Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat in Patients with CKD: Pooled Analysis by Baseline Inflammation Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
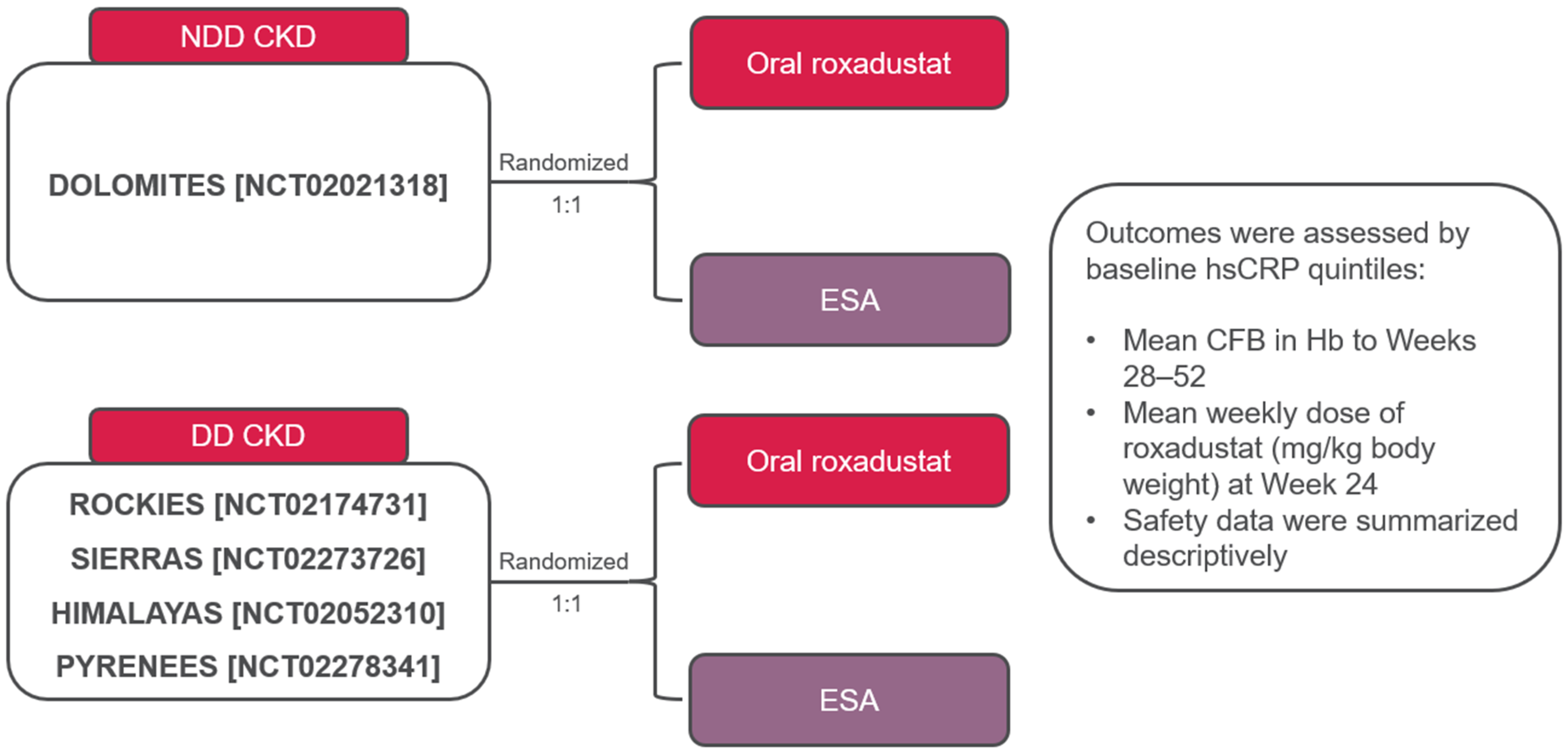
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02021318 (accessed on 19 December 2024)
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02174731 (accessed on 19 December 2024)
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02273726 (accessed on 19 December 2024)
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02052310 (accessed on 19 December 2024)
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02278341 (accessed on 19 December 2024)
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Baseline Disease Characteristics
3.2. Efficacy Outcomes
3.3. Iron Parameters
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Trial Registration Numbers
References
- Nakhoul, G.; Simon, J.F. Anemia of chronic kidney disease: Treat it, but not too aggressively. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Fishbane, S.; Block, G.A.; Macdougall, I.C. Targeting hypoxia-inducible factors for the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrieva, O.; de Lusignan, S.; Macdougall, I.C.; Gallagher, H.; Tomson, C.; Harris, K.; Desombre, T.; Goldsmith, D. Association of anaemia in primary care patients with chronic kidney disease: Cross sectional study of quality improvement in chronic kidney disease (QICKD) trial data. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, L.; Locatelli, F. An overview on safety issues related to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for the treatment of anaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KDIGO Anemia Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 279–335. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, F.; Del Vecchio, L.; Elliott, S. The anaemia treatment journey of CKD patients: From epoetins to hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, B.D.; Critchlow, C.W.; Weir, M.R.; Stewart, R.; Krishnan, M.; Hakim, R.H. Impact of elevated C-reactive protein levels on erythropoiesis- stimulating agent (ESA) dose and responsiveness in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 24, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Olszewski, R.; Rysz, J. The influence of inflammation on anemia in CKD patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xu, G. A novel choice to correct inflammation-induced anemia in CKD: Oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jensen, D.E.; Maroni, B.J.; Brunelli, S.M. Spectrum and burden of erythropoiesis-stimulating agent hyporesponsiveness among contemporary hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.; Gaete, D.; Rodriguez, D.; Hoogewijs, D.; Rauner, M.; Sormendi, S.; Wielockx, B. Hypoxia pathway proteins are master regulators of erythropoiesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, V.H. Hypoxia-inducible factor-proyl hydroxylase inhibitors in the treatment of anemia of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2021, 11, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Wish, J.B. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors: A potential new treatment for anemia in patients with CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T. Hepcidin and iron regulation, 10 years later. Blood 2011, 117, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Besarab, A.; Wright, S.; Dua, S.; Zeig, S.; Nguyen, P.; Poole, L.; Saikali, K.G.; Saha, G.; Hemmerich, S.; et al. Roxadustat (FG-4592) versus epoetin alfa for anemia in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: A phase 2, randomized, 6- to 19-week, open-label, active-comparator, dose-ranging, safety and exploratory efficacy study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, A.; Samouda, H.; Dohet, F.; Loap, S.; Ellulu, M.S.; Bohn, T. Common and novel markers for measuring inflammation and oxidative stress ex vivo in research and clinical practice—Which to use regarding disease outcomes? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Andric, B.; Tataradze, A.; Schömig, M.; Reusch, M.; Valluri, U.; Mariat, C. Roxadustat for the treatment of anaemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: A Phase 3, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (DOLOMITES). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1616–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbane, S.; Pollock, C.A.; El-Shahawy, M.; Escudero, E.T.; Rastogi, A.; Van, B.P.; Frison, L.; Houser, M.; Pola, M.; Little, D.J.; et al. Roxadustat versus epoetin alfa for treating anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis: Results from the randomized phase 3 ROCKIES study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charytan, C.; Manllo-Karim, R.; Martin, E.R.; Steer, D.; Bernardo, M.; Dua, S.L.; Moustafa, M.A.; Saha, G.; Bradley, C.; Eyassu, M.; et al. A randomized trial of roxadustat in anemia of kidney failure: SIERRAS Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Shutov, E.; Eremeeva, L.; Korneyeva, S.; Poole, L.; Saha, G.; Bradley, C.; Eyassu, M.; Besarab, A.; Leong, R.; et al. Roxadustat for anemia in patients with end-stage renal disease incident to dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiky, B.; Schomig, M.; Esposito, C.; Barratt, J.; Reusch, M.; Valluri, U.; Sulowicz, W. Roxadustat for the maintenance treatment of anemia in patients with end-stage kidney disease on stable dialysis: A European phase 3, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (PYRENEES). Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5361–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Locatelli, F.; Arici, M.; Akizawa, T.; Reusch, M. Iron parameters in patients treated with roxadustat for anemia of chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.W.; Pollock, C.A.; Macdougall, I.C. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent hyporesponsiveness. Nephrology 2007, 12, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akizawa, T.; Ueno, M.; Shiga, T.; Reusch, M. Oral roxadustat three times weekly in ESA-naïve and ESA-converted patients with anemia of chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis: Results from two phase 3 studies. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2020, 24, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Tanaka-Amino, K.; Otsuka, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. Factors affecting doses of roxadustat versus darbepoetin alfa for anemia in nondialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Majikawa, Y.; Reusch, M. Factors affecting the doses of roxadustat vs darbepoetin alfa for anemia treatment in hemodialysis patients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021, 25, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wei, X.; Long, M.; Du, Y. Roxadustat: Not just for anemia. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 971795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, J.W. The anemia of chronic renal failure: Pathophysiology and the effects of recombinant erythropoietin. Kidney Int. 1989, 35, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, P.E.; Charytan, C.; Little, D.J.; Tham, S.; Szczech, L.; Leong, R.; Fishbane, S. Changes in iron availability with roxadustat in nondialysis- and dialysis-dependent patients with anemia of CKD. