Dynamic Contour Irregularities in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Long-Term Aesthetic Outcomes After Direct-to-Implant Versus Tissue Expander Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Complications & Secondary Corrections
3.3. BREAST-Q Evaluation
3.4. Cosmetic Results
3.5. Animation Deformity (AD)
3.6. Confounding Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | animation deformity |
| ADM | acellular dermal matrix |
| CC | capsular contracture |
| DICI | dynamic implant contour irregularity |
| DTI | direct-to-implant |
| NAC | nipple-areola-complex |
| NSME | nipple-sparing mastectomy |
| PROM | patient-reported outcome measure |
| SSME | skin-sparing mastectomy |
| TE | tissue expander |
References
- Lucas, D.J.; Sabino, J.; Shriver, C.D.; Pawlik, T.M.; Singh, D.P.; Vertrees, A.E. Doing more: Trends in breast cancer surgery, 2005 to 2011. Am. Surg. 2015, 81, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomard, V.; Leinster, S.; Wilkinson, M. Systematic review of studies of patients’ satisfaction with breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Breast 2007, 16, 547–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, A.; Morandi, E.M.; Winkelmann, S.; Schoberleitner, I.; Egle, D.; Ritter, M.; Bauer, T.; Wachter, T.; Wolfram, D. Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurauter, S.; Casari, M.E.; Augustin, A.; Stigger, T.; Brunner, C.; Wolfram, D. Challenging Autologous Breast Reconstruction in Low BMI Patients with Profunda Artery Perforator (PAP) Flap: Impact of Skin Island Design on Complication Rates and Long-Term Aesthetic Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosa, K.B.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.N.; Keane, A.M.; Ribaudo, J.G.; Tao, Y.; Margenthaler, J.A.; Tenenbaum, M.M.; Myckatyn, T.M. Direct-to-Implant vs Tissue Expander Placement in Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Cohort Study. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2024, 44, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdanasari, A.T.; Abu-Ghname, A.; Raj, S.; Winocour, S.J.; Largo, R.D. Update in Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2019, 33, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, E.; Pesce, M.; Santi, P.; Raposio, E. Two-Stage Tissue-Expander Breast Reconstruction: A Focus on the Surgical Technique. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1791546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Baril, J.A.; Fisher, C.S.; Danforth, R.M.; Bamba, R.; Lester, M.E.; Hassanein, A.H. Direct-to-Implant in the Era of Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: Evaluation of the National Trend in 59,313 Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2025, 13, e6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.M.; Farmer, R.L.; Afifi, A.M. Current Trends in Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: A Survey of American Society of Plastic Surgeons Members. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, C. Postoperative Complications Following Prepectoral Versus Partial Subpectoral Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction Using ADM: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, D.R.; Garvey, P.B.; Qi, J.; Hamill, J.B.; Kim, H.M.; Pusic, A.L.; Kronowitz, S.J.; Wilkins, E.G.; Butler, C.E.; Clemens, M.W. Direct-to-Implant versus Two-Stage Tissue Expander/Implant Reconstruction: 2-Year Risks and Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Prospective, Multicenter Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, A.A.; Seth, A.K.; Wang, E.; Hanwright, P.; Bilimoria, K.; Fine, N.; Kim, J.Y. Human Acellular Dermis versus Submuscular Tissue Expander Breast Reconstruction: A Multivariate Analysis of Short-Term Complications. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2013, 40, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, M.L.; Rios-Diaz, A.J.; Kimia, R.; Cunning, J.; Broach, R.; Wu, L.; Serletti, J.; Fosnot, J. Direct-to-Implant Versus 2-Stage Breast Reconstruction: Which Technique Is Better? An Analysis of 104 Patients at a Single Institution. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 89, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, E.; Alfieri, S.; Toffoli, E.; Borreani, C. A descriptive comparison of satisfaction and well-being between expander-based and direct-to-implant breast reconstruction after Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Odom, E.B.; Parikh, R.P.; Myckatyn, T.M.; Tenenbaum, M.M. Patient-Reported Outcomes of Aesthetics and Satisfaction in Immediate Breast Reconstruction After Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy with Implants and Fat Grafting. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2017, 37, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, E.; Nixdorf, L.; Devyatko, Y.; Exner, R.; Wimmer, K.; Fitzal, F. Prepectoral Versus Subpectoral Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, M.; Patanè, L.; Redi, U.; Turriziani, G.; Vietti, V.; Zoccali, G.; De Vita, R. Managing the animation deformity in breast reconstruction transposing the implant to a partial prepectoral pocket: Early experience and preliminary results with a new technique. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 86, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumilia, A.; Le, P.B.; Bian, J.; Becker, M.E.; Friedman, H.I. Implant-based breast reconstruction—A systematic review and meta-analysis of prepectoral versus submuscular implant placement. Ann. Breast Surg. 2025, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracol, M.; Feld, L.N.; Chiu, W.K.; Kim, J.Y.S. An overview of animation deformity in prosthetic breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2019, 8, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.; Fregosi, N. The Impact of Animation Deformity on Quality of Life in Post-Mastectomy Reconstruction Patients. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2017, 37, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrberg, D.L.; Bille, C.; Koudahl, V.; Gerke, O.; Sørensen, J.A.; Thomsen, J.B. Evaluation of Breast Animation Deformity following Pre- and Subpectoral Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2022, 49, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangaris, E.; Pusic, A.L.; Kaur, M.N.; Voineskos, S.; Bordeleau, L.; Zhong, T.; Vidya, R.; Broyles, J.; Klassen, A.F. Development