Analysis of Potential Subtypes of SAPHO Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
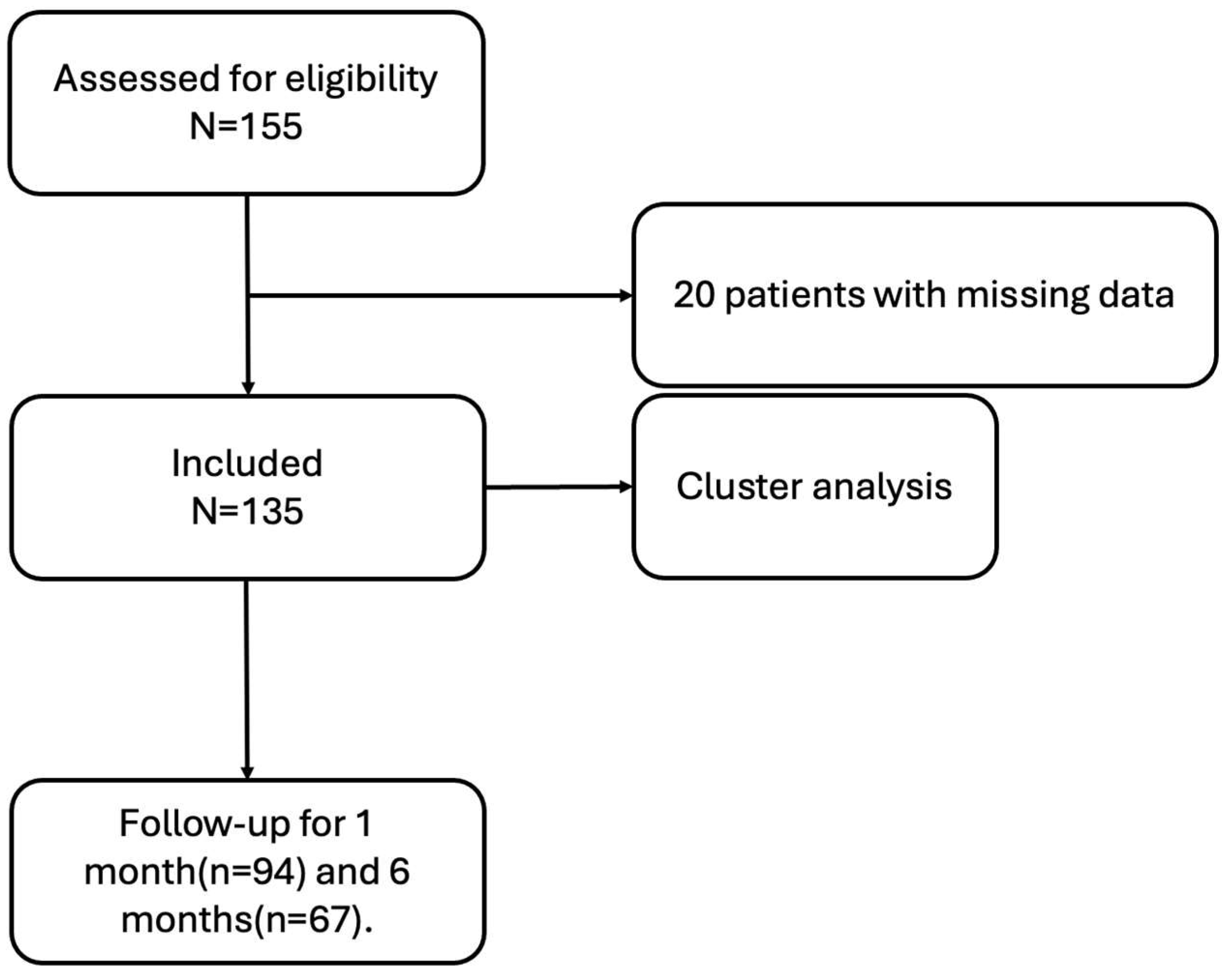
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
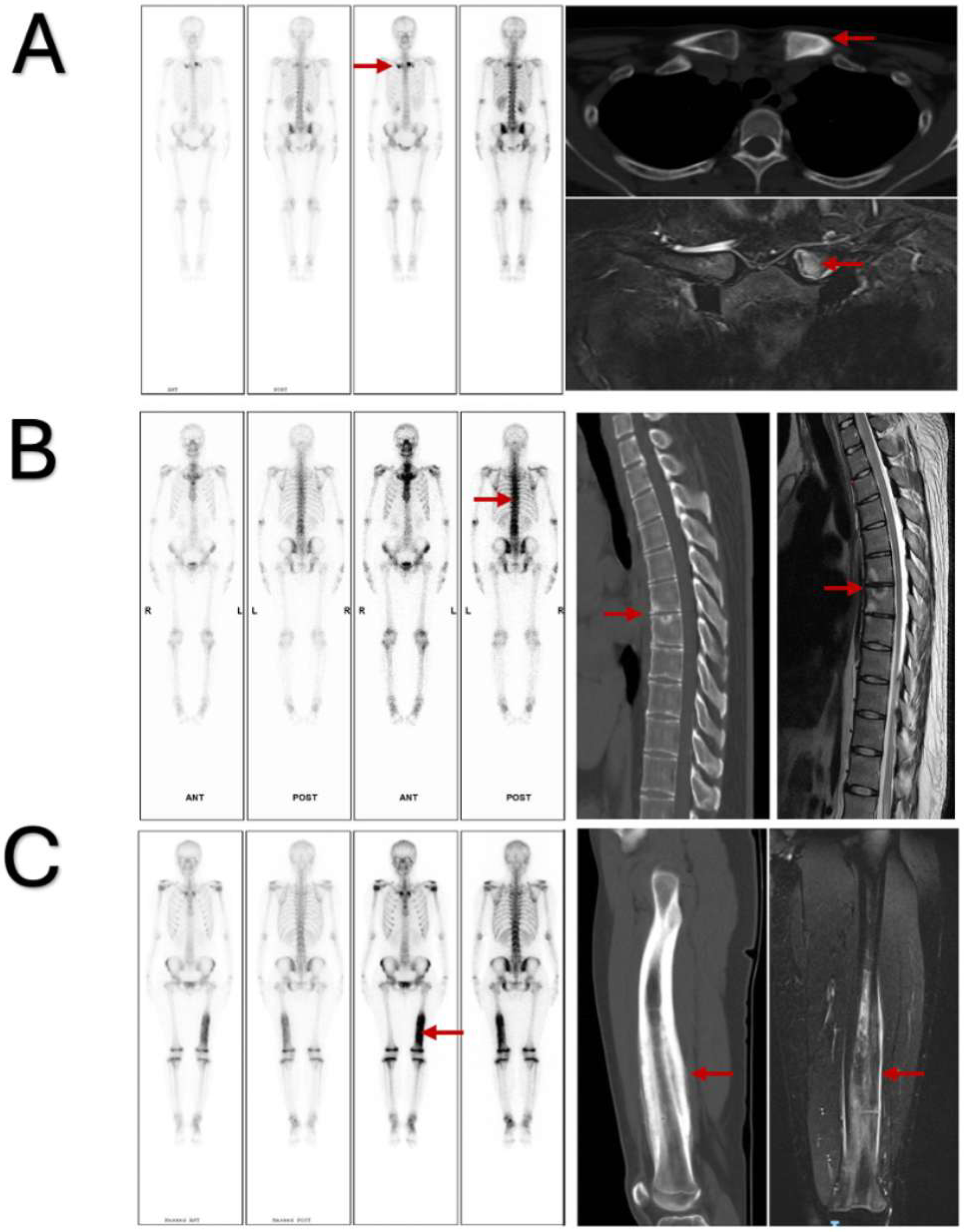
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
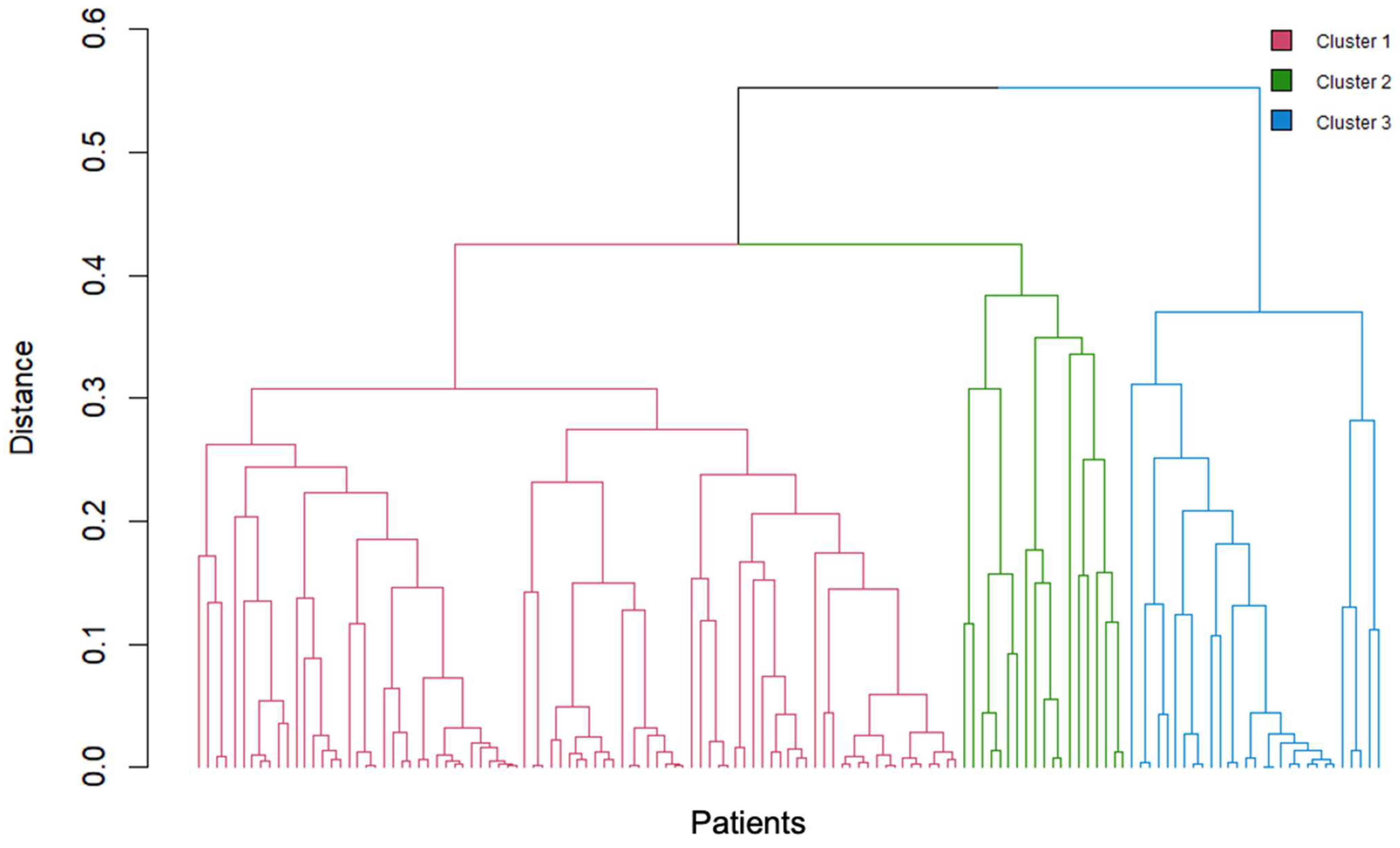
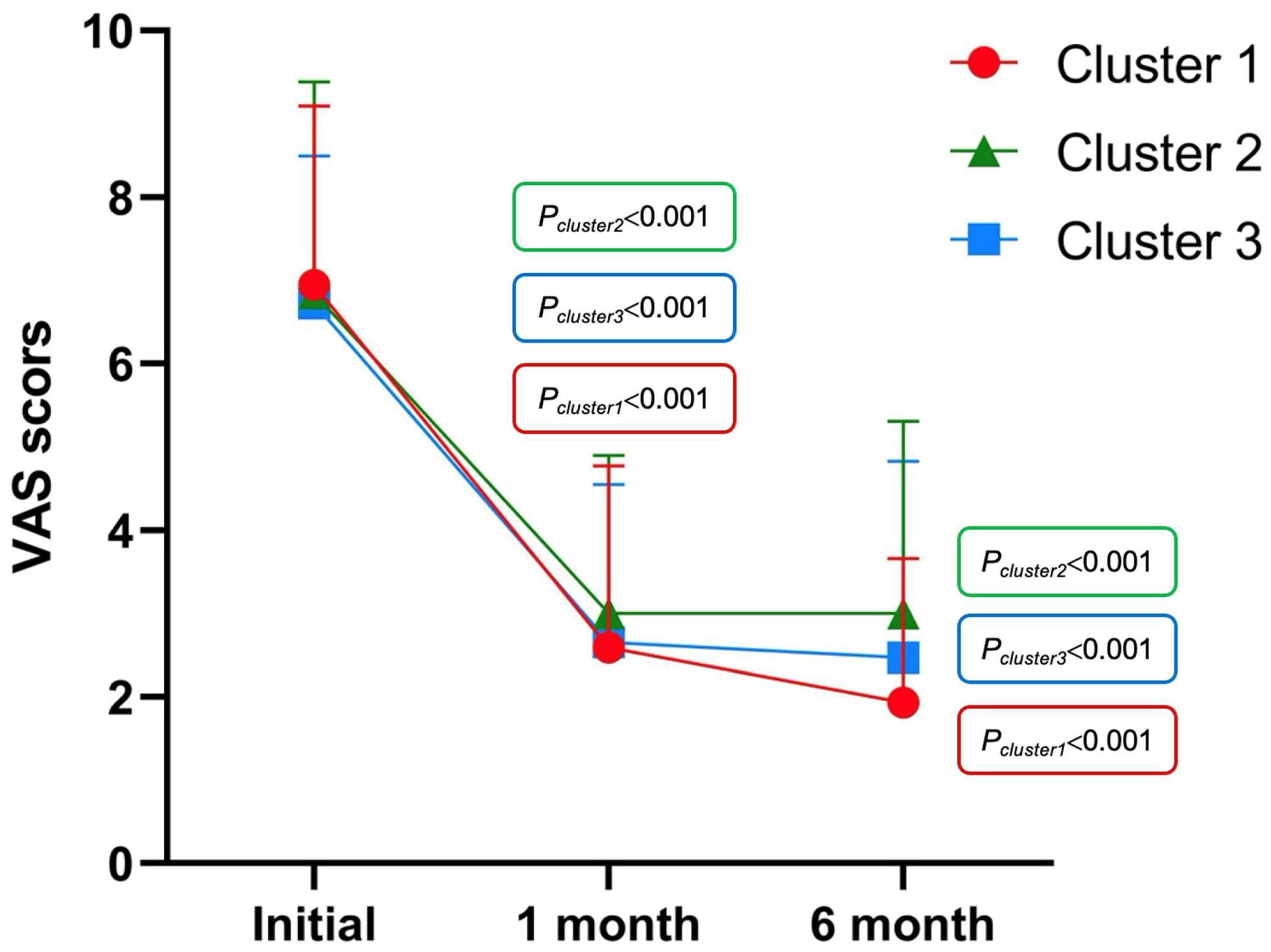
3.2. Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAPHO | synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis |
| CRMO | chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis |
| CNO | chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis |
| PAO | pustular osteoarthritis |
| ACW | anterior chest wall |
| PPP | palmoplantar pustulosis |
| SA | severe acne |
| ESR | erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| BASDAI | Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index |
| BASFI | Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index |
| HAQ | Health Assessment Questionnaire |
| PV | psoriasis vulgaris |
| axSpA | axial spondyloarthritis |
References
- Chamot, A.M.; Benhamou, C.L.; Kahn, M.F.; Beraneck, L.; Kaplan, G.; Prost, A. Acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis syndrome. Results of a national survey. 85 cases. Rev. Rhum. Mal. Osteoartic. 1987, 54, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benhamou, C.L.; Chamot, A.M.; Kahn, M.F. Synovitis-acne-pustulosis hyperostosis-osteomyelitis syndrome (SAPHO). A new syndrome among the spondyloarthropathies? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1988, 6, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, M.F.; Khan, M.A. The SAPHO syndrome. Baillieres Clin. Rheumatol. 1994, 8, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Shao, Y.; Huo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jing, H.; Zhang, F.; Yu, C.