Lipoprotein(a) and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Certainty of Evidence Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results Summary
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. Meta-Analysis
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.5. Meta-Regression
3.6. Publication Bias Assessment
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| apo(a) | Apolipoprotein(a) |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CTA | Computed tomography angiography |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| EAT | Epicardial adipose tissue |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation |
| HF | Heart failure |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LOO | Leave-one-out |
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein(a) |
| MD | Mean difference |
| OxPLs | Oxidized phospholipids |
| PET/CT | Positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| ROBINS-E | Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies of Exposures |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.H.; Nattel, S.; Kalman, J.M.; Sanders, P. Modifiable Risk Factors and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2017, 136, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimikas, S. A Test in Context: Lipoprotein(a): Diagnosis, Prognosis, Controversies, and Emerging Therapies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, R.; Peden, J.F.; Hopewell, J.C.; Kyriakou, T.; Goel, A.; Heath, S.C.; Parish, S.; Barlera, S.; Franzosi, M.G.; Rust, S.; et al. Genetic variants associated with Lp(a) lipoprotein level and coronary disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamstrup, P.R.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Steffensen, R.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Genetically elevated lipoprotein(a) and increased risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA 2009, 301, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampsas, S.; Xenou, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Pantelidis, P.; Lysandrou, A.; Sarantos, S.; Goliopoulou, A.; Kalogeras, K.; Tsigkou, V.; Kalpis, A.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Diseases: From Pathophysiology to Diagnosis and Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamstrup, P.R.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated lipoprotein(a) and risk of aortic valve stenosis in the general population. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhi, L.; Lu, Y. The effect of apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and Lp(a) levels on coronary artery disease with atrial fibrillation. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221109387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronis, K.N.; Zhao, D.