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1511–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Dellanna, F.; Portoles, J.; Choukroun, G.; De Nicola, L.; Young, J.; Dimković, N.; Reusch, M. Safety of roxadustat versus erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in patients with anemia of non-dialysis-dependent or incident-to-dialysis chronic kidney disease: Pooled analysis of four phase 3 studies. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 1546–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.; Sulowicz, W.; Schomig, M.; Esposito, C.; Reusch, M.; Young, J.; Csiky, B. Efficacy and cardiovascular safety of roxadustat in dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: Pooled analysis of four phase 3 studies. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5345–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minutolo, R.; Liberti, M.E.; Simeon, V.; Sasso, F.C.; Borrelli, S.; De Nicola, L.; Garofalo, C. Efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease: Meta-analysis of phase 3 randomized controlled trials. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 17, sfad143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quencer, K.B.; Oklu, R. Hemodialysis access thrombosis. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 7, S299–S308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astellas Pharma Europe. Evrenzo [Summary of Product Characteristics]; Astellas Pharma Europe: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; McMahon, L.P.; Hao, C.M.; Hu, N.; Okada, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kim, S.G.; Lim, S.K.; Vareesangthip, K.; Hung, C.-C.; et al. Recommendations by the Asian Pacific society of nephrology (APSN) on the appropriate use of HIF-PH inhibitors. Nephrology 2021, 26, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoumpos, S.; Crowe, K.; Sarafidis, P.; Barratt, J.; Bolignano, D.; Del Vecchio, L.; Małyszko, J.; Więcek, A.; Ortiz, A.; Cozzolino, M. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for anaemia in chronic kidney disease: A clinical practice document by the European Renal Best Practice board of the European Renal Association. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 1710–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Oliveira, B.; Spencer, S.; Mikhail, A.; Brooks, O.; Bryant, G.; Willicombe, M.; Baines, R.; Alldridge, L.; Haslam, S. Clinical Practice Guideline: Anaemia of Chronic Kidney Disease; United Kingdom Kidney Association: Bristol, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, F.; Ravera, M.; Esposito, C.; Grandaliano, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Minutolo, R. A novel scenario in the therapeutic management of anemia of chronic kidney disease: Placement and use of roxadustat. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.T.; Willox, G.P.; Jhund, P.S.; Hawkins, N.M.; Huang, F.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J. Reporting of lost to follow-up and treatment discontinuation in pharmacotherapy and device trials in chronic heart failure: A systematic review. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e002842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| hsCRP Q1 ≤0.88 mg/L | hsCRP Q2 >0.88–≤2.09 mg/L | hsCRP Q3 >2.09–≤4.39 mg/L | hsCRP Q4 >4.39–≤11.43 mg/L | hsCRP Q5 >11.43 mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roxadustat n = 71 | ESA n = 53 | Roxadustat n = 66 | ESA n = 55 | Roxadustat n = 63 | ESA n = 59 | Roxadustat n = 59 | ESA n = 64 | Roxadustat n = 61 | ESA n = 61 | |
| Ferritin (µg/L) | ||||||||||
| n | 69 | 51 | 65 | 55 | 59 | 57 | 55 | 61 | 59 | 56 |
| Baseline, mean | 229.65 | 184.67 | 200.36 | 194.73 | 203.24 | 213.77 | 274.44 | 243.50 | 270.54 | 268.82 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | −20.54 (17.55) | −44.31 (19.73) | −52.95 (11.85) | −42.13 (12.76) | −33.30 (14.48) | −14.36 (15.31) | −60.37 (21.54) | −39.91 (20.76) | −53.11 (26.73) | −65.18 (26.48) |
