Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
- Adults (≥18 years of age)
- Patients with a CIED who present with signs or symptoms suggestive of endocarditis (e.g., fever, chills, new heart murmur, pocket infection, or evidence of infection on imaging) and who have been diagnosed with a definite CIED-RIE.
- Patients with active infective endocarditis unrelated to a CIED (e.g., native valve endocarditis, prosthetic valve endocarditis) or those with leadless and subcutaneous pacemakers.
- Patients were initially diagnosed according to the diagnostic criteria applied at the respective time and center. All cases were subsequently reassessed using the current diagnostic criteria (2023 ESC and 2023 Duke-ISCVID), and those not fulfilling these definitions were excluded.
2.2. Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Definitions
- Persistent bacteremia is defined as continued positive blood cultures for ≥7 days despite initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy [4].
- Heart failure is defined as Ventricular ejection fraction < 50%. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553115/, accessed on 22 June 2025.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Data
3.1.1. Complications of IE
3.1.2. Microbiological Data
3.1.3. Antimicrobial Therapy
3.1.4. Surgical Procedures
3.1.5. Outcomes
3.2. Statistical Results
3.2.1. Univariate Analyses
3.2.2. Multivariate Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Outcome
4.1.1. Comorbidity
4.1.2. Cardiac Involved and Embolic Events
4.1.3. Surgery
4.1.4. The Timing of Infection and Microbiology
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIEDs | Cardiac implantable electronic devices |
| PPMs | Permanent pacemakers |
| ICDs | Implantable cardioverter–defibrillators |
| CRT | Cardiac resynchronization therapy |
| CIED-RIE | Cardiac implantable electronic device-related infective endocarditis |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| ISCVID | International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases |
| ID-IRI | Infectious Diseases—International Research Initiative |
| CCI | Charlson comorbidity index |
| FDG-PET | Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| TLE | Transvenous lead extraction |
| TTE | Transthoracic echocardiography |
| TEE | Transesophageal echocardiography |
| MR | Magnetic resonance |
| PET-CT | Positron emission tomography-computerize tomography |
| MSSA | Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MRCoNS | Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. |
| IQR | interquartile range |
References