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Alonso, A.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Guallar, E.; Jones, S.R.; Martin, S.S.; Nazarian, S.; Steffen, B.T.; et al. Associations of Lipoprotein(a) Levels With Incident Atrial Fibrillation and Ischemic Stroke: The ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e007372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, S.; Akinkuolie, A.O.; Sandhu, R.K.; Conen, D.; Albert, C.M. Paradoxical association of lipoprotein measures with incident atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Guan, W.; Karger, A.B.; Steffen, B.T.; O’Neal, W.; Heckbert, S.R.; Michos, E.D.; Tsai, M.Y. Lp(a) (Lipoprotein [a]) and Risk for Incident Atrial Fibrillation: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yang, X.; Qiu, Q.; Gao, F.; Chen, W.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Hu, H.; Jiang, L. Low lipoprotein(a) concentration is associated with atrial fibrillation: A large retrospective cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goette, A.; Corradi, D.; Dobrev, D.; Aguinaga, L.; Cabrera, J.A.; Chugh, S.S.; de Groot, J.R.; Soulat-Dufour, L.; Fenelon, G.; Hatem, S.N.; et al. Atrial cardiomyopathy revisited-evolution of a concept: A clinical consensus statement of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC, the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), the Asian Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and the Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS). Europace 2024, 26, euae204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Morgan, R.L.; Rooney, A.A.; Taylor, K.W.; Thayer, K.A.; Silva, R.A.; Lemeris, C.; Akl, E.A.; Bateson, T.F.; Berkman, N.D.; et al. A tool to assess risk of bias in non-randomized follow-up studies of exposure effects (ROBINS-E). Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultcrantz, M.; Rind, D.; Akl, E.A.; Treweek, S.; Mustafa, R.A.; Iorio, A.; Alper, B.S.; Meerpohl, J.J.; Murad, M.H.; Ansari, M.T.; et al. The GRADE Working Group clarifies the construct of certainty of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 87, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br. Med. J. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Peromingo, J.A.; Albán-Salgado, A.; García-Suárez, F.; Sánchez-Leira, J.; Saborido-Froján, J.; Iglesias-Gallego, M. Lipoprotein(a) and lipid profile in patients with atrial fibrillation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, CR122–CR125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Tao, J.; Qiu, Q.; Gao, F.; Chen, W.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y.; Yi, Y. Low lipoprotein(a) concentration is associated with higher atrial risk: A large retrospective cohort study. Res. Sq. 2022, Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Li, M.