Early Autonomic Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Article Review on the Impact on Multiple Organ Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategies
2.1. Results
2.2. The Epidemiology and Definition of Early Autonomic Dysfunction in TBI
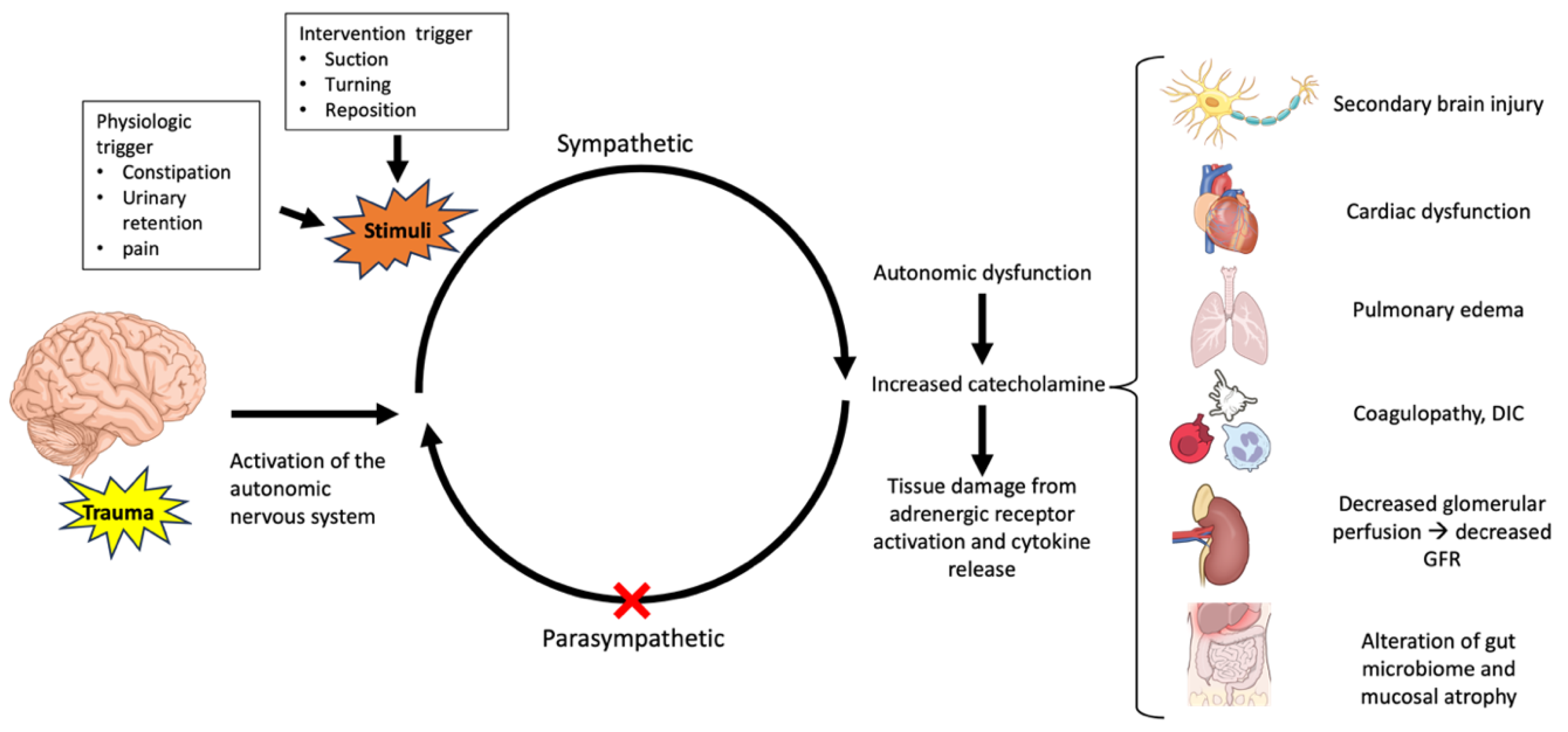
2.3. Pathophysiology
2.4. Diagnostic Criteria
2.5. Clinical Settings
2.6. The Impact of Autonomic Dysfunction on Organ Dysfunction
- -
- The cardiovascular system
- -
- The respiratory system
- -
- Renal function
- -
- Gastrointestinal function
- -
- The coagulation system
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Georges, A.; Das, J.M. Traumatic Brain Injury; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alexis, B.; Peterson, L.X.; Daugherty, J.; Breiding, M.J. Surveillance Report of Traumatic Brain Injury-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths—United States, 2014; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 56–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, C.; Miller, G.F.; Barnett, S.B.L.; Florence, C. Economic Cost of Injury—United States, 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Daneshvar, D.H. The neuropathology of traumatic brain injury. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 127, pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Temkin, N.; Barber, J.; Foreman, B.; Komisarow, J.; Korley, F.K.; Laskowitz, D.T.M.; Mathew, J.P.M.; Hernandez, A.M.; Sampson, J.M.; et al. Association of Early Multiple Organ Dysfunction With Clinical and Functional Outcomes Over the Year Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Transforming Research and Clinical Knowledge in Traumatic Brain Injury Study. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Komisarow, J.M.; Laskowitz, D.T.; Vavilala, M.S. Multiorgan Dysfunction After Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Clinical Management. Chest 2021, 160, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygun, D.A.; Kortbeek, J.B.; Fick, G.H.; Laupland, K.B.; Doig, C.J. Non-neurologic organ dysfunction in severe traumatic brain injury. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Liu, X.; Donnelly, J.; Nasr, N.; Diedler, J.; Okoroafor, F.; Hutchinson, P.; Menon, D.; Smielewski, P. Autonomic Impairment in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multimodal Neuromonitoring Study. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, V.; Giannakou, M.; Maglaveras, N.; Sofianos, E.; Giala, M. Investigation of heart rate and blood pressure variability, baroreflex sensitivity, and approximate entropy in acute brain injury patients. J. Crit. Care 2008, 23, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, I.J.; Slewa-Younan, S.; Heriseanu, R.E.; Nott, M.T.; Mudaliar, Y.; Nayyar, V. The incidence of dysautonomia and its relationship with autonomic arousal following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2007, 21, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ortega, J.F.; Prieto-Palomino, M.A.; Garcia-Caballero, M.; Galeas-Lopez, J.L.; Quesada-Garcia, G.; Baguley, I.J. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity after traumatic brain injury: Clinical and prognostic implications. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinstein, A.A. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity in the neurological intensive care unit. Neurol. Res. 2007, 29, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilz, M.J.; Wang, R.; Markus, J.; Ammon, F.; Hosl, K.M.; Flanagan, S.R.; Winder, K.; Koehn, J. Severity of traumatic brain injury correlates with long-term cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyfroidt, G.; Baguley, I.J.; Menon, D.K. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity: The storm after acute brain injury. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, M.M.; Patterson, D.R.; Questad, K.A.; Cardenas, D.; Farrel-Roberts, L. The treatment of agitation during initial hospitalization after traumatic brain injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1992, 73, 917–921. [Google Scholar]
