The Impact of Aortic Arch Morphology on Periprocedural Stroke in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
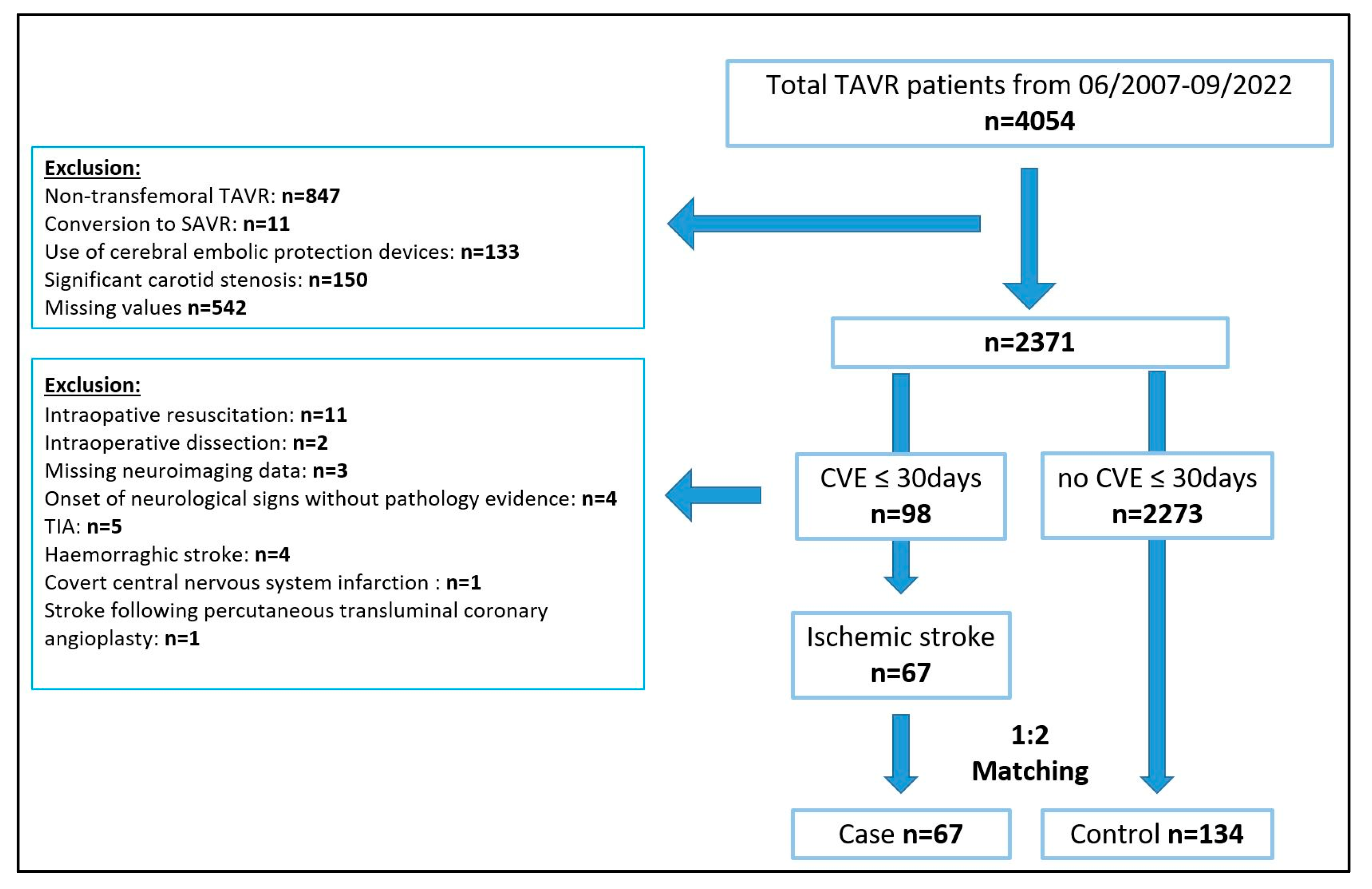
2.1. Patients
2.2. Stroke Definition
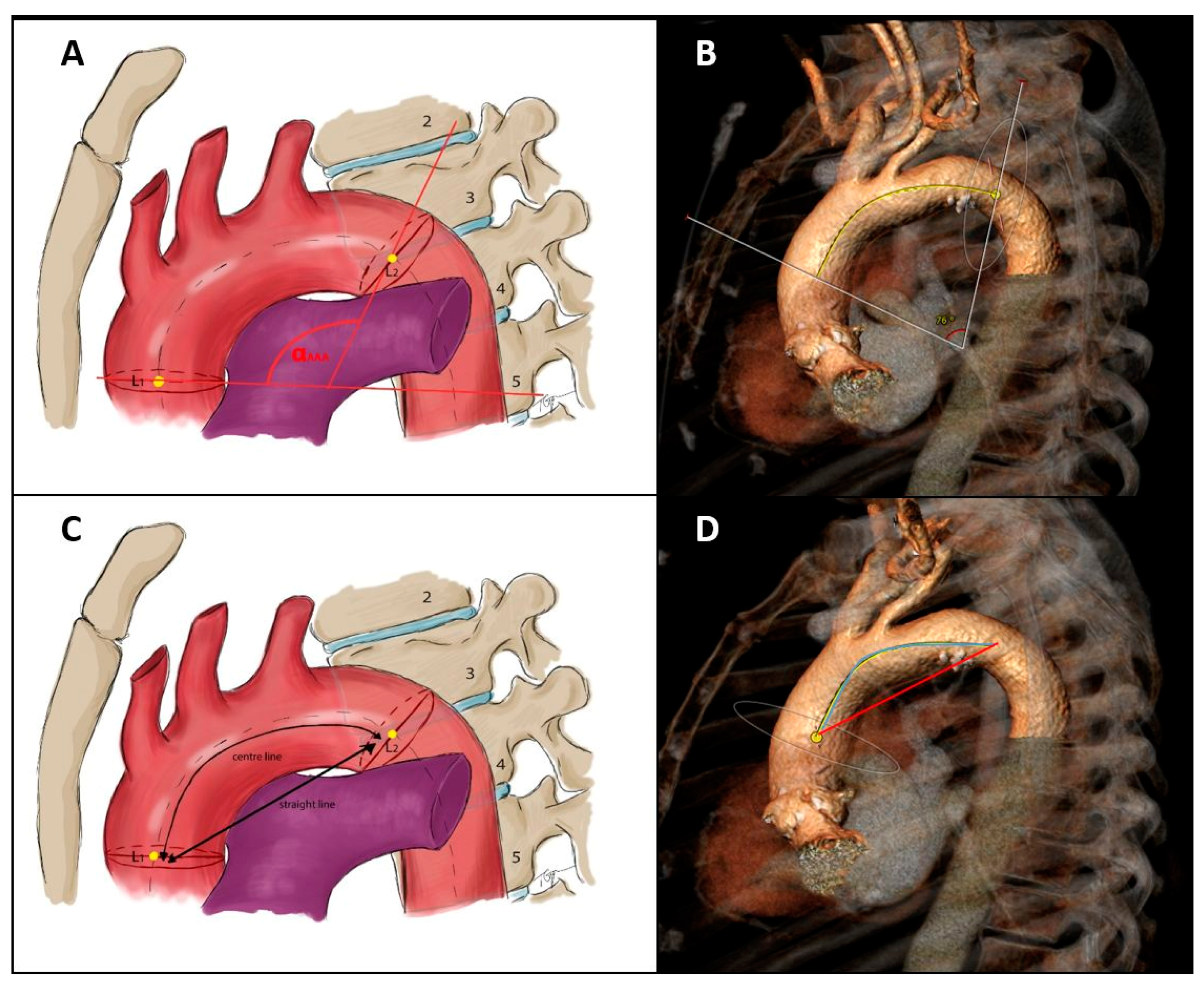
2.3. Aortic Arch MSCT Measurements and Definitions
- 1.
- Anatomical variations of the aortic arch
- Normal aortic arch with a separated origin of the brachiocephalic, left common carotid, and left subclavian artery.
