Necrotizing Enterocolitis Due to Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with Craniofrontonasal Dysplasia: Casual or Causal Association?
Abstract
1. Introduction
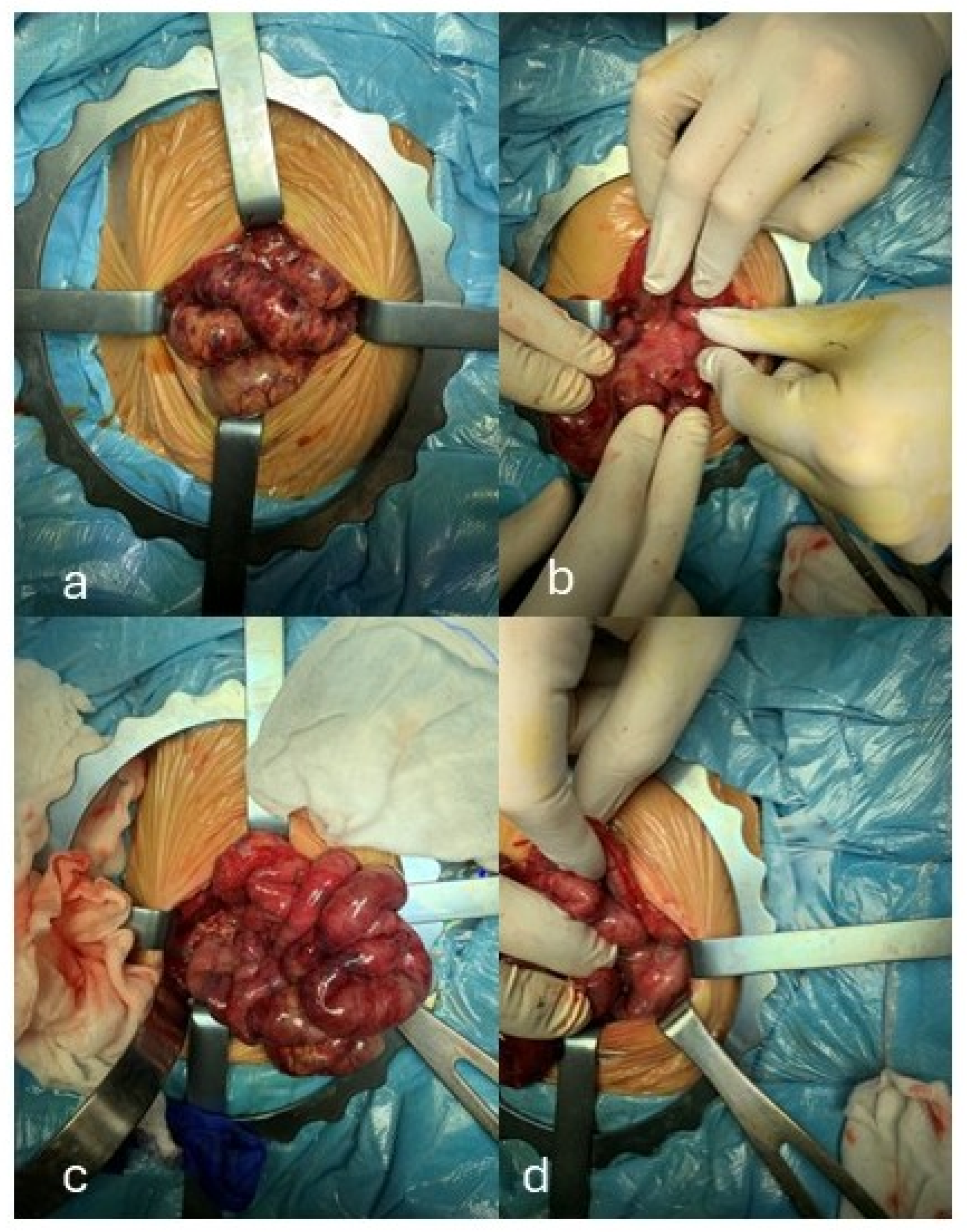
2. Case Report
3. Discussion and Literature Review
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFND | Craniofrontonasal dysplasia |
| CFNS | Craniofrontonasal syndrome |
| CDH | Congenital diaphragmatic hernia |
| EFNB1 | Ephrin-B1 gene |
| NEC | Necrotizing enterocolitis |
| n.v. | normal values |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Cohen, M.M., Jr. Craniofrontonasal dysplasia. Birth Defects Orig. Art. Ser. 1979, 15, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Pasquale, E.B. Eph receptors in the adult brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howaldt, A.; Nampoothiri, S.; Yesodharan, D.; Udayakumaran, S.; Subash, P.; Kornak, U. Four novel mutations in EFNB1 in Indian patients with craniofrontonasal syndrome. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valutazione Antropometrica Neonatale. Riferimento Carte INeS. Available online: http://www.inescharts.com (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- DECIPHER (DatabasE of genomiC varIation and Phenotype in Humans Using Ensembl Resources). Available online: https://www.deciphergenomics.org/browser (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Hernanz-Schulman, M.; Ambrosino, M.M.; Freeman, P.C.; Quinn, C.B. Common bile duct in children: Sonographic dimensions. Radiology 1995, 195, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Child Growth Standards. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/standards (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Rosenberg, H.K.; Markowitz, R.I.; Kolberg, H.; Park, C.; Hubbard, A.; Bellah, R.D. Normal splenic size in infants and children: Sonographic measurements. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 157, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, D.; Richieri-Costa, A.; Guion-Almeida, M.L.; Cohen, M.M., Jr. Craniofrontonasal syndrome: Study of 41 patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996, 61, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogue, J.; Shankar, S.; Perry, H.; Patel, R.; Vargervik, K.; Slavotinek, A. A novel EFNB1 mutation (c.712delG) in a family with craniofrontonasal syndrome and diaphragmatic hernia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 152, 2574–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagni, A.; Logan, M.; Klein, R.; Adams, R.H. Control of skeletal patterning by ephrinB1-EphB interactions. Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, I.; Jakubiczka, S.; Muschke, P.; Cohen, M.; Thiele, H.; Gerlach, K.L.; Adams, R.H.; Wieacker, P. Mutations of the ephrin-B1 gene cause craniofrontonasal syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, L.; Willard, H.F. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature 2005, 434, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Luo, H.; Thorin, E.; Tremblay, J.; Peng, J.; Lavoie, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, S.; Wu, T.; Wu, J. Possible role of Efnb1 protein, a ligand of Eph receptor tyrosine kinases, in modulating blood pressure. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15557–15569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, G.; Antona, V.; Di Pace, M.R.; Giuffrè, M.; Morgante, G.; Piro, E.; Pirrello, R.; Salerno, S.; Schierz, I.A.M.; Verde, V.; et al. Intestinal malrotation in a female newborn affected by Osteopathia Striata with Cranial Sclerosis due to a de novo heterozygous nonsense mutation of the AMER1 gene. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasken, M.B.; Losh, J.S.; Leung, S.W.; Brutus, S.; Avin, B.; Vaught, J.C.; Potter-Birriel, J.; Craig, T.; Conn, G.L.; Mills-Lujan, K.; et al. Insight into the RNA exosome complex through modeling pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 1b disease mutations in yeast. Genetics 2017, 205, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, J.E.; Harel, T.; Liu, P.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; James, R.A.; Coban Akdemir, Z.H.; Walkiewicz, M.; Bi, W.; Xiao, R.; Ding, Y.; et al. Resolution of disease phenotypes resulting from multilocus genomic variation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosina, E.; Pezzani, L.; Pezzoli, L.; Marchetti, D.; Bellini, M.; Pilotta, A.; Calabrese, O.; Nicastro, E.; Cirillo, F.; Cereda, A.; et al. Atypical, composite, or blended phenotypes: How different molecular mechanisms could associate in double-diagnosed patients. Genes 2022, 13, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.H.; Diella, F.; Hennig, S.; Helmbacher, F.; Deutsch, U.; Klein, R. The cytoplasmic domain of the ligand ephrinB2 is required for vascular morphogenesis but not cranial neural crest migration. Cell 2001, 104, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmonizome. STARD8 Gene: GTPase-Activating Protein Regulating RhoA and Vascular Stability. Ma’ayan Lab. Available online: https://maayanlab.cloud/Harmonizome/gene/STARD8 (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- GeneCards. PJA1 Gene. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=PJA1 (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Savarino, G.; Carta, M.; Cimador, M.; Corsello, A.; Giuffrè, M.; Schierz, I.A.M.; Serra, G.; Corsello, G. Necrotizing enterocolitis in the preterm: Newborns medical and nutritional Management in a Single-Center Study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2024, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierz, I.A.M.; Giuffrè, M.; Cimador, M.; D’Alessandro, M.M.; Serra, G.; Favata, F.; Antona, V.; Piro, E.; Corsello, G. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis masked by kidney failure in a male infant with a contiguous gene deletion syndrome at Xp22.31 involving the steroid sulfatase gene: Case report. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, G.; Antona, V.; Cimador, M.; Collodoro, G.; Guida, M.; Piro, E.; Schierz, I.A.M.; Verde, V.; Giuffrè, M.; Corsello, G. New insights on partial trisomy 3q syndrome: De novo 3q27.1-q29 duplication in a newborn with pre and postnatal overgrowth and assisted reproductive conception. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2023, 49, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, F.; Andrieux, J.; Holder-Espinasse, M.; Bouquillon, S.; Pennaforte, T.; Storme, L.; Manouvrier-Hanu, S. Xq12q13.1 microduplication encompassing the EFNB1 gene in a boy with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 54, e525–e527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Kiyota, M.; Seike, J.; Deki, Y.; Yagisawa, H. START-GAP3/DLC3 is a GAP for RhoA and Cdc42 and is localized in focal adhesions regulating cell morphology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Chen, Y.; Tagle, D.A.; Cai, T. PJA1, encoding a RING-H2 finger ubiquitin ligase, is a novel human X chromosome gene abundantly expressed in brain. Genomics 2002, 79, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, M.; Lo Verso, C.; Serra, G.; Moceri, G.; Cimador, M.; Corsello, G.; Study Group of Neonatal Infectious Diseases Affiliated to the Italian Society of Neonatology. Portal Vein Thrombosis in a Preterm Newborn with Mutation of the MTHFR and PAI-1 Genes and Sepsis by Candida parapsilosis. Am. J. Perinatol. 2016, 33, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.; Scriver, T.; Basalom, S.A. No, it is not mutually exclusive! A case report of a girl with two genetic diagnoses: Craniofrontonasal dysplasia and pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 1B. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotelersuka, V.; Kamolvisita, W.; Rojvachiranondac, N.; Suphapeetiporna, K.; Porntaveetusd, T.; Shotelersuka, V. Severe craniofrontonasal syndrome in a male patient mosaic for a novel nonsense mutation in EFNB1. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Fernández, E.; Zenteno, J.C.; Chacón-Camacho, O.F.; Peña-Padilla, C.; Bobadilla-Morales, L.; Corona-Rivera, A.; Romo-Huerta, C.O.; Zepeda-Romero, L.C.; López-Marure, E.; Acosta-León, J.; et al. Extracranial midline defects in a patient with craniofrontonasal syndrome with a novel EFNB1 mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Gestational Age | Sex | Concurrent Risk Factors/Conditions | Involved Genes | Dysmorphic Features | Other Manifestations | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petit F et al. [25] | 32 | M | Congenital right diaphragmatic hernia diagnosed during the second trimester of pregnancy. | Xq12q13.1 microduplication including five contiguous genes (OPHN1, YIPF6, STARD8, EFNB1 and PJA1). | Hypertelorism, epicanthic folds, bifid nasal tip, laterally interrupted eyebrows, low-set and dysplastic ears, right camptodactyly of the second and third fingers, low-set right nipple, and ectopic left testis. | The congenital diaphragmatic hernia was surgically repaired on day 4 of life. At 6 months of age, he underwent a fundoplicatio and gastrostomy tube placement due to severe gastroesophageal reflux. | Walking achieved at age 19 months. Speech delay, mild developmental delay. |
| Ibrahim I et al. [29] | 39 + 4 | F | Mother affected by CFND | Homozygous pathogenic variant in EXOSC3: C.395A > C, p.ASp132Ala, inherited from the mother. Likely pathogenic duplication at Xq13.1 (including EFNB1) and a paternally inherited 16p11.2 duplication, classified as VUS. | Ocular hypertelorism, broad nasal tip and bifid nose, upturned earlobes, clinodactyly, craniosynostosis, polysyndactyly, left hip dislocation, and scoliosis. | At 2 years of age, she was unable to walk independently and showed severe motor and language delays. Brain MRI revealed agenesis of the corpus callosum, cerebellar hypoplasia, and loss of cortical gray-white matter differentiation. | She passed away at 30 months due to respiratory complications. |
| Shotelersuka V et al. [30] | Full term | M | - | c.253C > T (p.Gln85Ter) in EFNB1. | Plagiocephaly, frontal bossing, mild widow’s peak, hypertelorism, telecanthus, orbital displacement, high-arched palate, broad nasal root, and bifid nasal tip. | Inferior vermian and right cerebellar hypoplasia seen on CT scan | Normal development. |
