Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Enhances Stem Cells Profile and May Contribute to Survival of Chronic Myeloid Leukemiastem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells Line Treatment
2.2. Proliferation Assay
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. Apoptosis Assay
2.7. ROS Measurement
2.8. Samples Preparation for HPLC-HRMS Analysis
2.9. HPLC-HRMS Metabolomic Analysis
2.10. Data Pre-Processing and Analysis
2.11. Gene Expression Analysis of CML Models
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
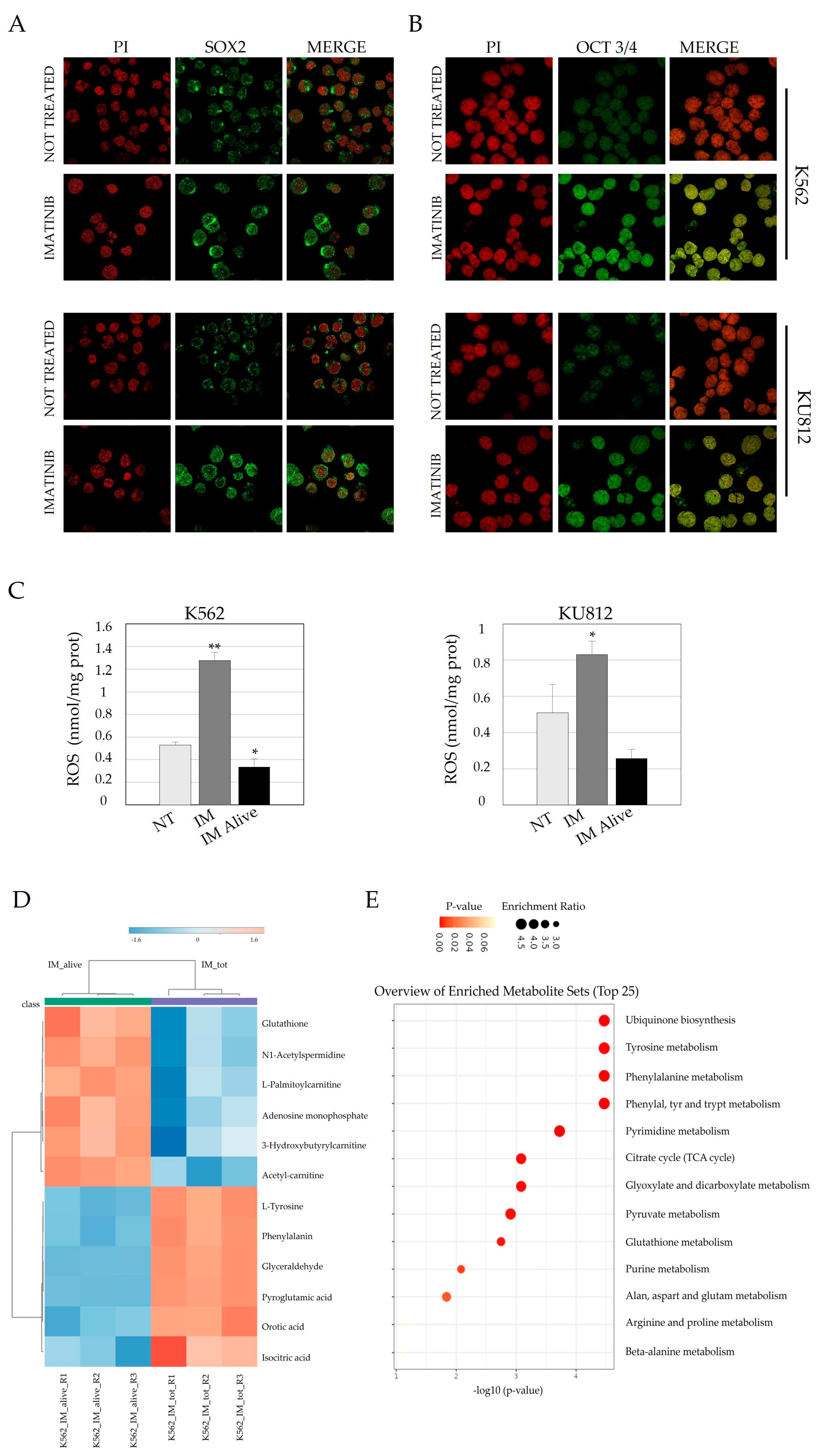
3.1. Imatinib Treatment Induces a Significant Increase of Genes Related to Stemness
3.2. Imatinib Treatment Induces Nuclear Localization of Both Sox2 and OCT 3/4 and Is Associated with an Increase in the LSC Phenotype
3.3. Imatinib Treatment Activate a Few SC Transcription Factors in Cell Lines and in CD34+ CML Cells After In Vitro Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Druker, B.J.; Talpaz, M.; Resta, D.J.; Peng, B.; Buchdunger, E.; Ford, J.M.; Lydon, N.B.; Kantarjian, H.; Capdeville, R.; Ohno-Jones, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Specific Inhibitor of the BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faderl, S.; Talpaz, M.; Estrov, Z.; O’Brien, S.; Kurzrock, R.; Kantarjian, H.M. The Biology of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, J.D. A New Consistent Chromosomal Abnormality in Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia Identified by Quinacrine Fluorescence and Giemsa Staining. Nature 1973, 243, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groffen, J.; Stephenson, J.; Heisterkamp, N.; Deklein, A.; Bartram, C.; Grosveld, G. Philadelphia Chromosomal Breakpoints Are Clustered within a Limited Region, Bcr, on Chromosome 22. Cell 1984, 36, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilloni, D.; Saglio, G. Molecular Pathways: BCR-ABL. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Garcia-Gutierrez, J.V.; Soverini, S.; Baccarani, M. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Prognosis and Therapy: Criticisms and Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Bi, L.; Ren, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Advances in Studies of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Their Acquired Resistance. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, S.; Dello Sbarba, P.; Lulli, M. Imatinib-Mesylate Enhances the Maintenance of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cell Potential in the Absence of Glucose. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 28, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: 2018 Update on Diagnosis, Therapy and Monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vener, C.; Banzi, R.; Ambrogi, F.; Ferrero, A.; Saglio, G.; Pravettoni, G.; Sant, M. First-Line Imatinib vs Second- and Third-Generation TKIs for Chronic-Phase CML: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Panuzzo, C.; Ulisciani, S.; Cilloni, D. Imatinib Resistance in CML. Cancer Lett. 2009, 274, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carofiglio, F.; Lopalco, A.; Lopedota, A.; Cutrignelli, A.; Nicolotti, O.; Denora, N.; Stefanachi, A.; Leonetti, F. Bcr-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Pediatric CML. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavalerchik, E.; Goff, D.; Jamieson, C.H.M. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2911–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.V.; He, S.; Bydon, M.; Morrison, S.J.; Pardal, R. Bmi-1 Promotes Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Neural Development but Not Mouse Growth and Survival by Repressing the P16 Ink4a and P19 Arf Senescence Pathways. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, D.; Hüser, L.; Elton, J.J.; Umansky, V.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J. SOX2 in Development and Cancer Biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 67, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusa, I.; Cheloni, G.; Poteti, M.; Silvano, A.; Tubita, A.; Lombardi, Z.; Gozzini, A.; Caporale, R.; Scappini, B.; Dello Sbarba, P.; et al. In Vitro Comparison of the Effects of Imatinib and Ponatinib on Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Progenitor/Stem Cell Features. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Radaeva, M.; Cherkasov, A.; Dong, X. Lin28 Regulates Cancer Cell Stemness for Tumour Progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wen, L.; Dong, J.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Liang, T.; Li, T.; Xia, Z.; Chen, C. Alterations in Cellular Metabolisms after TKI Therapy for Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemia in Children: A Review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1072806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Sheth, V.; Yan, C.; Liu, J.; Chacko, B.K.; Li, H.; Crossman, D.K.; Fortmann, S.D.; Aryal, S.; Rennhack, A.; et al. Metabolic Adaptation to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Leukemia Stem Cells. Blood 2023, 142, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostazo, M.G.C.; Kurrle, N.; Casado, M.; Fuhrmann, D.; Alshamleh, I.; Häupl, B.; Martín-Sanz, P.; Brüne, B.; Serve, H.; Schwalbe, H.; et al. Metabolic Plasticity Is an Essential Requirement of Acquired Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattigan, K.M.; Brabcova, Z.; Sarnello, D.; Zarou, M.M.; Roy, K.; Kwan, R.; de Beauchamp, L.; Dawson, A.; Ianniciello, A.; Khalaf, A.; et al. Pyruvate Anaplerosis Is a Targetable Vulnerability in Persistent Leukaemic Stem Cells. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panuzzo, C.; Pironi, L.; Maglione, A.; Rocco, S.; Stanga, S.; Riganti, C.; Kopecka, J.; Ali, M.S.; Pergolizzi, B.; Bracco, E.; et al. mTORC2 Is Activated under Hypoxia and Could Support Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; Panuzzo, C.; Stanga, S.; Andreani, G.; Ravera, S.; Maglione, A.; Pironi, L.; Petiti, J.; Shahzad Ali, M.; Scaravaglio, P.; et al. Deferasirox-Dependent Iron Chelation Enhances Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Restores P53 Signaling by Stabilization of P53 Family Members in Leukemic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatshoar, Y.; Karadag Gurel, A.; Ozkan, T.; Rahbar Saadat, Y.; Koc, A.; Karabay, A.Z.; Bozkurt, S.; Sunguroglu, A. Phenotypic and Functional Characterization of Subpopulation of Imatinib Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cell Line. Adv. Med. Sci. 2023, 68, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Castañeda, E.; Hopcroft, L.; Rogers, S.; Munje, C.; Bittencourt-Silvestre, J.; Copland, M.; Vetrie, D.; Holyoake, T.; Jørgensen, H. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Independent Gene Expression Signature in CML Offers New Targets for LSPC Eradication Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and Collaborative HTML5 Gene List Enrichment Analysis Tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetti, S.; Cesaro, E.; Catapano, R.; Sessa, R.; Lo Bianco, A.; Izzo, P.; Grosso, M. Oxidative Stress and ROS-Mediated Signaling in Leukemia: Novel Promising Perspectives to Eradicate Chemoresistant Cells in Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykal-Köse, S.; Acikgoz, E.; Yavuz, A.S.; Gönül Geyik, Ö.; Ateş, H.; Sezerman, O.U.; Özsan, G.H.; Yüce, Z. Adaptive Phenotypic Modulations Lead to Therapy Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shi, G.; Zhang, L.; Guan, F.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q.; Cong, Y.-S.; Zhang, L. Cav-1 Deletion Impaired Hematopoietic Stem Cell Function. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Hope, K.J.; Zhai, Q.; Smadja-Joffe, F.; Dick, J.E. Targeting of CD44 Eradicates Human Acute Myeloid Leukemic Stem Cells. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuzzo, C.; Jovanovski, A.; Pergolizzi, B.; Pironi, L.; Stanga, S.; Fava, C.; Cilloni, D. Mitochondria: A Galaxy in the Hematopoietic and Leukemic Stem Cell Universe. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoake, T.L.; Vetrie, D. The Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cell: Stemming the Tide of Persistence. Blood 2017, 129, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.M.; Masszi, T.; Gómez Casares, M.T.; Hellmann, A.; Stentoft, J.; Conneally, E.; Garcia-Gutierrez, V.; Gattermann, N.; le Coutre, P.D.; Martino, B.; et al. Durable Treatment-Free Remission in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase Following Frontline Nilotinib: 96-Week Update of the ENESTfreedom Study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.M.; Hughes, T.P. Treatment-Free Remission in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, E.; Schiffer, C.A. Discontinuation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: When and for Whom? Haematologica 2020, 105, 2738–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lin, B.; Zhao, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Gao, A.; Liu, F.; Que, J.; Lan, X. The Multiple Roles for Sox2 in Stem Cell Maintenance and Tumorigenesis. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.A.; Mannoor, K.; Cao, J.; Qadri, F.; Song, X. SOX2 in Cancer Stemness: Tumor Malignancy and Therapeutic Potentials. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Kim, D.K.; Jang, I.H.; Choi, E.J.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, S.I.; Kwon, S.-M.; Kim, K.-H.; Suh, D.-S.; Kim, J.H. Hypoxia-NOTCH1-SOX2 Signaling Is Important for Maintaining Cancer Stem Cells in Ovarian Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55624–55638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, S.; Khaled, O.; Menshawy, N.E.; Azmy, E.; Aref, M.; Salama, O.; Khaled, N. Significance of OCT3/4 and SOX2 Antigens Expression by Leukemic Blast Cells in Adult Acute Leukemia. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2024, 36, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosic, N.; Petrovic, I.; Grujicic, N.K.; Davidovic, S.; Virijevic, M.; Vukovic, N.S.; Pavlovic, S.; Stevanovic, M. Prognostic Significance of SOX2, SOX3, SOX11, SOX14 and SOX18 Gene Expression in Adult de Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2018, 67, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, T.; Aanei, C.M.; Fayard, A.; Flandrin-Gresta, P.; Tondeur, S.; Gouttenoire, M.; Tavernier-Tardy, E.; Wattel, E.; Guyotat, D.; Campos, L. Expression of Embryonic Stem Cell Markers in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 101042831771662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliaro, S.; Desterke, C.; Acloque, H.; Bennaceur-Griscelli, A.; Turhan, A.G. Single Cell Transcriptome in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Pseudotime Analysis Reveals a Rare Population with Embryonic Stem Cell Features and Druggable Intricated Transitional Stem Cell States. Blood 2018, 132, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.-J.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.-Q.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.-Y.; Tin, V.P.-C.; Qin, J.; Wang, J.-W.; Wong, M.P. NFATc2 Enhances Tumor-Initiating Phenotypes through the NFATc2/SOX2/ALDH Axis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. eLife 2017, 6, e26733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chung, Y.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Yang, T.-J.; Fang, J.-M.; Hu, C.-M.; Chang, Z.-F. Glutathione Determines Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Vulnerability to an Inhibitor of CMPK and TMPK. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.B.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; Welner, R.S. Deciphering Metabolic Adaptability of Leukemic Stem Cells. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 846149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griessinger, E.; Pereira-Martins, D.; Nebout, M.; Bosc, C.; Saland, E.; Boet, E.; Sahal, A.; Chiche, J.; Debayle, D.; Fleuriot, L.; et al. Oxidative Phosphorylation Fueled by Fatty Acid Oxidation Sensitizes Leukemic Stem Cells to Cold. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Adane, B.; Khan, N.; Sullivan, T.; Minhajuddin, M.; Gasparetto, M.; Stevens, B.; Pei, S.; Balys, M.; Ashton, J.M.; et al. Leukemic Stem Cells Evade Chemotherapy by Metabolic Adaptation to an Adipose Tissue Niche. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Chapple, R.H.; Lin, A.; Kitano, A.; Nakada, D. AMPK Protects Leukemia-Initiating Cells in Myeloid Leukemias from Metabolic Stress in the Bone Marrow. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.E.; Eom, J.-I.; Jeung, H.-K.; Cheong, J.-W.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Min, Y.H. AMPK–ULK1-Mediated Autophagy Confers Resistance to BET Inhibitor JQ1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boët, E.; Sarry, J.-E. Targeting Metabolic Dependencies Fueling the TCA Cycle to Circumvent Therapy Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Hou, Y. Targeting Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation Eradicates Acute Myeloid Leukemic Stem Cells. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 899502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Liu, W.; Xiao, X.; Gajendran, B.; Ben-David, Y. Targeting Pivotal Amino Acids Metabolism for Treatment of Leukemia. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.L.; Stevens, B.M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Reisz, J.A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Nemkov, T.; Pei, S.; Khan, N.; Adane, B.; Ye, H.; et al. Inhibition of Amino Acid Metabolism Selectively Targets Human Leukemia Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 724–740.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S. Recruiting TP53 to Target Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1172–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-H.; Qi, J.; Cook, G.J. Regain Control of P53: Targeting Leukemia Stem Cells by Isoform-Specific HDAC Inhibition. Exp. Hematol. 2016, 44, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Liu, Y.; Bae, N.; Nimer, S.D. The P53 Tumor Suppressor Protein Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Fate. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.T.; Liu, W.; Mitchell, R.; Clarke, C.; Almasoudi, H.; Warren, F.; Kinstrie, R.; Dunn, K.; Pritchard, J.; Drotar, M.E.; et al. Uncoupling P53 from an Embryonic Regulome Exhausts Quiescent CML Stem Cells through Inhibition of a HIF1alpha Molecular Program. Blood 2021, 138, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshmand, M.; Kazemi, A.; Anjam Najmedini, A.; Ali, M.S.; Gaidano, V.; Cignetti, A.; Fava, C.; Cilloni, D.; Saglio, G.; Circosta, P. Shedding Light on Targeting Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Kong, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K.; Qin, X.; Miao, Z.-H.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, W. Multi-Drug–Resistant Cells Enriched From Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells by Doxorubicin Possess Tumor-Initiating–Cell Properties. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 122, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocco, S.; Maglione, A.; Schiavo, V.; Ferrando, A.; Fava, C.; Cilloni, D.; Pergolizzi, B.; Panuzzo, C. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Enhances Stem Cells Profile and May Contribute to Survival of Chronic Myeloid Leukemiastem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020392
Rocco S, Maglione A, Schiavo V, Ferrando A, Fava C, Cilloni D, Pergolizzi B, Panuzzo C. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Enhances Stem Cells Profile and May Contribute to Survival of Chronic Myeloid Leukemiastem Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020392
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocco, Simone, Alessandro Maglione, Valentina Schiavo, Alessandro Ferrando, Carmen Fava, Daniela Cilloni, Barbara Pergolizzi, and Cristina Panuzzo. 2025. "Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Enhances Stem Cells Profile and May Contribute to Survival of Chronic Myeloid Leukemiastem Cells" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020392
APA StyleRocco, S., Maglione, A., Schiavo, V., Ferrando, A., Fava, C., Cilloni, D., Pergolizzi, B., & Panuzzo, C. (2025). Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Enhances Stem Cells Profile and May Contribute to Survival of Chronic Myeloid Leukemiastem Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020392