-H.; Yin, R.; Cui, Y.-Q.; Jiang, S.-L.; Cui, L.-Q.; Chen, L.-M. The prospective effect of lipoprotein(a) on new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 18316–18323. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Su, S.; Hu, Z.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Peng, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, M.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) elevation independently associates with incident atrial fibrillation irrespective of inflammatory status. Heart Rhythm, 2025; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Qi, C. Clinical prediction study on the risk of atrial fibrillation in hypertensive patients based on metabolism, inflammation, and gender differences. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagonas, N.; Mueller, R.; Weiland, L.; Jaensch, M.; Dammermann, W.; Seibert, F.S.; Hillmeister, P.; Buschmann, I.; Christ, M.; Ritter, O.; et al. Oxidized high-density lipoprotein associates with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2024, 21, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.B.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, Y.N. Study on the correlation between red cell distribution width, homocysteine, lipoprotein(a), and left atrial diameter in newly diagnosed nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Jiao, H.; Zhong, X.; Wang, W.; Li, L. The association between serum albumin levels and related metabolic factors and atrial fibrillation A retrospective study. Medicine 2022, 101, e31581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.H.; Tsimikas, S.; Pawade, T.; Kroon, J.; Jenkins, W.S.A.; Doris, M.K.; White, A.C.; Timmers, N.K.L.M.; Hjortnaes, J.; Rogers, M.A.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Oxidized Phospholipids Promote Valve Calcification in Patients with Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2150–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Nasr, B.; Liu, J.; Du, Y.; Yang, J. The association between lipoprotein(a) and atrial fibrillation: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2023, 46, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Baars, D.P.; Desai, R.; Singh, D.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.J. Association Between Lipoprotein (a) and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchareb, R.; Mahmut, A.; Nsaibia, M.J.; Boulanger, M.C.; Dahou, A.; Lépine, J.L.; Laflamme, M.H.; Hadji, F.; Couture, C.; Trahan, S.; et al. Autotaxin Derived From Lipoprotein(a) and Valve Interstitial Cells Promotes Inflammation and Mineralization of the Aortic Valve. Circulation 2015, 132, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehab, O.; Abdollahi, A.; Whelton, S.P.; Wu, C.O.; Ambale-Venkatesh, B.; Post, W.S.; Bluemke, D.A.