1. Introduction
The lifetime risk for fragility fracture is approximately 50% in women and 20% in men over 50 years of age [
1,
2]. The risk of osteoporotic fracture is doubled in patients with a history of prior osteoporotic fractures [
3]. In an extensive US database, the incidence of a second fracture after a hip fracture was 22–25.5% within the first post-fracture year; the second fracture was most likely of the same type as the incident fracture [
4]. Osteoporotic fractures have significant effects on morbidity and quality of life and have been shown to increase mortality risk [
5]. Furthermore, they have substantial economic ramifications [
4].
Despite the high risk for additional fractures, osteoporosis treatment rates in patients after osteoporotic fracture are dismal, remaining at approximately 20% [
6]. Fracture Liaison Services (FLS) were initiated in the 1990s [
7,
8] and brought into international use in 2012 with the launch of the pivotal International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) global ‘Capture the Fracture’ campaign [
9]. The IOF Capture the Fracture Best Practice Framework (BPF) provides criteria for recognition and rating of successful FLS worldwide [
10]. The campaign aims to close the secondary fracture prevention treatment ‘gap’ and reduce the risk of future fractures. Various FLS models exist, and intensive services incorporating patient identification, assessment, and treatment tend to deliver the best outcomes [
11]. FLS programs require the collaboration of healthcare workers within a multidisciplinary team and the implementation of meticulously planned protocols with multiple phases [
12]. Observational studies have shown an association between the establishment of FLS programs and an increase in antiresorptive therapy rates, as well as a reduction in fracture and mortality rates within 12 months of an incident fracture [
13]. Hundreds of FLS programs exist in 55 countries; however, the map of Best Practices indicates a dearth of programs in resource-poor regions throughout the developing world [
14].
Therapeutic decision-making for hip fracture patients in the FLS setting requires consideration of drug efficacy, economic factors, drug contraindications, side effects and potential risks. Drugs that have demonstrated a reduction in hip fracture rates in randomized controlled trials include alendronate, risedronate, zoledronic acid, denosumab, and Romosozumab [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. Meta-analyses have also demonstrated a reduction in hip fractures with teriparatide [
20]. However, head-to-head osteoporosis drug trials with fracture endpoints are scarce [
19,
20]. In secondary fracture prevention, the initiation of osteoporosis treatment has been associated with lower recurrent fracture rates [
21]. The HORIZON recurrent fracture trial demonstrated a reduction in recurrent fractures and mortality in patients after hip fractures treated with Zoledronic acid [
22]. The American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) and the Center for Medical Technology Policy (CMTP) multistakeholder coalition consensus clinical recommendations for secondary fracture prevention recommend oral bisphosphonates as first-line therapy for such patients and intravenous zoledronate or denosumab if oral bisphosphonates pose difficulties; while anabolic agents are recommended for patients with high risk [
23]. Our National Health Basket authorizes first-line osteoporosis treatment with zoledronic acid or denosumab after hip fracture [
24]. While denosumab is not incorporated into the bone matrix and must be administered every 6 months, the antiresorptive effects of a single 5 mg IV dose of zoledronate are sustained for 3 years [
25].
Specific relevant clinical and laboratory scenarios should be considered in therapeutic decision-making. For instance, the prevalence of secondary osteoporosis is higher in younger patients, accounting for more than 50% of cases in premenopausal women; therefore, more extensive investigations are necessary in young patients with osteoporosis [
26]. Furthermore, fractures that occur despite osteoporosis therapy may allude to treatment failure and raise considerations for changing therapy [
27]. Patients with chronic kidney disease pose unique therapeutic dilemmas due to the coexistence of varied pathophysiological forms of chronic kidney disease-related mineral bone disease [
28], estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) cutoffs of the various therapies, and risk of hypocalcemia after anti-resorptive treatment. Pre-treatment Vitamin D levels are necessary as vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased mortality and complications as well as reduced post-surgical functional recovery in hip fracture patients [
29]. Additionally, patients in HORIZON with vitamin D deficiency developed hypocalcemia after receiving zoledronic acid treatment [
15]; therefore, patients in the HORIZON recurrent fracture trial with vitamin D deficiency were given a loading dose of vitamin D before receiving zoledronic acid therapy [
22].
This study evaluated the functionality of a low-cost, low-resource, streamlined, computerized, algorithm-supported, Nurse Practitioner-managed institutional FLS model.
2. Methods
This is a retrospective study evaluating the functionality of the computerized algorithm for FLS in patients admitted to the Orthopedic Department with hip fractures between 1 April and 31 October 2024, identified by a dedicated Nurse Practitioner.