- Blomströ M-Lundqvist, C.; Traykov, V.; Erba, P.A.; Burri, H.; Nielsen, J.C.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Poole, J.; Boriani, G.; Costa, R.; Deharo, J.-C.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) international consensus document on how to prevent, diagnose, and treat cardiac implantable electronic device infections-endorsed of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Europace 2020, 22, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, V.G.; Durack, D.T.; Selton-Suty, C.; Athan, E.; Bayer, A.S.; Chamis, A.L.; Dahl, A.; DiBernardo, L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Duval, X.; et al. The 2023 Duke-International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases Criteria for Infective Endocarditis: Updating the Modified Duke Criteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławiński, G.; Kempa, M.; Przybylski, A. Prevention of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections: A Review. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; De Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Hear. J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, R.; Ravikumar, N.; Sarodaya, V.; Haq, M.; Sherif, M.; Harky, A. Outcomes in cardiac implantable electronic device-related infective endocarditis: A systematic review of current literature. Futur. Cardiol. 2022, 18, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.; Krahn, A.D.; Andrade, J.G.; Chakrabarti, S.; Thompson, C.R.; Harris, D.J.; Forman, J.M.; Karim, S.S.; Sterns, L.D.; Fedoruk, L.M.; et al. Treatment and Prevention of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Infections. CJC Open 2022, 4, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacheć, W.; Polewczyk, A.; Nowosielecka, D.; Kutarski, A. Clinical profile and outcomes among patients with cardiac implantable electronic device presenting as isolated pocket infection, pocket-related infective endocarditis, or lead-related infective endocarditis. Europace 2025, 27, euaf053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaloo, P.; Uzomah, U.A.; Shaqdan, A.; Ledesma, P.A.; Galvin, J.; Ptaszek, L.M.; Ruskin, J.N. Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized With Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device– Related Infective Endocarditis, Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis, and Native Valve Endocarditis: A Nationwide Study, 2003 to 2017. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2022, 11, e025600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Polewczyk, M.; Nowosielecka, D.; Brzozowski, W.; Kutarski, A. Outcomes in patients with definite and possible infective endocarditis related to a cardiac implantable electronic device. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2024, 134, 16775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hasan, M.N.; Lahr, B.D.; Eckel-Passow, J.E.; Baddour, L.M. Predictive scoring model of mortality in Gram-negative bloodstream infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Martínez, A.; Domínguez, F.; Muñoz, P.; Marín, M.; Pedraz, Á.; Fariñas, M.C.; Tascón, V.; de Alarcón, A.; Rodríguez-García, R.; Miró, J.M.; et al. Clinical presentation, microbiology, and prognostic factors of prosthetic valve endocarditis. Lessons learned from a large prospective registry. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athan, E.; Chu, V.H.; Tattevin, P.; Selton-Suty, C.; Jones, P.; Naber, C.; Miró, J.M.; Ninot, S.