Abstract
Multiple myeloma is a clonal plasma cell malignancy with a highly variable range of clinical manifestations. Over recent decades, substantial progress has been made in laboratory diagnostics, which has deepened our understanding of disease biology, improved risk stratification, and informed treatment strategies. In an era of transformation and innovation, conventional laboratory methods remain essential, as cutting-edge technologies might not be immediately accessible to all laboratories. Nonetheless, even widely used laboratory methodologies present many challenges, such as variability in assay performance, interpretative criteria, and standardization. This review by the Portuguese Multiple Myeloma Group of the Portuguese Society of Hematology provides a comprehensive overview and practical appraisal of current conventional laboratory methods employed for multiple myeloma diagnosis.
1. Introduction
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant plasma cell disorder characterized by the clonal proliferation of plasma cells (PC) within the bone marrow (BM), resulting in a complex and heterogeneous clinical presentation [1]. The diagnostic process begins with clinical suspicion. Primary care and emergency staff are frequently the first to encounter patients with subtle or nonspecific symptoms. Recognizing warning signs, such as unexplained anemia, persistent bone pain, hypercalcemia, renal impairment, or recurrent infections, is critical for timely referral and appropriate laboratory evaluation. The disease spectrum includes asymptomatic precursor states, such as monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM), as well as symptomatic MM. This stage is defined by at least 10% of clonal bone marrow PC (or biopsy-proven bony or extramedullary plasmacytoma) and at least one of the myeloma-defining events, summarized by the SLiM-CRAB criteria. These criteria, in addition to the classic features hypercalcemia (C), renal dysfunction (R), anemia (A), and bone lesions (B), consider biomarker-defined events: percentage of abnormal PC in the BM ≥ 60% (S), ratio of involved to uninvolved free light chains in the blood ≥ 100 (Li), Magnetic Resonance Imaging with more than one focal bone lesion (M) [2]. Given this wide clinical variability, accurate diagnosis and risk stratification require the integration of clinical and imaging findings with a diverse range of laboratory data (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of exams and laboratory parameters that represent the basis of multiple myeloma (MM) diagnosis, classification, and risk stratification.
Diagnostic delay (the interval from symptom onset to definitive diagnosis) remains a major challenge in MM, with median delays of 4–6 months reported [3]. Systematic reviews estimate a median diagnostic interval of ~108 days and a total interval of ~163 days [4]. Delays beyond 3 months are associated with increased risk of complications, including bone disease and renal impairment [5]. These findings highlight the necessity of timely recognition and efficient diagnostic pathways to reduce morbidity and improve outcomes.
In this review, we focus on routinely widely used laboratory methodologies that, when applied to blood, urine, and bone marrow, help in identifying, quantifying, and characterizing monoclonal proteins (MPs) and neoplastic PC.
In recent decades, laboratory diagnostics in MM have undergone changes that have enhanced sensitivity, specificity, and clinical applicability. Traditional core techniques such as serum protein electrophoresis (SPE), serum and urine immunofixation electrophoresis (sIFE/uIFE), and serum free light chain (sFLC) quantification, remain essential to diagnostic algorithms and are indispensable for both initial detection and longitudinal monitoring of monoclonal gammopathies (and more so as cutting-edge technologies might not be immediately accessible to all laboratories) [6]. However, these methods have intrinsic limitations, including analytical variability, interpretive expertise, and awareness of potential confounding factors such as polyclonal background activity or renal dysfunction, which can obscure or mimic pathological signals.
In parallel, other methodologies such as multicolor flow cytometry (FC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) added a new dimension to MM diagnostics and have become essential tools for characterizing clonal burden and detecting cytogenetic abnormalities of prognostic significance, including t(4;14), t(14;16), del(17p), and 1q21 gain [7,8]. These genetic alterations are now integrated into risk-adapted treatment strategies, further emphasizing the potential role of these abnormalities in guiding therapeutic decisions [9]. Despite existing challenges, significant progress has been made toward the standardization of FC and FISH protocols across laboratories, reflecting ongoing efforts to enhance diagnostic accuracy and ensure greater consistency in prognostic assessment.
More recently, next-generation flow (NGF) has been incorporated as a sensitive methodology for measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment in MM, with implications in treatment decisions [10]. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has enabled high-resolution characterization of somatic mutations in key genes, including KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, and TP53, thereby offering important insights into the molecular biology of MM and its clonal evolution [11].
Although traditional laboratory methodologies are extensively validated and integral to clinical practice, they continue to be influenced by interpretative differences and analytical variability. Overall, enhancing the diagnostic landscape in MM will require greater harmonization of protocols, refinement of interpretive criteria, and strengthened multidisciplinary collaboration among clinicians, pathologists, and laboratory scientists. As advancements in automation and cost reduction continue to make both established and emerging techniques more accessible, an increasing number of laboratories are likely to implement them. As such, it remains essential that laboratory staff receive appropriate education to ensure expertise in this field. However, access to these technologies remains uneven across different regions. In underdeveloped countries and underserved areas, limited infrastructure, financial constraints, and a lack of trained personnel pose significant barriers. These disparities can delay diagnosis and compromise patient outcomes. Efforts to promote equitable access, including international collaborations and scalable diagnostic solutions, are essential to ensure that all patients benefit from recent innovations. As MM management continues to evolve toward increasingly personalized approaches, the integration of robust laboratory data into clinical workflows is critical for delivering accurate diagnoses and supporting evidence-based treatment strategies. These changes, along with the emergence of new therapeutic options, have contributed to the development of more advanced laboratory tests.
In this context, the present review, developed by the Portuguese Multiple Myeloma Group of the Portuguese Society of Hematology, aims to provide a comprehensive and practical overview of established laboratory tests and offer a critical appraisal of key methodologies currently employed in MM.
2. Immunoglobulins in Multiple Myeloma
Immunoglobulins (Ig) are highly diversified proteins, which reflect their essential role in binding a wide range of foreign antigens in the human body. Each Ig molecule has a characteristic “Y” shape, composed of two identical heavy chains (HC) and two identical light chains (LC). A complete Ig is formed by one of the five HC isotypes—IgA, IgG, IgM, IgD, or IgE—and either a kappa (κ) or lambda (λ) LC. The synthesis of HC and LC is independently regulated by genes located on chromosome 14 for HC, and chromosomes 2 and 22 for κ and λ light chains, respectively [12].
Under normal physiological conditions, the LCs are produced in excess, approximately 10–40% more than the HCs to ensure efficient Ig assembly and prevent the formation of potentially toxic HCs aggregates [13]. The excess LC, known as free light chains (FLC), is released into the bloodstream and primarily cleared by the kidneys. Although there are approximately twice as many PC producing the κ isotype compared to λ, this disproportion is not reflected in the serum FLC ratio (rFLC) in individuals with normal renal function, owing to differences in the renal catabolism rates of the two isotypes [14]. Type κ LC circulates mainly in monomeric form (~25 kDa) and is more efficiently cleared by the kidneys compared to λ LC, which is mainly found in dimeric or oligomeric forms [15].
Understanding the complexity of immunoglobulin synthesis is essential for interpreting variations in the type and concentration of MPs found in pathological conditions and for identifying their function as disease biomarkers.
3. Laboratory Methodologies
3.1. Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) is a cornerstone methodology in the diagnosis and monitoring of MM, enabling the separation of serum proteins based on their charge-to-mass ratio. Due to its complete automation, increased throughput, and enhanced resolution, particularly between the β1 and β2 fractions, capillary electrophoresis (CE) has largely replaced traditional agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE) in modern laboratories [16]. As discussed in Section 3.2, sIFE complements the information given by SPE and confirms monoclonality [16,17,18].
MPs typically migrate in the γ region of the electrophoretic spectrum but can also appear in the β region (especially IgA) [19]. However, any suspicious change in SPE spectrum should be considered. FLC are difficult to detect by SPE but may become visible, especially in cases of high sFLC concentration combined with hypogammaglobulinemia (Figure 1).
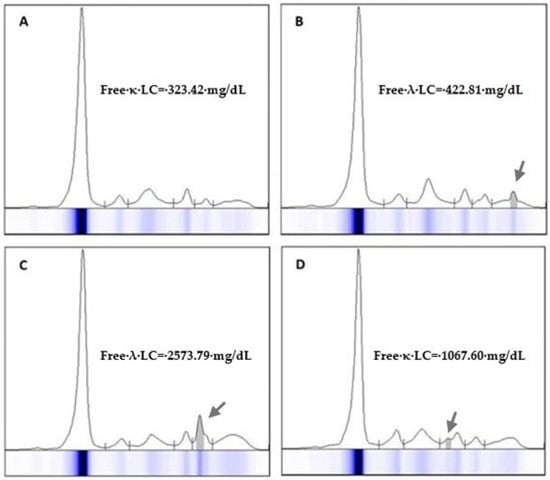
Figure 1.
Eletrophoresis of proteins in the serum of 4 patients (A–D) diagnosed with light chain myeloma. The monoclonal light chain component may migrate in any fraction of the electrophoresis spectrum but is seldom visible at concentrations below 300 mg/dL. Serum free light chain measurement is recommended for the quantification of monoclonal protein in light-chain myeloma. Arrows indicate the migration zone where the free light chain was detected in the electrophoretic trace.
Despite methodological improvements, MP quantification remains semi-quantitative, and significant variability can arise from differences in gating strategies and operator interpretation. MP concentration is determined by integrating the monoclonal peak area in the electrophoretic spectrum, a process that is influenced by factors such as the relative peak area, the position of the monoclonal component, and the polyclonal background. Additionally, the accuracy of quantification relies on the operator’s interpretation of the peak’s characteristics and boundaries.
There have been various attempts to develop methods to enhance the precision of M-protein peak measurement in SPE, with perpendicular drop (PD) and tangential skimming (TS) being the most common techniques. PD is the most frequently used technique. In this approach, the demarcation starts where the M-spike meets the underlying polyclonal region and extends straight down to the baseline, encompassing both the area above and below. The TS method attempts to include as M-Protein only the area above the peak. This technique, in contrast to the PD approach, allows for more precise delineation of MP boundaries by tracing a tangent line along the gamma background. TS works well in the γ region but is unreliable for M-proteins migrating in the α- or β-regions, where proteins like transferrin and C3 distort the trace (Figure 2). Both methods have advantages and limitations; however, to ensure reproducibility in serial measurements, it is recommended to apply the same method within the same laboratory [20,21].