| 95% CI | −54.94, 13.85 | −82.98, −5.64 | −76.17, −29.73 | −67.13, −17.12 | −61.69, −4.92 | −44.37, 15.64 | −102.59, −18.16 | −80.60, 0.79 | −105.49, −0.72 | −11.7.08, −13.29 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | 23.77 (−28.08, 75.63) | −10.83 (−44.98, 23.33) | −18.94 (−60.62, 22.74) | −20.47 (−79.52, 38.59) | 12.07 (−62.01, 86.16) | |||||
| p value | 0.369 | 0.534 | 0.373 | 0.497 | 0.749 | |||||
| Serum iron (µg/dL) | ||||||||||
| n | 69 | 51 | 65 | 55 | 59 | 57 | 55 | 61 | 59 | 56 |
| Baseline, mean | 71.34 | 71.03 | 74.36 | 64.85 | 64.37 | 63.26 | 58.58 | 56.46 | 44.71 | 45.25 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | 6.49 (3.53) | 13.13 (4.31) | 4.27 (3.09) | −0.08 (3.22) | 7.47 (2.85) | 5.67 (2.97) | 11.12 (3.37) | 13.76 (3.14) | 13.51 (3.38) | 20.30 (3.30) |
| 95% CI | −0.43, 13.41 | 4.68, 21.58 | −1.78, 10.32 | −6.39, 6.24 | 1.88, 13.06 | −0.15, 11.49 | 4.51, 17.72 | 7.60, 19.91 | 6.88, 20.15 | 13.83, 26.78 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | −6.65 (−17.51, 4.21) | 4.34 (−4.52, 13.21) | 1.80 (−6.30, 9.89) | −2.64 (−11.79, 6.52) | −6.79 (−16.17, 2.59) | |||||
| p value | 0.230 | 0.337 | 0.663 | 0.572 | 0.156 | |||||
| TSAT (%) | ||||||||||
| n | 69 | 51 | 65 | 55 | 59 | 57 | 55 | 61 | 59 | 56 |
| Baseline, mean | 26.91 | 27.29 | 27.57 | 25.25 | 24.00 | 24.19 | 22.95 | 21.85 | 18.14 | 18.13 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | 1.03 (1.13) | 4.63 (1.33) | 0.39 (1.12) | 1.49 (1.18) | 0.85 (1.15) | 2.58 (1.17) | 1.76 (1.08) | 5.62 (1.02) | 3.40 (1.36) | 7.58 (1.33) |
| 95% CI | −1.18, 3.24 | 2.03, 7.23 | −1.81, 2.59 | −0.82, 3.80 | −1.41, 3.10 | 0.28, 4.88 | −0.36, 3.88 | 3.61, 7.62 | 0.73, 6.07 | 4.97, 10.18 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | −3.61 (−7.01, −0.20) | −1.10 (−4.30, 2.10) | −1.73 (−4.97, 1.51) | −3.86 (−6.83, −0.89) | −4.18 (−7.94, −0.42) | |||||
| p value | 0.038 | 0.501 | 0.295 | 0.011 | 0.029 | |||||
| hsCRP Q1 ≤1.4 mg/L | hsCRP Q2 >1.4–≤2.97 mg/L | hsCRP Q3 >2.97–≤5.98 mg/L | hsCRP Q4 >5.98–≤13.545 mg/L | hsCRP Q5 >13.545 mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roxadustat n = 405 | ESA n = 413 | Roxadustat n = 411 | ESA n = 402 | Roxadustat n = 373 | ESA n = 440 | Roxadustat n = 433 | ESA n = 381 | Roxadustat n = 400 | ESA n = 414 | |
| Ferritin (µg/L) | ||||||||||
| n | 390 | 404 | 391 | 391 | 347 | 407 | 398 | 354 | 349 | 368 |
| Baseline, mean | 534.03 | 533.29 | 549.00 | 570.03 | 596.13 | 659.16 | 649.34 | 684.33 | 733.24 | 682.07 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | −189.70 (16.07) | −98.38 (16.18) | −215.23 (17.16) | −130.62 (16.95) | −208.58 (19.90) | −163.01 (19.55) | −205.73 (20.49) | −142.76 (21.20) | −257.78 (27.04) | −177.08 (25.82) |
| 95% CI | −221.19, −158.20 | −130.10, −66.65 | −248.86, −181.60 | −163.86, −97.39 | −247.60, −169.57 | −201.34, −124.69 | −245.90, −165.55 | −184.32, −101.21 | −310.80, −204.76 | −227.69, −126.47 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | −91.32 (−129.56, −53.08) | −84.60 (−125.16, −44.05) | −45.57 (−91.31, 0.18) | −62.97 (−108.56, −17.37) | −80.71 (−141.27, −20.14) | |||||
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.051 | 0.007 | 0.009 | |||||
| Serum iron (µg/dL) | ||||||||||
| n | 390 | 404 | 391 | 391 | 347 | 407 | 398 | 354 | 349 | 368 |
| Baseline, mean | 83.86 | 81.62 | 73.74 | 71.65 | 69.46 | 71.30 | 63.79 | 66.48 | 58.74 | 57.07 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | −3.74 (1.92) | −17.29 (1.74) | 1.38 (1.83) | −9.11 (1.67) | 2.74 (1.99) | −8.88 (1.78) | 7.07 (1.87) | −2.23 (1.84) | 7.60 (1.97) | −1.45 (1.78) |
| 95% CI | −7.50, 0.02 | −20.70, −13.88 | −2.21, 4.97 | −12.39, −5.83 | −1.16, 6.65 | −12.36, −5.41 | 3.40, 10.74 | −5.84, 1.37 | 3.75, 11.46 | −4.94, 2.03 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | 13.55 (9.28, 17.82) | 10.49 (6.34, 14.64) | 11.63 (7.35, 15.90) | 9.31 (5.29, 13.33) | 9.06 (4.88, 13.23) | |||||
