Update on the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pharmacological Approaches to NSCLC Therapy
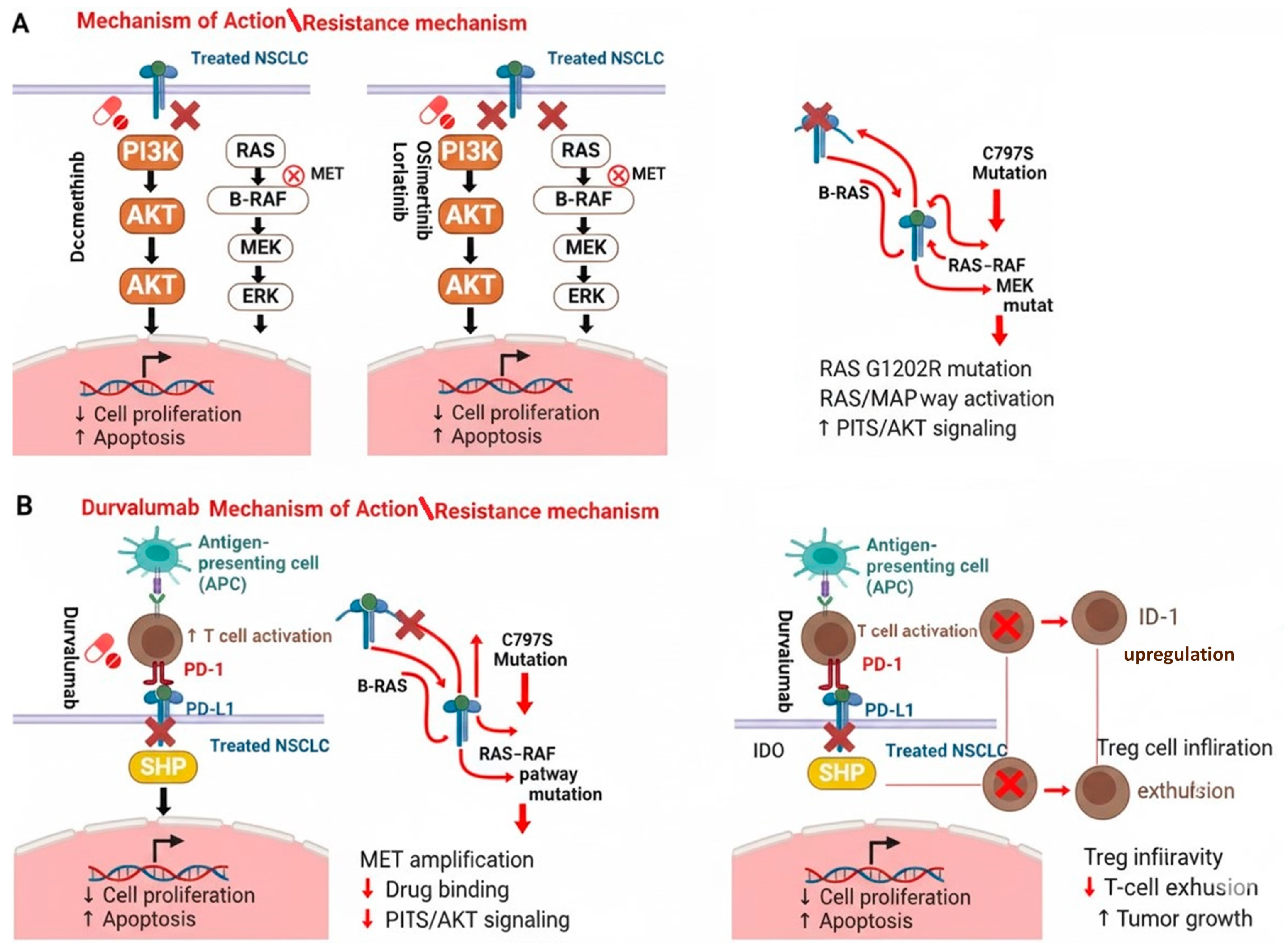
2.1. Molecular Pharmacological Treatments
2.2. Immune Target Pharmacological Treatments
3. Completed Phase IV Clinical Trials for NSCLC Treatment
3.1. Dacomitinib
3.2. Lorlatinib
3.3. Durvalumab
3.4. Osimertinib
4. Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
5. Anti-Angiogenic Agents in the Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
6. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T-Cell Therapy for NSCLC
7. Bispecific Antibodies for NSCLC
8. Alternative Medicine
9. Emerging Treatments
10. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirley, M. Dacomitinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Popat, S.; Ahn, M.J.; de Marinis, F. Recent Advances on the Role of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Management of NSCLC with Uncommon, Non Exon 20 Insertions, EGFR Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, J.C.; Shih, J.Y. The effectiveness of afatinib in patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring complex epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.X.; Wang, Y.T.; Lu, N.; Sun, J.F.; Nie, P.; Herdewijn, P. Advances of clinically approved small-molecule drugs for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R.; Shah, D.R. Safety and Tolerability of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Kato, T.; Niho, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Takahashi, T.; Nogami, N.; Kaneda, H.; Fujita, Y.; Wilner, K.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of first-line dacomitinib in Japanese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Park, S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Sun, J.M. Dacomitinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastasis: A single-arm, phase II study. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaku, M.; Uchino, J.; Yamada, T.; Chihara, Y.; Shimamoto, T.; Tamiya, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Kiyomi, F.; Takayama, K. Rationale and design of a phase II study to evaluate prophylactic treatment of dacomitinib-induced dermatologic adverse events in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (SPIRAL-Daco study). Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Giri, N.; Quinn, S.; Wilner, K.; Parivar, K. Evaluation of the potential effect of dacomitinib, an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on ECG parameters in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Chawla, A.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; et al. Updated Overall Survival in a Randomized Study Comparing Dacomitinib with Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. Drugs 2021, 81, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; TS, K.M.; Nakagawa, K.; Rosell, R.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Miglorino, M.R.; et al. Efficacy in patients with EGFR-positive non-small-cell lung cancer treated with dacomitinib who had skin adverse events: Post hoc analyses from ARCHER 1050. Future Oncol. 2024, 20, 2971–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Mok, T.S.; Zhou, X.; Lu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Yu, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of first-line dacomitinib in Asian patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial (ARCHER 1050). Lung Cancer 2021, 154, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.R.; Soo, R.A. Lorlatinib for the treatment of ALK-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2020, 20, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Shukuya, T.; Murata, A.; Kikkawa, H.; Emir, B.; Wiltshire, R.; Miura, S. Real-world therapeutic effectiveness of lorlatinib after alectinib in Japanese patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Liu, G.; Felip, E.; Mok, T.S.K.; Soo, R.A.; Mazieres, J.; Shaw, A.T.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Wu, Y.L.; et al. Lorlatinib Versus Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes from the Phase III CROWN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3400–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Kawashima, Y.; Chiba, S.; Hara, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Doman, T.; Saito, S.; Odaka, T.; Ogasawara, T.