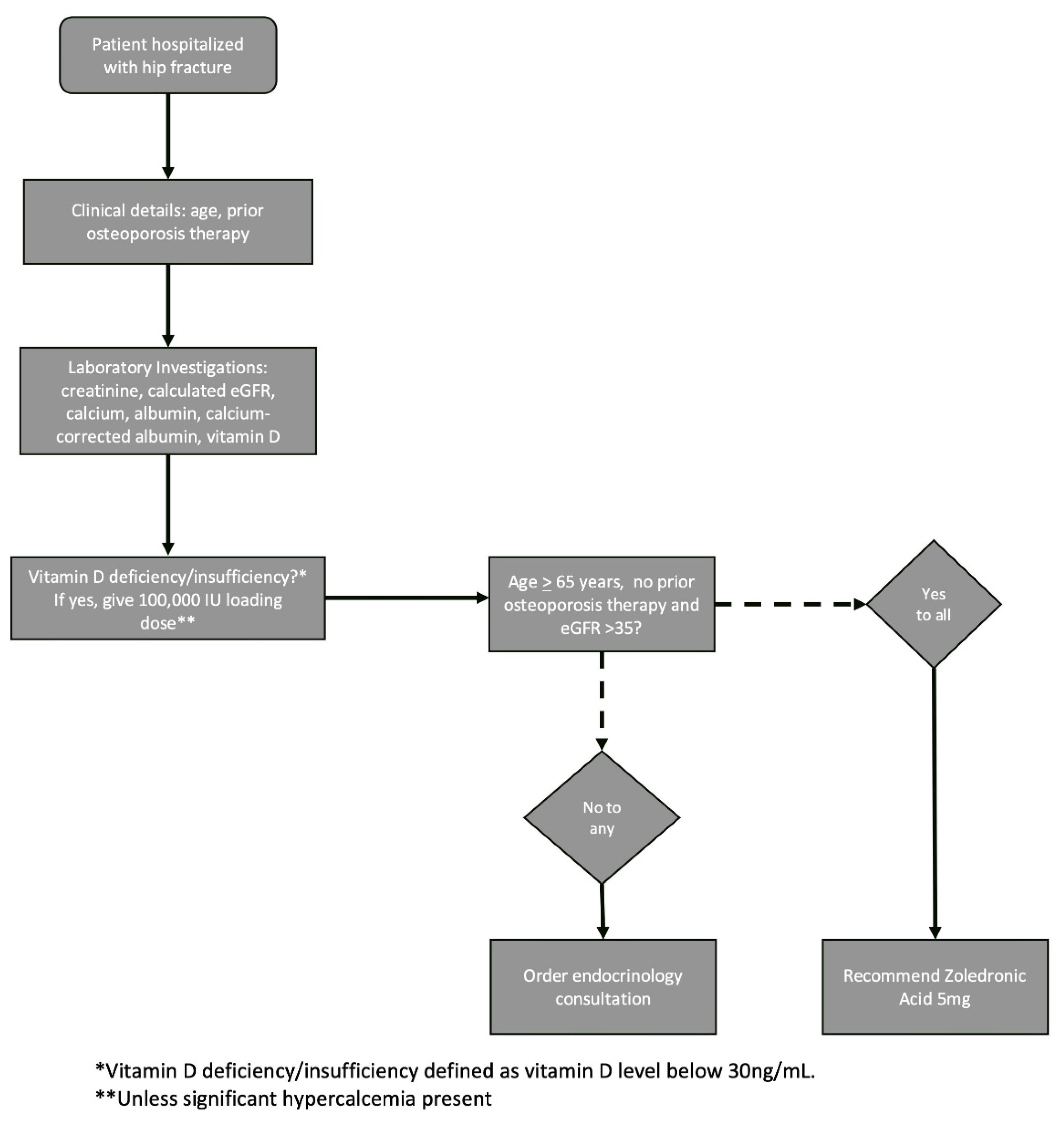
Osteoporosis therapy recommendations were provided based on a decision-making algorithm developed by the endocrinology team. Zoledronic acid was chosen as the algorithm’s default therapy recommendation due to the drug’s authorization as a first-line therapy for hip fracture in the Israeli Health Basket, its demonstrated mortality benefit in this setting, and its long-lasting activity. Denosumab, which can also be given as a first-line treatment after hip fracture in Israel, was not chosen as the protocol standard due to the importance of continued adherence with this drug and the risks associated with its discontinuation. The therapeutic decision-making algorithm (
Figure 1) requires only three inputs: patient age, current eGFR and use of prior osteoporosis therapy. For treatment-naïve patients aged 65 years and above with eGFR > 35, zoledronic acid is recommended. An endocrinology consultation was recommended for patients who did not fit these criteria to provide an individualized treatment decision.
The described FLS protocol was integrated as a computerized component into the electronic medical records (EMR). The Orthopedic Department’s dedicated nurse practitioner was responsible for identifying patients, running the algorithm, and ordering endocrinology consultations as necessary.
Exclusion criteria included patients with a high-energy fracture mechanism or non-proximal femoral fracture sites, including subtrochanteric, distal or unknown fracture sites.
