Abstract
Keratoconus is a progressive corneal disorder that can lead to irreversible visual impairment if not detected early. Despite its high prevalence, early diagnosis is often delayed, especially in low-to-middle-income countries due to limited awareness and restricted access to advanced diagnostic tools such as corneal topography, tomography, optical coherence tomography, and corneal biomechanical assessments. These technologies are essential for identifying early-stage keratoconus, yet their high cost limits accessibility in resource-limited settings. While cost and portability are important for accessibility, the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tools must be considered as primary metrics to ensure accurate and effective detection of early keratoconus. This review examines both traditional and advanced diagnostic techniques, including the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence, to enhance early diagnosis. Artificial intelligence-based approaches show significant potential for transforming keratoconus diagnosis by improving the accuracy and sensitivity of early diagnosis, especially when combined with imaging devices. Notable innovations include tools such as SmartKC, a smartphone-based machine-learning application, mobile corneal topography through the null-screen test, and the Smartphone-based Keratograph, providing affordable and portable solutions. Additionally, contrast sensitivity testing demonstrates potential for keratoconus detection, although a precise platform for routine clinical use has yet to be established. The review emphasizes the need for increased awareness among clinicians, particularly in underserved regions, and advocates for the development of accessible, low-cost diagnostic tools. Further research is needed to validate the effectiveness of these emerging technologies in detecting early keratoconus.
1. Introduction
Keratoconus is a progressive corneal disease that affects both eyes asymmetrically [1,2,3,4,5], leading to impaired vision. Early diagnosis of keratoconus is crucial since collagen cross-linking can prevent the disease from progressing [6,7,8] and potentially avoid the need for more invasive treatments such as corneal transplantation [1,9]. Despite the high prevalence of keratoconus in many countries [10], many patients remain undiagnosed [11]. Therefore, affordable detection techniques should be deployed in screening studies and in primary eye care. Advanced stages of the disease are relatively easy to identify [8]; the challenge is to diagnose eyes with keratoconus at early stages [12].
Many people with keratoconus are unaware that they have the disease, resulting in delayed treatment and an increased risk of irreversible visual impairment. For example, in two different population-based studies, in Israel [13,14], 40% and 60% of participants were unaware of their keratoconus status despite having recently seen an ophthalmologist or optometrist. Another study in Iran showed [15] that 42% of keratoconus subjects were unaware of their condition. Therefore, the best way to identify patients with early keratoconus may be via population-based screening, particularly in regions of the world where the prevalence is high.
In the Middle East, the prevalence has been shown to be over 2.0% [10,13,14,16,17,18,19,20]. Similarly, in India, the prevalence was found to be 2.3%, and in China, it was found to be 1.1% [21,22]. It should be noted that all these studies are population-based. The lower rates found in some studies [23,24,25,26] may stem from the fact that they were conducted in hospitals or clinics, and thus suffer from an ascertainment bias: people with mild keratoconus may not present to secondary and tertiary centers [27]. Furthermore, people with known risk factors for keratoconus should be closely monitored for the development of the disease. These include being a first-degree relative of a subject with keratoconus, [17,26], or being the offspring of families with consanguinity [13,14,18,19,20,21,28,29].
While clinical signs enable the clinician to detect intermediate and advanced keratoconus easily, the detection of early keratoconus and forme fruste remains a challenge [30].
This review aims to evaluate various methods for the early detection of keratoconus, providing a comprehensive overview of the current diagnostic approaches. The article includes traditional techniques, as well as advanced methods that incorporate machine learning/artificial intelligence, offering insights into the latest advancements in the field and their potential to improve early diagnosis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Method of Literature Review
We conducted a literature review using two databases, PubMed and Google Scholar, covering publications available up to October 2024. The search strategy employed combinations of the following keywords: “detecting”, “early keratoconus”, “subclinical keratoconus”, “form fruste keratoconus”, “retinoscopy”, “keratometer”, “ophthalmoscope”, “slit lamp bio-microscopy”, “corneal hysteresis”, “corneal biomechanics”, “artificial intelligence”, and “machine learning”. Studies that answered the review objectives were included. We also reviewed the reference lists of relevant articles to identify additional studies that may have been missed in our initial search. Our review addresses different methods for the detection of keratoconus at early stages, with a focus on the suitability for screening and identification of the condition. Studies were excluded if they were not peer-reviewed or not published in English, and papers that focused on general keratoconus diagnosis without specific emphasis on early-stage detection were excluded.
2.2. Definitions
This review will assess early keratoconus (KC) detection based on affordability, required expertise, patient cooperation, and diagnostic performance in terms of sensitivity/specificity.
The early stages of keratoconus are often referred to as subclinical, forme fruste keratoconus, or keratoconus suspect, though there is a lack of unified criteria in the use of these terms [31]. These stages are typically characterized by a topographic pattern consistent with keratoconus but without apparent clinical signs [5,17,32].
For the purpose of this review, studies using any of these terms will be included, and all will be collectively referred to as “early keratoconus”.
The affordability of instruments was categorized into three levels [11,33]: unaffordable instruments, which are typically available only in tertiary clinics; moderately affordable instruments, which are usually found in secondary care and primary care settings; and affordable methods, which are commonly used in primary care clinics.
The expertise required to perform the technique is divided into three categories: clinician (optometrist or ophthalmologist), trained technician, and layperson.
Instruments that use validated indices to automatically generate diagnoses are considered to be low-skill instruments. Some instruments have the potential for telemedicine, while others require clinical skills for interpretation of test results.
The level of patient cooperation required was evaluated, with some techniques demanding high patient cooperation (i.e., focus on a specific point with a wide-open eye), while others require minimal cooperation and are faster. Sensitivity and specificity and patient cooperation are based on scientific literature when possible.
The terms “sensitivity” and “specificity” are commonly used to describe the performance characteristics of diagnostic tests or screening tools. Sensitivity quantifies the ability of a screening test to correctly identify individuals who have the target condition or disease [34]. The specificity of a test is defined as the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals who do not have the target condition or disease (true negatives) [34].
A technique that is defined as suitable for community screening should be simple, portable, and affordable to enable access to early-stage screening [35].
In this review, we examined studies that included both artificial intelligence and machine learning, treating the two terms interchangeably due to the overlap in their usage and the difficulty in clearly distinguishing between them in the literature.
3. Results
The literature search yielded a total of 2613 articles and papers from Google Scholar and 758 from PubMed. Following an initial screening of titles and abstracts, 297 potentially relevant articles were selected for further review. Duplicate studies identified across PubMed and Google Scholar (n = 147) were removed. Additionally, articles that were not peer-reviewed (n = 6) and those not published in English (n = 3) were excluded. This process resulted in the inclusion of 141 articles that met the eligibility criteria and were incorporated into the review (Figure 1). These articles were analyzed to provide a comprehensive overview of methods for detecting early-stage keratoconus, with a particular focus on their suitability for screening and identification.
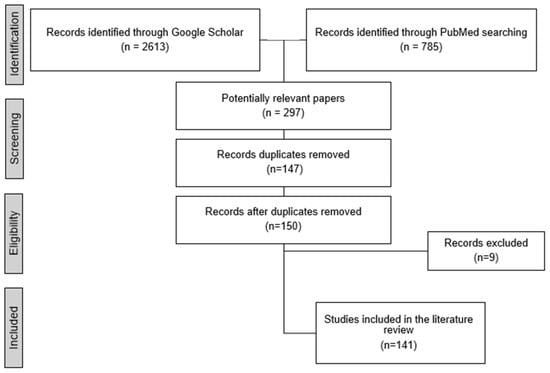
Figure 1.
Filtering steps for study inclusion in this review.
3.1. Instruments in Secondary and Tertiary Clinics
There are several instruments used in the diagnosis of keratoconus that are typically found only in tertiary centers due to affordability issues. These instruments include corneal topography and tomography, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and corneal biomechanical parameter testing.
The Placido-based corneal topography is a non-invasive imaging technique that measures the anterior surface of the cornea, providing quantitative data on curvature and surface irregularities through computational algorithms [36,37,38,39]. While corneal topographers do not require specialized clinical skills [40], technicians need training for accurate image acquisition. Although most devices offer indices to identify abnormal corneas and suggest keratoconus diagnoses, studies indicate that results are more reliable when performed by experienced clinicians [41,42]. Interpreting results may still require clinical expertise [40], as corneal irregularities can lead to misleading topographic maps, complicating the differentiation of keratoconus from conditions such as contact lens-induced warpage [43], poor tear film quality, or lid artifacts [44]. Placido-based topography mainly analyzes the central anterior corneal surface [12], potentially missing posterior elevation abnormalities characteristic of early keratoconus [32]. Therefore, the technique alone may not be sufficient to detect the early stages of the disease [12,45]. While videokeratography indices often detect early keratoconus, they are inadequate to diagnose cases that are not yet clinically apparent [45,46,47], with a modest classification rate for potential keratoconus [46] and widely varying sensitivity and specificity across parameters [38,48,49,50,51,52] (11–100%/5–100%, respectively, Table 1). Although corneal topographers have been widely used as a community screening tool, they do have several limitations. Image acquisition in non-optimal conditions (such as dry eye syndrome, narrow palpebral apertures, long eyelashes, or nystagmus) can affect the accuracy of measurements and diagnoses [53], especially in early cases of keratoconus [32]. Poor repeatability, particularly in young children (where poor cooperation and poor ability to focus exist) can also negatively impact the quality of the image captured [54]. Additionally, the high cost and limited portability of corneal topographers hinder their large-scale deployment [35]. Furthermore, in many countries, these instruments are only found in tertiary centers and are not available for large-scale screening.

Table 1.
Instrument utility assessment for detecting early keratoconus.
Table 1.