- Bovine arch Type I presenting with a common origin for the brachiocephalic and left common carotid artery.
- Bovine arch Type II with a separate origin of the left common carotid artery from the brachiocephalic artery.
- 2.
- Configuration of the aortic arch according to the origin of the supra-aortic arteries
- Aortic arch Type I with all supra-aortic branches originating at the level of the outer aortic curvature.
- Aortic arch Type II with at least one of the supra-aortic branches originating between the level of the outer and inner aortic curvature.
- 3.
- Aortic arch curvature
- 4.
- Aortic arch take-off angles
- AA/BA angle = angle between the aortic arch and the brachiocephalic artery.
- AA/LCC angle = angle between the aortic arch and the left common carotid artery.
2.4. Clinical Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
- -
- ≤0.5: poor reliability;
- -
- 0.5–0.75: moderate reliability;
- -
- 0.75–0.9: good reliability;
- -
- ≥0.9: excellent reliability.
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Matching Results
3.2. Baseline and Perioperative Patient Characteristics
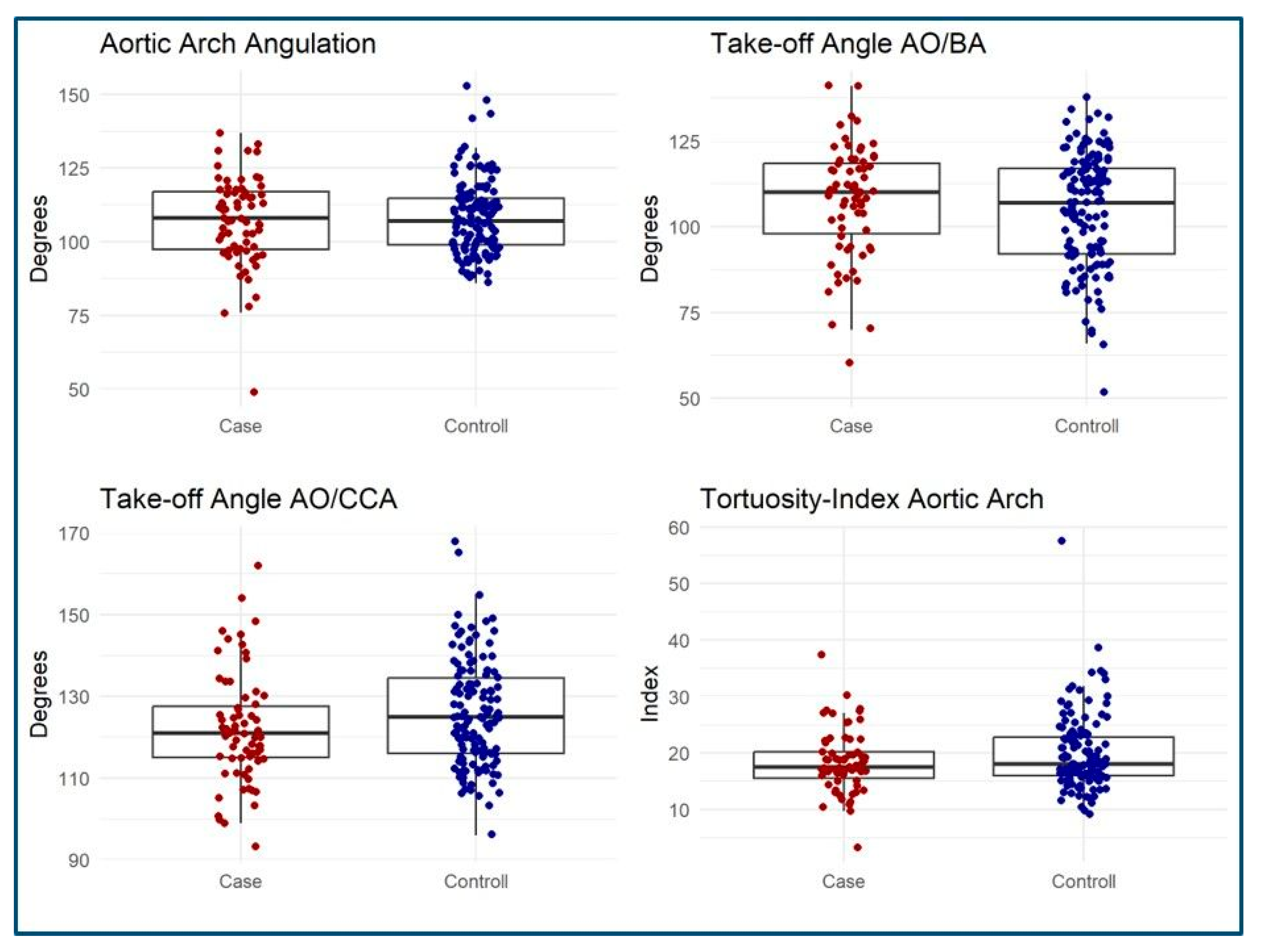
3.3. MSCT Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations:
| AAA | Aortic arch angulation |
| AA/BA | Angle aortic arch/brachiocephalic artery angle |
| AA/LCCA | Angle aortic arch/left common carotid artery angle |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| ICC | Intra-class correlation coefficient |
| MSCT | Multi-slice computed tomography |
| VARC III | Valve Academic Research Consortium III |
| TAVR | Transcatheter aortic valve replacement |
| THV | Transcatheter heart valve |
| TI | Tortuosity index |
References
- Levi, A.; Linder, M.; Seiffert, M.; Witberg, G.; Pilgrim, T.; Tomii, D.; Talmor-Barkan, Y.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Adrichem, R.; Codner, P.; et al. Management and Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke Complicating Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 15, 1808–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huded, C.P.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Krishnaswamy, A.; Mick, S.L.; Kleiman, N.S.; Svensson, L.G.; Carroll, J.; Thourani, V.H.; Kirtane, A.J.; Manandhar, P.; et al. Association Between Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement and Early Postprocedural Stroke. JAMA 2019, 321, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, A.; Thiagarajan, K.; Van Ham, R.; Gleason, T.G.; Mulukutla, S.; Schindler, J.T.; Jeevanantham, V.; Thirumala, P.D. Meta-Analysis of Perioperative Stroke and Mortality in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gils, L.; Kroon, H.; Daemen, J.; Ren, C.; Maugenest, A.M.; Schipper, M.; De Jaegere, P.P.; Van Mieghem, N.M. Complete filter-based cerebral embolic protection with transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. Off. J. Soc. Card. Angiogr. Interv. 