Sacral and Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
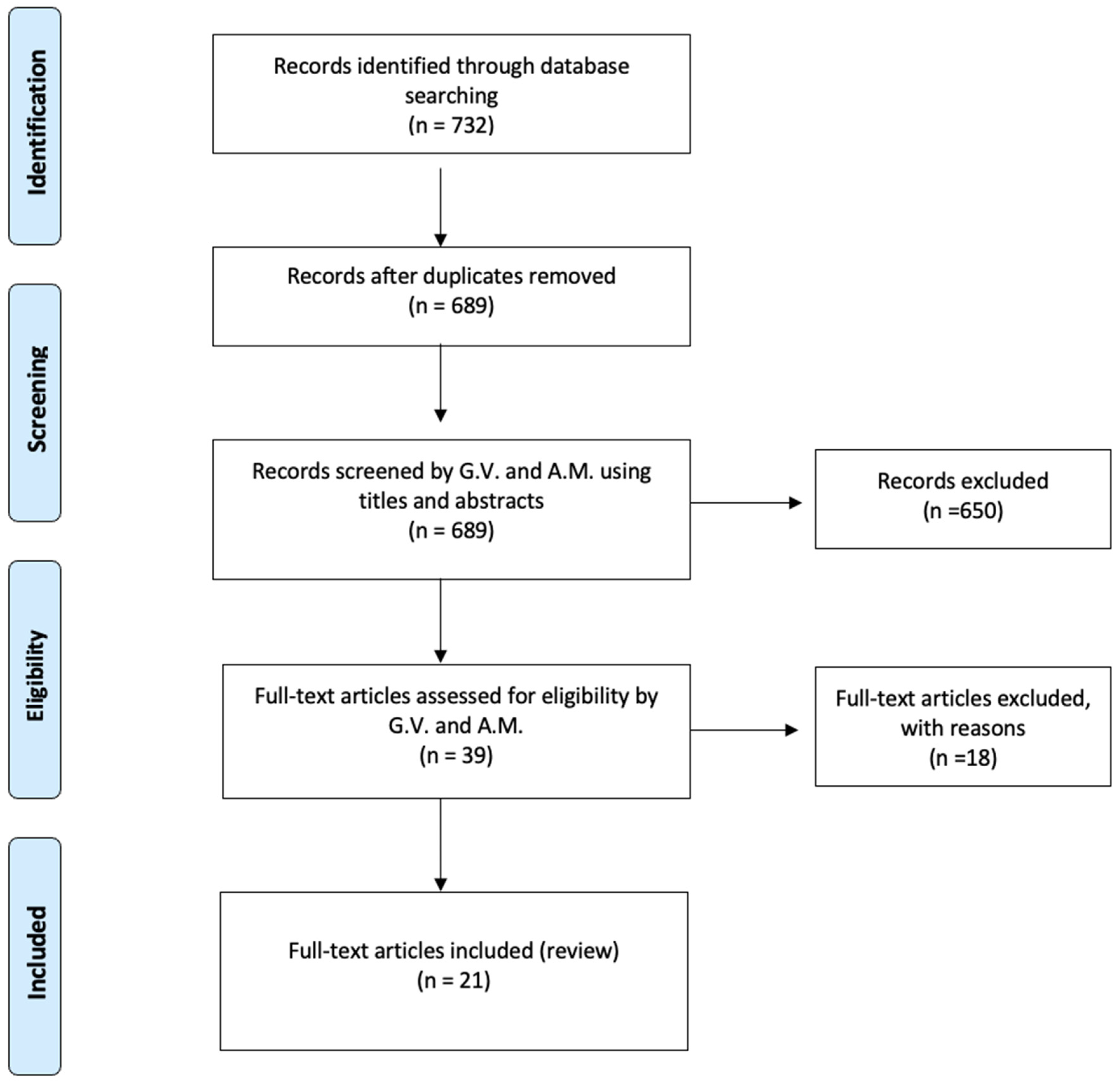
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
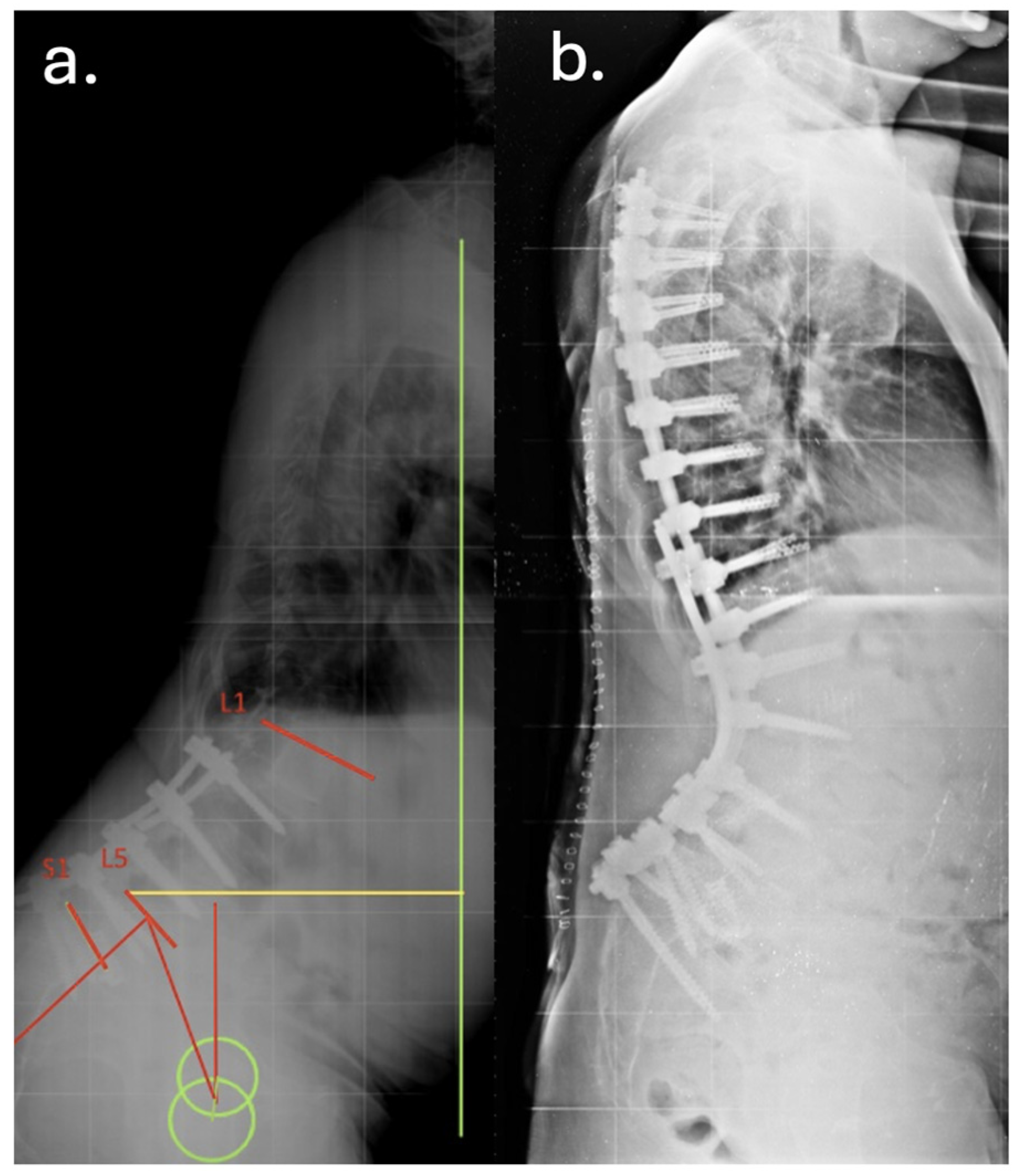
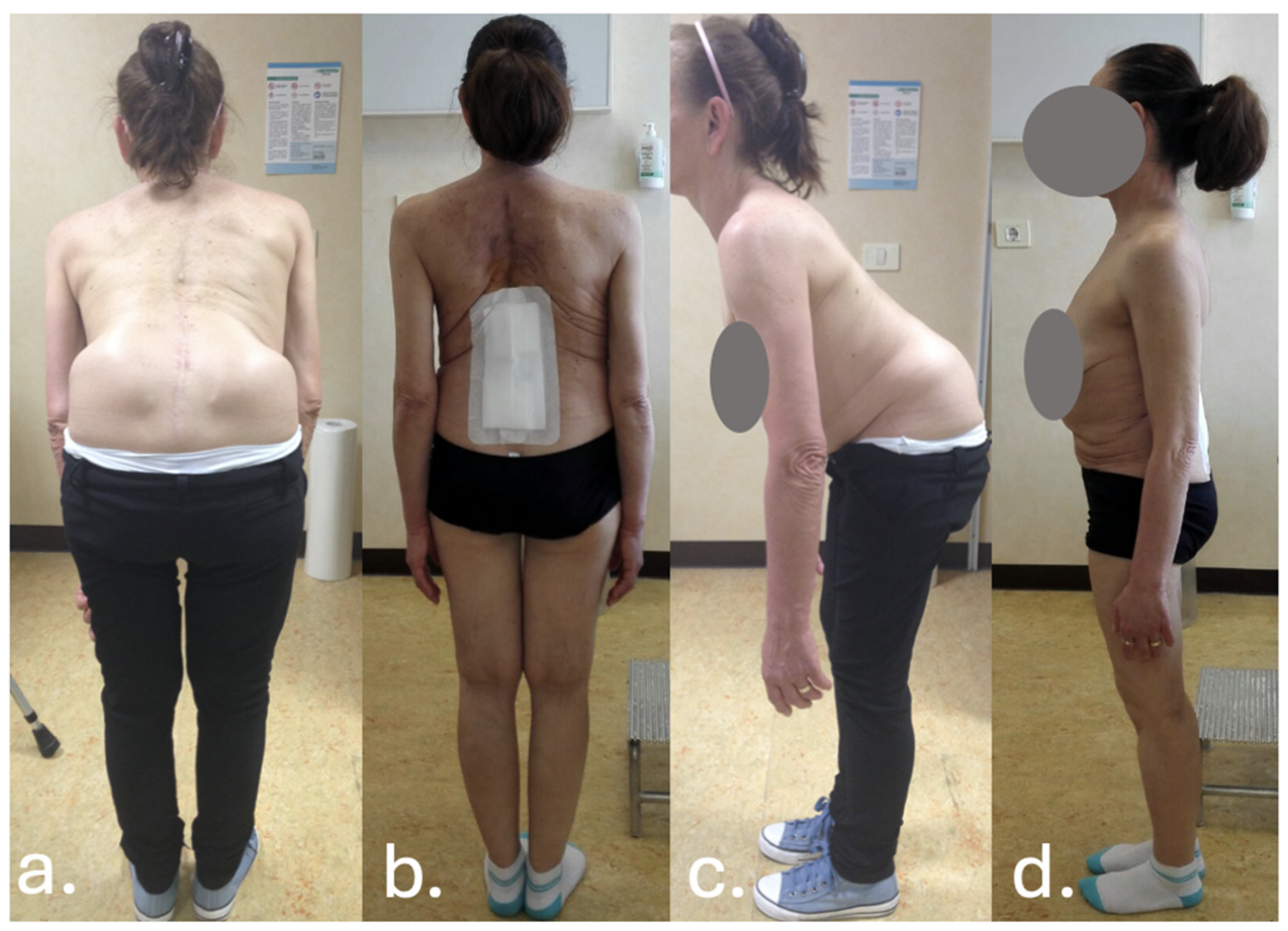
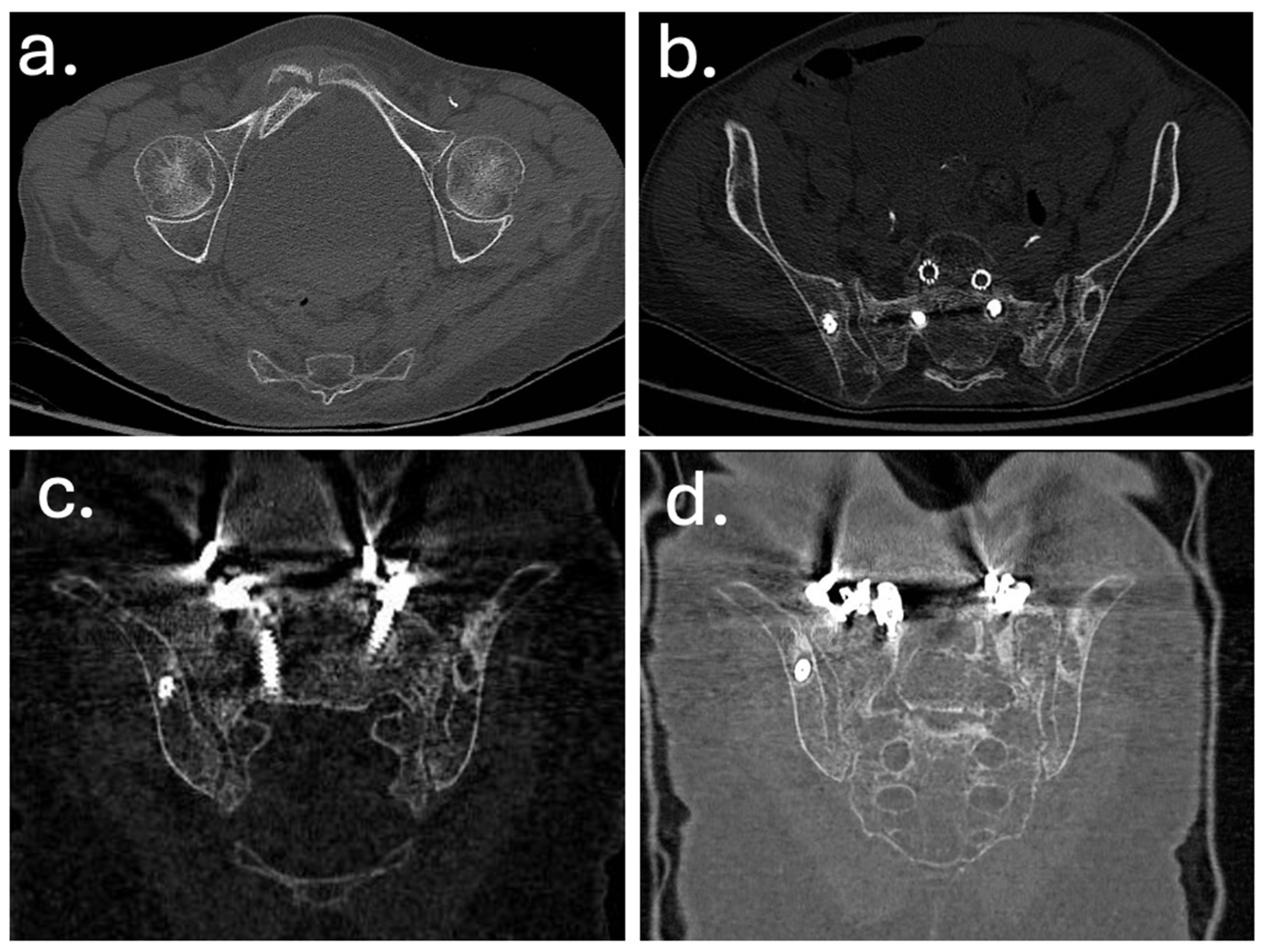
3. Case Report
4. Literature Review
4.1. Demographical Data
4.2. Risk Factors and Pathophysiology
4.3. Diagnostic Workup and Imaging
4.4. Treatment Strategies
4.5. Outcomes
| Author | Year | N° Patients | Sex | Age | Surgical Treatment | Stress Fracture | Timing | Diagnostic Imaging | T Score | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velluto et al. [this paper] | 2025 | 1 | F | 65 | T4-Pelvis | Sacral and Ischiopubic fractures | 1 year after surgery | CT | T < −3.1 | Operative revision surgery: removed iliac screws, flap for exposure of screws and bed rest | Restoration and osteoporosis therapy |
| Ganeshan et al. [9] | 2023 | 1 | F | 73 | T4–S1 ciao | Sacral insufficiency fracture | 1.5 month after surgery | CT | - | Operative. Bilateral percutaneous sacroplasty with spinal cement + bilateral percutaneous ileosacral fixation | Restoration |
| Holderread et al. [6] | 2022 | 7 | 2 (M) and 5 (F) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 non operative/4 operative | - |
| F | 78 | L2–L5 | Bilateral L5 pedicle fractures, L5–S1 fracture with spondylolisthesis, L5–S1 discoligamentous injury | 2 wk | CT/MRI | - | Operative: L5–S1 posterior SF with instrumentation, autogenous BG and allograft bone morcellized | Ambulating with walker, no symptoms after 14 months | |||
| F | 71 | L2–S1 | - | 2 wk | CT | - | Operative: L3 pelvic fusion with S1/S2 Lam | - | |||
| F | 67 | L3–S1 | S1–S2 subluxation with sacral fracture below level of previous fusion | 4 wk | CT/MRI | - | Operative: L3–S1 posterior SF with instrumentation and allograft bone, L5–S1 revision Lam, autogenous BG | Surgical site infection, chronic L2 compression fracture after 4 months | |||
| F | 77 | L4–S1 | S1 sacral insufficiency fracture below hardware | 2 wk | CT/MRI | - | Nonoperative: Lumbar bracing | Restoration after 20 months | |||
| F | 67 | L2–S1 | Sacral fracture with early loosening of inferior pedicle screws | 8 mo | CT/MRI | - | Operative: L4–S1 removal of hardware, L3–L4 revision with discectomy, revision L2–S1 posterolateral SF with instrumentation, application of incisional wound vac | C. albicans T12–L2 discitis/osteomyelitis with epidural abscess 10 mo postoperatively; another revision surgery (T12–L1 Lam, T8–L3 fusion, T12, L1 corpectomy) (1 yr) | |||
| M | 71 | L3–S1 | Transverse sacral ala fracture involving central body and bilateral ala | 3 wk | XR/CT | - | Nonoperative: Bone stimulator, lumbar bracing | Ambulating with walker, no symptoms (9 mo) | |||
