Plasmapheresis for Suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge
Abstract
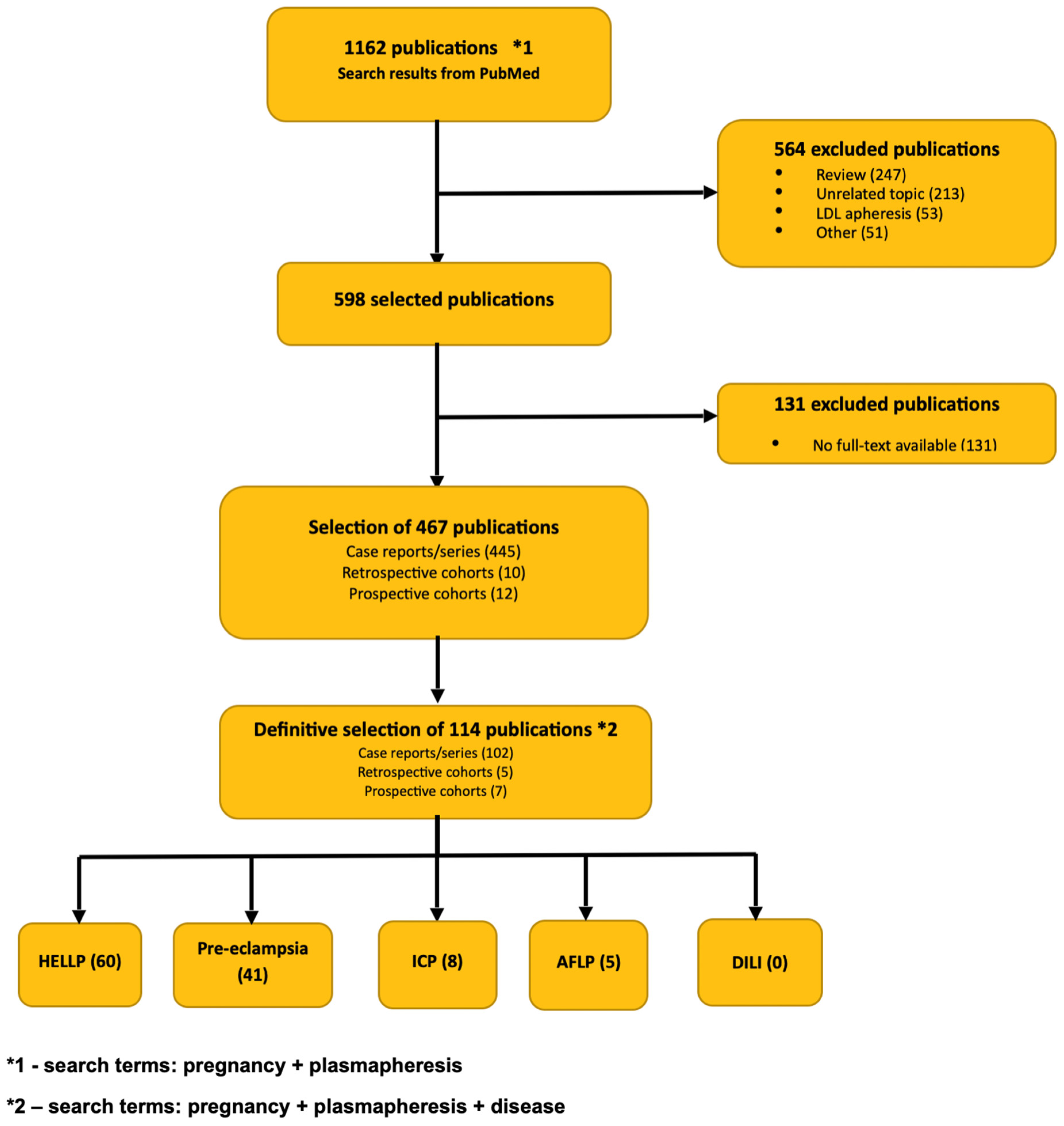
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. TPE and DFPP Methods
4. Differential Diagnosis
5. Discussion
6. Literature Review
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFLP | Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy |
| AIHA | Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia |
| ALF | Acute Liver Failure |
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| ANA | Antinuclear Antibody |
| ASMA | Anti-Smooth Muscle Antibody |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| CIOMS | Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| DILI | Drug-Induced Liver Injury |
| DFPP | Double-Filtration Plasmapheresis |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr Virus |
| GCs | Glucocorticoids |
| GGT | Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase |
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| HEp-2 | Human Epithelial Type 2 |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| HSV | Herpes Simplex Virus |
| ICP | Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| LVPE | Low-Volume Plasma Exchange |
| PBC | Primary Biliary Cirrhosis |
| PE | Preeclampsia |
| RUCAM | Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method |
| sFlt-1/PlGF | Soluble Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase-1 / Placental Growth Factor |
| SMA | Smooth Muscle Antibody |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| TBA | Total Bile Acid |
| TPE | Therapeutic Plasma Exchange |
| UDCA | Ursodeoxycholic Acid |
| ULN | Upper Limit of Normal |
References
- Gayam, V.; Khalid, M.; Shrestha, B.; Hossain, M.R.; Dahal, S.; Garlapati, P.; Gill, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Sangha, R. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: An Institutional Case Series and Review of Literature. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2018, 6, 2324709618761754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, T.T. Drug-induced liver injury in pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 68, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. RUCAM v5.0. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547852/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Slim, R.; Ben Salem, C.; Hmouda, H.; Bouraoui, K. Hepatotoxicity of alpha-methyldopa in pregnancy. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolasevic, I.; Filipec-Kanizaj, T.; Jakopcic, I.; Majurec, I.; Brncic-Fischer, A.; Sobocan, N.; Hrstic, I.; Stimac, T.; Stimac, D.; Milic, S. Liver Disease During Pregnancy: A Challenging Clinical Issue. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 4080–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoz, T.; Webber, D.; Rowe, H. Drug-induced fulminant hepatic failure in pregnancy. Obstet. Med. 2015, 8, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foureau, D.M.; Walling, T.L.; Maddukuri, V.; Anderson, W.; Culbreath, K.; Kleiner, E.D.; Ahrens, A.W.; Jacobs, C.; Watkins, P.B.; Fontana, R.J.; et al. Comparative analysis of portal hepatic infiltrating leucocytes in acute drug-induced liver injury, idiopathic autoimmune and viral hepatitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of cholestatic liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 237–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessone, F.; Hernandez, N.; Tagle, M.; Arrese, M.; Parana, R.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Ridruejo, E.; Mendizabal, M.; Dagher, L.; Contreras, F.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury: A management position paper from the Latin American Association for Study of the liver. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 24, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.H.; Abt, P.L. Treatment options and strategies for antibody mediated rejection after renal transplantation. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewska, B. Therapeutic plasmapheresis in clinical practice. Hematol. Clin. Pract. 2018, 4, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly-Smith, L.; Alquist, C.R.; Aqui, N.A.; Hofmann, J.C.; Klingel, R.; Onwuemene, O.A.; Patriquin, C.J.; Pham, H.P.; Sanchez, A.P.; Schneiderman, J.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Ninth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2023, 38, 77–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Feng, W.; Liao, S.; Luo, X.; Huang, W.; Huang, Z.; Jin, S.; Liu, K.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y. Risk factors for acute fatty liver of pregnancy complicated by acute liver failure: A retrospective study of 133 cases. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A.; Laurie, J. Physiological changes of pregnancy and the Swansea criteria in diagnosing acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Obstet. Med. 2018, 11, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, D.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Shi, Q.; Guo, Q. The assessment in patients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) treated with plasma exchange: A cohort study of 298 patients. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2023, 23, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, F.; Mahendraker, N.; Tonismae, T. HELLP Syndrome. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560615/ (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Fitzpatrick, K.E.; Hinshaw, K.; Kurinczuk, J.J.; Knight, M. Risk factors, management, and outcomes of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome and elevated liver enzymes, low platelets syndrome. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 123, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souissi, R.; Haddad, Z.; Trabelsi, W.; Baffoun, N.; Boubaker, M.; Kaddour, C.; Skandrani, L. HELLP syndrome: Utility of specific classifications as prognostic tools. Crit. Care 2007, 11 (Suppl. 2), P383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, X. Intraoperatively diagnosed spontaneous rupture of a subcapsular liver hematoma with incomplete hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets (HELLP) syndrome: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2025, 104, e44186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhry, M.; Agrawal, S.; Gajulapalli, S.P.; Thakur, U.K. Therapeutic plasma exchange in HELLP syndrome: A life savior. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2022, 16, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacq, Y.; Sentilhes, L. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Diagnosis and management. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 4, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillarisetty, L.S.; Sharma, A. Pregnancy Intrahepatic Cholestasis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551503/ (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Lee, N.M.; Brady, C.W. Liver disease in pregnancy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadia, C.; Lövgren-Sandblom, A.; Edwards, L.A.; Langedijk, J.; Geenes, V.; Chambers, J.; Cheng, F.; Clarke, L.; Begum, S.; Noori, M.; et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange as a novel treatment for severe intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Case series and mechanism of action. J. Clin. Apher. 2018, 33, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrar, S.A.; Martingano, D.J.; Hong, P.L. Preeclampsia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570611/ (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Iannaccone, A.; Reisch, B.; Kimmig, R.; Schmidt, B.; Mavarani, L.; Oppong, M.D.; Tyczynski, B.; Dzietko, M.; Jahn, M.; Gellhaus, A.; et al. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Early-Onset Preeclampsia: A 7-Year Monocentric Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548173/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Allison, R.; Guraka, A.; Shawa, I.T.; Tripathi, G.; Moritz, W.; Kermanizadeh, A. Drug induced liver injury—A 2023 update. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2023, 26, 442–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, U.; Pacyna, K.; Kunysz, M. The influence of methyldopa on immunohematological tests during pregnancy. J. Transfus. Med. Hemost. 2024, 17, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.S.; Schmidt, L.E.; Bernsmeier, C.; Rasmussen, A.; Isoniemi, H.; Patel, V.C.; Triantafyllou, E.; Bernal, W.; Auzinger, G.; Shawcross, D.; et al. High-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure: An open randomised controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothimani, D.; Sachan, D.; Saha, S.; Kalyamoorthy, I.; Rela, M. Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with drug-induced liver injury. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.A.; Kumar, S.E.; Zachariah, U.G.; Daniel, D.; David, V.; Subramani, K.; Pichamuthu, K.; Jacob, E.; Kodiatte, T.A.; Eapen, C.E.; et al. Single-Centre Experience with Low-Volume Plasma Exchange and Low-Dose Steroid to Treat Patients with Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Acute Liver Failure. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2024, 14, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwatch, S.; De, A.; Kaur, B.; Lamba, D.S.; Kaur, S.; Singh, V.; Periyasamy, A.G. Safety and efficacy of plasmapheresis in treatment of acute fatty liver of pregnancy-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1433324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, N.K.; Grzybowska, M.E.; Ejankowski, M. Plasmapheresis in pregnancy: A novel treatment for acute liver disease of unknown origin with favourable maternal and fetal outcomes. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 64 (Suppl. 1), s.231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Day of Treatment | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | 9. | 10. | 12. | 16. | 18. | 20. | 22. | 30. | 50. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Intervention | Admission Methyldopa discontinuation UDCA initiation | UDCA | UDCA | UDCA Prednisone Initiation | UDCA Prednisone | UDCA Prednisone | UDCA Prednisone First TPE | UDCA Prednisone Second TPE | UDCA Prednisone Third TPE | UDCA Prednisone Fourth TPE | UDCA Prednisone First DFPP | UDCA Prednisone Second DFPP | UDCA Prednisone Third DFPP | UDCA Prednisone Fourth DFPP | UDCA Prednisone Fifth DFPP | UDCA | UDCA |
| TBA [µmol/L] Normal value <6 | 224 | - | 350 | 432 | 412 | 350 | 324 | 251 212 | 231 | 157 | 263 103 | 276 | 160 158 | 131 22 | 62 31 | 10 | 5 |
| BIL [mg/dL] Normal value 0.1–1.2 | 17.3 | - | 20.5 | - | 14.6 | 12.4 | 7.6 | - | - | - | 14.7 | - | - | - | - | 4.5 | 2 |
| ALB [g/L] Normal value 35–50 | 22 | - | - | - | - | 29 | 34 | 35 | 28 | - | 33 | - | - | - | - | ||
| AST [U/L] Normal Value 11–34 | 3050 | 2757 | 3059 | 2764 | - | 948 | 825 | 661 | - | - | 241 | - | - | 116 | 61 | 52 | 39 |
| ALT [U/L] Normal Value <34 | 2086 | 1892 | 1949 | - | 1824 | 1477 | - | 463 | - | - | 149 | - | - | 103 | 47 | 48 | 36 |
| GGT [U/L] Normal value <38 | 57 | 52 | - | - | - | 53 | - | - | - | - | 31 | - | - | - | - | - | 36 |
| ALP [U/L] Normal value 46–122 | 166 | 152 | - | - | 119 | - | - | 72 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| INR Normal Value 0.9–1.3 | 1.33 | - | 1.85 | 4.95 | - | - | 2.20 | - | 2.40 | - | 1.21 | 1.15 | 1.05 | 1.26 | 0.92 | 0.99 | - |
| LDH [U/L] Normal Value 125–220 | 563 | 454 | 557 | 424 | - | 246 | 215 | - | 190 | - | 216 | 144 | - | 141 | - | 48 | 13 |