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lima, J.A.C. Association of Lipoprotein(a) Levels With Myocardial Fibrosis in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2280–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, H.S.; Wandel, S.; Willeit, P.; Lesogor, A.; Bailey, K.; Ridker, P.M.; Nestel, P.; Simes, J.; Tonkin, A.; Schwartz, G.G.; et al. Independence of Lipoprotein(a) and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol-Mediated Cardiovascular Risk: A Participant-Level Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2025, 151, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Valk, F.M.; Bekkering, S.; Kroon, J.; Yeang, C.; Van den Bossche, J.; van Buul, J.D.; Ravandi, A.; Nederveen, A.J.; Verberne, H.J.; Scipione, C.; et al. Oxidized Phospholipids on Lipoprotein(a) Elicit Arterial Wall Inflammation and an Inflammatory Monocyte Response in Humans. Circulation 2016, 134, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliner, J.A.; Leitinger, N.; Tsimikas, S. The role of oxidized phospholipids in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S207–S212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Soffer, G.; Westerterp, M. Beyond Lipoprotein(a) plasma measurements: Lipoprotein(a) and inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 169, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Nattel, S. Implications of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa, M.B.; Koschinsky, M.L. Oxidized phospholipids as a unifying theory for lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dudley, S.C., Jr. Evidence for Inflammation as a Driver of Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, S.A. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnuolo, R.; Marcovina, S.M.; Boffa, M.B.; Koschinsky, M.L. Inhibition of plasminogen activation by apo(a): Role of carboxyl-terminal lysines and identification of inhibitory domains in apo(a). J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa, M.B. Beyond fibrinolysis: The confounding role of Lp(a) in thrombosis. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplice, N.M.; Panetta, C.; Peterson, T.E.; Kleppe, L.S.; Mueske, C.S.; Kostner, G.M.; Broze, G.J., Jr.; Simari, R.D. Lipoprotein (a) binds and inactivates tissue factor pathway inhibitor: A novel link between lipoproteins and thrombosis. Blood 2001, 98, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spronk, H.M.; De Jong, A.M.; Verheule, S.; De Boer, H.C.; Maass, A.H.; Lau, D.H.; Rienstra, M.; van Hunnik, A.; Kuiper, M.; Lumeij, S.; et al. Hypercoagulability causes atrial fibrosis and promotes atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.; Shantsila, E.; Lip, G.Y. Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: Virchow’s triad revisited. Lancet 2009, 373, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.Y.; Protty, M.B.; Davies, I.G.; Lip, G.Y.H. Relationship between lipoproteins, thrombosis, and atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, Y.; Yamaura, M.; Ito, M.; Inuzuka, H.; Ojima, K.; Aizawa, Y. Elevated serum lipoprotein(a) is a risk factor for left atrial thrombus in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation: A transesophageal echocardiographic study. Am. Heart J. 1998, 136, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G. Epicardial adipose tissue in contemporary cardiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, I.; Kousta, M.; Kossyvakis, C.; Paraskevaidis, N.T.; Vrachatis, D.; Deftereos, S.; Giannopoulos, G. Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence following Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momot, K.; Krauz, K.; Pruc, M.; Szarpak, L.; Rodkiewicz, D.; Mamcarz, A. Association Between Left Atrial Epicardial Adipose Tissue Attenuation Assessed by Cardiac Computed Tomography and Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Following Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmohamed, N.S.; Gaillard, E.L.; Malkasian, S.; de Groot, R.J.; Ibrahim, S.; Bom, M.J.; Kaiser, Y.; Earls, J.P.; Min, J.K.; Kroon, J.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Long-Term Plaque Progression, Low-Density Plaque, and Pericoronary Inflammation. JAMA Cardiol. 2024, 9, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
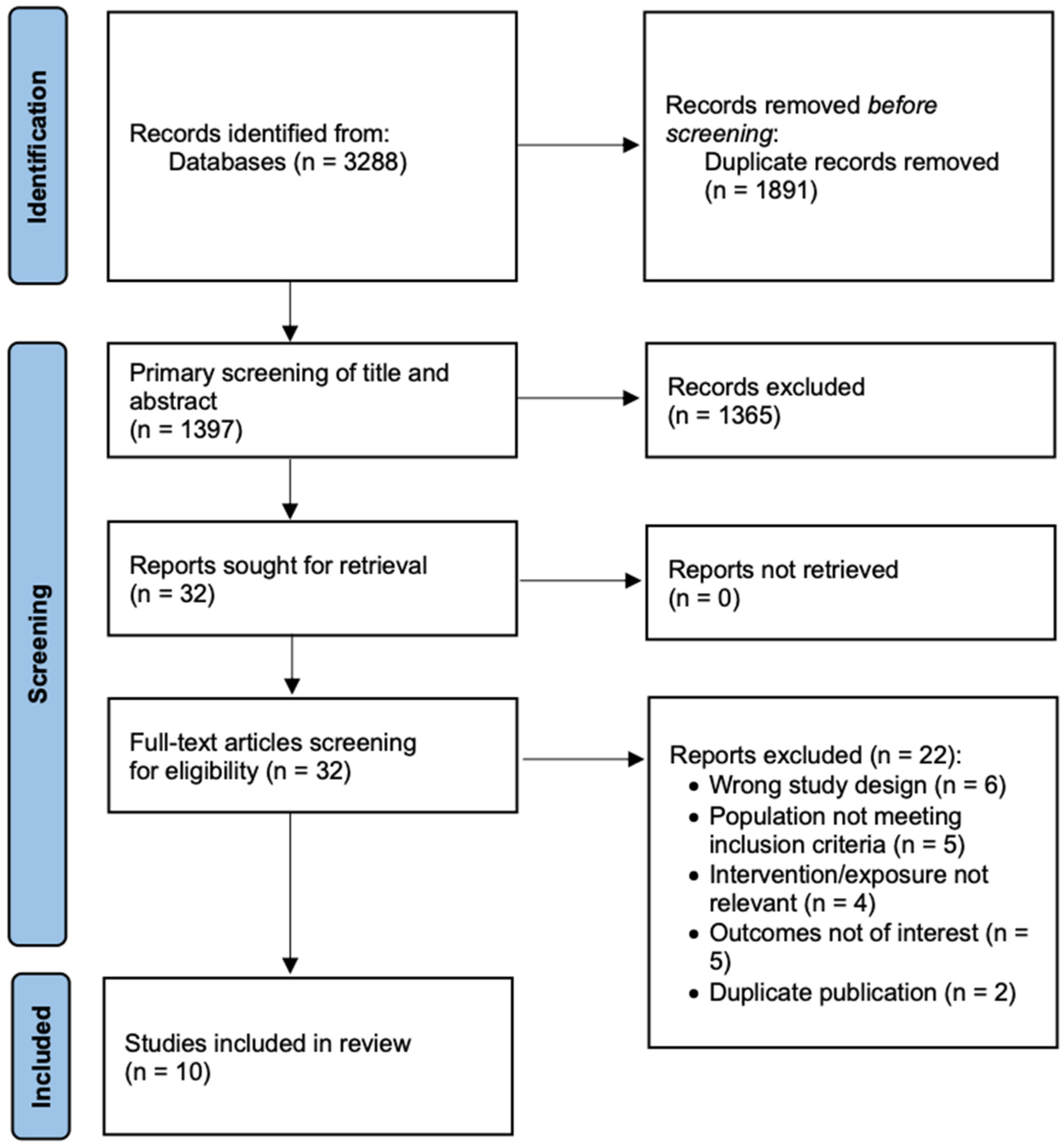
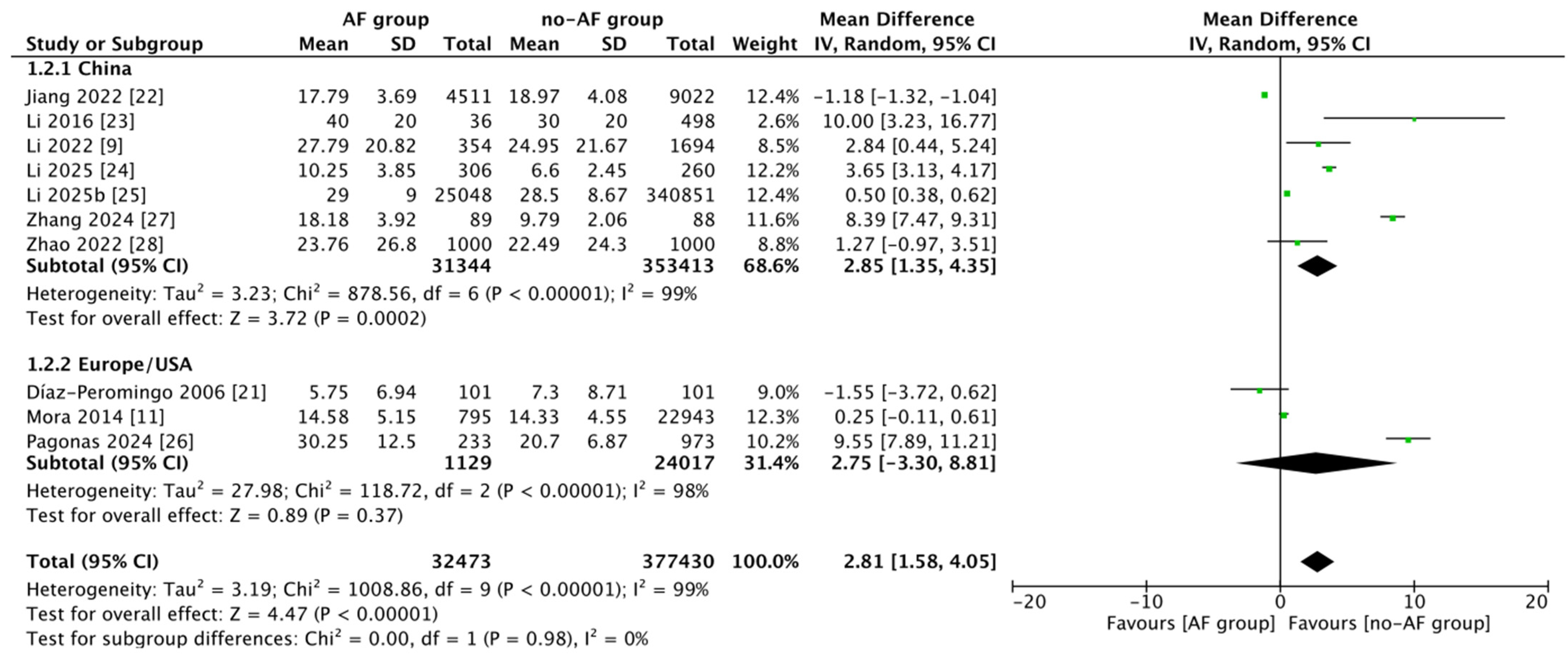
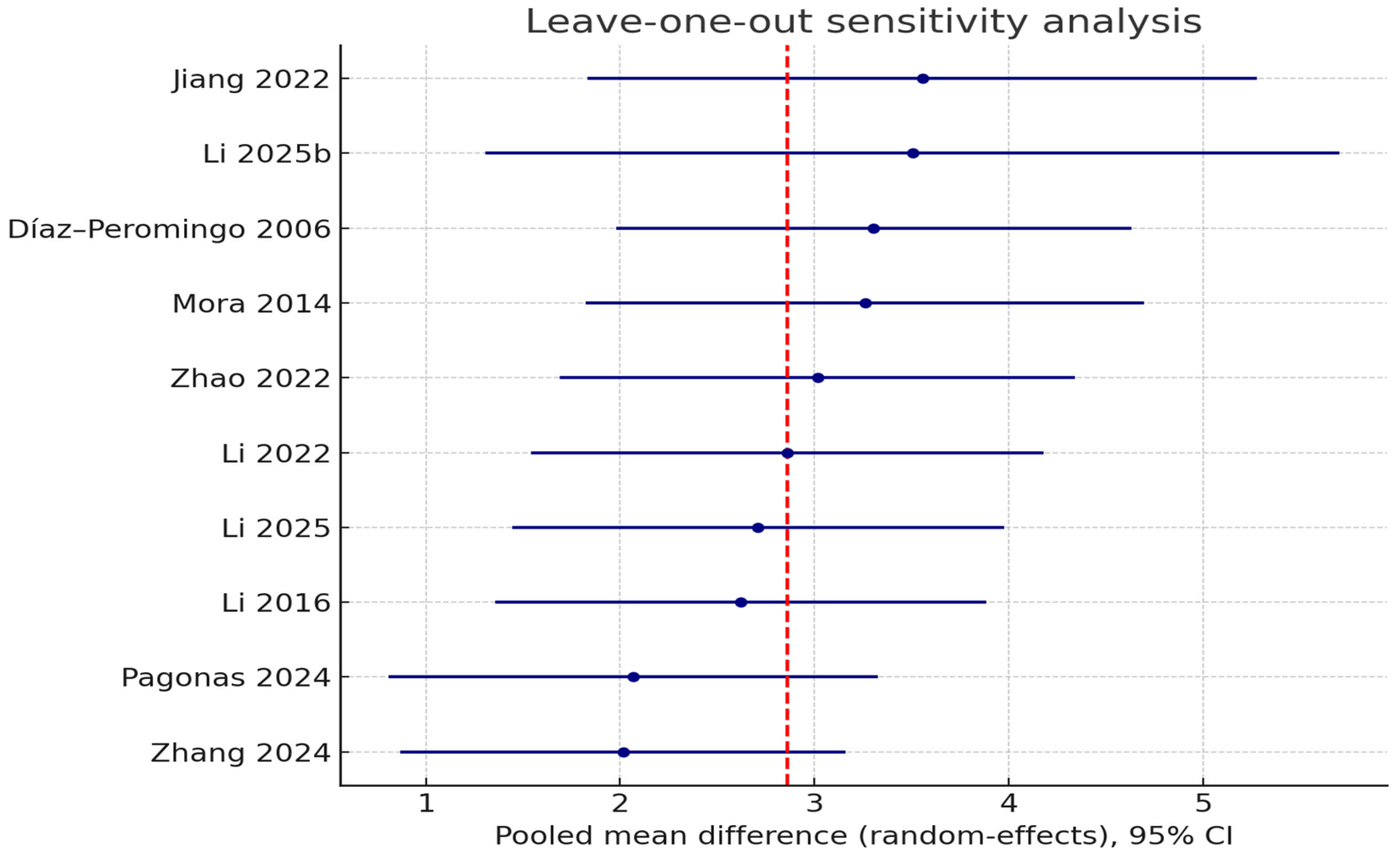
| Study | Country | Study Design | Study Group | Sample Size | Male (%) | Age | BMI | HTN (%) | DM2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Díaz-Peromingo et al., 2006 [21] | Spain | Case–control study | AF | 101 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Non-AF | 101 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |||
| Jiang et al., 2022 [22] | China | Retrospective study | AF | 4511 | 2388 (52.9%) | 67.85 (44.95, 90.75) | 23.62 (21.55, 25.78) | 2505 (55.53%) | 728 (16.14%) |
| Non-AF | 9022 | 4797 (53.2%) | 67.85 (44.97, 90.73) | 23.56 (21.45, 25.55) | 5018 (55.62%) | 1908 (21.14%) | |||
| Li et al., 2016 [23] | China | Prospective cohort study | AF | 36 | 18 (50.0%) | 71.9 (10.6) | NS | 23 (63.9%) | 20 (55.6%) |
| Non-AF | 498 | 300 (60.2%) | 70.0 (14.6) | NS | 301 (60.4%) | 170 (34.1%) | |||
| Li et al., 2022 [9] | China | Observational case–control study | AF | 354 | 65.69 (10.69) | 202 | 24.15 (3.84) | 209 | 83 |
