. 2023, 182, e196–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 29,274 |
| Gender | |
| Female | 14,002 (47.8) |
| Male | 15,272 (52.2) |
| Age | 56.23 ± 16.45 |
| 57 [46–68] | |
| Time from initial emergency visit to CT scan, minutes | 12 [4–114] |
| Time from initial emergency visit to diagnosis, hours | 3 [0–23] |
| Intubation in the first 24 h | 10,017 (34.2) |
| EVD in the first 72 h | 2840 (9.7) |
| Lab values in the initial emergency visit | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13 [11.4–14.4] |
| RBC (×103 cells/μL) | 4.5 [4–4.9] |
| WBC (×103 cells/μL) | 12.01 [9.2–15.6] |
| Platelets (×103 cells/μL) | 230 [184–282] |
| Lymphocyte (×103 cells/μL) | 4.3 [1.4–10.5] |
| Neutrophil (×103 cells/μL) | 22.34 [10–82.9] |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138.8 [136–141] |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 131 [105–167] |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.91 [1.3–3.2] |
| Comorbidities | |
| Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DM) | 7460 (25.5) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 6968 (23.8) |
| Atherosclerosis | 356 (1.2) |
| Hypertension | 16,313 (55.7) |
| Acute ischemic heart disease | 2994 (10.2) |
| Chronic ischemic heart disease | 7845 (26.8) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 5565 (19) |
| Peripheral artery disease | 2563 (8.8) |
| Renal failure | 1402 (4.8) |
| Malignancy | 1118 (3.8) |
| Inflammatory disease | 1110 (3.8) |
| Rheumatic heart diseases | 640 (2.2) |
| Liver disease | 836 (2.9) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) | 3529 (12.1) |
| Other aneurysms | 682 (2.3) |
| Obesity | 553 (1.9) |
| Pregnancy | 788 (2.7) |
| Neurocutaneous disorders | 8 (0.02) |
| Coagulation disorders | 554 (1.9) |
| Primary intervention for aneurysm | |
| Yes | 11,068 (37.8) |
| Clipping | 6643 (22.7) |
| Coiling | 4425 (15.1) |
| No | 18,206 (62.2) |
| Time from initial emergency visit to intervention for aneurysm, days | 1.95 [0.75–4.75] |
| Clipping | 1.95 [0.77–4.4] |
| Coiling | 2.07 [0.8–5.8] |
| Facilities in which intervention for aneurysm was performed | |
| Government-owned hospitals | 5461 (49.3) |
| University hospitals | 3396 (30.7) |
| Private hospitals | 1674 (15.1) |
| Private university hospitals | 537 (4.6) |
| Interventions for SAH complications | |
| Yes | 8323 (28.4) |
| Decompressive craniectomy | 648 (2.2) |
| Epidural hematoma evacuation | 125 (0.4) |
| Subdural hematoma evacuation | 938 (3.2) |
| Intracerebral hemorrhage evacuation | 1233 (4.2) |
| CSF drainage | |
| EVD and/or ELD placement | 3090 (10.6) |
| VPS placement | 345 (1.2) |
| Tracheostomy | 747 (2.6) |
| PEG placement | 522 (1.8) |
| No | 20,951 (71.6) |
| Length of hospitalization, days | 19.01 ± 15.94 |
| 15.9 [8.6–24.8] | |
| Emergency revisit within 90 days of discharge | 5100 (17.4) |
| Death within 7 days | 2757 (9.4) |
| Death within 30 days | 6668 (22.8) |
| Death within the first year | 9737 (33.3) |
| Post-treatment complications | |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) | 331 (1.1) |
| Respiratory failure | 4502 (15.4) |
| Acute ischemic heart disease | 1781 (6.1) |
| Sepsis | 1380 (4.7) |
| Meningitis | 294 (1) |
| Encephalitis | 48 (0.2) |
| Intracranial and intraspinal abscess | 69 (0.2) |
| Urinary tract infection (UTI) | 3691 (12.6) |
| Epilepsy | 8220 (28.1) |
| Hydrocephalus | 960 (3.3) |
| Cerebral edema | 1937 (6.6) |
| Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) | 506 (1.7) |
| Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) | 1137 (3.9) |
| Pneumonia | 4914 (16.8) |
| Paralysis | 3148 (10.8) |
| Status epilepticus | 216 (0.7) |
| Decubitus ulcer | 1382 (4.7) |
| Cerebral Ischemia | 1191 (4.1) |
| Machine Learning Methods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Features | Sample | Metric | Logistic Regression | Decision Tree | Random Forest | Artificial Neural Network |
| Pre-admission | Training | AUC | 0.845 | 0.861 | 0.882 | 0.855 |
| Average Precision | 0.654 | 0.692 | 0.750 | 0.673 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.830 | 0.842 | 0.852 | 0.834 | ||
| Test | AUC | 0.849 | 0.835 | 0.855 | 0.850 | |