Instrument utility assessment for detecting early keratoconus.
| Technique | Cost | Need for Clinical Skills to Perform | Need of Clinical Interpretation Skills | Patient Cooperation (Interaction) | Study | Sensitivity and Specificity | Community Screening |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corneal tomography | High | Trained technician [40] | Medium [55,56] | High [35,57] | [41,45,49,50,52,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66] | Range: 57–98%/29–100% Specific values: Sib: 67.7–82%/85–100% [50,52,67,68] light backscatter: 90%/95% [61] KVb: 74%/72% [52] ThkMin: 92%/45% [52] CCT: 91%/46% [52] BAD-D: 70–98%/32–85% [60,61,63,64,67,68,69] BCVb: 64.5%/97.7% [68] BAD-Dt: 87%/29% [60] BAD-Da: 74.3–80%/35% [60] BAD-PImax: 93%/47% [60] SDP: 57–89%/81–86% [49] PRFI: 71.7–97.4%/84.7–87.9% [47,67] Combination of morpho-geometric, volumetric and clinical parameters: 96.8%/94.5% [41] PPI min + CH: 80%/80% [64] ARTmax: 83.3%/74.3% [70] CKI: 0.27–77.3%/41.3–97.7% [65] IHD: 75–83.3%/60.3–88.6% [65,68] PE: 53–95.5%/66.7–95.4% [65,68] RMS, and RMS/A KVb and the apex front curvature: Showed high sensitivity for differentiating early KC [71] Combined parameters (I-S, SteepK-OppK, PostKmax-Position Y, Pr/Ar, PTI2): 99%/99% [72] RMS HOA: 70%/69.77% [69] B-Ele-Thin: 70%/70.54% [69] PPI avg: 73.33–77.4%/70.4–73.64% [68,69] Da: 70–73.6%/70.54–88.3% [69,73] TPpach. 87.0%/71.4% [70] | No |
| Corneal topography | High | Trained technician [40] | Low [40] | High [53] | [38,45,46,48,49,50,51,52,58] | Range: 11–100%/5–100% Specific values: AAI: 77–94%/67–97% [49] CSI: 22–97%/5–100% [50] DSI: 54.1%/69.8% [48] IHA 67–83.3%/0.5–86.3% [65,68] I-S: 11–81%/79–91% [48,49,51] ISV: 74.5–100%/61.8–96% [48,50,65] IVA: 10.8%/95% [48] KISA%: 60%/100% [38] Kavg: 63–85%/52–74% [45,52] KI: 86.4–100%/63.5–100% [48,65,68] KPI: 57%/58–84% [49] OSI: 22–84%/45–99% [49,50] Sif: 74–95%/76% [45,50,52,67] SAI: 43–44%/91–92% [48,49] SRI: 68–83%/51–86% [48,49,67] Rmin: 69.8%/61.4% [65] | No |
| OCT | High | Trained technician [74] | High [12] | High [75] | [58,66,76,77,78,79,80] | Range: 48–90%/88–94% Specific values: Fourier Posterior indices asymmetry: 58%/88% [76] Fourier Posterior indices Higher-order: 48%/94% [76] Several OCT parameters sensitivity: 90% [78] The coincident thinning (CTN) index 93% [81] As/Ps: 92%/96% [47] | No |
| Corneal biomechanical parameters and Hysteresis measurements | High | Trained Technician * | High * | High * | [58,64,66,82,83,84,85,86] | Biomechanics improve diagnosis [82,84] ΔDAR2: 88.9%/NA [87] ΔIR: 88.4%/NA [87] ΔMax ICR: 80.5%/NA [87] ΔSP-A1: 76.2%/NA [87] SP-A1: 82.1%/74.4% [68] SP-A1: 84.93%/33.33% [88] TBI: 70.8–99%/67–95.4% [47,88,89] A1 dArc Length: 86.6%/84.4% [73] HC-Radius: 83.5%/80.5% [73] A2 Time: 83.5%/76.3% [73] CBI: 67.7–78.08%/71–97.7% [68,73,88] SSIv1: 88.14%/27.14% [90] SSIv2: 79.38%/93.47% [90] DA ratio: 73.97%/47.83% [88] ARTh: 78.08%/79.71% [88] | No |
| Slit lamp biomicroscopy | medium | Clinician [35] | High [91] | High [91] | [92,93] | Not tested, but A positive association between the presence of clinical signs and topographic parameters [92] No clear clinical signs in slit lamp examination [93] | No £ |
| Keratometry | medium | Clinician [94,95] | High [96] | High [97] | [39,66,94,98] | Miss inferior steepening [66] limitations in providing information about the corneal topography beyond the points of measurements [98] | No |
| Retinoscopy | Low | Clinician [95,99] | High [99] | Low [99] | [66,95,99] | 98%/80% Scissoring reflex is sensitive for detecting early stages of KC 98%/80% [95,99] | Yes |
| Ophthalmoscopy | Low | Clinician [8] | High but has potential for telemedicine * | Low [8] | [8] | Not tested Sensitive in detecting early KC with the ability to classify the stage of the disease. On going research | Yes |
| Smart-phone based technologies | Low | Layperson [35] | High but has potential for telemedicine * | Low [35] | [35,100,101,102,103] | Not tested SmartKC [100]; SBK [35]; the null-screen test method; On going research | Yes |
| Contrast sensitivity | Low | Trained technician | High [104] | High * | [105,106,107,108,109] | Not tested CS can help in detecting and grading keratoconus in different severity and even with good visual acuity | yes |
£ (unless portable device used). * Not evidence based. Colors: Colors used in the table indicate levels based on cost, clinical interpretation skills, and patient cooperation. Color code: Green: Low cost, minimal need for clinical interpretation skills, and low patient cooperation. Yellow: Medium cost, moderate need for clinical interpretation skills, and moderate patient cooperation. Red: High cost, significant need for clinical interpretation skills, and high patient cooperation. Regarding the need for clinical skills to perform the test: Green: Test can be performed by a layperson. Yellow: Trained technician required to perform the test. Red: Clinician needed to perform the test. Notes: Abbreviations: KC, keratoconus; AAI, asphericity asymmetry index; SAI, surface asymmetry index; SRI, surface regularity index; CSI, center/surround index; DSI, differential sector index; IHA, index of height asymmetry; I-S, inferior–superior index; ISV, index of surface variance; IVA, index of vertical asymmetry; KISA%, keratoconus percentage index; Kavg, average keratometry value; KI, keratoconus index; KPI, keratoconus probability index; OSI, opposite sector index; Sif, symmetry index front; Sib, symmetry index back; SAI, surface asymmetry index; SRI, surface regularity index; KVb, keratoconus vertex back; ThkMin, minimum corneal thickness; CCT, central corneal thickness; BAD-D, Belin–Ambrosio-enhanced ectasia display total deviation value; BAD-Dt Belin–Ambrosio-enhanced ectasia display thinnest point; BAD-Da Belin–Ambrosio-enhanced ectasia display thinnest point displacement; BAD-PImax, Belin–Ambrosio-enhanced ectasia display; pachymetric progression index maximum; SDP, standard deviation of corneal power index; PPI Min minimum pachymetric progression index; CH, corneal hysteresis; OCT, optical coherence tomograph; SBK, smartphone-based keratography; CS, contrast sensitivity. RMS, root mean square: RMS/A, root mean square/area; (KVf, KVb) elevation at KC vertex; SteepK-OppK, steepest K–opposed K; PostKmax, posterior steepest keratometry; Pr/Ar, ratio between the steepest posterior radius and the steepest anterior radius; PTI, percentage of thickness increase; ΔDAR2, change in dynamic apex radius 2; ΔIR, change in inward radius; ΔMax ICR, change in maximum intra-corneal resistance; ΔSP-A1, change in stiffness parameter A1; TBI, tomographic and biomechanical index, HC-radius, radius of curvature of the corneal apex at the highest concavity; A2, time taken to reach the second applanation; CBI, corvis biomechanical index; Da, deformation amplitude; PRFI, Pentacam random forest index; PE, posterior elevation(microns); KI, keratocononus index; IHA, index of height asymmetry; IHD, index of height decentration; BCVb, baiocchi-calossi-versaci back; SP-A1, stiffness parameter at first applanation; ARTh, ambrósio relational thickness to the horizontal profile; SSIv2, stress–strain index (version 2); TPpach, thinnest point pachymetry; CKI, central keratoconus index; KI, keratoconus index; Rmin, minimum radius of curvature; B-Ele-Thin, back elevation at the thinnest location; ARTmax, ambrósio relational Thickness; RMS HOA, root mean square of higher-order aberration; Da, deviation of normality of ambrỏsio relational thickness; DA Ratio, the ratio between DA measured at the apex and 2 mm from the center of the cornea.
According to the consensus established by Gomes et al. in 2015 [32], corneal tomography is widely considered the gold standard for identifying early keratoconus. This non-invasive imaging technique is capable of accurately mapping both the anterior and posterior surfaces of the cornea, providing high-precision results. Its sensitivity allows detection of early signs of keratoconus, making it the most reliable method for early diagnosis [5,32,41,45,46,47,49,50,52,58,60,61,62,63,65,66,110,111]. Furthermore, the indices obtained through corneal tomography enable accurate severity staging of the disease, and its results are easily interpretable. Performing corneal tomography requires a trained technician [40]. However, an experienced examiner with clinical skills will yield a more reliable assessment when interpreting the results [55,56]. Different indices showed different ranges of sensitivity and specificity (between 57–90%/29–100%, respectively [49,50,52,60,61,63,64,71], Table 1). The Belin–Ambrosio-enhanced ectasia display (BAD), which is available on Pentacam, has a strong diagnostic performance [5,32,41,45,46,47,49,50,52,58,60,61,62,63,65,66,110,111] and is widely used to differentiate normal corneas from abnormal ones and even eyes with the potential of developing the disease [69,78,112]. However, a combination of several tomography indices, along with a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s clinical picture [65] and other clinical parameters, increases sensitivity and specificity [41,64]. Due to their high cost, corneal tomography instruments are typically only available at tertiary centers, with few clinics equipped with such technology. Furthermore, corneal tomography instruments are not portable, need clinical skills to interpret the results [55,56], and require patient cooperation, which limits their use in large-scale community screening [35,57]. These limitations pose significant challenges to the widespread adoption of corneal tomography as a tool for large-scale screening programs and are not a viable option in many countries or regions [35].
