Cranial Neuropathy Secondary to Carotid Artery Dissection: Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Screening Process
2.3. Data Extraction and Outcome Measures
2.4. Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
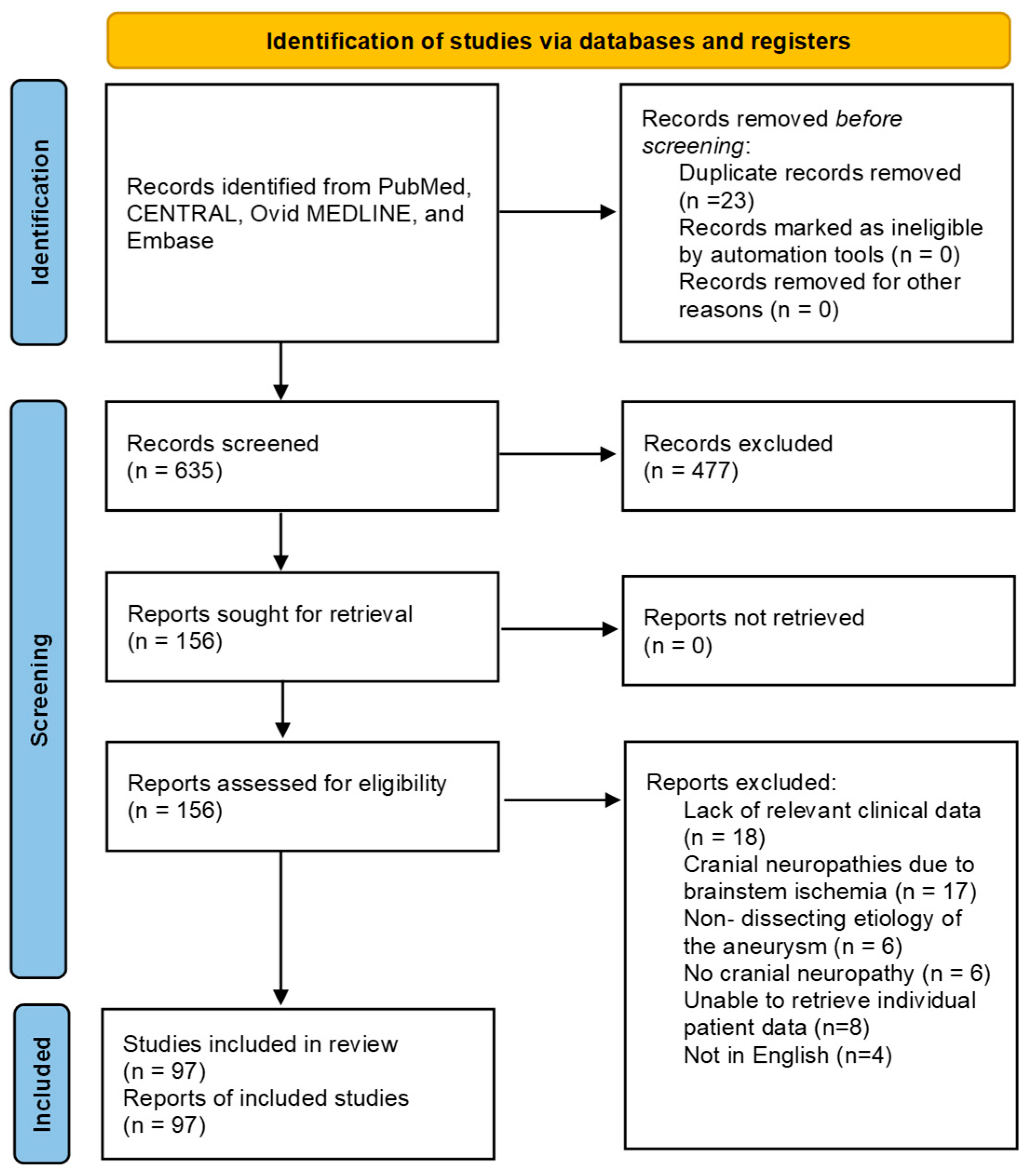
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
3.3. Baseline Characteristics
3.4. Clinical Course
3.5. Follow-Up and Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CADs | Carotid Artery Dissections |
| dPSA | Dissecting Pseudoaneurysms |
| CN XII | Hypoglossal Nerve |
| ICA | Internal Carotid Artery |
| RoB | Cochrane Risk of Bias |
| RCTs | Randomized Control Trials |
| NRSIs | Non-randomized studies of interventions |
| JBI | Joanna Brigg Institute |
| FMD | Fibromuscular Dysplasia |
| CN X | Vagus Nerve |
| CN XI | Glossopharyngeal Nerve |
| CN VII | Facial Nerve |
| CN VIII | Vestibulocochlear Nerve |
| CN V | Trigeminal Nerve |
| CN III | Oculomotor Nerve |
| CN IV | Trochlear Nerve |
| CN VI | Abducens Nerve |
| CeAD | Cervical Artery Dissection |
References
- Keser, Z.; Meschia, J.F.; Lanzino, G. Craniocervical Artery Dissections: A Concise Review for Clinicians. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, K.M.; Krings, T.; Lanzino, G.; Brinjikji, W. Intracranial dissections: A pictorial review of pathophysiology, imaging features, and natural history. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 48, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keser, Z.; Chiang, C.C.; Benson, J.C.; Pezzini, A.; Lanzino, G. Cervical Artery Dissections: Etiopathogenesis and Management. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.J.; Harmsen, W.S.; Mandrekar, J.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Keser, Z. Epidemiology of Spontaneous Cervical Artery Dissection: Population-Based Study. Stroke 2024, 55, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Engelter, S.; Del Brutto, V.J.; Field, T.S.; Jadhav, A.P.; Kicielinski, K.; Madsen, T.E.; Mistry, E.A.; Omran, S.S.; Pandey, A.; et al. Treatment and Outcomes of Cervical Artery Dissection in Adults: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Stroke 2024, 55, e91–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejakum, B.; Kiechl, S.; Knoflach, M.; Mayer-Suess, L. A narrative review on cervical artery dissection-related cranial nerve palsies. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1364218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokri, B.; Silbert, P.L.; Schievink, W.I.; Piepgras, D.G. Cranial nerve palsy in spontaneous dissection of the extracranial internal carotid artery. Neurology 1996, 46, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, D.; Pisanello, A.; Giovanardi, F.; Morandi, C.; Zuccoli, G.; Troiso, A. Spontaneous carotid dissection presenting lower cranial nerve palsies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 184, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, S.W.; Passe, T.J.; Lindell, E.P.; Klaas, J.P. Multiple cranial neuropathies as a presentation of spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection: A case report and literature review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 50, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himstead, A.S.; Gustafson, K.M.; Hasso, A.N.; Ediriwickrema, L.S. Internal Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm Causing an Abducens Nerve Palsy: A Case Report. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2023, 43, e50–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioni, A.; Paciaroni, M.; Sarchielli, P.; Murasecco, D.; Pelliccioli, G.P.; Calabresi, P. Multiple cranial nerve palsies in a patient with internal carotid artery dissection. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 58, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, T.; Röttger, C.; Kaps, M.; Traupe, H.; Stolz, E. Upper cranial nerve palsy resulting from spontaneous carotid dissection. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, M. JBI Critical appraisal checklist for systematic reviews and research syntheses. J. Can. Health Libr. Assoc. 2024, 45, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukeshek, T.; Gbande, P.; Hamed, R. Hypoglossal nerve palsy due to internal carotid artery dissection with pseudoaneurysm formation: An unusual presentation. Acta Radiol. Open 2022, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Baghomian, A.; Travis, P.; Doran, M. Internal Carotid Artery dissection presenting as Isolated Hypoglossal nerve palsy. Acute. Med. 2009, 8, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akova-Oztürk, E.; Husstedt, I.W.