FRIDA: A Four-Factor Adaptive Screening Tool for Demoralization, Anxiety, Irritability, and Depression in Hospital Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
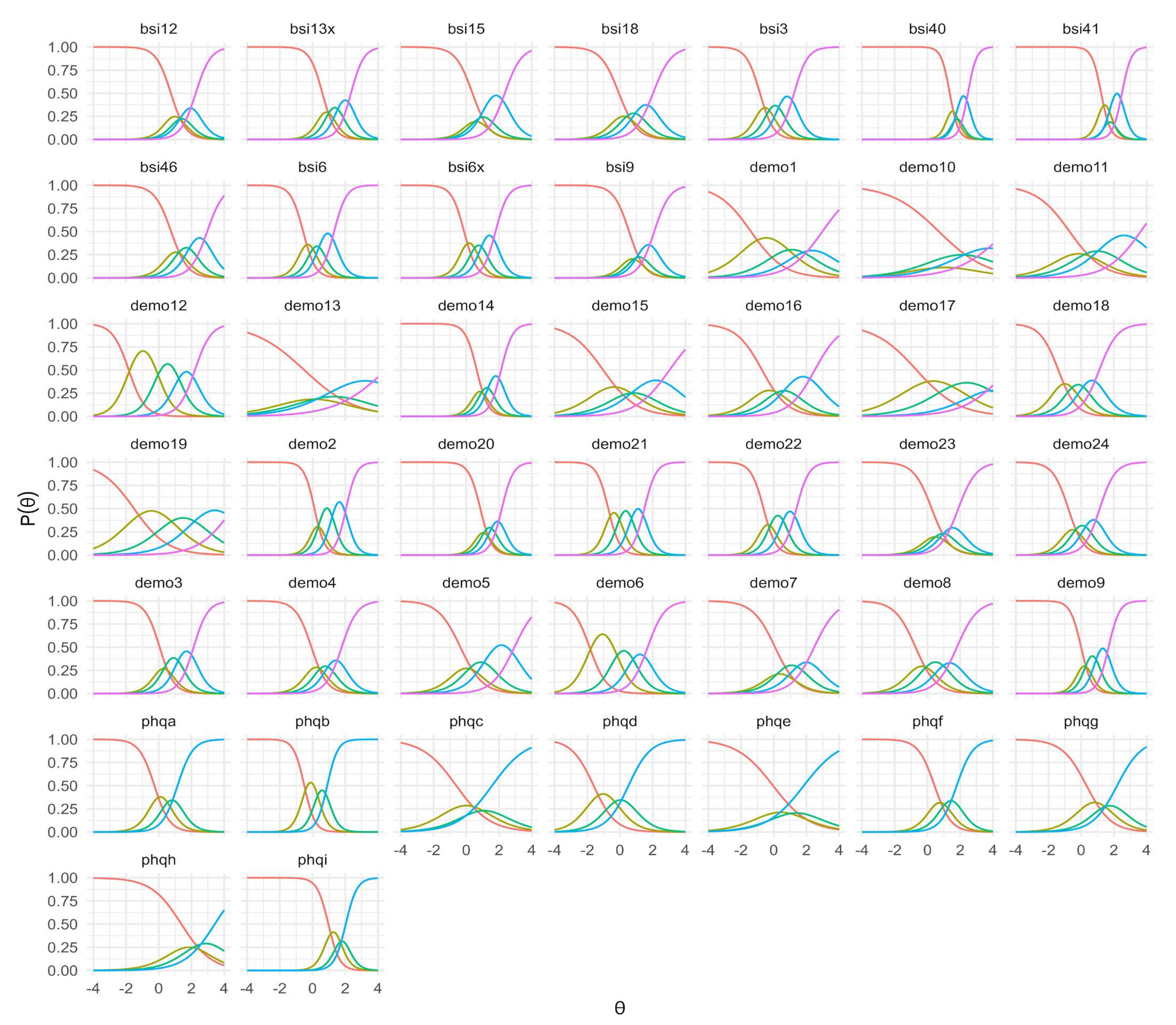
3.2. Item Response Theory Model
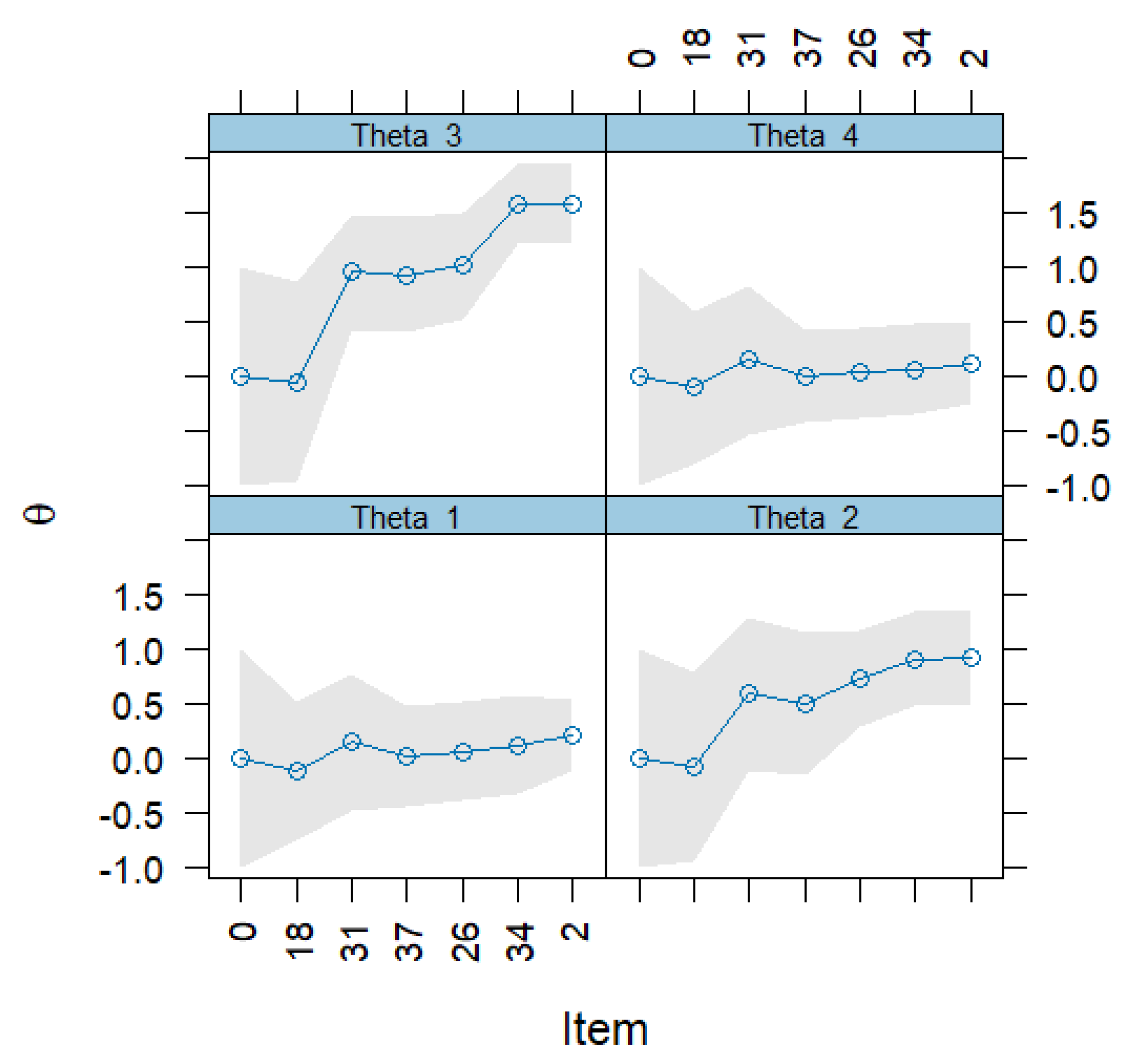
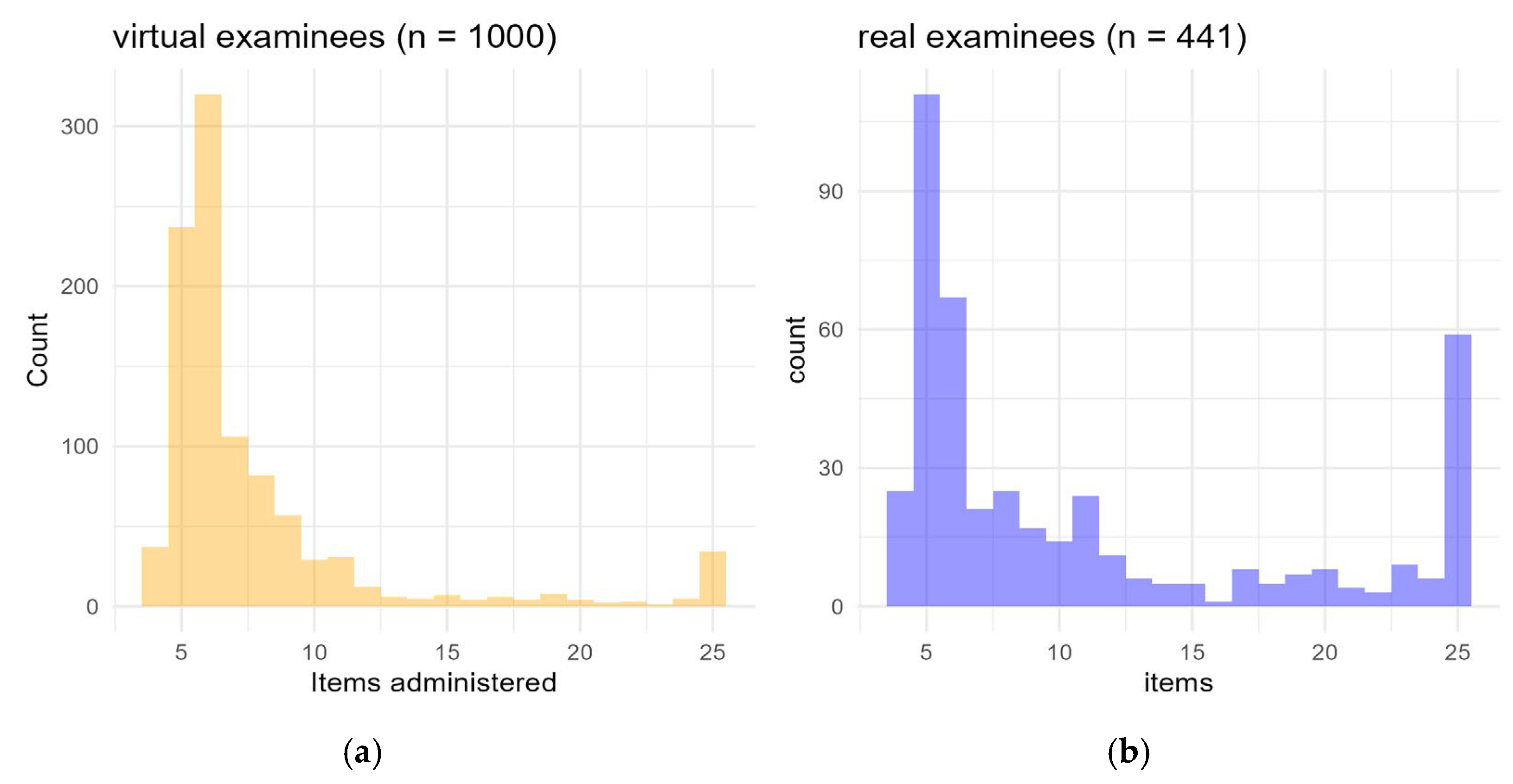
3.3. Computerized Adaptive Testing
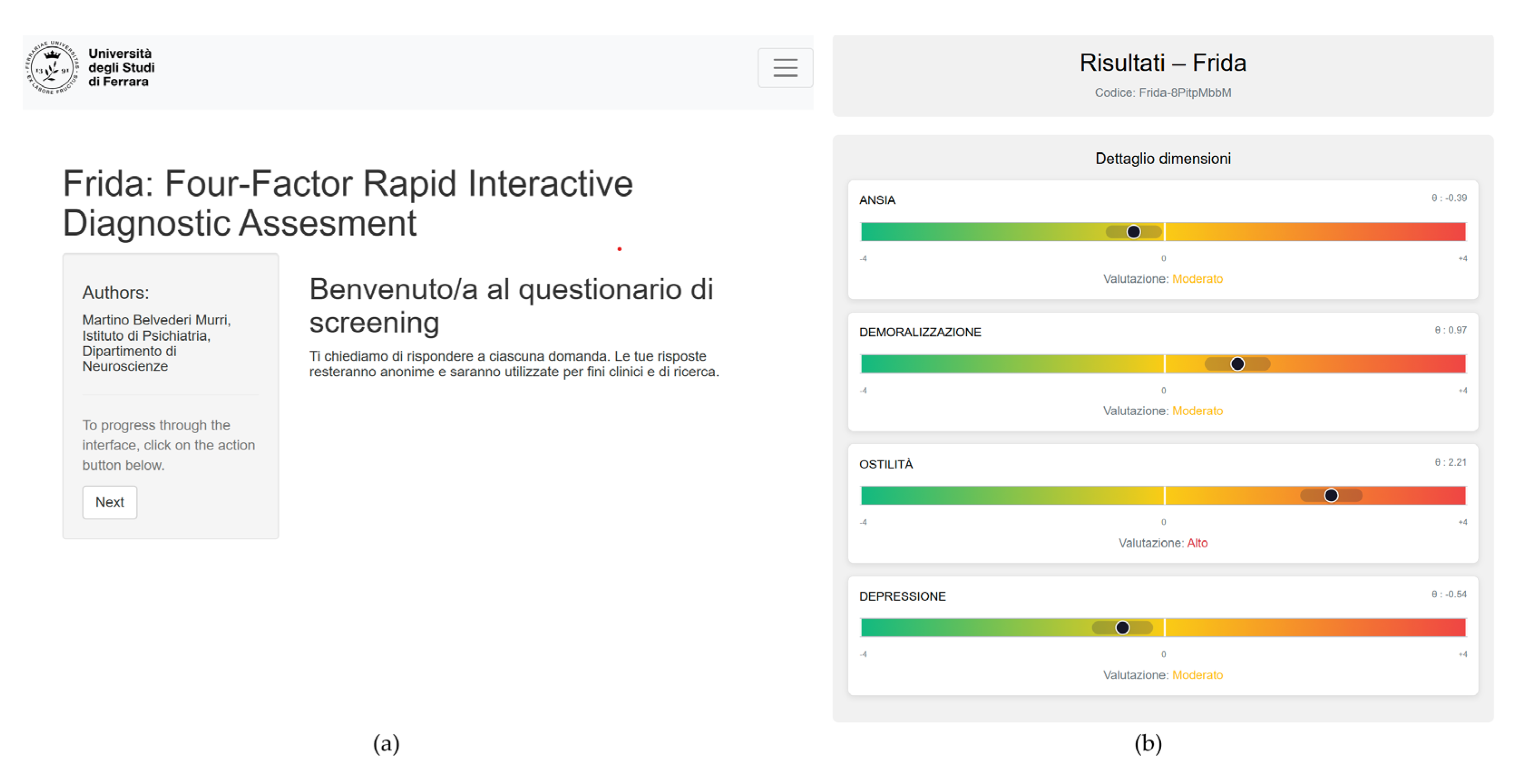
3.4. Development of the Web-Based Screening Tool
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BSI-18 | Brief Symptom Inventory-18 |
| BSI-53 | Brief Symptom Inventory-53 |
| CAT | Computerized Adaptive Testing |
| CAT-MH | Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health |
| CFI | Comparative Fit Index |
| CLP | Consultation Liaison Psychiatry |
| DCPR | Diagnostic Criteria for Psychosomatic Research |
| DCPR/D | Diagnostic Criteria for Psychosomatic Research—Demoralization module |
| DSM-IV | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition |
| DS-24 | Demoralization Scale, 24 items |
| FRIDA | Four-factor Rapid Interactive Diagnostic Assessment |
| GRM | Graded Response Model |
| IRT | Item Response Theory |
| KL | Kullback–Leibler divergence |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
| PROMIS | Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System |
| QMCEM | Quasi Monte Carlo Expectation-Maximization |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RMSEA | Root Mean Square Error of Approximation |
| RMSD | Root Mean Square Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SRMSR | Standardized Root Mean Square Residual |
| TLI | Tucker–Lewis Index |
References
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Caruso, R.; Ounalli, H.; Zerbinati, L.; Berretti, E.; Costa, S.; Recla, E.; Folesani, F.; Kissane, D.; Nanni, M.G.; et al. The relationship between demoralization and depressive symptoms among patients from the general hospital: Network and exploratory graph analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 276, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, L.; Belvederi Murri, M.; Riba, M.; de Padova, S.; Bertelli, T.; Sabato, S.; Nanni, M.G.; Caruso, R.; Ounalli, H.; Zerbinati, L. Hostility in cancer patients as an underexplored