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Successful application of lorlatinib in a 23-year-old patient with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive lung cancer and multiple brain metastases. Cancer Rep. 2024, 7, e1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Akagi, K.; Dotsu, Y.; Yamada, T.; Ono, S.; Imamura, E.; Gyotoku, H.; Takemoto, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sen, T.; et al. Pan-HER inhibitors overcome lorlatinib resistance caused by NRG1/HER3 activation in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Lorlatinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.; Beavers, N.; Nilsson, F.O.L.; Iadeluca, L.; Lowry, C. Cost—Effectiveness of Lorlatinib in First-Line Treatment of Adult Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)—Positive Non—Small—Cell Lung Cancer in Sweden. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2023, 21, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Felip, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Navarro, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Johnson, M.; Dietrich, J.; James, L.P.; et al. Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: An international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, K.C.; Park, J.R.; Kayser, K.; Malvar, J.; Chi, Y.Y.; Groshen, S.G.; Villablanca, J.G.; Krytska, K.; Lai, L.M.; Acharya, P.T.; et al. Lorlatinib with or without chemotherapy in ALK-driven refractory/relapsed neuroblastoma: Phase 1 trial results. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.; Du, Y.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J.; et al. Lorlatinib for Previously Treated ALK-Positive Advanced NSCLC: Primary Efficacy and Safety from a Phase 2 Study in People’s Republic of China. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, E.; Shaw, A.T.; Bearz, A.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Bauman, J.R.; Bauer, T.M.; Peters, S.; Toffalorio, F.; Abbattista, A.; et al. Intracranial and extracranial efficacy of lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with second-generation ALK TKIs. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.I.; Solomon, B.J.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Besse, B.; Soo, R.A.; Abbattista, A.; Toffalorio, F.; Wiltshire, R.; Bearz, A. Continuation of Lorlatinib in ALK-Positive NSCLC Beyond Progressive Disease. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.; Morrow, M.; Hammond, S.A.; Mulgrew, K.; Marcus, D.; Poon, E.; Watkins, A.; Mullins, S.; Chodorge, M.; Andrews, J.; et al. Identification and Characterization of MEDI4736, an Antagonistic Anti-PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibody. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Jassem, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with advanced, ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated analysis of data from the phase 3, randomised, open-label CROWN study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salama, Z.T. Durvalumab: A Review in Extensive-Stage SCLC. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstraZeneca. MFINZI (Durvalumab): EU Summary of Product Characteristics. 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/imfinzi-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Banna, G.L.; Cantale, O.; Bersanelli, M.; Del Re, M.; Friedlaender, A.; Cortellini, A.; Addeo, A. Are anti-PD1 and anti-PD-L1 alike? The non-small-cell lung cancer paradigm. Oncol. Rev. 2020, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Sagara, H. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Refractory or Relapsed Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, Z.; Ning, J.; Sun, N. Safety of PD-L1 inhibitors versus PD-1 inhibitors in the treatment of lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2025, 25, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Cho, B.C.; Luft, A.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Geater, S.L.