In-hospital laboratory assessment included serum creatinine, calcium, albumin, and vitamin D levels. Laboratory assays used were creatinine testing by kinetic colorimetric assay (CREJ2, Jaffe Gen.2, Cobas), calcium testing by photometric assay (CA2, Cobas, Basel, Switzerland), albumin testing by colorimetric assay (ALB2, Cobas), and total 25-hydroxyvitamin D by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (Elecsys Vitamin D total III, Cobas), all by Roche Diagnostics. eGFR was estimated by the hospital laboratory using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula, and in cases where the calculated eGFR was above 120, it was corrected to 120. Serum calcium was corrected for albumin using the formula: corrected calcium = 0.8 × (4-patient albumin) + serum calcium. Hypercalcemia was defined as a corrected calcium level above the upper limit of normal and was considered mild if the corrected calcium level was below 12 mg/dL. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as a level below 20 ng/mL, and insufficiency was defined as a level between 20 and <30 ng/mL. Hypoalbuminemia was defined as a serum albumin level <3.5 g/dL, and clinically significant hypoalbuminemia as <2.5 g/dL. Patients with vitamin D deficiency/insufficiency were given a loading dose of 100,000 units during hospitalization as long as hypercalcemia was not present. Endocrinology consultation was advised for all patients with hypercalcemia to consider in-hospital therapy and evaluate for relevant causes of secondary osteoporosis.
At discharge, patients were recommended a high-calcium diet and continued vitamin D treatment at a dose of 1000 IU per day. The algorithm treatment recommendation or endocrinology consultation appeared in the hospital discharge letter. Patients could then receive the recommended osteoporosis therapy in the treating rehabilitation department or in the outpatient setting. After discharge, patients received telephone communications from the FLS program coordinator to remind them of the importance of continuing this therapy and to assist with any related difficulties. Patients who required further investigation were followed up at the outpatient clinic in the hospital’s endocrinology department.