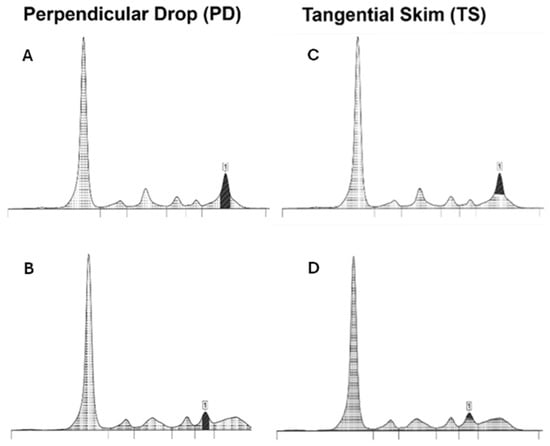
Figure 2.
Examples of the perpendicular drop (PD) and tangential skimming (TS) techniques, showing the demarcation of the M-protein peak (1). In the PD technique (A,B), the peak area begins where the M-spike meets the underlying polyclonal region and extends straight down to the baseline. The TS technique (C,D) includes only the area above the peak by tracing a tangent line along the gamma background. This technique is not reliable if the M-protein migrates in alpha or beta-regions (D).
The limit of quantification (LOQ) for MPs is not fixed. It varies depending on the location of the MP in the electrophoretic trace (γ vs. β or even α), background immunoglobulin concentration, and electrophoretic system. Katzmann et al. reported that LOQ may range from 1 g/L to >25 g/L (with β-migrating MP being the most challenging to accurately quantify due to co-migrating proteins) [20,22].
Notably, the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) defines measurable disease as a serum MP concentration ≥ 10 g/L, which serves as a clinical decision threshold rather than a reflection of analytical sensitivity. MP below this level is technically detectable but may exhibit poor reproducibility, particularly when concentrations fall below 1 g/L. In such cases, quantification should be accompanied by appropriate disclaimers, and results expressed as “<1 g/L” or “trace” where applicable. For this reason, laboratories should adopt method-specific protocols and remain aware of the analytical limitations. Each laboratory is expected to know, validate, and document the limit of detection (LOD) of their SPE system and apply this understanding to result interpretation [21,23].
Polymerized MP, often associated with IgA or IgM isotypes, can appear as multiple adjacent peaks [20]. In these cases, the peaks must be quantified as a single MP. Only peaks from Ig of different isotypes should be considered independent (Figure 3). The presence of monoclonal Ig is not solely associated with monoclonal gammopathies. The growing application of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs), typically of the IgG subtype (e.g., anti-CD38), may cause subtle alterations in the SPE trace. Other detectable interferences include iodinated radiological contrast agents, antibiotics, hemolysis, and fibrinogen presence [24,25].
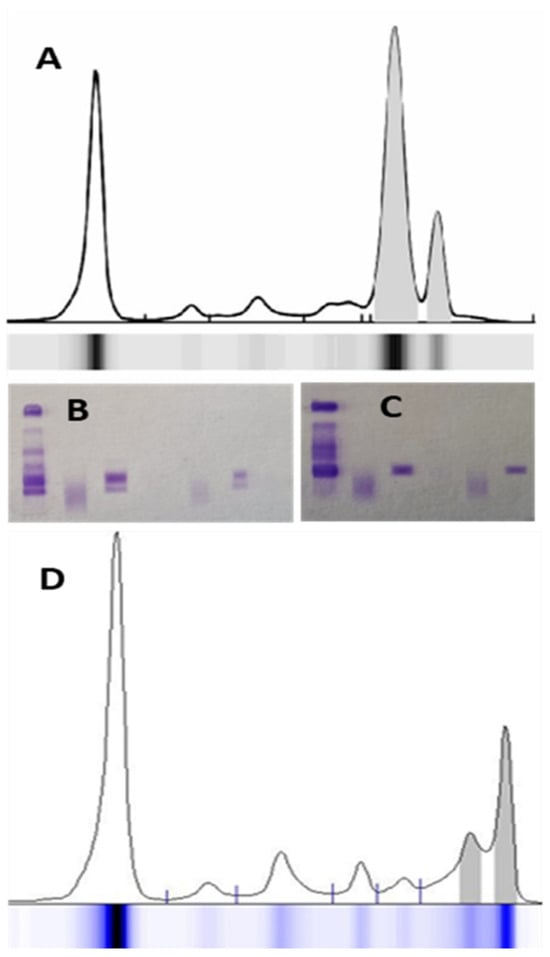
Figure 3.
An example of polymerized monoclonal IgAλ protein in serum protein electrophoresis (A); the immunofixation (B) shows 2 bands corresponding to IgAλ, which, after treatment of the sample with a depolymerizing agent, result in only one band (C). Therefore, the total monoclonal protein corresponds to the sum of the areas of the 2 peaks. In another case (D), 2 monoclonal components of different Ig isotypes migrate in the gamma zone of the electrophoresis spectrum—IgMλ and IgGλ (from left to right).
Some other diseases that affect the immune system (e.g., autoimmune diseases, especially rheumatoid arthritis) can cause changes in SPE and sIFE; for this reason, the results must always be evaluated in the patient’s clinical context. The presence of polyclonal Ig in an inflammatory or infectious context is also common; therefore, clonality must be confirmed by sIFE or immunosubtraction (ISUB) (Figure 4).
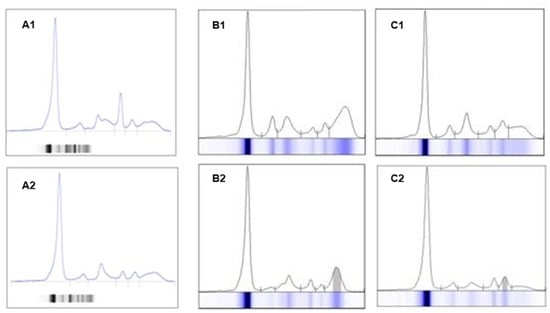
Figure 4.
Representation of an electrophoresis spectrum of a sample with hemolysis and fibrinogen interference, with changes in the alpha zone and a peak in beta zone 1 of the spectrum (A1) vs. the sample without changes, from a new collection from the same patient (A2). Examples of increased polyclonal IgG (B1) vs. monoclonal IgGλ protein (B2); increased polyclonal IgA (C1) vs. monoclonal IgAλ protein (C2).
This variability in electrophoretic patterns, arising from overlapping polyclonal responses, artifacts, or disease-related alterations, underscores the importance of interpretative expertise, particularly when differentiating monoclonal spikes from reactive polyclonal elevations or artifacts. The laboratory professional plays a crucial role in evaluating peak morphology and utilizing confirmatory tests, such as sIFE, to confirm clonality.
In summary, while SPE remains a foundational tool in MM diagnostics, its full clinical utility depends on a detailed understanding of electrophoretic behavior, analytical limitations, and standardization of quantification techniques. Continuous education in interpretation, along with the integration of complementary methods, is essential for maintaining diagnostic accuracy and clinical relevance.
3.2. Serum Immunofixation Electrophoresis and Immunosubtraction
Serum immunofixation electrophoresis (sIFE) combines gel electrophoresis with the use of specific antisera that defines the Ig phenotype at diagnosis. sIFE is more sensitive, with a limit of detection (LOD) ≈ 0.1 g/L (0.01 g/dL), when compared to SPE, with LOD ≈ 1.0 g/L (0.1 g/dL). Thus, the confirmation of a complete response requires a negative sIFE [26].
A more recent methodology than sIFE, ISUB combines SPE with the use of specific antisera to identify the Ig isotype. This approach is more automated and efficient, enabling individual sample analysis at a significantly faster pace. Although it has not yet been incorporated into the IMWG recommendations, studies indicate that its sensitivity for detecting quantifiable Ig in SPE is comparable to that of sIFE and it is routinely applied by several laboratories across the world [16,27,28]. However, it is important to note that ISUB demonstrates reduced sensitivity in detecting low concentrations of MPs (those lacking a visible peak in SPE), and FLC, and it lacks specific antisera for identifying IgD and IgE [28]. sIFE remains the reference technique and should be employed whenever ISUB yields inconclusive results, such as negative or ambiguous findings, and/or when meeting IMWG response assessment criteria is required.
The use of sensitive techniques such as sIFE requires considerable operator expertise. Subtle banding patterns may occasionally appear, which are not necessarily indicative of MM. The detection of minor bands, particularly oligoclonal bands following stem cell transplantation, is a frequently observed transient phenomenon reflecting the reconstitution of a restricted clonal immune response [29,30].
Similarly, post-treatment electrophoretic patterns resulting from MoAb therapies, such as daratumumab, elotuzumab, or isatuximab, must be precisely recognized by the operator [31,32]. The primary concern with these therapies lies in their potential to confound response assessment, as therapeutic bands may mimic residual disease and lead to misclassification, particularly mistaking complete response (CR) for very good partial response (VGPR) [33]. To address interference from therapeutic MoAbs, manufacturers are developing targeted solutions to differentiate them from endogenous MPs. One such approach, the Hydrashift 2/4 Daratumumab assay (Sebia), builds upon the principles of the daratumumab-specific immunofixation electrophoresis reflex assay (DIRA); it uses an anti-daratumumab antibody to modify the drug’s electrophoretic migration, enabling a clear distinction from MP [34]. Similar principles are applied to the recent Hydrashift 2/4 Isatuximab assay (Sebia, Lisses, France) [35].
It is important to reinforce that, although ISUB offers an automated and efficient workflow, sIFE remains the gold standard for evaluating equivocal cases or fulfilling IMWG response criteria. For detecting monoclonal proteins accuracy remains operator-dependent and requires specific interpretive expertise. When there is high clinical suspicion of MM without the presence of a monoclonal band in sIFE, we suggest performing the test in a new serum sample. The timing for collecting this new sample should be guided by the patient’s clinical evolution; alternatively, we suggest an interval of 3 months between samples.
