Is the Development of Hypo-Gammaglobulinemia Associated with Better Treatment Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Rituximab?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, J.C.W.; Cambridge, G. Sustained improvement in rheumatoid arthritis following a protocol designed to deplete B lymphocytes. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.C.W.; Szczepański, L.; Szechiński, J.; Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A.; Emery, P.; Close, D.R.; Stevens, R.M.; Shaw, T. Efficacy of B-Cell–Targeted Therapy with Rituximab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murawski, N.; Pfreundschuh, M. New drugs for aggressive B-cell and T-cell lymphomas. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Emery, P.; Greenwald, M.W.; Dougados, M.; Furie, R.A.; Genovese, M.C.; Keystone, E.C.; Loveless, J.E.; Burmester, G.R.; Cravets, M.W.; et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 54, 2793–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; van Paassen, P.; et al. Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide in ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keystone, E.; Emery, P.; Peterfy, C.G.; Tak, P.P.; Cohen, S.; Genovese, M.C.; Dougados, M.; Burmester, G.R.; Greenwald, M.; Kvien, T.K.; et al. Rituximab inhibits structural joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitor therapies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennie, M.J.; French, R.R.; Cragg, M.S.; Taylor, R.P. Mechanisms of killing by anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3823–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.P.; Lindorfer, M.A. Immunotherapeutic mechanisms of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, R.; Dervovic, E.; Chasset, F.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Sibilia, J.; Scher, F.; Arnaud, L. The 2018 pipeline of targeted therapies under clinical development for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A systematic review of trials. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favalli, E.G.; Raimondo, M.G.; Becciolini, A.; Crotti, C.; Biggioggero, M.; Caporali, R. The management of first-line biologic therapy failures in rheumatoid arthritis: Current practice and future perspectives. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Pendergraft, W.F.; Wenger, J.; Owens, C.T.; Laliberte, K.; Niles, J.L. Effect of Continuous B Cell Depletion With Rituximab on Pathogenic Autoantibodies and Total IgG Levels in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Furst, D.E.; Lacey, S.; Lehane, P.B. Longterm Safety of Rituximab: Final Report of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Global Clinical Trial Program over 11 Years. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.R.; Kleiner, A.; Rich, L.; Conners, C.; Fisher, R.I.; Anolik, J.; Friedberg, J.W. Profound Hypogammaglobulinemia 7 Years after Treatment for Indolent Lymphoma. Cancer Investig. 2008, 26, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, E.; Shirota, Y.; Suzuki, C.; Tajima, Y.; Ishizawa, K.; Kameoka, J.; Harigae, H.; Ishii, T. Severe hypogammaglobulinemia persisting for 6 years after treatment with rituximab combined chemotherapy due to arrest of B lymphocyte differentiation together with alteration of T lymphocyte homeostasis. Int. J. Hematol. 2010, 91, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Li, H.H.; Huang, W.R.; Gao, C.J.; Yu, L. Change of serum immunoglobulin level in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma after rituximab combined with chemotherapy. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2011, 19, 676–679. [Google Scholar]
- Boleto, G.; Avouac, J.; Wipff, J.; Forien, M.; Dougados, M.; Roux, C.; Kahan, A.; Dieude, P.; Allanore, Y. Predictors of hypogammaglobulinemia during rituximab maintenance therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: A 12-year longitudinal multi-center study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 48, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.S.; Turpcu, A.; Shi, N.; Fowler, R.; Chu, B.C.; Alexander, K. Risk of infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients switching from anti-TNF agents to rituximab, abatacept, or another anti-TNF agent, a retrospective administrative claims analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilopoulos, D.; Delicha, E.M.; Settas, L.; Andrianakos, A.; Aslanidis, S.; Boura, P.; Katsounaros, M.; Athanassiou, P.; Tempos, K.; Skarantavos, G.; et al. Safety profile of repeated rituximab cycles in unselected rheumatoid arthritis patients: A long-term, prospective real-life study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 893–900. [Google Scholar]
- Keystone, E.; Fleischmann, R.; Emery, P.; Furst, D.E.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Bathon, J.; Dougados, M.; Baldassare, A.; Ferraccioli, G.; Chubick, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of additional courses of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: An open-label extension analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3896–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yusof, M.Y.; Vital, E.M.; McElvenny, D.M.; Hensor, E.M.A.; Das, S.; Dass, S.; Rawstron, A.C.; Buch, M.H.; Emery, P.; Savic, S. Predicting Severe Infection and Effects of Hypogammaglobulinemia during Therapy with Rituximab in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelatos, G.