Patient data were extracted from institutional electronic medical records, including age, sex, fracture date, fracture subtype, osteoporosis therapy before fracture, hospital laboratory results, use of the FLS treatment algorithm, endocrinology consultation recommendations, and administration of a vitamin D loading dose.
The Institutional Ethics Committee approved the study (0213-21-WOMC). Following Helsinki regulations regarding clinical studies based on chart review, informed consent was waived.
Statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel for Mac version 16.66.1. Categorical variables are presented as counts and percentages. In contrast, continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for normally distributed variables or as the median and interquartile range (IQR) where appropriate. Differences between groups were assessed using the independent samples t-test for continuous variables and Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. A two-tailed p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
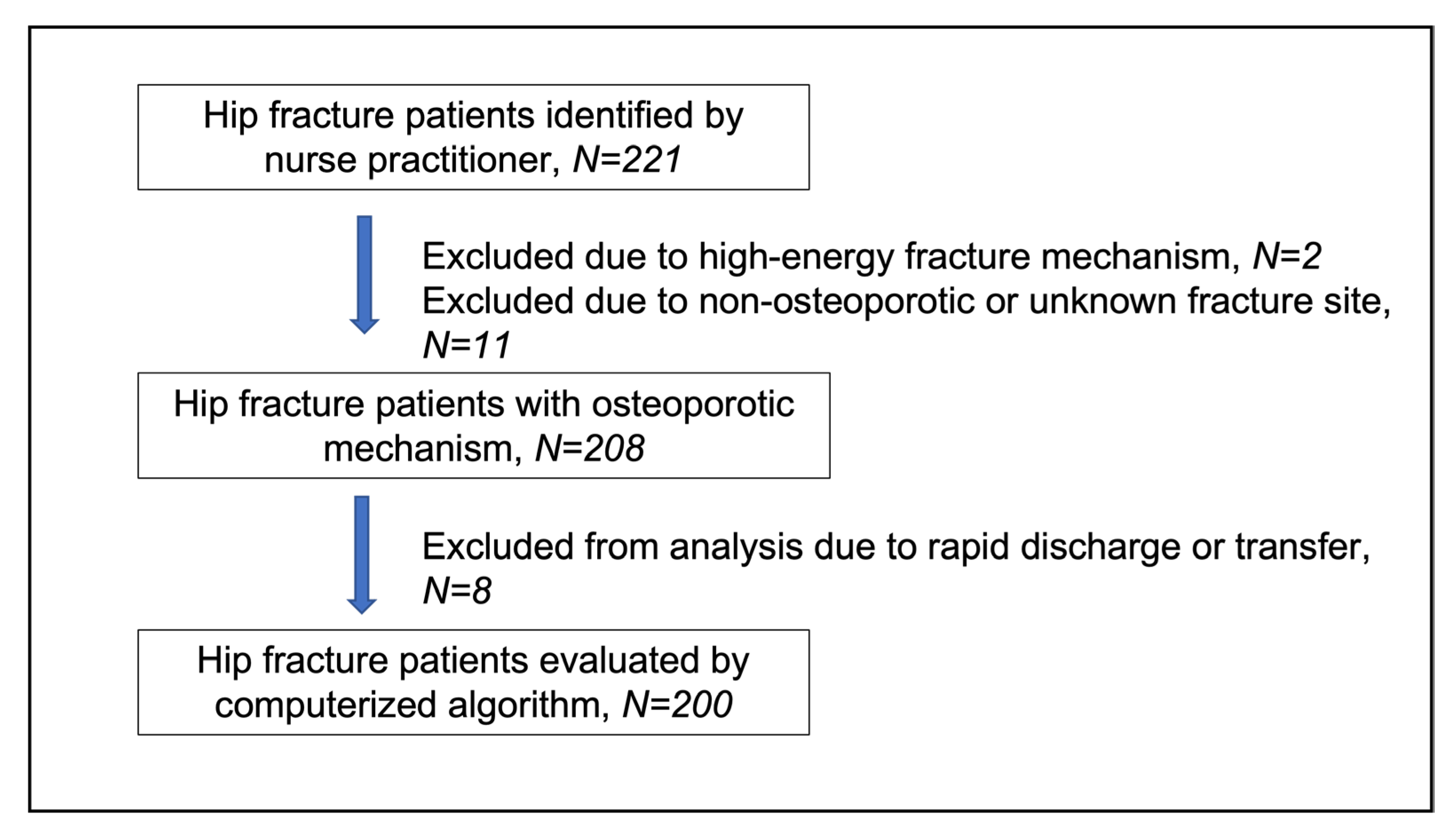
Two hundred and twenty-two hospitalizations with hip fractures were identified in 221 patients by the nurse practitioner within the specified time frame. Of these, 13 were excluded from the study due to high-energy fracture mechanism (n = 2), subtrochanteric or distal femoral fracture site (n = 10), and unspecified fracture site (n = 1). Therefore, a cohort of 208 patients with osteoporotic hip fractures was included in the analysis. A study flow-chart is shown in
Figure 2.
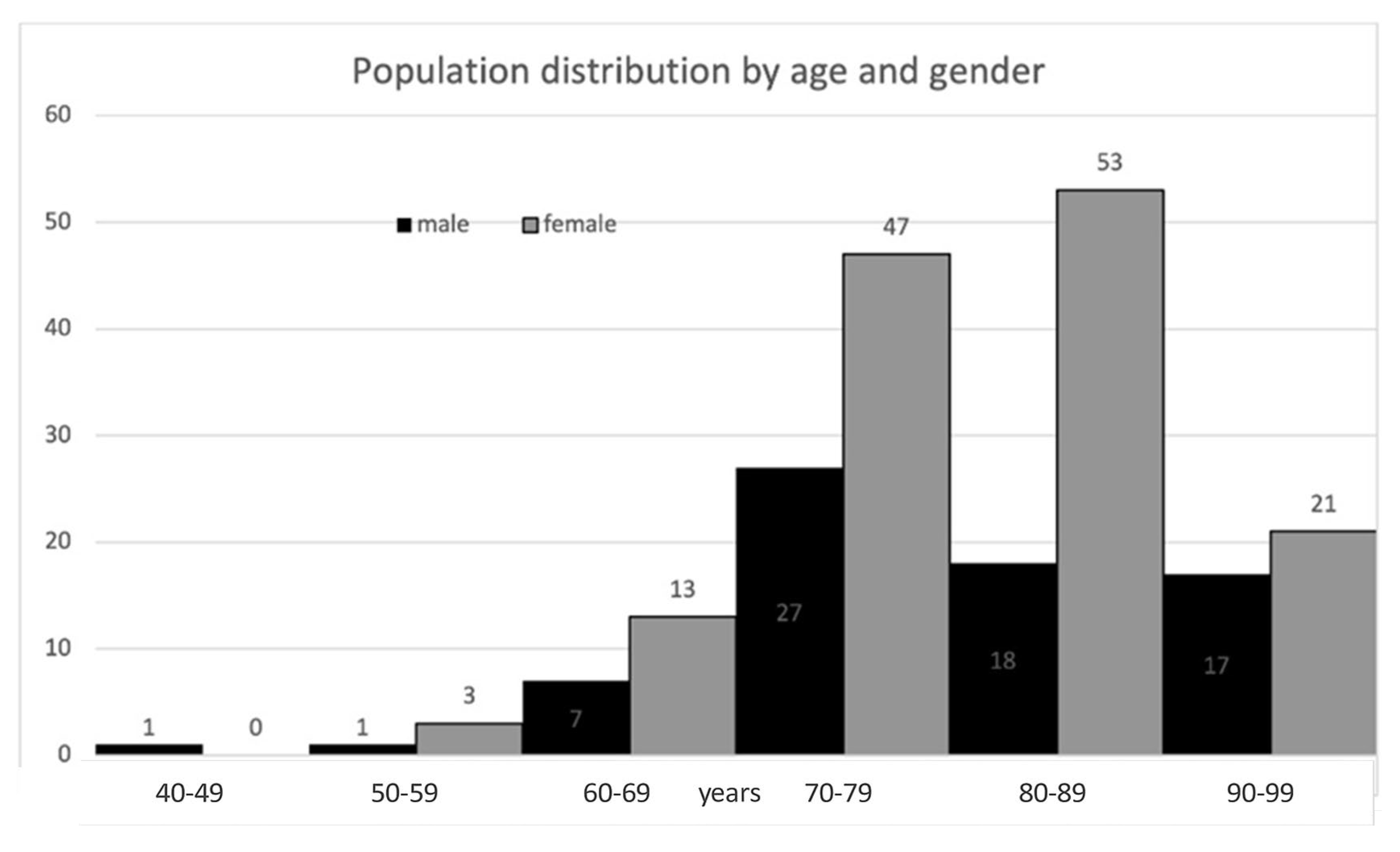
The cohort consisted chiefly of elderly patients and was predominantly female. Baseline characteristics are described in
Table 1, and age and gender distribution are depicted in
Figure 3. Twelve fracture cases (5.8%) were diagnosed below age 65 years; 8 of these patients (66.7%) had at least one documented risk factor or secondary cause of osteoporosis, including malignancy with bone metastases (n = 1), spinal muscular atrophy (n = 1), primary hyperparathyroidism (n = 1), diabetes mellitus (n = 1), epilepsy (n = 1), premature ovarian insufficiency (n = 1), family history of osteoporosis (n = 2), smoking (n = 2), drug abuse (n = 1), and hepatitis C virus infection (n = 1).