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Clinical characteristics of pediatric synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome: The first Chinese case series from a single center. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrison, C.; Davidson, J.E.; Cleary, A.G.; Beresford, M.W. Pamidronate in the treatment of childhood SAPHO syndrome. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccora, I.; Marrani, E.; Maniscalco, V.; Mastrolia, M.V.; Pagnini, I.; Simonini, G. Diagnostic challenge of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome in pediatric age: A monocentric case series. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colina, M.; Govoni, M.; Orzincolo, C.; Trotta, F. Clinical and radiologic evolution of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis syndrome: A single center study of a cohort of 71 subjects. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, M.; Meier, J.; Hammitzsch, A.; Proft, F.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Grunke, M. Disease burden, disease manifestations and current treatment regimen of the SAPHO syndrome in Germany: Results from a nationwide patient survey. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W. Clinical heterogeneity of SAPHO syndrome: Challenge of diagnosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, R.D.; Resnick, D. The SAPHO syndrome: An evolving concept for unifying several idiopathic disorders of bone and skin. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 170, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayem, G.; Bouchaud-Chabot, A.; Benali, K.; Roux, S.; Palazzo, E.; Silbermann-Hoffman, O.; Kahn, M.F.; Meyer, O. SAPHO syndrome: A long-term follow-up study of 120 cases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 29, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoussis, D.; Konstantopoulou, G.; Kraniotis, P.; Sakkas, L.; Liossis, S.N. Biologics in SAPHO syndrome: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slouma, M.; Bettaieb, H.; Rahmouni, S.; Litaiem, N.; Dhahri, R.; Gharsallah, I.; Metoui, L.; Louzir, B. Pharmacological Management of Synovitis, Acne, Pustulosis, Hyperostosis, and Osteitis Syndrome Syndrome: A Proposal of a Treatment Algorithm. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 28, e545–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.W.S.; Roberts, E.; Hedrich, C. Treatment and monitoring of SAPHO syndrome: A systematic review. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depasquale, R.; Kumar, N.; Lalam, R.K.; Tins, B.J.; Tyrrell, P.N.; Singh, J.; Cassar-Pullicino, V.N. SAPHO: What radiologists should know. Clin. Radiol. 2012, 67, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihlmann, W.; Dihlmann, S.W. Acquired hyperostosis syndrome: Spectrum of manifestations at the sternocostoclavicular region. Radiologic evaluation of 34 cases. Clin. Rheumatol. 1991, 10, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyschmidt, J.; Sternberg, A. The bullhead sign: Scintigraphic pattern of sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis and pustulotic arthroosteitis. Eur. Radiol. 1998, 8, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przepiera-Bedzak, H.; Brzosko, M. Clinical symptoms, imaging, and treatment of SAPHO syndrome: A single-center study of 52 cases. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2018, 128, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Han, S.B.; Song, L.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, X.L.; Yuan, H.S. Comparative analysis and differentiation between SAPHO syndrome and spondyloarthropathies using whole-spine MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 394.e9–394.