Advances in the Management of Craniopharyngioma: A Narrative Review of Recent Developments and Clinical Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. History
3. Epidemiology of Craniopharyngiomas
3.1. Age Distribution and Bimodal Peak
3.2. Global Incidence and Prevalence
3.3. Subtypes and Their Prevalence
3.4. Demographic Disparities
3.5. Diagnostic and Treatment Trends
3.6. Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life
4. Genetic Mutations in Craniopharyngiomas
5. Clinical Signs and Symptoms
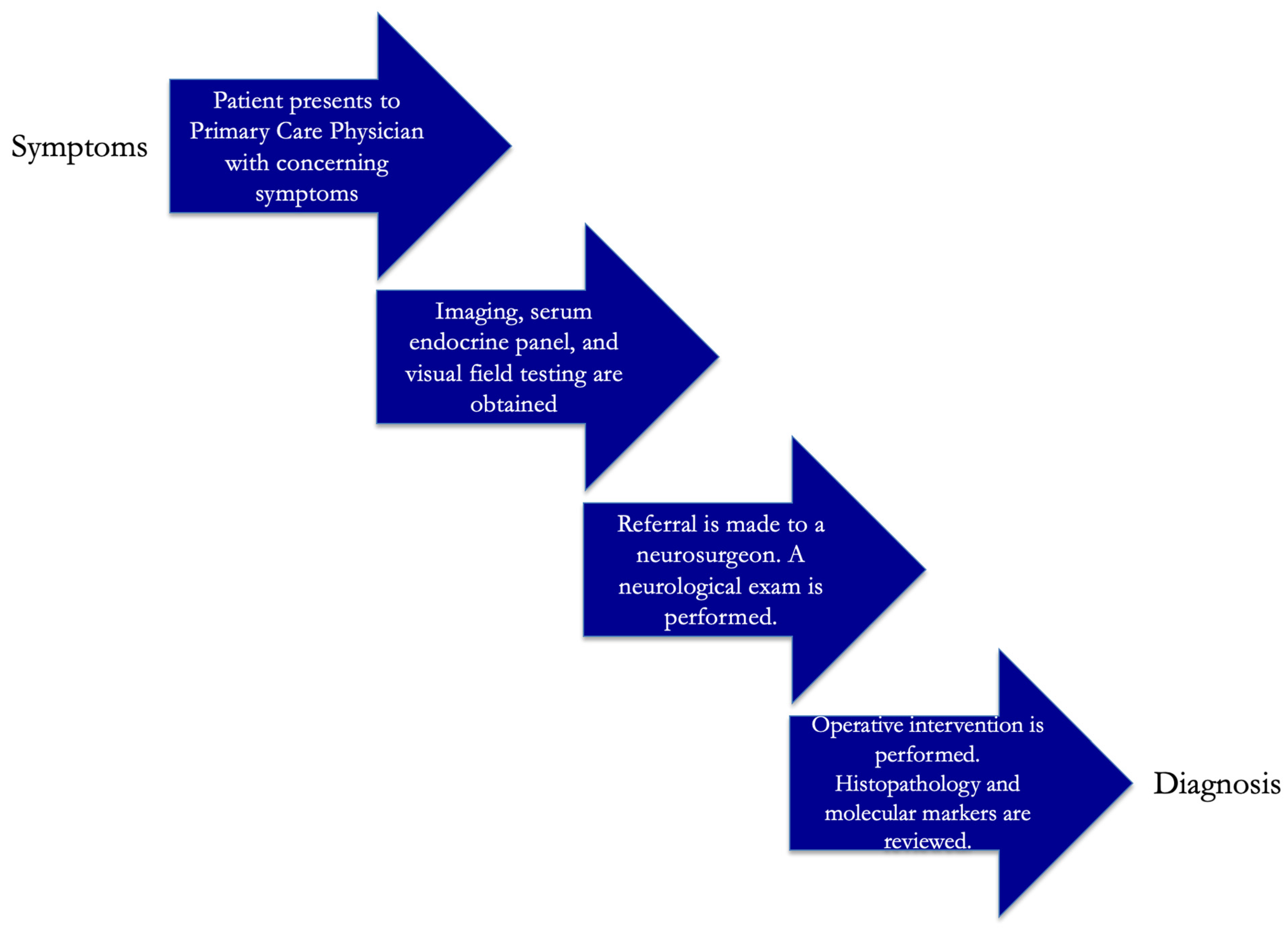
6. Diagnosis and Management of Craniopharyngioma
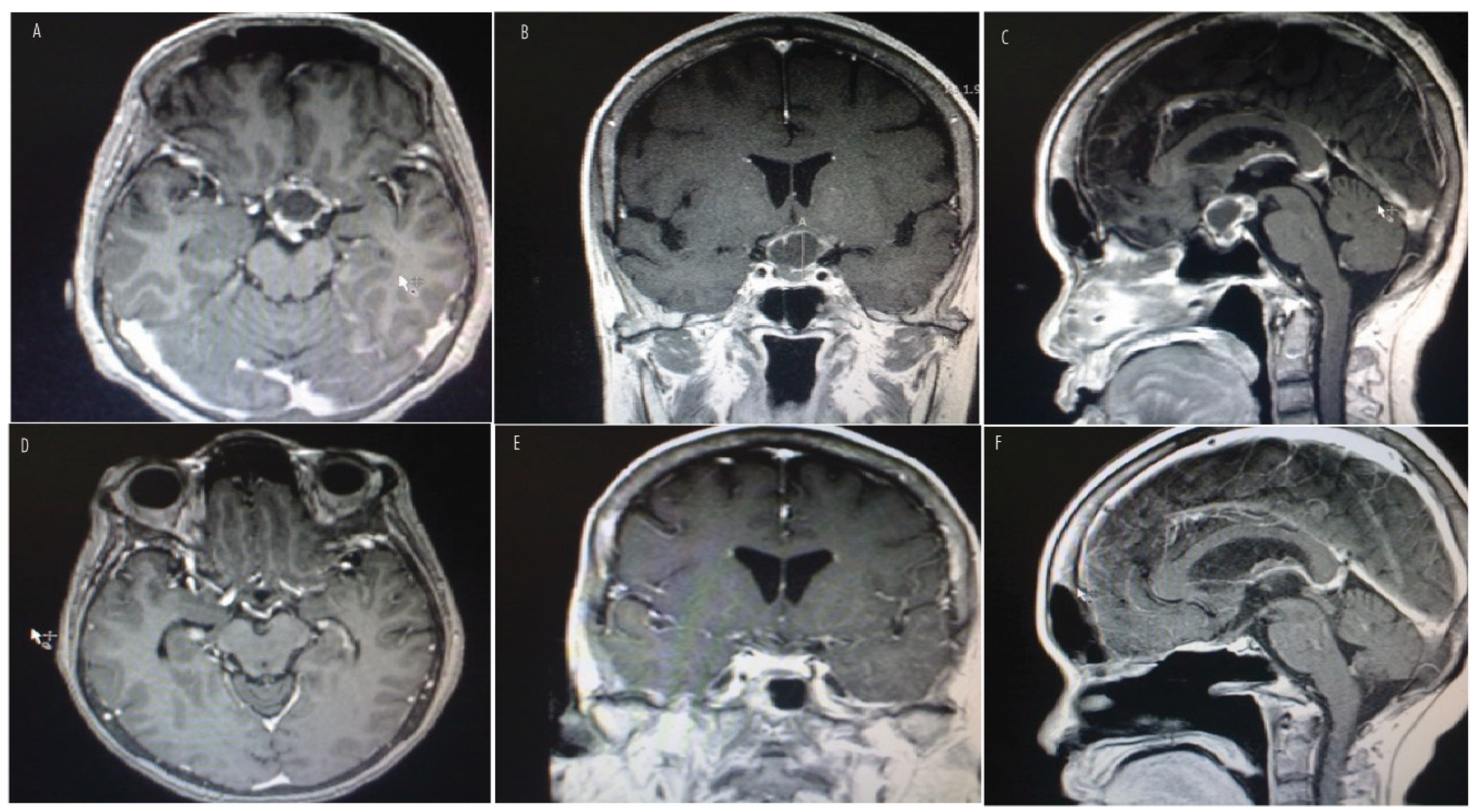
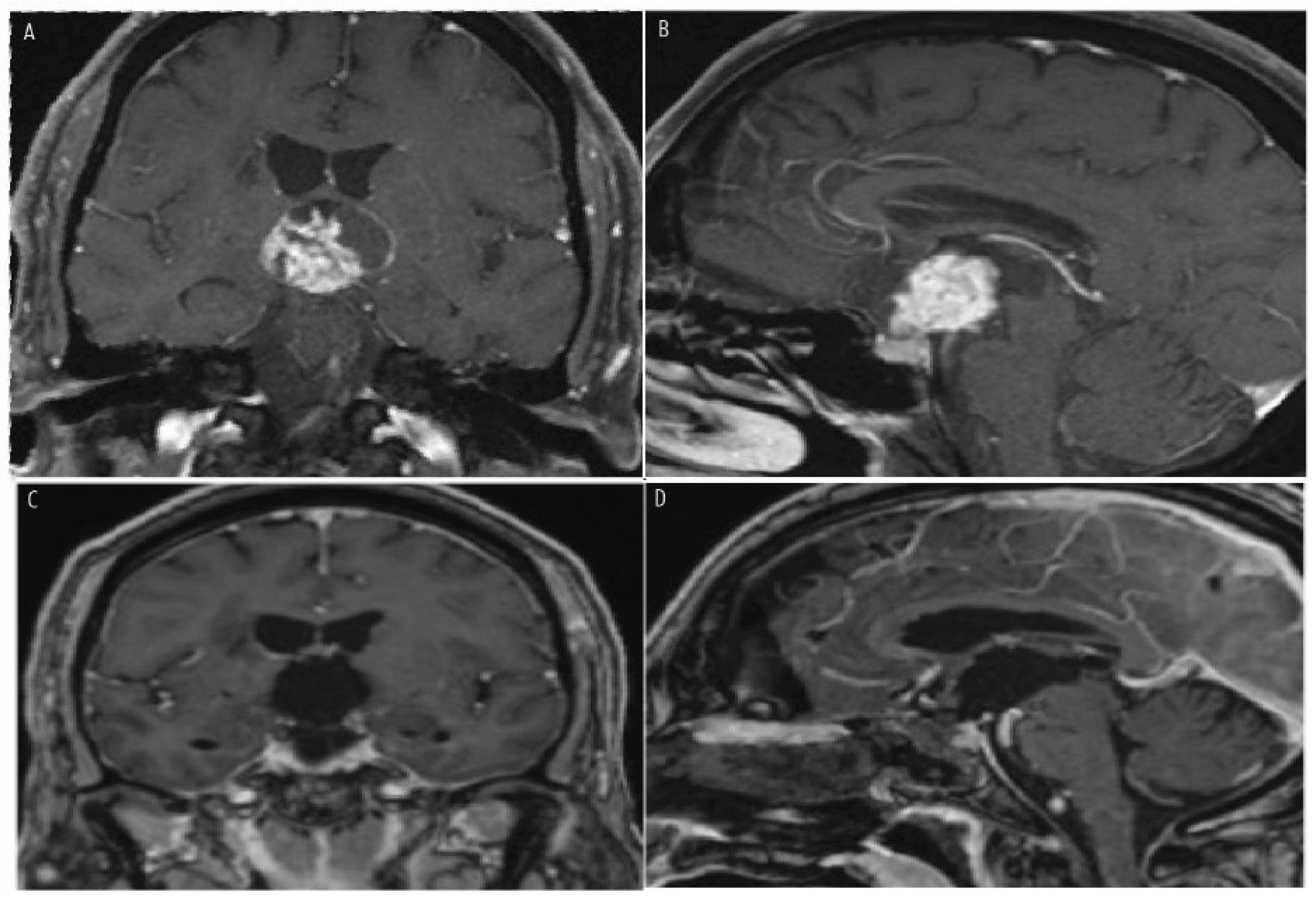
7. Histopathologic Features and Radiologic Features
8. Treatment
8.1. Targeted Therapies for Craniopharyngiomas Based on Genetic Mutations
8.2. Surgery
8.3. Intracavitary Adjuncts
8.4. Radiation Therapy
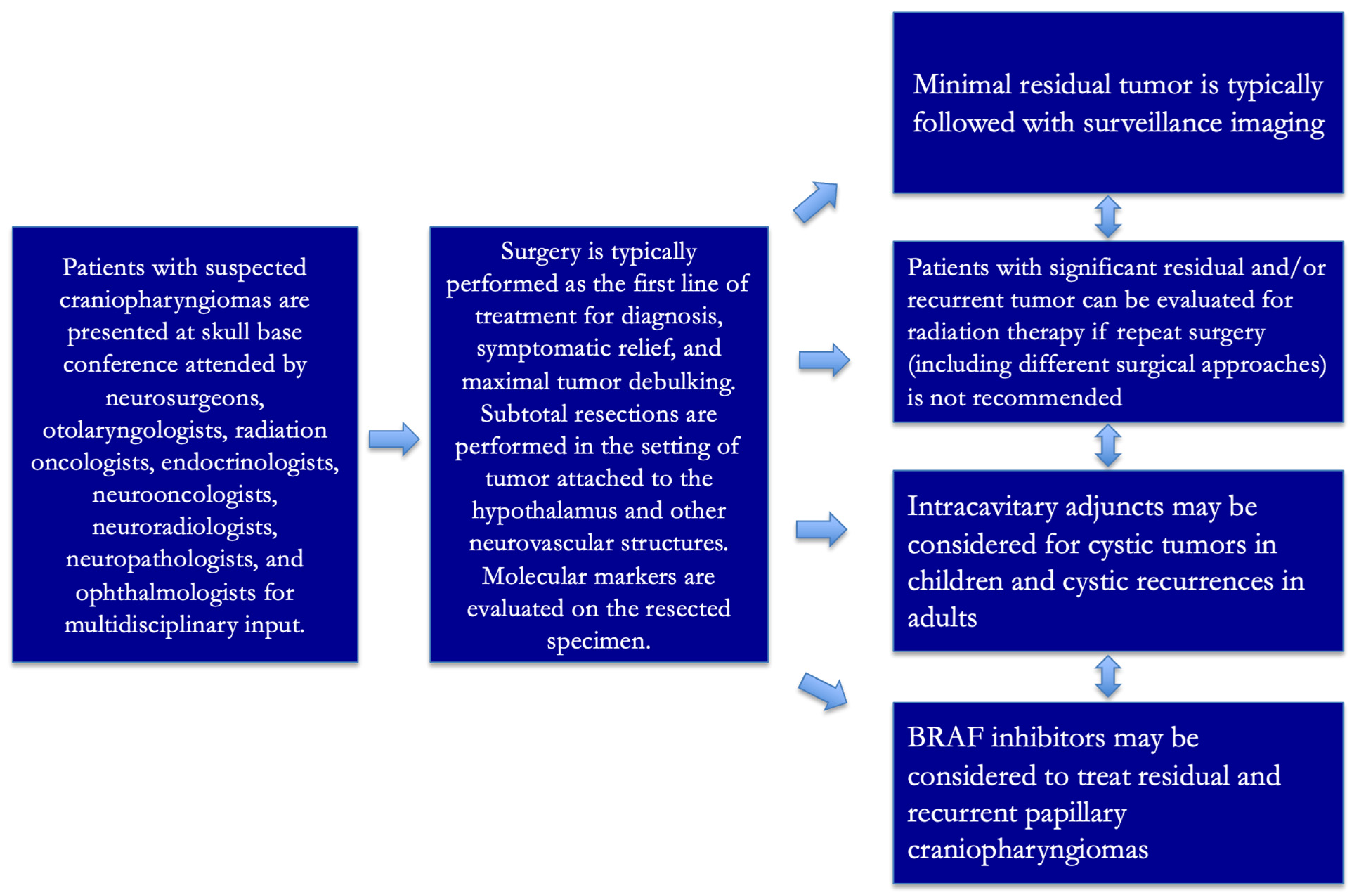
8.5. Multidisciplinary Approach
9. Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
10. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DiPatri, A.J., Jr.; Prabhu, V. A history of the treatment of craniopharyngiomas. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfurth, E.M. Craniopharyngioma-An update on metabolic and cognitive complications and new therapy. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 294, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunin, G.R.; Surawicz, T.S.; Witman, P.A.; Preston-Martin, S.; Davis, F.; Bruner, J.M. The descriptive epidemiology of craniopharyngioma. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Hu, F. Endocrine Disorder in Patients With Craniopharyngioma. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 737743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poretti, A.; Grotzer, M.A.; Ribi, K.; Schönle, E.; Boltshauser, E. Outcome of craniopharyngioma in children: Long-term complications and quality of life. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2004, 46, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogiparthi, J.; Teru, S.S.; Bonitz, T.J.; Buzas, C. Craniopharyngioma in a 58-Year-Old Adult Male: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Cureus 2023, 15, e45493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.L.; Merchant, T.E.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Martinez-Barbera, J.P.; Puget, S. Craniopharyngioma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Barbera, J.P.; Andoniadou, C.L. Biological Behaviour of Craniopharyngiomas. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figarella-Branger, D.; Appay, R.; Metais, A.; Tauziède-Espariat, A.; Colin, C.; Rousseau, A.; Varlet, P. The 2021 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Ann. Pathol. 2022, 42, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitaki, N.; Cudlip, S.; Adams, C.B.; Wass, J.A. Craniopharyngiomas. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvanese, F.; Jacquesson, T.; Manet, R.; Vasiljevic, A.; Lasolle, H.; Ducray, F.; Raverot, G.; Jouanneau, E. Neoadjuvant B-RAF and MEK Inhibitor Targeted Therapy for Adult Papillary Craniopharyngiomas: A New Treatment Paradigm. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 882381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.; Taghvaei, M.; Yu, S.; Sathe, A.; Collopy, S.; Prashant, G.; Evans, J.J.; Karsy, M. Targeted Therapy in the Management of Modern Craniopharyngiomas. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowczynski, O.D.; Langan, S.T.; Rizk, E.B. Craniopharyngiomas: A systematic review and evaluation of the current intratumoral treatment landscape. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 166, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, S.; Merchant, T.E.; Boop, F.A.; Roth, J.; Constantini, S. Shifting Strategies in the Treatment of Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Goda, J.S.; Chatterjee, A.; Shetty, P.; Sahay, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Epari, S.; Sahu, A.; Singh, V.; Gupta, T.; et al. Patterns of Care in Craniopharyngioma: Clinical Outcomes After Surgery and Radiation Therapy in a Real-World Setting. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, e809–e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.J.; Rougerie, J. A critical review of personal experiences with craniopharyngioma: Clinical history, surgical technique and operative results. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1994, 21, 134–150; discussion 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdheim, J. Über Hypophysenganggeschwülste und Hirncholesteatome; Gerold: Vienna, Austria, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Susman, W. Embryonic epithelial rests in the pituitary. Br. J. Surg. 1932, 19, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, A. Remarks on an operative treatment of tumors of the hypophysis. Gynecol. Obstet. 1910, 10, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Cushing, H. Intracranial Tumors; Charles C Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Jusue-Torres, I.; Hulbert, A.; Germanwala, A.A.; Patel, C.R.; Germanwala, A.V. The 100 Most-Cited Reports About Craniopharyngioma. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, e910–e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, H. The Craniopharyngiomas. In Intracranial Tumors: Notes Upon a Series of Two Thousand Verified Cases with Surgical Mortality Percentage Pertaining Thereto; Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1932; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, R.; Magnani, C.; Pavanello, M.; Caruso, S.; Dama, E.; Garrè, M.L. Epidemiological aspects of craniopharyngioma. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 19 (Suppl. S1), 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, E.H.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Poulsgaard, L.; Kristensen, L.Ø.; Astrup, J.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Bjerre, P.; Andersen, M.; Andersen, C.; Jørgensen, J.; et al. Incidence of craniopharyngioma in Denmark (n = 189) and estimated world incidence of craniopharyngioma in children and adults. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momin, A.A.; Recinos, M.A.; Cioffi, G.; Patil, N.; Soni, P.; Almeida, J.P.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Recinos, P.F.; Kshettry, V.R. Descriptive epidemiology of craniopharyngiomas in the United States. Pituitary 2021, 24, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharia, B.E.; Bruce, S.S.; Goldstein, H.; Malone, H.R.; Neugut, A.I.; Bruce, J.N. Incidence, treatment and survival of patients with craniopharyngioma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolecek, T.A.; Propp, J.M.; Stroup, N.E.; Kruchko, C. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14 (Suppl. S5), v1–v49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, M.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Janssen, J.A.; Catsman-Berrevoets, C.E.; Michiels, E.M.; van Veelen-Vincent, M.L.C.; Dallenga, A.H.; van den Berge, J.H.; Van Rij, C.M.; van der Lely, A.J.; et al. Very long-term sequelae of craniopharyngioma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitaki, N. Management of craniopharyngiomas. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tali, T.A.; Amin, F.; Khan, N.A.; Sofi, M.A. Clinico-epidemiological profile and treatment outcome of craniopharyngioma: A case series. Int. J. Sci. Rep. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craus, S.; Gruppetta, M. Epidemiology of craniopharyngiomas: A population-based study in Malta. Endocr. Oncol. 2021, 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, L.C.; Ersbøll, A.K. When the entire population is the sample: Strengths and limitations in register-based epidemiology. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, F.; Humayun, K.N.; Riaz, Q.; Arif, M.; Huda, N.U.; Laghari, A.A.; Hilal, K.; Mushtaq, N. Pediatric craniopharyngioma: A 20-year study on epidemiological features, clinical presentation, and survival outcomes in a tertiary care center from LMIC. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2024, 40, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, M.; Ayuk, J.