and Psychometric Validation of the BREAST-Q Animation Deformity Scale for Women Undergoing an Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction After Mastectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5183–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.S.; Qiu, C.S.; Chiu, W.K.; Feld, L.N.; Mioton, L.M.; Kearney, A.; Fracol, M. A Quantitative Analysis of Animation Deformity in Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, R.; Tafazal, H.; Salem, F.; Iqbal, F.M.; Sircar, T. Management based on grading of animation deformity following implant-based subpectoral breast reconstruction. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2018, 45, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.M.; Klok, J.A.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Cano, S.J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shauly, O.; Olson, B.; Marxen, T.; Menon, A.; Losken, A.; Patel, K.M. Direct-to-implant versus autologous tissue transfer: A meta-analysis of patient-reported outcomes after immediate breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 84, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitsamer, R.; Peintinger, F. Prepectoral implant placement and complete coverage with porcine acellular dermal matrix: A new technique for direct-to-implant breast reconstruction after nipple-sparing mastectomy. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2015, 68, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoberleitner, I.; Faserl, K.; Tripp, C.H.; Pechriggl, E.J.; Sigl, S.; Brunner, A.; Zelger, B.; Hermann-Kleiter, N.; Baier, L.; Steinkellner, T.; et al. Silicone implant surface microtopography modulates inflammation and tissue repair in capsular fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1342895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.; Sigalove, S.; Sigalove, N.M.; Storm-Dickerson, T.L.; Rice, J.; Pope, N.; Maxwell, G.P. Prepectoral Revision Breast Reconstruction for Treatment of Implant-Associated Animation Deformity: A Review of 102 Reconstructions. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2018, 38, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.; Alcon, A.; Sbitany, H. Correction of animation deformity with subpectoral to prepectoral implant exchange. Gland Surg. 2019, 8, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangialardi, M.L.; Salgarello, M.; Baldelli, I.; Raposio, E. Prepectoral implant pocket conversion in breast reconstruction. JPRAS Open 2020, 26, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Abu-Ghname, A.; Davis, M.J.; Winocour, S.J.; Hanson, S.E.; Chu, C.K. Fat Grafting in Breast Reconstruction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2020, 34, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) n = 128 | Tissue Expander (TE) n = 121 | Total n = 249 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deceased | 7 | 7 | 14 |
| Lost to Follow-up | 37 | 36 | 73 |
| Participation declined | 16 | 8 | 24 |
| Severe Disease | 9 | 1 | 10 |
| Lack of photographic Documentation | 16 | 10 | 26 |
| Loss of Implant | 10 | 15 | 25 |
| TE: no Exchange of TE for final Implant | - | 10 | 10 |
| Participants | 33 | 34 | 67 |