3.3. Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis and Urine Protein Electrophoresis
For many years, MP testing in 24 h urine was used to characterize and monitor light chain MM and AL amyloidosis. Several studies suggest that 24 h urine testing can be effectively replaced by sFLC measurement in most light chain MM patients [36,37,38]. sFLC eliminates the need for urine collection, offers greater sensitivity and precision than urine protein electrophoresis (UPE) for MP quantification, and serves as an established prognostic marker [39]. Exceptions include patients with suspected AL amyloidosis or light chain deposition disease, in whom urine immunofixation electophoresis (uIFE) is mandatory [40].
Despite these advances, the IMWG recommendations (dated from 2014) support the use of 24 h urine analysis for diagnosis [2], response assessment [26] and monitoring of MM patients with renal impairment [41]. Quantification of MP in urine should be based on the area under the monoclonal peak on UPE. Although some laboratories measure total urinary light chains to estimate MP levels, no formal recommendations in the literature currently support this approach.
The use of sFLC assay allows for a more selective use of 24 h urine testing; however, in cases of result discrepancies or diagnostic uncertainty, uIFE on a 24 h specimen remains recommended.
3.4. Serum Free Light Chains Measurements
MP may be secreted as a complete Ig, complete Ig associated with κ or λ LC, or as FLC alone, which occurs in approximately 20% of cases. The LC neo-epitope is exposed only in the unbound (free) form, which enabled the development of the sFLC assay, for more precise quantification in circulation. Free κ and λ LCs and the free κ/λ ratio (rFLC) must be evaluated simultaneously, as it is the alteration of this ratio that indicates monoclonality [14]. Interpreting these three parameters together enhances diagnostic accuracy. For example, an abnormal rFLC combined with immunoparesis of one LC type is more suggestive of monoclonality than an abnormal ratio accompanied by elevations in both chains. Clinical context and understanding of FLC physiology are essential, as various factors, such as renal dysfunction, inflammatory or reactive conditions, liver disease, and autoimmune disorders, may influence FLC concentrations.
The sFLC assay has significantly advanced the detection and monitoring of FLC-related disease in MM [2], and the rFLC has emerged as a valuable biomarker for both diagnosis and prognosis [42,43].
In pathological conditions, FLC production may vary significantly, both in absolute value and relative to intact Ig; in fact, FLCs and complete Ig are regarded as independent biomarkers [44]. Given the potential for significantly elevated FLC concentrations, laboratories must be prepared to detect antigen excess, which can be readily identified by analyzers equipped for kinetic monitoring [45]. In cases of unexpectedly low results, repeating quantification with higher dilutions is recommended, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
LOD in sFLC assay can reach approximately 0.1 mg/dL [14,46], making it substantially more sensitive than sIFE (sIFE; LOD ≈ 10 mg/dL) (Appendix A Table A1), particularly in scenarios involving coexisting FLC isoforms or polymerization. Subtle variations or progressive increases in the involved FLC, even when minimal and observed across two to three sequential assessments, may indicate disease progression, changes that are unlikely to be detected by electrophoresis (LOD ≈ 100 mg/dL). Conversely, a decrease in FLC levels provides a more rapid indication of treatment response compared to conventional markers [47].
Patients with renal impairment require special consideration, as rFLC may be affected by abnormal renal clearance. Some studies recommend using sFLC reference ranges adjusted for renal function [48,49].
Since 2014, an rFLC ≥ 100 (with involved FLC ≥ 100 mg/L) has been included in the diagnostic criteria for MM under the SLiM-CRAB framework [2]. rFLC is also used to assess the risk of progression in patients with MGUS according to the by Mayo score (abnormal rFLC < 0.26 or >1.65; rFLC < 8 in LC-MGUS) [44,50] and SMM by 2/20/20 risk stratification model (≥20) [51]. Additionally, rFLC monitoring is valuable in patients with intact immunoglobulin MM, given the potential for relapses through light chain escape [43].
The difference between the involved and uninvolved FLC (dFLC) serves as a biomarker for risk stratification in AL amyloidosis [52,53] and for treatment response assessment in MM [26]. As dFLC is unaffected by suppression of the uninvolved chain, which may distort the rFLC, it offers improved reproducibility in certain clinical settings as AL amyloidosis [53].
Currently, various methodologies are available for sFLC measurement, using either polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies. Comparative studies have demonstrated that these assays are not interchangeable and underscore the need for standardization through the development of an international reference standard [54,55,56].
Method selection remains at the discretion of individual laboratories. However, the clinical decision thresholds cited in this document reflect those endorsed by the IMWG, established and validated using the Freelite® assay (The Binding Site Group Ltd., Birmingham, UK) [57]. Alternative assays, such as N-Latex FLC (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Bavaria, Germany) or Sebia FLC, may be used in clinical practice but differences in calibration, reference ranges, and sensitivity must always be considered when interpreting results. In the event of a methodology switch, given the lack of assay equivalence, a baseline must be established by concurrently testing patient samples with both assays over a defined period to ensure the clinical applicability of the selected method.
3.5. Immunoglobulin Measurements
Total Ig quantification typically performed using automated methods such as nephelometry or turbidimetry, measures both monoclonal and polyclonal components and is therefore not recommended for identifying or quantifying MP [19]. Nonetheless, Ig measurement is advised at diagnosis to assess immunoparesis and, in IgA and IgD MM subtypes, can complement SPE, particularly when accurate delineation of the monoclonal peak is challenging. In these scenarios, the same principles applied to MP quantification in SPE should guide Ig monitoring during treatment response assessment [26]. These limitations can be addressed through the measurement of immunoglobulin heavy/light chain (HLC) ratios, enabled by the development of the Hevylite® assay (The Binding Site Group Ltd., Birmingham, UK), which quantifies specific IgGκ/IgGλ, IgAκ/IgAλ, or IgMκ/IgMλ pairs [58,59,60]. Beyond analytical utility, HLC measurement also carries prognostic value by enabling quantification of the uninvolved Ig, thus facilitating immunoparesis evaluation [61,62]. This assay is not yet included in the routine biomarker panel for MM diagnosis. Nevertheless, it has been employed in various studies and clinical trials demonstrating its utility in patient follow-up [63,64], particularly in cases involving MPs that migrate within the β fraction on SPE or appear as multiple peaks due to polymerization [60].
The IMWG has also acknowledged its potential as an alternative method for MP quantification when peak migration occurs in the β zone [26]. Given the methodological differences between SPE and HLC assay, their results are not interchangeable.
3.6. Morphological Examination
Peripheral blood morphologic examination has been historically of help in diagnosing MM by identifying characteristic features such as erythrocyte rouleaux formation (due to paraproteins in high concentrations) and the observation of morphologically abnormal PC in circulation (which indicates plasma cell leukemia if above 5% of the leucocyte differential count) [65,66].
BM morphologic examination can be performed in samples obtained by aspiration or core-needle biopsy to identify and quantify infiltration by PC. The samples are usually collected in the posterior superior iliac crest, the breastbone, or, more seldom, the anterior superior iliac crest. At diagnosis, it is recommended that both BM aspiration and biopsy are performed [6], and, in case of differences in counting PC, the highest value should be considered [2].
The BM is usually heterogeneously affected by MM (in patches, or interstitial or diffuse patterns). In 5% of BM aspirations, diagnosis is not possible due to a lack of representativeness or hemodilution. In 5 to 10% of BM biopsies, diagnosis is not possible due to a lack of representativeness or because the disease is in a very early phase [2,67,68]. In these cases, as well as in those with PC below 10% but with a high suspicion of MM, a new aspiration/biopsy sample should be obtained in a different anatomical location or, if there are suggestive lesions, an image-guided biopsy should be performed [2,69].
Plasma cell clonality should be determined by FC in a BM aspiration or by immunohistochemistry in a BM biopsy [68].
In the minority of patients with non-secretory MM (with negative MP by SPE/sIFE, UPE/uIFE, and sFLC), the medullary plasmacytosis, observed by morphologic examination or immunophenotyping by FC, is the only measurable marker both at diagnosis and follow-up [70,71].
An accurate and efficient BM morphological examination depends on the quality of the sample, the smear/section, and coloration (of the Romanowsky type, as May-Grünwald-Giemsa or Wright-Giemsa). An experienced observer should look at a minimum of 200 cells [72,73]. Morphologic features in BM examination are variable and are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Most common cytologic features of abnormal plasma cells (PC) and plasmablasts in bone marrow examination. Adapted from [67,68,74,75].
Although nuclear morphologic abnormalities, such as binucleated or multinucleated PC, immature PC, or plasmablasts, are not included in diagnostic or staging criteria, their presence has been linked to poorer prognosis and an increased risk of relapse (Figure 5) [68,74].
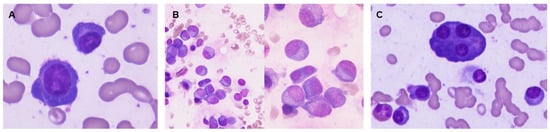
Figure 5.
Examples of bone marrow samples colored by May-Grünwald-Giemsa, 1000× magnification. Plasma cell with morphologic immaturity: high nucleus/cytoplasm ratio and dispersed chromatin (A). Binucleated plasma cell and several plasma cells (PC) with dispersed chromatin (B). Bone marrow showing mature PC and a multinucleated plasma cell (C).
3.7. Flow Cytometry
In 2014, the IMWG specified that while ≥10% clonal PC in the bone marrow defines multiple myeloma, the presence of ≥60% PC was introduced as a myeloma-defining event, indicating symptomatic disease [2]. Flow cytometry (FC) represents a rapid, sensitive, and reliable method to identify and quantify aberrant PC, even when present at small percentages in a BM sample. Applying FC allows for unequivocal distinction of neoplastic PC from their normal counterparts and assessment of plasma cell clonality [76]. It provides important information for diagnosis and classification, while simultaneously contributing to prognostic stratification of MM patients. Previous studies have demonstrated that less than 5% of normal PC among total PC indicate poor outcomes in MM and higher progression risk of MGUS and SMM into symptomatic disease [77], and that specific immunophenotypic profiles are associated with MM outcome [78].