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of infective endocarditis involving implantable cardiac devices. JAMA 2012, 307, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitán, R.M.; Boix-Palop, L.; García, P.M.; Mestres, C.A.; Arriaza, M.M.; Prieto, Á.P.; Gonzalez, A.d.A.; Carretero, E.G.; Meneses, M.H.; Sánchez, M.Á.G.; et al. Infective endocarditis in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices: A nationwide study. Europace 2020, 22, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Tate, J.; Dresen, W.F.; Papa, F.C.; Bloch, K.C.; Kalams, S.A.; Ellis, C.R.; Baker, M.T.; Lenihan, D.J.; Mendes, L.A. Cardiac implanted electronic device-related infective endocarditis: Clinical features, management, and outcomes of 80 consecutive patients. PACE—Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2014, 37, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarakji, K.G.; Chan, E.J.; Cantillon, D.J.; Doonan, A.L.; Hu, T.; Schmitt, S.; Fraser, T.G.; Kim, A.; Gordon, S.M.; Wilkoff, B.L. Cardiac implantable electronic device infections: Presentation, management, and patient outcomes. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, R.; Toschi, A.; Aslan, A.T.; Massaro, G.; Maccaro, A.; Fabbricatore, D.; Dell’AQuila, A.; Ripa, M.; Işık, M.E.; Kızmaz, Y.U.; et al. Risk factors for Gram-negative bacterial infection of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices: Multicentre observational study (CarDINe Study). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 61, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejczyk-Patej, E.; Mazurek, M.; Kowalski, O.; Sokal, A.; Adamczyk, K.; Morawski, S.; Szulik, M.; Podolecki, T.; Sawicka, M.; Kalarus, Z.; et al. Outcomes in patients undergoing cardiac resynchronisation therapy complicated by device-related infective endocarditis. Kardiol. Pol. 2018, 76, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armiñanzas, C.; Fariñas-Alvarez, C.; Zarauza, J.; Muñoz, P.; González Ramallo, V.; Martínez Sellés, M.; Meda, J.M.M.; Pericás, J.M.; Goenaga, M.Á.; Burgos, G.O.; et al. Role of age and comorbidities in mortality of patients with infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 64, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Ursi, M.P.; Andini, R.; Mattucci, I.; Della Ratta, E.E.; Iossa, D.; Bertolino, L.; De Vivo, S.; Manduca, S.; Torella, M.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Infective Endocarditis Involving Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Impact of Comorbidities and Lead Extraction. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbar, T.; Patel, R.; Thomas, G.; Cheung, J. Strategies to Prevent Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infection. J. Innov. Card. Rhythm. Manag. 2020, 11, 3949–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezon, G.; Pulido, P.; Díaz, J.L.; De Miguel-Álava, M.; Vilacosta, I.; García-Azorin, D.; Lozano, A.; Oña, A.; Arenillas, J.F.; Román, J.