Short-Term Laboratory Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
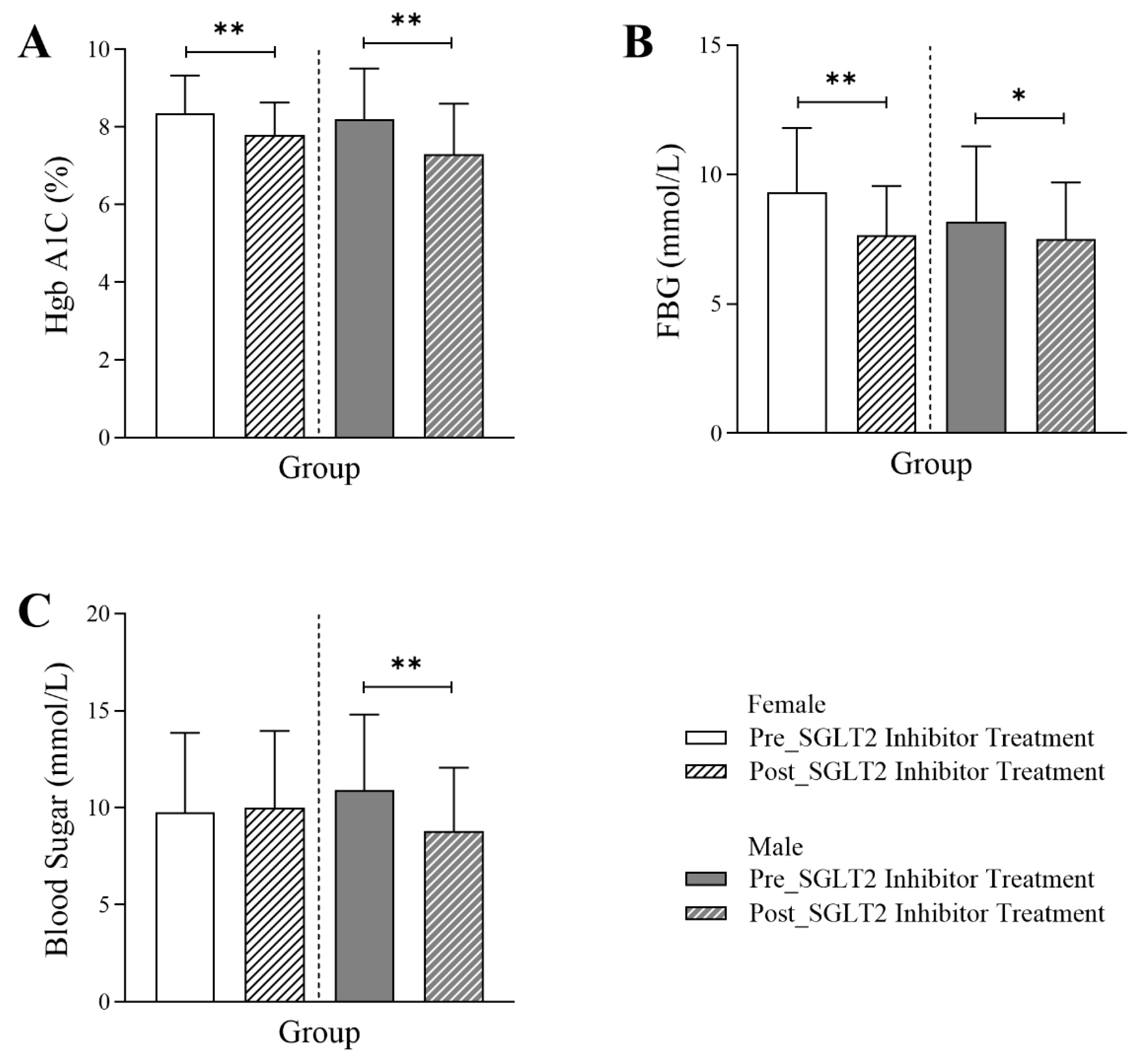
3.2. Changes in Glycemic Markers Following SGLT2 Inhibitor Treatment in Diabetic Patients
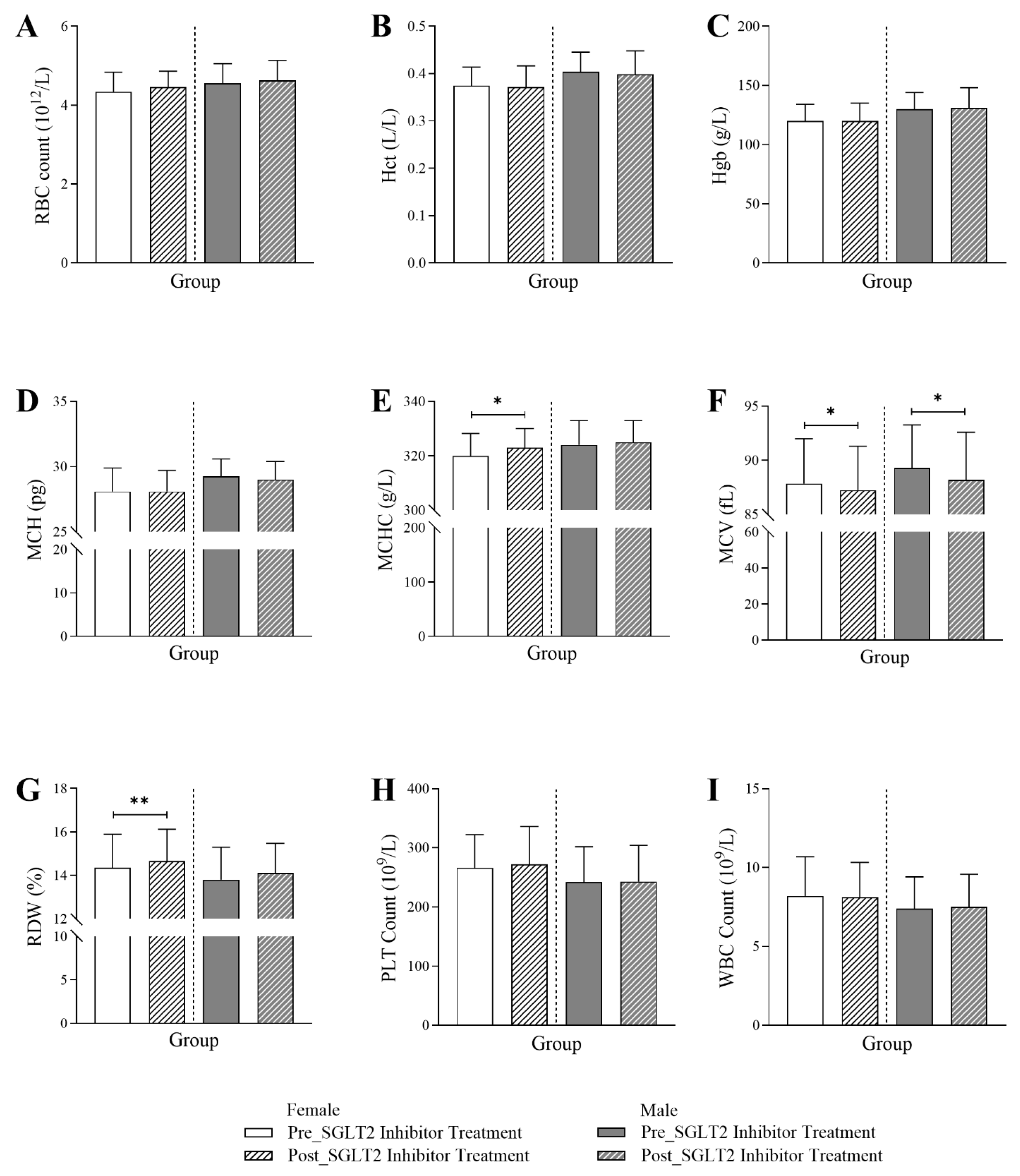
3.3. Changes in Hematological Markers Following SGLT2 Inhibitor Treatment in Diabetic Patients
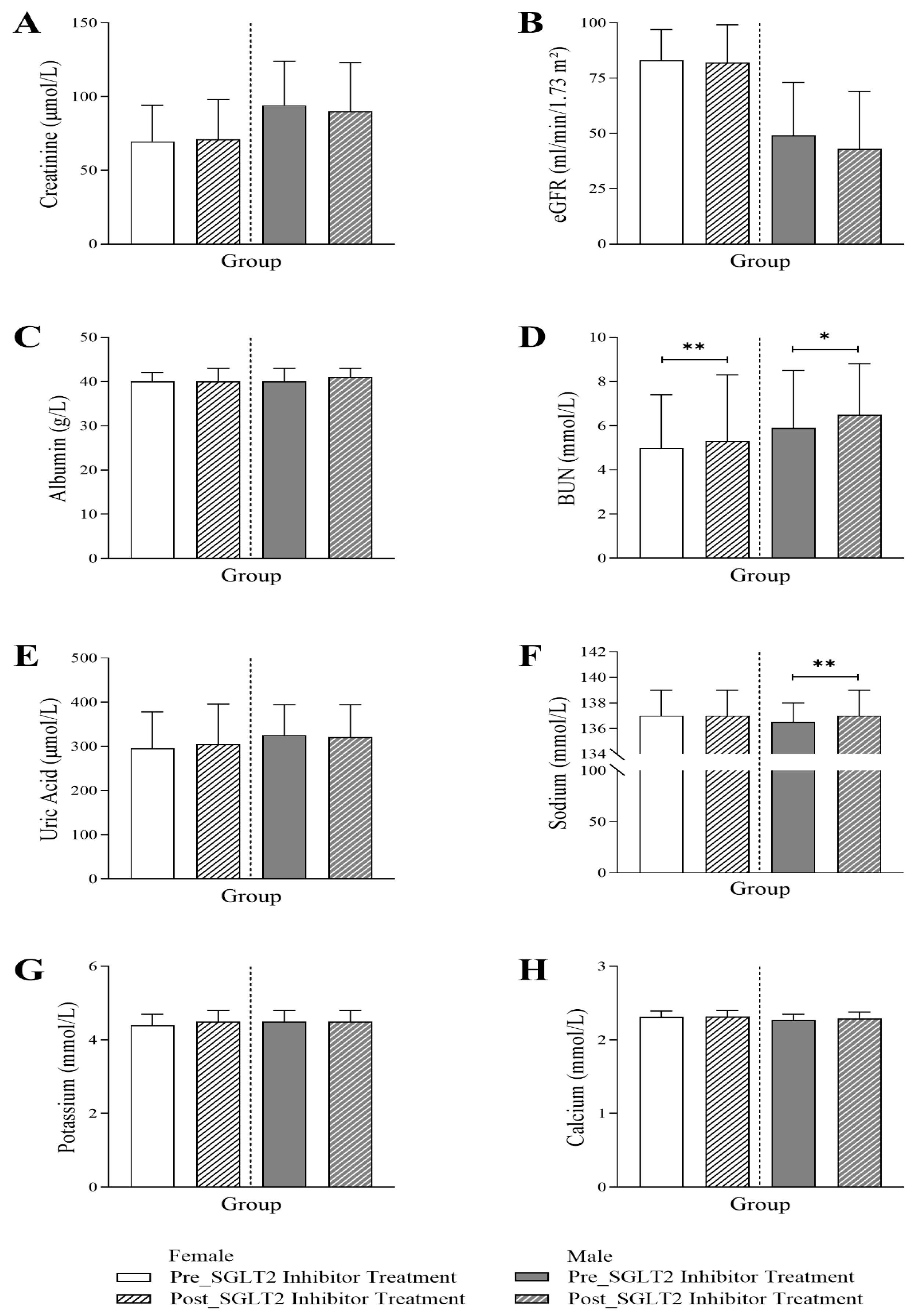
3.4. Changes in Renal Profile Following SGLT2 Inhibitor Treatment in Diabetic Patients
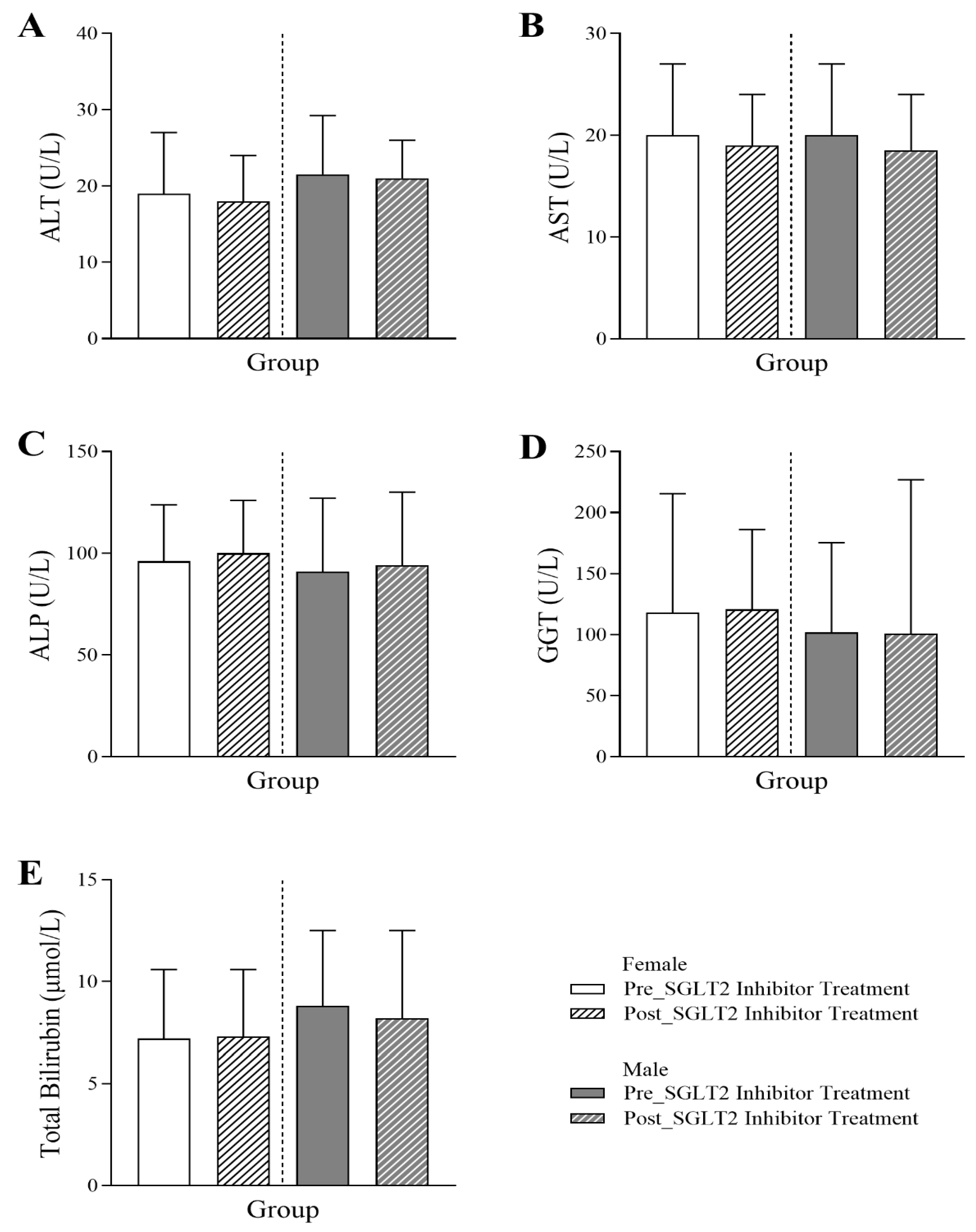
3.5. Changes in Liver Profile Following SGLT2 Inhibitor Treatment in Diabetic Patients
3.6. Assessment of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Lipid Indices in Diabetic Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.; Xie, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Peng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Tong, N. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults: Pathogenesis, Prevention and Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates of Diabetes Prevalence for 2017 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B. Globalization of Diabetes: The Role of Diet, Lifestyle, and Genes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quwaidhi, A.J.; Pearce, M.S.; Sobngwi, E.; Critchley, J.A.; O’Flaherty, M. Comparison of Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence Estimates in Saudi Arabia from a Validated Markov Model against the International Diabetes Federation and Other Modelling Studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dawish, M.A.; Robert, A.A.; Braham, R.; Al Hayek, A.A.; Al Saeed, A.; Ahmed, R.A.; Al Sabaan, F.S. Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: A Review of the Recent Literature. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2016, 12, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive Diabetes Treatment and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes: The DCCT/EDIC Study 30-Year Follow-Up. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive Blood-Glucose Control with Sulphonylureas or Insulin Compared with Conventional Treatment and Risk of Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padda, I.S.; Mahtani, A.U.; Parmar, M. Sodium-Glucose Transport 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors; StatPearls Publishing: Saint Petersburg, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Perkins, B.A.; Fitchett, D.H.; Husain, M.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Cardiovascular and Kidney Effects, Potential Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Circulation 2016, 134, 752–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarrán, O.G.; Ampudia-Blasco, F.J. Dapagliflozin, the First SGLT-2 Inhibitor in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Clin. 2013, 141 (Suppl S2), 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, P.; Mudaliar, S. Increase in Hematocrit with SGLT-2 Inhibitors-Hemoconcentration from Diuresis or Increased Erythropoiesis after Amelioration of Hypoxia? Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2023, 17, 102702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, W.; Malik, A.; Qureshi, W.; Dennis, B.; Mumtaz, M.; Haider, R.; Jamal, S.; Jaura, F.; Ahmed, A. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Improve Liver Enzymes in Patients with Co-Existing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2022, 17, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Caramori, M.L.; Chan, J.C.N.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hurst, C.; Khunti, K.; Liew, A.; Michos, E.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Olowu, W.A.; et al. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, J.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Kuang, H.; Shi, L.; Xue, Y.; et al. Dapagliflozin plus Calorie Restriction for Remission of Type 2 Diabetes: Multicentre, Double Blind, Randomised, Placebo Controlled Trial. BMJ 2025, 388, e081820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, B.; Gu, X.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Jia, L.; He, J.; Huang, C.; Wei, X.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Multicentre, Double Blind, Randomised, Placebo Controlled Trial. BMJ 2025, 389, e083735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.-N.; Chong, K.-S.; Peng, Z.-Y.; Ou, H.-T.; Wang, M.-C. Comparative Effectiveness and Prescribing Patterns of Dapagliflozin vs Empagliflozin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Target Trial Emulation. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 228, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. Mechanisms of Enhanced Renal and Hepatic Erythropoietin Synthesis by Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 5027–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, F.B.; Tang, V.A.S.; De Luna, D.V.; Lerma, E.V.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Kazory, A.; Shah, N.S.; Volgman, A.S. Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Outcomes of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure Randomized Controlled Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. Heart J. Plus Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2023, 26, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, P.G. Disorders of Erythrocyte Hydration. Blood 2017, 130, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; Dong, M.; Luo, J.; Xu, C.; Wen, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Z. Relationship between Red Blood Cell Indices (MCV, MCH, and MCHC) and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Anemic and Nonanemic Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2193343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R. Gender Difference in Cardiovascular Outcomes with SGLT-2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cardio-Vascular Outcome Trials. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.H. SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Evolving Evidence and Clinical Application. Diabetes Metab. J. 2025, 49, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ji, L. Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in the Real World. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1376850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembillo, G.; Cernaro, V.; Giuffrida, A.E.; Russo, G.; Giandalia, A.; Siligato, R.; Longhitano, E.; Santoro, D. Gender Differences in New Hypoglycemic Drug Effects on Renal Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minisola, S.; Cipriani, C.; Colangelo, L.; Labbadia, G.; Pepe, J.; Magnusson, P. Diagnostic Approach to Abnormal Alkaline Phosphatase Value. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2025, 100, 712–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Guo, K.; Deng, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, L. Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Haematocrit and Haemoglobin Levels and the Associated Cardiorenal Benefits in T2DM Patients: A Meta-analysis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Sánchez-García, A.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Hepatic Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaya, O.A.; Korayem, G.B.; Alghwainm, M.; Alyami, W.; Alotaibi, A.; Alyami, M.S.; Almohammed, O.A. The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Obesity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Description of Concurrent Treatments: A Two-Center Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 102054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabalawi, R.A.; Bamuflih, M.A.; Farid, A.A.; Almramhi, K.G.; Dawood, M.S.; Ahmed, M.S.; Alfawaz, K.S.; Adnan, A.M. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients at King Abdulaziz University Hospital (KAUH). Cureus 2024, 16, e57409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, M.A.; Alkhlady, H.Y.; Awan, Z.A.; Algethami, M.R.; Al Mahdi, H.B.; Daghistani, H.; Orayj, K. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Saudi Arabia: An Epidemiological Population-Based Study. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrani, I.; Mahdi, H.; Aljabr, Q.; AlHaddad, S.; Khalaf, M.; Olayan, A.; Eid, O.; Shakhiss, F.; Ghafli, A. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease among Type-2 Diabetic Patients in Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Med. Dev. Ctries. 2024, 8, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguwaihes, A.M.; Alhozali, A.; Yahia, M.M.; Abdel-Nabi, T.; Hatahet, M.H.; Albalkhi, N.I.; Al Sifri, S. The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia-CAPTURE Study. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosén, H.C.; Mohammad, M.A.; Jernberg, T.; James, S.; Oldgren, J.; Erlinge, D. SGLT2 Inhibitors for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after Myocardial Infarction: A Nationwide Observation Registry Study from SWEDEHEART. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 45, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefits of Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: A State-of-the-Art Review. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, D.K.; Shih, W.J.; Cosentino, F.; Charbonnel, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Pratley, R.; Greenberg, M.; Wang, S.; Huyck, S.; et al. Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors with Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Female (n = 384) | Male (n = 399) | |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 64 (56–71) | 65 (56–73) |
