Persistent Need for Ophthalmic Follow-Up After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation: Long-Term Effects on Diabetic Retinopathy and Quality of Life
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
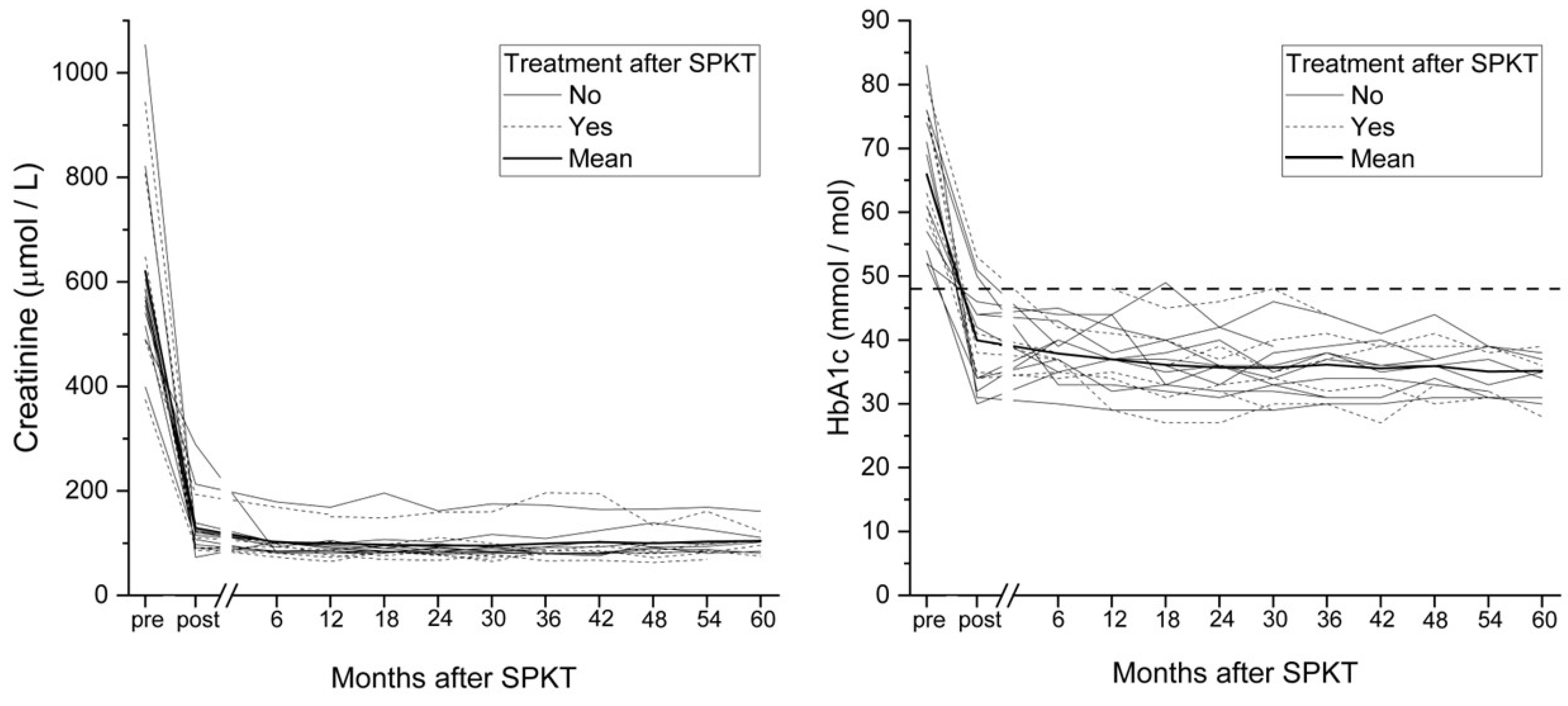
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, J.W.Y.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.-J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global Prevalence and Major Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautala, N.; Aikkila, R.; Korpelainen, J.; Keskitalo, A.; Kurikka, A.; Falck, A.; Bloigu, R.; Alanko, H. Marked reductions in visual impairment due to diabetic retinopathy achieved by efficient screening and timely treatment. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Molitch, M. Are All Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Destined for Dialysis if They Live Long Enough? Probably Not. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.C.; Goetz, F.C.; Sutherland, D.E.; Mauer, S.M.; Robison, L.L.; Cantrill, H.L.; Knobloch, W.H.; Najarian, J.S. Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy after Pancreas Transplantation for Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipman, K.E.; Patel, C.K. The effect of combined renal and pancreatic transplantation on diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2009, 3, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, I.A.; Ilango, B.; Sells, R.A.; Wong, D. Stabilisation of diabetic retinopathy following simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplant. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 84, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voglová, B.; Hladíková, Z.; Nemétová, L.; Zahradnická, M.; Kesslerová, K.; Sosna, T.; Lipár, K.; Kožnarová, R.; Girman, P.; Saudek, F. Early worsening of diabetic retinopathy after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation—Myth or reality? Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Klein, R.; Moss, S.E.; Klein, B.E.; Hoyer, C.; Burke, K.; Sollinger, H.W. The Influence of Combined Kidney-pancreas Transplantation on the Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy—A case series. Ophthalmology 1994, 101, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KožNarová, R.; Saudek, F.; Sosna, T.; Adamec, M.; Jedináková, T.; BoučEk, P.; Bartoš, V.; Lánská, V. Beneficial Effect of Pancreas and Kidney Transplantation on Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy. Cell Transplant. 2000, 9, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, J.C.; Trepsat, D.; Gain-Gueugnon, M.; Lefrancois, N.; Martin, X.; Dubernard, J.M. Ophthalmological follow-up of Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients after kidney and pancreas transplantation. Diabetologia 1991, 34 (Suppl. 1), S89–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chow, V.C.; Pai, R.P.; Chapman, J.R.; O’Connell, P.J.; Allen, R.D.; Mitchell, P.; Nankivell, B.J. Diabetic retinopathy after combined kidney-pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 1999, 13, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abendroth, D.; Schmand, J.; Landgraf, R.; Illner, W.D.; Land, W. Diabetic microangiopathy in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients after successful pancreatic and kidney or solitary kidney transplantation. Diabetologia 1991, 34, S131–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbig, M.; Kampik, A.; Thurau, S.; Land, W.; Landgraf, R. Long-term follow-up of diabetic retinopathy for up to 71 months after combined renal and pancreatic transplantation. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1991, 229, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham-Rowe, E.; Lorencatto, F.; Lawrenson, J.G.; Burr, J.M.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Ivers, N.M.; Presseau, J.; Vale, L.; Peto, T.; Bunce, C.; et al. Barriers to and enablers of diabetic retinopathy screening attendance: A systematic review of published and grey literature. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwick, E.K.; Cheng, G.H.-L.; Man, R.E.K.; Khadka, J.; Rees, G.; Wong, T.Y.; Pesudovs, K.; Lamoureux, E.L. Inter-relationship between visual symptoms, activity limitation and psychological functioning in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassart, J.; Luyckx, K.; Oris, L.; Goethals, E.; Moons, P.; Weets, I. Coping with type 1 diabetes through emerging adulthood: Longitudinal associations with perceived control and haemoglobin A1c. Psychol. Health 2016, 31, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.H.; Braffett, B.H.; Kuo, S.; Lee, J.M.; Brandle, M.; Jacobson, A.M.; Prosser, L.A.; Lachin, J.M. What are the clinical, quality-of-life, and cost consequences of 30 years of excellent vs. poor glycemic control in type 1 diabetes? J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, A.; Michalak, G.; Czerwinski, J.; Wszola, M.; Nosek, R.; Ostrowski, K.; Chmura, A.; Danielewicz, R.; Lisik, W.; Adadynski, L.; et al. Quality of Life After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 3558–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, J.; Esteban, C.; Iglesias, M.J.; González, L.M.; Quiñones, J.E.; González-Muñoz, J.I.; Tabernero, G.; Iglesias, R.A.; Fraile, P.; Muñoz-González, J.I.; et al. Factors affecting diabetic patient’s long-term quality of life after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: A single-center analysis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahopelto, K.; Sallinen, V.; Helanterä, I.; Bonsdorff, A.; Grasberger, J.; Beilmann-Lehtonen, I.; Mäkisalo, H.; Nordin, A.; Ortiz, F.; Savikko, J.; et al. The first 10 years of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in Finland. Clin. Transplant. 2023, 37, e14992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintonen, H. The 15D instrument of health-related quality of life: Properties and applications. Ann. Med. 2001, 33, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, J.; Mikhailova, A.; Ojamo, M.; Nättinen, J.; Väätäinen, S.; Gissler, M.; Koskinen, S.; Rissanen, H.; Sainio, P.; Uusitalo, H. Low vision status and declining vision decrease Health-Related Quality of Life: Results from a nationwide 11-year follow-up study. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 3225–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braffett, B.H.; Bebu, I.; Lorenzi, G.M.; Martin, C.L.; Perkins, B.A.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.; Nathan, D.M.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. The NIDDK Takes on the Complications of Type 1 Diabetes: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.W.