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| TSAT (%) | ||||||||||
| n | 390 | 404 | 389 | 389 | 347 | 407 | 398 | 353 | 349 | 368 |
| Baseline, mean | 37.40 | 36.54 | 33.42 | 32.95 | 32.71 | 33.86 | 30.74 | 31.52 | 29.45 | 28.01 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | −6.64 (0.71) | −7.45 (0.66) | −5.06 (0.71) | −4.39 (0.69) | −4.97 (0.71) | −5.60 (0.67) | −2.15 (0.77) | −2.80 (0.75) | −2.29 (0.78) | −2.68 (0.71) |
| 95% CI | −8.03, −5.24 | −8.73, −6.16 | −6.46, −3.66 | −5.74, −3.05 | −6.36, −3.58 | −6.91, −4.29 | −3.65, −0.64 | −4.27, −1.33 | −3.82, −0.77 | −4.08, −1.29 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | 0.81 (−0.75, 2.37) | −0.67 (−2.30, 0.96) | 0.63 (−0.96, 2.22) | 0.65 (−0.99, 2.30) | 0.39 (−1.32, 2.10) | |||||
| p value | 0.307 | 0.422 | 0.440 | 0.438 | 0.653 | |||||
| Hepcidin (ng/mL) | ||||||||||
| n | 375 | 386 | 391 | 382 | 346 | 412 | 393 | 355 | 347 | 363 |
| Baseline, mean | 186.21 | 185.89 | 187.17 | 181.32 | 200.31 | 204.27 | 196.84 | 212.14 | 258.77 | 238.15 |
| Adjusted LS mean change (SE) | −47.02 (6.15) | −23.31 (6.20) | −42.50 (5.29) | −23.09 (5.54) | −52.72 (6.91) | −32.80 (6.49) | −43.29 (6.94) | −22.46 (7.11) | −90.25 (7.64) | −72.34 (7.00) |
| 95% CI | −59.07, −34.97 | −35.46, −11.17 | −52,87, −32.13 | −33.96, −12.23 | −66.15, −39.08 | −45.53, −20.08 | −56.90, −29.68 | −36.39, −8.53 | −105.23, −75.28 | −86.05, −58.62 |
| LSMD (95% CI) | −23.71 (−38.90, −8.51) | −19.40 (−32.77, −6.04) | −19.81 (−35.49, −4.13) | −20.83 (−37.08, −4.59) | −17.91 (−35.12, −0.71) | |||||
| p value | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.041 | |||||
| hsCRP Q1 ≤0.88 mg/L | hsCRP Q2 >0.88–≤2.09 mg/L | hsCRP Q3 >2.09–≤4.39 mg/L | hsCRP Q4 >4.39–≤11.43 mg/L | hsCRP Q5 >11.43 mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roxadustat n = 71 | ESA n = 53 | Roxadustat n = 66 | ESA n = 56 | Roxadustat n = 63 | ESA n = 59 | Roxadustat n = 59 | ESA n = 64 | Roxadustat n = 61 | ESA n = 61 | |
| TEAE | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 67 (94.4) | 46 (86.6) | 59 (89.4) | 54 (96.4) | 56 (88.9) | 53 (89.8) | 57 (96.6) | 61 (95.3) | 56 (91.8) | 57 (93.4) |
| PY a; FAIR | 25.2; 266.4 | 26.0; 176.7 | 30.6; 193.1 | 22.5; 240.1 | 22.8; 245.9 | 25.0; 212.2 | 14.9; 383.3 | 27.3; 223.3 | 17.5; 319.5 | 20.6; 276.7 |
| Serious TEAE | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 51 (71.8) | 26 (49.1) | 35 (53.0) | 37 (66.1) | 34 (54.0) | 30 (50.8) | 44 (74.6) | 45 (70.3) | 44 (72.1) | 43 (70.5) |
| PY a; FAIR | 80.1; 63.7 | 69.1; 37.6 | 81.4; 43.0 | 65.9; 56.1 | 77.4; 43.9 | 75.3; 39.8 | 51.6; 85.3 | 70.4; 63.9 | 48.3; 91.0 | 63.1; 68.2 |
| TEAE leading to discontinuation of study drug b | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 8 (11.3) | 0 (0) | 5 (7.6) | 2 (3.6) | 3 (4.8) | 1 (1.7) | 4 (6.8) | 6 (9.4) | 5 (8.2) | 2 (3.3) |
| PY a; FAIR | 121.8; 6.6 | 92.8; 0.0 | 115.3; 4.3 | 104.2; 1.9 | 104.4; 2.9 | 99.8; 1.0 | 101.4; 3.9 | 109.0; 5.5 | 90.9; 5.5 | 99.1; 2.0 |
| Grade ≥3 TEAE | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 42 (59.2) | 23 (43.4) | 32 (48.5) | 32 (57.1) | 29 (46.0) | 29 (49.2) | 39 (66.1) | 43 (67.2) | 38 (62.3) | 37 (60.7) |
| PY a; FAIR | 88.7; 47.4 | 74.6; 30.8 | 88.1; 36.3 | 71.0; 45.1 | 85.4; 34.0 | 74.5; 38.9 | 58.7; 66.4 | 73.4; 58.6 | 59.1; 64.3 | 71.2; 52.0 |
| TEAE leading to death | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 4 (5.6) | 4 (7.5) | 3 (4.5) | 1 (1.8) | 4 (6.3) | 4 (6.8) | 8 (13.6) | 11 (17.2) | 11 (18.0) | 11 (18.0) |
| PY a; FAIR | 122.6; 3.3 | 92.8; 4.3 | 117.6; 2.6 | 104.4; 1.0 | 104.6; 3.8 | 99.9; 4.0 | 101.6; 7.9 | 109.9; 10.0 | 91.6; 12.0 | 99.4; 11.1 |
