The Effects of Biomechanical Loading on the Tibial Insert After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
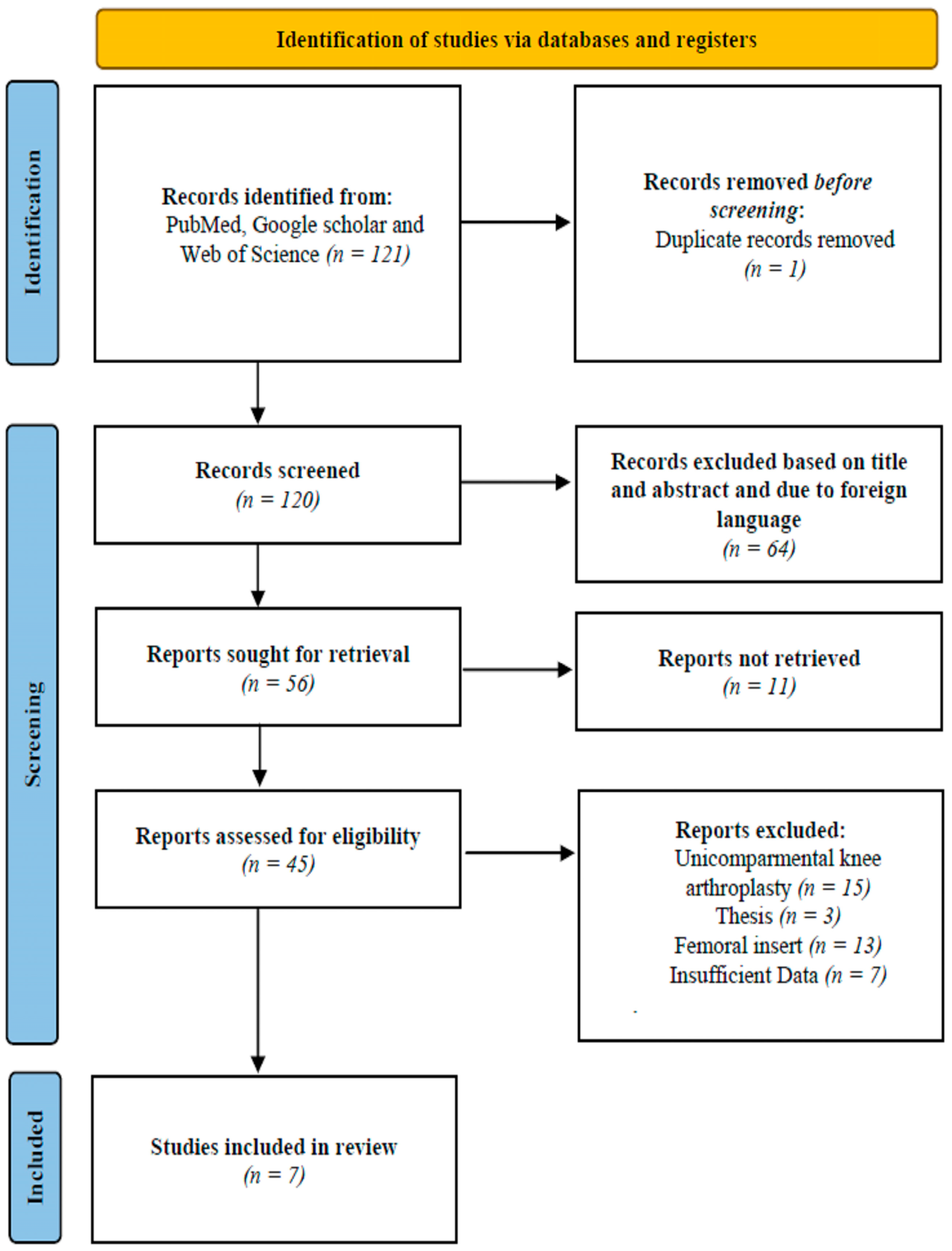
2. Methods
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TKA | Total knee arthroplasty |
| PTS | Posterior tibial slope |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| TF | Tibiofemoral |
| PS | Posterior-stabilized |
| CR | Cruciate-retaining |
| PCL | Posterior cruciate ligament |
| ROM | Range of motion |
| TEA | Transepicondylar axis |
| ML | Mediolateral |
| FEM | Finite element model |
| MSC | Musculoskeletal |
| A-P | Antero-posterior |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| PF | Patellofemoral |
References
- Postler, A.; Lützner, C.; Beyer, F.; Tille, E.; Lützner, J. Analysis of total knee arthroplasty revision causes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalyan, S.; Ozan, F.; Altun, İ.; Kahraman, M.; Günay, A.E.; Özdemir, K. The Influence of Component Rotational Malalignment on Early Clinical Outcomes in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Cureus 2022, 14, e22444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Essen, J.; Stevens, J.; Dowsey, M.M.; Choong, P.F.; Babazadeh, S. Kinematic alignment results in clinically similar outcomes to mechanical alignment: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee 2023, 40, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Bozic, K.J. Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: Updated projections to 2021. JBJS 2014, 96, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroer, W.C.; Berend, K.R.; Lombardi, A.V.; Barnes, C.L.; Bolognesi, M.P.; Berend, M.E.; Ritter, M.A.; Nunley, R.M. Why are total knees failing today? Etiology of total knee revision in 2010 and 2011. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, P.F.; Hozack, W.J.; Rothman, R.H.; Shastri, S.; Jacoby, S.M. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. (1976–2007) 2002, 404, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitta, M.; Esposito, C.I.; Li, Z.; Lee, Y.-y.; Wright, T.M.; Padgett, D.E. Failure after modern total knee arthroplasty: A prospective study of 18,065 knees. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleaca, R.; Mitariu, S.; Oleksik, V.; Oleksik, M.; Roman, M. Mechanical behaviour of orthopaedic cement loaded with antibiotics in the operation room. Mater Plast 2017, 54, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocea, B.A.; Roman, M.D.; Fleaca, R.S.; Ion, N.C.; Necula, R.; Diconi, A.F.; Mihaila, R.G. Challenges and Complications in Treating Total Knee Arthroplasty in Morbidly Obese Patients. Cureus 2024, 16, e71433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.; Haritinian, E.G.; Cristea, S. Methods of intra-and post-operative determination of the position of the tibial component during total knee replacement. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehl, M.; Bulaid, Y.; Chelli, M.; Belhaouane, R.; Gabrion, A.; Havet, E.; Mertl, P. Total knee arthroplasty with the Medial-Pivot knee system: Clinical and radiological outcomes at 9.5 years’ mean follow-up. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Bates, T.; Kampfer, C.; Hope, D. Biomechanics and outcomes of modern tibial polyethylene inserts. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2022, 15, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.-T.; Son, J.; Kwon, S.K.; Kwon, O.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Koh, Y.-G. Finite element analysis for the biomechanical effect of tibial insert materials in total knee arthroplasty. Compos. Struct. 2018, 201, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudhon, J.