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, W.; Wu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Jing, H.; Gu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Li, L.; et al. Spinal and sacroiliac involvement in SAPHO syndrome: A single center study of a cohort of 354 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earwaker, J.W.; Cotten, A. SAPHO: Syndrome or concept? Imaging findings. Skeletal Radiol. 2003, 32, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leerling, A.T.; Dekkers, O.M.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M.; Winter, E.M. Clinical and therapeutic diversity in adult chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) of the sternocostoclavicular region: A meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, W. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of SAPHO syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1427784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthelot, J.M.; Corvec, S.; Hayem, G. SAPHO, autophagy, IL-1, FoxO1, and Propionibacterium (Cutibacterium) acnes. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographic and Clinical Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | |
| Sex, female/male | 95/40 |
| Age, mean (S.D.), years | 44.49 (13.89) |
| Disease duration, mean (S.D.), months | 59.10 (81.50) |
| Smoking, n (%) | 26 (19.3%) |
| Alcohol intake, n (%) | 30 (22.2%) |
| Clinical characteristics | |
| Osteoarticular symptoms | |
| Single site involvement, n (%) | 26 (19.3%) |
| Symmetry of lesion site, n (%) | 85 (63.0%) |
| Bone destruction, n (%) | 12 (8.9%) |
| Osteosclerosis, n (%) | 102 (75.6%) |
| Anterior chest wall, n (%) | 88 (65.2%) |
| Spine, n (%) | 55 (40.7%) |