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Laffel, L.M.; Pickup, J.C. Advances in technology for management of type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2019, 394, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelino, T.; Alexander, C.M.; A Amiel, S.; Arreaza-Rubin, G.; Beck, R.W.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buckingham, B.A.; Carroll, J.; Ceriello, A.; Chow, E.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and metrics for clinical trials: An international consensus statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, N.C.; Beck, R.W.; Miller, K.M.; Clements, M.A.; Rickels, M.R.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Maahs, D.M.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bergenstal, R.; Smith, E.; et al. State of Type 1 Diabetes Management and Outcomes from the T1D Exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, P.; Rickels, M.R.; Senior, P.A.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Maffi, P.; Kay, T.W.; Keymeulen, B.; Inagaki, N.; Saudek, F.; Lehmann, R.; et al. Evidence-Informed Clinical Practice Recommendations for Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Complicated by Problematic Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choksi, H.B.; Pleass, H.M.; Robertson, P.; Au, E.M.; Rogers, N.M. Long-term Metabolic Outcomes Post–Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation in Recipients with Type 1 Diabetes. Transplantation 2025, 109, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | All (n = 18) | Stable DR (n = 11) | Progression of DR (n = 7) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, males, n (%) | 12 (67) | 6 (55) | 6 (86) | 0.171 |
| Age at diagnosis of dm | 8.5 (8.1) [1–34] | 9.6 (9.1) | 6.7 (6.6) | 0.476 |
| Duration of diabetes pre-SPKT | 30.2 (8.6) [15–43] | |||
| Age at SPKT, years (SD) [min-max] | 38.7 (7.3) [29–53] | 41.5 (7.9) | 34.4 (3.4) | 0.01 * |
| History of ketoacidosis, n (%) | 10 (56) | 7 (64) | 3 (43) | 0.387 |
| Insulin treatment before SPKT | 0.629 | |||
| Multiple daily injections, n (%) | 9 (50) | 5 (46) | 4 (57) | |
| Insulin pump, n (%) | 9 (50) | 6 (54) | 3 (43) | |
| Duration of dialysis pre-SPKT, years (SD) [min-max] | 1.5 (1.2) [0–4] | 1.3 (0.8) | 1.9 (1.6) | 0.343 |
| Dialysis type | 0.557 | |||
| Peritoneal, n (%) | 8 (44) | 4 (36) | 4 (57) | |
| Hemodialysis, n (%) | 10 (56) | 7 (64) | 6 (86) | |
| Duration of DR pre-SPKT, years (SD) [min-max] | 16.0 (8.5) [1–31] | 18.0 (9.3) | 11.9 (5.2) | 0.204 |
| Severity of DR | 0.688 | |||
| NPDR, n (%) | 2 (11) | 1 (9) | 1 (14) | |
| PDR, n (%) | 16 (89) | 10 (91) | 6 (86) | |
| Previous treatments for DR | ||||
| Anti-VEGF-treatment, n (%) | 9 (50) | 5 (46) | 4 (57) | 0.629 |
| Retinal photocoagulation, n (%) | 16 (89) | 10 (91) | 6 (86) | 0.732 |
| Pars plana vitrectomy, n (%) | 9 (50) | 6 (55) | 3 (43) | 0.629 |
| Previous medical history | ||||
| Medication for arterial hypertension, n (%) | 18 (100) | 11 (100) | 7 (100) | - |
| Medication for dyslipidemia, n (%) | 11 (61) | 6 (55) | 5 (71) | 0.474 |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 5 (28) | 5 (45) | - | 0.351 |
| Asthma, n (%) | 1 (6) | 1 (9) | - | 0.412 |
| Arthritis, n (%) | 1 (6) | 1 (9) | - | 0.412 |