- Baguley, I.J.; Heriseanu, R.E.; Cameron, I.D.; Nott, M.T.; Slewa-Younan, S. A critical review of the pathophysiology of dysautonomia following traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit. Care 2008, 8, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, I.J.; Perkes, I.E.; Fernandez-Ortega, J.F.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Dolce, G.; Hendricks, H.T. For the Consensus Working Group. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity after acquired brain injury: Consensus on conceptual definition, nomenclature, and diagnostic criteria. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertab, J.L.; Merkley, T.L.; Cramond, A.J.; Cramond, K.; Paxton, H.; Wu, T. Concussion and the autonomic nervous system: An introduction to the field and the results of a systematic review. NeuroRehabilitation 2018, 42, 397–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeve, B.F.; Wijdicks, E.F.; Benarroch, E.E.; Schmidt, K.D. Paroxysmal sympathetic storms (“diencephalic seizures”) after severe diffuse axonal head injury. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1998, 73, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorry, L.K. Physiology of the autonomic nervous system. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2007, 71, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.-Z.; Lei, Z.-Q.; Yang, R.-Z.; Huang, G.-H.; Zhang, G.-M. Identification and management of paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity after traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J. Physiology and immunology of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Mohapatra, S.; Mohapatra, S.S. New perspectives on central and peripheral immune responses to acute traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Venkat, P.; Seyfried, D.; Chopp, M.; Yan, T.; Chen, J. Brain-Heart Interaction: Cardiac Complications After Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, J.A.; Patrick, P.D.; Buck, M.L.; Rust, R.S., Jr. Paroxysmal autonomic instability with dystonia after brain injury. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ortega, J.F.; Baguley, I.J.; Gates, T.A.; Garcia-Caballero, M.; Quesada-Garcia, J.G.; Prieto-Palomino, M.A. Catecholamines and Paroxysmal Sympathetic Hyperactivity after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koiv, L.; Merisalu, E.; Zilmer, K.; Tomberg, T.; Kaasik, A.E. Changes of sympatho-adrenal and hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical system in patients with head injury. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1997, 96, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizoli, S.B.; Jaja, B.N.; Di Battista, A.P.; Rhind, S.G.; Neto, A.C.; da Costa, L.; Inaba, K.; da Luz, L.T.; Nascimento, B.; Perez, A.; et al. Catecholamines as outcome markers in isolated traumatic brain injury: The COMA-TBI study. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.J.; Deepika, A.; Shukla, D.; Devi, B.I.; Ramesh, V.J. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity in severe traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir. 2016, 158, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkes, I.; Baguley, I.J.; Nott, M.T.; Menon, D.K. A review of paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity after acquired brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaji, J.P.; Curnier, D.; Moore, R.D.; Ellemberg, D. Persisting Effects of Concussion on Heart Rate Variability during Physical Exertion. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 33, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, V.E.; Maglaveras, N.; Houvarda, I.; Antoniadou, E.; Vretzakis, G. Investigation of altered heart rate variability, nonlinear properties of heart rate signals, and organ dysfunction longitudinally over time in intensive care unit patients. J. Crit. Care 2006, 21, 95–103; discussion 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, H.M.; Fisher, A.; Rushby, J.A.; McDonald, S. Reduced heart rate variability in chronic severe traumatic brain injury: Association with impaired emotional and social functioning, and potential for treatment using biofeedback. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2016, 26, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Perdomo, W.A.; Garcia-Ballestas, E.; Moscote-Salazar, L.R.; Konar, S.K.; Raj, S.; Chouksey, P.; Shrivastava, A.; Mishra, R.; Agrawal, A. Heart Rate Variability as a Predictor of Mortality in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riordan, W.P., Jr.; Norris, P.R.; Jenkins, J.M.; Morris, J.A., Jr. Early loss of heart rate complexity predicts mortality regardless of mechanism, anatomic location, or severity of injury in 2178 trauma patients. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 156, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, R.L.; Conder, A.A. Heart rate variability interventions for concussion and rehabilitation. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fountaine, M.F.; Toda, M.; Testa, A.J.; Hill-Lombardi, V. Autonomic Nervous System Responses to Concussion: Arterial Pulse Contour Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uryga, A.; Kasprowicz, M.; Burzynska, M.; Kazimierska, A.; Czosnyka, M.; Nasr, N. Association between temporal patterns of baroreflex sensitivity after traumatic brain injury and prognosis: A preliminary study. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, I.J.; Nott, M.T.; Slewa-Younan, S.; Heriseanu, R.E.; Perkes, I.E. Diagnosing dysautonomia after acute traumatic brain injury: Evidence for overresponsiveness to afferent stimuli. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Scott, W.A.; Sommerauer, J.F.; Luckett, P.M. Heart rate variability after acute traumatic brain injury in children. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 3907–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhoseini, M.F.; Hosay, M.A.; McPherson, M.; Patel, M.B. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity: Diagnostic criteria, complications, and treatment after traumatic brain injury. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2018, 6, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tanti, A.; Gasperini, G.; Rossini, M. Paroxysmal episodic hypothalamic instability with hypothermia after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2005, 19, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.M.; Vichayanrat, E.; Del Giovane, M.; Lai, H.H.L.; Iodice, V. Autonomic dysfunction after moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury: Symptom spectrum and clinical testing outcomes. BMJ Neurol. Open 2022, 4, e000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, C.; Hinson, H.E.; Baguley, I.J. Autonomic dysfunction syndromes after acute brain injury. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 128, pp. 539–551. [Google Scholar]
- Zaroff, J.G.; Rordorf, G.A.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Picard, M.H. Regional patterns of left ventricular systolic dysfunction after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Evidence for neurally mediated cardiac injury. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2000, 13, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bree, M.D.; Roos, Y.B.; van der Bilt, I.A.; Wilde, A.A.; Sprengers, M.E.; de Gans, K.; Vergouwen, M.D. Prevalence and characterization of ECG abnormalities after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2010, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, M.A. Neurogenic heart disease: A unifying hypothesis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 60, J15–J19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathep, S.; Sharma, D.; Hallman, M.; Joffe, A.; Krishnamoorthy, V.; Mackensen, G.B.; Vavilala, M.S. Preliminary report on cardiac dysfunction after isolated traumatic brain injury. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Rowhani-Rahbar, A.; Gibbons, E.F.; Rivara, F.P.; Temkin, N.R.; Pontius, C.; Luk, K.; Graves, M.B.; Lozier, D.B.; Chaikittisilpa, N.; et al. Early Systolic Dysfunction Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Cohort Study. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanin, A.; Kamal, A.; Amin, S.; Zakaria, D.; El Sayed, R.; Mahmoud, K.; Mukhtar, A. Incidence and outcome of cardiac injury in patients with severe head trauma. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2016, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, A.M.; Ahmadi, K.; Taherinia, A.; Sharifi, M.D.; Ramezani, J.; Jazayeri, S.B.; Saadat, S.; Rahimi-Movaghar, V. ECG changes of cardiac origin in elderly patients with traumatic brain injury. Med. J. Islam Repub. Iran 2015, 29, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Prathep, S.; Sharma, D.; Gibbons, E.; Vavilala, M.S. Association between electrocardiographic findings and cardiac dysfunction in adult isolated traumatic brain injury. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 18, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata, C.; Kasal, J. Cardiac Dysfunction in Adult Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Med. Res. 2018, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, R.; Jayant, A.; Mahajan, S.; Jangra, K.; Panda, N.B.; Grover, V.K.; Tewari, M.K.; Bhagat, H. Perioperative cardiovascular changes in patients with traumatic brain injury: A prospective observational study. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincon, F.; Ghosh, S.; Dey, S.; Maltenfort, M.; Vibbert, M.; Urtecho, J.; McBride, W.; Moussouttas, M.; Bell, R.; Ratliff, J.K.; et al. Impact of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome after traumatic brain injury in the United States. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratton, S.L.; Davis, R.L. Acute lung injury in isolated traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhard, L.W.; Morabito, D.J.; Matthay, M.A.; Mackersie, R.C.; Campbell, A.R.; Marks, J.D.; Alonso, J.A.; Pittet, J.-F. Initial severity of metabolic acidosis predicts the development of acute lung injury in severely traumatized patients. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.S.; Valadka, A.B.; Hannay, H.J.; Contant, C.F.; Gopinath, S.P.; Cormio, M.; Uzura, M.; Grossman, R.G. Prevention of secondary ischemic insults after severe head injury. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, D.L.; Terek, M.; Chawla, L.S. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, C.; Keller, M.; Pangalu, A.; Fortunati, M.; Yonekawa, Y.; Keller, E. Neurogenic pulmonary edema in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2008, 20, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, F.B.; Shackford, S.R.; Trevisani, G.T.; Davis, J.W.; Mackersie, R.C.; Hoyt, D.B. Neurogenic pulmonary edema in fatal and nonfatal head injuries. J. Trauma 1995, 39, 860–866; discussion 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.A.; Pichelmann, M.A.; Piepgras, D.G.; McIver, J.I.; Toussaint, L.G., 3rd; McClelland, R.L.; Nichols, D.A.; Meyer, F.B.; Atkinson, J.L.; Wijdicks, E.F. Pulmonary complications of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 1025–1031; discussion 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Solenski, N.J.; Haley, E.C., Jr.; Kassell, N.F.; Kongable, G.; Germanson, T.; Truskowski, L.; Torner, J.C. Medical complications of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A report of the multicenter, cooperative aneurysm study. Participants of the Multicenter Cooperative Aneurysm Study. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 23, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J. Neurological Perspectives of Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema. Eur. Neurol. 2019, 81, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busl, K.M.; Bleck, T.P. Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, R.B.; Aguiar, P.H.; Zanetti, M.V.; Andrade, F.; Mandel, M.; Teixeira, M.J. Acute neurogenic pulmonary edema: Case reports and literature review. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2003, 15, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K. Radiographical investigations of organic lesions of the hypothalamus in patients suffering from neurogenic pulmonary edema due to serious intracranial diseases: Relationship between radiographical findings and outcome of patients suffering from neurogenic pulmonary edema. No Shinkei Geka 2003, 31, 757–765. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, Y.K.; Chugh, A.; Kacker, V.; Mehta, V.S.; Tandon, P.N. Development of neurogenic pulmonary edema at different grades of intracranial pressure in cats. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1998, 42, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Theodore, J.; Robin, E.D. Pathogenesis of neurogenic pulmonary oedema. Lancet 1975, 2, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.B. Mechanisms of neurogenic pulmonary edema. Circ. Res. 1985, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avlonitis, V.S.; Wigfield, C.H.; Kirby, J.A.; Dark, J.H. The hemodynamic mechanisms of lung injury and systemic inflammatory response following brain death in the transplant donor. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5 Pt 1, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Thakkar, M.B. Pulmonary venous sphincter constriction is attenuated by alpha-adrenergic antagonism. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, D.L.; Chawla, L.S.; Selassie, L.; Tevar, R.; Junker, C.; Seneff, M.G. Neurogenic pulmonary edema: Successful treatment with IV phentolamine. Chest 2012, 141, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Zhang, T.; Jin, J.; Zeng, X.; Yue, Z. Stellate ganglion block may prevent the development of neurogenic pulmonary edema and improve the outcome. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 80, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhao, W.G.; Zhang, W.F. Acute kidney injury in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: Implementation of the acute kidney injury network stage system. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.M.; Bellomo, R.; Nichol, A.; Harley, N.; Macisaac, C.; Cooper, D.J. The incidence of acute kidney injury in patients with traumatic brain injury. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; He, M.; Xu, J. Incidence and Burden of Acute Kidney Injury among Traumatic Brain-Injury Patients. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 4571–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Banzato, E.; Rebora, P.; Iaquaniello, C.; Huang, C.Y.; Wiegers, E.J.A.; Meyfroidt, G.; Citerio, G. Acute Kidney Injury in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: Results From the Collaborative European NeuroTrauma Effectiveness Research in Traumatic Brain Injury Study. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongnuch, A.; Panorchan, K.; Davenport, A. Brain-kidney crosstalk. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; You, H.; Chen, B.; Xu, Z.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, Y.; Lin, S.; et al. Mannitol is an independent risk factor of acute kidney injury after cerebral trauma: A case-control study. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, L.E.; Morgan, A.S.; Bernstein, B.A. Factors affecting oral feeding with severe traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 1999, 14, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terre, R.; Mearin, F. Prospective evaluation of oro-pharyngeal dysphagia after severe traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2007, 21, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alain-Pascal, B.B.; Wei, H.J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.N. Evaluation of stress hormones in traumatic brain injury patients with gastrointestinal bleeding. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2010, 13, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.H.; ChangLai, S.P.; Chieng, P.U.; Yen, T.C. Gastric emptying in head-injured patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, L.; Young, B.; Phillips, R.; McClain, C.; Adams, L.; Dempsey, R.; Tibbs, P.; Ryo, U.Y. Altered gastric emptying in the head-injured patient: Relationship to feeding intolerance. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 74, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.B.; Hetz, R.A.; Xue, H.; Aroom, K.R.; Bhattarai, D.; Johnson, E.; Bedi, S.; Cox, C.S.; Uray, K. Effects of traumatic brain injury on intestinal contractility. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 593-e463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, J.M.; Ledgerwood, A.M.; Lucas, C.E.; Lucas, W.F. Lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction precludes safe gastric feeding after head injury. J. Trauma 1994, 37, 581–584; discussion 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmayer, T.; O’Dell, M.W.; Jones, M.; Martin, V.; Hawkins, H.H. Cisapride as a treatment for gastroparesis in traumatic brain injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1996, 77, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, A.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, P.; Tu, M.; Wang, H.; Wen, L.; Yang, X. Traumatic Brain Injury Induces Gastrointestinal Dysfunction and Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota Accompanied by Alterations of Bile Acid Profile. J. Neurotrauma 2022, 39, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.A.; Adams, L.M.; Weaver, J.L. The Brain–Gut Axis in Traumatic Brain Injury: Implications for Nutrition Support. Curr. Surg. Rep. 2022, 10, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, J.E.; Blennerhassett, P.; Kumar-Ondiveeran, H.; Verdu, E.F.; Collins, S.M. The vagus nerve: A tonic inhibitory influence associated with inflammatory bowel disease in a murine model. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Kui, G.