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Toogood, A.A.; Aragon-Alonso, A.; Sheppard, M.C.; Bates, A.S.; Stewart, P.M. Mortality in patients with pituitary disease. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 301–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, C.J.; Hung, Y.C.; Wu, H.M.; Shiau, C.Y.; Guo, W.Y.; Pan, D.H.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Liu, K.D. Gamma Knife surgery for craniopharyngioma: Report on a 20-year experience. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121 (Suppl. S2), 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Boekhoff, S.; Gebhardt, U.; Sterkenburg, A.S.; Daubenbüchel, A.M.; Eveslage, M.; Müller, H.L. History before diagnosis in childhood craniopharyngioma: Associations with initial presentation and long-term prognosis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, D.S.; Andersson, E.; Bryngelsson, I.L.; Nilsson, A.G.; Johannsson, G. Excess mortality and morbidity in patients with craniopharyngioma, especially in patients with childhood onset: A population-based study in Sweden. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Lohle, K.; Reichel, J.; Daubenbüchel, A.M.; Sterkenburg, A.S.; Müller, H.L. Fusiform dilatation of the internal carotid artery in childhood-onset craniopharyngioma: Multicenter study on incidence and long-term outcome. Pituitary 2016, 19, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Liang, R.; Zan, X.; et al. Characterization of novel CTNNB1 mutation in Craniopharyngioma by whole-genome sequencing. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, C.; Liehr, T.; Hülsken, J.; Behrens, J.; Birchmeier, W.; Grzeschik, K.H.; Ballhausen, W.G. Localization of the human beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1) to 3p21: A region implicated in tumor development. Genomics 1994, 23, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, P.; Prince, E.; Lu, S.; Santagata, S.; Ligon, K.; Manley, P.; Beroukhim, R.; Hankinson, T.; Bandopadhayay, P. RARE-07. THE LANDSCAPE OF GENOMIC ALTERATIONS IN ADAMANTINOMATOUS CRANIOPHARYNGIOMAS. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22 (Suppl. S3), iii443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölsken, A. Pathogenesis of Human ACP. In Basic Research and Clinical Aspects of Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma; Martinez-Barbera, J.P., Lilian Andoniadou, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, L.M.; Okuno, S.H.; Ransom, R.C.; Van Gompel, J.J.; Humes, A.L.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Ruff, M.W. Recurrent adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma stabilized with tocilizumab and bevacizumab: Illustrative case. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2025, 9, CASE24410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, S.; Mirsky, D.M.; Donson, A.M.; Dahl, N.; Foreman, N.K.; Hoffman, L.M.; Hankinson, T.C.; Mulcahy Levy, J.M. Targeting IL-6 is a potential treatment for primary cystic craniopharyngioma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos-Kerkhof, E.; Buis, D.R.; Lequin, M.H.; Bennebroek, C.A.; Aronica, E.; Hulleman, E.; Zwaveling-Soonawala, N.; van Santen, H.M.; Schouten-van Meeteren, A.Y. Tocilizumab for the fifth progression of cystic childhood craniopharyngioma—A case report. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1225734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, A.; Calvanese, F.; Ducray, F.; Vasiljevic, A.; Manet, R.; Raverot, G.; Jouanneau, E. First evidence of anti-VEGF efficacy in an adult case of adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma: Case report and illustrative review. Ann. Endocrinol. 2023, 84, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, J.K.; Cho, H.; Park, C.K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.H. Analysis of the BRAF(V600E) Mutation in Central Nervous System Tumors. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Twohy, E.; Geyer, S.; Gerstner, E.R.