| hsCRP Q1 ≤0.88 mg/L | hsCRP Q2 >0.88–≤2.09 mg/L | hsCRP Q3 >2.09–≤4.39 mg/L | hsCRP Q4 >4.39–≤11.43 mg/L | hsCRP Q5 >11.43 mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEAE, n (%) PY a; FAIR | Roxadustat n = 71 | ESA n = 53 | Roxadustat n = 66 | ESA n = 56 | Roxadustat n = 63 | ESA n = 59 | Roxadustat n = 59 | ESA n = 64 | Roxadustat n = 61 | ESA n = 61 |
| Overall TEAEs | 67 (94.4) 25.2; 266.4 | 46 (86.8) 26.0; 176.7 | 59 (89.4) 30.6; 193.1 | 54 (96.4) 22.5; 240.1 | 56 (88.9) 22.8; 245.9 | 53 (89.8) 25.0; 212.2 | 57 (96.6) 14.9; 383.3 | 61 (95.3) 27.3; 223.3 | 56 (91.8) 17.5; 319.5 | 57 (93.4) 20.6; 276.7 |
| Anemia | 3 (4.2) 120.5; 2.5 | 3 (5.7) 89.0; 3.4 | 3 (4.5) 114.5; 2.6 | 4 (7.1) 101.9; 3.9 | 2 (3.2) 103.8; 1.9 | 2 (3.4) 98.0; 2.0 | 2 (3.4) 101.4; 2.0 | 3 (4.7) 108.8; 2.8 | 4 (6.6) 88.5; 4.5 | 7 (11.5) 95.3; 7.3 |
| Cardiac failure | 4 (5.6) 118.1; 3.4 | 2 (3.8) 92.4; 2.2 | 1 (1.5) 116.9; 0.9 | 4 (7.1) 101.9; 3.9 | 5 (7.9) 101.1; 5.0 | 3 (5.1) 96.7; 3.1 | 6 (10.2) 96.2; 6.2 | 1 (1.6) 109.7; 0.9 | 2 (3.3) 90.5; 2.2 | 8 (13.1) 96.1; 8.3 |
| Constipation | 4 (5.6) 118.1; 3.4 | 3 (5.7) 88.9; 3.4 | 3 (4.5) 113.8; 2.6 | 3 (5.4) 102.6; 2.9 | 3 (4.8) 101.7; 2.9 | 4 (6.8) 95.0; 4.2 | 8 (13.6) 93.5; 8.6 | 1 (1.6) 108.0; 0.9 | 3 (4.9) 89.8; 3.3 | 4 (6.6) 93.7; 4.3 |
| Diarrhea | 4 (5.6) 117.0; 3.4 | 5 (9.4) 86.3; 5.8 | 4 (6.1) 110.7; 3.6 | 2 (3.6) 102.8; 1.9 | 6 (9.5) 94.3; 6.4 | 10 (16.9) 90.4; 11.1 | 6 (10.2) 95.3; 6.3 | 5 (7.8) 106.0; 4.7 | 8 (13.1) 86.0; 9.3 | 8 (13.1) 90.4; 8.8 |
| Nausea | 7 (9.9) 114.6; 6.1 | 2 (3.8) 91.3; 2.2 | 6 (9.1) 111.9; 5.4 | 7 (12.5) 98.6; 7.1 | 4 (6.3) 99.5; 4.0 | 8 (13.6) 91.2; 8.8 | 9 (15.3) 92.9; 9.7 | 5 (7.8) 104.9; 4.8 | 9 (14.8) 85.9; 10.5 | 3 (4.9) 95.9; 3.1 |
| Vomiting | 0 (0) 122.6; 0.0 | 1 (1.9) 91.9; 1.1 | 2 (3.0) 116.8; 1.7 | 6 (10.7) 97.5; 6.2 | 3 (4.8) 99.8; 3.0 | 7 (11.9) 91.9; 7.6 | 8 (13.6) 93.4; 8.6 | 5 (7.8) 105.5; 4.7 | 8 (13.1) 83.8; 9.5 | 0 (0) 99.4; 0.0 |
| Asthenia | 2 (2.8) 120.8; 1.7 | 1 (1.9) 91.0; 1.1 | 2 (3.0) 115.8; 1.7 | 0 (0) 104.4; 0.0 | 4 (6.3) 100.5; 4.0 | 2 (3.4) 97.2; 2.1 | 2 (3.4) 98.1; 2.0 | 7 (10.9) 101.7; 6.9 | 1 (1.6) 89.8; 1.1 | 1 (1.6) 98.1; 1.0 |
| Edema, peripheral | 13 (18.3) 107.4; 12.1 | 5 (9.4) 86.7; 5.8 | 10 (15.2) 104.9; 9.5 | 8 (14.3) 95.0; 8.4 | 5 (7.9) 99.4; 5.0 | 7 (11.9) 91.6; 7.6 | 9 (15.3) 90.0; 10.0 | 7 (10.9) 101.0; 6.9 | 12 (19.7) 78.7; 15.2 | 9 (14.8) 85.7; 10.5 |
| Bronchitis | 5 (7.0) 118.7; 4.2 | 4 (7.5) 88.2; 4.5 | 2 (3.0) 114.1; 1.8 | 3 (5.4) 101.8; 2.9 | 5 (7.9) 97.6; 5.1 | 3 (5.1) 96.8; 3.1 | 6 (10.2) 94.6; 6.3 | 2 (3.1) 108.2; 1.8 | 4 (6.6) 85.6; 4.7 | 6 (9.8) 92.0; 6.5 |
| Pneumonia | 4 (5.6) 119.4; 3.3 | 3 (5.7) 90.7; 3.3 | 3 (4.5) 115.8; 2.6 | 5 (8.9) 101.5; 4.9 | 4 (6.3) 103.6; 3.9 | 2 (3.4) 98.9; 2.0 | 5 (8.5) 99.6; 5.0 | 5 (7.8) 108.2; 4.6 | 9 (14.8) 84.5; 10.6 | 7 (11.5) 95.1; 7.4 |
| Urinary tract infection | 3 (4.2) 120.4; 2.5 | 2 (3.8) 91.7; 2.2 | 4 (6.1) 114.5; 3.5 | 3 (5.4) 102.1; 2.9 | 6 (9.5) 99.4; 6.0 | 6 (10.2) 95.2; 6.3 | 4 (6.8) 99.6; 4.0 | 4 (6.3) 107.5; 3.7 | 4 (6.6) 88.6; 4.5 | 12 (19.7) 87.3; 13.7 |
| Viral upper respiratory tract infection | 7 (9.9) 116.8; 6.0 | 3 (5.7) 90.6; 3.3 | 5 (7.6) 112.4; 4.4 | 6 (10.7) 96.2; 6.2 | 3 (4.8) 100.3; 3.0 | 6 (10.2) 88.8; 6.8 | 8 (13.6) 91.4; 8.7 | 6 (9.4) 104.3; 5.8 | 6 (9.8) 84.5; 7.1 | 4 (6.6) 94.2; 4.2 |
| Arteriovenous fistula thrombosis | 3 (4.2) 121.2; 2.5 | 2 (3.8) 91.6; 2.2 | 2 (3.0) 115.7; 1.7 | 3 (5.4) 101.1; 3.0 | 2 (3.2) 102.4; 2.0 | 0 (0) 99.9; 0.0 | 8 (13.6) 95.1; 8.4 | 3 (4.7) 108.2; 2.8 | 1 (1.6) 91.3; 1.1 | 2 (3.3) 98.1; 2.0 |
| Fall | 3 (4.2) 118.3; 2.5 | 0 (0) 92.8; 0.0 | 0 (0) 117.6; 0.0 | 3 (5.4) 102.1; 2.9 | 3 (4.8) 103.1; 2.9 | 2 (3.4) 97.4; 2.1 | 7 (11.9) 98.9; 7.1 | 0 (0) 109.9; 0.0 | 2 (3.3) 88.1; 2.3 | 4 (6.6) 94.9; 4.2 |
