Evaluating In-Hospital Safety and Perioperative Costs of Total Hip Arthroplasty in Super-Elderly Patients: A Nationwide Propensity Score–Matched Analysis in Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Date Source
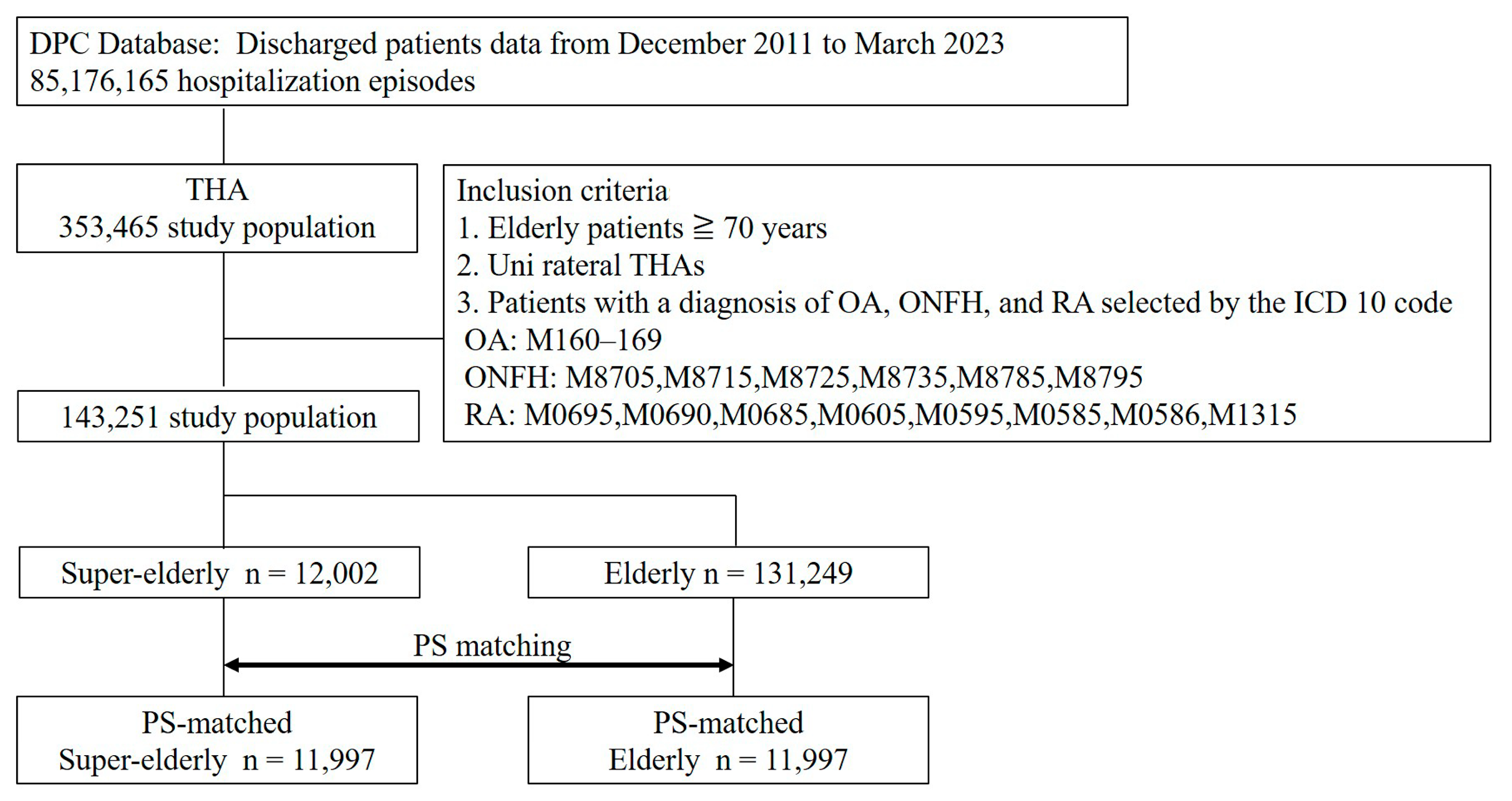
2.3. Data Selection
2.4. Outcomes of Interest
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Propensity Score Matching
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THA | total hip arthroplasty |
| DPC | Diagnosis Procedure Combination |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| PS | Propensity score |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| DVT | deep vein thrombosis |
| PE | pulmonary embolization |
| SDs | standard deviations |
| SMD | Standardized mean differences |
| OR | odds ratios |
References
- Learmonth, I.D.; Young, C.; Rorabeck, C. The operation of the century: Total hip replacement. Lancet 2007, 370, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iidaka, T.; Horii, C.; Muraki, S.; Oka, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Akune, T.; Tanaka, S.; Yoshimura, N. Trends in prevalence of hip osteoarthritis over a 10-year period in Japan: The ROAD study 2005–2015. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2022, 4, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Yamaguchi, R.; Utsunomiya, T.; Inaba, Y.; Ike, H.; Kinoshita, K.; Doi, K.; Kawano, T.; Shiomoto, K.; Hara, T.; et al. Etiology and clinical trends in hip osteoarthritis in Japan: Insights from a multicenter cross-sectional study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, M.; Lau, E.M.; Kurtz, S.M.; Alt, V. Projections of Primary TKA and THA in Germany from 2016 Through 2040. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.M.; Vollmann, P.; Weissenberger, M.; Rudert, M. Total hip arthroplasty in geriatric patients—A single-center expe-rience. SICOT J. 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, D.T.; Howell, R.D.; Strauss, E.J.; Di Cesare, P.E. Total hip and knee arthroplasty in nonagenarians. J Arthroplast. 2007, 22, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, T.; Adamczyk, E.; Synder, M.; Sibiński, M. Elective total hip arthroplasty for patients 75 years of age and older. Chir. Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2008, 73, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, B.P.; Dowsey, M.M.; Choong, P.F. The Impact of Advanced Age on the Outcomes of Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. JBJS Rev. 2018, 6, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Dugdale, E.M.; Tybor, D.; Kain, M. Comparing Inpatient Complication Rates between Octogenarians and Nonagenarians following Primary and Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Nationally Representative Sample, 2010–2014. Geriatrics 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, A.E.; Plantz, M.A.; Hardt, K.D. Outcomes of Elective Total Hip Arthroplasty in Nonagenarians and Centenarians. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohe, N.; Weisberg, M.D.; Ciminero, M.; Mannino, A.; Erez, O.; Saleh, A. Complications and Readmissions After Total Hip Re-placement in Octogenarians and Nonagenarians. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2020, 11, 2151459320940959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Alcaraz, J.; Pardo Garcia, J.M.; Sevilla Fernandez, J.; Delgado Diaz, E.; Moreno Beamud, J.A. Primary total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients over 85 years old: Risks, complications and medium-long term results. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 65, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurapatti, M.; Patel, V.; Arraut, J.; Oakley, C.; Rozell, J.C.; Schwarzkopf, R. Primary total hip arthroplasty in patients older than 90 years of age: A retrospective matched cohort study. HIP Int. 2023, 33, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, V.J.; Krull, P.; Hardt, S.; Hipfl, C.; Melsheimer, O.; Steinbrück, A.; Giebel, G.M. Is Elective Total Hip Arthroplasty Safe in Nona-genarians?: An Arthroplasty Registry Analysis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2023, 105, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjayan, S.K.; Swamy, G.N.; Yellu, S.; Yallappa, S.; Abuzakuk, T.; Straw, R. In-hospital complications following primary total hip and knee arthroplasty in octogenarian and nonagenarian patients. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 15, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tarasawa, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kamimura, M.; Harada, K.; Mori, N.; Fushimi, K.; Aizawa, T.; Fujimori, K. Thromboembolic and infectious complication risks in TKA and UKA: Evidence from a Japanese nationwide cohort. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2025, 37, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tarasawa, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kanabuchi, R.; Kuriyama, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Mori, N.; Fushimi, K.; Aizawa, T.; Fujimori, K. Increased early complication rates following total hip arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis patients based on a Japanese nationwide medical claims database study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tarasawa, K.; Tanaka, H.; Mori, N.; Fushimi, K.; Aizawa, T.; Fujimori, K. Nationwide database study of postoperative sequelae and in-hospital mortality in super-elderly hip fracture patients. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2025, 43, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Tarasawa, K.; Mori, Y.; Fushimi, K.; Fujimori, K.; Aizawa, T. Increased complications of proximal femur fractures during the COVID-19 pandemic: A nationwide medical claims database study in Japan. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2025; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Tarasawa, K.; Mori, Y.; Kuriyama, Y.; Kawamata, H.; Fushimi, K.; Fujimori, K.; Aizawa, T. Does Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Increase Early Complication Rates After Total Hip Arthroplasty? A Japanese Nationwide Medical Claims Database Study. J. Arthroplast. 