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.W.; Ursol, G.; Hussein, M.; Lim, F.L.; et al. Durvalumab with or Without Tremelimumab in Combination with Chemotherapy as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Phase III POSEIDON Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymach, J.V.; Harpole, D.; Mitsudomi, T.; Taube, J.M.; Galffy, G.; Hochmair, M.; Winder, T.; Zukov, R.; Garbaos, G.; Gao, S.; et al. Perioperative Durvalumab for Resectable Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, S.I.; Zippelius, A.; Eboulet, E.I.; Savic Prince, S.; Betticher, D.; Bettini, A.; Früh, M.; Joerger, M.; Lardinois, D.; Gelpke, H.; et al. SAKK 16/14: Durvalumab in Addition to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Stage IIIA(N2) Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—A Multicenter Single-Arm Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstraZeneca. IMFINZI™ (Durvalumab) Significantly Reduces the Risk of Disease Worsening or Death in the Phase III PACIFIC Trial for Stage III Unresectable Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2017/imfinzi-significantly-reduces-the-risk-of-disease-worsening-or-death-in-the-phase-iii-pacific-trial-for-stage-iii-unresectable-lung-cancer-12052017.html#! (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- AstraZeneca. IMFINZI®® (Durvalumab) Injection, for Intravenous Use: US Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/761069s029lbl.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Faivre-Finn, C.; Vicente, D.; Kurata, T.; Planchard, D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Spigel, D.R.; Garassino, M.C.; Reck, M.; Senan, S.; et al. Four-Year Survival with Durvalumab After Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC—An Update from the PACIFIC Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Pons-Tostivint, E.; Park, K.; Hartl, S.; Forde, P.M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Awad, M.M.; Thomas, M.; Goss, G.; Wheatley-Price, P.; et al. Biomarker-directed targeted therapy plus durvalumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 2 umbrella trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Reck, M.; Chouaid, C.; Bischoff, H.; Reinmuth, N.; Cove-Smith, L.; Mansy, T.; Cortinovis, D.; Migliorino, M.R.; et al. Durvalumab After Sequential Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III, Unresectable NSCLC: The Phase 2 PACIFIC-6 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Nadal, E.; Girard, N.; Filippi, A.R.; Martin, L.W.; Gay, C.M.; Petersen, C.; Gale, D.; Emeribe, U.A.; Georgoulia, N.; et al. MDT-BRIDGE: Neoadjuvant Durvalumab Plus Chemotherapy Followed by Either Surgery and Adjuvant Durvalumab or Chemoradiotherapy and Consolidation Durvalumab in Resectable or Borderline-resectable Stage IIB-IIIB NSCLC. Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 25, 587–593.e583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, J.D.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Ranasinghe, S.; Kao, K.Z.; Lako, A.; Tsuji, J.; Liu, Y.; Brennick, R.C.; Gentzler, R.D.; Lee, C.; et al. Durvalumab plus tremelimumab alone or in combination with low-dose or hypofractionated radiotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer refractory to previous PD(L)-1 therapy: An open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Ramalingam, S.; Urbanic, J.; Gerber, D.E.; Tan, D.S.W.; Cai, J.; Li, A.; Peters, S. CheckMate 73L: A Phase 3 Study Comparing Nivolumab Plus Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Followed by Nivolumab with or Without Ipilimumab Versus Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Followed by Durvalumab for Previously Untreated, Locally Advanced Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e264–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Fang, L. Structural modifications on indole and pyrimidine rings of osimertinib lead to high selectivity towards L858R/T790M double mutant enzyme and potent antitumor activity. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 116094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Mok, T.S.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Delmonte, A.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, S.W.; Shepherd, F.A.; Laskin, J.; He, Y.; et al. Osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC and progression on a prior EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: AURA3 overall survival analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, Y.; Kubota, K.; Shimokawa, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Kawashima, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Wakui, H.; Murakami, S.; Okishio, K.; Hayashihara, K.; et al. First-Line Osimertinib for Previously Untreated Patients with NSCLC and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: The UNICORN Phase 2 Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Wu, Y.L.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Wang, J.; Kato, T.; Goldman, J.W.