| M | 79 | L4–S1 | L5–S1 anterolisthesis | 3 mo | CT | - | Nonoperative: Standard postoperative rehabilitation with observation | Ambulating without assistance (1 yr) | |||
| Buell et al. [4] | 2020 | 9 | 4 (M) and 5 (F) | 73 ± 6 (mean) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M | 80 | L2–S1 PSIF, PCO (L2–S1), TLIF (L5–S1) | S1 peri-screw lucency, superior S1 body Fx w/ventral implant displacement, high-grade L5–S1 anterolisthesis, rt sacral ala Fx | 4 wk | CT | - | Operative. Upsize L5 screws (8.5 mm), remove S1 screws, quad iliac bolts (9.5 mm), 3rd and 4th accessory rods | Healed on CT (8 mo) | |||
| F | 79 | T10–S1 PSIF | H-type sacral Fx, transverse Fx below S1 foramina | 2 wk | CT | Hx of osteoporosis, DEXA hip T-score −2.4, no recent Tx | Operative. Re-instrumentation, quad iliac bolts (9.5 mm), 3rd and 4th accessory rods | Healed on XR (10 mo) | |||
| F | 64 | T3–S1 PSIF, PCO (T11–L4) | H-type sacral Fx, transverse Fx below S1 screws | 5.5 yr | CT | None | Operative. Quad iliac bolts (9.5 mm), 3rd and 4th accessory rods | Healed on XR (1 yr.) | |||
| F | 79 | L2–S1 PSIF, PCO (L3–5) | Transverse sacral Fx involves S1 screws, lt sacral ala Fx | 3 wk | CT | Hx of osteoporosis, no recent DEXA or Tx | Operative. Quad iliac bolts (9.5 mm), Grafton DBF | Healed on XR (1 yr.) | |||
| M | 70 | T10–S1 PSIF, PCO (T12–L2) | Complex T-like sacral Fx, transverse Fx from rt L5–S1 disk space (prior fusion) to lt S1 screw, lt sacral ala Fx extends to lt S2–3 foramen | 1 yr | CT | - | Operative. Extension to T4 (for PJK), quad iliac bolts (9.5 mm) | ||||
| M | 70 | L4–S1 PSIF, TLIF (L4–5, L5–S1) | H-type sacral Fx, transverse Fx below S1 foramina, L5–S1 pseudarthrosis | 3 wk | CT | Osteopenia, DEXA hip T-score −1.3, no recent Tx | Operative. Upsize L4–S1 screws, quad iliac bolts (9.5 mm superiorly, 10.5 mm inferiorly) | S1-Iliac rod Fx requiring revision surgery approximately 2 yrs postop | |||
| M | 66 | L5–S1 PSIF, TLIF (L5–S1) | U-type sacral Fx, transverse Fx below S1 screws, L5–S1 pseudarthrosis | 4 wk | CT | Hx of osteoporosis, DEXA hip T-score −1.0, teriparatide | Operative. Extension to L4, replace L5–S1 screws, L5–S1 cross-link, iliac bolts (9.5 mm) | Early CT, healed on XR (4 yrs) | |||
| F | 76 | L4–S1 PSIF, L5 Gill laminectomy, TLIF (L5–S1) | U-type sacral Fx, transverse Fx involves S1 screws | 3 wk | CT | Osteoporosis, no recent DEXA, calcitonin nasal spray | Operative. Upsize S1 screws, decompress lt L5 nerve root, quad iliac bolts (8.5 mm) | Healed on CT, (7.5 yrs) | |||
| F | 69 | L4–S1 PSIF, TLIF (L4–5, L5–S1) | H-type sacral Fx, transverse Fx involves S1 screws | 3 wk | CT | Steroid-induced osteoporosis, DEXA hip T-score −1.6, wrist T-score −1.5, alendronate | Operative. Upsize S1 screws, quad iliac bolts (8.5 mm, 9.5 mm) | Healed on CT (3.5 yrs) | |||
| Scemama et al. [15] | 2016 | 3 | 3 (F) | 72 (mean) | |||||||