| History of Treatment, n (%) | ||
| Dapagliflozin | 384 (100) | 399 (100) |
| Metformin | 342 (89.1) | 341 (85.5) |
| Statin | 374 (97.4) | 387 (97.0) |
| Steroids | 317 (82.6) | 272 (68.2) |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | ||
| T2DM | 384 (100) | 399 (100) |
| CKD | 62 (16.1) | 83 (20.8) |
| Acute MI | 46 (12.0) | 80 (20.1) |
| Chronic Ischaemic HD | 121 (31.5) | 210 (52.6) |
| Chronic Hepatitis | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.5) |
| Heart Failure | 121 (31.5) | 112 (28.1) |
| Hypertension | 293 (76.3) | 275 (68.9) |
| Stroke | 46 (12.0) | 54 (13.5) |
| SLE | 2 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlSudais, H.; AlSulaiman, T.; Alotaibi, B.A.; Alshalani, A.; Almuqrin, A.M.; Albakr, R.B.; Aldali, J.A. Short-Term Laboratory Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227985
AlSudais H, AlSulaiman T, Alotaibi BA, Alshalani A, Almuqrin AM, Albakr RB, Aldali JA. Short-Term Laboratory Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):7985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227985
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlSudais, Hamood, Turky AlSulaiman, Badi A. Alotaibi, Abdulrahman Alshalani, Abdulaziz M. Almuqrin, Rehab B. Albakr, and Jehad A. Aldali. 2025. "Short-Term Laboratory Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 7985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227985
APA StyleAlSudais, H., AlSulaiman, T., Alotaibi, B. A., Alshalani, A., Almuqrin, A. M., Albakr, R. B., & Aldali, J. A. (2025). Short-Term Laboratory Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 7985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227985