2025, 40, 2053–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S. Development of Case Mix Based Evaluation System in Japan. Jpn. Hosp. 2016, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiboer, B.; Layer, M.A.; Cafuir, L.A.; Cuker, A.; Escobar, M.; Eyster, M.E.; Kraut, E.; Leavitt, A.D.; Lentz, S.R.; Quon, D.; et al. Postoperative bleeding complications in patients with hemophilia undergoing major orthopedic surgery: A prospective multicenter observational study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, B.; Chen, A.F. Reducing the risk of infection after total joint arthroplasty: Preoperative optimization. Arthroplasty 2019, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.G.; Hunter, J.M. Recent developments in the perioperative management of adult patients with chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, K.J.; Saleh, K.J.; Rosenberg, A.G.; Rubash, H.E. Economic evaluation in total hip arthroplasty: Analysis and review of the literature. J. Arthroplast. 2004, 19, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangehl, M.J. Health care economics and total joint arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2017, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, M.; Wirtz, D.C. Patient optimization before hip revision arthroplasty: How to handle comorbidities. Orthopadie 2022, 51, 619–630. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, M.K.; Lam, A.; Diamond, K.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Roche, M.; Erez, O.; Mont, M.A. What are the Causes, Costs, and Risk-Factors for Emergency Department Visits Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty? An Analysis of 1,018,772 Patients. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeboom, T.J.; Dronkers, J.J.; Ende, C.H.v.D.; Oosting, E.; van Meeteren, N.L. Preoperative therapeutic exercise in frail elderly scheduled for total hip replacement: A randomized pilot trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2010, 24, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosting, E.; Jans, M.P.; Dronkers, J.J.; Naber, R.H.; Dronkers-Landman, C.M.; Vries, S.M.A.-D.; van Meeteren, N.L. Preoperative home-based physical therapy versus usual care to improve functional health of frail older adults scheduled for elective total hip arthroplasty: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, S.; Ruan, T.; Liu, L.; Fang, L. Is it necessary to perform prehabilitation exercise for patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Physician Sportsmed. 2018, 46, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahic, D.; Omerovic, D.; Tanovic, A.; Dzankovic, F.; Campara, M. The Effect of Prehabilitation on Postoperative Outcome in Patients Following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. Med. Arch. 2018, 72, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Before PS Matching | After PS Matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super-Elderly | Elderly | p-Value | Super-Elderly (Matched) | Elderly (Matched) | SMD | |
| n | 12,002 | 131,249 | 11,997 | 11,997 | ||
| Age | 76.0 ± 4.1 | 87.0 ± 2.1 | <0.001 | 87.0 ± 2.1 | 76.4 ± 4.1 | |
| Gender | ||||||