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Adjuvant Osimertinib for Resected EGFR-Mutated Stage IB-IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results from the Phase III Randomized ADAURA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Kato, T.; Dong, X.; Ahn, M.J.; Quang, L.V.; Soparattanapaisarn, N.; Inoue, T.; Wang, C.L.; Huang, M.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Osimertinib after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remon, J.; Besse, B.; Aix, S.P.; Callejo, A.; Al-Rabi, K.; Bernabe, R.; Greillier, L.; Majem, M.; Reguart, N.; Monnet, I.; et al. Overall Survival from the EORTC LCG-1613 APPLE Trial of Osimertinib Versus Gefitinib Followed by Osimertinib in Advanced EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, J.Z.; Modi, S.; Chandarlapaty, S. Unlocking the potential of antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Shen, R.; Buonocore, D.; Olah, Z.T.; Ni, A.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Ulaner, G.A.; Offin, M.; Feldman, D.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine for Patients with HER2-Mutant Lung Cancers: Results from a Phase II Basket Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Tanaka, K.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cornelissen, R.; Girard, N.; Pons-Tostivint, E.; Vicente Baz, D.; Sugawara, S.; Cobo, M.; Pérol, M.; et al. Datopotamab Deruxtecan Versus Docetaxel for Previously Treated Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Randomized, Open-Label Phase III TROPION-Lung01 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Felip, E.; Chih-Hsin Yang, J.; Reck, M.; Yoh, K.; Lee, S.H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Besse, B.; et al. HERTHENA-Lung01, a Phase II Trial of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer After Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5363–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; et al. IMpower150 Final Overall Survival Analyses for Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in First-Line Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Mei, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Current status and future perspectives. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J.W.; Wolner, Z.; Pannu, S.; Mitchell, C.; Hsu, M.; Aijaz, A.; Johnson, M.; Naqash, A.R. Bispecific Antibodies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Targeted Innovation to Real-World Integration. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2025, 45, e472792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentzas, S.; Austria Mislang, A.R.; Lemech, C.; Nagrial, A.; Underhill, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, B.; Xia, Y.; Coward, J.I.G. Phase 1a dose escalation study of ivonescimab (AK112/SMT112), an anti-PD-1/VEGF—A bispecific antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wei, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Ying, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, S.; Luo, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, B.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics Evaluation of Ivonescimab, a Novel Bispecific Antibody Targeting PD-1 and VEGF, in Chinese Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, G.Y.; Henning, M.; Chen, Y. Measurements of traditional Chinese medicine health literacy regarding chronic pain: A scoping review. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Li, L.; Yang, R.N.; Liang, S.D. Compounds of traditional Chinese medicine and neuropathic pain. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Chen, J.; Zuo, F.; Guo, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, C. Traditional Chinese Medicine has great potential as candidate drugs for lung cancer: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 300, 115748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.S.; Shen, L.P.; Han, Z.F.; Jian, H.; Liu, J.X.; Xu, L.; Li, H.G.; Tian, J.H.; Mao, Z.J. Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment as maintenance therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther. Med. 2016, 24, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feiyue, Z.; Gaofeng, L. Traditional Chinese medicine and lung cancer—From theory to practice. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 137, 111381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, W.