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y. Neuroprotective effects of vagus nerve stimulation on traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, V.; Ryu, S.Y.; Lopez, N.; Allexan, S.; Krzyzaniak, M.; Eliceiri, B.; Baird, A.; Coimbra, R. Vagal stimulation modulates inflammation through a ghrelin mediated mechanism in traumatic brain injury. Inflammation 2012, 35, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faries, P.L.; Simon, R.J.; Martella, A.T.; Lee, M.J.; Machiedo, G.W. Intestinal permeability correlates with severity of injury in trauma patients. J. Trauma 1998, 44, 1031–1035; discussion 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, V.; Costantini, T.; Kroll, L.; Peterson, C.; Loomis, W.; Eliceiri, B.; Baird, A.; Wolf, P.; Coimbra, R. Traumatic brain injury and intestinal dysfunction: Uncovering the neuro-enteric axis. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.S.; Grandhi, R.; Patterson, T.T.; Nicholson, S.E. A Review of Traumatic Brain Injury and the Gut Microbiome: Insights into Novel Mechanisms of Secondary Brain Injury and Promising Targets for Neuroprotection. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maegele, M. Coagulopathy after traumatic brain injury: Incidence, pathogenesis, and treatment options. Transfusion 2013, 53 (Suppl. S1), 28S–37S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, R.; Liu, L.; Watkins, T.; Zhang, F.; Dong, J.F. Traumatic brain injury-associated coagulopathy. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Dong, J.F. Coagulopathy induced by traumatic brain injury: Systemic manifestation of a localized injury. Blood 2018, 131, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, R.U.; Spangenberg, P. Procoagulant activity in patients with isolated severe head trauma. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| - Clinical Feature Scale (CFS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Heart rate | <100 | 100–119 | 129–139 | ≥140 |
| Respiratory rate | <18 | 18–23 | 24–29 | ≥30 |
| Systolic pressure | <140 | 140–159 | 160–179 | ≥180 |
| Temperature | <37.0 | 37.0–37.9 | 38.0–38.9 | ≥39.0 |
| Sweating | No | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| Posturing during episodes | No | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| - Diagnosis Likelihood Tool (DLT) score | ||||
| Characteristics | Presence | Absence | ||
| Antecedent acquired brain injury | 1 | 0 | ||
| Clinical features occurring simultaneously | 1 | 0 | ||
| Episodes are paroxysmal in nature | 1 | 0 | ||
| Sympathetic overactivity to normally non-painful stimuli | 1 | 0 | ||
| Absence of parasympathetic features during episodes | 1 | 0 | ||
| Features persisting for ≥ 3 consecutive days | 1 | 0 | ||
| Features persisting for ≥ 2 weeks post-injury | 1 | 0 | ||
| ≥2 episodes daily | 1 | 0 | ||
| The absence of other presumed causes of features | 1 | 0 | ||
| Feature persisting despite treatment for an alternative diagnosis | 1 | 0 | ||
| Medication administered to decrease sympathetic features | 1 | 0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wongsripuemtet, P.; Ohnuma, T.; Minic, Z.; Vavilala, M.S.; Miller, J.B.; Laskowitz, D.T.; Meurer, W.J.; Hu, X.; Korley, F.K.; Sheng, H.; et al. Early Autonomic Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Article Review on the Impact on Multiple Organ Dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020557
Wongsripuemtet P, Ohnuma T, Minic Z, Vavilala MS, Miller JB, Laskowitz DT, Meurer WJ, Hu X, Korley FK, Sheng H, et al. Early Autonomic Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Article Review on the Impact on Multiple Organ Dysfunction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020557
Chicago/Turabian StyleWongsripuemtet, Pattrapun, Tetsu Ohnuma, Zeljka Minic, Monica S. Vavilala, Joseph B. Miller, Daniel T. Laskowitz, William J. Meurer, Xiao Hu, Frederick K. Korley, Huaxin Sheng, and et al. 2025. "Early Autonomic Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Article Review on the Impact on Multiple Organ Dysfunction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020557
APA StyleWongsripuemtet, P., Ohnuma, T., Minic, Z., Vavilala, M. S., Miller, J. B., Laskowitz, D. T., Meurer, W. J., Hu, X., Korley, F. K., Sheng, H., & Krishnamoorthy, V. (2025). Early Autonomic Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Article Review on the Impact on Multiple Organ Dysfunction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020557