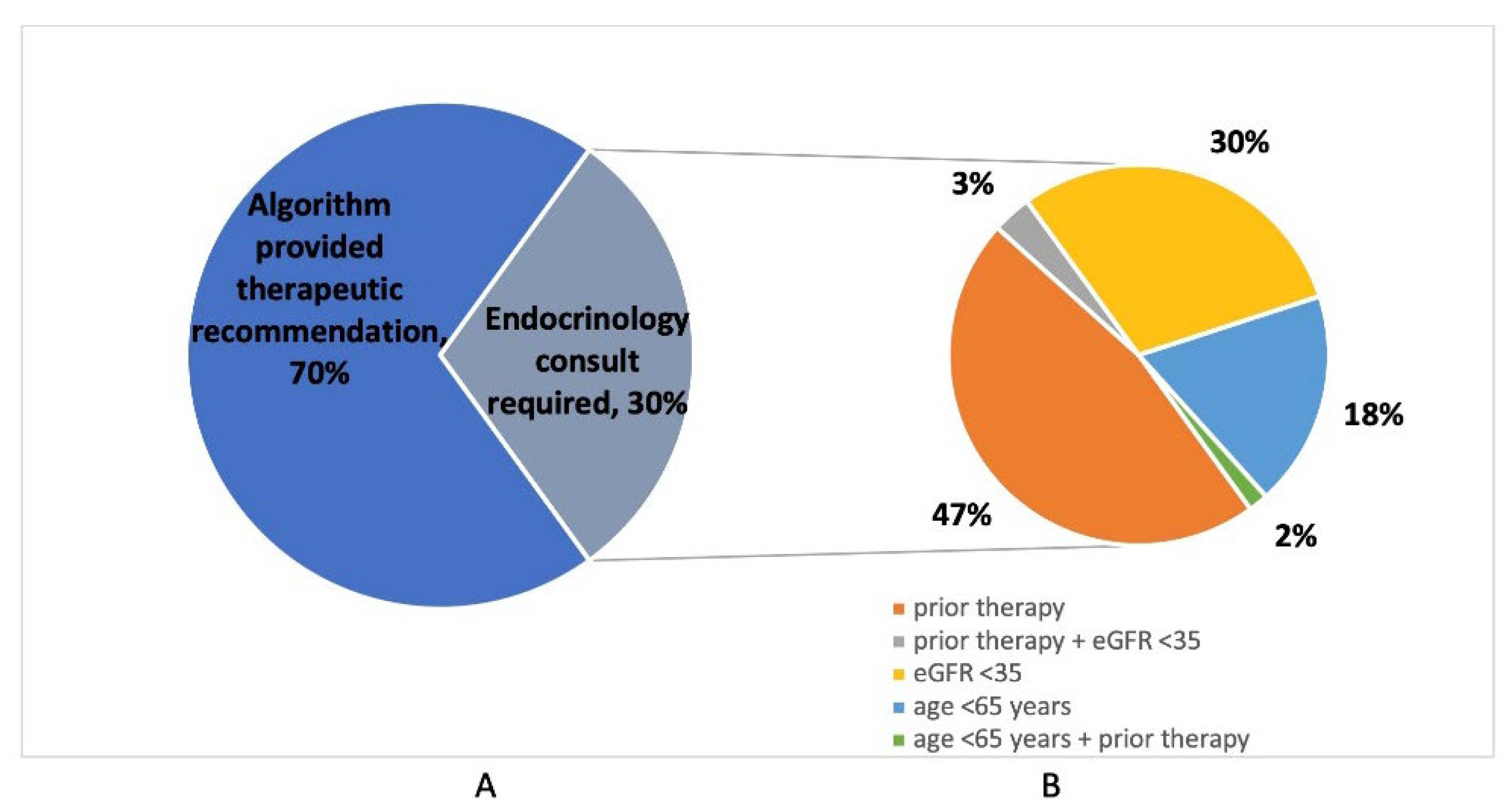
Nurse Practitioner assessments using a computerized algorithm were performed in 200 out of 208 osteoporotic fracture cases (96.2%); cases were missed due to rapid patient discharge or transfer. Of those assessed, the computerized FLS algorithm provided a direct recommendation for zoledronic acid in 140/200 (70.0%) of cases, while 60/200 (30.0%) required an endocrinology consultation (
Table 2). Reasons for requests for endocrinology consultation included known or suspected previous osteoporosis therapy in 31/60 (51.7%), eGFR <35 in 20/60 (33.3%), and age below 65 years in 12/60 (20.0%) of patients (
Figure 4). Previous osteoporosis therapies included oral bisphosphonates (n = 20), zoledronic acid (n = 2), denosumab (n = 4), and teriparatide (n = 2); a further three patients were suspected of having received previous therapy, but additional details were unknown.