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Klavdianou, K.; Moschopoulou, M.; Vassilopoulos, D.; Iliopoulos, A. Hypogammaglobulinemia after rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis is not rare and is related with good response: 13 years real-life experience. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, E.A.A.; Giardino, G.; Worth, A.; Ladomenou, F. Risk factors predisposing to the development of hypogammaglobulinemia and infections post-Rituximab. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 36, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worch, J.; Makarova, O.; Burkhardt, B. Immunreconstitution and Infectious Complications After Rituximab Treatment in Children and Adolescents: What Do We Know and What Can We Learn from Adults? Cancers 2015, 7, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athni, T.S.; Barmettler, S. Hypogammaglobulinemia, late-onset neutropenia, and infections following rituximab. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmacharya, P.; Poudel, D.R.; Pathak, R.; Donato, A.A.; Ghimire, S.; Giri, S.; Aryal, M.R.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd. Rituximab-induced serum sickness: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Emery, P.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Keystone, E.C.; Fleischmann, R.; Furst, D.E.; Macey, K.; Sweetser, M.; Kelman, A.; Rao, R. Longterm Safety of Patients Receiving Rituximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, I.; Leandro, M.J.; Valor, L.; Becerra, E.; Edwards, J.C.W.; Cambridge, G. Total serum immunoglobulin levels in patients with RA after multiple B-cell depletion cycles based on rituximab: Relationship with B-cell kinetics. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Emery, P.; Bingham, C.O.; Keystone, E.C.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Furst, D.E.; Yson, N.; Collinson, N.; Lehane, P.B. Long-term safety of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: 9.5-year follow-up of the global clinical trial programme with a focus on adverse events of interest in RA patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, J.T.; Evert, M.; Geborek, P.; Saxne, T.; Lundgren, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C. Rituximab in clinical practice: Dosage, drug adherence, Ig levels, infections, and drug antibodies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Martinez, L.; Isenberg, D.A.; Leandro, M.J.; Cambridge, G. Pragmatic Treatment of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Rituximab: Long-Term Effects on Serum Immunoglobulins: Hypogammaglobulinemia After Rituximab in SLE. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Bayona, B.; Ramos-Amaya, A.; Pérez-Venegas, J.J.; Rodríguez, C.; Brieva, J.A. Decreased frequency and activated phenotype of blood CD27 IgD IgM B lymphocytes is a permanent abnormality in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.; Cambridge, G.; Isenberg, D.A.; Glennie, M.J.; Cragg, M.S.; Leandro, M. Internalization of Rituximab and the Efficiency of B Cell Depletion in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.L.; Gale, R.P.; Yap, P.L. Use of ıntravenous ımmunoglobulın to prevent or treat ınfectıons IN persons wıth ımmune defıcıency. Annu. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kridin, K.; Ahmed, A.R. Post-rituximab immunoglobulin M (IgM) hypogammaglobulinemia. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bai, W.; Jiang, N.; Qiao, L.; Huang, C.; et al. Hypogammaglobulinemia and Infection Events in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases Treated with Rituximab: 10 Years Real-Life Experience. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 44, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdam, M.A.A.; Campisi, L.M.; De Leijer, J.H.; Ten Cate, D.; Den Broeder, A.A. Hypogammaglobulinemia in rheumatoid arthritis patients on rituximab: Prevalence and risk factors. Rheumatology 2024, 63, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen Hansen, I.M.; Asmussen Andreasen, R.; van Bui Hansen, M.N.; Emamifar, A. The Reliability of Disease Activity Score in 28 Joints-C-Reactive Protein Might Be Overestimated in a Subgroup of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, When the Score Is Solely Based on Subjective Parameters: A Cross-sectional, Exploratory Study. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 23, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 165) | Hypo-Gamma-Globulinemia Absent (n = 130) | Hypo-Gamma-Globulinemia Present (n = 35) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years + | 56 (48–62.5) | 55.8 (47.9–62.5) | 56 (49–66.5) | 0.430 |
| Female gender * | 121 (73.3) | 94 (72.3) | 27 (77.1) | 0.566 |
| Disease duration, years + | 9 (4–15) | 9 (4–16.5) | 10 (4.8–14) | 0.590 |
| RF titer, IU/mL + | 87 (28.5–224.5) | 98.6 (39.2–279.9) | 45.8 (11.3–150) | 0.007 |
| CCP titer, U/mL +¥ | 127.6 (27.6–463.5) | 158.1 (38.1–680.5) | 37.8 (12.3–231.5) | 0.002 |
| IgG +§ | 11.9 (10.3–14.2) | 12.3 (10.7–14.8) | 10.2 (9.1–12) | <0.001 |
| IgM +§ | 1.25 (0.83–1.8) | 1.34 (0.94–1.85) | 0.84 (0.54–1.27) | <0.001 |
| IgA +§ | 2.46 (1.81–3.39) | 2.55 (1.91–3.42) | 2.12 (1.55–3.21) | 0.119 |
| CRP, mg/L +§ | 21.6 (10.1–43) | 21.4 (9.9–45.3) | 22.1 (10.5–38.1) | 0.899 |
| ESR, mm/hours +§ | 34 (23–51.5) | 34 (23–52.5) | 35 (23–47) | 0.660 |
| DAS28-ESR +§ | 5.5 (5.4–6) | 5.5 (5.4–6) | 5.8 (5.4–6.7) | 0.203 |
| Methotrexate * | 39 (23.6) | 34 (26.2) | 5 (14.3) | 0.142 |
| Leflunomide * | 65 (39.4) | 52 (40) | 13 (37.1) | 0.759 |
| Sulphasalazine * | 58 (35.2) | 50 (38.5) | 8 (22.9) | 0.086 |
| Hidroxychloroquine * | 64 (38.8) | 52 (40) | 12 (34.3) | 0.538 |
| GC * | 115 (69.7) | 93 (71.5) | 22 (62.9) | 0.321 |