The European Myeloma Network (EMN) issued consensus recommendations in 2008 regarding the clinical utility of FC in MM and other clonal plasma cell-related disorders and how to apply it in a routine diagnostic laboratory [7]. In the later 2018 guidelines, and the recent 2025 European Hematology Association (EHA)-EMN evidence-based guidelines, FC was confirmed as a recommended tool for diagnosis in MM [6,79]. Plasma cell clonality is confirmed by intracellular κ (cyIgκ) or λ (cyIgλ) light chain restriction. Aberrant antigen expression patterns are identified using a specific antibody panel that includes markers to precisely identify PC, CD38 and CD138, as well as discriminatory markers between normal and neoplastic cells, including CD19, CD45, CD56, CD117, CD27, CD28, and CD81. The characteristic light scatter of PC should also be considered (Forward Scatter-FSC—representing size and Side Scatter–SSC—representing internal cell complexity or granularity). Neoplastic PC typically exhibit CD38 intermediate/high (dim positive in 80% of MM cases) and CD138-positive expression, with intermediate to high FSC and SSC characteristics, usually negative CD19, CD27 and CD81 (negative or dim positive in 40–50% and 55%, respectively), CD45 (negative in 73%), CD56 (strong positive in 60–75%), CD28 and CD117 (strong positive in 15–45% and positive in 30%, respectively), and beta2-microglobulin cell surface expression (serving as a prognostic marker) (Figure 6) [7,80]. DNA ploidy and cell cycle analysis employing propidium iodide are used to determine ploidy status, as a percentage of S-phase PC above 2% of PC has long been shown to have prognostic value, with shorter disease-free survival and overall survival [81].
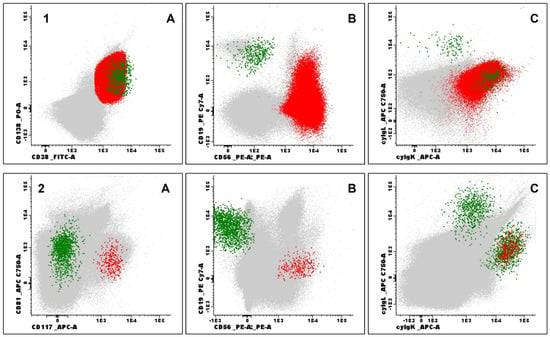
Figure 6.
Examples of immunophenotypic evaluation by flow cytometry in patients with multiple myeloma. (1) Bone marrow aspirate evaluation at diagnosis: Normal plasma cells (PC) (green) and neoplastic PC (red) based on CD138 (positive) and strong CD38 (positive) expression (1A), CD19 (negative) and CD56 (positive) expression (1B), cyIgλ (negative) and cyIgκ (positive) expression (1C), all other events represented in grey; (2) Measurable residual disease by Next Generation Flow: Normal PC (green) and aberrant PC (red) based on CD81 (negative) and CD117 (positive) expression (2A), CD19 (negative) and CD56 (positive) expression (2B), cyIgλ (negative) and cyIgκ (positive) expression (2C). Processing, antibody panels, and acquisition followed the protocols established by the EuroFlow consortium (samples acquired using the FACSLyric® flow cytometer and analyzed with Infinicyt® software version 2.1, both by BDBiosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
Immunophenotypic evaluation by FC should be performed on BM samples of 1–2 mL in dipotassium (K2) or tripotassium (K3) ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)—particularly relevant for staining of the CD138 antigen, whose expression levels on PC are higher in EDTA- vs. heparin anticoagulated samples. These should be processed within 12–24 h post-collection [82],), with measurements of at least 0.5 to 1 × 105 events after excluding platelets and debris/doublets [7]. Discrepancies in plasma cell quantification between BM morphological evaluation and FC usually occur in hypocellular samples, mostly due to the order in which samples are collected and low-quality samples, including coagulated, aged (beyond 48 h), and hemodiluted. Samples lacking hematopoietic precursor populations, such as erythroblasts and myeloid or B-cell precursors, and mast cells should be interpreted with caution, as these populations serve as internal quality controls to exclude hemodilution [83].
Following the advances in therapeutic efficacy, MRD was included in response criteria [26]. Achieving undetectable MRD in patients with CR is one of the most important prognostic factors, as it is associated with longer progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) [79,84]. Currently, clinical trials are exploring how therapy adjustments based on MRD status impact patient survival [85]. Sensitivity in MRD assessment by FC has increased with the introduction of the NGF approach developed by the EuroFlow consortium and included in the IMWG criteria [86]. For MRD assessment, the first BM aspirate (first pull) should be used. Bulk lysis processing of at least 107 cells and a standardized two-tube, 8-color antibody panel (including a multi-epitope anti-CD38 antibody to avoid interference in patients treated with anti-CD38 therapy, along with CD138, CD45, CD19, CD56, CD27, CD81 and CD117, cyIgκ and cyIgλ) allows sensitivity levels between 10−5 and 10−6 to be achieved. The LOD and LOQ depend on the number of total cells evaluated and the number of pathological PC identified (e.g., total number of cells evaluated = 2,000,000; clonal PC = 1000/0.05% of total cells; LOD = 0.0015% and LOQ = 0.0025%) [87]. Populations whose low or absent values indicate hemodilution (such as mast cells, erythroblasts, and myeloid and B lymphoid precursors) should be identified and compared to reference values (Figure 6) [88].
The NGF approach works without the need for a diagnostic sample (i.e., a basal FC characterization), as it identifies clonal PC by detecting immunophenotypic aberrancies. This method efficiently evaluates sample quality while remaining cost-effective. Low sample quality and quantity (coagulated, processed after more than 48 h, or hemodiluted) may result in false negative results. Ongoing innovations, such as automated analysis with a reference database, can enhance the detection of malignant plasma cell populations by reducing analysis time, diminishing operator variability, and facilitating inter-laboratory harmonization, as demonstrated in other hematological malignancies [89,90]. Nevertheless, these automated analysis techniques must be robust and deliver high-quality data output so that results can be reported with confidence.
Despite its strengths, NGF has limitations. As previously stated, sample quality can significantly impact assay performance. Additionally, it remains invasive, requiring BM sampling, which may not always reflect the full spatial heterogeneity of disease, particularly in cases with patchy medullary or extramedullary involvement. Peripheral blood-based detection strategies are being explored. Circulating tumor plasma cells (CTPC) released from primary or metastatic sites into the bloodstream may be responsible for MM spreading and can be used as a biomarker for diagnosis and disease progression, eventually outperforming tumor burden BM quantification in the differentiation between precursor stages of disease and active disease [91,92]. Evaluation of CTPC has prognostic value in MM [93], and several studies have shown its association with stage of disease, disease progression, and even higher relapse rate [94]. Differences in the immunophenotypic pattern of antigen expression between normal PC circulating in peripheral blood and those present in the BM have already been identified in earlier studies, including dimmer expression of CD27, CD38, and CD138 in CTPC, thus impacting their identification [76]. Detection methods for CTPC assessment, like the NGF assay developed and validated by the EuroFlow Consortium, have been used in clinical trial settings but need further testing and standardization [91]. While these approaches are not yet validated for routine clinical use, they promise to make MM diagnosis and MRD assessment by NGF more accessible and less invasive.
3.8. Cytogenetics
MM is a genetically heterogeneous disease. Primary cytogenetic abnormalities (CA), which occur early in disease development and are often already present in precursor conditions, are considered the foundational or initiating genetic events of MM [95,96]. Their two main categories are hyperdiploidy and Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain (IgH) translocations, which do not co-occur. Hyperdiploidy is characterized by the presence of extra odd-numbered chromosomes, which are believed to result from mitotic errors that lead to chromosomal gains. This subtype often has a better prognosis than some IgH-translocated subtypes. IgH translocations involve translocations between the IGH locus on chromosome 14q32 and various partner oncogenes, leading to deregulation of gene expression [97]. These include:
- t(4;14)(p16;q32), deregulating the expression of FGFR3 and NSD2;
- t(14;16)(q32;q23), deregulating the expression of MAF;
- t(11;14)(q13;q32), deregulating the expression of CCND1;
- t(6;14)(p21;q32), deregulating the expression of CCND3;
- t(14;20)(q32;q11), deregulating the expression of MAFB.
Their detection provides critical stratification of risk, allowing for more informed therapeutic strategies. For instance, the identification of t(11;14) has gained clinical relevance with the advent of BCL-2 inhibitors, highlighting the utility of cytogenetics for targeted therapy selection, besides prognosis [98]. Secondary cytogenetic events, such as del(17p) (TP53), chromosome 13 monosomy/deletion, and 1q21 gain/amplification, are frequently associated with disease progression and therapeutic resistance, underscoring their role in indicating poor outcomes (Figure 7) [9].
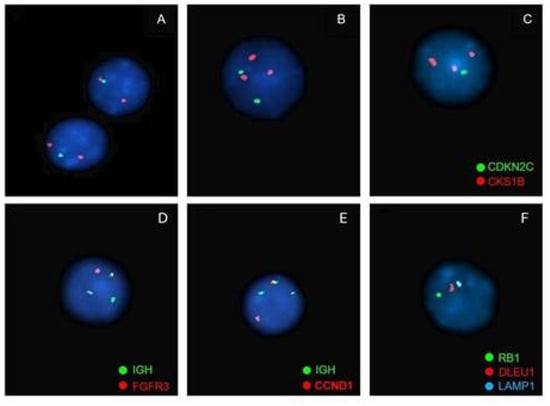
Figure 7.
Examples of the most frequent alterations detected by FISH in patients with multiple myeloma. (1) Chromosome 1 abnormalities: loss of 1p31 and gain of 1q21. (probe used: XL 1p32/1q21 Amplification/Deletion Probe, MetaSystems—1p32 (gene CDKN2C Spectrum Green) and 1q21 (gene CKS1B Spectrum Orange)) (A). Loss of 1p32: 1 green signal and 2 orange signals; (B). Gain of 1q21: 2 green signals and 3 or more orange signals; (C). Loss of 1p32 and gain of 1q21: 1 green signal and 3 or more orange signals. (D) IGH::FGFR3 t(4;14) rearrangement. 2 fusion signals (derived from the translocation), 1 green signal (locus IGH) and 1 orange signal (gene FGFR3) (probe used: Vysis LSI IGH/FGFR3 DCDF Probes, Abbott—locus IGH Spectrum Green and gene FGFR3 Spectrum Orange). (E) IGH::CCND1 t(4;11) rearrangement. 2 fusion signals (derived from the translocation), 1 green signal (locus IGH) and 1 orange signal (gene CCND1) (probe used: Vysis LSI IGH/CCND1-XT DCDF Probes, Abbott—locus IGH Spectrum Green and gene CCND1 Spectrum Orange). (F) Chromosome 13 abnormalities: Monosomy 13. 1 green signal, 1 orange signal and 1 aqua signal (probe used: XL RB1/DLEU/LAMP Deletion Probe, MetaSystems—gene RB1 Spectrum Green, gene DLEU1 Spectrum Orange and gene LAMP1 Spectrum Aqua).