Hypercalcemia was noted in 4/208 patients (1.9%); all cases were mild. Hypoalbuminemia was noted in 68/208 cases (32.7%); only one case was clinically significant. Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency accounted for 79.7% (161/202) of the cohort with known vitamin D levels. Vitamin D loading doses were given in 89/99 (89.9%) of deficiency and 44/62 (71.0%) of insufficiency cases (
Table 3).
An endocrinology consultation was performed in 56 out of 60 requested cases (93.3%);
Table 2 describes the therapies recommended during the consultation. For patients with a history of prior osteoporosis therapy, treatment recommendations included zoledronic acid (n = 17), denosumab (n = 2), and further investigations (n = 8); consultation was not performed in one case. For those with an eGFR <35, treatment recommendations included zoledronic acid (n = 1), further investigations (n = 7), and no therapy (n = 8); consultation was not performed in two cases. For patients under 65, recommendations included zoledronic acid (n = 3) and further investigations (n = 7); consultation was not performed in one case. One young patient with prior treatment was recommended for teriparatide treatment. Two patients with low eGFR and a history of prior treatment were recommended denosumab and further investigations, respectively. Further investigations were requested in cases where anabolic therapy was considered, eGFR was low, or patients were young, and secondary osteoporosis was suspected.
Comparing the clinical and laboratory characteristics of patients who received treatment recommendations via the computerized FLS algorithm and those requiring endocrinology consultation, the latter were more likely to be female and have a lower eGFR (
Table 4).
4. Discussion
Numerous FLS programs exist worldwide and are implemented in varying performance models tailored to fit the structure of local or regional healthcare systems. Straightforward approaches that require minimal clinical and laboratory data, as well as minimal physician intervention, may encourage the implementation of such programs in resource-constrained institutions and regions. We developed an FLS model involving a simple flowchart, an EMR-integrated algorithm-based decision-making tool which a nurse practitioner could perform.
In this FLS model, 96.2% of patients identified by the Nurse Practitioner were evaluated during admission to the Orthopedic Department. Prior osteoporosis medications were reviewed in all tracked cases. The application of the algorithm generated a direct therapeutic recommendation in 70% of cases, while an endocrinology consultation was required in only 30%. The most frequent reason for endocrinology consultation was prior osteoporosis therapy, accounting for over 50% of consultations; almost all prior treatments were bisphosphonates, as would be expected in an elderly hip fracture cohort. Anabolic therapies were considered for several of these patients; however, further investigations were requested in most cases to allow individualized decision-making. A third of consultations were due to low eGFR, alluding to the presence of chronic kidney disease-related metabolic bone disease. This complex phenomenon raises multiple questions, including the underlying pathophysiology of the individual case, the current and predicted eGFR of the patient, and the ability to discontinue therapy in this context if necessary. Ultimately, while some of these patients were recommended denosumab, in other cases, no treatment was recommended. Only a few consultations were due to young patient age; most of these patients had documented risk factors or secondary causes of osteoporosis, and the others were recommended to undergo extensive evaluation.
Overall, therapeutic recommendations for osteoporosis were provided during hospitalization in 165/200 (82.5%) of the evaluated patients; further investigations were recommended in 23/200 (11.5%), and no therapy was recommended in 8/200 (4.0%). Implementation of treatment recommendations was followed up post-discharge by the FLS coordinator.
Vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency was noted in the vast majority (almost 80%) of the cohort, alluding to the increased mortality and complication risk in this cohort, [
29], as well as an increased risk of hypocalcemia after zoledronic acid treatment, if left untreated [
15]. Over 80% of patients with insufficiency or deficiency were given an in-hospital loading dose of vitamin D, thereby enabling the early provision of osteoporosis therapy post-discharge with a reduced risk of hypocalcemia. A loading dose was not administered if hypercalcemia was present or if the vitamin D level was unavailable at the time of the nurse practitioner evaluation.