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a high-resolution imaging technique that uses near-infrared light and low-coherence interferometry to provide detailed information on tissue morphology, including thickness maps of the individual corneal layers [76,113]. This imaging modality can generate both anterior and posterior topography, as well as cross-sectional images of the cornea [114]. Various types of OCT have been developed and proved to be effective in detecting early KC [5,32,41,45,46,47,49,50,52,58,60,61,62,63,65,66,110,111], allowing for the identification of small corneal shape irregularities [72] and thickness variations, as well as subtle changes that may indicate early disease onset [115,116,117]. One example is polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (PS-OCT), which measures how light splits into two beams when passing through the organized tissue of the cornea. This non-invasive method can detect early structural changes in the cornea [45,46,47], aiding in the early diagnosis of keratoconus [12,77,78,79,80,81]. Moreover, research has unveiled the presence of a distinctive “epithelial doughnut pattern” observable through OCT imaging in individuals afflicted with keratoconus. This phenomenon is attributed to an epithelial compensatory mechanism wherein the epithelial layer appears to undergo structural adjustments aimed at rectifying irregularities within the corneal layers [118,119,120]. While epithelial mapping can be useful for diagnosing keratoconus in general, its effectiveness is limited, particularly for detecting eyes with the potential of having the disease since it could diagnose 40% of the cases when used alone [121]. Therefore, corneal epithelial thickness mapping using OCT is useful for early diagnosis [122] when combined with other imaging techniques [47,115,116,121] and/or artificial intelligence methods [121,123].
OCT is an expensive and generally non-portable diagnostic device that requires technician training for proficient generation of corneal images [12]. Furthermore, its dependency on patient cooperation [75] and its limited effectiveness when used alone for detecting early keratoconus highlight the need to complement it with other imaging techniques or AI-based methods to enhance diagnostic accuracy [47,115,116,121].
Corneal biomechanical parameters and corneal hysteresis: Corneal biomechanical properties refer to the measurable characteristics that describe how the cornea responds to external forces [124]. These properties are crucial for the early detection of keratoconus [51]. Two commercial instruments frequently used in clinical practice to assess corneal biomechanics are the corneal visualization Scheimpflug technology (Corvis ST) and the ocular response analyzer (ORA) [125,126,127].
The Corvis ST, a non-contact air-puff tonometer, combines Pentacam data for integrated analysis of corneal shape and biomechanics. It captures high-speed images of the eye to monitor corneal deformation [51]. Research shows that the Corvis ST is highly effective in evaluating corneal biomechanics, particularly in distinguishing keratoconus, early keratoconus, and normal eyes. However, its accuracy in detecting early keratoconus is slightly lower compared to the Sirius corneal tomographer and the Pentacam [51], and its clinical application is still limited [67]. A recent study suggests two key modifications to improve the Corvis ST device’s ability to detect keratoconus: rotating the device’s camera by 90 degrees during clinical examinations, particularly in the nasal-inferior quadrant where keratoconus often develops, and incorporating asymmetry-based analyses by evaluating additional sectional images. These adjustments could enhance the device’s effectiveness in detecting keratoconus, even in cases where topographic analysis does not reveal obvious signs [128].
The ORA instrument measures corneal biomechanics, including corneal hysteresis (CH) and corneal resistance factor (CRF). While these parameters have shown limited sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing early keratoconus [66], the overall efficacy of corneal hysteresis measurement in this context remains uncertain. Some studies have found that corneal hysteresis can differentiate between early keratoconus and healthy controls [84,86,87,89,129,130], even in the absence of topographical abnormalities [131,132,133]. Conversely, some studies have indicated that corneal hysteresis has low sensitivity and specificity unless used in conjunction with other indices or models [64,82,84,134] (Table 1). However, when tomography, biomechanics, and artificial intelligence methods are combined, they can significantly improve the precision and reliability of early detection [47,66,73,83,135]. Nonetheless, identifying early KC remains a challenge and requires further technological advancements [51,136].
The measurement of corneal hysteresis requires a trained technician, as well as an understanding of corneal biomechanics to interpret the results. The high cost and requirement for expertise and patient cooperation have limited the widespread utilization of these instruments.
Motion-tracking Brillouin microscopy is an emerging noninvasive 3D mapping technique that measures the Brillouin frequency shift to estimate the cornea’s viscoelastic properties without corneal deformation. It shows promise for detecting biomechanical changes in keratoconus and evaluating corneal crosslinking efficacy [137]. However, its clinical use faces challenges, including sensitivity to eye movements and the need for faster data acquisition [126]. Further technological advancements are needed to enhance its practicality and accuracy for early keratoconus diagnosis.
Unfortunately, the unaffordability of these techniques presents a significant barrier to the diagnosis and monitoring of keratoconus, particularly in low-to-low-middle income-countries where access to contemporary diagnostic and therapeutic equipment is limited [35].
3.2. Primary Eye-Care Clinics
This section will address the diagnosis of early keratoconus with tools often found in primary eye-care clinics. These tools are generally affordable but require clinical skill in performance and in interpretation of the results.
The keratometer is a tool that requires the user to align mires to the patient’s eye to measure the minimum and maximum keratometry (K) readings and their corresponding axes. This is achieved by focusing on four points within the 3.0–4.0 mm central corneal zone [138]. The process of focusing and alignment requires clinical skill to perform and patient cooperation [94,95,96,97]. The keratometer is a cost-effective tool, which may be suitable for community-based screening. Furthermore, manual keratometry provides a qualitative visualization of mires, which is useful in diagnosing manifest keratoconus [94]. The disadvantage is that it may not be a good tool for the identification of early keratoconus [38,39,66,139] in patients who do not have steep anterior corneas. In addition, since measurements are limited to the central anterior curvature of the cornea, it may not detect manifest keratoconus with cones offset from the center of the cornea [94] or pellucid marginal degeneration. Since these patients are good candidates for cross-linking, this is a considerable limitation. According to Hashemi et al. [98], manual keratometry exhibits comparable repeatability to other advanced imaging modalities for manifest keratoconus, but its reliability depends on the user’s experience, which should have high clinical expertise [94].
Slit lamp biomicroscopy is a comprehensive exam that involves using a microscope with a narrow beam of light to examine the cornea. It is often used to diagnose advanced keratoconus as it can reveal any structural abnormalities found with advanced disease in the cornea, such as Munson sign [140], Vogt striae, and Fleischer rings [5,141,142,143]. Advantages include its ability to provide detailed images of the cornea and its accessibility in most primary eye-care clinics. Disadvantages include the need for trained eye-care professionals to perform and interpret the results of the exam and the need for patient cooperation [91]. Furthermore, in early stages of the condition, structural abnormalities may not be present or may be very subtle [92,93].
3.3. Primary Eye-Care Diagnosis with Affordable and Portable Equipment
Several low-cost tools for detecting keratoconus are currently in development and testing, using different methods such as ophthalmoscopy [8] and contrast sensitivity testing [144] to detect early signs of keratoconus. While these methods offer affordability and portability, their effectiveness relies heavily on examiner skills, and they may not match the sensitivity and specificity of advanced technologies like corneal topography. However, if successfully implemented, these tools have the potential to enable extensive screening initiatives and are widely used in low- and middle-income countries and could prove to be a valuable asset for eye care practitioners without access to advanced technology.
The retinoscope is a non-invasive, affordable, handheld instrument that is used to measure the refractive error of the eye. In keratoconus, the cornea becomes irregularly shaped, causing distorted light reflection, and a scissoring reflex is observed [4,5,95,143]. Several studies have shown that the retinoscope proves to have high sensitivity and moderate specificity in detecting keratoconus (when compared to Pentacam) [95,99], especially in cases of mild, intermediate, and advanced stages [92,99,140,145]. The retinoscope can be particularly useful for testing children or non-compliant patients, such as individuals with Down’s syndrome [99], because it does not require patient cooperation. However, it has limitations in accurately diagnosing and classifying the disease in its early stages [92,99]. Another disadvantage is that using the retinoscope is challenging and necessitates clinical skills to perform and interpret the results [95,99].
Ophthalmoscopy is a non-invasive, inexpensive, widely available, and handheld tool that examines the retina without the need for high patient cooperation. Some studies have shown that ophthalmoscopy can detect signs of keratoconus [141,146,147,148,149] but may not be as sensitive and/or specific as other tests. In addition, the use of ophthalmoscopy requires clinical skills. Recently, Gideon Abou Said et al. [8] revisited the oil droplet sign in keratoconus and its utility for early diagnosis and screening using an ophthalmoscope attached to an iPhone. The study found that the oil droplet sign (annular dark shadow, ADS) was a good tool for detecting early keratoconus [8]. This sign was present in all 37 eyes with keratoconus and 13 eyes of early disease, but in none of the 37 control eyes. The study also found a correlation between the height of the sign and the severity of keratoconus. This tool is superior to retinoscopy in terms of its ability to classify the stages of the disease but, like retinoscope, it requires skill to perform [8]. Nonetheless, the output can be photographed and analyzed automatically for easy interpretation, so either a trained technician or even a layperson can perform the test.
Due to the affordability and portability of the technique, it could be an excellent tool for community-based screening. However, the sensitivity and specificity of this tool have not been tested on a large population.
SmartKC is a low-cost, smartphone-based tool that uses machine-learning algorithms to detect keratoconus [100,101]. The system comprises a 3D-printed cone-shaped Placido ring attachment on a smartphone’s camera and an off-the-shelf USB blue-colored LED light strip to project concentric black-and-blue rings on the human eye. The captured corneal images are analyzed by SmartKC’s software, which uses an image processing pipeline to generate assessments that are similar to clinical gold-standard topographers. The SmartKC system was evaluated in a clinical study involving 101 eyes, achieving a high sensitivity of 94.1% and a specificity of 100% [100]. SmartKC is relatively low cost, portable, does not require specialized clinical skill or patient cooperation, and it has the potential to be widely available to patients who may not have access to specialized eye care. However, it is still in the early stages of development and has not yet been widely tested.