| Men | 1650 (13.7%) | 19,585 (14.9%) | <0.001 | 1649 (13.7%) | 1611 (13.4%) | 0.009 |
| Women | 10,352 (86.3%) | 111,664 (85.1%) | 10,348 (86.3%) | 10,386 (86.6%) | ||
| BMI | 22.8 ± 3.5 | 23.8 ± 3.7 | <0.001 | 22.8 ± 3.5 | 22.8 ± 3.4 | 0.017 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertension | 3697 (30.8%) | 31,180 (23.8%) | <0.001 | 3692 (30.8%) | 3641 (30.4%) | 0.009 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1233 (10.3%) | 12,665 (9.6%) | 0.028 | 1232 (10.3%) | 1175 (9.8%) | 0.016 |
| Diabetes | 1397 (11.6%) | 16,778 (12.8%) | <0.001 | 1397 (11.6%) | 1315 (11.0%) | 0.021 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 455 (3.8%) | 2964 (2.3%) | <0.001 | 453 (3.8%) | 456 (3.8%) | 0.001 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 851 (7.1%) | 5281 (4.0%) | <0.001 | 847 (7.1%) | 814 (6.8%) | 0.000 |
| Chronic renal dysfunction | 336 (2.8%) | 887 (0.7%) | 0.861 | 332 (2.8%) | 303 (2.5%) | 0.015 |
| Chronic lung disease | 79 (0.7%) | 1925 (1.5%) | <0.001 | 79 (0.7%) | 65 (0.5%) | 0.000 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 270 (2.2%) | 2759 (2.1%) | 0.289 | 270 (2.2%) | 229 (1.9%) | 0.101 |
| CCI | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | <0.001 | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 0.029 |
| p-value | p-value | |||||
| Use of bone cement | 2668 (22.2%) | 24,608 (18.7%) | <0.001 | 2665 (22.2%) | 2368 (19.7%) | <0.001 |
| Medications | ||||||
| Anticoagulant agent | 8056 (67.1%) | 97,214 (84.0%) | <0.001 | 8052 (67.1%) | 8734 (72.8%) | <0.001 |
| Antiplatelet agent | 1981 (16.5%) | 13,307 (10.1%) | <0.001 | 1978 (16.5%) | 1447 (12.1%) | <0.001 |
| Before PS Matching | After PS Matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super-Elderly | Elderly | p-Value | Super-Elderly (Matched) | Elderly (Matched) | p-Value | |
| Dislocation | 121 (1.0%) | 1025 (0.8%) | 0.101 | 121 (1.0%) | 107 (0.9%) | 0.387 |
| Infection | 83 (0.7%) | 1063 (0.8%) | 0.185 | 83 (0.7%) | 109 (0.9%) | 0.070 |
| Periprosthetic fracture | 77 (0.6%) | 625 (0.5%) | 0.166 | 77 (0.6%) | 74 (0.6%) | 0.870 |
| Nerve palsy | 9 (0.1%) | 70 (0.1%) | 0.309 | 9 (0.1%) | 10 (0.1%) | 0.999 |
| Wound dehiscence | 14 (0.1%) | 147 (0.1%) | 0.886 | 14 (0.1%) | 15 (0.1%) | 0.999 |
| Reoperation | 201 (1.6%) | 2026 (1.5%) | 0.264 | 201 (1.6%) | 213 (1.8%) | 0.586 |
| Hospital-acquired pneumonia | 46 (0.4%) | 204(0.2%) | <0.001 | 46 (0.4%) | 27 (0.2%) | 0.034 |
| DVT | 704 (5.9%) | 7366 (5.6%) | 0.247 | 704 (5.9%) | 674 (5.6%) | 0.421 |
| PE | 33 (0.3%) | 261 (0.2%) | 0.091 | 33 (0.3%) | 34 (0.3%) | 0.999 |
| Cardiac event | 6 (0.1%) | 28 (0.0%) | 0.061 | 6 (0.1%) | 5 (0.0%) | 0.999 |
| Cerebrovascular event | 70 (0.6%) | 315 (0.2%) | <0.001 | 70 (0.6%) | 35 (0.3%) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 70 (0.6%) | 821 (0.6%) | 0.627 | 70 (0.6%) | 84 (0.7%) | 0.293 |
| Acute renal failure | 12 (0.1%) | 35 (0.0%) | <0.001 | 12 (0.1%) | 2 (0.0%) | 0.013 |
| Mortality during hospitalization | 25 (0.2%) | 71 (0.1%) | <0.001 | 25 (0.2%) | 5 (0.0%) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay | 32.6 ± 21.3 | 28.5 ± 17.3 | <0.001 | 32.6 ± 21.3 | 29.5 ± 19.5 | <0.001 |