-A.S. Embolic Events in Infective Endocarditis: A Comprehensive Review. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galzerano, D.; Pergola, V.; Kinsara, A.J.; Vriz, O.; Elmahi, I.; Al Sergani, A.; Khaliel, F.; Cittadini, A.; Di Giannuario, G.; Colonna, P. Right-sided infective endocarditis and pulmonary embolism: A multicenter study. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2022, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldonazo, T.; Fischer, J.; Spagnolo, A.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Kirov, H.; Tasoudis, P.; Treml, R.E.; Vervoort, D.; Sá, M.P.; Doenst, T.; et al. Outcomes of complete removal versus conservative therapy in cardiac implantable electronic device infections—A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 411, 132264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawon, M.S.R.; Yu, J.; Gomes, S.; Ooi, S.Y.; Jorm, L. Real-World Evidence on Lead Extraction Following Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Infections and Its Association With 1-year Mortality. Am. J. Cardiol. 2025, 251, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, C.; Elchouemi, M.; Helmy, R.; Spinetta, L.; La Fazia, V.M.; Pierucci, N.; Asfour, I.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Mohanty, S.; Bassiouny, M.A.; et al. Safety and feasibility of same-day discharge following uncomplicated transvenous lead extraction. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 35, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Foresti, S.; De Ambroggi, G.; Cappato, R.; Lupo, P. Practical Considerations for Cardiac Electronic Devices Reimplantation Following Transvenous Lead Extraction Due to Related Endocarditis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donal, E.; Tribouilloy, C.; Sadeghpour, A.; Laroche, C.; Rodrigues, A.C.T.; do Carmo Pereira Nunes, M.; Kang, D.-H.; Hernadez-Meneses, M.; Kobalava, Z.; De Bonis, M.; et al. Cardiac device-related infective endocarditis need for lead extraction whatever the device according to the ESC EORP EURO-ENDO registry. Eur. Hear. J. Open 2023, 3, oead064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandler, A.G.; Sciria, C.T.; Kogan, E.V.; Kim, I.; Yeo, I.; Simon, M.S.; Kim, L.K.; E Ip, J.; Liu, C.F.; Markowitz, S.M.; et al. Impact of hospital lead extraction volume on management of cardiac implantable electronic device-associated infective endocarditis. Europace 2024, 27, euae308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Meneses, M.; Llopis, J.; Sandoval, E.; Ninot, S.; Almela, M.; Falces, C.; Pericàs, J.M.; Vidal, B.; Perissinotti, A.; Marco, F.; et al. Forty-Year Trends in Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infective Endocarditis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Polewczyk, M.; Szczęśniak-Stańczyk, D.; Kutarski, A. Early, Delayed and Late Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections: Do the Timing of Onset and Pathogens Matter? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latal, J.; Pazdernik, M.; Holicka, M.; Pelouch, R.; Widimsky, J.; Pudich, J.; Vancata, R.; Siranec, M.; Blechova, K.; Butta, T.; et al. Cardiac device-related infective endocarditis in the Czech Republic: Prospective data from the ESC EORP EURO-ENDO registry. Biomed. Pap. 2022, 166, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterovics, N.; Nesterovics, G.; Stradins, P.; Kalejs, M.; Ansabergs, J.; Blumbergs, M.; Maca, A.; Kamzola, G.; Lejnieks, A.; Kalejs, O.; et al. Lead-related infective endocarditis in latvia: A single centre experience. Medicina 2019, 55, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polewczyk, A.; Janion, M.; Podlaski, R.; Kutarski, A. Clinical manifestations of lead-dependent infective endocarditis: Analysis of 414 cases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All, n = 197 | 90-Day Mortality | Univariable HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survived, n = 159 | Died, n = 38 | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 49 (24.9%) | 39 (79.6%) | 10 (20.4%) | Ref. |
| Male | 148 (75.1%) | 120 (81.1%) | 28 (18.9%) | 0.94 [0.46; 1.94] |
| Age, mean ± SD | 65.3 ± 14.4 | 65.0 ± 15.1 | 66.6 ± 11.0 | 1.01 [0.99; 1.03] |
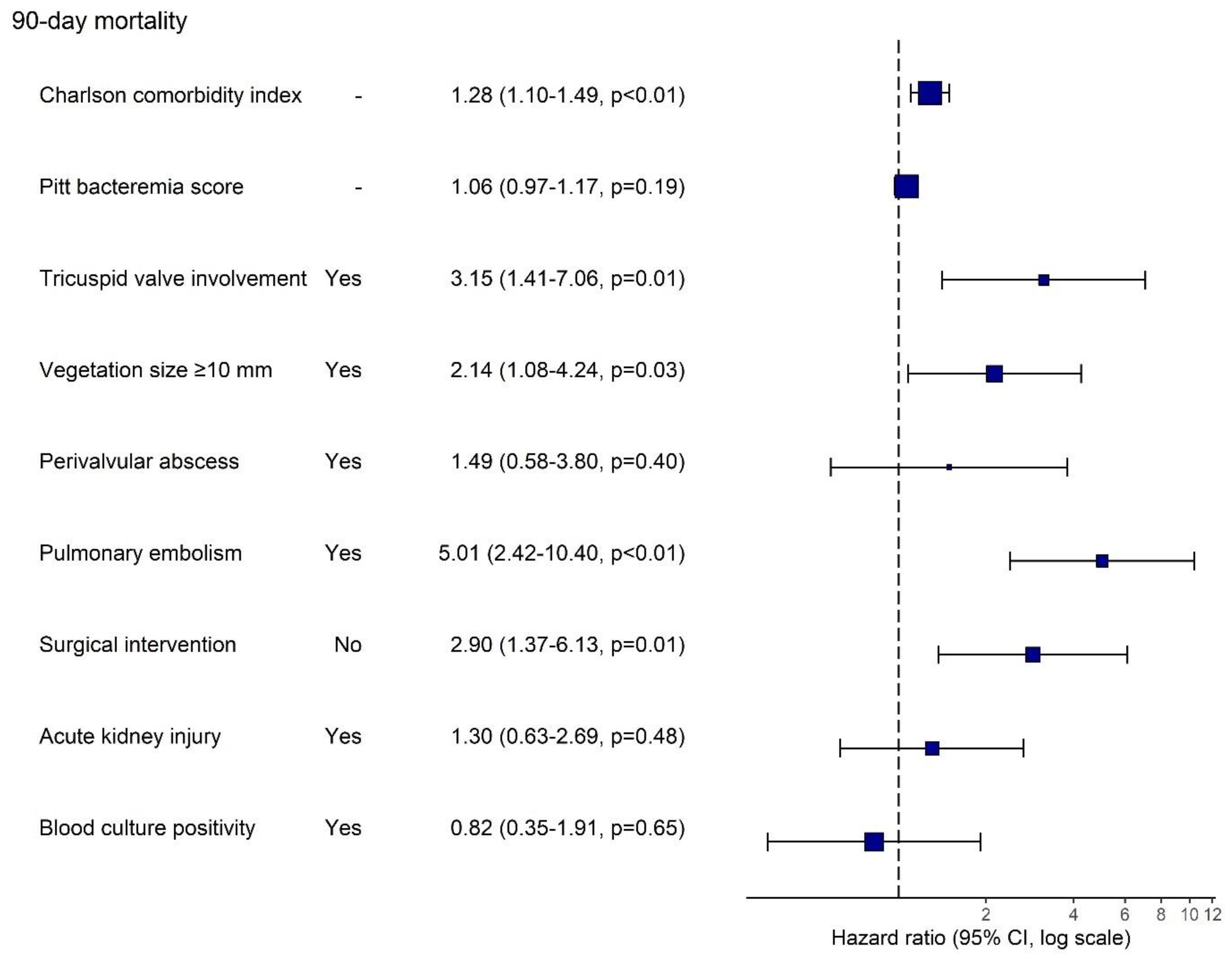
| Charlson comorbidity index, median (25–75%) | 4.00 [2.00; 5.00] | 4.00 [2.00; 5.00] | 5.00 [3.25; 6.00] | 1.25 [1.10; 1.42] * |
| Pitt bacteremia score, n = 184, median (25–75%) | 1.00 [0.00; 5.00] | 1.00 [0.00; 4.25] | 3.00 [1.00; 7.00] | 1.15 [1.05; 1.26] * |
| Type of cardiac implantable device | ||||
| CRT | 34 (17.3%) | 29 (85.2%) | 5 (14.7%) | Ref. |
| ICD | 68 (34.5%) | 51 (75.0%) | 17 (25.0%) | 1.86 [0.69; 5.04] |
| PPM | 95 (48.2%) | 79 (83.2%) | 16 (16.8%) | 1.24 [0.46; 3.40] |
| Timing of IE according to implantation of CIED | ||||
| Early onset (<1 year) | 94 (47.7%) | 73 (77.7%) | 21 (22.3%) | Ref. |
| Late onset (>1 year) | 103 (52.3%) | 86 (83.5%) | 17 (16.5%) | 0.72 [0.38; 1.37] |
| Pocket infection history | ||||
| No | 158 (80.2%) | 126 (79.7%) | 32 (20.3%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 39 (19.8%) | 33 (84.6%) | 6 (15.4%) | 0.70 [0.29; 1.67] |
| Current pocket infection | ||||
| No | 96 (48.7%) | 68 (70.8%) | 28 (29.2%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 101 (51.3%) | 91 (90.1%) | 10 (9.90%) | 0.30 [0.14; 0.61] * |
| History of CIED-related IE | ||||
| No | 183 (92.9%) | 147 (80.3%) | 36 (19.7%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 14 (7.11%) | 12 (85.7%) | 2 (14.3%) | 0.70 [0.17; 2.89] |
| All, n = 197 | 90-Day Mortality | HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survived, n = 159 | Died, n = 38 | |||
| Pacemaker leads involvement | ||||
| No | 63 (32.0%) | 47 (74.6%) | 16 (25.4%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 134 (68.0%) | 112 (83.6%) | 22 (16.4%) | 0.64 [0.34; 1.22] |
| Tricuspid valve involvement | ||||
