Effects of Intragastric Helicobacter pylori Distribution on Clinical Presentation, Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Esophageal Manometry, and pH–Impedance Metrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
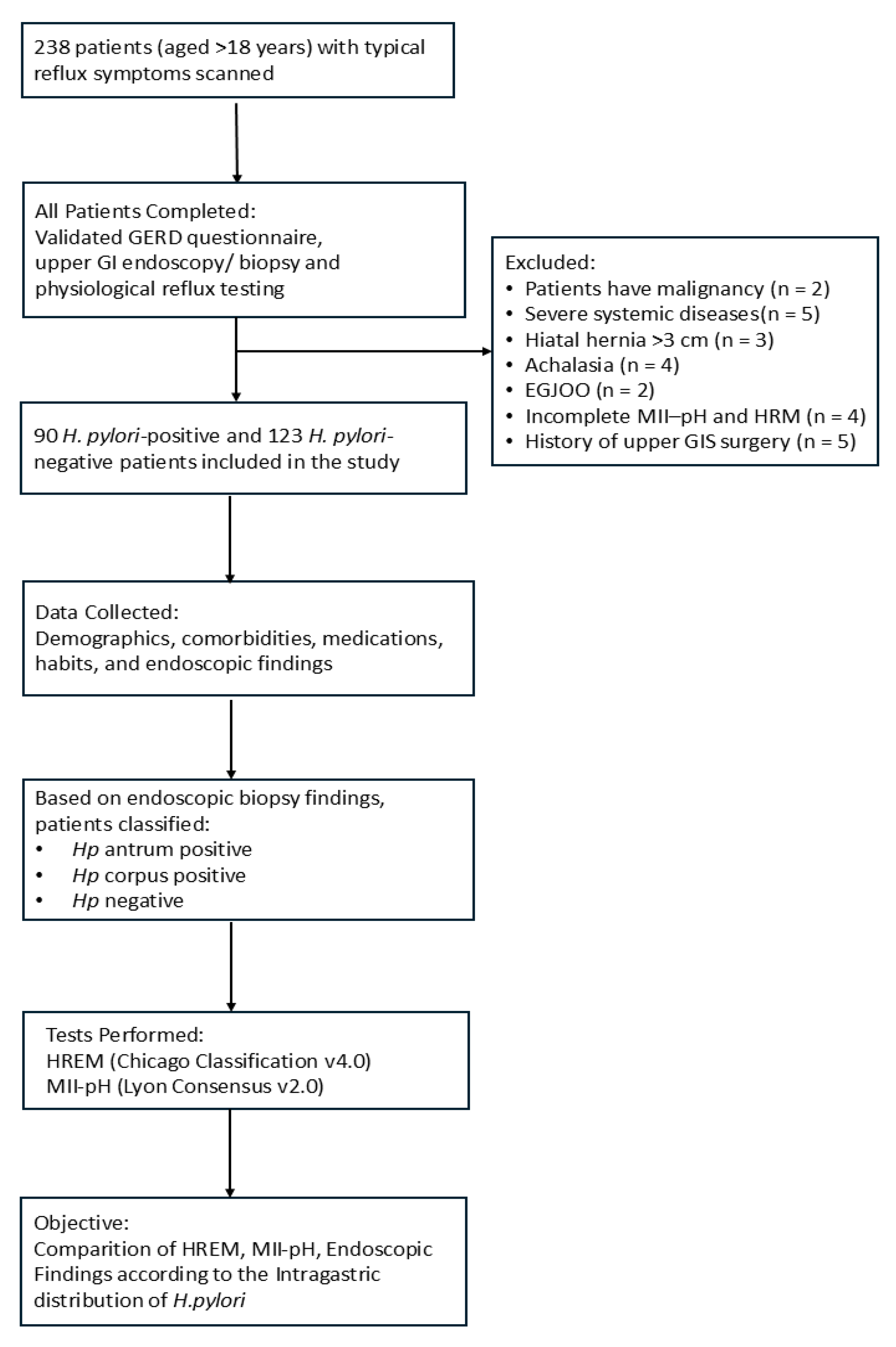
2.2. Patient Selection and Data Collection
2.3. Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
2.4. Histopathological Evaluation and Detection of Helicobacter pylori
2.5. Esophageal pH Monitoring
2.6. Esophageal Manometry Evaluation
2.7. Esophageal Motility Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Symptomatology
3.3. Comorbidities
3.4. Endoscopic Findings
3.5. Twenty-Four-Hour Impedance–pH Monitoring
3.6. High-Resolution Esophageal Manometry (HREM)
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Limitations
4.2. Study Strengths
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AET | Acid exposure time |
| CFV | Contractile front velocity |
| DCI | Distal contractile integral |
| FD | Functional dyspepsia |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| H. pylori | Helicobacter pylori |
| HREM | High-resolution esophageal manometry |
| IEM | Ineffective esophageal motility |
| LA | Los Angeles classification of esophagitis |
| LES | Lower esophageal sphincter |
| MII-pH | Multichannel intraluminal impedance–pH monitoring |
| MNBI | Mean nocturnal baseline impedance |
| PPI | Proton pump inhibitor |
| RE | Number of reflux episodes |
References
- Li, Y.; Choi, H.; Leung, K.; Jiang, F.; Graham, D.Y.; Leung, W.K. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection between 1980 and 2022: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, J.; Epplein, M. How do global trends in Helicobacter pylori prevalence inform prevention planning? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaydin, N.; Turkyilmaz, S.A.; Cali, S. Prevalence and risk factors of Helicobacter pylori in Turkey: A nationally-representative, cross-sectional, screening with the 13C-urea breath test. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalaki, S.; Caglar, R.; Pulat, H. Effect of gastric Helicobacter pylori colonization in the development of erosive esophagitis in patients with hiatal hernia. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2023, 26, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalaki, S.; Pulat, H.; Ilhan, A. Localization of Helicobacter pylori gastritis and the relation of existing histopathological features with reflux esophagitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Kupcinskas, J. Helicobacter pylori and non-malignant upper gastrointestinal diseases. Helicobacter 2020, 25 (Suppl. S1), e12738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, S.; Karakan, T.; Dogan, I.; Cindoruk, M.; Dumlu, S. The influence of Helicobacter pylori infection on the prevalence of endoscopic erosive esophagitis. Helicobacter 2006, 11, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruma, K. Review article: Influence of Helicobacter pylori on gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in Japan. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20 (Suppl. S8), 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Uotani, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Andoh, A.; Furuta, T. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in time covering eradication for all patients infected with Helicobacter pylori in Japan. Digestion 2016, 93, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, F.; Li, Y. Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on esophageal motility, esophageal acid exposure, and gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1082620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Jackson, W.; Floum, S.; Giaffer, M.H. Gastroesophageal reflux before and after Helicobacter pylori eradication: A prospective study using ambulatory 24 h esophageal pH monitoring. Dis. Esophagus 2003, 16, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; de Pedro, A.; Losa, C.; Barreiro, A.; Pajares, J.M. Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease: Lack of influence of infection on twenty-four-hour esophageal pH monitoring and endoscopic findings. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2001, 32, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, A.P.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Benvengo, Y.H.; Vitiello, L.; Miranda, M.d.e.C.; Mendonça, S.; Pedrazzoli, J., Jr. Analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence factors in Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. BMC Gastroenterol. 2003, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavalipour, A.; Malekpour, H.; Dabiri, H.; Kazemian, H.; Zojaji, H.; Bahroudi, M. Prevalence of cytotoxin-associated genes of Helicobacter pylori among Iranian GERD patients. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2017, 10, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kitapcioglu, G.; Mandiracioglu, A.; Bor, S. Psychometric and methodological characteristics of a culturally adjusted gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire. Dis. Esophagus 2004, 17, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Yadlapati, R.; Fass, R.; Katzka, D.; Pandolfino, J.; Savarino, E.; Sifrim, D.; Spechler, S.; Zerbib, F.; Fox, M.R.; et al. Updates to the modern diagnosis of GERD: Lyon consensus 2.0. Gut 2024, 73, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundell, L.R.; Dent, J.; Bennett, J.R.; Blum, A.L.; Armstrong, D.; Galmiche, J.P.; Johnson, F.; Hongo, M.; Richter, J.E.; Spechler, S.J.; et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: Clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut 1999, 45, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadlapati, R.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Fox, M.R.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Gyawali, C.P.; Roman, S.; Babaei, A.; Mittal, R.K.; Rommel, N.; Savarino, E.; et al. Esophageal motility disorders on high-resolution manometry: Chicago classification version 4.0©. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, G.; Vargas, J.I.; Shah, S.C.; Ivanovic-Zuvic, D.; Achurra, P.; Fritzsche, M.; Leung, J.S.; Ramos, B.; Jensen, E.; Uribe, J.; et al. Implementation of the updated Sydney system biopsy protocol improves the diagnostic yield of gastric preneoplastic conditions: Results from a real-world study. Gastroenterol. Y Hepatol. 2024, 47, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.F.; Genta, R.M.; Yardley, J.H.; Correa, P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashktorab, H.; Entezari, O.; Nouraie, M.; Dowlati, E.; Frederick, W.; Woods, A.; Lee, E.; Brim, H.; Smoot, D.T.; Ghadyari, F.; et al. Helicobacter pylori protection against reflux esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2924–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, O. Interactions between Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Esophagus 2019, 16, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chourasia, D.; Misra, A.; Tripathi, S.; Krishnani, N.; Ghoshal, U.C. Patients with Helicobacter pylori infection have less severe gastroesophageal reflux disease: A study using endoscopy, 24-hour gastric and esophageal pH metry. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 30, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Comparison of Esophageal Function Tests to Investigate the Effect of Helicobacter Pylori Infection on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirota, T.; Kusano, M.; Kawamura, O.; Horikoshi, T.; Mori, M.; Sekiguchi, T. Helicobacter pylori infection correlates with severity of reflux esophagitis: With manometry findings. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 34, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.H.; Sheu, B.S.; Yang, H.B.; Lee, S.C.; Kao, A.W.; Cheng, H.C.; Chang, W.L.; Yao, W.J. Gender difference of circulating ghrelin and leptin concentrations in chronic Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, R.M., Jr.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nature reviews. Cancer 2002, 2, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Morais, S.; Ferro, A.; Lunet, N.; Peleteiro, B. Sex-differences in the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in pediatric and adult populations: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 244 studies. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Us, D.; Hasçelik, G. Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in an Asymptomatic Turkish population. J. Infect. 1998, 37, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Doğan, Y.; Gürgöze, M.K.; Unal, S. Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among children and their parents in eastern Turkey. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2002, 38, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, S.; Kay, L.; Rosenstock, C.; Andersen, L.P.; Bonnevie, O.; Jørgensen, T. Relation between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastrointestinal symptoms and syndromes. Gut 1997, 41, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullo, A.; Hassan, C.; De Francesco, V.; Repici, A.; Manta, R.; Tomao, S.; Annibale, B.; Vaira, D. Helicobacter pylori and functional dyspepsia: An unsolved issue? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8957–8963. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Morain, C. Role of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2677–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Dong, Z.; Wang, C.; Xiao, J.; Yang, W. Incidence and risk factors of postoperative nausea and vomiting following laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and its relationship with Helicobacter pylori: A propensity score matching analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooten, I.J.; Den Hollander, W.J.; Roseboom, T.J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Gaillard, R.; Painter, R.C. Helicobacter pylori infection: A predictor of vomiting severity in pregnancy and adverse birth outcome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 512.e1–512.