facet of distress. Psychooncology 2021, 30, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Burke, K.; Wanat, M.; Fisher, R.; Fielding, J.; Mulick, A.; Puntis, S.; Sharpe, J.; Esposti, M.D.; Harriss, E.; et al. The prevalence of depression in general hospital inpatients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of interview-based studies. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.; van Niekerk, M.; Hobbs, H.; Toynbee, M.; Magill, N.; Bold, R.; Hampsey, E.; Harriss, E.; Frost, C.; Sharpe, M. The prevalence of anxiety in general hospital inpatients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2021, 72, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, E.; Simonelli, G.; Ferrara, M.; Escelsior, A.; Folesani, F.; Bovio, A.; Muscettola, A.; Toffanin, T.; De Bellis, G.A.; Nanni, M.G.; et al. Correlates of Impaired Timing Abilities in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2024, 212, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Grassi, L.; Caruso, R.; Nanni, M.G.; Zerbinati, L.; Andreas, S.; Ausín, B.; Canuto, A.; Härter, M.; Lopez, M.M.; et al. Depressive symptom complexes of community-dwelling older adults: A latent network model. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folesani, F.; Luviè, L.; Palazzi, C.; Marchesi, C.; Rossi, R.; Belvederi Murri, M.; Ossola, P. Psychopathology, Personality and Depression after Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Network Analysis in an Italian Population. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murri, M.B.; Caruso, R.; Christensen, A.P.; Folesani, F.; Nanni, M.G.; Grassi, L. The facets of psychopathology in patients with cancer: Cross-sectional and longitudinal network analyses. J. Psychosom. Res. 2023, 165, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Folesani, F.; Azzolina, D.; Muscettola, A.; Bobevski, I.; Triolo, F.; Farkas, G.; Braccia, F.; Gavesi, M.; Toffanin, T.; et al. A tale of two constructs: Combined assessment of demoralization and subjective incompetence. Psychol. Health Med. 2024, 29, 1635–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecuta, L.; Tomba, E.; Grandi, S.; Fava, G.A. Demoralization: A systematic review on its clinical characterization. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, W.; Falkai, P. The epidemiology of comorbidity between depression, anxiety disorders and somatic diseases. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1999, 14 (Suppl. S2), S1–S6. [Google Scholar]