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Evers, S. Carotid artery dissection in ergotamine abuse. Headache 2004, 44, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allingham, W.; Devakumar, V.; Herwadkar, A.; Punter, M. Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy Due to Internal Carotid Artery Dissection. Neurohospitalist 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldner, C.; Riss, D.; Wagenblast, J.; Starlinger, V.; Hamzavi, J.S. Tenth and twelfth nerve palsies in a patient with internal carotid artery dissection mistaken for cervical mass lesion. Skull Base 2010, 20, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athuraliya, N.; Miteff, F. Internal carotid artery dissection and Villeret’s syndrome. QJM 2017, 110, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.L.; Pedroso, J.L.; Pieri, A. Spontaneous carotid dissection with hypoglossal nerve palsy as residual deficit: The importance of magnetic resonance evaluation. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2009, 67, 1109–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkowsky, V.; Steinbach, S.; Arnold, W. Vertigo and cranial nerve palsy caused by different forms of spontaneous dissections of internal and vertebral arteries. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2002, 259, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukobza, M.; Ast, G.; Reizine, D.; Merland, J.J. Internal carotid artery dissection causes hypoglossal nerve palsy: CT, MRI, and angiographic findings. J. Neuroimaging 1998, 8, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brajkovic, S.; Riboldi, G.; Govoni, A.; Corti, S.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.P. Growing Evidence about the Relationship between Vessel Dissection and Scuba Diving. Case Rep. Neurol. 2013, 5, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.R.; Massaro, A.R.; Scaff, M. Isolated oculomotor nerve palsy in spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection: Case report. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2003, 61, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, L.R.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Buonanno, F.S. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 18-2012. A 35-year-old man with neck pain, hoarseness, and dysphagia. N Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caranci, G.; Giacomelli, E.; Inghilleri, M. Unilateral lower cranial nerve palsies as the sole manifestation of internal carotid artery dissection: Case report. Muscle Nerve. 2018, 57, E134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, C.; Yin, K.; Liang, S.; Li, P.; Wu, M. Isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy from internal carotid artery dissection related to PKD-1 gene mutation. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciata, G.; Parikh, R.; Pradhan, M.; Shah, J.; Greif, E.; Stein, E.G. Internal carotid artery dissection and pseudoaneurysm formation with resultant ipsilateral hypoglossal nerve palsy. Radiol. Case Rep. 2017, 12, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, F.; Martini, G.; Thüringen, P.; Thaler, M.; Mani, G.; Steckholzer, K. Internal carotid artery dissection after inferior alveolar nerve block for third molar dental care presented as hypoglossal nerve palsy. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2012, 46, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihné, M.; Block, F.; Thron, A.; Küker, W. Raeder’s syndrome: A rare presentation of internal carotid artery dissection. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epifanov, Y.; Back, T. Oculosympathetic paratrigeminal paralysis with isolated v2 involvement in carotid artery dissection. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 448–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E.; Khan, M.A.; Francis, D.; Sada, P.; Thuse, M. Carotid artery dissection causing hypoglossal nerve palsy. BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr0120125636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, Y.; Ghare, M.I.; Patel, A.; Mojibian, H.; Matouk, C. Collet-Sicard syndrome secondary to internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 1596–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, J.; Johansen, M.; Akst, L.M. Dysphagia, dysphonia and a deviated tongue: Diagnosing Collet-Sicard syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e243154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlazzo, E.; Gasparini, S.; Arcudi, L.; Versace, P.; Aguglia, U. Isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy due to spontaneous carotid artery dissection: A neuroimaging study. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 2043–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.N.; Anderson, T.J. Lower cranial nerve palsies due to carotid artery dissection. N. Z. Med. J. 1998, 111, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Freilinger, T.; Heuck, A.; Strupp, M.; Jund, R. Images in vascular medicine: Hypoglossal nerve palsy due to internal carotid artery dissection. Vasc. Med. 2010, 15, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Ohtsuki, T.; Takeda, I.; Hosomi, N.; Matsumoto, M. Isolated unilateral hypoglossal nerve paralysis caused by internal carotid artery dissection. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, e405–e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, U.M.; Magorrian, M.; Burns, P.; Lindsay, J.R. An unusual headache. BMJ 2014, 349, g5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, N.; Deffond, D.; Gabrillargues, J.; Carriere, N.; Dordain, G.; Clavelou, P. Spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection with lower cranial nerve palsy. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 28, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafkamp, H.C.; Van Der Goten, A.; Manni, J.J. Unilateral spontaneous dissection of the internal carotid artery presenting as hypoglossal nerve palsy. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2004, 261, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, V.; Coutinho, C.M.; Mitchell, J.D. Dissection of the intracranial internal carotid artery producing isolated oculomotor nerve palsy with sparing of pupil. Acta. Neurol. Scand. 2002, 105, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennings, J.M.; Hoehn, D.; Schumann-Spaeth, E.; Weber, F. Painless hypoglossal palsy as an isolated symptom of spontaneous carotid dissection. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 1988–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, H.; Pahalagamage, S.P.; Withana, D.; Senanayake, S. Complete ophthalmoplegia, complete ptosis and dilated pupil due to internal carotid artery dissection: As the first manifestation of Takayasu arteritis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, T.; Mbydeen, T.H.S.; Alagoda, S.; Saleh, M.; Naidu, L.; Wimalaratna, S. Simultaneous Horner’s syndrome with anhidrosis and facial nerve palsy in internal carotid artery dissection. Pract. Neurol. 2024, 24, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.C.; Sethi, K.D.; Nichols, F.T. Carotid dissection: A new false localising sign. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1990, 53, 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.; Kim, Y.W. A Very Rapidly Growing, Spontaneous, Internal Carotid Artery Dissecting Aneurysm Triggering Simultaneous Complete Ophthalmoplegia and a Cerebral Infarct. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introna, A.; Chiumarulo, L.; Petruzzellis, M. Dissecating aneurysm of extracranial internal carotid artery presenting with Tapia syndrome in patient with essential thrombocythemia. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1893–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaume, F.; Alobid, I.; Langdon, C. Traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. A rare cause of cranial nerve palsy. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2015, 66, e38–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkiewicz, M.T.; Stein, J.M.; Learned, K.O.; Nasrallah, I.M.; Loevner, L.A. Hypoglossal nerve palsy due to carotid artery dissection: An uncommon presentation of a common problem. Neuroradiol. J. 2019, 32, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasravi, N.; Leung, A.; Silver, I.; Burneo, J.G. Dissection of the internal carotid artery causing Horner syndrome and palsy of cranial nerve XII. CMAJ 2010, 182, E373–E377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Abhishek, K.; Sofi, U. Spontaneous dissection of internal carotid artery masquerading as angioedema. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2009, 24, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoguchi, T.; Fukui, I.; Abe, H.; Mori, K.; Tamase, A.; Yamashita, R.; Takeda, M.; Nakano, T.; Nomura, M. Carotid artery stenting for spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection presenting with hypoglossal nerve palsy: A case report. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2022, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klossek, J.M.; Neau, J.P.; Vandenmarq, P.; Fontanel, J.P. Unilateral lower cranial nerve palsies due to spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1994, 103, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibb, J.; Lenthall, R.; Bajaj, N. Internal carotid artery dissection presenting with ipsilateral tenth and twelfth nerve palsies and apparent mass lesion on MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2005, 78, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Kitagawa, T.; Hata, Y.; Fukuyama, K.; Honda, K. Carotid artery dissection due to an elongated styloid process: A case report and implications for the otolaryngologist. Acta Oto-Laryngol. Case Rep. 2022, 7, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Davis, S.; Tress, B.M.; Ebeling, P. Spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection presenting as hypoglossal nerve palsy. Stroke. 1988, 19, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, F.W.; Mullin, D.; Keefe, M.A. Subacute hypoglossal nerve paresis with internal carotid artery dissection. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1530–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Zhou, L.; Hong, D. Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm Presenting as Lower Cranial Nerve Palsies. World Neurosurg. May 2023, 173, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, N.; Sardella, A.; Lodi, G. Tongue deviation and dysarthria in painless patient. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2022, 139, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Ribeiro, N.P.; Ali, A.; Hijazi, M.; Farook, H. A rare presentation of spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection with Horner’s syndrome, VIIth, Xth and XIIth nerve palsies. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 2016, omw078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, F.; Scolan, V.; Detante, O.; Barret, L.; Paysant, F. Post-traumatic dissection of the internal carotid artery associated with ipsilateral facial nerve paralysis: Diagnostic and forensic issues. J. Forensic. Leg. Med. 2013, 20, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, L.F.; Bichuetti, D.B.; Felício, A.C.; Santos, W.A.C.D.; Oliveira, F.F.D.; Morita, M.E.; Avelar, W.M.; Braga-Neto, P.; Lima, E.C.D.S.; Martins, R.J. Hypoglossal nerve palsy as the sole manifestation of spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2009, 67, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, M.O.; Metcalfe, R.A.; Muir, K.W. Facial nerve palsy secondary to internal carotid artery dissection. Eur. J. Neurol. 2000, 7, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussouttas, M.; Tuhrim, S. Spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection with isolated vagus nerve deficit. Neurology 1998, 51, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnane, M.; Proano, L. Raeder’s paratrigeminal syndrome: A case report. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1996, 3, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Kusuyama, T.; Ogawa, K. Isolated vagus nerve paralysis associated with internal carotid artery dissection. Auris. Nasus. Larynx. 2014, 41, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neau, J.-P.; Klossek, J.-M.; Vandermarq, P.; Rosolacci, T.; Gil, R. Lower-Cranial-Nerve Palsies due to Spontaneous Internal Carotid Dissection. Cerebrovascular. Diseases. 1993, 3, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.A.; Linden, R.; Arnold, P.; Seitz, V.; Stangl, K.; Wendl, C.; Schlachetzki, F. Case report: A complicated course of Collet-Sicard syndrome after internal carotid artery dissection and lenticulo-striatal artery infarction. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 939236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunomiya, T.; Kageyama, T.; Suenaga, T. Teaching NeuroImages: Isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy due to internal carotid artery dissection. Neurology 2012, 79, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdemirli, E.; Usal, D.; Tali, E.T. Spontaneous bilateral internal carotid artery dissection with hypoglossal nerve palsy. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2001, 25, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panisset, M.; Eidelman, B.H. Multiple cranial neuropathy as a feature of internal carotid artery dissection. Stroke 1990, 21, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlukowska, W.; Mross, K.; Jankowska, M.; Zwarzany, Ł.; Poncyljusz, W.; Masztalewicz, M. Acute Tongue Swelling as a Still Unexpected Manifestation of Internal Carotid Artery Dissection: A Case Report. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltz, E.; Köhrmann, M. Images in clinical medicine. Internal-carotid-artery dissection and cranial-nerve palsies. N Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pica, R.A., Jr.; Rockwell, B.H.; Raji, M.R.; Dastur, K.J.; Berkey, K.E. Traumatic internal carotid artery dissection presenting as delayed hemilingual paresis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1996, 17, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pikija, S.; Unterkreuter, P. Ipsilateral hypoglossal and oculosympathetic paresis in carotid dissection. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongmoragot, J.; Bharatha, A.; Saposnik, G. Pearls and oy-sters: Carotid dissection with normal arterial lumen. Neurology 2013, 80, e115–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, P.; Chapot, R.; Tanasković, S.; Vekić, B.; Sotirovic, V.; Ilijevski, N.; Radak, D. Vocal Cord Paralysis as the First Sign of Spontaneous Carotid Dissection in a Patient With Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2016, 50, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Lu, Z.C.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.P. Bilateral dissecting aneurysms of the internal carotid arteries misdiagnosed as skull base tumors: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riancho, J.; Infante, J.; Mateo, J.I.; Berciano, J.; Agea, L. Unilateral isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy associated with internal carotid artery dissection. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.; Rehman, S.; Prince, S. Acute tongue swelling, the only initial manifestation of carotid artery dissection: A case report with differentiation of clinical picture. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 29, 365.e17–365.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliou, V.; Ben Salem, D.; Ognard, J.; Guellec, D.; Marcorelles, P.; Rouhart, F.; Zagnoli, F.; Timsit, S. A Collet-Sicard syndrome due to internal carotid artery dissection associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2018, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.; Morais, H.; Oliveira, G.; Barros, P. Isolated oculomotor nerve palsy: A rare manifestation of internal carotid artery dissection. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014205413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, R.; Yamashita, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Shang, J.; Sato, K.; Takemoto, M.; Hishikawa, N.; Ohta, Y.; Abe, K. A case of bilateral internal carotid artery dissection in young adult with cranial nerve IX and X palsies. Neurol. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 6, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I.; Mokri, B.; Garrity, J.A.; Nichols, D.A.; Piepgras, D.G. Ocular motor nerve palsies in spontaneous dissections of the cervical internal carotid artery. Neurology. 1993, 43, 1938–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selky, A.K.; Pascuzzi, R. Raeder’s paratrigeminal syndrome due to spontaneous dissection of the cervical and petrous internal carotid artery. Headache. 1995, 35, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, R.; Savy, L.E.; Croft, C.B.; Hung, T. Isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy due to internal carotid artery dissection. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2001, 115, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ma, S.; Du, S.; Cheng, Y.; Qu, H.; et al. Be careful of Collet-Sicard syndrome: A rare result of carotid artery dissection. Headache 2022, 62, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, M.; Schneck, M.J.; Origitano, T.C.; Biller, J. “Spontaneous” Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Following Cough Induced by ACE Inhibitor Therapy. Semin. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Stroke 2004, 4, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.; David, O.; Nasr, F. An unusual presentation of dysarthria in a young patient, a stroke mimic. Acute Med. 2021, 20, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Tassone, P.; Saada, J. Collet-Sicard syndrome as a result of unilateral carotid artery dissection. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013200358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, C.; Mull, M.; Töpper, R. Isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy caused by carotid artery dissection the necessity of MRI for diagnosis. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.; Nwosu, J.; Foy-Yamah, A.; Ejohwomu, C.O. Carotid artery dissection: A case of recurrence. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e241718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, P.; Monti, L.; Pacini, M.; Barontini, F.; Maurri, S. Case report: Sequential bilateral carotid dissection leading to Raeder’s syndrome. Br. J. Radiol. 1996, 69, 1184–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stübgen, J.P. Unilateral macroglossia as sole presenting manifestation of internal carotid artery dissection. Ear Nose Throat J. 2011, 90, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturzenegger, M.; Huber, P. Cranial nerve palsies in spontaneous carotid artery dissection. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, A.; Lachanis, S.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Maili, M.; Pachi, I.; Velonakis, G.; Bakola, E.; Vassilopoulou, S.; Tsivgoulis, G. Collet-Sicard syndrome due to cervical artery dissection disclosed by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbus-Paluszczak, M.; Mucha, S.; Wawrzyńczyk, M.; Pierzchała, K.; Bartman, W.; Adamczyk-Sowa, M. Hypoglossal nerve palsy in the course of dissection of the internal carotid arteries-Case reports. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2018, 52, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursekar, M.A.; Singhal, B.S.; Konin, B.L. Hypoglossal nerve palsy due to spontaneous dissection of the internal carotid artery. Clin. Radiol. 2000, 55, 978–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwet, K.V.M.; Brown, A.V.; Bakker, S.L.M. Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Presenting With Dysgeusia, Horner Syndrome, and Hypesthesia of the Fifth Cranial Nerve: A Case Report. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 58, e27–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdalle, P.; Herve, S.; Kossowski, M.; Felten, D.; Courtois, A.; Garcia, D.; Poncet, J.L. Spontaneous dissection of the internal carotid artery in its extracranial portion, revealed by a hypoglossal paralysis: Report of four cases. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2001, 110, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waespe, W.; Niesper, J.; Imhof, H.G.; Valavanis, A. Lower cranial nerve palsies due to internal carotid dissection. Stroke 1988, 19, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.; McCarron, M.O.; Flynn, P.A.; Watt, M. Left internal carotid artery dissection presenting with headache, Collet-Sicard syndrome and sustained hypertension. Eur. J. Neurol. 2003, 10, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeleňák, K.; Zeleňáková, J.; DeRiggo, J.; Kurča, E.; Kantorová, E.; Poláček, H. Treatment of cervical internal carotid artery spontaneous dissection with pseudoaneurysm and unilateral lower cranial nerves palsy by two silk flow diverters. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, G.; Lu, T.; Xu, G.; Liu, X. Tolosa-Hunt syndrome with reversible dissection aneurysm. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 31, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Goeggel Simonetti, B.; Schilling, S.; Martin, J.J.; Kloss, M.; Sarikaya, H.; Hausser, I.; Engelter, S.; Metso, T.M.; Pezzini, A.; et al. Familial occurrence and heritable connective tissue disorders in cervical artery dissection. Neurology 2014, 83, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, R.; Heidbreder, A.; Rohsbach, D.; Schmalhorst, J.; Nassenstein, I.; Maintz, D.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Nabavi, D.G.; Kuhlenbäumer, G. Connective tissue and vascular phenotype in patients with cervical artery dissection. Neurology 2007, 68, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian-Dodov, D.; Gornik, H.L.; Gu, X.; Froehlich, J.; Bacharach, J.M.; Chi, Y.W.; Gray, B.H.; Jaff, M.R.; Kim, E.S.; Mace, P.; et al. Dissection and Aneurysm in Patients With Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Findings From the U.S. Registry for FMD. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Kappeler, L.; Georgiadis, D.; Berthet, K.; Keserue, B.; Bousser, M.G.; Baumgartner, R.W. Gender differences in spontaneous cervical artery dissection. Neurology 2006, 67, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipani, E.; Griffin, K.J.; Oakley, C.I.; Keser, Z. Sex differences in the epidemiology of spontaneous and traumatic cervical artery dissections. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2025, 10, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.; Boehme, C.; Toell, T.; Dejakum, B.; Willeit, J.; Schmidauer, C.; Berek, K.; Siedentopf, C.; Gizewski, E.R.; Ratzinger, G.; et al. Local Signs and Symptoms in Spontaneous Cervical Artery Dissection: A Single Centre Cohort Study. J. Stroke. 2019, 21, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboix, A.; Bechich, S.; Oliveres, M.; Garcia-Eroles, L.; Massons, J.; Targa, C. Ischemic stroke of unusual cause: Clinical features, etiology and outcome. Eur. J. Neurol. 2001, 8, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.S.; Levi, C.; King, A.; Madigan, J.; Norris, J. Antiplatelet Therapy vs Anticoagulation Therapy in Cervical Artery Dissection: The Cervical Artery Dissection in Stroke Study (CADISS) Randomized Clinical Trial Final Results. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.E.; Harshfield, E.L.; Gensicke, H.; Wegener, S.; Michel, P.; Kägi, G.; Nedeltchev, K.; Kellert, L.; Rosenbaum, S.; Nolte, C.H.; et al. Antithrombotic Treatment for Cervical Artery Dissection: A Systematic Review and Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelter, S.T.; Traenka, C.; Gensicke, H.; Schaedelin, S.A.; Luft, A.R.; Simonetti, B.G.; Fischer, U.; Michel, P.; Sirimarco, G.; Kägi, G.; et al. Aspirin versus anticoagulation in cervical artery dissection (TREAT-CAD): An open-label, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. Neurol. 2021, 20, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Number (%) or Mean (Range) |
|---|---|
| Age in years, mean (range) | 48 (26–68) |
| Sex (female) | 26 (24) |
| Cranial nerve involved | |
| CN III Isolated Combined | 9 (8) 4 5 |
| CN IV Isolated Combined | 3 (3) 0 3 |
| CN V Isolated Combined | 8 (7) 6 2 |
| CN VI Isolated Combined | 5 (5) 1 4 |
| CN VII Isolated Combined | 7 (6) 4 3 |
| CN VIII Isolated Combined | 1 (1) 0 1 |
| CN IX Isolated Combined | 30 (28) 0 30 |
| CN X Isolated Combined | 38 (35) 3 35 |
| CN XI Isolated Combined | 21 (19) 1 20 |
| CN XII Isolated Combined | 82 (76) 45 37 |
| Pseudoaneurysms | |
| Yes | 36 (33) |
| No | 72 (67) |
| ICA segment involved | |
| Cavernous | 6 (6) |
| Petrous | 21 (19) |
| Proximal cervical | 7 (6) |
| Mid-cervical | 23 (21) |
| Distal cervical | 96 (89) |
| Etiology | |
| Minor trauma | 22 (20) |
| Spontaneous | 86 (80) |
| Variable | Number of Patients with Available Data | Number (%) or Mean (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Antithrombotic regimen | 100 | |
| Anticoagulant Pre-CADISS Post-CADISS | 43 (43) 39 4 | |
| Single antiplatelet Pre-CADISS Post-CADISS | 37 (37) 20 15 | |
| Dual antiplatelet Pre-CADISS Post-CADISS | 12 (12) 4 8 | |
| No medical treatment | 10 (10) | |
| Duration of antithrombotic therapy in weeks, mean (range) | 80 | 16 (2–104) * |
| Interventional approach | 13 | |
| Stent | 4 (30.77) | |
| Flow diverter | 3 (23.08) | |
| Coil embolization | 3 (23.08) | |
| Stent coiling | 2 (15.38) | |
| Detachable balloon | 1 (7.69) | |
| Final follow-up time in weeks, mean (range) | 98 | 21 (2–154) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xeros, H.K.; Yesiloglu, I.; Keser, Z. Cranial Neuropathy Secondary to Carotid Artery Dissection: Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196854
Xeros HK, Yesiloglu I, Keser Z. Cranial Neuropathy Secondary to Carotid Artery Dissection: Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196854
Chicago/Turabian StyleXeros, Helena K., Irem Yesiloglu, and Zafer Keser. 2025. "Cranial Neuropathy Secondary to Carotid Artery Dissection: Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196854
APA StyleXeros, H. K., Yesiloglu, I., & Keser, Z. (2025). Cranial Neuropathy Secondary to Carotid Artery Dissection: Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196854