This study has several limitations. A major limitation is its retrospective, single-center nature, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other healthcare systems, particularly those with different reimbursement structures or scope-of-practice regulations for nurse practitioners. Second, the study did not assess post-discharge treatment initiation, adherence, or long-term outcomes such as fracture recurrence or mortality. These data are essential for evaluating the actual clinical impact of the FLS model and are planned for future analysis. Third, the use of the simple decision-making algorithm eliminates the element of personalized medicine in therapeutic decision-making. The decision-making algorithm prioritized zoledronic acid as the default therapy, in line with national health policy, which may have limited the use of other therapies with higher rates of fracture prevention, including anabolic therapies and denosumab. These were not included as first-line recommendations due to cost and policy constraints for anabolic therapies, as well as adherence concerns for denosumab. The use of zoledronic acid as a first-line treatment may not reflect the optimal treatment strategy in all cases. Ultimately, anabolic therapy was recommended in very few cases in our study. Finally, the reliance on nurse practitioners has its drawbacks, including the reduced involvement of treating physicians in osteoporosis care and limited authorizations granted to nurse practitioners. The model’s applicability may also be limited in healthcare settings where electronic medical record integration is not feasible.
The study group aims to facilitate the implementation of a streamlined, computerized EMR algorithm-based FLS model in other medical institutions across Israel. The development of the algorithm as an automated component in the Chameleon EMR program, utilized by many Israeli medical institutions, makes this a feasible goal. We further propose that this simple, low-cost FLS model be adopted by other institutions worldwide, particularly those with limited resources. A crucial potential improvement to the model would be broadening its scope to include other types of osteoporotic fractures; however, this would necessitate the development of fracture-specific, appropriate treatment algorithms.
In conclusion, this low-cost, low-resource nurse-practitioner-mediated, computerized algorithm-based FLS model provided osteoporosis treatment recommendations for most hip fracture patients, demonstrating its potential in providing therapeutic recommendations to large cohorts of hip fracture patients in settings with limited resources. Large, prospective multi-center studies are necessary to determine the value of the model in a broader clinical setting.
Author Contributions
R.C.R.—Study design, acquisition of data, analysis/interpretation of data, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work; A.K.—Acquisition of data, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work; D.H.—Study design, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work; M.N.—Study design, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work; O.H.—Study design, analysis/interpretation of data, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work; O.T.—Study design, acquisition of data, analysis/interpretation of data, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work; R.L.—Study design, acquisition of data, analysis/interpretation of data, critical revision, final approval, and accountability for all aspects of the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Israel Foundation for Osteoporosis and Bone Diseases provided an ongoing grant of 1000 NIS per month from January 2022 to support the operation of the Fracture Liaison Service at Wolfson Medical Center.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Edith Wolfson Medical Center obtained IRB approval, located in Holon, Israel, and affiliated with the Sackler Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel (Approval Study 0213-21- WOMC on 28 December 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Edith Wolfson Medical Center obtained IRB approval, exempting it from the need for informed consent due to its retrospective nature.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Rachel Chava Rosenblum, Arthur Kogan, Dana Herzberg, Maysara Najjar, Oded Hershkovich, Orit Twito, and Raphael Lotan declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ström, O.; Borgström, F.; Kanis, J.A.; Compston, J.; Cooper, C.; McCloskey, E.V.; Jönsson, B. Osteoporosis: Burden, Health Care Provision and Opportunities in the EU: A Report Prepared in Collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van Staa, T.; Dennison, E.; Leufkens, H.; Cooper, C.J.B. Epidemiology of fractures in England and Wales. Bone 2001, 29, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotzbuecher, C.M.; Ross, P.D.; Landsman, P.B.; Abbott, T.A., III; Berger, M. Patients with prior fractures have an increased risk of future fractures: A summary of the literature and statistical synthesis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.; Sajjan, S.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Harris, S.T.; Marvos, P. Prevalence and cost of subsequent fractures among US patients with an incident fracture. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2017, 23, 461–471. [Google Scholar]