| Glomerular filtration rate decrease | 17 (23.9) 105.5; 16.1 | 7 (13.2) 86.2; 8.1 | 13 (19.7) 103.6; 12.6 | 14 (25.0) 86.5; 16.2 | 8 (12.7) 95.5; 8.4 | 9 (15.3) 88.9; 10.1 | 9 (15.3) 91.7; 9.8 | 11 (17.2) 99.0; 11.1 | 7 (11.5) 83.6; 8.4 | 8 (13.1) 95.0; 8.4 |
| Hyperkalemia | 9 (12.7) 108.7; 8.3 | 5 (9.4) 88.4; 5.7 | 8 (12.1) 107.8; 7.4 | 11 (19.6) 92.5; 11.9 | 8 (12.7) 94.6; 8.5 | 12 (20.3) 90.7; 13.2 | 9 (15.3) 91.7; 9.8 | 6 (9.4) 102.7; 5.8 | 4 (6.6) 88.0; 4.5 | 8 (13.1) 91.0; 8.8 |
| Hyperphosphatemia | 5 (7.0) 118.8; 4.2 | 4 (7.5) 87.6; 4.6 | 7 (10.6) 110.4; 6.3 | 3 (5.4) 100.3; 3.0 | 6 (9.5) 96.7; 6.2 | 1 (1.7) 99.4; 1.0 | 4 (6.8) 98.1; 4.1 | 4 (6.3) 106.2; 3.8 | 6 (9.8) 84.5; 7.1 | 3 (4.9) 97.0; 3.1 |
| Iron deficiency | 6 (8.5) 115.0; 5.2 | 2 (3.8) 89.3; 2.2 | 2 (3.0) 115.0; 1.7 | 3 (5.4) 101.6; 3.0 | 3 (4.8) 100.7; 3.0 | 3 (5.1) 98.2; 3.1 | 8 (13.6) 96.7; 8.3 | 8 (12.5) 103.6; 7.7 | 2 (3.3) 89.4; 2.2 | 9 (14.8) 83.4; 10.8 |
| Back Pain | 2 (2.8) 121.0; 1.7 | 1 (1.9) 92.3; 1.1 | 6 (9.1) 111.5; 5.4 | 3 (5.4) 102.2; 2.9 | 3 (4.8) 99.6; 3.0 | 1 (1.7) 98.8; 1.0 | 4 (6.8) 97.7; 4.1 | 7 (10.9) 103.0; 6.8 | 5 (8.2) 86.1; 5.8 | 5 (8.2) 93.8; 5.3 |
| End-stage kidney failure | 25 (35.2) 101.3; 24.7 | 15 (28.3) 80.0; 18.8 | 21 (31.8) 97.7; 21.5 | 24 (42.9) 81.3; 29.5 | 12 (19.0) 93.3; 12.9 | 18 (30.5) 85.3; 21.1 | 29 (49.2) 72.7; 39.9 | 27 (42.2) 89.4; 30.2 | 20 (32.8) 72.4; 27.6 | 22 (36.1) 80.7; 27.3 |
| Dyspnea | 8 (11.3) 115.3; 6.9 | 0 (0) 92.8; 0.0 | 3 (4.5) 114.9; 2.6 | 2 (3.6) 103.6; 1.9 | 3 (4.8) 102.2; 2.9 | 1 (1.7) 97.8; 1.0 | 2 (3.4) 100.5; 2.0 | 5 (7.8) 105.7; 4.7 | 8 (13.1) 83.9; 9.5 | 4 (6.6) 94.9; 4.2 |
| Pruritus | 4 (5.6) 118.5; 3.4 | 1 (1.9) 91.9; 1.1 | 2 (3.0) 115.7; 1.7 | 3 (5.4) 101.7; 3.0 | 1 (1.6) 102.7; 1.0 | 3 (5.1) 98.2; 3.1 | 8 (13.6) 92.4; 8.7 | 4 (6.3) 105.3; 3.8 | 5 (8.2) 84.8; 5.9 | 2 (3.3) 98.0; 2.0 |
| Hypertension | 22 (31.0) 99.4; 22.1 | 23 (43.4) 61.2; 37.6 | 15 (22.7) 99.2; 15.1 | 24 (42.9) 67.8; 35.4 | 22 (34.9) 81.9; 26.9 | 18 (30.5) 74.0; 24.3 | 21 (35.6) 71.0; 29.6 | 15 (23.4) 90.5; 16.6 | 16 (26.2) 73.8; 21.7 | 19 (31.1) 76.4; 24.9 |
| hsCRP Q1 ≤1.40 mg/L | hsCRP Q2 >1.40–≤2.97 mg/L | hsCRP Q3 >2.97–≤5.98 mg/L | hsCRP Q4 >5.98–≤13.545 mg/L | hsCRP Q5 >13.545 mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roxadustat n = 405 PEY a = 733.9 | ESA n = 413 PEY a = 812.2 | Roxadustat n = 411 PEY a = 750.2 | ESA n = 402 PEY a = 790.1 | Roxadustat n = 373 PEY a = 619.8 | ESA n = 438 PEY a = 855.3 | Roxadustat n = 433 PEY a = 712.4 | ESA n = 381 PEY a = 743.9 | Roxadustat n = 400 PEY a = 624.2 | ESA n = 412 PEY a = 741.6 | |
| TEAE | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 351 (86.7) | 345 (83.5) | 362 (88.1) | 340 (84.6) | 323 (86.6) | 398 (90.9) | 384 (88.7) | 336 (88.2) | 360 (90.0) | 364 (88.3) |
| IR/100 PEY | 47.8 | 42.5 | 48.3 | 43.0 | 52.1 | 46.5 | 53.9 | 45.2 | 57.7 | 49.1 |
| Serious TEAE | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 205 (50.6) | 184 (44.6) | 214 (52.1) | 190 (47.3) | 191 (51.2) | 239 (54.6) | 246 (56.8) | 229 (60.1) | 259 (64.8) | 255 (61.9) |
| IR/100 PEY | 27.9 | 22.7 | 28.5 | 24.0 | 30.8 | 27.9 | 34.5 | 30.8 | 41.5 | 34.4 |
| TEAE leading to discontinuation of study drug b | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 35 (8.6) | 20 (4.8) | 42 (10.2) | 26 (6.5) | 40 (10.7) | 37 (8.4) | 52 (12.0) | 40 (10.5) | 64 (16.0) | 42 (10.2) |
| IR/100 PEY | 4.8 | 2.5 | 5.6 | 3.3 | 6.5 | 4.3 | 7.3 | 5.4 | 10.3 | 5.7 |
| Grade ≥3 TEAE | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 152 (37.5) | 128 (31.0) | 168 (40.9) | 151 (37.6) | 152 (40.8) | 187 (42.7) | 211 (48.7) | 190 (49.9) | 225 (56.3) | 208 (50.5) |
| IR/100 PEY | 20.7 | 15.8 | 22.4 | 19.1 | 24.5 | 21.9 | 29.6 | 25.5 | 36.0 | 28.0 |
| TEAE leading to death | ||||||||||