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, F.; Ahmadi, A.; Ghourchian, S.; Daneshi, A.; Memari, F.; Khadivi, E.; Mohammadi, S. Detection of helicobacter pylori in benign laryngeal lesions by polymerase chain reaction: A cross sectional study. Infect. Agents Cancer 2012, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matić, I.P.; Matić, I.; Maslovara, S.; Veselski, K.; Stojadinović, T.; Vučković, I. Helicobacter pylori gastric infection in patients with laryngeal cancer and chronic laryngitis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Kürschner, A.; Weckesser, S.; Wittmer, A.; Rauberger, H.; Jakob, T.; Hellwig, E.; Kist, M.; Waidner, B. Is Helicobacter pylori resident or transient in the human oral cavity? J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspersen, D.; Weber, R.; Diehl, K.L.; Kind, M.; Arps, H.; Draf, W. Ist die chronische Laryngitis Helicobacter-pylori-assoziiert? Ergebnisse einer prospektiven Studie [Is chronic laryngitis associated with Helicobacter pylori? Results of a prospective study]. Z. Fur Gastroenterol. 1998, 36, 369–372. [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski, G.; Sudhoff, H.; Koslowski, F.; Hackstedt, G.; Radü, H.J.; Luckhaupt, H. A possible role of Helicobacter pylori infection in the etiology of chronic laryngitis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 1997, 254, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siupsinskiene, N.; Jurgutaviciute, V.; Katutiene, I.; Janciauskas, D.; Vaitkus, S.; Adamonis, K. Helicobacter pylori infection in laryngeal diseases. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013, 270, 2283–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, M.C. Cigarette smoking and Helicobacter pylori infection. Postgrad. Med. J. 1993, 69, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, P.; Qin, X.; Li, C.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X. Impact of smoking on the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirkeci, Ö.; Sirkeci, E.E.; Ulaş, T. Does waterpipe smoking increase the risk of Helicobacter pylori infection? J. Res. Med. Sci. 2022, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, H.; Rothenbacher, D.; Bode, G.; Adler, G. Relation of smoking and alcohol and coffee consumption to active Helicobacter pylori infection: Cross sectional study. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1997, 315, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinchi, K.; Ishii, H.; Imanishi, K.; Kono, S. Relationship of cigarette smoking, alcohol use, and dietary habits with Helicobacter pylori infection in Japanese men. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.A.; Camacho, S. Helicobacter pylori infection and hiatal hernia do not affect acid reflux and esophageal motility in patients with gastro-esophageal reflux. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lagergren, J.; Yuan, S.; Ness-Jensen, E.; Jiang, W.; Xie, S.H. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Eradication in Relation to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, M.; Lisi, G.; De Sanctis, F.; Grande, S.; Esser, A.; Campanelli, M.; Balassone, V.; Milito, G.; Villa, M. Does a relationship still exist between gastroesophageal reflux and Helicobacter pylori in patients with reflux symptoms? World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeraerts, A.; Van Houtte, B.; Clevers, E.; Geysen, H.; Vanuytsel, T.; Tack, J.; Pauwels, A. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-Functional Dyspepsia Overlap: Do Birds of a Feather Flock Together? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hp (−) (n = 123) | Hp Antrum (+) (n = 60) | Hp Corpus (+) (n = 30) | p-Value | sig. Diff. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 42 (36–56) | 44 (34–51) | 46 (39–52) | 0.434 | — |
| Weight | 72.92 ± 12.75 | 72.5 ± 12.84 | 75.73 ± 16.37 | 0.851 | — |