| Peripheral bones and joints, n (%) | 37 (27.4%) |
| Skin manifestations | |
| PPP, n (%) | 38 (28.1%) |
| PV, n (%) | 5 (3.7%) |
| SA, n (%) | 11 (8.1%) |
| Nonspecific rash, n (%) | 22 (16.7%) |
| None | 61 (45.2%) |
| Disease assessment index | |
| VAS, mean (S.D.) | 6.88 (2.12) |
| BASDAI, mean (S.D.) | 3.46 (1.92) |
| BASFI, mean (S.D.) | 1.79 (2.02) |
| HAQ, mean (S.D.) | 0.41 (0.48) |
| Laboratory tests | |
| Elevated ESR (n = 108), n (%) | 56 (41.5%) |
| Elevated CRP (n = 106), n (%) | 33 (24.4%) |
| TNF-α (n = 81), mean (S.D.) | 2.50 (1.41) |
| IL-6 (n = 82), mean (S.D.) | 8.82 (7.57) |
| IL-8 (n = 82), mean (S.D.) | 10.10 (12.07) |
| tP1NP (n = 71), mean (S.D.) | 74.28 (97.57) |
| β-CTX (n = 36), mean (S.D.) | 4.69 (11.91) |
| PTH (n = 99), mean (S.D.) | 35.31 (13.11) |
| 25-(OH)VD3 (n = 108), mean (S.D.) | 22.88 (9.33) |
| Pathogenic bacteria (n = 21), n (%) | 10 (47.6%) |
| Demographic Characteristics | Cluster 1 (n = 87) | Cluster 2 (n = 19) | Cluster 3 (n = 29) | p Values * | p Values ** | p Values *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, female | 64 (73.6%) | 11 (57.9%) | 20 (69.0%) | 0.264 | 0.638 | 0.541 |
| Age | 46.75 (12.83) | 45.68 (10.09) | 36.92 (16.62) | 0.547 | 0.003 | 0.047 |
| Disease duration | 60.68 (76.77) | 54.90 (70.45) | 57.14 (102.34) | 0.401 | 0.012 | 0.374 |
| Smoking | 18 (20.7%) | 4 (21.1%) | 4 (13.8%) | 0.972 | 0.586 | 0.509 |
| Alcohol intake | 23 (26.4%) | 6 (31.6%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.777 | 0.007 | 0.007 |
| Osteoarticular symptoms | ||||||
| Single site involvement | 0 | 1 (5.3%) | 25 (86.2%) | 0.032 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Symmetry of lesion site | 77 (88.5%) | 7 (36.6%) | 1 (3.4%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| Bone destruction | 6 (6.9%) | 1 (5.3%) | 5 (17.2%) | 0.795 | 0.100 | 0.220 |