| Acosta-Fernández E et al. [31] | Full term | F | - | Heterozygous c.646G > T transversion in exon 5 of EFNB1. | Brachyplagiocephaly, frontal bossing, hypertelorism, facial asymmetry, and various cranial and facial abnormalities. | A CT scan revealed cranium bifidum occultum and other skull issues. | At age 4, diagnosed with pigmentary glaucoma. Normal intelligence, treated for ADHD. |
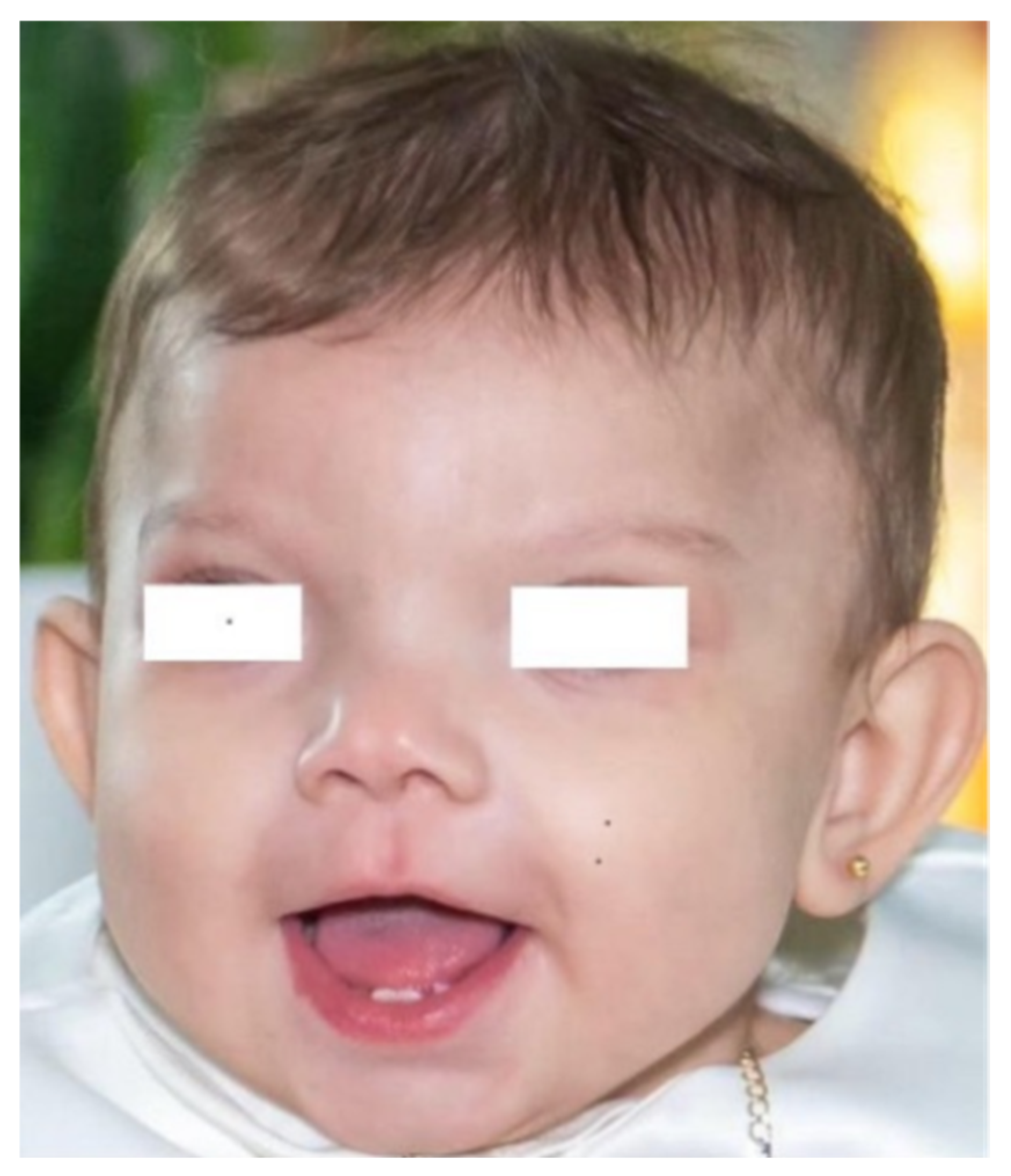
| Our patient | 36 + 4 | F | Mother with type 1 diabetes mellitus. | Microduplication of 791 Kb on chromosome Xq13.1 including the EFNB1, STARD8, and PJA1 genes. The A1298C polymorphism of MTHFR in homozygosity. | Plagiocephaly, craniofacial asymmetry, prominent frontal drafts, epicanthus, hypertelorism, broad and bifid nasal tip, short and thick philtrum, high-arched palate, brachydactyly and clinodactyly. | NEC due to thrombosis of the superior mesenteric artery. She developed short bowel syndrome leading to malabsorption, cholestatic liver disease and growth impairment. | Global neurodevelopmental delay. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serra, G.; Bacile, D.; Di Pace, M.R.; Giliberti, A.; Giuffré, M.; Pensabene, M.; Ranucci, G.; Sergio, M.; Corsello, G.; Nardello, R. Necrotizing Enterocolitis Due to Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with Craniofrontonasal Dysplasia: Casual or Causal Association? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197055
Serra G, Bacile D, Di Pace MR, Giliberti A, Giuffré M, Pensabene M, Ranucci G, Sergio M, Corsello G, Nardello R. Necrotizing Enterocolitis Due to Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with Craniofrontonasal Dysplasia: Casual or Causal Association? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerra, Gregorio, Deborah Bacile, Maria Rita Di Pace, Alessandra Giliberti, Mario Giuffré, Marco Pensabene, Giusy Ranucci, Maria Sergio, Giovanni Corsello, and Rosaria Nardello. 2025. "Necrotizing Enterocolitis Due to Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with Craniofrontonasal Dysplasia: Casual or Causal Association?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197055
APA StyleSerra, G., Bacile, D., Di Pace, M. R., Giliberti, A., Giuffré, M., Pensabene, M., Ranucci, G., Sergio, M., Corsello, G., & Nardello, R. (2025). Necrotizing Enterocolitis Due to Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with Craniofrontonasal Dysplasia: Casual or Causal Association? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197055