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) * n = 33 | Tissue Expander (TE) * n = 34 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 49.50 | 12.6 | 52.28 | 7.61 | 0.38 |
| Follow-up (months) | 87.22 | 43.78 | 69.44 | 45.76 | 0.03 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.61 | 2.73 | 23.29 | 4.64 | 0.89 |
| Mastectomy Volume (g) | 274.71 | 169.2 | 227.19 | 237.75 | 0.22 |
| Reconstruction Volume (g) | 267.96 | 114.29 | 332.19 | 115.73 | 0.06 |
| Expander Filling at Time of Surgery (mL) | 144.6 | 136.1 | |||
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Active smoker * | 6 | 18.18 | 7 | 20.59 | 0.76 |
| Hypertension * | 5 | 15.15 | 7 | 20.59 | 0.75 |
| Diabetes mellitus Type II * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mastectomy * | 0.08 | ||||
| 4 | 12.12 | 10 | 29.41 | |
| 29 | 87.88 | 24 | 70.59 | |
| Reconstruction Side * | 0.81 | ||||
| 19 | 57.58 | 21 | 61.76 | |
| 14 | 42.42 | 13 | 38.24 | |
| Implant Plane * | 0.08 | ||||
| 8 | 24.24 | 3 | 8.82 | |
| 25 | 75.76 | 31 | 91.18 | |
| Radiotherapy * | 1.0 | ||||
| 3 | 9.09 | 3 | 8.82 | |
| 30 | 90.91 | 31 | 91.18 | |
| Chemotherapy * | 0.36 | ||||
| 12 | 36.36 | 5 | 14.71 | |
| 5 | 15.15 | 6 | 17.65 | |
| 7 | 21.21 | 3 | 8.82 | |
| 21 | 63.64 | 25 | 73.53 | |
| Indication for Mastectomy ♦ | 0.76 | ||||
| 32 | 68.09 | 34 | 72.34 | |
| 15 | 31.91 | 13 | 27.66 | |
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) * n = 33 | Tissue Expander (TE) * n = 34 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * n | % | * n | % | p-Value | |
| Secondary Wound Revision | 1 | 3.03 | 2 | 5.88 | 0.97 |
| Necrosectomy | 3 | 9.09 | 2 | 5.88 | |
| Haematoma Evacuation | 2 | 6.06 | 2 | 5.88 | |
| Surgical Infection Control | 1 | 3.03 | 0 | 0 | |
| Seroma Evacuation | 1 | 3.03 | 1 | 2.94 | |
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) * n = 33 | Tissue Expander (TE) * n = 34 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * n | % | * n | % | p-Value | |
| NAC Reconstruction/Areola Tattoo | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14.71 | 0.57 |
| Lipofilling | 2 | 6.06 | 4 | 11.76 | |
| Capsulectomy | 1 | 3.03 | 1 | 2.94 | |
| Implant Exchange | 10 | 30.30 | 5 | 14.71 | |
| Scar Correction | 1 | 3.03 | 2 | 5.88 | |
| Mastopexy | 1 | 3.03 | 2 | 5.88 | |
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) * n = 33 | Tissue Expander (TE) * n = 34 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | p-Value | |
| Psychosocial Well-Being | 74.70 | 19.45 | 71.94 | 17.43 | 0.71 |
| Sexual Well-Being | 58.31 | 22.29 | 58.56 | 23.81 | 0.79 |
| Satisfaction with Breasts | 63.97 | 19.17 | 61.70 | 15.45 | 0.97 |
| Satisfaction with Implants (a) | 2.94 | 1.01 | 3.21 | 0.78 | 0.34 |
| Satisfaction with Implants (b) | 3.03 | 0.97 | 3.21 | 0.82 | 0.51 |
| Physical Well-Being Chest | 71.00 | 22.49 | 75.76 | 12.51 | 0.57 |
| Breast Animation Deformity | 66.78 | 21.61 | 68.97 | 21.55 | 0.54 |
| Adverse Effects of Radiation a | 1.75 | 0.96 | 1.43 | 0.79 | 0.65 |
| Adverse Effects of Radiation b | 1.25 | 0.50 | 1.29 | 0.76 | 0.93 |
| Adverse Effects of Radiation c | 1.75 | 0.96 | 1.33 | 0.52 | 0.61 |
| Adverse Effects of Radiation d | 1.25 | 0.50 | 1.43 | 0.53 | 0.65 |