| Medical costs (yen) | 1,423,694 ± 412,256 | 1,433,864 ± 400,044 | 0.010 | 1,423,705 ± 401,389 | 1,431,398 ± 412,330 | 0.072 |
| Preoperative BI | 16.2 ± 5.0 | 18.5 ± 3.5 | <0.001 | 16.2 ± 5.1 | 18.2 ± 3.8 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative BI | 16.7 ± 4.4 | 18.6 ± 3.1 | <0.001 | 16.7 ± 4.4 | 18.4 ± 3.3 | <0.001 |
| Before PS Matching | After PS Matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Difference | 95% CI | p-Value | Risk Difference | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Dislocation | 0.0023 | 0.0004 to 0.0041 | 0.101 | 0.0012 | −0.0013 to 0.0036 | 0.387 |
| Infection | −0.0012 | −0.0027 to 0.0004 | 0.185 | −0.0022 | −0.0044 to 0.000 | 0.070 |
| Periprosthetic fracture | 0.0017 | 0.0002 to 0.0031 | 0.166 | 0.0003 | −0.0018 to 0.0023 | 0.870 |
| Nerve palsy | 0.0002 | −0.0003 to 0.0007 | 0.309 | 0.0000 | −0.0008 to 0.0006 | 0.999 |
| Wound dehiscence | 0.0000 | −0.0006 to 0.0007 | 0.886 | 0.0000 | −0.0001 to 0.0008 | 0.999 |
| Reoperation | 0.0013 | −0.0011 to 0.0037 | 0.264 | −0.001 | −0.0043 to 0.0023 | 0.586 |
| Hospital-acquired pneumonia | 0.0023 | 0.0012 to 0.0034 | <0.001 | 0.0016 | 0.0002 to 0.0030 | 0.034 |
| DVT | 0.0025 | −0.0019 to 0.0069 | 0.247 | 0.0025 | −0.0034 to 0.0084 | 0.421 |
| PE | 0.0008 | −0.0002 to 0.0017 | 0.091 | 0.0000 | −0.0014 to 0.0012 | 0.999 |
| Cardiac event | 0.0003 | −0.0001 to 0.0007 | 0.061 | 0.0000 | −0.0005 to 0.0006 | 0.999 |
| Cerebrovascular event | 0.0034 | 0.0020 to 0.0048 | <0.001 | 0.0029 | 0.0012 to 0.0046 | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | −0.0004 | −0.0019 to 0.0010 | 0.627 | −0.0012 | −0.0032 to 0.0009 | 0.293 |
| Acute renal failure | 0.0007 | 0.0002 to 0.0013 | <0.001 | 0.0008 | −0.002 to 0.001 | 0.013 |
| Mortality during hospitalization | 0.0015 | 0.0007 to 0.0024 | <0.001 | 0.0017 | 0.0007 to 0.0026 | <0.001 |
| Caliper Widths of 0.2 | Caliper Widths of 0.05 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Dislocation | 1.132 | 0.872 to 1.470 | 0.387 | 1.461 | 0.989 to 2.156 | 0.056 |
| Infection | 0.760 | 0.570 to 1.012 | 0.070 | 0.720 | 0.433 to 1.200 | 0.203 |
| Periprosthetic fracture | 1.041 | 0.756 to 1.433 | 0.870 | 1.151 | 0.815 to 1.627 | 0.240 |
| Nerve palsy | 0.900 | 0.366 to 2.215 | 0.999 | 0.886 | 0.359 to 2.185 | 0.792 |
| Wound dehiscence | 0.933 | 0.450 to 1.934 | 0.999 | 0.992 | 0.470 to 2.062 | 0.982 |
| Reoperation | 0.943 | 0.776 to 1.145 | 0.586 | 0.768 | 0.565 to 1.043 | 0.09 |
| Hospital-acquired pneumonia | 1.706 | 1.060 to 2.746 | 0.034 | 1.538 | 0.945 to 2.496 | 0.077 |
| DVT | 1.047 | 0.939 to 1.168 | 0.421 | 1.054 | 0.945 to 1.175 | 0.345 |
| PE | 0.971 | 0.601 to 1.568 | 0.999 | 0.923 | 0.570 to 1.496 | 0.746 |
| Cardiac event | 1.200 | 0.366 to 3.933 | 0.999 | 1.174 | 0.358 to 3.854 | 0.791 |
| Cerebrovascular event | 2.006 | 1.336 to 3.012 | <0.001 | 1.998 | 1.330 to 3.000 | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 0.832 | 0.606 to 1.144 | 0.293 | 1.112 | 0.633 to 1.952 | 0.712 |
| Acute renal failure | 6.005 | 1.344 to 26.84 | 0.013 | 5.654 | 1.257 to 25.43 | 0.007 |