| Ammonia [µmol/L] Normal Value 18–72 | 81 | - | 79 | 81 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 58 | - |
| Disorder of Pregnancy | Time of Onset | Risk Factors | Symptoms | Liver Enzimes | Platelet Count | Bile Acids | Hypertension/Proteinuria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFLP | Typically from 28th to 40th week of pregnancy | Multifetal pregnancy, male fetus, co-existing liver disorders, history of AFLP, diabetes mellitus | Jaundice, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, polydipsia/poliuria, fatigue, fever, anorexia, ascites | ALT and ASPAT from 1 to 3× norm, up to 200 U/L | Thrombocythopenia +/− | Normal | 20–40% of patients |
| HELLP | Typically from 27th week of pregnancy and in early postpartum | Nulliparity, multifetal pregnancy, maternal age > 40 years old, BMI > 35, previous history of HELLP | Abdominal pain, headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue | ALT and ASPAT from 1 to 100× norm | Thrombocytopenia present usually from 50 to 150 G/L | Normal | 85% of patients |
| ICP | Typically in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, rarely before 26th week of gestation | History of liver disease, multifetal pregnancy, advanced maternal age, in vitro fertilization | Pruritus, darker urine, jaundice in less than 10% of women | ALT and ASPAT from 1 to 100× norm | Normal | Increased | No |
| Preeclampsia | Typically after 24th week of gestation | History of preeclampsia, hypertension, diabetes, kidney disease, autoimmune conditions, multifetal pregnancy, first pregnancy, BMI > 35, in vitro fertilization | Abdominal pain, vomiting, headaches, peripheral edema, visual disturbances | ALT and ASPAT from 1 to 5× norm | Thrombocytopenia present | Normal | Yes |
| DILI | Typically after 1st trimester of pregnancy | Advanced age, obesity, history of liver disease, female sex, diabetes, alcohol, smoking, pregnancy | Jaundice, abdominal pain, pruritus, fatigue, nausea, vomiting | ALT and ASPAT usually over 2× norm | Possible thrombocytopenia | Increased | No |
| Our Patient | 23rd week of pregnancy | 39 years old, in vitro fertilization, gestational hypertension, BMI 33, singleton pregnancy, no history of liver disease | Jaundice, pruritus | ALT 2083 U/L; ASPAT 3050 U/L | Normal, >150 G/L | Extremely high, 251 umol/L | Yes |
| RUCAM Scale: DILI Hepatocellular Type | Score |
|---|---|
| Time to onset from the beginning of drug intake: 5–90 days | 2 |
| After stopping the drug, change in ALT between peak value: decrease ≥ 50% within 8 days | 3 |
Exclusion of other causes of liver injury:
| 2 |
| Previous information on hepatotoxicity of the drug: reaction labeled in the product characteristics | 2 |
| Total score | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakrzewska, A.; Grzybowska, M.E.; Wydra, D.G.; Mazur-Ejankowska, N.K.; Adrych, K.; Tylicki, L.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Biedunkiewicz, B. Plasmapheresis for Suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238385
Zakrzewska A, Grzybowska ME, Wydra DG, Mazur-Ejankowska NK, Adrych K, Tylicki L, Dębska-Ślizień A, Biedunkiewicz B. Plasmapheresis for Suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238385
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakrzewska, Agnieszka, Magdalena Emilia Grzybowska, Dariusz Grzegorz Wydra, Natalia Katarzyna Mazur-Ejankowska, Krystian Adrych, Leszek Tylicki, Alicja Dębska-Ślizień, and Bogdan Biedunkiewicz. 2025. "Plasmapheresis for Suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238385
APA StyleZakrzewska, A., Grzybowska, M. E., Wydra, D. G., Mazur-Ejankowska, N. K., Adrych, K., Tylicki, L., Dębska-Ślizień, A., & Biedunkiewicz, B. (2025). Plasmapheresis for Suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238385