| F | 72 | L3–S1 decompression, posterolateral fusion and instrumentation L2–S1 (bilateral S1 screws only) with one level Smith-Petersen osteotomy without iliac crest bone graft | Transversal S1 fracture with L5–S1 pseudarthrosis | 2 mo | XR/CT | - | Operative two-time revision surgery, firstly posterior revision with bilateral iliac extension, secondly an anterior interbody L4–L5 and L5-S1 fusion using cage + 3 months protection brace | Healed on CT (6 mo) | |||
| F | 77 | Posterior liberation posterolateral fusion and instrumentation extension to S1 (bilateral S1 pedicular screws only) | Sacral proximal plate fracture with S1 screws failure | 2 wk | XR/CT | - | Operative. L5-S1 decompression, bilateral iliac extension of posterolateral fusion and instrumentation | Healed last FU XR (8 mo) | |||
| F | 67 | T12–S1, bilateral iliac extension posterolateral fusion and instrumentation (modular fixation, pedicular S1 and iliac screws | U-Type sacral Fracture, with a proximal implants failure | 2 mo | CT | - | Operative. Revision surgery with proximal extension to T11 and distal posterior extension with 2 iliac implants on the right side and 1 implant on the left side. Bilateral iliac crest graft and artificial bone were used. Additional anterior approach with anterior L1–L2, L2–L3, L3–L4, L4–L5 and L5–S1 cage interbody fusions + additional protection brace for three months | Sacral fracture consolidation on CT, last FU (1 yo p.o.) | |||
| Koh et al. [10] | 2005 | 1 | F | 48 | L4–S1 decompression and fusion; 11 revisions for pseudarthrosis, adjacent level failure, infection, and hardware failure | transverse fracture of the bilateral pelvic wing-sacrum | 7 mo | XR/CT | - | Nonoperative. brace and gradual rehabilitation and pain control | - |
| Asad et al. [23] | 2019 | 1 | M | 73 | L2–S1 | Sacral insufficiency fracture | 2 days | XR/CT | - | Operative S2 sacral alar iliac screws to extend fixation | - |
| Ha et al. [14] | 2021 | 8 | F | 72.13 (mean) | |||||||
| F | 83 | L3–S1, PLF | Bilateral vertical sacral fracture | 17 yr | SPECT/CT | −2.8 | Operative. Bilateral S2AI screw | - | |||
| F | 74 | L3–S1, PLIF | Bilateral vertical sacral fracture | 8 mo | CT | −4 | Operative. Bilateral S2AI screw | - | |||
| F | 75 | L5–S1, PLIF | Unilateral vertical sacral fracture | 10 yr | SPECT/CT | −4.2 | Nonoperative | Resolution 8–16 weeks | |||
| F | 83 | L4–S1, PLIF | Bilateral vertical sacral fracture | 10 yr | SPECT/CT | −2 | Nonoperative | Resolution 8–16 weeks | |||
| F | 53 | L1–S1, PLF | Unilateral vertical sacral fracture | 3.5 yr | SPECT/CT | −3.2 | Nonoperative. | Resolution 8–16 weeks | |||
| F | 54 | L1–S1, PLIF | Unilateral vertical sacral fracture | 6 yr | Bone scan/CT/MRI | −2.7 | Nonoperative. | Resolution 8–16 weeks | |||