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, M. Research Status of Mouse Models for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Antitumor Therapy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in Mouse Models. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 6404853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.L.; Fitzgerald, B.G.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cappuzzo, F.; Jänne, P.A.; Peters, S.; Hirsch, F.R. New promises and challenges in the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2024, 404, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, T.; Podder, V.; Margolin, K.; Velcheti, V.; Maharaj, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Management of Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Current Trials, Guidelines and Future Directions. Cancers 2024, 16, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Chamoto, K.; Hatae, R.; Kurosaki, T.; Togashi, Y.; Fukuoka, K.; Goto, M.; Chiba, Y.; Tomida, S.; Ota, T.; et al. Soluble immune checkpoint factors reflect exhaustion of antitumor immunity and response to PD-1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e168318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessede, A.; Peyraud, F.; Besse, B.; Cousin, S.; Cabart, M.; Chomy, F.; Rey, C.; Lara, O.; Odin, O.; Nafia, I.; et al. TROP2 Is Associated with Primary Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas-Dias, C.; Gonçalves, F.; Martins, F.; Lemos, I.; Gonçalves, L.G.; Serpa, J. Interaction between NSCLC Cells, CD8+ T-Cells and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Potentiates Coagulation and Promotes Metabolic Remodeling-New Cues on CAT-VTE. Cells 2024, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benariba, M.A.; Hannachi, K.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, N. A liposome-based assay for cancer biomarker detection: Exploring the correlation between platelet-derived microvesicles and NSCLC-associated miRNAs. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 22037–22046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N | Authors/Reference | Clinical Trails | Phase of the Studies | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jung H. et al. [7] | (NCT04339829) | Phase II | 30 |
| 2 | Iwasaku M. et al. [8] | (jRCTs071190015) | Phase II | 41 |
| 3 | Tan W. et al. [9] | (NCT01858389) | Phase II | 41 |
| 4 | Mok T. et al. [10] | (NCT01774721) | Phase III | 227 |
| 5 | Pu X. et al. [11] | (NCT01774721) | Phase III | 227 |
| 6 | Cheng Y. et al. [12] | (NCT01774721) | Phase III | 346 |
| N | Authors/Reference | Clinical Trails | Phase of the Studies | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Goldsmith K. et al. [22] | (NCT03107988) | Phase I | 65 |
| 2 | Solomon B. et al. [21] | (NCT01970865) | Phase I & II | 364 |
| 3 | Lu S. et al. [23] | (NCT03909971) | Phase II | 109 |
| 4 | Felip E et al. [24] | (NCT01970865) | Phase II | 139 |
| 5 | Ou S. et al. [25] | (NCT01970865) | Phase I & II | 364 |
| 6 | Solomon B. et al. [27] | (NCT03052608) | Phase III | 296 |
| N | Authors/Reference | Clinical Trails | Phase of the Studies | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Besse B. et al. [39] | (NCT03334617) | Phase II | 268 |
| 2 | Garassino M. et al. [40] | (NCT03693300) | Phase II | 117 |
| 3 | Reck M. et al. [41] | (NCT05925530) | Phase II | 140 |
| 4 | Schoenfeld J. et al. [42] | (NCT02888743) | Phase II | 90 |
| 5 | Johnson M. et al. [33] | (NCT03164616) | Phase III | 1013 |
| 6 | Ruysscher D. et al. [43] | (NCT04026412) | Phase III | 888 |
| N | Authors/Reference | Clinical Trails | Phase of the Studies | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Okuma Y. et al. [49] | (jRCTs071200002) | Phase II | 40 |
| 2 | Herbst R. et al. [50] | (NCT02511106) | Phase III | 682 |
| 3 | Lu S. et al. [51] | (NCT03521154) | Phase III | 216 |
| 4 | Planchard D. et al. [52] | (NCT04035486) | Phase III | 557 |
| 5 | Remon J. et al. [53] | (NCT02856893) | Phase III | 156 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kariri, Y.A. Update on the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196960
Kariri YA. Update on the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196960
Chicago/Turabian StyleKariri, Yousif A. 2025. "Update on the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196960
APA StyleKariri, Y. A. (2025). Update on the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196960