| osteosclerosis | 70 (80.5%) | 4 (21.1%) | 28 (96.6%) | <0.001 | 0.038 | <0.001 |
| Anterior chest wall | 77 (88.5%) | 7 (36.8%) | 4 (13.8%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.063 |
| Spine | 45 (51.7%) | 9 (47.4%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.803 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Peripheral bones and joints | 12 (13.8%) | 3 (15.8%) | 22 (75.9%) | 0.821 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Skin manifestations | 65 (74.7%) | 2 (10.5%) | 7 (24.1%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.237 |
| VAS | 6.94 (2.15) | 6.84 (2.54) | 6.72 (1.77) | 0.950 | 0.457 | 0.482 |
| BASDAI | 3.79 (2.09) | 3.42 (1.57) | 2.51 (1.18) | 0.578 | 0.003 | 0.033 |
| BASFI | 1.99 (2.12) | 2.26 (2.01) | 0.89 (1.37) | 0.396 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| HAQ | 0.42 (0.51) | 0.57 (0.46) | 0.25 (0.33) | 0.103 | 0.060 | 0.008 |
| Laboratory tests | ||||||
| Elevated ESR (n = 92) | 33 (50.0%) | 10 (66.7%) | 13 (48.1%) | 0.269 | 1.000 | 0.337 |
| Elevated CRP (n = 90) | 20 (30.8%) | 4 (30.8%) | 9 (32.1%) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.930 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, H.; Tang, W.; Deng, X. Analysis of Potential Subtypes of SAPHO Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228116
Duan H, Tang W, Deng X. Analysis of Potential Subtypes of SAPHO Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228116
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Hongji, Wangna Tang, and Xiaoli Deng. 2025. "Analysis of Potential Subtypes of SAPHO Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228116
APA StyleDuan, H., Tang, W., & Deng, X. (2025). Analysis of Potential Subtypes of SAPHO Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228116