| Average Precision | 0.651 | 0.636 | 0.667 | 0.649 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.832 | 0.826 | 0.835 | 0.829 | ||
| Pre-admission + Post-admission | Training | AUC | 0.940 | 0.937 | 0.942 | 0.952 |
| Average Precision | 0.825 | 0.797 | 0.840 | 0.858 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.895 | 0.886 | 0.892 | 0.906 | ||
| Test | AUC | 0.942 | 0.916 | 0.931 | 0.946 | |
| Average Precision | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.813 | 0.844 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.901 | 0.885 | 0.893 | 0.905 | ||
| Machine Learning Methods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Features | Sample | Metric | Logistic Regression | Decision Tree | Random Forest | Artificial Neural Network |
| Preadmission | Training | AUC | 0.837 | 0.853 | 0.863 | 0.846 |
| Average Precision | 0.744 | 0.772 | 0.796 | 0.755 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.786 | 0.801 | 0.807 | 0.793 | ||
| Test | AUC | 0.831 | 0.825 | 0.839 | 0.835 | |
| Average Precision | 0.733 | 0.717 | 0.747 | 0.733 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.782 | 0.777 | 0.789 | 0.780 | ||
| Pre-admission + Post-admission | Training | AUC | 0.929 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.949 |
| Average Precision | 0.885 | 0.889 | 0.898 | 0.914 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.874 | 0.864 | 0.865 | 0.893 | ||
| Test | AUC | 0.927 | 0.907 | 0.926 | 0.941 | |
| Average Precision | 0.881 | 0.848 | 0.877 | 0.898 | ||
| Accuracy | 0.875 | 0.851 | 0.861 | 0.884 | ||
| First Month Prediction | First Year Prediction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Std. | Error | Pr (>|z|) | Estimate | Std. | Error | Pr (>|z|) | |
| Age | 2.350475 | 0.151 | 15.48 | <0.001 | 4.188651 | 0.143 | 29.097 | <0.001 |
| Cardiopulmonary Arrest | 4.138183 | 0.234 | 17.613 | <0.001 | 4.488835 | 0.328 | 13.684 | <0.001 |
| Endotracheal Intubation | −2.117409 | 0.234 | −9.026 | <0.001 | −2.797108 | 0.328 | −8.524 | <0.001 |
| EVD (First 72 h) | −0.10164 | 0.116 | −0.87 | −0.452086 | 0.107 | −4.187 | <0.001 | |
| Glucose | 5.339468 | 0.599 | 8.913 | <0.001 | 6.429198 | 0.582 | 11.036 | <0.001 |
| Lactate | 5.014475 | 1.330 | 3.77 | <0.001 | 4.807589 | 1.233 | 3.896 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil | 1.006599 | 0.325 | 3.093 | <0.01 | 0.228911 | 0.305 | 0.748 | |
| Basophil | 3.633494 | 1.309 | 2.774 | <0.01 | 2.950229 | 1.216 | 2.425 | <0.05 |
| White Blood Cell Count | 7.284652 | 0.523 | 13.917 | <0.001 | 6.646928 | 0.510 | 13.023 | <0.001 |
| Eosinophil | −3.618516 | 1.089 | −3.321 | <0.001 | −2.604965 | 0.879 | −2.961 | <0.01 |
| Hematocrit | −0.351574 | 0.129 | −2.719 | <0.01 | −0.339932 | 0.117 | −2.901 | <0.01 |
| Erythrocyte | 0.246341 | 0.481 | 0.511 | −1.133348 | 0.436 | −2.598 | <0.01 | |
| Mean Platelet Volume | 0.528842 | 0.239 | 2.209 | <0.05 | 0.635336 | 0.221 | 2.872 | <0.01 |
| Platelet Distribution Width | 1.124736 | 0.248 | 4.528 | <0.001 | 0.835278 | 0.225 | 3.710 | <0.001 |
| Platelet | −0.409396 | 0.168 | −2.424 | <0.05 | −0.413981 | 0.153 | −2.705 | <0.01 |
| Platelet to WBC Ratio | −5.862795 | 0.908 | −6.452 | <0.001 | −1.629248 | 0.736 | −2.213 | <0.05 |
| Pre-existing Hypertension | 0.290937 | 0.053 | 5.415 | <0.001 | 0.31136 | 0.047 | 6.528 | <0.001 |
| Pre-existing Chronic Heart Disease | 0.227944 | 0.065 | 3.496 | <0.001 | 0.408031 | 0.058 | 6.960 | <0.001 |
| Pre-existing Stroke | 0.089569 | 0.063 | 1.409 | 0.327823 | 0.056 | 5.841 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-existing Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | 0.188741 | 0.081 | 2.313 | <0.05 | 0.20692 | 0.072 | 2.844 | <0.01 |
| Pre-existing Chronic Kidney Disease | 0.583693 | 0.10 | 5.832 | <0.001 | 0.627275 | 0.092 | 6.812 | <0.001 |
| Pre-existing Malignancy | 0.124178 | 0.110 | 1.123 | 0.831856 | 0.095 | 8.754 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-existing Rheumatic Vascular Disease | 0.574583 | 0.146 | 3.935 | <0.001 | 0.212816 | 0.133 | 1.596 | |
| Pre-existing Chronic Liver Failure | 0.284246 | 0.088 | 3.212 | <0.01 | 0.558313 | 0.081 | 6.883 | <0.001 |
| Pre-existing Epilepsy | 0.272037 | 0.118 | 2.301 | <0.05 | 0.736211 | 0.098 | 7.444 | <0.001 |