The null-screen test method [102,103] uses a small conical null screen for corneal topography attached to the camera of a mobile device for performing topography measurements. By comparing the actual image of the corneal surface with the ideal image produced by the null screen, it is possible to determine any deviations from a perfect surface and, thus, obtain accurate measurements of corneal topography. The null screen is an artificial intelligence-based tool that is an affordable and cost-effective tool, and it does not require specialized clinical skill or patient cooperation to measure the shape of aspherics and free-form surfaces. It is a non-contact test and does not require specially designed optics, making it a cheap and easy technique to implement. Specifically, the null screen remains in the early stages of development and has yet to be subjected to widespread testing. Consequently, it is unclear whether the null screen can effectively replace corneal tomography or detect early-stage keratoconus. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity of the null screen have not been evaluated, which represents a crucial limitation in terms of its clinical application. Therefore, further investigation is warranted to determine the feasibility and accuracy of the null screen as a diagnostic tool for keratoconus.
Similarly, the smartphone-based keratograph (SBK; EMAGine AG) [35] is a cost-effective and portable Placido-based topography tool that employs artificial intelligence and smartphone processing power to detect keratoconus. While it has not been validated, it presents an attractive solution since it is affordable, portable, and specifically designed to be user-friendly for unskilled workers, enabling them to easily administer it outside of a clinical setting with the needs of minimal patient cooperation [35].
In addition, contrast sensitivity has been found to be significantly lower for keratoconus subjects when compared with healthy controls [106,107,108]. This was also true for keratoconus patients who presented good “best corrected visual acuity” [105]. Therefore, contrast sensitivity may be a useful tool for screening or even detecting and monitoring keratoconus. However, no simple and precise platform currently exists for detecting keratoconus based on contrast sensitivity, and further studies are needed to develop and validate portable, affordable devices for this purpose.
Although low-cost tools are essential for improving accessibility in underserved regions, it is crucial to validate their diagnostic performance in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Tools with inadequate diagnostic accuracy may lead to false positives or missed cases, limiting their clinical utility for early keratoconus detection.
3.4. Integration of Artificial Intelligence Methods for Improving Early Detection Keratoconus
Several low-cost tools for detecting keratoconus are currently in development, and artificial intelligence (AI) methods have gained traction in medical fields, including ophthalmology, for improving diagnostic accuracy across various pathologies [150,151,152,153,154,155]. While modern ophthalmic instruments, such as tomographers and topographers, include built-in software with advanced computational algorithms, it is essential to distinguish these pre-trained, task-specific algorithms from the broader application of AI in clinical practice. In this context, “AI” refers to advanced algorithms capable of analyzing and integrating multiple diagnostic parameters—such as corneal topography, tomography, and biomechanical assessments—to improve accuracy and reduce variability in detecting early keratoconus. Unlike embedded algorithms in devices like SmartKC or Keratograph, which are pre-configured for specific applications, modern AI methods employ iterative training on large datasets to continually refine and optimize diagnostic capabilities. In the following section, we present the effectiveness of AI methods in early keratoconus detection, including their integration with advanced imaging technologies and a summary of recent findings.
In the context of early keratoconus detection, AI methods have demonstrated enhanced accuracy, with high sensitivity and specificity, particularly when integrated with imaging technologies such as corneal topography, tomography, and biomechanical assessments [47,68,123,156,157,158,159]. A systematic meta-analysis reported a pooled sensitivity of 0.88 for early keratoconus detection using machine-learning methods [160], with some neural networks achieving sensitivities and specificities exceeding 90%. However, the study did not differentiate between early and established cases, limiting insights into early detection accuracy [161]. Table 2 provides a comprehensive summary of findings from the meta-analysis supplemented by additional recent studies, highlighting the sensitivity and specificity of various diagnostic tools for early keratoconus detection. The table includes studies from the past 5 years, focusing on various methods for detecting early keratoconus. These methods include artificial intelligence (AI) approaches such as machine learning and deep learning, as well as traditional image processing and analysis techniques, selected through a systematic search. These studies were identified through a systematic search incorporating the following keywords, “artificial intelligence” and “machine learning”, added to the original search strategy. Of the 141 articles included in the review, 25 met these specific inclusion criteria. Studies that were already covered in the meta-analyses or reviews were excluded from the table. However, individual studies published in the last 5 years, which addressed early keratoconus detection and were not part of any review, were included. Only studies that provided data on sensitivity and specificity for early keratoconus detection were considered for inclusion. As a result, a total of 20 studies met these criteria and were included in Table 2.
The table provides an overview of sensitivity and specificity ranges for various AI-based tools in keratoconus detection. Sensitivity across studies varied widely, from as low as 28.5% [85,161] to as high as 100% [123,151,157,158,162], with specificity ranging from 14% [85] to 100% [85,123,151,157,158,162,163]. Many studies reported high sensitivity and specificity levels, with several reaching above 90%, indicating strong diagnostic potential. Some studies also reported high accuracy or AUC (area under the curve) values [67,123,135,150,153,154,156,157,158,159,162,163,164,165,166,167,168], spanning from 0.575 to nearly 1.0, reinforcing AI’s capability for reliable keratoconus detection.
However, variability in sensitivity and specificity across models and datasets suggests that while AI offers promising diagnostic accuracy, consistency may vary based on specific model types, imaging devices, and data quality. For instance, certain models achieved nearly perfect specificity and sensitivity, while others were more modest, indicating room for optimization in identifying early or potential keratoconus cases. This variability highlights the potential for AI to significantly impact early diagnosis but also underscores the need for standardization and validation to ensure reliability across different clinical settings.

Table 2.
Summary of studies on machine-learning methods for early keratoconus detection.
Table 2.
Summary of studies on machine-learning methods for early keratoconus detection.
| Author, Year | Study Type | Number of Papers That Are Specified for Ekc (Years of Data Included in the Study) | Name of Included Devices/Imaging Modality | Type of Data | Sensitivity% | Specificity% | AUC/Accuracy% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashemi et al., 2024 [156] | A systemic and meta-analysis review | 22 (Up to March 2022) | Pentacam Sirius Galilei Tomy Orbscan CORVIS OCT OPD-Scan | Tomographic Topographic Aberrometric Biomechanics | 70.8–100 | 84.95–99.7 | 0.92–0.999/85.3–99.7 |
| Afifah et al., 2024 [161] | A systematic review and meta-analysis | 6 (2018–2023) | Pentacam Pentacam-HR TMS-4 UHR-OCT | Tomographic Topographic | 97 £ | 96–98 £ | NA |
| Bodmer et al., 2024 [163] | A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis | 7 (Up to February 2022) | Pentacam TMS-4 | Tomographic Topographic | 93.7–95.1 | 94.4–100 | 0.99/86.4–98.9 |
| Goodman and Zhu, 2024 [154] | A systemic review | 24 (Up to October 2023) | Pentacam HR Pentacam Sirius Orbscan OPD-Scan III SD-OCT UHR -OCT OCT (CASIA) Corvis ST Air-puff Slit lamp | Tomographic Topographic Aberrometric Biomechanics Clinical findings Demographic VA Geometric Tonometric | 75–98 | 89.8–97.9 | 0.81–0.99/68.7–99.78 |
| Nguyen et al., 2024 [158] | A narrative review | 13 (1997–2024) | Pentacam-HR Galilei Sirius TMS-1 MS-39 Corvis-ST AS-OCT SD-OCT MS-39 | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics Tonometric | 41.3–100 | 40.5–100 | 0.57–0.98/93–100 |
| Hashemian et al., 2024 [167] | Comprehensive review | 4 (*) | Pentacam ORA Corvis ST | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics | 80–85.2% | 90–96.6% | 0.945 |
| Tey et al., 2024 [166] | Review | 17 (Up to August 2023) | Pentacam Galilei Sirius Oculyzer TMS-1 TMS-4 SmartKC Corvis ST APT SD-OC AS-OCT OPD-Scan III | Tomographic Topographic Aberometric Biomechanics Tonometric | 71.5–100 | 83.97–100 | 0.80–0.99/ 88.7–100 |
| Huo et al., 2024 [150] | Review | 11 (June 2013 to September 2022) | ORA Corvis ST Pentacam AS-OCT SD-OCT | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics Abberometric Tonometric | 75–100 | 82.07–100 | NA/83.33–99.6 |
| Niazi et al., 2023 [67] | A systematic narrative review | 18 (Up to October 2022) | Pentacam Pentacam HR Orbscan II Sirius Corvis ST Air puff SD-OCT | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics Genetic data Tonometric | 66.6–100 | 70–100 | 0.81–0.99/89–98.7 |
| Vandevenne et al., 2023 [151] | A systematic review | 28 (2013–2022) | Pentacam Sirius Orbscan IIz Orbscan Galilei TMS-1 ARK-1 Corvis-ST OCT (CASIA, RCTVue) | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics | 47–100 | 54–100 | NA |
| Zhang et al., 2023 [162] | A systematic review | 18 (1997–2022) | Pentacam Sirius Galilei Orbscan IIz TMS-1 TMS-4 MS-39 OPD Scan III Corvis-ST AS-OCT (CASIA) UHR-OCT | Tomographic Topographic Abberometric Biomechanics | 76.92–100 | 83.1–100 | 0.96–1.0/85.4–100 |
| Cao et al., 2022 [160] | A systematic review and meta-analysis | 17 (1995–2020) | Pentacam HR Orbscan IIz Sirius Galilei TMS-4 ORA Corvis ST UHR-OCT OCT (CASIA) | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics | 82.2–92.3 | 91.4–96.7 | NA |
| Shanthi et al., 2022 [159] | A systematic review | 14 (2010–2020) | Pentacam Sirius Galilei Corvis ST OPD Scan III VX120 OCT (CASIA) | Tomographic Topographic Abberometric Biomechanics Geometric Demographic | 63–97.59 | 82–98.72 | 0.69–0.98/88.8–98.2 |
| Kang et al., 2022 [165] | Systematic review | 7 (2020–2022) | Tomography * Topography * AS-OCT | Tomographic Topographic | 99–86 | 99–85 | 0.995–0.93/69–99 |
| Maile et al., 2021 [85] | A systematic review | 26 (2012–2020) | Pentacam Pentacam HR Orbscan IIz Sirius Galilei Corvis-ST TMS-4 MS-39 OCT (RCTVue, SS-1000 CASIA) OPD scan | Tomographic Topographic Abberometric Biomechanics Demographic | 28.5–98.5 | 14–100 | NA |
| Jiang et al., 2024 [164] | Multicenter diagnostic study | Pentacam HR | Tomographic Topographic | 98 | 98 | 0.96/98 | |
| Yang et al., 2024 [157] | Retrospective case-control study | Corvis-ST | Biomechanics | 100 | 75–100 | 0.92–1.00/ 85–95 | |
| Mourgues et al., 2024 [123] | Retrospective case-control study | SS-OCT (CASIA 2) | Tomographic Topographic Pachymetric Abberometric | 100 84 | 100 90 | 0.98–0.99/NA | |
| Ren et al., 2023 [168] | Case-control study | Pentacam Corvis ST | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics | 76.9 | 90.4 | 0.91/NA | |
| Chen et al., 2023 [153] | Prospective diagnostic study | Corvis-ST | Tomographic Topographic Biomechanics UDVA, CDVA Demographic Refraction Tonometric Slit lamp Fundus Examination | 70.30–75.25 | 89.4–99.7 | 0.88–0.89/ 86.3–93.4 |
* Not specified. £ Specified only for two studies. Notes: Abbreviations: HR, high resolution; OPD, optical path difference; OCT, optical coherence tomography; AS, anterior segment; SD, spectral domain; UHR, ultra-high resolution; SS, swept source; RCTVue, retina comprehensive total vue; TMS, tomey corneal topographer system; SmartKC, smart keratoconus detection system; ORA, ocular response analyzer; APT, air-puff tonometry; ARK, automated keratometer; UDVA, uncorrected distance visual acuity; CDVA, corrected distance visual acuity; VA, visual acuity, NA, not available.