| Adverse Effects of Radiation e | 1.25 | 0.50 | 1.71 | 0.76 | 0.41 |
| Adverse Effects of Radiation f | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.29 | 0.49 | 0.53 |
| Satisfaction with Information | 77.59 | 18.29 | 72.74 | 17.96 | 0.24 |
| Satisfaction with Surgeon | 88.55 | 21.33 | 93.18 | 14.99 | 0.21 |
| Satisfaction with Medical Team | 95.24 | 12.97 | 95.26 | 11.83 | 0.84 |
| Satisfaction with Office Staff | 97.26 | 7.38 | 95.21 | 11.76 | 0.99 |
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) ♦ n = 47 | Tissue Expander (TE) ♦ n = 47 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEDIAN | Q1 | Q3 | MEDIAN | Q1 | Q3 | p-Value | |
| Breast Symmetry | 3.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 3.25 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 0.51 |
| Breast Position | 3.50 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 3.50 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 0.53 |
| Inframammary Fold | 4.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 0.38 |
| Volume | 3.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 3.75 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 0.90 |
| Shape and Contour | 3.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 0.67 |
| Scar | |||||||
| Appearance | 4.00 | 3.50 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 0.31 |
| NAC | |||||||
| Nipple Symmetry | 3.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 3.50 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 0.84 |
| Nipple Position | 3.00 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 3.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 0.65 |
| Overall Appearance | 3.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 3.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 0.83 |
| Direct-to-Implant (DTI) * n = 33 | Tissue Expander (TE) * n = 34 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Definition | Subpectoral | Prepectoral | Subpectoral | Prepectoral |
| KIM [19] | |||||
| Grade I | NAC dislocation <2 cm and contour irregularity <25% of breast surface | 11 | 7 | 20 | 3 |
| Grade II | NAC dislocation ≥2 cm and contour irregularity <25% of breast surface NAC dislocation <2 cm and contour irregularity ≥25% of breast surface | 11 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Grade III | NAC dislocation >2 cm and contour irregularity ≥25% of breast surface | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| VIDYA [20] | |||||
| Grade I | No visible distortion and displacement of implant | 6 | 2 | 15 | 3 |
| Grade II | Minimally visible distortion with displacement of implant; unnoticed by patient | 7 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Grade III | Moderately visible distortion with displacement of implant; noticed by patient | 10 | 2 | 9 | 0 |
| Grade IV | Severe distortion and persistent displacement of implant; disturbing for patient | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Pat. | Age (Years) | BMI (kg/m2) | NSME vs. SSME | DTI vs. TE | Implant Plane | Reconstruction Side | Reconstruction Volume (g) | Radiotherapy | Clavien Dindo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 50 | 20.6 | NSME | DTI | prepectoral | unilateral | 120 | no | 0 |