-L.; Verdier, R. Cemented or cementless total knee arthroplasty?: Comparative results of 200 cases at a minimum follow-up of 11 years. Sicot-J 2017, 3, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyński, M.; Bieniek, M.; Krakowski, P.; Karpiński, R. Cemented vs. Cementless Fixation in Primary Knee Replacement: A Narrative Review. Materials 2024, 17, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.-W.; Chang, C.-F. Biomechanics of human movement and its clinical applications. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2012, 28, S13–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logerstedt, D.S.; Ebert, J.R.; MacLeod, T.D.; Heiderscheit, B.C.; Gabbett, T.J.; Eckenrode, B.J. Effects of and Response to Mechanical Loading on the Knee. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 201–235. [Google Scholar]
- Grieco, T.F.; Sharma, A.; Dessinger, G.M.; Cates, H.E.; Komistek, R.D. In vivo kinematic comparison of a bicruciate stabilized total knee arthroplasty and the normal knee using fluoroscopy. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cofaru, N.F.; Roman, M.D.; Cofaru, I.I.; Oleksik, V.S.; Fleaca, S.R. Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy in knee osteoarthritis—A biomechanical approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaienti, E.; Scita, G.; Ceccarelli, F.; Pogliacomi, F. Understanding the human knee and its relationship to total knee replacement. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm. 2017, 88, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Stronach, B.M.; Adams, J.C.; Jones, L.C.; Farrell, S.M.; Hydrick, J.M. The effect of sacrificing the posterior cruciate ligament in total knee arthroplasties that use a highly congruent polyethylene component. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorger, J.I.; Federle, D.; Kirk, P.G.; Grood, E.; Cochran, J.; Levy, M. The posterior cruciate ligament in total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 1997, 12, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, U.G.; Viganò, M.; Candela, V.; De Girolamo, L.; Cella, E.; Thiebat, G.; Salvatore, G.; Ciccozzi, M.; Denaro, V. Epidemiology of posterior cruciate ligament reconstructions in Italy: A 15-year study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chang, S.-S.; Yeh, W.-L.; Chen, A.C.-Y.; Hsu, K.-Y.; Weng, C.-J.; Chan, Y.-S. Clinical and functional outcomes of isolated posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in patients over the age of 40 years. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postac, P.; Matejczyk, M.; Greenwald, A. Stability characteristics of total knee replacements. In Scientific Exhibit, 56th Annual Meeting of the AAOS; Orthopaedic Research Society: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hamelynck, K.; Briard, J.-L.; Pappas, M. Biomechanics of Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA). In LCS® Mobile Bearing Knee Arthroplasty: A 25 Years Worldwide Review; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Aljehani, M.S.; Christensen, J.C.; Snyder-Mackler, L.; Crenshaw, J.; Brown, A.; Zeni, J.A., Jr. Knee biomechanics and contralateral knee osteoarthritis progression after total knee arthroplasty. Gait Posture 2022, 91, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feczko, P.Z.; Pijls, B.G.; van Steijn, M.J.; van Rhijn, L.W.; Arts, J.J.; Emans, P.J. Tibial component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Okanoue, Y.; Ueta, E.; Tani, T. Determining the rotational alignment of the tibial component at total knee replacement: A comparison of two techniques. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2007, 89, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indelli, P.F.; Graceffa, A.; Marcucci, M.; Baldini, A. Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.-M.; Bauer, L.; Thorwächter, C.; Woiczinski, M.; Simon, F.; Müller, P.E.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Niethammer, T.R. The Influence of Kinematic Alignment on Patellofemoral Joint Biomechanics in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Lian, Q.; Li, D.; Jin, Z. Effect of component mal-rotation on knee loading in total knee arthroplasty using multi-body dynamics modeling under a simulated walking gait. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, K. The biomechanical effect of different posterior tibial slopes on the tibiofemoral joint after posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, F.W.; Ayers, D.C.; Maletsky, L.P.; Rullkoetter, P.J. The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in total knee replacements. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.D.; Howell, S.M.; Hull, M.L. Kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty limits high tibial forces, differences in tibial forces between compartments, and abnormal tibial contact kinematics during passive flexion. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.-T.; Kwon, S.K.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.-R.; Lee, J.-S.; Koh, Y.-G. The increase in posterior tibial slope provides a positive biomechanical effect in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 3188–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, B.J.; Tilan, J.U.; McGarry, M.H.; Takenaka, N.; Kim, W.C.; Lee, T.Q. The biomechanical effect of increased valgus on total knee arthroplasty: A cadaveric study. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, D.; Kang, K.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.; Baek, C.; Koh, Y. Computational study on the effect of malalignment of the tibial component on the biomechanics of total knee arthroplasty: A Finite Element Analysis. Bone Jt. Res. 2017, 6, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchett, J.W. Patients prefer a bicruciate-retaining or the medial pivot total knee prosthesis. J. Arthroplast. 2011, 26, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, W.F.; Miller, M.A.; Cleary, R.J.; Izant, T.H.; Mann, K.A. Damage in total knee replacements from mechanical overload. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, W. A 3D finite element model to investigate prosthetic interface stresses of different posterior tibial slope. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, A.G.; Raso, V.J.; Liggins, A.; Amirfazli, A. Contribution of loading conditions and material properties to stress shielding near the tibial component of total knee replacements. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbrück, A.; Schröder, C.; Woiczinski, M.; Fottner, A.; Pinskerova, V.; Müller, P.E.; Jansson, V. Femorotibial kinematics and load patterns after total knee arthroplasty: An in vitro comparison of posterior-stabilized versus medial-stabilized design. Clin. Biomech. 2016, 33, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalury, D.F.; Pomeroy, D.L.; Gorab, R.S.; Adams, M.J. Why are total knee arthroplasties being revised? J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Lima, D.D.; Hermida, J.C.; Chen, P.C.; Colwell, C.W., Jr. Polyethylene wear and variations in knee kinematics. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. (1976–2007) 2001, 392, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, V.Y.; DeClaire, J.H.; Berend, K.R.; Gulick, B.C.; Lombardi, A.V., Jr. Improved accuracy of alignment with patient-specific positioning guides compared with manual instrumentation in TKA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res.® 2012, 470, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Lee, G.Y.; Steklov, N.; Colwell, C.W., Jr.; Ezzet, K.A.; D’Lima, D.D. Effect of tibial component varus on wear in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2012, 19, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berend, M.E.; Ritter, M.A.; Meding, J.B.; Faris, P.M.; Keating, E.M.; Redelman, R.; Faris, G.W.; Davis, K.E. The Chetranjan Ranawat Award: Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res.