- Benarous, X.; Lahaye, H.; Consoli, A.; Cohen, D.; Labelle, R.; Guilé, J.-M. Prevalence and comorbidity rates of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder in epidemiological and clinical samples: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Psychiatry J. Assoc. Eur. Psychiatr. 2025, 68, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, M.; Tebeka, S.; Dubertret, C.; Le Strat, Y. Prevalence, correlates and comorbidity of irritability in adults with major depressive episode in the U.S. population (2012–2013). J. Psychiatr. Res. 2025, 181, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Zerbinati, L.; Ounalli, H.; Kissane, D.; Casoni, B.; Leoni, M.; Rossi, G.; Dall’Olio, R.; Caruso, R.; Nanni, M.G.; et al. Assessing demoralization in medically ill patients: Factor structure of the Italian version of the demoralization scale and development of short versions with the item response theory framework. J. Psychosom. Res. 2020, 128, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yohannes, A.M.; Murri, M.B.; Hanania, N.A.; Regan, E.A.; Iyer, A.; Bhatt, S.P.; Kim, V.; Kinney, G.L.; Wise, R.A.; Eakin, M.N.; et al. Depressive and anxiety symptoms in patients with COPD: A network analysis. Respir. Med. 2022, 198, 106865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, L.; Gotelli, S.; Cervetti, A.; Respino, M.; Natta, W.; Marcenaro, M.; Serafini, G.; Vaggi, M.; Amore, M.; Belvederi Murri, M. Duration of untreated depression influences clinical outcomes and disability. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 175, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Wand, A.P.F. The effectiveness of consultation-liaison psychiatry in the general hospital setting: A systematic review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 76, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonen, T.; Ford, S.; Chan, G.C.K.; Hides, L.; Connor, J.P.; Leung, J. What is the short-term remission rate for