Conventional karyotyping has limited sensitivity in MM because PC have a low proliferative index, resulting in few metaphases. This limitation restricts its clinical utility, relegating it largely to the identification of rare chromosomal abnormalities [99]. Therefore, cytogenetic analysis using FISH on purified CD138-positive PC is the standard method and should be routinely performed in newly diagnosed and overt relapsed cases. Its greater sensitivity allows for better classification and prognostic stratification of MM patients [8]. To ensure consistency and accuracy in interphase FISH, the EMN established a set of technical consensus guidelines intended to harmonize FISH testing across centers, reduce inter-laboratory variability, and support reliable risk stratification in multiple myeloma [8]. These include using preferably the first BM aspiration to optimize sample quality, collected in sodium or lithium heparin, and performing timely processing (within 24 h of collection) to preserve cellular integrity. As PC often constitute a small fraction of BM cells, without enrichment, FISH results may be diluted or misleading. Plasma cell enrichment techniques include Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS) using antibodies conjugated to magnetic beads that target CD138, highly expressed on PC, and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) using fluorescently labeled antibodies (e.g., CD138, CD38, CD45) to sort PC by FC individually [100]. In the study of plasmacytomas, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue is used. The recommended positivity thresholds are ≥10% for translocations detected by fusion or break-apart probes and ≥20% for numerical abnormalities. A standardized probe panel should be employed, using commercially validated reagents, and a minimum of 100 PC should be scored per sample. Each laboratory must establish confidence limits and validate methods using both normal and abnormal samples to define patterns of aberrant signals. A trained analyst should be designated for result interpretation, and reports should clearly state the percentage of abnormal cells, the methodology used, and the type of abnormality detected.
CA that are associated with poorer outcomes, including shorter PFS, OS, and generally worse responses to therapy, represent adverse prognostic markers. Patients with favorable markers are classified as standard or low risk and typically have better long-term outcomes [101]. The major molecular/genomic prognostic markers have been integrated into risk stratification systems such as the Second Revision of the International Staging System (R2-ISS) [102], mSMART [103], and IMWG guidelines [104]. A consensus genomic staging recommendation on the definition of high-risk MM was recently proposed by the International Myeloma Society (IMS)-IMWG, which relies upon the presence of at least one of the following abnormalities that confer higher risk: del(17p), with a cutoff of >20% clonal fraction, and/or TP53 mutation, an IgH translocation including t(4;14), t(14;16), or t(14;20) along with 1q+ and/or del(1p32), or monoallelic del(1p32) along with 1q+ or biallelic del(1p32) (Table 3) [105].

Table 3.
Summary of the major adverse and favorable prognostic markers in multiple myeloma (MM).
While FISH can reliably identify CA that was previously undetected by conventional cytogenetics, its targeted nature limits detection to known rearrangements, potentially overlooking novel or complex structural variants such as small deletions or cryptic translocations [106]. Also, FISH’s sensitivity is limited by the proportion of PC analyzed and cannot comprehensively capture subclonal heterogeneity, which is increasingly recognized as a driver of treatment failure [107].
3.9. Molecular Genetics
Gene expression profiling (GEP) and single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assay-based platforms can accurately detect cytogenetic subtypes and are becoming useful for classification and clinical decision-making [108,109]. More recently, NGS has revolutionized molecular profiling in MM by enabling high-resolution interrogation of the mutational landscape and clonal architecture [110]. NGS can detect a broad spectrum of somatic mutations that appear later, contributing to malignant progression, commonly involving RAS/RAF pathway genes (KRAS, NRAS, BRAF), TP53 mutations indicative of high-risk disease, and alterations in NF-κB signaling components (TRAF3, CYLD), that bear significant prognostic and therapeutic implications [111]. There also appears to be a link between specific mutations and primary CA, such as the KRAS mutation, which is more common in patients with t(11;14), and the co-occurrence of del17p with TP53 mutations, which is associated with a poorer prognosis in relapsed patients [95]. The ability to track clonal evolution longitudinally via NGS provides a dynamic view of disease biology that cytogenetics alone cannot achieve. These capabilities could enhance diagnostic clarity and therapy guidance. Nonetheless, bioinformatic complexities and variability in assay standardization raise concerns regarding reproducibility and inter-laboratory comparability [112]. In the context of diagnosis, NGS is not yet used in routine clinical diagnosis and remains limited to clinical trials.
NGS, along with NGF, has been recognized as a reference method for MRD assessment by the IMWG and the EMN. This involves studying the specific rearrangement pattern of the IgH gene (VDJ, DJ, IgK, and IgL) present in each patient [113]. For NGS-based MRD assessment, the first BM aspiration should be used to optimize sample quality, collected in EDTA, and processed promptly (within 24 h of collection). Generally, 2–3 million PC (CD138-positive) magnetically separated by MACS or sorted by FACS (equivalent to approximately 21.6–27 μg of DNA) are required to achieve a minimum sensitivity of 10−6 with 95% confidence in available assays such as clonoSEQ (Adaptive Biotechnologies, Seattle, WA, USA) and LymphoTrack [114]. Although it can be performed on cryopreserved samples, this methodology is demanding in routine practice because relatively large volumes of BM are required for clinical testing. NGS faces other practical challenges, including the requirement of diagnostic baseline samples to establish clonotypes, higher costs, and longer turnaround times compared to NGF [115].
4. Discussion
MM represents a biologically and clinically heterogeneous disease that requires a multifaceted diagnostic approach. While the clinical landscape is rapidly evolving with the advent of precision medicine and novel therapies, the integration of traditional and modern laboratory techniques remains essential to achieving diagnostic accuracy and optimizing patient outcomes.
Conventional assays such as SPE, sIFE, and sFLC quantification continue to serve as foundational tools in clinical laboratories and are essential for the detection and longitudinal monitoring of monoclonal proteins. Likewise, the clinical value of urine studies, though now more selectively employed, remains relevant in specific contexts. Advanced techniques, including FC and FISH, have significantly enhanced our ability to characterize the immunophenotypic and genetic profiles of neoplastic PC, provide critical prognostic information, and help refine risk-adapted treatment strategies (Figure 8).
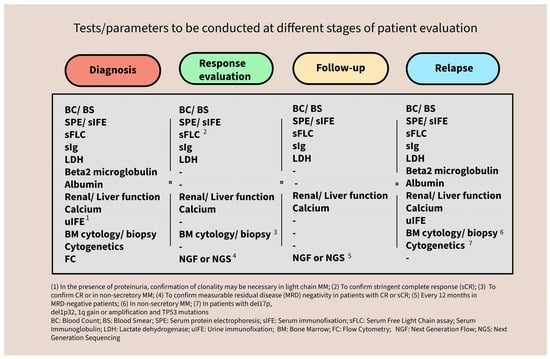
Figure 8.
Summary of the tests to be conducted at the different stages of patient evaluation.
Importantly, this review emphasizes that diagnostic precision depends not only on technical sophistication but also on pre-analytical quality, methodological standardization, and interdisciplinary collaboration. The heterogeneity in sample types, collection protocols, and interpretation frameworks underscores the need for harmonization across institutions and national guidelines. Laboratory professionals play a critical role in navigating analytical limitations, identifying artifacts, and communicating clinically relevant findings to the treating team. In this context, pursuing accreditation under the ISO 15189 standard [116] represents a key step toward ensuring consistent quality, reliability, and international alignment in clinical laboratory practice.
Looking ahead, several key trends are anticipated to influence the evolution of MM diagnostics. These trends include the expanded clinical implementation of MRD-guided therapeutic strategies, enhanced automation and digitalization within laboratory workflows, and the advancement of minimally invasive monitoring methods, such as the detection of CTPC. As technologies like NGF and NGS become increasingly accessible and standardized, their adoption into routine clinical practice is expected to rise.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, laboratory methodologies are central to multiple myeloma management, from detection and risk assessment to treatment monitoring and MRD evaluation. Their practical application requires a deep understanding of each method’s strengths, limitations, and appropriate clinical context. With the growth of diagnostic options, laboratories need to have proper technology and expertise to provide results that are accurate, timely, and clinically relevant. Continuous education, quality assurance, and collaboration among clinicians, pathologists, and laboratory scientists are vital to advancing diagnostic excellence and supporting patient care.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, original draft preparation, review and editing, J.C., A.M.P. and J.P.B.; review and editing, all other authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used Adobe Express for the purpose of figure design. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| PC | Plasma cells |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| MGUS | Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance |
| SMM | Smoldering multiple myeloma |
| MP | Monoclonal protein |
| SPE | Serum protein electrophoresis |
| sIFE | Serum immunofixation electrophoresis |
| uIFE | Urine immunofixation electrophoresis |
| sFLC | Serum free light chains |
| FC | Flow cytometry |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| NGF | Next-generation flow |
| MRD | Measurable residual disease |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| Ig | Immunoglobulins |
| HC | Heavy chains |
| LC | Light chains |
| FLC | Free light chains |
| rFLC | Free light chain ratio |
| CE | Capillary electrophoresis |
| AGE | Agarose gel electrophoresis |
| PD | Perpendicular drop |
| TS | Tangential skimming |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| IMWG | International Myeloma Working Group |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| MoAbs | Monoclonal Antibodies |
| ISUB | Immunosubtraction |
| CR | Complete response |
| VGPR | Very good partial response |
| DIRA | Daratumumab-specific immunofixation electrophoresis reflex assay |
| uIFE | Urine immunofixation eletrophoresis |
| UPE | Urine protein electrophoresis |
| dFLC | Difference between involved and uninvolved FLC |
| HLC | Heavy/light chain |
| EMN | European Myeloma Network |
| EHA | European Hematology Association |
| EDTA | Ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| OS | Overall survival |
| CTPC | Circulating tumor plasma cells |
| CA | Cytogenetic abnormalities |
| IgH | Immunoglobulin heavy chain |
| MACS | Magnetic-activated cell sorting |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| R2-ISS | Second Revision of the International Staging System |
| IMS | International Myeloma Society |
| GEP | Gene expression profiling |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Monoclonal protein detection limits. The table is based on information provided by suppliers and previously published [19,59,117].