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Tabrizi, S.; Kabat, B.; Thierauf, J.; Ruff, M.W.; Bota, D.A.; et al. BRAF–MEK Inhibition in Newly Diagnosed Papillary Craniopharyngiomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occhi, G.; Barollo, S.; Regazzo, D.; Bertazza, L.; Galuppini, F.; Guzzardo, V.; Jaffrain-Rea, M.L.; Vianello, F.; Ciato, D.; Ceccato, F.; et al. A constitutive active MAPK/ERK pathway due to BRAFV600E positively regulates AHR pathway in PTC. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32104–32114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor-Weiner, A.N.; Brastianos, P.K.; Manley, P.E.; Jones, R.T.; Dias-Sangata, D.; Thorner, A.; Rodriguez, F.; Bernardo, L.; Schubert, L.; Stewart, C.; et al. Exome sequencing reveals BRAF mutations in papillary craniopharyngiomas. Cancer Res. 2014, 74 (Suppl. S19), 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, A.; Odia, Y. BRAF-V600E mutant papillary craniopharyngioma dramatically responds to combination BRAF and MEK inhibitors. CNS Oncol. 2017, 6, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboqami, M.N.; Albaiahy, A.K.S.; Bukhari, B.H.; Alkhaibary, A.; Alharbi, A.; Khairy, S.; Alassiri, A.H.; AlSufiani, F.; Alkhani, A.; Aloraidi, A. Craniopharyngioma: A comprehensive review of the clinical presentation, radiological findings, management, and future Perspective. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.L. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Craniopharyngioma. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrè, M.L.; Cama, A. Craniopharyngioma: Modern concepts in pathogenesis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2007, 19, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuijts, M.A.; Veldhuis, N.; Stegeman, I.; van Santen, H.M.; Porro, G.L.; Imhof, S.M.; Schouten–van Meeteren, A.Y. Visual functions in children with craniopharyngioma at diagnosis: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz Torres, M.; Shafiq, I.; Mesfin, F.B. Craniopharyngioma. In StatPearls [Internet]; Updated 24 April 2023; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, W.; Freidenberg, G.R.; James, H.E.; Hesselink, J.R.; Jones, K.L. Prenatal diagnosis of a craniopharyngioma using ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging. Prenat. Diagn. 1990, 10, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Scholden, J.; Lehrnbecher, T.; Müller, H.L.; Bensch, J.; Hengen, R.H.; Sörensen, N.; Stockhausen, H.B.V. Radical surgery in a neonate with craniopharyngioma. report of a case. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2000, 33, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apps, J.R.; Hutchinson, J.C.; Arthurs, O.J.; Virasami, A.; Joshi, A.; Zeller-Plumhoff, B.; Moulding, D.; Jacques, T.S.; Sebire, N.J.; Martinez-Barbera, J.P. Imaging Invasion: Micro-CT imaging of adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma highlights cell type specific spatial relationships of tissue invasion. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, X. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis of Craniopharyngioma. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 752119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckhaus, J.; Boekhoff, S.; Scheinemann, K.; Schilling, F.H.; Fleischhack, G.; Binder, G.; Bison, B.; Pietsch, T.; Friedrich, C.; Müller, H.L. Perinatally diagnosed congenital craniopharyngiomas in the KRANIOPHARYNGEOM trials. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e230294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckhaus, J.; Peng, J.; Boekhoff, S.; Bison, B.; Friedrich, C.; Müller, H.L. Head circumferences measured during developmental monitoring visits before diagnosis of childhood-onset craniopharyngioma. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lania, A.; Spada, A.; Lasio, G. Diagnosis and Management of Craniopharyngiomas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Agosti, E.; Zeppieri, M.; Antonietti, S.; Piazza, A.; Ius, T.; Fontanella, M.M.; Fiorindi, A.; Panciani, P.P. Advancing Craniopharyngioma Management: A Systematic Review of Current Targeted Therapies and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengartner, A.C.; Prince, E.; Vijmasi, T.; Hankinson, T.C. Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma: Moving toward targeted therapies. Neurosurg. Focus. 2020, 48, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, R.; Hengartner, A.; Folzenlogen, Z.; Prince, E.; Hankinson, T.C. Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma in the molecular age and the potential of targeted therapies: A review. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Robert, C.; Larkin, J.; Haanen, J.B.; Ribas, A.; Hogg, D.; Hamid, O.; Ascierto, P.A.; Testori, A.; Lorigan, P.C.; et al. Vemurafenib in patients with BRAFV600 mutation-positive metastatic melanoma: Final overall survival results of the randomized BRIM-3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondak, V.K.; Flaherty, L.E. Targeted therapies: Improved outcomes for patients with metastatic melanoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, C.; Mansur, G.; Wu, K.C.; Prevedello, D.M.; Ghalib, L. Practical application of precision oncology in adult onset craniopharyngiomas. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1488958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queirolo, P.; Picasso, V.; Spagnolo, F. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garutti, M.; Bergnach, M.; Polesel, J.; Palmero, L.; Pizzichetta, M.A.; Puglisi, F. BRAF and MEK Inhibitors and Their Toxicities: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.J.; Kwak, S.H.; Root, K.T.; Fadil, A.; Nguyen, A.; Ladehoff, L.; Batchu, S.; Lucke-Wold, B. Current Approaches to Craniopharyngioma Management. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandurand, C.; Sepehry, A.A.; Asadi Lari, M.H.; Akagami, R.; Gooderham, P. Adult Craniopharyngioma: Case Series, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2018, 83, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, Y.; Nie, C.; Huang, X.; Yan, K.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach improves endocrine function and surgical outcome in primary craniopharyngioma resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, R.; Hofmann, B.M. Surgical management of giant craniopharyngiomas. Acta Neurochir. 2008, 150, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, B.M.; Nimsky, C.; Fahlbusch, R. Benefit of 1.5-T intraoperative MR imaging in the surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 1377–1390; discussion 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.E.; Jane, J.A., Jr.; Wisoff, J.H. Surgical management of craniopharyngiomas in children: Meta-analysis and comparison of transcranial and transsphenoidal approaches. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, 630–643; discussion 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, I.; Gerges, M.M.; Uribe-Cardenas, R.; Morgenstern, P.F.; Eljalby, M.; Tabaee, A.; Greenfield, J.P.; Kacker, A.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. How ling is the tail end of the learning curve? Results from 1000 consecutive endoscopic endonasal skull base cases following the initial 200 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komotar, R.J.; Starke, R.M.; Raper, D.M.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic endonasal compared with microscopic transsphenoidal and open transcranial resection of craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg. 2012, 77, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandapani, S.; Singh, H.; Negm, H.M.; Cohen, S.; Souweidane, M.M.; Greenfield, J.P.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endonasal endoscopic reoperation for residual or recurrent craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan, G.E.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, G.; Mani, S.; Thomas, R.; Chacko, A.G. A randomized controlled trial to determine the role of intraoperative lumbar cerebrospinal fluid drainage in patients undergoing endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenomas. Neurol. India 2018, 66, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, R.H.; Raju, S.; Kim, M.; Gardner, P.; Zenonos, G.A.; Snyderman, C.; Wang, E.W.; Patel, C.; Germanwala, A.V. Endocopic endonasal approach for residual and recurrent craniopharyngioma after transcranial approach. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2023, 84 (Suppl. S1), S1–S344. [Google Scholar]