people with untreated depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J.; Bisby, M.A.; Heriseanu, A.I.; Hathway, T.; Karin, E.; Gandy, M.; Dudeney, J.; Staples, L.G.; Titov, N.; Dear, B.F. Understanding the untreated course of anxiety disorders in treatment-seeking samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Anxiety Disord. 2022, 89, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri, M.; Rucci, P.; Murri, M.B.; Caruso, R.; D’Agostino, A.; Ferrari, S.; Nanni, M.G.; Palagini, L.; Pini, S.; Politi, P.; et al. Suicide risk in medically ill inpatients referred to consultation-liaison psychiatric services: A multicenter study. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 319, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbinati, L.; Palagini, L.; Balestrieri, M.; Belvederi Murri, M.; Caruso, R.; D’Agostino, A.; Ferrara, M.; Ferrari, S.; Minervino, A.; Milia, P.; et al. Changes of consultation-liaison psychiatry practice in Italian general hospitals: A comparative 20-year multicenter study. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 959399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, L.; Karter, J.M.; Vaswani, A.; Thombs, B.D. Unexamined assumptions and unintended consequences of routine screening for depression. J. Psychosom. Res. 2018, 109, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, H.; Vekety, B.; Kovacs, K. The Effect of Computerized Adaptive Testing on Motivation and Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Assessment 2023, 30, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, R.D.; de Gruy, F.V. Without Wasting a Word: Extreme Improvements in Efficiency and Accuracy Using Computerized Adaptive Testing for Mental Health Disorders (CAT-MH). Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulvershorn, L.A.; Adams, Z.W.; Smoker, M.P.; Aalsma, M.C.; Gibbons, R.D. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening, measurement and diagnosis—The CAT-SUD-E. Drug Alcohol Depend. Rep. 2022, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, H.F.; Klug, C.; Roeper, K.; Blozik, E.; Edelmann, F.; Eisele, M.; Störk, S.; Wachter, R.; Scherer, M.; Rose, M.; et al. Screening for mental disorders in heart failure patients using computer-adaptive tests. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, T.A.; Kallen, M.A.; Deutscher, D.; George, S.Z. Development of Reliable and Valid Negative Mood Screening Tools for Orthopaedic Patients with Musculoskeletal Pain. Clin. Orthop. 2022, 480, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Weiss, D.J.; Su, S.; Suen, K.Y.; Basford, J.; Cheville, A.L. Multidimensional Computerized Adaptive Testing: A Potential Path Toward the Efficient and Precise Assessment of Applied Cognition, Daily Activity, and Mobility for Hospitalized Patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, L.; Costantini, A.; Kissane, D.; Brunetti, S.; Caruso, R.; Piazza, G.; Marchetti, P.; Sabato, S.; Nanni, M.G. The factor structure and use of the Demoralization Scale (DS-IT) in Italian cancer patients. Psychooncology 2017, 26, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, G.A.; Freyberger, H.J.; Bech, P.; Christodoulou, G.; Sensky, T.; Theorell, T.; Wise, T.N. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychosomatic research. Psychother. Psychosom. 1995, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelli, L.; Rafanelli, C.; Porcelli, P.; Fava, G.A. Appendix 2. Interview for the diagnostic criteria for psychosomatic research. Adv. Psychosom. Med. 2007, 28, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, P.; Guidi, J. The Clinical Utility of the Diagnostic Criteria for Psychosomatic Research: A Review of Studies. Psychother. Psychosom. 2015, 84, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcelli, P.; Rafanelli, C. Criteria for psychosomatic research (DCPR) in the medical setting. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2010, 12, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derogatis, L.R. Symptom Checklist-90-Revised, Brief Symptom Inventory, and BSI-18. In Handbook of Psychological Assessment in Primary Care Settings; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-65840-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, R.; Piccinelli, M.; Mazzi, M.; Bellantuono, C.; Tansella, M. The Personal Health Questionnaire: A new screening instrument for detection of ICD-10 depressive disorders in primary care. Psychol. Med. 2000, 30, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001, 16, 606-613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, R.P. Mirt: A Multidimensional Item Response Theory Package for the R Environment. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappenburg-ten Holt, J. A Comparison Between Factor Analysis and Item Response Theory Modeling in Scale Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2014. Available online: https://www.rug.nl/research/portal/publications/a-comparison-between-factor-analysis-and-item-response-theory-modeling-in-scale-analysis(5a4e44c0-a8ab-4ac4-8ce2-33caa55a8fa5).html (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Chalmers, R.P. Generating Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Test Interfaces for Multidimensional Item Response Theory Applications. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 71, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghaenel, D.U.; Schneider, S.; Stone, A.A.; Christodoulou, C.; Broderick, J.E. Ecological validity and clinical utility of Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS®) instruments for detecting premenstrual symptoms of depression, anger, and fatigue. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 76, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, R.D.; Weiss, D.J.; Frank, E.; Kupfer, D. Computerized Adaptive Diagnosis and Testing of Mental Health Disorders. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2016, 12, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, V.; Brown, F.; Beiser, D.G.; Peterson, T.; Gibbons, R.D.; Nagele, P. Preoperative Assessment of Anxiety and Depression Using Computerized Adaptive Screening Tools: A Pilot Prospective Cohort Study. Anesth. Analg. 2022, 134, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, D.; Meyer, C.; Senderling, S.; Fiore, E.; Lee, L.; Lum, J.; Hildebrand, A.; Kellogg, M.; Callahan, M. Adaptive mental health screening in veterans admitted to an epilepsy monitoring unit. Epilepsy Behav. EB 2025, 171, 110628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.I.; Staab, E.M.; Zhu, M.; Knitter, A.; Wan, W.; Gibbons, R.; Vinci, L.; Shah, S.; Yohanna, D.; Beckman, N.; et al. Pragmatic Clinical Trial of