| Number of RTX cycles, median (IQR) | 7 (4–9) | 6 (3–9) | 8 (5–13) | 0.006 |
| Serious infections, n (%) | 6 (3.6) | 3 (2.3) | 3 (8.6) | 0.110 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | 37 (22.4) | 30 (23.1) | 7 (20) | 0.698 |
| Interstitial lung disease (ILD), n (%) | 17 (10.3) | 15 (11.5) | 2 (5.7) | 0.531 |
| Pulmonary nodule, n (%) | 12 (7.3) | 10 (7.7) | 2 (5.7) | 1.000 |
| Anti-HBc positivity, n (%) | 37 (22.4) | 30 (23.1) | 7 (20) | 0.698 |
| Diabetes mellitus (DM), n (%) | 28 (17) | 22 (16.9) | 6 (17.1) | 0.975 |
| Chronic kidney disease (CKD), n (%) | 7 (4.2) | 7 (5.4) | 0 (0) | 0.347 |
| Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), n (%) | 8 (4.8) | 7 (5.4) | 1 (2.9) | 1.000 |
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Hypo-gamma-globulinemia | 35 (21.2) |
| Low IgG | 18 (10.9) |
| Mild | 16 (88.9) |
| Moderate | 2 (11.1) |
| Severe | 0 (0) |
| Low IgM | 20 (12.1) |
| Low IgA | 9 (5.5) |
| IgG g/L, Median (Q1–Q3) | IgM g/L, Median (Q1–Q3) | IgA g/L, Median (Q1–Q3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Rtx | After Rtx | p | Before Rtx | After Rtx | p | Before Rtx | After Rtx | p | |
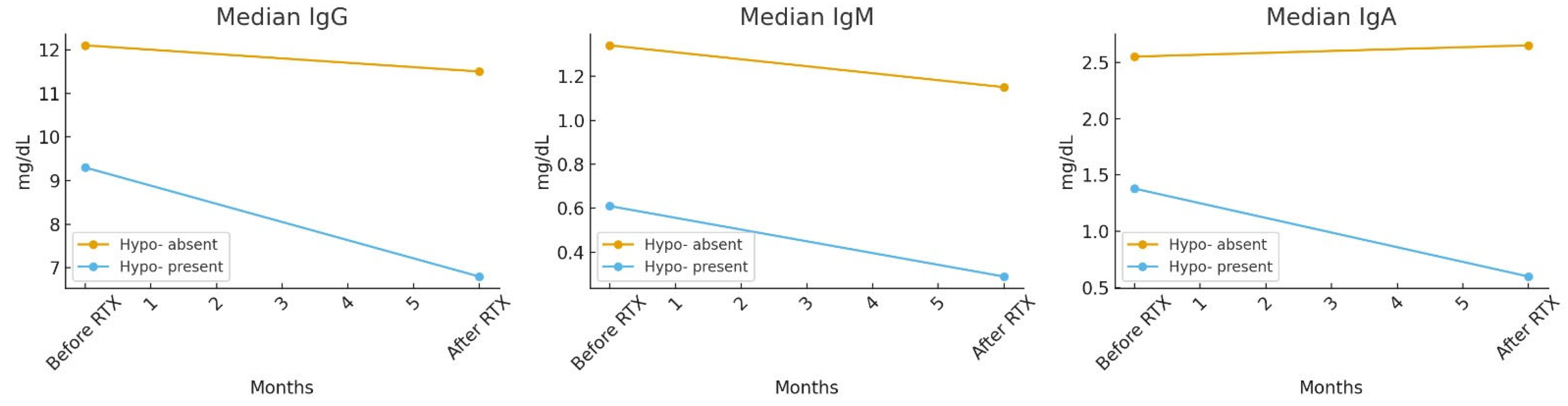
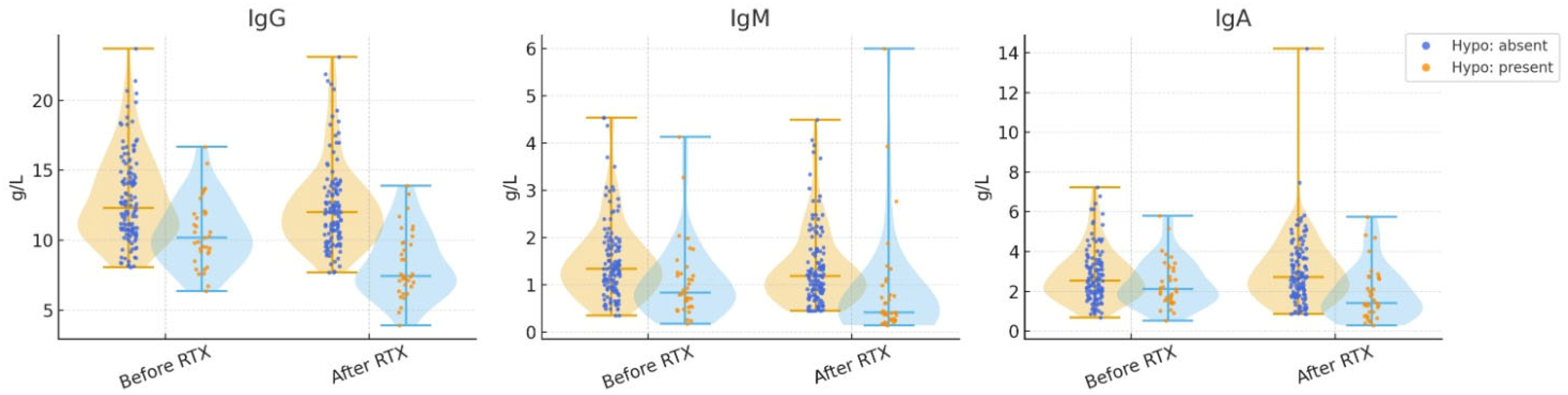
| Hypo-gamma-globulinemia absent | 12.1 (10.6–14.5) | 11.5 (9.9–13.3) | <0.001 * | 1.34 (0.94–1.86) | 1.15 (0.76–1.67) | <0.001 * | 2.55 (1.91–3.4) | 2.65 (1.79–3.67) | 0.975 * |
| Hypo-gamma-globulinemia present | 9.3 (7.8–11.2) | 6.8 (5.9–7.2) | <0.001 * | 0.61 (0.46–0.87) | 0.29 (0.21–0.41) | <0.001 * | 1.38 (0.97–1.85) | 0.6 (0.44–0.76) | 0.008 * |
| p | <0.001 + | <0.001 + | 0.002 + | ||||||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
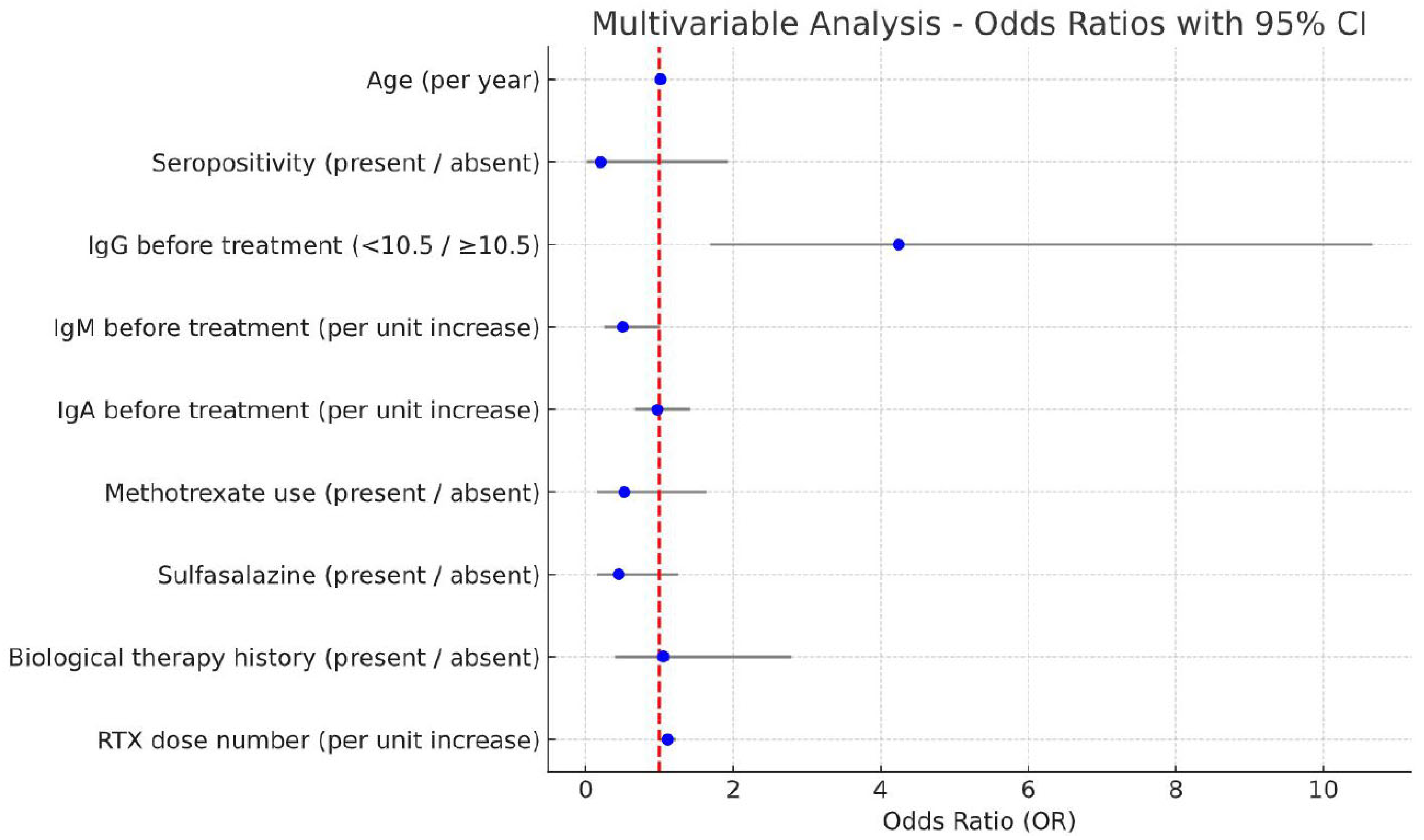
| Age, years (for every year) | 1.02 (0.99–1.06) | 0.240 | 1.01 (0.97–1.05) | 0.610 |
| Seropositivity (present → absent) | 0.25 (0.03–1.84) | 0.170 | 0.20 (0.02–1.93) | 0.160 |
| IgG before treatment (<10.5 → ≥10.5) | 4.33 (1.97–9.49) | <0.001 | 4.24 (1.69–10.66) | 0.002 |
| IgM before treatment (for every unit increase) | 0.43 (0.23–0.82) | 0.010 | 0.50 (0.25–1.01) | 0.054 |
| IgA before treatment (for every unit increase) | 0.78 (0.56–1.08) | 0.130 | 0.97 (0.67–1.41) | 0.870 |
| Methotrexate use (present → absent) | 0.47 (0.17–1.31) | 0.150 | 0.52 (0.16–1.64) | 0.270 |
| Sulfasalazine (present → absent) | 0.47 (0.20–1.13) | 0.091 | 0.45 (0.16–1.25) | 0.120 |
| Biological therapy history (present → absent) | 1.60 (0.73–3.53) | 0.240 | 1.05 (0.40–2.79) | 0.920 |
| RTX dose number (for every unit increase) | 1.12 (1.04–1.22) | 0.004 | 1.11 (1.01–1.22) | 0.036 |
| Hypo-Gamma-Globulinemia Absent (n = 130) | Hypo-Gamma-Globulinemia Present (n = 35) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAS28-ESR + | 3 (2.3–5.1) | 2.5 (2.1–3.4) | 0.101 |