| No | 168 (85.3%) | 140 (83.3%) | 28 (16.7%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 29 (14.7%) | 19 (65.5%) | 10 (34.5%) | 2.39 [1.16; 4.92] * |
| Pulmonary valve involvement | ||||
| No | 194 (98.5%) | 156 (80.4%) | 38 (19.6%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 3 (1.52%) | 3 (100%) | 0 (0.00%) | - |
| Right atrium involvement | ||||
| No | 163 (82.7%) | 132 (81.0%) | 31 (19.0%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 34 (17.3%) | 27 (79.4%) | 7 (20.6%) | 1.03 [0.45; 2.33] |
| Right ventricle involvement | ||||
| No | 178 (90.4%) | 144 (80.9%) | 34 (19.1%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 19 (9.64%) | 15 (78.9%) | 4 (21.1%) | 1.15 [0.41; 3.23] |
| Vegetation size ≥ 10 mm, n = 191 | ||||
| No | 112 (58.6%) | 97 (86.6%) | 15 (13.4%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 79 (41.4%) | 56 (70.9%) | 23 (29.1%) | 2.40 [1.25; 4.59] * |
| Multiple vegetations, n = 187 | ||||
| No | 134 (71.7%) | 106 (79.1%) | 28 (20.9%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 53 (28.3%) | 44 (83.0%) | 9 (17.0%) | 0.79 [0.38; 1.68] |
| Mobile vegetation, n = 184 | ||||
| No | 118 (64.1%) | 95 (80.5%) | 23 (19.5%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 66 (35.9%) | 54 (81.8%) | 12 (18.2%) | 0.92 [0.46; 1.86] |
| Heart failure with EF < 50% | ||||
| No | 114 (57.9%) | 95 (83.3%) | 19 (16.7%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 83 (42.1%) | 64 (77.1%) | 19 (22.9%) | 1.43 [0.76; 2.70] |
| Valvular perforation/rupture | ||||
| No | 183 (92.9%) | 148 (80.9%) | 35 (19.1%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 14 (7.11%) | 11 (78.6%) | 3 (21.4%) | 1.15 [0.35; 3.75] |
| Perivalvular abscess | ||||
| No | 184 (93.4%) | 152 (82.6%) | 32 (17.4%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 13 (6.60%) | 7 (53.8%) | 6 (46.2%) | 3.05 [1.28; 7.31] * |
| Intracardiac fistula | ||||
| No | 190 (96.4%) | 155 (81.6%) | 35 (18.4%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 7 (3.55%) | 4 (57.1%) | 3 (42.9%) | 2.31 [0.71; 7.52] |
| Pulmonary embolism | ||||
| No | 158 (80.2%) | 138 (87.3%) | 20 (12.7%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 39 (19.8%) | 21 (53.8%) | 18 (46.2%) | 4.47 [2.36; 8.46] * |
| Acute kidney injury | ||||
| No | 145 (73.6%) | 125 (86.2%) | 20 (13.8%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 52 (26.4%) | 34 (65.4%) | 18 (34.6%) | 3.02 [1.60; 5.72] * |
| Surgical intervention | ||||
| No | 64 (32.5%) | 44 (68.8%) | 20 (31.2%) | 2.79 [1.48; 5.28] * |
| Yes | 133 (67.5%) | 115 (86.5%) | 18 (13.5%) | Ref. |
| All, n = 197 | 90-Day Mortality | HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survived, n = 159 | Died, n = 38 | |||
| Any culture positivity | ||||
| None | 32 (16.2%) | 27 (84.4%) | 5 (15.6%) | Ref. |
| Monomicrobial | 156 (79.2%) | 127 (81.4%) | 29 (18.6%) | 1.21 [0.47; 3.13] |
| Polimicrobial | 9 (4.57%) | 5 (55.6%) | 4 (44.4%) | 3.76 [1.01; 14.0] |
| MRSA growth | ||||
| No | 162 (82.2%) | 134 (82.7%) | 28 (17.3%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 35 (17.8%) | 25 (71.4%) | 10 (28.6%) | 1.83 [0.89; 3.78] |