| n (%) | 34 (8.4) | 31 (7.5) | 54 (13.1) | 46 (11.4) | 60 (16.1) | 69 (15.8) | 72 (16.6) | 67 (17.6) | 94 (23.5) | 84 (20.4) |
| IR/100 PEY | 4.6 | 3.8 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 9.7 | 8.1 | 10.1 | 9.0 | 15.1 | 11.3 |
| hsCRP Q1 ≤1.40 mg/L | hsCRP Q2 >1.40–≤2.97 mg/L | hsCRP Q3 >2.97–≤5.98 mg/L | hsCRP Q4 >5.98–≤13.545 mg/L | hsCRP Q5 >13.545 mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEAE, n (%), IR | Roxadustat n = 405 PEY a = 733.9 | ESA n = 413 PEY a = 812.2 | Roxadustat n = 411 PEY a = 750.2 | ESA n = 402 PEY a = 790.1 | Roxadustat n = 373 PEY a = 619.8 | ESA n = 438 PEY a = 855.3 | Roxadustat n = 433 PEY a = 712.4 | ESA n = 381 PEY a = 743.9 | Roxadustat n = 400 PEY a = 624.2 | ESA n = 412 PEY a = 741.6 |
| Overall TEAEs | 351 (86.7), 47.8 | 345 (83.5), 42.5 | 362 (88.1), 48.3 | 340 (84.6), 43.0 | 323 (86.6), 52.1 | 398 (90.9), 46.5 | 384 (88.7), 53.9 | 336 (88.2), 45.2 | 360 (90.0), 57.7 | 364 (88.3), 49.1 |
| Diarrhea | 55 (13.6), 7.5 | 42 (10.2), 5.2 | 46 (11.2), 6.1 | 48 (11.9), 6.1 | 36 (9.7), 5.8 | 43 (9.8), 5.0 | 49 (11.3), 6.9 | 53 (13.9), 7.1 | 54 (13.5), 8.7 | 39 (9.5), 5.3 |
| Nausea | 25 (6.2), 3.4 | 41 (9.9), 5.0 | 31 (7.5), 4.1 | 22 (5.5), 2.8 | 28 (7.5), 4.5 | 25 (5.7), 2.9 | 41 (9.5), 5.8 | 28 (7.3), 3.8 | 46 (11.5), 7.4 | 31 (7.5), 4.2 |
| Pneumonia | 32 (7.9), 4.4 | 36 (8.7), 4.4 | 37 (9.0), 4.9 | 33 (8.2), 4.2 | 27 (7.2), 4.4 | 56 (12.8), 6.5 | 48 (11.1), 6.7 | 38 (10.0), 5.1 | 35 (8.8), 5.6 | 38 (9.2), 5.1 |
| Arteriovenous fistula-site complication | 28 (6.9), 3.8 | 27 (6.5), 3.3 | 36 (8.8), 4.8 | 28 (7.0), 3.5 | 27 (7.2), 4.4 | 33 (7.5), 3.9 | 32 (7.4), 4.5 | 41 (10.8), 5.5 | 34 (8.5), 5.4 | 33 (8.0), 4.5 |
| Arteriovenous fistula thrombosis | 33 (8.1), 4.5 | 26 (6.3), 3.2 | 43 (10.5), 5.7 | 33 (8.2), 4.2 | 38 (10.2), 6.1 | 42 (9.6), 4.9 | 43 (9.9), 6.0 | 34 (8.9), 4.6 | 50 (12.5), 8.0 | 30 (7.3), 4.0 |
| Pain in extremity | 22 (5.4), 3.0 | 16 (3.9), 2.0 | 22 (5.4), 2.9 | 26 (6.5), 3.3 | 21 (5.6), 3.4 | 17 (3.9), 2.0 | 21 (4.8), 2.9 | 40 (10.5), 5.4 | 21 (5.3), 3.4 | 27 (6.6), 3.6 |
| Headache | 39 (9.6), 5.3 | 30 (7.3), 3.7 | 50 (12.2), 6.7 | 32 (8.0), 4.1 | 25 (6.7), 4.0 | 37 (8.4), 4.3 | 42 (9.7), 5.9 | 27 (7.1), 3.6 | 34 (8.5), 5.4 | 32 (7.8), 4.3 |
| Hypertension | 72 (17.8), 9.8 | 58 (14.0), 7.1 | 61 (14.8), 8.1 | 72 (17.9), 9.1 | 52 (13.9), 8.4 | 70 (16.0), 8.2 | 73 (16.9), 10.2 | 44 (11.5), 5.9 | 51 (12.8), 8.2 | 48 (11.7), 6.5 |
| Hypotension | 27 (6.7), 3.7 | 32 (7.7), 3.9 | 44 (10.7), 5.9 | 23 (5.7), 2.9 | 29 (7.8), 4.7 | 32 (7.3), 3.7 | 43 (9.9), 6.0 | 38 (10.0), 5.1 | 40 (10.0), 6.4 | 32 (7.8), 4.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choukroun, G.; Strutz, F.; Harkavyi, A.; Santos, V.; Jiletcovici, A.; Del Vecchio, L. Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat in Patients with CKD: Pooled Analysis by Baseline Inflammation Status. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020303
Choukroun G, Strutz F, Harkavyi A, Santos V, Jiletcovici A, Del Vecchio L. Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat in Patients with CKD: Pooled Analysis by Baseline Inflammation Status. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020303
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoukroun, Gabriel, Frank Strutz, Alexander Harkavyi, Vicki Santos, Alina Jiletcovici, and Lucia Del Vecchio. 2025. "Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat in Patients with CKD: Pooled Analysis by Baseline Inflammation Status" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020303
APA StyleChoukroun, G., Strutz, F., Harkavyi, A., Santos, V., Jiletcovici, A., & Del Vecchio, L. (2025). Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat in Patients with CKD: Pooled Analysis by Baseline Inflammation Status. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020303