2018, 91, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlert, P.; Al-Rashid, F.; Dottger, P.; Mori, K.; Plicht, B.; Wendt, D.; Bergmann, L.; Kottenberg, E.; Schlamann, M.; Mummel, P.; et al. Cerebral embolization during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A transcranial Doppler study. Circulation 2012, 126, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufi, M.; Guivier-Curien, C.; Loundou, A.D.; Deplano, V.; Boiron, O.; Chaumoitre, K.; Gariboldi, V.; Alimi, Y.S. Morphological Analysis of Healthy Aortic Arch. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 53, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatius, A.; Eng, M.H.; Frisoli, T.M. Neurologic Complications in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 10, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafii-Tari, H.; Riga, C.V.; Payne, C.J.; Hamady, M.S.; Cheshire, N.J.; Bicknell, C.D.; Yang, G.Z. Reducing contact forces in the arch and supra-aortic vessels using the Magellan robot. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbusch, P.; Kotelis, D.; Muller-Eschner, M.; Hyhlik-Durr, A.; Bockler, D. Complications after aortic arch hybrid repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotelis, D.; Bischoff, M.S.; Jobst, B.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Hinz, U.; Geisbusch, P.; Bockler, D. Morphological risk factors of stroke during thoracic endovascular aortic repair. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2012, 397, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, N.; Bigliardi, G.; Dell’Acqua, M.L.; Vandelli, L.; Ciolli, L.; Picchetto, L.; Borzi, G.; Ricceri, R.; Pentore, R.; Vallone, S.; et al. The Relation Between Aortic Arch Branching Types and the Laterality of Cardio-Embolic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2020, 29, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.W.; Luo, T.; Navia, J.A.; Kassab, G.S. Role of Aortic Geometry on Stroke Propensity based on Simulations of Patient-Specific Models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matakas, J.D.; Gold, M.M.; Sterman, J.; Haramati, L.B.; Allen, M.T.; Labovitz, D.; Slasky, S.E. Bovine Arch and Stroke Laterality. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, S.R.; Kodali, S.; Makkar, R.; Mehran, R.; Lazar, R.M.; Zivadinov, R.; Dwyer, M.G.; Jilaihawi, H.; Virmani, R.; Anwaruddin, S.; et al. Protection Against Cerebral Embolism During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansky, A.J.; Schofer, J.; Tchetche, D.; Stella, P.; Pietras, C.G.; Parise, H.; Abrams, K.; Forrest, J.K.; Cleman, M.; Reinohl, J.; et al. A prospective randomized evaluation of the TriGuard HDH embolic DEFLECTion device during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Results from the DEFLECT III trial. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodes-Cabau, J.; Dumont, E.; Boone, R.H.; Larose, E.; Bagur, R.; Gurvitch, R.; Bedard, F.; Doyle, D.; De Larochelliere, R.; Jayasuria, C.; et al. Cerebral embolism following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Comparison of transfemoral and transapical approaches. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansky, A.J.; Messe, S.R.; Brickman, A.M.; Dwyer, M.; van der Worp, H.B.; Lazar, R.M.; Pietras, C.G.; Abrams, K.J.; McFadden, E.; Petersen, N.H.; et al. Proposed Standardized Neurological Endpoints for Cardiovascular Clinical Trials: An Academic Research Consortium Initiative. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Alu, M.C.; Nazif, T.; Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Bax, J.J.; Leipsic, J.A.; Blanke, P.; Blackstone, E.H.; et al. Valve Academic Research Consortium 3: Updated endpoint definitions for aortic valve clinical research. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1825–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, S.; Campanella, C.; Burri, M.; Trenkwalder, T.; Sideris, K.; Erlebach, M.; Ruge, H.; Krane, M.; Vitanova, K.; Lange, R. Anatomical reasons for failure of dual-filter cerebral embolic protection application in TAVR: A CT-based analysis. J. Card. Surg. 2021, 36, 4537–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, S.; Schechtl, J.; Nobauer, C.; Bleiziffer, S.; Lange, R. Patient eligibility for application of a two-filter cerebral embolic protection device during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Does one size fit all? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 30, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, C.; Vitanova, K.; Burri, M.; Ruge, H.; Lange, R.; Voss, S. Does Aortic Arch Anatomy Affect Stroke Laterality in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation? J. Card. Surg. 2023, 2023, 5563121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.D.; Ahlhelm, F.J.; von Hessling, A.; Doig, D.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Macdonald, S.; Lyrer, P.A.; van der Lugt, A.; Hendrikse, J.; Stippich, C.; et al. Vascular Anatomy Predicts the Risk of Cerebral Ischemia in Patients Randomized to Carotid Stenting Versus Endarterectomy. Stroke A J. Cereb. Circ. 2017, 48, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Moorehead, P.A.; Kim, A.H.; Miller, C.P.; Kashyap, T.V.; Kendrick, D.E.; Kashyap, V.S. Prevalence of Bovine Aortic Arch Configuration in Adult Patients with and without Thoracic Aortic Pathology. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 30, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syperek, A.; Angermaier, A.; Kromrey, M.L.; Hosten, N.; Kirsch, M. The so-called “bovine aortic arch”: A possible biomarker for embolic strokes? Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadhiya, S.; Sardana, V.; Bhushan, B.; Maheshwari, D.; Yadav, S.R.; Goyal, R. Propensity of Stroke in Standard versus Various Aortic Arch Variants: A 200 Patients Study. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2022, 25, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Russo, G.V.; Alarouri, H.S.; Al-Abcha, A.; Vogl, B.; Mahayni, A.; Sularz, A.; Hatoum, H.; Collins, J.; Crestanello, J.A.; Alkhouli, M. Association of Bovine Arch Anatomy With Incident Stroke After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e032963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabert, S.; Lange, R.; Bleiziffer, S. Incidence and causes of silent and symptomatic stroke following surgical and transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A comprehensive review. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 23, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahlouh, M.; Chenoune, Y.; Blanc, R.; Piotin, M.; Escalard, S.; Fahed, R.; Szewczyk, J.; Passat, N. Automated Aortic Anatomy Analysis: From Image to Clinical Indicators. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2023, 2023, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Dhaliwal, A.S.; Sohal, S.; Gwon, Y.; Gupta, S.; Bhatia, K.; Dominguez, A.C.; Basman, C.; Tamis-Holland, J. Role of Cerebral Embolic Protection Devices in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: An Updated Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e030587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliari, A.P.; Ferrari, E.; Haager, P.K.; Schmiady, M.O.; Vicentini, L.; Gavazzoni, M.; Gennari, M.; Jorg, L.; Khattab, A.A.; Blochlinger, S.; et al. Feasibility and Safety of Cerebral Embolic Protection Device Insertion in Bovine Aortic Arch Anatomy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Prematch | Postmatch | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Control | SMD | p-Value | Case | Control | SMD | p-Value | |
| n = 67 | n = 2273 | n = 67 | n = 134 | |||||
| Female gender | 35 (52.2%) | 1089 (47.9%) | 0.087 | 0.5 | 35 (52.2%) | 70 (52.2%) | 0 | 1.0 |
| Atrial fibrilation | 16 (23.9%) | 640 (28.2%) | 0.095 | 0.5 | 16 (23.9%) | 26 (19.4%) | 0.11 | 0.5 |
| Preoperative stroke | 9 (13.4%) | 241 (10.6%) | 0.092 | 0.4 | 9 (13.4%) | 14 (10.4%) | 0.094 | 0.6 |
| Previous operation | 4 (6.0%) | 323 (14.2%) | 0.238 | 0.07 | 4 (6.0%) | 8 (6.0%) | 0 | 1.0 |
| Age (Y) | 80.0 ± 13.2 | 79.7 ± 8.9 | 0.042 | 0.8 | 80.0 ± 13.2 | 81.2 ± 6.4 | 0.128 | 0.5 |
| Euroscore 2 | 4.1 ± 3.6 | 5.0 ± 6.2 | 0.145 | 0.058 | 4.1 ± 3.6 | 4.3 ± 4.1 | 0.055 | 0.7 |
| Valve type | <0.001 | 1.0 | ||||||
| Medtronic CoreValve (Metdronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) | 19 (28.4%) | 229 (10.1%) | 19 (28.4%) | 38 (28.4%) | ||||
| Medtronic Evolut R (Metdronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) | 14 (20.9%) | 561 (24.7%) | 14 (20.9%) | 28 (20.9%) | ||||
| Edwards Sapien Ultra (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA, USA) | 12 (17.9%) | 527 (23.2%) | 12 (17.9%) | 24 (17.9%) | ||||
| Edwards Sapien 3 (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA, USA) | 10 (14.9%) | 523 (23.0%) | 10 (14.9%) | 20 (14.9%) | ||||
| Medtronic Evolut Pro (Metdronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) | 5 (7.5%) | 90 (4.0%) | 5 (7.5%) | 10 (7.5%) | ||||
| Boston Scientific Lotus (Boston Scientific, Watertown, MA, USA) | 4 (6.0%) | 134 (5.9%) | 4 (6.0%) | 8 (6.0%) | ||||
| Symetis Acurate Neo (Boston Scientific, Watertown, MA, USA) | 2 (3.0%) | 80 (3.5%) | 2 (3.0%) | 4 (3.0%) | ||||
| Edwards Sapien XT (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA, USA) | 1 (1.5%) | 24 (1.1%) | 1 (1.5%) | 2 (1.5%) | ||||
| Other | 0 (0.0%) | 105 (4.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| Characteristics | Case | Control | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 67 | 134 | |