| Non-AF | 1694 | 63.89 (11.1) | 1007 | 24.16 (3.97) | 945 | 390 | |||
| Li et al., 2025 [24] | China | Retrospective cohort study | AF | 306 | 180 (58.8%) | 71 (62, 77) | NS | NS | 119 (38.9%) |
| Non-AF | 260 | 106 (40.8%) | 66 (62, 76) | NS | NS | 67 (25.8%) | |||
| Li et al., 2025 [25] | UK | Retrospective cohort study | AF | 25,048 | 15,291 (61.1%) | 64.0 (59.0, 66.0) | 27.9 (25.3, 31.4) | 11,289 (45.1%) | 1401 (5.6%) |
| Non-AF | 340,851 | 150,016 (44.0%) | 57.0 (49.0, 63.0) | 26.7 (24.1, 29.6) | 83,062 (24.4%) | 9381 (2.8%) | |||
| Mora et al., 2014 [11] | USA | Prospective cohort study | AF | 795 | 0 (0.0%) | 58.7 (52.7, 65.0) | 26.0 (23.2, 30.1) | 323 (40.6%) | 35 (4.4%) |
| Non-AF | 22,943 | 0 (0.0%) | 52.6 (48.8, 58.3) | 24.8 (22.3, 28.3) | 5299 (23.1%) | 528 (2.3%) | |||
| Pagonas et al., 2024 [26] | Germany | Cross-sectional observational multicenter study | AF | 233 | 158 (67.8%) | 73 (66, 77) | 29 (26–32) | 211 (90.6%) | 77 (33.0%) |
| Non-AF | 973 | 624 (64.1%) | 66 (57, 75) | 28 (25, 32) | 793 (81.5%) | 256 (26.3%) | |||
| Zhang et al., 2024 [27] | China | Case–control study | AF | 89 | 46 (51.7%) | 68.2 (11.2) | NS | 6 (6.7%) | 51 (57.3%) |
| Non-AF | 88 | 44 (50.0%) | 56.2 (13.8) | NS | 2 (2.3%) | 33 (37.5%) | |||
| Zhao et al., 2022 [28] | China | Case–control study | AF | 1000 | 506 (50.6%) | 70.45 (10.46) | NS | 674 (67.4%) | 306 (30.6%) |
| Non-AF | 1000 | 496 (49.6%) | 69.80 (9.84) | NS | 329 (32.9%) | 160 (16.0%) |
| No. of Studies | Study Design | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other Considerations | Effect (95% CI)/ Certainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Observational studies | Serious (ROBINS-E: mostly moderate) | Very serious (I2 = 99%) | Serious (heterogeneous populations/biomarkers) | Serious (wide CIs) | Potential publication bias | MD = 2.81 (95%CI: 1.58–4.05) Certainty: ⨁○○○ very low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maj, B.; Pruc, M.; Czubak, P.; Romanska, I.; Momot, K.; Klos, M.; Krauz, K.; Mielnik, A.; Siudak, Z.; Kotfis, K.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217770
Maj B, Pruc M, Czubak P, Romanska I, Momot K, Klos M, Krauz K, Mielnik A, Siudak Z, Kotfis K, et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217770
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaj, Bartosz, Michal Pruc, Pawel Czubak, Iga Romanska, Karol Momot, Marta Klos, Kamil Krauz, Aleksandra Mielnik, Zbigniew Siudak, Katarzyna Kotfis, and et al. 2025. "Lipoprotein(a) and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217770
APA StyleMaj, B., Pruc, M., Czubak, P., Romanska, I., Momot, K., Klos, M., Krauz, K., Mielnik, A., Siudak, Z., Kotfis, K., & Szarpak, L. (2025). Lipoprotein(a) and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217770