| F | 76 | L2–S1, OLIF/PLF | Horizontal sacral fracture | 1 mo | CT/MRI | −2.7 | Operative. Bilateral S2AI screw | - | |||
| F | 79 | T7–S1, PLF | Unilateral vertical sacral fracture | 12 yr | SPECT/CT | −2.3 | Operative. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy at L4 with S2AI fixation for ipsilateral SIF | - | |||
| Kolz et al. [13] | 2020 | 6 | 4 M and 2 F | 59.83 (mean) | |||||||
| M | 60 | L5–S1, 2-stage anterior–posterior fusion | fracture of the superior sacral endplate + subsidence of his anterior cage | 3 wks | CT | −1.6 | Operative, Bed rest for 3 weeks, then revision L4 to pelvic fusion with bilateral iliac screws | Healed at 6 months | |||
| M | 76 | L5–S1, 2-stage ALIF and PSF | S1 insufficiency fracture | 4 wks | CT | −2.2 | Operative. L4 to pelvis revision fusion | Healed at 6 months | |||
| M | 66 | L5–S1, 2-stage ALIF and PSF | S1 insufficiency fracture with cage subsidence and screw loosening | 3 mo | CT | - | Operative. Initial management included rest, transforaminal epidural steroid injection but did not control pain. L4-pelvis decompression and L4–L5 transforaminal lumbar fusion with instrumentation (TLIF) and iliac screws | Healed at 1 year | |||
| F | 73 | L5–S1, ALIF | S1 insufficiency fracture | 17 days | CT | −1.5 | Operative. L5–S2 sacral alar-iliac fusion | Healed at 2 years | |||
| M | 53 | L5–S1, ALIF | S1 insufficiency fracture | 1 mo | CT | - | Operative. L5–S2 sacral alar-iliac fusion | ||||
| F | 31 | L5–S1, LAIF | S1 insufficiency fracture | 3 mo | CT | - | Previous 3 months conservative then degeneration of the superior adjacent level with L5–S1 pseudarthrosis and subsidence of the ALIF cage. Operative. 2-stage L4–S1 anterior spinal fusion with instrumentation and posterior spinal fusion | ||||
| Mathews et al. [17] | 2001 | 3 | F | 71.33 (mean) | |||||||
| F | 74 | L3–S1 decompression, pedicle screw fixation, and fusion with right-sided iliac crest bone graft | fracture of the sacrum with additional fractures of the right superior and inferior pubic rami | 2 wks | XR | - | Nonoperative. Physical therapy (gradual), pain control | Healed on XR (8 mo) | |||
| F | 70 | L1–S1 decompression, pedicle screw instrumentation, and fusion with right-sided iliac crest bone graft | displaced transverse sacral insufficiency fracture | 1 mo | XR | - | Nonoperative. Bedrest followed by mobilization (gradual) | Radiographs at 8 months revealed scarla fracture healing but in a forward displaced position | |||
| F | 70 | Superior pubic ramus fracture and a right iliac fracture | 2 wks | XR | - | Nonoperative. | Healed 2 yr. | ||||
| Khan et al. [21] | 2005 | 3 | F | 64.33 (mean) | |||||||
| F | 57 | L4–L5 laminectomy with bilateral foraminotomies, with L4 S1 posterior spinal fusion with instrumentation and left-sided iliac crest bone graft | Junctional S2 stress fracture | 2 mo | XR | - | Nonoperative Continue functional exercise with observation | Healed on XR (1 yr.) | |||