| Age (y) | 83 [65–93] | 82 [53–94] | 0.7 |
| Female gender (n) | 35 (52.2%) | 70 (52.2%) | 1.0 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.7 [16.5–46.8] | 27.0 [3.3–45.7] | 0.09 |
| Coronary artery disease (n) | 37 (55.2%) | 70 (52.2%) | 0.8 |
| Hypertension (n) | 59 (88.1%) | 123 (91.8%) | 0.4 |
| Diabetes (n) | 18 (26.9%) | 43 (32.1%) | 0.5 |
| Peripheral artery disease (n) | 11 (16.4%) | 17 (12.7%) | 0.5 |
| Previous cardiac procedure (n) | 4 (6.0%) | 8 (6.0%) | 1.0 |
| Previous stroke (n) | 9 (13.4%) | 14 (10.4%) | 0.6 |
| COPD (n) | 11 (16.4%) | 13 (9.7%) | 0.2 |
| LV-EF (n) | 0.3 | ||
| >50% | 49 (73.1%) | 88 (65.7%) | |
| 35–50% | 13 (19.4%) | 34 (25.4%) | |
| <35% | 5 (7.5%) | 11 (8.2%) | |
| GFR (MDR) (n) | 58 ± 20 | 65 ± 24 | 0.059 |
| STS Score | 4.1 ± 3.0 | 4.2 ± 3.3 | 0.8 |
| Euroscore II | 4.1 ± 3.6 | 4.3 ± 4.1 | 0.7 |
| Year of procedure (n) | 0.4 | ||
| 2007–2012 | 12 (17.9%) | 16 (11.9%) | |
| 2012–2017 | 24 (35.8%) | 47 (35.1%) | |
| 2017–2023 | 31 (46.3%) | 71 (53.0%) | |
| Ballon-expandable valve (n) | 23 (34.3%) | 46 (34.3%) | 1.0 |
| Second valve implantation (n) | 2 (3.0%) | 1 (0.7%) | 0.3 |
| Puncture to suture (min) | 73 ± 38 | 66 ± 39 | 0.2 |
| Pre-dilatation (n) | 40 (59.7%) | 78 (58.2%) | 0.9 |
| Post-dillatation (n) | 22 (32.8%) | 45 (33.6%) | 1.0 |
| MSCT Data | Case | Control | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 67 | 134 | |
| Anatomy | 0.2 | ||
| Normal | 50 (74.6%) | 89 (66.4%) | |
| Bovine I | 7 (10.4%) | 27 (20.1%) | |
| Bovine II | 10 (14.9%) | 18 (13.4%) | |
| Configuration | 0.8 | ||
| Type I | 9 (13.4%) | 15 (11.2%) | |
| Type II | 48 (71.6%) | 96 (71.6%) | |
| Type III | 10 (14.9%) | 23 (17.2%) | |
| AO/BA Angle (degree) | 110 [60–141] | 107 [52–138] | 0.3 |
| AO/CCA Angle (degree) | 121 [93–162] | 125 [96–168] | 0.058 |
| Arch Angulation (degree) | 108 [49–137] | 107 [86–153] | 0.9 |
| Tortuosity Index | 17.5 [3.3–37.4] | 18.1 [9.2–57.5] | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voss, S.; Rusa, K.; Campanella, C.; Georgescu, T.; Vitanova, K.; Ruge, H.; Amabile, A.; Sideris, K.; Krane, M.; Burri, M. The Impact of Aortic Arch Morphology on Periprocedural Stroke in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041045
Voss S, Rusa K, Campanella C, Georgescu T, Vitanova K, Ruge H, Amabile A, Sideris K, Krane M, Burri M. The Impact of Aortic Arch Morphology on Periprocedural Stroke in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041045
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoss, Stephanie, Katerina Rusa, Caterina Campanella, Teodora Georgescu, Keti Vitanova, Hendrik Ruge, Andrea Amabile, Konstantinos Sideris, Markus Krane, and Melchior Burri. 2025. "The Impact of Aortic Arch Morphology on Periprocedural Stroke in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041045
APA StyleVoss, S., Rusa, K., Campanella, C., Georgescu, T., Vitanova, K., Ruge, H., Amabile, A., Sideris, K., Krane, M., & Burri, M. (2025). The Impact of Aortic Arch Morphology on Periprocedural Stroke in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041045