® 2004, 428, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.M.; Ritter, M.A.; Davis, K.E. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: Just how important is it? J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.W.; Wood, A.R.; Kosmopoulos, V.; Sanchez, H.B.; Wagner, R.A. Effect of posterior tibial slope on flexion and anterior-posterior tibial translation in posterior cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujito, T.; Tomita, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Oda, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Sugamoto, K. Influence of posterior tibial slope on kinematics after cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 3778–3782.e3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, E.; Sasashige, Y.; Tomita, T.; Iwamoto, K.; Masuda, Y.; Hisatome, T. Significant effect of the posterior tibial slope on the weight-bearing, midflexion in vivo kinematics after cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Mizu-uchi, H.; Okazaki, K.; Hamai, S.; Nakahara, H.; Iwamoto, Y. Effect of tibial posterior slope on knee kinematics, quadriceps force, and patellofemoral contact force after posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, Y.; Hino, K.; Watanabe, S.; Watamori, K.; Kutsuna, T.; Miura, H. The influence of tibial resection on the PCL in PCL-retaining total knee arthroplasty: A clinical and cadaveric study. J. Orthop. Sci. Off. J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 2016, 21, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Muratsu, H.; Kubo, S.; Matsushita, T.; Ishida, K.; Kuroda, R.; Kurosaka, M. The influence of the tibial slope on intra-operative soft tissue balance in cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, B.; Baez, J.; Testa, N.N.; Kummer, F.J. Effect of posterior cut angle on tibial component loading. J. Arthroplast. 2000, 15, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullaji, A.; Shetty, G.M. Persistent hindfoot valgus causes lateral deviation of weightbearing axis after total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res.® 2011, 469, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.T.; Moskal, J.T. Evaluation of knee and hindfoot alignment before and after total knee arthroplasty: A prospective analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2004, 19, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naili, J.E.; Iversen, M.D.; Esbjörnsson, A.-C.; Hedström, M.; Schwartz, M.H.; Häger, C.K.; Broström, E.W. Deficits in functional performance and gait one year after total knee arthroplasty despite improved self-reported function. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 3378–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.-G.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.-R.; Kwon, S.K.; Kang, K.-T. Tibiofemoral conformity variation offers changed kinematics and wear performance of customized posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, K. Tibiofemoral joint contact area and stress after single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with transtibial versus anteromedial portal drilling techniques. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.L.; Yi, S.J.; Ren, Y.; Zimmerman, T.A.; Zhang, L.-Q. Tibiofemoral contact mechanics with horizontal cleavage tear and resection of the medial meniscus in the human knee. JBJS 2016, 98, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Year | Study Design | Population | Type of Intervention | Results | Effect on Biomechanics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [32] | 2015 | Musculoskeletal study | Human female knees | Effect of tibial insert malrotation on biomechanical loading | Peak TF contact force increased by 11.0% with a 5° varus alignment of the tibial insert. | Greater than 3° varus malrotation of the tibial component may lead to medial bone collapse |