- Jodar Gimeno, E. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Mortality and morbidity. Rev. Osteoporos. Metab. Miner. 2010, 2, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, S.L.; Wyman, A.; Hooven, F.H.; Adami, S.; Gehlbach, S.; Anderson, F.A., Jr.; Boone, S.; Lacroix, A.Z.; Lindsay, R.; Coen Netelenbos, J.; et al. Predictors of treatment with osteoporosis medications after recent fragility fractures in a multinational cohort of postmenopausal women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, A.; Reid, D.; Forbes, K.; Reid, R.; Campbell, C.; Gregori, A.; Raby, N.; Simpson, A. Effectiveness of strategies for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in Scotland (CEPS 99/03). NHS Qual. Improv. Scotl. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher, S.J. Setting up an osteoporosis fracture liaison service: Background and potential outcomes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, K.; Marsh, D.; Mitchell, P.J.; McLellan, A.; Stenmark, J.; Pierroz, D.; Kyer, C.; Cooper, C.; IOF Fracture Working Group. Capture the fracture: A best practice framework and global campaign to break the fragility fracture cycle. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 2135–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Osteoporosis Foundation. Available online: www.capturethefracture.org (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Walters, S.; Khan, T.; Ong, T.; Sahota, O. Fracture liaison services: Improving outcomes for patients with osteoporosis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, U.; Greggi, C.; Visconti, V.; Cariati, I.; Bonanni, R.; Gasperini, B.; Iundusi, R.; Gasbarra, E.; Tranquilli Leali, P.; Brandi, M.L. Fracture liaison service model: Project design and accreditation. Osteoporos. Int. 2023, 34, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, D.W.; Piple, A.S.; Smith, C.T.; Moskal, S.A.; Carmouche, J.J. The clinical impact of fracture liaison services: A systematic review. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2021, 12, 2151459320979978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.D.; Evangelisti, G.; Andreani, L.; Girardi, F.; Darren, L.; Sama, A.; Lisanti, M. Postoperative Spine Infections. Orthop. Rev. 2015, 7, 5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, D.M.; Delmas, P.D.; Eastell, R.; Reid, I.R.; Boonen, S.; Cauley, J.A.; Cosman, F.; Lakatos, P.; Leung, P.C.; Man, Z. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.M.; Cummings, S.R.; Karpf, D.B.; Cauley, J.A.; Thompson, D.E.; Nevitt, M.C.; Bauer, D.C.; Genant, H.K.; Haskell, W.L.; Marcus, R. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Lancet 1996, 348, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, M.R.; Geusens, P.; Miller, P.D.; Zippel, H.; Bensen, W.G.; Roux, C.; Adami, S.; Fogelman, I.; Diamond, T.; Eastell, R.; et al. Effect of risedronate on the risk of hip fracture in elderly women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, S.R.; Martin, J.S.; McClung, M.R.; Siris, E.S.; Eastell, R.; Reid, I.R.; Delmas, P.; Zoog, H.B.; Austin, M.; Wang, A. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saag, K.G.; Petersen, J.; Brandi, M.L.; Karaplis, A.C.; Lorentzon, M.; Thomas, T.; Maddox, J.; Fan, M.; Meisner, P.D.; Grauer, A. Romosozumab or alendronate for fracture prevention in women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, D.L.; Marin, F.; Zerbini, C.A.; Russo, L.A.; Greenspan, S.L.; Zikan, V.; Bagur, A.; Malouf-Sierra, J.; Lakatos, P.; Fahrleitner-Pammer, A.J.T.L. Effects of teriparatide and risedronate on new fractures in post-menopausal women with severe osteoporosis (VERO): A multicentre, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.J.; Mahesri, M.; Abdia, Y.; Barberio, J.; Tong, A.; Zhang, D.; Mavros, P.; Kim, S.C.; Franklin, J.M. Association of osteoporosis medication use after hip fracture with prevention of subsequent nonvertebral fractures: An instrumental variable analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyles, K.W.; Colón-Emeric, C.S.; Magaziner, J.S.; Adachi, J.D.; Pieper, C.F.; Mautalen, C.; Hyldstrup, L.; Recknor, C.; Nordsletten, L.; Moore, K.A.; et al. Zoledronic acid and clinical fractures and mortality after hip fracture. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, R.B.; Adib, G.; Adler, R.A.; Åkesson, K.E.; Alexander, I.M.; Amenta, K.C.; Blank, R.D.; Brox, W.T.; Carmody, E.E.; Chapman-Novakofski, K.; et al. Secondary fracture prevention: Consensus clinical recommendations from a multistakeholder coalition. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Israel. Available online: https://www.health.gov.il/Subjects/UninsuredRights/HealthInsuranceLawRights/Pages/SalServicesMOH.aspx (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Silverman, S.L. Defining zoledronate’s duration of action and optimal dosing interval for an effective therapy. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2011, 9, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ebeling, P.R.; Nguyen, H.H.; Aleksova, J.; Vincent, A.J.; Wong, P.; Milat, F.J. Secondary osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 240–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastell, R.; Rosen, C.J.; Black, D.M.; Cheung, A.M.; Murad, M.H.; Shoback, D. Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1595–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Cunningham, J.; Ferrari, S.; Haarhaus, M.; Javaid, M.; Lafage-Proust, M.-H.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Torres, P.; Cannata-Andia, J.; European Renal Osteodystrophy (EUROD) workgroup; et al. Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in chronic kidney disease stages 4 to 5D: A call for a shift from nihilism to pragmatism. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 2397–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, D.S.; Tay, K.; Howe, T.S.; Koh, S.B.J. Preoperative severe vitamin D deficiency is a significant independent risk factor for poorer functional outcome and quality of life 6 months after surgery for fragility hip fractures. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).