| Pre-existing Hemiplegia/Paraplegia | 0.769522 | 0.170 | 4.51 | <0.001 | 0.829921 | 0.146 | 5.677 | <0.001 |
| Institution Type | −3.231709 | 0.433 | −7.462 | <0.001 | −3.539716 | 0.630 | −5.618 | <0.001 |
| Procedure-related Complications | −0.005564 | 0.143 | −0.039 | 1.231947 | 0.114 | 10.728 | <0.001 | |
| Decompressive Craniectomy | 0.941764 | 0.174 | 5.404 | <0.001 | 0.446239 | 0.157 | 2.839 | <0.01 |
| Subdural Hematoma | −0.097749 | 0.180 | −0.54 | −0.704535 | 0.149 | −4.727 | <0.001 | |
| Intracerebral Hemorrhage | 0.598519 | 0.159 | 3.741 | <0.001 | 0.064577 | 0.137 | 0.469 | |
| Tracheostomy | −1.026597 | 0.137 | −7.454 | <0.001 | 0.510161 | 0.114 | 4.447 | <0.001 |
| Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy | −2.665337 | 0.257 | −10.352 | <0.001 | 0.283103 | 0.129 | 2.190 | <0.05 |
| EVD (anytime during the hospitalization) | 0.726111 | 0.181 | 3.99 | <0.001 | 0.470255 | 0.161 | 2.916 | <0.01 |
| Postoperative Sepsis | −0.099639 | 0.106 | −0.932 | 1.04247 | 0.088 | 11.825 | <0.001 | |
| Postoperative Epilepsy | −2.163765 | 0.081 | −26.651 | <0.001 | −1.755134 | 0.054 | −32.30 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Hemiplegia/Paraplegia | −1.732357 | 0.141 | −12.216 | <0.001 | −1.111446 | 0.077 | −14.29 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Hydrocephalus | −0.821742 | 0.169 | −4.856 | <0.001 | −0.388568 | 0.115 | −3.351 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Brain Edema | 0.345695 | 0.080 | 4.286 | <0.001 | 0.422068 | 0.075 | 5.598 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Pulmonary Thromboembolism | −0.833607 | 0.264 | −3.155 | <0.01 | −0.040277 | 0.157 | −0.256 | |
| Postoperative Deep Vein Thrombosis | −1.830364 | 0.277 | −6.607 | <0.001 | −0.836692 | 0.128 | −6.490 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Stroke | −0.662205 | 0.044 | −15.043 | <0.001 | −0.572621 | 0.040 | −14.004 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Pneumonia | −1.23275 | 0.051 | −24.065 | <0.001 | −0.979274 | 0.042 | −22.84 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | −1.681855 | 0.101 | −16.526 | <0.001 | −1.311541 | 0.062 | −20.96 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Decubitus Ulcers | −2.255048 | 0.221 | −10.172 | <0.001 | 0.421185 | 0.092 | 4.552 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Respiratory Failure | 0.479471 | 0.059 | 8.024 | <0.001 | 0.930121 | 0.053 | 17.294 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative Chronic Heart Disease | −1.715899 | 0.081 | −20.984 | <0.001 | −1.838105 | 0.062 | −29.58 | <0.001 |
| 30-day Emergency Re-admission After Discharge | −1.259397 | 0.123 | −10.163 | <0.001 | 0.31285 | 0.106 | 2.925 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khaniyev, T.; Cekic, E.; Gecici, N.N.; Can, S.; Ata, N.; Ulgu, M.M.; Birinci, S.; Isikay, A.I.; Bakir, A.; Arat, A.; et al. Predicting Mortality in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients Using Big Data and Machine Learning: A Nationwide Study in Türkiye. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041144
Khaniyev T, Cekic E, Gecici NN, Can S, Ata N, Ulgu MM, Birinci S, Isikay AI, Bakir A, Arat A, et al. Predicting Mortality in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients Using Big Data and Machine Learning: A Nationwide Study in Türkiye. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041144
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhaniyev, Taghi, Efecan Cekic, Neslihan Nisa Gecici, Sinem Can, Naim Ata, Mustafa Mahir Ulgu, Suayip Birinci, Ahmet Ilkay Isikay, Abdurrahman Bakir, Anil Arat, and et al. 2025. "Predicting Mortality in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients Using Big Data and Machine Learning: A Nationwide Study in Türkiye" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041144
APA StyleKhaniyev, T., Cekic, E., Gecici, N. N., Can, S., Ata, N., Ulgu, M. M., Birinci, S., Isikay, A. I., Bakir, A., Arat, A., & Hanalioglu, S. (2025). Predicting Mortality in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients Using Big Data and Machine Learning: A Nationwide Study in Türkiye. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041144