| Werner et al. [35] | 2005 | Retrospective cadaveric study | Human cadaveric knees (n = 7) | The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in TKA | A 3° variation in angulation caused biomechanical changes in the medial and lateral compartments of the tibial component. | Tibial contact pressures measured during a trial reduction could predict the contact mechanics under higher loading conditions |
| Roth et al. [36] | 2017 | Retrospective cadaveric study | Human cadaveric knees (n = 13) | Effect of tibial forces on aligned TKA | Contact locations shifted posteriorly by an average of 14 mm in the medial compartment and 18 mm in the lateral compartment from 0° to 120° of flexion. | Alignment methods reduce high tibial forces, minimize force differences between compartments, and limit anterior tibial contact shift during passive flexion |
| Wang et al. [33] | 2020 | Retrospective cadaveric study | Human cadaveric knees (n = 9) | Different PTSs were compared | After TKA, the TF contact area decreased from 586.2 mm2 to 130.2 mm2, while contact pressures increased. | TKA with a larger PTS results in more posterior femoral translation, a larger contact area, and less contact pressure |
| Kang et al. [37] | 2017 | Computational study | Computational model | Forces on the quadriceps, tibial posterior translation, the PE insert, and knee joint were compared | Increase in the PTS led to decrease in medial and collateral ligaments, as well as decrease in the maximum force on the quadriceps. | Excessive increase in PTS may cause progressive loosening of the knee joint due to reduced collateral ligament tension and failure of the posterior of the PE insert |
| Bryant et al. [38] | 2014 | Retrospective cadaveric study | Human cadaveric knees (n = 8) | Effect of increased valgus after TKA | Increases in valgus loading led to strain of anterior MCL when compared to neutral conditions at 0° (2.5%), 30° (3.1%), and 60° (3.7%) of knee flexion. | A 5° valgus angle was associated with increased lateral tibiofemoral contact pressures and increased strain on the MCL |
| Suh et al. [39] | 2017 | Computational FEM study | Computational model | Effect of varus and valgus malalignment on biomechanics after TKA | In varus alignment, the medial contact stress increased by 24.0% at 3° and 35.0% at 5°, while the lateral stress decreased. In contrast, valgus alignment decreased the medial stress by 37.2% at 3° and 50.7% at 5°, while the lateral stress increased. | Varus malalignment caused maximum stress on the medial PE insert, while valgus malalignment increased the medial ligament force, raising the risk of TKA failure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diconi, A.F.; Roman, M.D.; Cristian, A.N.; Boicean, A.G.; Mohor, C.I.; Ion, N.C.I.; Bocea, B.A.; Teodoru, C.A.; Oprinca, G.-C.; Fleaca, S.R. The Effects of Biomechanical Loading on the Tibial Insert After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041043
Diconi AF, Roman MD, Cristian AN, Boicean AG, Mohor CI, Ion NCI, Bocea BA, Teodoru CA, Oprinca G-C, Fleaca SR. The Effects of Biomechanical Loading on the Tibial Insert After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041043
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiconi, Alexandru Florin, Mihai Dan Roman, Adrian Nicolae Cristian, Adrian Gheorghe Boicean, Cosmin Ioan Mohor, Nicolas Catalin Ionut Ion, Bogdan Axente Bocea, Cosmin Adrian Teodoru, George-Calin Oprinca, and Sorin Radu Fleaca. 2025. "The Effects of Biomechanical Loading on the Tibial Insert After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041043
APA StyleDiconi, A. F., Roman, M. D., Cristian, A. N., Boicean, A. G., Mohor, C. I., Ion, N. C. I., Bocea, B. A., Teodoru, C. A., Oprinca, G.-C., & Fleaca, S. R. (2025). The Effects of Biomechanical Loading on the Tibial Insert After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041043