| F | 79 | L3–L5 laminectomy with bilateral foraminotomies as well as L3–S1 posterior spinal fusion with instrumentation and left-sided iliac crest bone graft were performed | Junctional sacral fracture just below the S1 screws | 6 wks | XR | - | Nonoperative. Instructed on level of activity, given donut pillow for sitting | Healed 14 mo | |||
| F | 57 | Lumbar laminectomy with instrumented fusion from L4 to sacrum, with right posterior iliac crest bone graft | Left parasymphyseal stress fracture + sacral stress fracture below the S1 pedicle screw | 6 wks | - | - | Nonoperative. Pain management and observation and water therapy | Healed 22 mo | |||
| Fourney et al. [11] | 2002 | 1 | F | 61 | L5 laminectomy with bilateral L5–S1 facetectomies and foraminotomies; L5–S1 pedicle screw fixation with reduction in spondylolisthesis; L5–S1 discectomy + PLIF with allograft; posterolateral fusion with allograft and autograft | sacral insufficiency fracture with anterolisthesis of S1 on S2 | 4 wks | XR/CT | - | Nonoperative Thoracolumbosacral orthosis for 3 months | Healed on XR (9 mo) |
| Vavken et al. [20] | 2008 | 4 | |||||||||
| F | 77 | T12–S1 | S2 fracture | 5 wks | CT | Operative: Extension of the arthrodesis to S2 with iliac screws | Resolution | ||||
| F | 65 | L2–S1 | S1 fracture | 4 mo | CT | severe osteoporosis | Nonoperative | Resolution | |||
| F | 79 | T10–S1 | S1 fracture | Immediate post-op | CT | Nonoperative | Resolution | ||||
| M | 78 | T11–S1 | S1 fracture | 5 wks | CT | Nonoperative | Resolution | ||||
| Wang et al. [22] | 2016 | 1 | F | 65 | L4–S1 | Horizontal sacral fracture at the S1/S2 level with complete displacement of S2 and associated neurological deficits | 5 yrs | CT | −3.7 | Operative: Decompression and extension of arthrodesis with iliac screw fixation | Resolution |
| Noh et al. [18] | 2016 | 1 | 1 F | 64 | L4–S1 | Sacral stress fracture | 5 yrs | CT | - | Operative | Resolution |
| Papadopoulos et al. [12] | 2008 | 5 | 4 F, 1 M | 67.4 | Thoraco-lumbar fusion | 5 Sacral stress fracture | 4–6 mo | CT | - | Operative: iliac screws and ALIF | Resolution |
| Bose et al. [19] | 2003 | 1 | F | 41 | Decompression and fusion L4–S1 | S1–S2 fractures | 7 mo | CT | - | Non Operative: bed rest for 3 months | Resolution |
| Pennekamp et al. [8] | 2005 | 1 | F | 57 | L4–S1 fusion | Sacral stress fracture | 9 days | XR and CT | - | Nonoperative | Resolution |
| Elias et al. [16] | 2002 | 1 | F | 53 | L4–S1 fusion | Sacral stress fracture | 4 mo | MRI and CT | - | Nonoperative | Resolution |