| BMI | 25.65 ± 3.86 | 26.36 ± 4.94 | 26.68 ± 4.14 | 0.635 | — |
| Female | 51 (49) a | 37 (35.6) b | 16 (15.4) c | 0.034 | b vs. c: p = 0.019 |
| Male | 72 (66.1) a | 23 (21.1) b | 14 (12.8) c | 0.034 | a vs. b: p = 0.012 |
| Endoscopic Appearance | Hp (−) (n = 123) | Hp Antrum (+) (n = 60) | Hp Corpus (+) (n = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Esophagitis | 102 (82.9) | 55 (91.7) | 24 (80.0) | 0.418 |
| LA-A Esophagitis | 13 (10.6) | 4 (6.7) | 3 (10.0) | |
| LA-B, C, or D Esophagitis | 8 (6.5) | 1 (1.7) | 3 (10.0) |
| Parameter | Hp (−) (n = 123) | Hp Antrum (+) (n = 60) | Hp Corpus (+) (n = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeMeester | 11.7 (3.5–26.3) | 9.2 (3.5–24.4) | 10.3 (3.8–27.3) | 0.919 |
| DeMeester ≥ 14.72 | 56 (46) | 23 (38) | 13 (43) | 0.650 |
| AET | 3.4 (0.7–6.3) | 2.3 (0.6–6.3) | 2.9 (0.8–7.2) | 0.697 |
| AET < 4 | 67 (55) | 38(63) | 17 (56) | 0.401 |
| AET 4–6 | 21 (17) | 6 (10) | 2 (7) | |
| AET > 6 | 35 (28) | 16 (27) | 11 (37) | |
| RE | 23 (10.0–40.0) | 28.5 (12.5–45.8) | 28 (18.2–49.5) | 0.523 |
| RE < 40 | 93 (75) | 43 (72) | 20 (67) | 0.627 |
| RE 40–80 | 22 (18) | 14 (23) | 9 (30) | |
| RE > 80 | 8 (7) | 3 (5) | 1 (3) | |
| SI | 12.5 (0.0–99.8) | 2.5 (0.0–42.0) | 70.0 (0.0–99.0) | 0.500 |
| SAP | 70.0 (0.0–99.0) | 70.3 (0.0–98.0) | 59.7 (0.0–99.0) | 0.693 |
| MNBI (Ω) | 2950 (1950–4200) | 3415 (2265–4585) | 2825 (1850–3697) | 0.213 |
| MNBI < 1500 | 13 (11) | 6 (10) | 4 (13) | 0.732 |
| MNBI 1500–2500 | 39 (32) | 14 (23) | 7 (23) | |
| MNBI > 2500 | 71 (57) | 40 (67) | 19 (64) |
| Parameter | Hp (−) (n = 123) | Hp Antrum (+) (n = 60) | Hp Corpus (+) (n = 30) | p-Value | Sig. Diff. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRP | 7.0 (4.0–11.0) | 9.0 (5.0–12.0) | 6.5 (3.0–12.0) | 0.386 | — |
| DCI | 708.0 (360.0–1179.0) | 640.0 (342.0–886.0) | 599.0 (395.0–926.0) | 0.603 | — |
| CFV | 4.6 (3.6–5.8) a | 4.0 (3.0–4.5) b | 4.4 (3.8–5.5) c | 0.002 | a vs. b: p = 0.002 b vs. c: p = 0.052 a vs. c: p = 1.000 |
| PB | 2.0 (0.6–4.0) | 1.7 (0.5–3.6) | 1.9 (0.7–4.7) | 0.584 | — |
| DL | 7.0 ± 1.00 | 7.2 ± 0.82 | 7.0 ± 1.22 | 0.353 | — |
| LES p. | 18.4 ± 10.3 | 20.0 ± 7.8 | 20.0 ± 9.9 | 0.839 | — |
| Normal Motility | 82 (67) | 41 (70) | 21 (70) | 0.931 | — |
| IEM | 40 (33) | 18 (30) | 9 (30) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eroğlu Haktanır, A.; Çelebi, A. Effects of Intragastric Helicobacter pylori Distribution on Clinical Presentation, Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Esophageal Manometry, and pH–Impedance Metrics. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196818
Eroğlu Haktanır A, Çelebi A. Effects of Intragastric Helicobacter pylori Distribution on Clinical Presentation, Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Esophageal Manometry, and pH–Impedance Metrics. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196818
Chicago/Turabian StyleEroğlu Haktanır, Ayça, and Altay Çelebi. 2025. "Effects of Intragastric Helicobacter pylori Distribution on Clinical Presentation, Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Esophageal Manometry, and pH–Impedance Metrics" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196818
APA StyleEroğlu Haktanır, A., & Çelebi, A. (2025). Effects of Intragastric Helicobacter pylori Distribution on Clinical Presentation, Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Esophageal Manometry, and pH–Impedance Metrics. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196818