| B | 36 | 18.7 | NSME | DTI | prepectoral | unilateral | 295 | no | 0 |
| C | 65 | 25.3 | NSME | DTI | prepectoral | unilateral | 560 | no | 3b |
| D | 43 | 26.5 | NSME | DTI | prepectoral | bilateral | 350 | yes | 3b |
| E | 57 | 24.0 | NSME | DTI | prepectoral | bilateral | 365 | no | 0 |
| F | 48 | 22.6 | NSME | DTI | prepectoral | unilateral | 235 | no | 0 |
| Feature | DICI | AD | CC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deformity Type | Implant displacement (any direction) Breast distortion | Implant displacement (superior or lateral) Breast distortion | Implant distortion (any direction) Hardening Asymmetry |
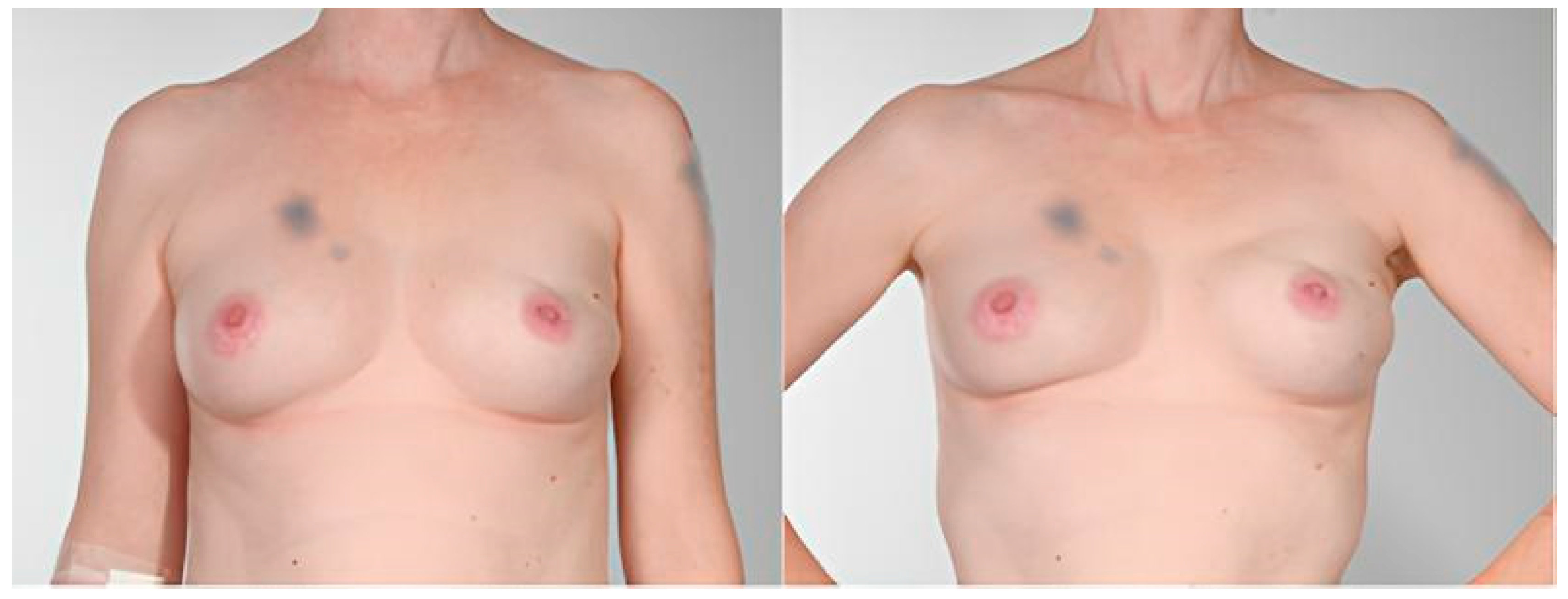
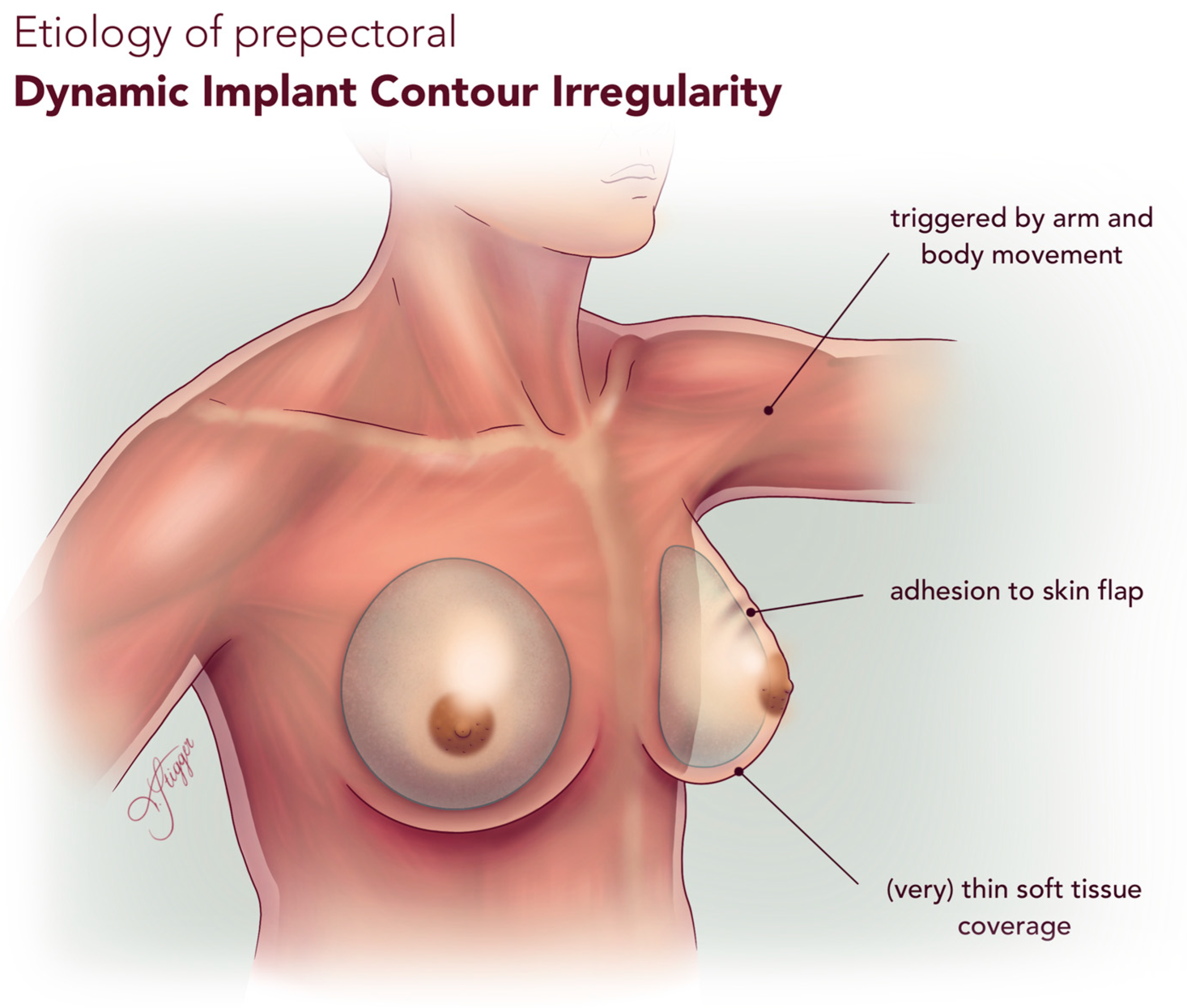
| Etiology | Implant adhesion to mastectomy skin flap Implant mobility during arm and body movement (Very) thin mastectomy skin flap | Pectoralis muscle contraction | Fibrotic capsule tightening around implant |
| Implant Placement | Prepectoral | Subpectoral | Either |
| Trigger | Arm/body movement | Pectoralis muscle contraction | None (static deformity) |
| Associated Pain | Rare | Rare | May be present |
| Diagnosis | Clinical observation Reproducible with motion, not necessarily by pectoralis muscle contraction | Clinical observation Reproducible with pectoralis muscle contraction | Clinical observation Baker grade (I-IV) Imaging |
| Management | Fat grafting Pocket revision | Conversion to prepectoral implant placement Muscle detachment | Capsulotomy/Capsulectomy Implant explantation/exchange |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stigger, T.; Neurauter, S.; Del Frari, B.; Spechtler, K.; Casari, M.E.; Neuwirt, H.; Schoberleitner, I.; Egle, D.; Brunner, C.; Wolfram, D. Dynamic Contour Irregularities in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Long-Term Aesthetic Outcomes After Direct-to-Implant Versus Tissue Expander Techniques. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238452
Stigger T, Neurauter S, Del Frari B, Spechtler K, Casari ME, Neuwirt H, Schoberleitner I, Egle D, Brunner C, Wolfram D. Dynamic Contour Irregularities in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Long-Term Aesthetic Outcomes After Direct-to-Implant Versus Tissue Expander Techniques. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238452
Chicago/Turabian StyleStigger, Theresia, Selina Neurauter, Barbara Del Frari, Katharina Spechtler, Maria Emilia Casari, Hannes Neuwirt, Ines Schoberleitner, Daniel Egle, Christine Brunner, and Dolores Wolfram. 2025. "Dynamic Contour Irregularities in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Long-Term Aesthetic Outcomes After Direct-to-Implant Versus Tissue Expander Techniques" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238452
APA StyleStigger, T., Neurauter, S., Del Frari, B., Spechtler, K., Casari, M. E., Neuwirt, H., Schoberleitner, I., Egle, D., Brunner, C., & Wolfram, D. (2025). Dynamic Contour Irregularities in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Long-Term Aesthetic Outcomes After Direct-to-Implant Versus Tissue Expander Techniques. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238452