| Mortality during hospitalization | 5.008 | 1.917 to 13.09 | <0.001 | 4.611 | 1.750 to 12.15 | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular Event | Mortality During Hospitalization | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | χ2 Statics | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | χ2 Statics | p-Value |
| Gender (Female) | 1.228 | 0.754 to 1.999 | 0.682 | 0.409 | 0.777 | 0.304 to 1.988 | 0.265 | 0.607 |
| BMI | 1.040 | 0.985 to 1.097 | 2.046 | 0.153 | 0.828 | 0.735 to 0.927 | 11.14 | <0.001 |
| Super-elderly | 2.125 | 1.403 to 3.219 | 12.67 | <0.001 | 5.565 | 2.106 to 14.71 | 16.300 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.151 | 0.756 to 1.734 | 0.43 | 0.512 | 0.769 | 0.333 to 1.775 | 0.392 | 0.531 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.520 | 0.866 to 2.671 | 2.124 | 0.145 | 0.692 | 0.160 to 3.000 | 0.267 | 0.606 |
| Diabetes | 0.379 | 0.210 to 0.682 | 10.44 | 0.001 | 0.428 | 0.122 to 1.494 | 2.118 | 0.146 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.702 | 0.318 to 1.548 | 0.769 | 0.381 | 0.514 | 0.068 to 3.890 | 0.507 | 0.477 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 1.737 | 0.989 to 3.050 | 3.686 | 0.055 | 3.274 | 1.313 to 8.165 | 5.125 | 0.024 |
| Chronic renal dysfunction | 0.423 | 0.190 to 0.942 | 7.209 | 0.007 | 1.018 | 0.271 to 3.825 | 0.001 | 0.979 |
| Chronic lung disease | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.993 | 4.821 | 1.048 to 22.17 | 2.861 | 0.091 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 0.454 | 0.014 to 1.493 | 1.692 | 0.193 | 0.000 | - | 3.127 | 0.077 |
| CCI | 2.433 | 2.152 to 2.742 | 208.3 | <0.001 | 1.856 | 1.398 to 2.371 | 15.07 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, H.; Tarasawa, K.; Mori, Y.; Kanabuchi, R.; Baba, K.; Kurishima, H.; Fushimi, K.; Fujimori, K.; Aizawa, T. Evaluating In-Hospital Safety and Perioperative Costs of Total Hip Arthroplasty in Super-Elderly Patients: A Nationwide Propensity Score–Matched Analysis in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217803
Tanaka H, Tarasawa K, Mori Y, Kanabuchi R, Baba K, Kurishima H, Fushimi K, Fujimori K, Aizawa T. Evaluating In-Hospital Safety and Perioperative Costs of Total Hip Arthroplasty in Super-Elderly Patients: A Nationwide Propensity Score–Matched Analysis in Japan. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217803
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Hidetatsu, Kunio Tarasawa, Yu Mori, Ryuichi Kanabuchi, Kazuyoshi Baba, Hiroaki Kurishima, Kiyohide Fushimi, Kenji Fujimori, and Toshimi Aizawa. 2025. "Evaluating In-Hospital Safety and Perioperative Costs of Total Hip Arthroplasty in Super-Elderly Patients: A Nationwide Propensity Score–Matched Analysis in Japan" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217803
APA StyleTanaka, H., Tarasawa, K., Mori, Y., Kanabuchi, R., Baba, K., Kurishima, H., Fushimi, K., Fujimori, K., & Aizawa, T. (2025). Evaluating In-Hospital Safety and Perioperative Costs of Total Hip Arthroplasty in Super-Elderly Patients: A Nationwide Propensity Score–Matched Analysis in Japan. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217803