| MRCoNS growth | ||||
| No | 183 (92.9%) | 146 (79.8%) | 37 (20.2%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 14 (7.11%) | 13 (92.9%) | 1 (7.14%) | 0.34 [0.05; 2.47] |
| Gram-negative organism growth | ||||
| No | 179 (90.9%) | 146 (81.6%) | 33 (18.4%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 18 (9.14%) | 13 (72.2%) | 5 (27.8%) | 1.68 [0.66; 4.31] |
| Blood culture positivity | ||||
| No | 80 (40.6%) | 71 (88.8%) | 9 (11.2%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 117 (59.4%) | 88 (75.2%) | 29 (24.8%) | 2.42 [1.14; 5.11] * |
| Pocket culture positivity | ||||
| No | 126 (64.0%) | 96 (76.2%) | 30 (23.8%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 71 (36.0%) | 63 (88.7%) | 8 (11.3%) | 0.43 [0.20; 0.93] * |
| Lead/vegetation culture positivity | ||||
| No | 149 (75.6%) | 116 (77.9%) | 33 (22.1%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 48 (24.4%) | 43 (89.6%) | 5 (10.4%) | 0.43 [0.17; 1.11] |
| Persistent bacteremia, n = 155 | ||||
| No | 121 (78.1%) | 102 (84.3%) | 19 (15.7%) | Ref. |
| Yes | 34 (21.9%) | 21 (61.8%) | 13 (38.2%) | 2.90 [1.43; 5.89] * |
| RME (Days) ± SE | Log-Rank p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
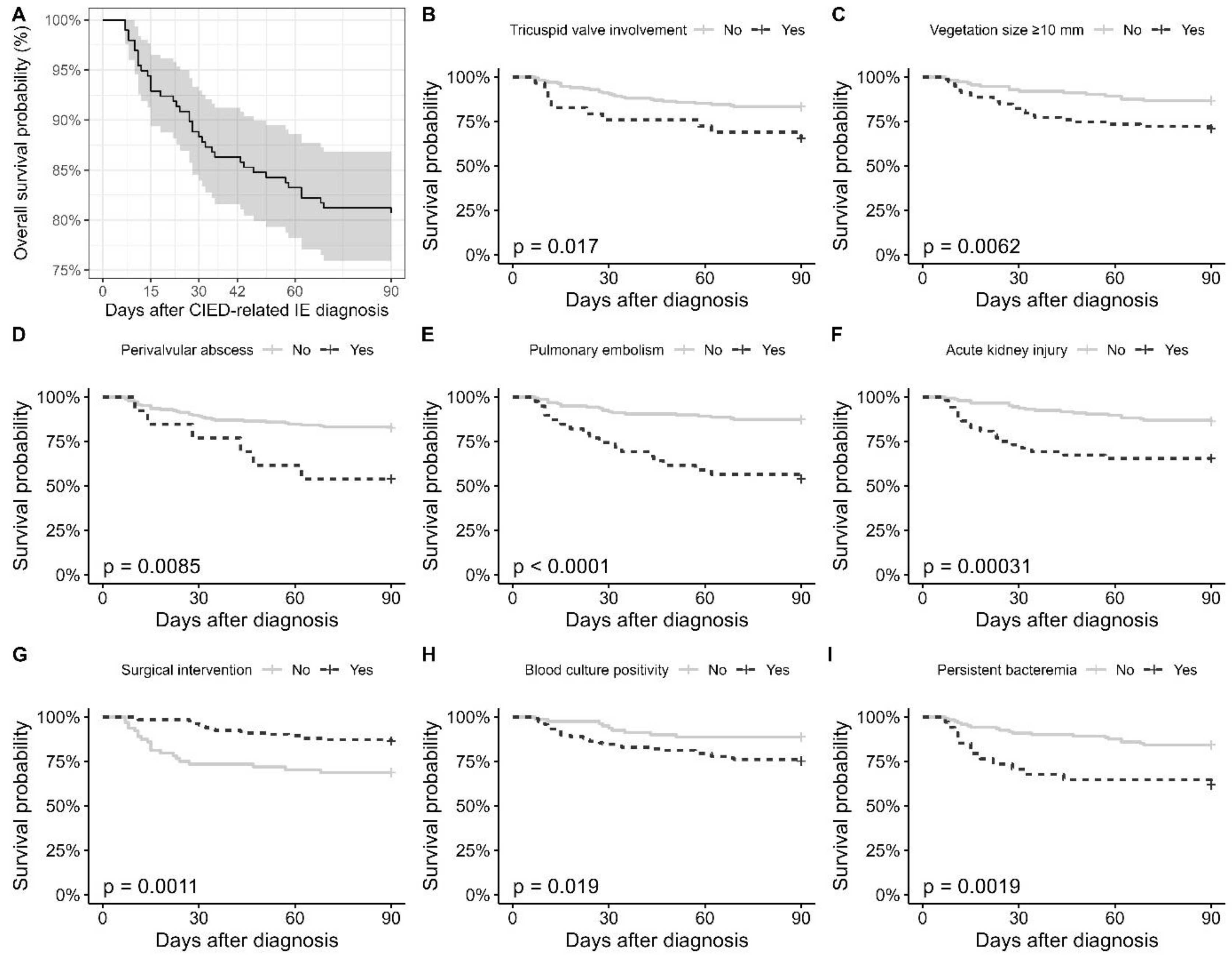
| Tricuspid valve involvement | No | 80.8 ± 2.3 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 51.4 ± 6.7 | ||
| Vegetation size ≥ 10 mm | No | 82.3 ± 2.2 | 0.002 |
| Yes | 67.6 ± 4.2 | ||
| Perivalvular abscess | No | 78.7 ± 2.3 | 0.035 |
| Yes | 61.4 ± 6.4 | ||
| Pulmonary embolism | No | 80.4 ± 2.4 | 0.002 |
| Yes | 61.2 ± 4.9 | ||
| Acute kidney injury | No | 81.9 ± 2.3 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 58.4 ± 4.8 | ||
| Surgical intervention | No | 68.4 ± 4.2 | 0.001 |
| Yes | 83.4 ± 1.6 | ||
| Blood culture positivity | No | 85.8 ± 2.4 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 62.2 ± 3.0 | ||
| Persistent bacteremia | No | 78.9 ± 2.5 | 0.002 |
| Yes | 59.1 ± 4.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydin, S.; Mert, A.; Emecen, A.N.; Szabo, B.G.; Aksoy, F.; Akyildiz, O.; Alkan, S.; Cascio, A.; Sipahi, O.R.; Lakatos, B.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196816
Aydin S, Mert A, Emecen AN, Szabo BG, Aksoy F, Akyildiz O, Alkan S, Cascio A, Sipahi OR, Lakatos B, et al. Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196816
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydin, Selda, Ali Mert, Ahmet Naci Emecen, Balint Gergely Szabo, Firdevs Aksoy, Ozay Akyildiz, Sevil Alkan, Antonio Cascio, Oğuz Reşat Sipahi, Botond Lakatos, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196816
APA StyleAydin, S., Mert, A., Emecen, A. N., Szabo, B. G., Aksoy, F., Akyildiz, O., Alkan, S., Cascio, A., Sipahi, O. R., Lakatos, B., Geçit, M. H., Bilgin, M. E., Arslan, Ş., Yıldız, M., Bulat, Z., Gökçe, M. E., Katkat, F., Okay, G., Acet, O., ... Erdem, H. (2025). Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196816