- Alalade, A.F.; Ogando-Rivas, E.; Boatey, J.; Souweidane, M.M.; Anand, V.K.; Greenfield, J.P.; Schwartz, T.H. Suprasellar and recurrent pediatric craniopharyngiomas: Expanding indications for the extended endoscopic transsphenoidal approach. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2018, 21, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.Z.; Greenfield, J.P.; Souweidane, M.M.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic, endonasal resection of craniopharyngiomas: Analysis of outcome including extent of resection, cerebrospinal fluid leak, return to preoperative productivity, and body mass index. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, 110–123; discussion 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Deng, J.; Liang, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Treatment of cystic craniopharyngioma with phosphorus-32 intracavitary irradiation. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, U.; Laperriere, N.; Bouffet, E.; Drake, J. Intracystic therapies for cystic craniopharyngioma in childhood. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldarelli, M.; Massimi, L.; Tamburrini, G.; Cappa, M.; Di Rocco, C. Long-term results of the surgical treatment of craniopharyngioma: The experience at the Policlinico Gemelli, Catholic University, Rome. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbok, P.; Hukin, J. Intracystic treatments for craniopharyngioma. Neurosurg. Focus. 2010, 28, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hukin, J.; Steinbok, P.; Lafay-Cousin, L.; Hendson, G.; Strother, D.; Mercier, C.; Samson, Y.; Howes, W.; Bouffet, E. Intracystic bleomycin therapy for craniopharyngioma in children: The Canadian experience. Cancer 2007, 109, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrantini, M.; Capone, I.; Belardelli, F. Interferon-alpha and cancer: Mechanisms of action and new perspectives of clinical use. Biochimie 2007, 89, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilday, J.P.; Caldarelli, M.; Massimi, L.; Chen, R.H.H.; Lee, Y.Y.; Liang, M.L.; Parkes, J.; Naiker, T.; Van Veelen, M.L.; Michiels, E.; et al. Intracystic interferon-alpha in pediatric craniopharyngioma patients: An international multicenter assessment on behalf of SIOPE and ISPN. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, F., Jr.; Schwartz, T.H. Update on management of craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 156, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elowe-Gruau, E.; Beltrand, J.; Brauner, R.; Pinto, G.; Samara-Boustani, D.; Thalassinos, C.; Busiah, K.; Laborde, K.; Boddaert, N.; Zerah, M.; et al. Childhood craniopharyngioma: Hypothalamus-sparing surgery decreases the risk of obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2376–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Kiehna, E.N.; Sanford, R.A.; Mulhern, R.K.; Thompson, S.J.; Wilson, M.W.; Lustig, R.H.; Kun, L.E. Craniopharyngioma: The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital experience 1984–2001. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odei, B.; Frandsen, J.E.; Boothe, D.; Ermoian, R.P.; Poppe, M.M. Patterns of Care in Proton Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Central Nervous System Malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.B.; Ahmed, S.; Johnson, A.; Thomas, H.; Depauw, N.; Horick, N.; Tansky, J.; Evans, C.L.; Pulsifer, M.; Ebb, D.; et al. Proton Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaminus, G.; Weinspach, S.; Teske, C.; Göbel, U. Quality of life in children and adolescents with cancer. First results of an evaluation of 49 patients with the PEDQOL questionnaire. Klin. Padiatr. 2000, 212, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Tian, H.; Wang, M.; Lin, R.; Bai, J.; Wang, D.; Dong, M. Proton beam therapy for craniopharyngioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, T.; Indelicato, D.; Hua, C.; Wu, S.; Conklin, H. Comparison of Academic Achievement Scores After Proton and Photon Therapy in Children and Young Adults with Craniopharyngioma; WILEY: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; p. S15. [Google Scholar]