| Disease activity * | 0.163 | ||
| Remission-low | 80 (61.5) | 26 (74.3) | |
| Moderate-high | 50 (35.8) | 9 (25.7) | |
| CRP + | 11.4 (5.1–24.1) | 6.8 (3.4–14.3) | 0.034 |
| ESR + | 22 (12–37.5) | 18 (9–26) | 0.068 |
| Normal IgG (n = 147) | Low IgG (n = 18) | ||
| DAS28-ESR + | 3 (2.2–4.1) | 2.5 (2.1–3.4) | 0.230 |
| Disease activity * | 0.454 | ||
| Remission-low | 93 (63.3) | 13 (72.2) | |
| Moderate-high | 54 (36.7) | 5 (27.8) | |
| CRP + | 11.1 (4.8–22.7) | 8.1 (3.3–13.6) | 0.131 |
| ESR + | 22 (12–35) | 13 (6.5–29.5) | 0.049 |
| Normal IgM (n = 145) | Low IgM (n = 20) | ||
| DAS28-ESR + | 3 (2.2–4.3) | 2.5 (2.1–3.7) | 0.395 |
| Disease activity * | 0.567 | ||
| Remission-low | 92 (63.4) | 14 (70) | |
| Moderate-high | 53 (36.6) | 6 (30) | |
| CRP + | 11.1 (4.9–22.7) | 6.7 (3.6–14.3) | 0.153 |
| ESR + | 22 (12–35) | 18.5 (9.5–24.5) | 0.180 |
| Normal IgA (n = 156) | Low IgA (n = 9) | ||
| DAS28-ESR + | 3 (2.2–4.1) | 2.5 (2.1–4.2) | 0.373 |
| Disease activity * | 0.575 | ||
| Remission-low | 99 (63.5) | 7 (77.8) | |
| Moderate-high | 57 (36.5) | 2 (22.2) | |
| CRP + | 10.4 (4.8–21.9) | 6.8 (1.9–19.3) | 0.382 |
| ESR + | 21.5 (11–35) | 20 (13.5–35) | 0.850 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydemir Guloksuz, E.G.; Sezer, S.; Sahin Eroglu, D.; Colak, S.; Kelesoglu Dincer, A.B.; Yayla, M.E.; Uslu, E.; Yuksel, M.L.; Yilmaz, R.; Ates, E.S.; et al. Is the Development of Hypo-Gammaglobulinemia Associated with Better Treatment Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Rituximab? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196967
Aydemir Guloksuz EG, Sezer S, Sahin Eroglu D, Colak S, Kelesoglu Dincer AB, Yayla ME, Uslu E, Yuksel ML, Yilmaz R, Ates ES, et al. Is the Development of Hypo-Gammaglobulinemia Associated with Better Treatment Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Rituximab? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196967
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydemir Guloksuz, Emine Gozde, Serdar Sezer, Didem Sahin Eroglu, Sevgi Colak, Ayse Bahar Kelesoglu Dincer, Mucteba Enes Yayla, Emine Uslu, Mehmet Levent Yuksel, Recep Yilmaz, Elif Sinem Ates, and et al. 2025. "Is the Development of Hypo-Gammaglobulinemia Associated with Better Treatment Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Rituximab?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196967
APA StyleAydemir Guloksuz, E. G., Sezer, S., Sahin Eroglu, D., Colak, S., Kelesoglu Dincer, A. B., Yayla, M. E., Uslu, E., Yuksel, M. L., Yilmaz, R., Ates, E. S., Turgay, T. M., Kinikli, G., & Ates, A. (2025). Is the Development of Hypo-Gammaglobulinemia Associated with Better Treatment Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Rituximab? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196967