Population Health, Portal-Based Depression Screening: The PORTAL-Depression Study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2023, 38, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscettola, A.; Belvederi Murri, M.; Specchia, M.; De Bellis, G.A.; Montemitro, C.; Sancassiani, F.; Perra, A.; Zaccagnino, B.; Olivetti, A.F.; Sciavicco, G.; et al. Development and Piloting of Co.Ge.: A Web-Based Digital Platform for Generative and Clinical Cognitive Assessment. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belvederi Murri, M.; Muscettola, A.; Specchia, M.; Montemitro, C.; Zerbinati, L.; Cruciata, M.; Toffanin, T.; Sciavicco, G.; Caruso, R.; Sancassiani, F.; et al. FRIDA: A Four-Factor Adaptive Screening Tool for Demoralization, Anxiety, Irritability, and Depression in Hospital Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6992. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196992
Belvederi Murri M, Muscettola A, Specchia M, Montemitro C, Zerbinati L, Cruciata M, Toffanin T, Sciavicco G, Caruso R, Sancassiani F, et al. FRIDA: A Four-Factor Adaptive Screening Tool for Demoralization, Anxiety, Irritability, and Depression in Hospital Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6992. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196992
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelvederi Murri, Martino, Angela Muscettola, Michele Specchia, Chiara Montemitro, Luigi Zerbinati, Marco Cruciata, Tommaso Toffanin, Guido Sciavicco, Rosangela Caruso, Federica Sancassiani, and et al. 2025. "FRIDA: A Four-Factor Adaptive Screening Tool for Demoralization, Anxiety, Irritability, and Depression in Hospital Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6992. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196992
APA StyleBelvederi Murri, M., Muscettola, A., Specchia, M., Montemitro, C., Zerbinati, L., Cruciata, M., Toffanin, T., Sciavicco, G., Caruso, R., Sancassiani, F., Carta, M. G., Grassi, L., & Nanni, M. G. (2025). FRIDA: A Four-Factor Adaptive Screening Tool for Demoralization, Anxiety, Irritability, and Depression in Hospital Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6992. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196992