- Ohhashi, G.; Miyazaki, S.; Ikeda, H.; Hori, T. Postoperative Long-term Outcomes of Patient with Craniopharyngioma Based on CyberKnife Treatment. Cureus 2020, 12, e7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, L.; Losa, M.; Barzaghi, L.R.; Niranjan, A.; Siddiqui, Z.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D.; Mortini, P. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Pituitary Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheesh, R.; Swallow, D.M.A.; Rajaratnam, S.; Jacob, K.S.; Chacko, G.; Joseph, M.; Chacko, A.G. Incidence, predictors and early post-operative course of diabetes Insipidus in paediatric craniopharygioma: A comparison with adults. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2013, 29, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountas, A.; Coulden, A.; Fernández-García, S.; Georgios Tsermoulas Allotey, J.; Karavitaki, N. Central diabetes insipidus (vasopressin deficiency) after surgery for pituitary tumours: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2024, 191, S1–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, M.H.; Ahmad, M.M.; Brema, I.; Almehthel, M.; AlDahmani, K.M.; Mahzari, M.; Beshyah, S.A. Management of Diabetes Insipidus following Surgery for Pituitary and Suprasellar Tumors. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2021, 21, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Fan, K.; Peng, X.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Bai, R.N.; Wei, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Q.; et al. Postoperative hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction and long-term hormone replacement in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1241145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Ru, S.; Cai, K.; Jia, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, S. Risk factors for cerebrospinal fluid leak after extended endoscopic endonasal surgery for adult patients with craniopharyngiomas: A multivariate analysis of 364 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 140, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Alkire, B.C.; Lam, A.C.; Curry, W.T.; Holbrook, E.H. Aseptic Meningitis with Craniopharyngioma Resection: Consideration after Endoscopic Surgery. J. Neurol. Surg. Rep. 2016, 77, e151–e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowithayasakul, P.; Beckhaus, J.; Boekhoff, S.; Friedrich, C.; Calaminus, G.; Müller, H.L. Vision-related quality of life in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serbis, A.; Tsinopoulou, V.R.; Papadopoulou, A.; Kolanis, S.; Sakellari, E.I.; Margaritis, K.; Litou, E.; Ntouma, S.; Giza, S.; Kotanidou, E.P.; et al. Predictive Factors for Pediatric Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: An Extensive Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.J.R.; Wee, R.G.M.; Aw, N.M.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Ho, C.W.L.; Teo, K.; Lwin, S.; Yeo, T.T.; Kimpo, M.; Nga, V.D.W. Management and Outcomes of Pediatric Craniopharyngioma: A 15-Year Experience in Singapore. World Neurosurg. 2023, 177, e415–e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Pei, L.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Gui, S.; Ni, M.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, L. Characteristics and factors influencing hypothalamic pituitary dysfunction in patients with craniopharyngioma. Front Endocrinol 2023, 14, 1180591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.; Butterfield, J.T.; Dhawan, S.; Tyler, M.A.; Venteicher, A.S. Prognostic Factors and Treatment Impact on Overall Survival in Adult Craniopharyngioma. World Neurosurg. 2023, 173, e132–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adamantinomatous Variant | Papillary Variant | |