4. Discussion
Currently, as summarized in Table 1, an optimal modality for community-based screening of early keratoconus does not exist. Instruments such as corneal tomographers and OCTs are highly specific and sensitive for the detection of early keratoconus but expensive and not portable. More accessible tools, such as keratometry and retinoscopy, are affordable and portable yet lack sufficient sensitivity for early keratoconus detection. Although several novel methods hold the potential to be both affordable and sensitive, they have not been extensively tested for community-based screening applications.
Portable tools like the retinoscope and ophthalmoscope could offer practical solutions for early keratoconus screening, particularly in remote or underserved areas, thus improving public health accessibility. However, these tools may not be sensitive enough to detect early cases. Furthermore, they have not yet been widely utilized in population-based studies for this purpose.
Recently, new tools have been developed to address this challenge. Gideon Abou Said et al. [8] demonstrated that the annular dark shadow observed with the ophthalmoscope can effectively detect early keratoconus and classify its stages [8]. This technique shows promise as a practical, low-cost alternative for keratoconus staging, complementing traditional methods like retinoscopy. Integrating automated image processing or machine learning with the annular dark shadow technique could further enhance its sensitivity and specificity. By eliminating the need for a trained clinician, this approach may enable automated screening for early keratoconus in community settings. This further highlights the potential of the annular dark shadow technique as a viable option for early detection in resource-limited settings, where advanced diagnostic tools may not be available. Future studies focusing on real-world validation analysis will be crucial to demonstrate its clinical utility.
In addition, the healthcare field has increasingly adopted artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms for automated early keratoconus screening, which achieve high sensitivity and specificity with minimal human intervention. These AI-driven systems integrate multiple clinical parameters from diverse instruments, enhancing diagnostic accuracy [66,85,169]. The performance of these artificial intelligence methods tools is comparable to that of experienced corneal specialists and can ease the workload on healthcare professionals, making the technology accessible to non-specialists [85,170]. Continued development and validation of these AI methods could significantly impact keratoconus screening and early treatment options, bridging the gap in community-level screening tools and enhancing early detection outcomes.
This review has several limitations. Emerging technologies in the early stages may be absent from peer-reviewed journals, leading to their exclusion. The narrative review approach introduces subjectivity, as study selection and interpretation may vary. Limiting the search to PubMed and Google Scholar, peer-reviewed papers, and English-language journals may have excluded relevant studies, further restricting the generalizability of findings across diverse healthcare settings and populations. Furthermore, Table 2 is limited by the lack of homogeneous inputs across studies, making direct comparisons of methodologies and outcomes challenging. Future research should utilize a broader range of databases for greater comprehensiveness.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the early diagnosis of keratoconus is crucial for effective management, preventing the progression of the disease and preserving vision. Studies indicate that keratoconus often progresses significantly during childhood and puberty, potentially leading to severe visual impairment. However, diagnosing the condition in this age group is challenging due to factors such as affordability and variability in test reliability, which can be affected by limited cooperation and difficulty maintaining focus during testing procedures. Future research should focus on enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of portable, low-cost tools to ensure their reliability for large-scale screening programs. With the advancements in diagnostic tools and techniques, including artificial intelligence, eye care professionals will be able to detect and treat keratoconus at an earlier stage and younger age, resulting in a better quality of life. Developing a screening tool for detecting early keratoconus can save vision and avoid expensive and penetrating procedures. While expensive tools may be of use in high-income countries, since they do not require a trained optometrist or ophthalmologist to perform or interpret, there is still a need for portable and affordable equipment that can be used in large-scale screening projects. Furthermore, low-cost portable instruments may offer significant benefits in remote areas, where unspecialized examiners could perform tests and interpret clinical results. Several low-cost tools for detecting keratoconus are currently in development and testing. If successfully implemented, these tools have the potential to improve awareness of the disease by initiating extensive screening in low- and middle-income regions and could prove to be a valuable asset for clinicians without access to advanced technology. However, the challenge lies in convincing the industry to prioritize the adaptation of existing technology rather than investing in even more sophisticated solutions. Moreover, as clinicians, we have a social responsibility to advocate for solutions that are accessible to everyone, regardless of the economic situation of their countries. This includes influencing companies to develop sensory devices that prioritize affordability, portability, and simplicity as key factors for success. As proposed by Hafezi and Hafezi [35], companies should consider shifting their business models towards a sales volume-based approach rather than solely targeting a limited number of elite users. By promoting these values, we can contribute to making these devices feasible and accessible for a larger global market.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.S., J.G. and A.G.A.S.; methodology, E.S., J.G. and A.G.A.S.; data curation, E.S., J.G. and A.G.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S., J.G. and A.G.A.S.; writing—review and editing, E.S., J.G. and A.G.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mohammadpour, M.; Heidari, Z.; Hashemi, H. Updates on Managements for Keratoconus. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2018, 30, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, M.W.; Meyer, J.J.; Duncan, J.K.; Gelman, R.; Borgstrom, M. Assessing Progression of Keratoconus and Cross-Linking Efficacy: The Belin ABCD Progression Display. Int. J. Keratoconus Ectatic Corneal Dis. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuft, S.J.; Moodaley, L.C.; Gregory, W.M.; Davison, C.R.; Buckley, R.J. Prognostic Factors for the Progression of Keratoconus. Ophthalmology 1994, 101, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krachmer, J.H.; Feder, R.S.; Belin, M.W. Keratoconus and Related Noninflammatory Corneal Thinning Disorders. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1984, 28, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S. Keratoconus. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1998, 42, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannis, M.J.; Ling, J.J.; Kyrillos, R.; Barnett, M. Keratoconus and Personality—A Review. Cornea 2018, 37, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporossi, A.; Mazzotta, C.; Baiocchi, S.; Caporossi, T. Long-Term Results of Riboflavin Ultraviolet A Corneal Collagen Cross-Linking for Keratoconus in Italy: The Siena Eye Cross Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gideon Abou Said, A.; Piñero, D.P.; Shneor, E. Revisiting the Oil Droplet Sign in Keratoconus: Utility for Early Keratoconus Diagnosis and Screening. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2023, 43, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobashi, H.; Rong, S.S. Corneal Collagen Cross-Linking for Keratoconus: Systematic Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8145651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.A.P.; Rodrigues, P.F.; Lamazales, L.L. Keratoconus Epidemiology: A Review. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 36, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, E.O.; Claerhout, I.; Koppen, C. Diagnostic Patterns in Keratoconus. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chamberlain, W.; Tan, O.; Brass, R.; Weiss, J.L.; Huang, D. Subclinical Keratoconus Detection by Pattern Analysis of Corneal and Epithelial Thickness Maps with Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2016, 42, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millodot, M.; Shneor, E.; Albou, S.; Atlani, E.; Gordon-Shaag, A. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Keratoconus in Jerusalem: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2011, 18, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shneor, E.; Millodot, M.; Gordon-Shaag, A.; Essa, M.; Anton, M.; Barbara, R.; Barbara, A. Prevalence of Keratoconus among Young Arab Students in Israel. Int. J. Keratoconus Ectatic Corneal Dis. 2014, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Yazdani, N.; Ostadimoghaddam, H.; Norouzirad, R.; Amanzadeh, K.; Miraftab, M.; Derakhshan, A.; Yekta, A. The Prevalence of Keratoconus in a Young Population in Mashhad, Iran. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waked, N.; Fayad, A.M.; Fadlallah, A.; El Rami, H. Dépistage Du Kératocône Dans Une Population Universitaire Au Liban. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2012, 35, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneor, E.; Frucht-Pery, J.; Granit, E.; Gordon-Shaag, A. The Prevalence of Corneal Abnormalities in First-Degree Relatives of Patients with Keratoconus: A Prospective Case-Control Study. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2020, 40, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, M.M.; Diakonis, V.F.; Jalil, S.A.; Younis, R.; Qadoumi, J.; Al-Labadi, L. Prevalence of Keratoconus Among a Palestinian Tertiary Student Population. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2016, 9, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Beiranvand, A.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Asgari, S.; Emamian, M.H.; Shariati, M.; Fotouhi, A. Prevalence of Keratoconus in a Population-Based Study in Shahroud. Cornea 2013, 32, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, E.A.T.; Al-Otaibi, W.M.; Hafezi, N.L.; Kling, S.; Al-Farhan, H.M.; Randleman, J.B.; Hafezi, F. Prevalence of Keratoconus in Paediatric Patients in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B.; Nangia, V.; Matin, A.; Kulkarni, M.; Bhojwani, K. Prevalence and Associations of Keratoconus in Rural Maharashtra in Central India: The Central India Eye and Medical Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 148, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Guo, Y.; You, Q.S.; Jonas, J.B.; Beijing Eye Study Group. Prevalence and Associations of Steep Cornea/Keratoconus in Greater Beijing. The Beijing Eye Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, R.H.; Bourne, W.M.; Dyer, J.A. A 48-Year Clinical and Epidemiologic Study of Keratoconus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 101, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.; Hjortdal, J.; Nohr, E.A.; Ehlers, N. Incidence and Prevalence of Keratoconus in Denmark. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2007, 85, 890–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihalainen, A. Clinical and Epidemiological Features of Keratoconus Genetic and External Factors in the Pathogenesis of the Disease. Acta Ophthalmol. Suppl. 1986, 178, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, U.; Fujiki, K.; Ogawa, A.; Ueda, S.; Kanai, A. Prevalence of Keratoconus Patients in Japan. Nihon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 1985, 89, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gordon-Shaag, A.; Millodot, M.; Shneor, E.; Liu, Y. The Genetic and Environmental Factors for Keratoconus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 795738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Shaag, A.; Millodot, M.; Essa, M.; Garth, J.; Ghara, M.; Shneor, E. Is Consanguinity a Risk Factor for Keratoconus? Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.; Chong, E.W.; Lingham, G.; Stevenson, L.J.; Sanfilippo, P.G.; Hewitt, A.W.; Mackey, D.A.; Yazar, S. Prevalence of Keratoconus Based on Scheimpflug Imaging: The Raine Study. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyce, S.D. Chasing the Suspect: Keratoconus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, M.A.; Hadid, M.; Izquierdo, L. A Systematic Review of Subclinical Keratoconus and Forme Fruste Keratoconus. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.A.P.; Tan, D.; Rapuano, C.J.; Belin, M.W.; Ambrósio, R.; Guell, J.L.; Malecaze, F.; Nishida, K.; Sangwan, V.S. Global Consensus on Keratoconus and Ectatic Diseases. Cornea 2015, 34, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Jelly, E.T.; Chu, K.K.; Kendall, W.Y.; Wax, A. A Review of Low-Cost and Portable Optical Coherence Tomography. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 3, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevethan, R. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Predictive Values: Foundations, Pliabilities, and Pitfalls in Research and Practice. Front. Public. Health 2017, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, N.L.; Hafezi, F. Developing Affordable, Portable and Simplistic Diagnostic Sensors to Improve Access to Care. Sensors 2022, 22, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, G.; Barboni, P.; Carbonelli, M.; Hoffer, K.J. Repeatability of Automatic Measurements by a New Scheimpflug Camera Combined with Placido Topography. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, D.P.; Alió, J.L.; Alesón, A.; Vergara, M.E.; Miranda, M. Corneal Volume, Pachymetry, and Correlation of Anterior and Posterior Corneal Shape in Subclinical and Different Stages of Clinical Keratoconus. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2010, 36, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S.; Rasheed, K. KISA% Index: A Quantitative Videokeratography Algorithm Embodying Minimal Topographic Criteria for Diagnosing Keratoconus. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1999, 25, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Klyce, S.D.; Smolek, M.K. Comparison of Methods for Detecting Keratoconus Using Videokeratography. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1995, 113, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, S.; Koushik, T. Corneal Topography. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Toprak, I.; Cavas, F.; Velázquez, J.S.; Alio del Barrio, J.L.; Alio, J.L. Subclinical Keratoconus Detection with Three-Dimensional (3-D) Morphogeometric and Volumetric Analysis. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e933–e942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-luna, G.; Jiménez-rodríguez, D.; Castaño-fernández, A.B.; Pérez-rueda, A. Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus Based on Machine Learning Techniques. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.E.; Lin, D.T.C.; Klyce, S.D.; Reidy, J.J.; Insler, M.S. Topographic Changes in Contact Lens-Induced Corneal Warpage. Ophthalmology 1990, 97, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, N.; Klyce, S.D.; Smolek, M.K.; Thompson, H.W. Automated Keratoconus Screening with Corneal Topography Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Mishra, S.K.; Joshi, N.D.; Subedi, M.; Puri, P.R.; Gyawali, P.; Bist, J.; Kandel, H. Evaluation of Corneal Topography, Pachymetry and Higher Order Aberrations for Detecting Subclinical Keratoconus. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2022, 42, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Rabinowitz, Y.S. Keratoconus: Classification Scheme Based on Videokeratography and Clinical Signs. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2009, 35, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bdour, M.; Sabbagh, H.M.; Jammal, H.M. Multi-Modal Imaging for the Detection of Early Keratoconus: A Narrative Review. Eye Vis. 2024, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, R.; Rao, H.; Khamar, P.; Sainani, K.; Vunnava, K.; Jayadev, C.; Kaweri, L. Keratoconus Screening Indices and Their Diagnostic Ability to Distinguish Normal From Ectatic Corneas. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 181, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshirfar, M.; Motlagh, M.N.; Murri, M.S.; Momeni-Moghaddam, H.; Ronquillo, Y.C.; Phillip, C.H. Galilei Corneal Tomography for Screening of Refractive Surgery Candidates: A Review of the Literature, Part II. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Doctor, K.; Vunnava, K.P.; Shroff, R.; Kaweri, L.; Lalgudi, V.G.; Gupta, K.; Kundu, G. Simplifying and Understanding Various Topographic Indices for Keratoconus Using Scheimpflug Based Topographers. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2732–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, Z.; Hashemi, H.; Mohammadpour, M.; Amanzadeh, K.; Fotouhi, A. Evaluation of Corneal Topographic, Tomographic and Biomechanical Indices for Detecting Clinical and Subclinical Keratoconus: A Comprehensive Three-Device Study. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.; Darwish, T.; Ali, A.; Ghabra, M.; Shaaban, R. Sensitivity and Specificity of Sirius Indices in Diagnosis of Keratoconus and Suspect Keratoconus. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 32, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Caneiro, D.; Iskander, D.R.; Collins, M.J. Estimating Corneal Surface Topography in Videokeratoscopy in the Presence of Strong Signal Interference. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Anitha, V.; Vanathi, M.; Raghavan, A.; Rajaraman, R.; Ravindran, M.; Tandon, R. Pediatric Keratoconus—Current Perspectives and Clinical Challenges. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshirfar, M.; Duong, A.; Ronquillo, Y. Corneal Imaging. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sinjab, M.M. Corneal Tomography in Clinical Practice (Pentacam System): Basics and Clinical Interpretation, 4th ed.; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kanclerz, P.; Khoramnia, R.; Wang, X. Current Developments in Corneal Topography and Tomography. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiwa, L.E.; Moodley, V. A Review of Corneal Imaging Methods for the Early Diagnosis of Pre-Clinical Keratoconus. J. Optom. 2020, 13, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynli, S.; Salgado-Borges, J.; Alio, J.L. Comparative Evaluation of Scheimpflug Tomography Parameters between Thin Non-Keratoconic, Subclinical Keratoconic, and Mild Keratoconic Corneas. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 28, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulasidas, M.; Teotia, P. Evaluation of Corneal Topography and Tomography in Fellow Eyes of Unilateral Keratoconus Patients for Early Detection of Subclinical Keratoconus. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consejo, A.; Jiménez-García, M.; Issarti, I.; Rozema, J.J. Detection of Subclinical Keratoconus With a Validated Alternative Method to Corneal Densitometry. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieb, H.M.; Othman, I.S.; Oreaba, A.H.; Abdelatif, M.K. Topographic, Elevation, and Keratoconus Indices for Diagnosis of Keratoconus by a Combined Placido and Scheimpflug Topography System. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynli, S.; Abdulaliyeva, F. Evaluation of Scheimpflug Tomography Parameters in Subclinical Keratoconus, Clinical Keratoconus and Normal Caucasian Eyes. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, E.; Özalp, O.; Erol, M.A.; Bilgin, M.; Yıldırım, N. A Combined Biomechanical and Tomographic Model for Identifying Cases of Subclinical Keratoconus. Cornea 2020, 39, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motlagh, M.N.; Moshirfar, M.; Murri, M.S.; Skanchy, D.F.; Momeni-Moghaddam, H.; Ronquillo, Y.C.; Hoopes, P.C. Pentacam® Corneal Tomography for Screening of Refractive Surgery Candidates: A Review of the Literature, Part I. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevara, A.; Vaddavalli, P.K. The Evolution of Diagnostics for Keratoconus: From Ophthalmometry to Biomechanics. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 38, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, S.; Jiménez-García, M.; Findl, O.; Gatzioufas, Z.; Doroodgar, F.; Shahriari, M.H.; Javadi, M.A. Keratoconus Diagnosis: From Fundamentals to Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, M.; Arora, R.; Titiyal, J.S. Combined Corneal Biomechanical and Tomographical Indices in Subclinical and Forme Fruste Keratoconus. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 72, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somali, A.A.; Najmi, H.; Alsawadi, H.; Alsawadi, H.; Almalki, A.; Alhamoud, M.; Alhatlan, H.; Alwohaibi, N. Analysis of Scheimpflug Tomography Parameters for Detecting Subclinical Keratoconus in the Fellow Eyes of Patients with Unilateral Keratoconus in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2024, 18, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, İ.; Martin, Ç.; Güneş, C.E.; Alio, J. Revisiting Pentacam Parameters in the Diagnosis of Subclinical and Mild Keratoconus Based on Different Grading System Definitions. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 53, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieb, H.M.; Abdelatif, M.K.; Gharieb, H.M.; Othman, I.S. Early, Forme Fruste Keratoconus and Normal Thin Cornea, Evaluation of Sensitive Parameters by Combined Placido Scheimpflug Topography. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 34, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Debellemanière, G.; Zeboulon, P.; Rizk, M.; Rouger, H.; Mazharian, A.; Grise-Dulac, A.; Panthier, C.; Gatinel, D. Discrimination between Keratoconus, Forme Fruste Keratoconus, and Normal Eyes Using a Novel OCT-Based Tomographer. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2023, 49, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cao, H.; Huo, Y.; Song, J.; Zou, H.; Li, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, Y. Screening of Sensitive in Vivo Characteristics for Early Keratoconus Diagnosis: A Multicenter Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1158299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, M.; Galor, A.; Nanji, A.; Joag, M.; Palioura, S.; Feuer, W.; Karp, C.L. Ability of Novice Clinicians to Interpret High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography for Ocular Surface Lesions. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 53, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Amorim Garcia Filho, C.A.; Yehoshua, Z.; Gregori, G.; Puliafito, C.A.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Optical Coherence Tomography. Retin. Fifth Ed. 2013, 1, 82–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, S.; Koh, S.; Inoue, R.; Oie, Y.; Maeda, N.; Jhanji, V.; Nishida, K. Fourier Analysis on Irregular Corneal Astigmatism Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Various Severity Stages of Keratoconus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 243, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Pavlatos, E.; Chamberlain, W.; Huang, D.; Li, Y. Keratoconus Detection Using OCT Corneal and Epithelial Thickness Map Parameters and Patterns. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2021, 47, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücekul, B.; Dick, H.B.; Taneri, S. Systematic Detection of Keratoconus in OCT: Corneal and Epithelial Thickness Maps. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Gu, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Lin, K.; Xia, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Corneal Vertical and Horizontal Thickness Profiles Generated by UHR-OCT for Suspected and Subclinical Keratoconus Diagnosis. J. Refract. Surg. 2021, 37, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamar, P.; Rao, K.; Wadia, K.; Dalal, R.; Grover, T.; Versaci, F.; Gupta, K. Advanced Epithelial Mapping for Refractive Surgery. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlatos, E.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, D.; Li, Y. A Coincident Thinning Index for Keratoconus Identification Using OCT Pachymetry and Epithelial Thickness Maps. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, P.; Elsheikh, A. Keratoconus: A Biomechanical Perspective. Curr. Eye Res. 2022, 48, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degle, S. Detection of Subclinical Keratoconus. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 2022, 239, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, V.A.; Son, H.S.; Baur, I.; Zhao, L.; Auffarth, G.U.; Khoramnia, R. Detecting Subclinical Keratoconus by Biomechanical Analysis in Tomographically Regular Keratoconus Fellow Eyes. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 32, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maile, H.; Li, J.P.O.; Gore, D.; Leucci, M.; Mulholland, P.; Hau, S.; Szabo, A.; Moghul, I.; Balaskas, K.; Fujinami, K.; et al. Machine Learning Algorithms to Detect Subclinical Keratoconus: Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inf. 2021, 9, e27363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herber, R.; Ramm, L.; Spoerl, E.; Raiskup, F.; Pillunat, L.E.; Terai, N. Assessment of Corneal Biomechanical Parameters in Healthy and Keratoconic Eyes Using Dynamic Bidirectional Applanation Device and Dynamic Scheimpflug Analyzer. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Ding, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, X.; et al. Comparison of Bilateral Differential Characteristics of Corneal Biomechanics between Keratoconus and Normal Eyes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1163223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyman, A.; Sepahvand, F.; Pourazizi, M.; Noorshargh, P.; Forouhari, A. Corneal Biomechanics in Normal and Subclinical Keratoconus Eyes. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023, 23, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.B.; Vellara, H.R.; Gokul, A.; McGhee, C.N.J.; Meyer, J.J. Comparison of Ectasia Detection in Early Keratoconus Using Scheimpflug-Based Corneal Tomography and Biomechanical Assessments. Cornea 2023, 42, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.Y.; Ma, X.M.; Qu, Z.X.; Eliasy, A.; Wu, B.W.; Xu, H.; Wang, P.; Zheng, X.B.; Wang, J.J.; Ye, Y.F.; et al. Performance of Corvis ST Parameters Including Updated Stress-Strain Index in Differentiating Between Normal, Forme-Fruste, Subclinical, and Clinical Keratoconic Eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 258, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Gurnani, B. Slit-Lamp Biomicroscope. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Naderan, M.; Jahanrad, A.; Farjadnia, M. Clinical Biomicroscopy and Retinoscopy Findings of Keratoconus in a Middle Eastern Population. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2018, 101, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.J.; Maier, P.; Böhringer, T.; Reinhard, T. Early Diagnosis of Keratoconus. Ophthalmologe 2022, 119, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Munir, S.Z.; Sami Karim, S.A.; Munir, W.M. A Review of Imaging Modalities for Detecting Early Keratoconus. Eye 2021, 35, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahrouqi, H.; Oraba, S.B.; Al-Habsi, S.; Mundemkattil, N.; Babu, J.; Panchatcharam, S.M.; Al-Saidi, R.; Al-Raisi, A. Retinoscopy as a Screening Tool for Keratoconus. Cornea 2019, 38, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.L.; Rizzuti, A. Optical Biometry. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gurnani, B.; Kaur, K. Keratometer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, H.; Yekta, A.; Khabazkhoob, M. Effect of Keratoconus Grades on Repeatability of Keratometry Readings: Comparison of 5 Devices. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2015, 41, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebels, S.; Käsmann-Kellner, B.; Eppig, T.; Seitz, B.; Langenbucher, A. Can Retinoscopy Keep up in Keratoconus Diagnosis? Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2015, 38, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gairola, S.; Bohra, M.; Shaheer, N.; Jayaprakash, N.; Joshi, P.; Balasubramaniam, A.; Murali, K.; Kwatra, N.; Jain, M. SmartKC: Smartphone-Based Corneal Topographer for Keratoconus Detection. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 5, p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gairola, S.; Joshi, P.; Balasubramaniam, A.; Murali, K.; Kwatra, N.; Jain, M. Keratoconus Classifier for Smartphone-Based Corneal Topographer. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Scotland, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Carranza, O.; Campos-García, M.; Moreno-Oliva, V.I.; Aguirre-Aguirre, D.; Pérez-Lomelí, J.S. Smartphone-Based Corneal Topography with Null-Screens. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-García, M.; Aguirre-Aguirre, D.; Lechuga-Núñez, J.A.; Peña-Conzuelo, A. Design of a Null-Screen for a Compact Corneal Topographer. In Proceedings of the Modeling Aspects in Optical Metrology VII, Munich, Germany, 24–26 June 2019; Volume 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Gurnani, B. Contrast Sensitivity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shneor, E.; Piñero, D.P.; Doron, R. Contrast Sensitivity and Higher-Order Aberrations in Keratoconus Subjects. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.A.; Abou Samra, W.A.; Torky, M.A.; El-Kannishy, A.M. Objective and Subjective Diagnostic Parameters in the Fellow Eye of Unilateral Keratoconus. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinabhai, A.; O’Donnell, C.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Nourrit, V. Forward Light Scatter and Contrast Sensitivity in Keratoconic Patients. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2012, 35, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesudovs, K.; Schoneveld, P.; Seto, R.J.; Coster, D.J. Contrast and Glare Testing in Keratoconus and after Penetrating Keratoplasty. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.X.; Yuhao, S.; Xiaoyu, Y.; Wuxiao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhong-Lin, S.; Xingtao, L.; Zhao, Z.J. The Characteristics of Quick Contrast Sensitivity Function in Keratoconus and Its Correlation with Corneal Topography. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023, 12, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, E.; Özalp, O.; Yıldırım, N. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Keratoconus. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2021, 13, 251584142110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudah, N. Keratoconus: Imaging Modalities and Management. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2024, 13, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, M.W.; Jang, H.S.; Borgstrom, M. Keratoconus: Diagnosis and Staging. Cornea 2022, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Meisler, D.M.; Tang, M.; Lu, A.T.H.; Thakrar, V.; Reiser, B.J.; Huang, D. Keratoconus Diagnosis with Optical Coherence Tomography Pachymetry Mapping. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, H.; Chan, E. Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging in Keratoconus. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokaitis, T.; Khoramnia, R.; Friedrich, M.; Son, H.S.; Auffarth, G.U.; Augustin, V.A. Inter-Zonal Epithelial Thickness Differences for Early Keratoconus Detection Using Optical Coherence Tomography. Eye 2024, 38, 2968–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, L.; Anselmi, G.; Greco, A.; Abdolrahimzadeh, B.; Costa, M.C.; Scuderi, G. Early Identification of Keratoconus Using Pachymetric Indexes Obtained with Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Clin. Ter. 2021, 172, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, A.D.; Truong, A.; Pasricha, N.D.; Indaram, M. Keratoconus Diagnosis and Treatment: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingopoulos, F.; Zisimopoulos, A.; Kanellopoulos, A.J. Concordance of Keratoconus in Monozygotic Twins before and after Combined Corneal Crosslinking/Photorefractive Keratectomy (Athens Protocol) Using Scheimpflug and OCT Tomography. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinstein, D.Z.; Gobbe, M.; Archer, T.J.; Silverman, R.H.; Coleman, J. Epithelial, Stromal, and Total Corneal Thickness in Keratoconus: Three-Dimensional Display with Artemis Very-High Frequency Digital Ultrasound. J. Refract. Surg. 2010, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.; Khan, M.S.; Dakhil, T.A. Understanding Corneal Epithelial Thickness Mapping. Middle East. Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 29, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenia, V.P.; Kenia, R.V.; Maru, S.; Pirdankar, O.H. Role of Corneal Epithelial Mapping, Corvis Biomechanical Index, and Artificial Intelligence-Based Tomographic Biomechanical Index in Diagnosing Spectrum of Keratoconus. Oman J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 16, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tan, O.; Brass, R.; Weiss, J.L.; Huang, D. Corneal Epithelial Thickness Mapping by Fourier-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Normal and Keratoconic Eyes. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourgues, E.; Saunier, V.; Smadja, D.; Touboul, D.; Saunier, V. Forme Fruste Keratoconus Detection with OCT Corneal Topography Using Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, V.S.; Dupps, W.J. Biomechanical Diagnostics of the Cornea. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2017, 57, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, M.R.; Momeni-Moghaddam, H.; Roberts, C.J.; Maddah, N.; Ambrósio, R.; Hosseini, S.R. Corneal Biomechanical Parameters in Keratoconus Eyes with Abnormal Elevation on the Back Corneal Surface Only versus Both Back and Front Surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninou, M.A.; Seiler, T.G.; Enzmann, V. Corneal Biomechanics and Diagnostics: A Review. Int. Ophthalmol. 2024, 44, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.F.; Marcos, A.V.; Peña, F.J.M. Early Diagnosis of Keratoconus: What Difference Is It Making? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redaelli, E.; Nana, M.; Calvo, B.; Matas, J.F.R.; Luraghi, G.; Rozema, J.; Grasa, J. Improving Early Detection of Keratoconus by Non Contact Tonometry. A Computational Study and New Biomarkers Proposal. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 152, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Yang, K. Accuracy of New Corvis ST Parameters for Detecting Subclinical and Clinical Keratoconus Eyes in a Chinese Population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rueda, A.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, D.; Castro-Luna, G. Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus with a Combined Model of Biomechanical and Topographic Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikielewicz, M.; Kotliar, K.; Barraquer, R.I.; Michael, R. Air-Pulse Corneal Applanation Signal Curve Parameters for the Characterisation of Keratoconus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, C.; Roberts, C.J.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Colin, J.; Maurice-Tison, S.; Kerautret, J. Screening of Forme Fruste Keratoconus with the Ocular Response Analyzer. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, J.D.; Ruiseñor Vázquez, P.R.; Fuentes Bonthoux, F.; Pförtner, T.; Galletti, J.G. Multivariate Analysis of the Ocular Response Analyzer’s Corneal Deformation Response Curve for Early Keratoconus Detection. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 496382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pniakowska, Z.; Jurowski, P. Detection of the Early Keratoconus Based on Corneal Biomechanical Properties in the Refractive Surgery Candidates. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 64, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esporcatte, L.P.G.; Salomão, M.Q.; Lopes, B.T.; Sena, N.; Ferreira, É.; Filho, J.B.R.F.; Machado, A.P.; Ambrósio, R. Biomechanics in Keratoconus Diagnosis. Curr. Eye Res. 2023, 48, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.; Ambrósio, R.; Inoue, R.; Maeda, N.; Miki, A.; Nishida, K. Detection of Subclinical Corneal Ectasia Using Corneal Tomographic and Biomechanical Assessments in a Japanese Population. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randleman, J.B.; Zhang, H.; Asroui, L.; Tarib, I.; Dupps, W.J.; Scarcelli, G. Subclinical Keratoconus Detection and Characterization Using Motion-Tracking Brillouin Microscopy. Ophthalmology 2024, 131, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefrooij, D.A.; Galvis, V.; Tello, A. Von Helmholtz’s Ophthalmometer: Historical Review and Experience with One of the Last Surviving Original Devices. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalia, H.; Swarup, R. Imaging Modalities in Keratoconus. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 61, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.; Chauhan, V.; Rojanasthien, S.; Fitzgerald, J. Munson’s Sign: An Obvious Finding to Explain Acute Vision Loss. Clin. Pract. Cases Emerg. Med. 2019, 3, 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadnik, K.; Barr, J.T.; Edrington, T.B.; Everett, D.F.; Jameson, M.; Mcmahon, T.T.; Shin, J.A.; Sterling, J.L.; Wagner, H.; Gordon, M.O. Baseline Findings in the Collaborative Longitudinal Evaluation of Keratoconus (CLEK) Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romero-Jiménez, M.; Santodomingo-Rubido, J.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Keratoconus: A Review. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2010, 33, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, M.; Coster, D.J.; Phillips, A.J.; Loane, M. Keratoconus: Diagnosis and Management. Aust. N. Z. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 17, 33–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, C.; Okamoto, F.; Samejima, T.; Miyata, K.; Oshika, T. Higher-Order Wavefront Aberration and Letter-Contrast Sensitivity in Keratoconus. Eye 2008, 22, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.E.M.; Foster, J.W.; Jun, A.S.; Soiberman, U.S. The Correlation between Corneal Findings and Disease Severity in Keratoconus per Scheimpflug Corneal Tomography. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 4130643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadnik, K.; Barr, J.T.; Gordon, M.O.; Edrington, T.B. Biomicroscopic Signs and Disease Severity in Keratoconus. Cornea 1996, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.A.; Tandon, R.; Singh, A.K. Automated ESR Analysis in 20 Minutes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 79, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pathmanathan, T.; Falcon, M.G.; Reck, A. Ophthalmoscopic Sign of Early Keratoconus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1994, 78, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nartey, I. Ophthalmoscopic Sign of Early Keratoconus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 79, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huo, Y.; Chen, X.; Khan, G.A.; Wang, Y. Corneal Biomechanics in Early Diagnosis of Keratoconus Using Artificial Intelligence. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2024, 262, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevenne, M.M.S.; Favuzza, E.; Veta, M.; Lucenteforte, E.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M.; Mencucci, R.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A.; Virgili, G.; Dickman, M.M. Artificial Intelligence for Detecting Keratoconus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 11, CD014911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, M.; Heidari, Z.; Hashemi, H.; Yaseri, M.; Fotouhi, A. Comparison of Artificial Intelligence-Based Machine Learning Classifiers for Early Detection of Keratoconus. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tan, Z.; Huo, Y.; Song, J.; Xu, Q.; Yang, C.; Jhanji, V.; Li, J.; Hou, J.; Zou, H.; et al. Localized Corneal Biomechanical Alteration Detected In Early Keratoconus Based on Corneal Deformation Using Artificial Intelligence. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 12, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, D.; Zhu, A.Y. Utility of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Management of Keratoconus: A Systematic Review. Front. Ophthalmol. 2024, 4, 1380701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.R.; Ladas, J.G.; Bahadur, G.G.; Al-Hashimi, S.; Pineda, R. A Review of Machine Learning Techniques for Keratoconus Detection and Refractive Surgery Screening. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 34, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Doroodgar, F.; Niazi, S.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Heidari, Z. Comparison of Different Corneal Imaging Modalities Using Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosis of Keratoconus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2024, 262, 1017–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qi, K.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, J.; Soha, H.; Jin, Y.; Ci, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Mei, Y.; et al. Diagnosis of Forme Fruste Keratoconus Using Corvis ST Sequences with Digital Image Correlation and Machine Learning. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Ong, J.; Masalkhi, M.; Waisberg, E.; Zaman, N.; Sarker, P.; Aman, S.; Lin, H.; Luo, M.; Ambrosio, R.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Corneal Diseases: A Narrative Review. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2024, 47, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, S.; Aruljyothi, L.; Balasundaram, M.B.; Janakiraman, A.; Nirmaladevi, K.; Pyingkodi, M. Artificial Intelligence Applications in Different Imaging Modalities for Corneal Topography. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 67, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Verspoor, K.; Sahebjada, S.; Baird, P.N. Accuracy of Machine Learning Assisted Detection of Keratoconus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifah, A.; Syafira, F.; Afladhanti, P.M.; Dharmawidiarini, D. Artificial Intelligence as Diagnostic Modality for Keratoconus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2024, 19, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Samusak, A.; Rao, H.; Xiao, C.; Abula, M.; Cao, Q.; Dai, Q. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Diagnosis of Ocular Surface Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1133680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, N.S.; Christensen, D.G.; Bachmann, L.M.; Faes, L.; Sanak, F.; Iselin, K.; Kaufmann, C.; Thiel, M.A.; Baenninger, P.B. Deep Learning Models Used in the Diagnostic Workup of Keratoconus: A Systematic Review and Exploratory Meta-Analysis. Cornea 2024, 43, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, F. The Development of a Machine Learning Model to Train Junior Ophthalmologists in Diagnosing the Pre-Clinical Keratoconus. Front Med. 2024, 11, 1458356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Ballouz, D.; Woodward, M.A. Artificial Intelligence and Corneal Diseases. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 33, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tey, K.Y.; Cheong, E.Z.K.; Ang, M. Potential Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Image Analysis in Cornea Diseases: A Review. Eye Vis. 2024, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, H.; Peto, T.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Lengyel, I.; Kafieh, R.; Noori, A.M.; Khorrami-Nezhad, M. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Ophthalmology: An Updated Comprehensive Review. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2024, 19, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Yang, K.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Pang, C.; Zhao, D. Machine learning analysis with the comprehensive index of corneal tomographic and biomechanical parameters in detecting pediatric subclinical keratoconus. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1273500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.T.; Ramos, I.C.; Salomão, M.Q.; Guerra, F.P.; Schallhorn, S.C.; Schallhorn, J.M.; Vinciguerra, R.; Vinciguerra, P.; Price, F.W.; Price, M.O.; et al. Enhanced Tomographic Assessment to Detect Corneal Ectasia Based on Artificial Intelligence. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 195, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zéboulon, P.; Debellemanière, G.; Gatinel, D. Unsupervised Learning for Large-Scale Corneal Topography Clustering. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).