Table A1.
Monoclonal protein detection limits. The table is based on information provided by suppliers and previously published [19,59,117].
| Methodology | Analytical Sensitivity 1 |
|---|---|
| SPE | 1.0 g/L |
| sIFE | 0.1 g/L |
| sFLC | 0.25–3 mg/L |
| UPE | 20 mg/L |
| uIFE | 3–5 mg/L |
1 The detection limits of monoclonal proteins are influenced by factors previously described, such as their electrophoretic migration pattern and the background level of polyclonal immunoglobulins. Abbreviations: SPE, Serum protein electrophoresis; UPE, Urine protein electrophoresis; sIFE, Serum immunofixation; uIFE, Urine immunofixation electrophoresis; sFLC, Measurement of free light chains in serum.
References
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, V.; Kyle, R.A.; van Duin, M.; Sonneveld, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Gay, F.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple Myeloma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Updated Criteria for the Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, G.; Herget, G.W.; Ihorst, G.; Zeissig, M.; Chaidos, A.; Auner, H.W.; Duyster, J.; Wäsch, R.; Engelhardt, M. Time from First Symptom Onset to the Final Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma (MM)—Possible Risks and Future Solutions: Retrospective and Prospective “Deutsche Studiengruppe MM” (DSMM) and “European Myeloma Network” (EMN) Analysis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshiaris, C.; Oke, J.; Abel, L.; Nicholson, B.D.; Ramasamy, K.; Van den Bruel, A. Quantifying Intervals to Diagnosis in Myeloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorlu, T.; Kayer, M.A.; Okumus, N.; Ulaş, T.; Dal, M.S.; Altuntas, F. Challenges, Difficulties, and Delayed Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caers, J.; Garderet, L.; Kortüm, K.M.; O’dwyer, M.E.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Binder, M.; Dold, S.M.; Gay, F.; Corre, J.; Beguin, Y.; et al. European Myeloma Network Recommendations on Tools for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Multiple Myeloma: What to Use and When. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Orfao, A.; Beksac, M.; Bezdickova, L.; Brooimans, R.A.; Bumbea, H.; Dalva, K.; Fuhler, G.; Gratama, J.; Hose, D.; et al. Report of the European Myeloma Network on Multiparametric Flow Cytometry in Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders. Haematologica 2008, 93, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, F.M.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Ameye, G.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Liebisch, P.; O’Connor, S.; Dalva, K.; Fabris, S.; Testi, A.M.; Jarosova, M.; et al. Report from the European Myeloma Network on Interphase FISH in Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, P.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Lonial, S.; Usmani, S.; Siegel, D.; Anderson, K.C.; Chng, W.-J.; Moreau, P.; Attal, M.; Kyle, R.A.; et al. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma with High-Risk Cytogenetics: A Consensus of the International Myeloma Working Group. Blood 2016, 127, 2955–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Boccadoro, M.; Quach, H.; Ho, P.J.; Beksac, M.; Hulin, C.; Antonioli, E.; Leleu, X.; Mangiacavalli, S.; et al. Daratumumab, Bortezomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Sherborne, A.L.; Walker, B.A.; Johnson, D.C.; Boyle, E.M.; Ellis, S.; Begum, D.B.; Proszek, P.Z.; Jones, J.R.; Pawlyn, C.; et al. Prediction of Outcome in Newly Diagnosed Myeloma: A Meta-Analysis of the Molecular Profiles of 1905 Trial Patients. Leukemia 2018, 32, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, R.A.; Massey, H.D. Laboratory Evaluation of Immunoglobulin Function and Humoral Immunity. In Henry’s Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 899–913. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Matsui, M.; Inoue, I.; Awata, T.; Katayama, S.; Murakoshi, T. Free Immunoglobulin Light Chain: Its Biology and Implications in Diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Clark, R.J.; Abraham, R.S.; Bryant, S.; Lymp, J.F.; Bradwell, A.R.; Kyle, R.A. Serum Reference Intervals and Diagnostic Ranges for Free κ and Free λ Immunoglobulin Light Chains: Relative Sensitivity for Detection of Monoclonal Light Chains. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, C.A.; Basnayake, K.; Cockwell, P. Serum Free Light Chain Assessment in Monoclonal Gammopathy and Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCudden, C.R.; Mathews, S.P.; Hainsworth, S.A.; Chapman, J.F.; Hammett-Stabler, C.A.; Willis, M.S.; Grenache, D.G. Performance Comparison of Capillary and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis for the Identification and Characterization of Monoclonal Immunoglobulins. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 129, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, X. Separation of Serum Proteins by Automated Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2003, 41, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoir, B.; Wallemacq, P.; Maisin, D. Serum Protein Electrophoresis: Comparison of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Capillarys (Sebia) and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Hydrasys (Sebia). Ann. Biol. Clin. 2003, 61, 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Willrich, M.A.V.; Katzmann, J.A. Laboratory Testing Requirements for Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2016, 54, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, D.F.; Schroeder, L. Challenges of Measuring Monoclonal Proteins in Serum. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2016, 54, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.A.; Frinack, J.L.; Ettore, M.W.; Tate, J.R.; Graziani, M.S.; Jacobs, J.F.M.; Booth, R.A.; McCudden, C.R.; Keren, D.F.; Delgado, J.C.; et al. An International Multi-Center Serum Protein Electrophoresis Accuracy and M-Protein Isotyping Study. Part I: Factors Impacting Limit of Quantitation of Serum Protein Electrophoresis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2020, 58, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Snyder, M.R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Kyle, R.A.; Therneau, T.M.; Benson, J.T.; Dispenzieri, A. Long-Term Biological Variation of Serum Protein Electrophoresis M-Spike, Urine M-Spike, and Monoclonal Serum Free Light Chain Quantification: Implications for Monitoring Monoclonal Gammopathies. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.F.M.; Turner, K.A.; Graziani, M.S.; Frinack, J.L.; Ettore, M.W.; Tate, J.R.; Booth, R.A.; McCudden, C.R.; Keren, D.F.; Delgado, J.C.; et al. An International Multi-Center Serum Protein Electrophoresis Accuracy and M-Protein Isotyping Study. Part II: Limit of Detection and Follow-up of Patients with Small M-Proteins. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2020, 58, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, X. Interferences in Clinical Capillary Zone Electrophoresis of Serum Proteins. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1485–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCudden, C.R.; Jacobs, J.F.M.; Keren, D.; Caillon, H.; Dejoie, T.; Andersen, K. Recognition and Management of Common, Rare, and Novel Serum Protein Electrophoresis and Immunofixation Interferences. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 51, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Criteria for Response and Minimal Residual Disease Assessment in Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genzen, J.R.; Murray, D.L.; Abel, G.; Meng, Q.H.; Baltaro, R.J.; Rhoads, D.D.; Delgado, J.C.; Souers, R.J.; Bashleben, C.; Keren, D.F.; et al. Screening and Diagnosis of Monoclonal Gammopathies: An International Survey of Laboratory Practice. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoren, K.L.; McCash, S.I.; Murata, K. Immunotyping Provides Equivalent Results to Immunofixation in a Population with a High Prevalence of Monoclonal Gammopathies. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2021, 6, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, N.; de Larrea, C.F.; Arostegui, J.I.; Cibeira, M.T.; Rosinol, L.; Rovira, M.; Elena, M.; Filella, X.; Yague, J.; Blade, J. Natural History and Prognostic Impact of Oligoclonal Humoral Response in Patients with Multiple Myeloma after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: Long-Term Results from a Single Institution. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.L.; Tate, J.; Gill, D.; Mollee, P. Significance of Abnormal Protein Bands in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Following Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2009, 30, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, J.; Wheeler, R.D.; Powles, R. Electrophoretic Patterns Post Daratumumab. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2018, 55, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, R.D.; Costa, M.V.; Crichlow, A.; Willis, F.; Reyal, Y.; Linstead, S.E.; Morris, J.E. Case Report: Interference from Isatuximab on Serum Protein Electrophoresis Prevented Demonstration of Complete Remission in a Myeloma Patient. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2022, 59, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durie, B.G.M.; Miguel, J.F.S.; Blade, J.; Rajkumar, S.V. Clarification of the Definition of Complete Response in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2416–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillon, H.; Irimia, A.; Simon, J.S.; Axel, A.; Sasser, K.; Scullion, M.J.; Ligneel, T.; Nouadje, G.; Moreau, P.; Dejoie, T. Overcoming the Interference of Daratumumab with Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE) Using an Industry-Developed Dira Test: Hydrashift 2/4 Daratumumab. Blood 2016, 128, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoren, K.; Menad, S.; Nouadje, G.; Macé, S. Isatuximab-Specific Immunofixation Electrophoresis Assay to Remove Interference in Serum M-Protein Measurement in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2024, 9, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowrousian, M.R.; Brandhorst, D.; Sammet, C.; Kellert, M.; Daniels, R.; Schuett, P.; Poser, M.; Mueller, S.; Ebeling, P.; Welt, A.; et al. Serum Free Light Chain Analysis and Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8706–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschautscher, M.; Rajkumar, V.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.; Gertz, M.; Buadi, F.; Dingli, D.; Hwa, L.; Fonder, A.; Hobbs, M.; et al. Serum Free Light Chain Measurements to Reduce 24-h Urine Monitoring in Patients with Multiple Myeloma with Measurable Urine Monoclonal Protein. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejoie, T.; Corre, J.; Caillon, H.; Moreau, P.; Attal, M.; Loiseau, H.A. Responses in Multiple Myeloma Should Be Assigned According to Serum, Not Urine, Free Light Chain Measurements. Leukemia 2019, 33, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejoie, T.; Attal, M.; Moreau, P.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Avet-Loiseau, H. Comparison of Serum Free Light Chain and Urine Electrophoresis for the Detection of the Light Chain Component of Monoclonal Immunoglobulins in Light Chain and Intact Immunoglobulin Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2016, 101, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Benson, J.; Larson, D.R.; Snyder, M.R.; Lust, J.A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A. Screening Panels for Detection of Monoclonal Gammopathies. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Merlini, G.; Bridoux, F.; Leung, N.; Mikhael, J.; Harrison, S.J.; Kastritis, E.; Garderet, L.; Gozzetti, A.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; et al. Management of Multiple Myeloma-Related Renal Impairment: Recommendations from the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, e293–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrtsonis, M.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Kafasi, N.; Sachanas, S.; Tzenou, T.; Papadogiannis, A.; Galanis, Z.; Kalpadakis, C.; Dimou, M.; Kyriakou, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of Serum Free Light Chain Ratio at Diagnosis in Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 137, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarin, D.; Giralt, S.; Landau, H.; Lendvai, N.; Lesokhin, A.; Chung, D.; Koehne, G.; Chimento, D.; Devlin, S.M.; Riedel, E.; et al. Patterns of Relapse and Progression in Multiple Myeloma Patients after Auto-SCT: Implications for Patients’ Monitoring after Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Kyle, R.A.; Therneau, T.M.; Melton, L.J.; Bradwell, A.R.; Clark, R.J.; Larson, D.R.; Plevak, M.F.; Dispenzieri, A.; Katzmann, J.A. Serum Free Light Chain Ratio Is an Independent Risk Factor for Progression in Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance. Blood 2005, 106, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X.; Delforge, M.; Reynders, M.; Dillaerts, D.; Sprangers, B.; Fostier, K.; Poesen, K.; Vercammen, M. Antigen Excess Detection by Automated Assays for Free Light Chains. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 59, e235–e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradwell, A.R.; Carr-Smith, H.D.; Mead, G.P.; Tang, L.X.; Showell, P.J.; Drayson, M.T.; Drew, R. Highly Sensitive, Automated Immunoassay for Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in Serum and Urine. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.T.; Pedersen, P.T.; Nielsen, L.C.; Abildgaard, N. Evaluation of the Serum Free Light Chain (SFLC) Analysis in Prediction of Response in Symptomatic Multiple Myeloma Patients: Rapid Profound Reduction in Involved FLC Predicts Achievement of VGPR. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.A.; Plant, T.; Drayson, M.; Cockwell, P.; Kountouri, M.; Basnayake, K.; Harding, S.; Bradwell, A.R.; Mead, G. Serum Free Light Chain Measurement Aids the Diagnosis of Myeloma in Patients with Severe Renal Failure. BMC Nephrol. 2008, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.E.; Indridason, O.S.; Palsson, R.; Rognvaldsson, S.; Love, T.J.; Thorsteinsdottir, S.; Sverrisdottir, I.S.; Vidarsson, B.; Onundarson, P.T.; Agnarsson, B.A.; et al. Defining New Reference Intervals for Serum Free Light Chains in Individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease: Results of the IStopMM Study. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Larson, D.R.; Therneau, T.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kumar, S.; Cerhan, J.R.; Rajkumar, S.V. Long-Term Follow-up of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; González-Calle, V.; Kastritis, E.; Hajek, R.; De Larrea, C.F.; Morgan, G.J.; Merlini, G.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Risk Stratification Model for Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM). Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Schönland, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Comenzo, R.; Kastritis, E.; et al. New Criteria for Response to Treatment in Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis Based on Free Light Chain Measurement and Cardiac Biomarkers: Impact on Survival Outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Colby, C.; Laumann, K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Leung, N.; Dingli, D.; et al. Revised Prognostic Staging System for Light Chain Amyloidosis Incorporating Cardiac Biomarkers and Serum Free Light Chain Measurements. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, R.; Perrone, A.; Cuomo, M.; Liotti, S.; Barchiesi, V.; Cantile, M.; Cavalcanti, E. Analytical Criticalities Associated to Different Immunological Methods for Serum Free Light Chain Detection in Plasma Cell Dyscrasias: A Description of Particular Clinical Cases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigliana, G.; Gulli, F.; Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; De Santis, E.; Colacicco, L.; Cordone, I.; Conti, L.; Basile, U. Serum Free Light Chain Quantitative Assays: Dilemma of a Biomarker. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.Y.; Rim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.-G.; Lim, J.-B. Clinical Implication by Differential Analytical Performances of Serum Free Light Chain Quantitation Analysis Using Fully Automated Analyzers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2023, 61, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.; Merlini, G.; Miguel, J.S.; Ludwig, H.; Hajek, R.; Palumbo, A.; Jagannath, S.; Blade, J.; Lonial, S.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Guidelines for Serum-Free Light Chain Analysis in Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders. Leukemia 2009, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.F.M.; Haagen, I.-A.; Lodder, A.; van der Kroft, C.; de Kat Angelino, C.M.; Croockewit, S.; Nieuwenhuys, E.; Gelderman, K.A. Analytical Validation of the Hevylite Assays for M-Protein Quantification. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2018, 56, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradwell, A.R.; Harding, S.J.; Fourrier, N.J.; Wallis, G.L.F.; Drayson, M.T.; Carr-Smith, H.D.; Mead, G.P. Assessment of Monoclonal Gammopathies by Nephelometric Measurement of Individual Immunoglobulin κ/λ Ratios. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Willrich, M.A.V.; Kohlhagen, M.C.; Kyle, R.A.; Murray, D.L.; Snyder, M.R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A. Monitoring IgA Multiple Myeloma: Immunoglobulin Heavy/Light Chain Assays. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, N.M.; Vardanyan, S.; Ghermezi, M.; Gottlieb, J.; Berenson, A.; Andreu-Vieyra, C.; Berenson, J.R. Levels of Uninvolved Immunoglobulins Predict Clinical Status and Progression--free Survival for Multiple Myeloma Patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, H.; Milosavljevic, D.; Berlanga, O.; Zojer, N.; Hübl, W.; Fritz, V.; Harding, S. Suppression of the Noninvolved Pair of the Myeloma Isotype Correlates with Poor Survival in Newly Diagnosed and Relapsed/Refractory Patients with Myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Tamayo, R.; Puig, N.; Algarín, M.; García de Veas Silva, J.L.; Barbosa, N.; Encinas, C.; Hernández, J.Á.; Alonso, R.; Campos, M.L.; Rodríguez, T.; et al. The Current Role of the Heavy/Light Chain Assay in the Diagnosis, Prognosis and Monitoring of Multiple Myeloma: An Evidence-Based Approach. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michallet, M.; Chapuis-Cellier, C.; Lombard, C.; Sobh, M.; Dejoie, T.; Caillon, H.; Attal, M.; Moreau, P.; Avet-Loiseau, H. Response Assignment Using Hevylite Correlates With Clinical Outcome in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, e44–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Anderson, K. Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández de Larrea, C.; Kyle, R.; Rosiñol, L.; Paiva, B.; Engelhardt, M.; Usmani, S.; Caers, J.; Gonsalves, W.; Schjesvold, F.; Merlini, G.; et al. Primary Plasma Cell Leukemia: Consensus Definition by the International Myeloma Working Group According to Peripheral Blood Plasma Cell Percentage. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, B.J.; Clark, D.M.; Wilkins, B.S. Bone Marrow Pathology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119398127. [Google Scholar]
- Ribourtout, B.; Zandecki, M. Plasma Cell Morphology in Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders. Morphologie 2015, 99, 38–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgren, O.; Rajkumar, S.V. New Developments in Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Assessment of Response in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5428–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Kaufman, J.L. Non-Secretory Myeloma: A Clinician’s Guide. Oncology 2013, 27, 924–928,930. [Google Scholar]
- The International Myeloma Working Group. Criteria for the Classification of Monoclonal Gammopathies, Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: A Report of the International Myeloma Working Group. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.A.; Patel, K.H.; Yang, T.; Koch, D.D.; Sivers, S.M.; Smith, G.H.; Jaye, D.L. Is a 500-Cell Count Necessary for Bone Marrow Differentials? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 150, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Tamayo, R.; Sánchez, M.J.; Gómez-Rojas, S.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Segura, G.P.; Redondo-Sánchez, D.; Carreño-Tarragona, G.; Nicolás, A.R.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; Jiménez, P.; et al. Cell Count Differentials by Cytomorphology and Next-Generation Flow Cytometry in Bone Marrow Aspirate: An Evidence-Based Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakuwa, T.; Araki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Fukuyama, T.; Miura, A.; Fujitani, Y.; Hisanabe, A.; Kaieda, A.; Fukada, E.; Yamamura, R. Morphologic Classification Is an Important Prognostic Factor in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Treated with Bortezomib or Lenalidomide. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 50, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Erber, W.N.; Porwit, A.; Tomonaga, M.; Peterson, L.C. ICSH Guidelines for the Standardization of Bone Marrow Specimens and Reports. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2008, 30, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; Almeida, J.; Pérez--Andrés, M.; Mateo, G.; López, A.; Rasillo, A.; Vídriales, M.; López--Berges, M.; Miguel, J.F.S.; Orfao, A. Utility of Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping in Multiple Myeloma and Other Clonal Plasma Cell-related Disorders. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78B, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Persona, E.; Vidriales, M.-B.; Mateo, G.; García-Sanz, R.; Mateos, M.-V.; de Coca, A.G.; Galende, J.; Martín-Nuñez, G.; Alonso, J.M.; de las Heras, N.; et al. New Criteria to Identify Risk of Progression in Monoclonal Gammopathy of Uncertain Significance and Smoldering Multiple Myeloma Based on Multiparameter Flow Cytometry Analysis of Bone Marrow Plasma Cells. Blood 2007, 110, 2586–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, G.; Montalbán, M.A.; Vidriales, M.-B.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Mateos, M.V.; Gutiérrez, N.; Rosiñol, L.; Montejano, L.; Bladé, J.; Martínez, R.; et al. Prognostic Value of Immunophenotyping in Multiple Myeloma: A Study by the PETHEMA/GEM Cooperative Study Groups on Patients Uniformly Treated With High-Dose Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Terpos, E.; Boccadoro, M.; Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Zweegman, S.; Cook, G.; Engelhardt, M.; Delforge, M.; Hajek, R.; et al. EHA–EMN Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up of Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 22, 680–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow Antibody Panels for Standardized N-Dimensional Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Normal, Reactive and Malignant Leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, J.F.; García-Sanz, R.; González, M.; Moro, M.J.; Hernández, J.M.; Ortega, F.; Borrego, D.; Carnero, M.; Casanova, F.; Jiménez, R. A New Staging System for Multiple Myeloma Based on the Number of S-Phase Plasma Cells. Blood 1995, 85, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sędek, Ł.; Flores-Montero, J.; van der Sluijs, A.; Kulis, J.; te Marvelde, J.; Philippé, J.; Böttcher, S.; Bitter, M.; Caetano, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; et al. Impact of Pre-Analytical and Analytical Variables Associated with Sample Preparation on Flow Cytometric Stainings Obtained with EuroFlow Panels. Cancers 2022, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadav, L.; Katz, B.; Baron, S.; Yossipov, L.; Polliack, A.; Deutsch, V.; Geiger, B.; Naparstek, E. Diverse Niches within Multiple Myeloma Bone Marrow Aspirates Affect Plasma Cell Enumeration. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 133, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, N.C.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Anderson, K.C.; Neri, P.; Paiva, B.; Samur, M.; Dimopoulos, M.; Kulakova, M.; Lam, A.; Hashim, M.; et al. A Large Meta-Analysis Establishes the Role of MRD Negativity in Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5988–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgren, O.; Prior, T.J.; Masterson, T.; Heuck, C.; Bueno, O.F.; Dash, A.B.; Einsele, H.; Goldschmidt, H.; Knop, S.; Li, C.; et al. EVIDENCE Meta-Analysis: Evaluating Minimal Residual Disease as an Intermediate Clinical End Point for Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2024, 144, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Sánchez, O.; Böttcher, S.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Pérez-Morán, J.-J.; Vidriales, M.-B.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Next Generation Flow for Highly Sensitive and Standardized Detection of Minimal Residual Disease in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroz, M.; Came, N.; Lin, P.; Chen, W.; Yuan, C.; Lagoo, A.; Monreal, M.; de Tute, R.; Vergilio, J.; Rawstron, A.C.; et al. Consensus Guidelines on Plasma Cell Myeloma Minimal Residual Disease Analysis and Reporting. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, N.; Flores-Montero, J.; Burgos, L.; Cedena, M.-T.; Cordón, L.; Pérez, J.-J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Manrique, I.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Rosiñol, L.; et al. Reference Values to Assess Hemodilution and Warn of Potential False-Negative Minimal Residual Disease Results in Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.S.; Pedreira, C.E.; Barrena, S.; Lecrevisse, Q.; Flores, J.; Quijano, S.; Almeida, J.; del Carmen García- Macias, M.; Bottcher, S.; Van Dongen, J.J.M.; et al. Automated Pattern-Guided Principal Component Analysis vs Expert-Based Immunophenotypic Classification of B-Cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A Step Forward in the Standardization of Clinical Immunophenotyping. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, L.; Mejstrikova, E.; van der Sluijs-Gelling, A.J.; Grigore, G.E.; Sedek, L.; Bras, A.E.; Gaipa, G.; Sobral da Costa, E.; Novakova, M.; Sonneveld, E.; et al. Automated Database-Guided Expert-Supervised Orientation for Immunophenotypic Diagnosis and Classification of Acute Leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoja-Flores, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Garcés, J.J.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Mateo, A.; García-Sánchez, O.; Corral-Mateos, A.; Burgos, L.; Blanco, E.; et al. Next Generation Flow for Minimally-Invasive Blood Characterization of MGUS and Multiple Myeloma at Diagnosis Based on Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells (CTPC). Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, J.-J.; Cedena, M.-T.; Puig, N.; Burgos, L.; Perez, J.J.; Cordon, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Calasanz, M.-J.; Ortiol, A.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells for the Staging of Patients With Newly Diagnosed Transplant-Eligible Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3151–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, N.; Tesfaluul, N.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Yue, B. Prognostic Value of Circulating Plasma Cells in Patients with Multiple Myeloma: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, W.I.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Gupta, V.; Morice, W.G.; Timm, M.M.; Singh, P.P.; Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Quantification of Clonal Circulating Plasma Cells in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma: Implications for Redefining High-Risk Myeloma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, S.V. The Multiple Myelomas—Current Concepts in Cytogenetic Classification and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Andersen, E.F.; Banerjee, R.; Eno, C.C.; Gonzales, P.R.; Kumar, S.; Lager, A.M.; Miron, P.M.; Pugh, T.; Quintero-Rivera, F.; et al. Guidelines for the Testing and Reporting of Cytogenetic Results for Risk Stratification of Multiple Myeloma: A Report of the Cancer Genomics Consortium Plasma Cell Neoplasm Working Group. Blood Cancer J. 2025, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, R.; Barlogie, B.; Bataille, R.; Bastard, C.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Chesi, M.; Davies, F.E.; Drach, J.; Greipp, P.R.; Kirsch, I.R.; et al. Genetics and Cytogenetics of Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Harrison, S.J.; Cavo, M.; de la Rubia, J.; Popat, R.; Gasparetto, C.; Hungria, V.; Salwender, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kim, I.; et al. Venetoclax or Placebo in Combination with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (BELLINI): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Multicentre, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellors, P.W.; Binder, M.; Ketterling, R.P.; Greipp, P.T.; Baughn, L.B.; Peterson, J.F.; Jevremovic, D.; Pearce, K.E.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; et al. Metaphase Cytogenetics and Plasma Cell Proliferation Index for Risk Stratification in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigyesi, I.; Adolfsson, J.; Ali, M.; Kronborg Christophersen, M.; Johnsson, E.; Turesson, I.; Gullberg, U.; Hansson, M.; Nilsson, B. Robust Isolation of Malignant Plasma Cells in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2014, 123, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Drach, J.; Shaughnessy, J.; Gutierrez, N.; Stewart, A.K.; Morgan, G.; Van Ness, B.; Chesi, M.; Minvielle, S.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Molecular Classification of Multiple Myeloma: Spotlight Review. Leukemia 2009, 23, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.; Cairns, D.A.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Wester, R.; Bertsch, U.; Waage, A.; Zamagni, E.; Mateos, M.-V.; Dall’Olio, D.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; et al. Second Revision of the International Staging System (R2-ISS) for Overall Survival in Multiple Myeloma: A European Myeloma Network (EMN) Report Within the HARMONY Project. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3406–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Gertz, M.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Kyle, R.A.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Lust, J.A.; Russell, S.J.; Hayman, S.R.; et al. Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Based on Mayo Stratification of Myeloma and Risk-Adapted Therapy (MSMART): Consensus Statement. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, K.C.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Shaughnessy, J.; Palumbo, A.; Durie, B.; Fonseca, R.; Stewart, A.K.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Dimopoulos, M.; et al. Consensus Recommendations for Risk Stratification in Multiple Myeloma: Report of the International Myeloma Workshop Consensus Panel 2. Blood 2011, 117, 4696–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avet-Loiseau, H.; Davies, F.E.; Samur, M.K.; Corre, J.; D’Agostino, M.; Kaiser, M.F.; Raab, M.S.; Weinhold, N.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Paiva, B.; et al. International Myeloma Society/International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Recommendations on the Definition of High-Risk Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 2739–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, K.; Vidrequin, S.; Dargent, J.-L. Genomic Profiling of Myeloma: The Best Approach, a Comparison of Cytogenetics, FISH and Array-CGH of 112 Myeloma Cases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martello, M.; Poletti, A.; Borsi, E.; Solli, V.; Dozza, L.; Barbato, S.; Zamagni, E.; Tacchetti, P.; Pantani, L.; Mancuso, K.; et al. Clonal and Subclonal TP53 Molecular Impairment Is Associated with Prognosis and Progression in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avet-Loiseau, H.; Li, C.; Magrangeas, F.; Gouraud, W.; Charbonnel, C.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Attal, M.; Marit, G.; Mathiot, C.; Facon, T.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Copy-Number Alterations in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4585–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano, A.; Tuchman, S.A.; Acharya, C.; Salter, K.; Gasparetto, C.; Zhan, F.; Dhodapkar, M.; Nevins, J.; Barlogie, B.; Shaughnessy, J.D.; et al. Gene Expression Profiles of Tumor Biology Provide a Novel Approach to Prognosis and May Guide the Selection of Therapeutic Targets in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4197–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa-Rosa, J.M.; Cuenca, I.; Medina, A.; Vázquez, I.; Sánchez-delaCruz, A.; Buenache, N.; Sánchez, R.; Jiménez, C.; Rosiñol, L.; Gutiérrez, N.C.; et al. NGS-Based Molecular Karyotyping of Multiple Myeloma: Results from the GEM12 Clinical Trial. Cancers 2022, 14, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perroud, C.; Thurian, D.; Andres, M.; Künzi, A.; Wiedemann, G.; Zeerleder, S.; Bacher, U.; Pabst, T.; Banz, Y.; Porret, N.; et al. Effect of MAPK Activation via Mutations in NRAS, KRAS and BRAF on Clinical Outcome in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Moreau, P.; Terpos, E.; Mateos, M.V.; Zweegman, S.; Cook, G.; Delforge, M.; Hájek, R.; Schjesvold, F.; Cavo, M.; et al. Multiple Myeloma: EHA-ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up†. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Bai, Y.; Orfao, A.; Kumar, S.; Chim, C.S. Upgraded Standardized Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Next-Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgren, O.; Rustad, E.H. Meeting Report: Advances in Minimal Residual Disease Testing in Multiple Myeloma 2018. Adv. Cell Gene Ther. 2019, 2, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Medina, A.; Puig, N.; Flores-Montero, J.; Jimenez, C.; Sarasquete, M.-E.; Garcia-Alvarez, M.; Prieto-Conde, I.; Chillon, C.; Alcoceba, M.; Gutierrez, N.C.; et al. Comparison of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and next-Generation Flow (NGF) for Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Assessment in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15189:2022; Medical laboratories—Requirements for quality and competence. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Tate, J.; Caldwell, G.; Daly, J.; Gillis, D.; Jenkins, M.; Jovanovich, S.; Martin, H.; Steele, R.; Wienholt, L.; Mollee, P. Recommendations for Standardized Reporting of Protein Electrophoresis in Australia and New Zealand. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2012, 49, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).