| Diabetic polyneuropathy, n (%) | 7 (39) | 5 (45) | 2 (29) | 0.474 |
| Charcot’s neuroarthropathy, n (%) | 4 (22) | 3 (27) | 1 (14) | 0.518 |
| Anterior uveitis, n (%) | 2 (11) | - | 2 (29) | 0.06 |
| Secondary glaucoma, n (%) | 2 (11) | 1 (9) | 1 (14) | 0.732 |
| SPKT associated adverse effects | ||||
| Chronic kidney transplant rejection, n (%) | 3 (17) | 1 (9) | 2 (29) | 0.28 |
| Pancreas transplant rejection, n (%) | 4 (22) | 3 (27) | 1 (14) | 0.518 |
| Post-transplant neutropenia, n (%) | 1 (6) | - | 1 (14) | 0.197 |
| Post-transplant lymphoma, n (%) | 3 (17) | 2 (18) | 1 (14) | 0.829 |
| Immunosupressive therapy | 0.434 | |||
| MMF + TAC, n (%) | 14 (78) | 9 (82) | 5 (71) | |
| MMF + TAC + PSL, n (%) | 3 (16) | 1 (9) | 2 (29) | |
| AZA + TAC + PSL, n (%) | 1 (6) | 1 (9) | - |
| Ophthalmological Feature | All n = 18 | Stable DR n = 11 | Progression of DR n = 7 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean BCVA pre-SPKT, ETDRS letters (SD), [min–max], worse eye | 64 (24) [0–90] | 60.5 (27.9) | 69.6 (15.8) | 0.443 |
| Mean BCVA post-SPKT, ETDRS letters (SD), [min–max], worse eye | 69 (21) [0–85] | 65.9 (25.9) | 74.3 (11.7) | 0.254 |
| Rate of visual impairment pre-SPKT, n (%) | 2 (11) | 2 (18) | 0 | 0.677 |
| Rate of visual impairment post-SPKT, n (%) | 1 (6) | 1 (9) | 0 | 0.412 |
| Lense status after SPKT, worse eye | ||||
| No progression or previous IOL, n (%) | 11 (61) | 7 (64) | 4 (57) | |
| Progression of cataract, n (%) | 7 (39) | 4 (36) | 3 (43) | |
| CRT pre-SPKT, mean (SD), [min–max], worse eye | 243 (36) [195–329] | 234 (32) | 257 (38) | 0.217 |
| CRT post-SPKT at the study visit, mean (SD), [min–max], worse eye | 251 (46) [195–346] | 232 (25) | 307 (55) | 0.29 |
| Stability of DR post-SPKT, n (%) | ||||
| No treatment | 11 (61) | |||
| Macular laser | 1 (6) | |||
| Panretinal photocoagulation | 2 (11) | |||
| Anti-VEGF | 1(6) | |||
| Laser + anti-VEGF | 3 (16) | |||
| Pars plana vitrectomy | 0 (0) | |||
| Time to DR treatment after SPKT, months, median (IQR) [min–max] | 9.9 (9.5) [2.7–68.3] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wirkkala, J.; Ikäheimo, R.; Kubin, A.-M.; Ohtonen, P.; Hautala, N. Persistent Need for Ophthalmic Follow-Up After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation: Long-Term Effects on Diabetic Retinopathy and Quality of Life. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217779
Wirkkala J, Ikäheimo R, Kubin A-M, Ohtonen P, Hautala N. Persistent Need for Ophthalmic Follow-Up After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation: Long-Term Effects on Diabetic Retinopathy and Quality of Life. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217779
Chicago/Turabian StyleWirkkala, Joonas, Risto Ikäheimo, Anna-Maria Kubin, Pasi Ohtonen, and Nina Hautala. 2025. "Persistent Need for Ophthalmic Follow-Up After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation: Long-Term Effects on Diabetic Retinopathy and Quality of Life" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217779
APA StyleWirkkala, J., Ikäheimo, R., Kubin, A.-M., Ohtonen, P., & Hautala, N. (2025). Persistent Need for Ophthalmic Follow-Up After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation: Long-Term Effects on Diabetic Retinopathy and Quality of Life. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217779