|---|---|---|
| Age group | Children and adults | Adults |
| Location | Pituitary stalk, subdiaphragmatic | Pituitary stalk, third ventricle |
| Texture | Calcified Multicystic components | Not calcified Predominantly solid |
| Hypothalamic and pituitary gland invasiveness | More with tumor noted to usually be very adherent to neurovascular structures | Less with tumor noted to usually be less adherent to neurovascular structures |
| Mutation | CTNNB1 (chromosome 3p21) with upregulation of Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway genes (including EGFR- and SHH-) | BRAF V600E (chromosome 7q34) with upregulation of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway genes |
| Symptom/Sign | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual impairment (temporal hemianopsia most common from chiasmatic compression) | 62–84% |
| Endocrine dysfunction (from involvement/compression of the pituitary stalk) | 40–87% |
| 85% |
| 40% |
| 25% |
| 25% |
| 20% |
| Headaches | 50% |
| Approach | Challenges/Limitations |
|---|---|
| TCA |
|
| EEA |
|
| Treatment Modality | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages/Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Subtotal or complete resection via the TCA or EEA | -tumor volume reduction and diagnosis -decreased RT dose post-resection -multiple corridors (TCA vs. EEA) with varying risk profiles -standard of care for adult and pediatric populations -potentially curative after GTR | -invasive -recurrence and risk for reoperation after STR -risk of endocrinologic disruption requiring hormone replacement -patient must meet surgical criteria and hold blood thinners perioperatively -added complexity in children 0–10 years old (incomplete paranasal sinus pneumatization) |
| Radiation Therapy | Stereotactic radiosurgery or proton beam RT (preferred in children) | -noninvasive -targets postop residual invasive CP -precise targeting with proton beam used in children -excellent local tumor control (up to 91.1%) | -limited use in pediatrics (radiosensitive) -radiotoxicity -may induce secondary tumors -delayed onset vasculopathies |
| Targeted Therapies | Genetic targets (CTNNB1 and BRAF V600E mutations) identified to interrupt molecular mechanisms of CP growth | -noninvasive -potentially decreased damage to non-CP tissue and preserved endocrinologic functioning -options for combination therapy | -requires crossing blood-brain barrier -potential acquired resistance -clinical trials ongoing, not currently approved for routine use in ACP treatment -adverse medication event |
| Intracavitary Treatments | Beta–gamma radiation and/or bleomycin | -additional volume reduction, particularly for cystic portions, after surgical resection | -may induce secondary tumors -radiotoxicity -delayed onset vasculopathies -limited radiation use in children (radiosensitive) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javidialsaadi, M.; Luy, D.D.; Smith, H.L.; Cecia, A.; Yang, S.D.; Germanwala, A.V. Advances in the Management of Craniopharyngioma: A Narrative Review of Recent Developments and Clinical Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041101
Javidialsaadi M, Luy DD, Smith HL, Cecia A, Yang SD, Germanwala AV. Advances in the Management of Craniopharyngioma: A Narrative Review of Recent Developments and Clinical Strategies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041101
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavidialsaadi, Mousa, Diego D. Luy, Heather L. Smith, Arba Cecia, Seunghyuk Daniel Yang, and Anand V. Germanwala. 2025. "Advances in the Management of Craniopharyngioma: A Narrative Review of Recent Developments and Clinical Strategies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041101
APA StyleJavidialsaadi, M., Luy, D. D., Smith, H. L., Cecia, A., Yang, S. D., & Germanwala, A. V. (2025). Advances in the Management of Craniopharyngioma: A Narrative Review of Recent Developments and Clinical Strategies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041101