| Klineberg et al. [2] | 2008 | 9 | F | 64 (mean) | Arthrodesis from 1 to 8 segments | Two sacral insufficiency fractures in short fusions (1.3%). Four sacral insufficiency fractures (3.1%) in long fusions. Three fractures referred from other centers | 5 wks | CT | - | Two operative cases: patients initially treated surgically. Seven non-operative cases: managed conservatively with bracing and analgesic therapy, four of whom discontinued treatment and subsequently underwent surgery. Surgical treatment consisted of decompression and L4–L5 laminectomy, L4–L5 arthrodesis with pedicle screws and two iliac screws per side (sacral screws placed at the surgeon’s discretion) | Resolution |
5. Discussion
5.1. Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Challenges
5.2. Management Strategies
5.3. Clinical Implications
5.4. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meredith, D.S.; Taher, F.; Cammisa, F.P., Jr.; Girardi, F.P. Incidence, diagnosis, and management of sacral fractures following multilevel spinal arthrodesis. Spine J. 2013, 13, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klineberg, E.; McHenry, T.; Bellabarba, C.; Wagner, T.; Chapman, J. Sacral insufficiency fractures caudal to instrumented posterior lumbosacral arthrodesis. Spine 2008, 33, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.P.; Mascarenhas, L.D.; Holderread, B.M.; Awad, M.; Botros, D.; Avramis, I.; Syed, I.; Rizkalla, J.M. Treatment for sacral insufficiency fractures: A systematic review. J. Orthop. 2022, 34, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Buell, T.J.; Yener, U.; Wang, T.R.; Buchholz, A.L.; Yen, C.P.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Smith, J.S. Sacral insufficiency fractures after lumbosacral arthrodesis: Salvage lumbopelvic fixation and a proposed management algorithm. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2020, 33, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoder, K.; Bartsokas, J.; Averell, K.; McBride, E.; Long, C.; Cook, C. Risk factors associated with sacral stress fractures: A systematic review. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2015, 23, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Holderread, B.M.; Shin, C.P.; Syed, I.Y.; Avramis, I.; Rizkalla, J.M. Sacral insufficiency fracture after lumbosacral decompression and fusion. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2022, 35, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yasuda, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamato, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Togawa, D.; Banno, T.; Arima, H.; Oe, S.; Matsuyama, Y. Lumbosacral Junctional Failures After Long Spinal Fusion for Adult Spinal Deformity-Which Vertebra Is the Preferred Distal Instrumented Vertebra? Spine Deform. 2016, 4, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennekamp, P.; Kraft, C.; Stütz, A.; Diedrich, O. Sakrumfraktur als seltene Frühkomplikation nach lumbosakraler Spondylodese. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 2005, 143, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, V.; Denis, D. A Case of U-shaped Sacral Fracture After Longstanding Spinopelvic Fixation Treated With Percutaneous Sacroiliac Joint Fusion and Iliosacral Osteosynthesis. Cureus 2023, 15, e47152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koh, Y.-D.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, J.J. Stress Fracture of the Pelvic Wing-Sacrum After Long-Level Lumbosacral Fusion: A Case Report. Spine 2005, 30, E161–E163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourney, D.R.; Prabhu, S.S.; Cohen, Z.R.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Rhines, L.D. Early sacral stress fracture after reduction of spondylolisthesis and lumbosacral fixation: Case report. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, E.C.; Cammisa, F.P., Jr.; Girardi, F.P. Sacral Fractures Complicating Thoracolumbar Fusion to the Sacrum. Spine 2008, 33, E699–E707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolz, J.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Elder, B.D.; Sebastian, A.S.; Huddleston, P.M.; Freedman, B.A. Sacral Insufficiency Fracture Following Short-Segment Lumbosacral Fusion: Case Series and Review of the Literature. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, H.-Y.; Chang, D.-G.; Cho, C.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Cho, R.-K.; Kim, S.-I. Sacral insufficiency fracture after instrumented lumbosacral fusion: Focusing pelvic deformation—A retrospective case series. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 83, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scemama, C.; D’astorg, H.; Guigui, P. Sacral stress fracture after lumbar and lumbosacral fusion. How to manage it? A proposition based on three cases and literature review. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2016, 102, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, W.J.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Whitehill, R. Sacral stress fracture following lumbosacral arthrodesis: Case illustration. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2002, 96, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, V.; McCance, S.E.; O’Leary, P.F. Early Fracture of the Sacrum or Pelvis: An Unusual Complication After Multilevel Instrumented Lumbosacral Fusion. Spine 2001, 26, E571–E575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, T.; Chedid, M.K. A novel technique to repair a transverse sacral fracture in a previously fused lumbosacral spondylolisthesis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7 (Suppl. 38), S914–S916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, B. Fracture of S1–S2 after L4—S1 decompression and fusion: Case report and review of the literature. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2003, 99, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavken, P.; Krepler, P. Sacral fractures after multi-segmental lumbosacral fusion: A series of four cases and systematic review of literature. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17 (Suppl. 2), 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, M.H.; Smith, P.N.; Kang, J.D. Sacral Insufficiency Fractures Following Multilevel Instrumented Spinal Fusion: Case Report. Spine 2005, 30, E484–E488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, C.D.; Yi, X.D.; Yu, Z.R. Surgical treatment of sacral fractures following lumbosacral arthrodesis: Case report and literature review. World J. Orthop. 2016, 7, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asad, A.; Junaid, J.; Hashmi, I. Sacral insufficiency fracture, a rare complication of posterior spinal instrumentation. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1380–1382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| Dec 2010 | Posterior decompression and L5–S1 fusion |
| Apr 2012 | Posterior extension of fusion to L3 for junctional failure |
| Nov 2014 | Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) at L3–L4 and L4–L5 |
| Jun 2016 | Major revision from T7 to pelvis with bilateral iliac fixation |
| Aug 2016 | Postoperative infection (Acinetobacter baumannii XDR), multiple antibiotic courses |
| Dec 2019 | Removal of left iliac and T4–T5 screws, new fixation at T2–T3 with 4-rod construct |
| Jan 2020 | Rotational musculocutaneous flap for soft tissue coverage |
| Feb 2022 | Diagnosis of sacral insufficiency fracture (CT: left sacral ala right ilio-pubic branch fracture, with loosening of iliac screws) |
| Sep 2022 | Surgical debridement, rod shortening, V-Y fasciocutaneous flap |
| Mar 2025 | Removal of fractured proximal thoracic screws; cultures positive for Staphylococcus epidermidis and Ralstonia pickettii |
| May 2025 | Stable condition on suppressive antibiotics; no further revision indicated |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velluto, C.; Marciano, A.; Vavalle, G.; Borruto, M.I.; Perna, A.; Scaramuzzo, L.; Proietti, L. Sacral and Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217572
Velluto C, Marciano A, Vavalle G, Borruto MI, Perna A, Scaramuzzo L, Proietti L. Sacral and Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217572
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelluto, Calogero, Achille Marciano, Gianmarco Vavalle, Maria Ilaria Borruto, Andrea Perna, Laura Scaramuzzo, and Luca Proietti. 2025. "Sacral and Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217572
APA StyleVelluto, C., Marciano, A., Vavalle, G., Borruto, M. I., Perna, A., Scaramuzzo, L., & Proietti, L. (2025). Sacral and Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217572







