From Prognostic Marker to Therapeutic Agent: The Role of Nitric Oxide in Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Nitric Oxide Signaling and Nitrosative Stress in Respiratory Pathophysiology
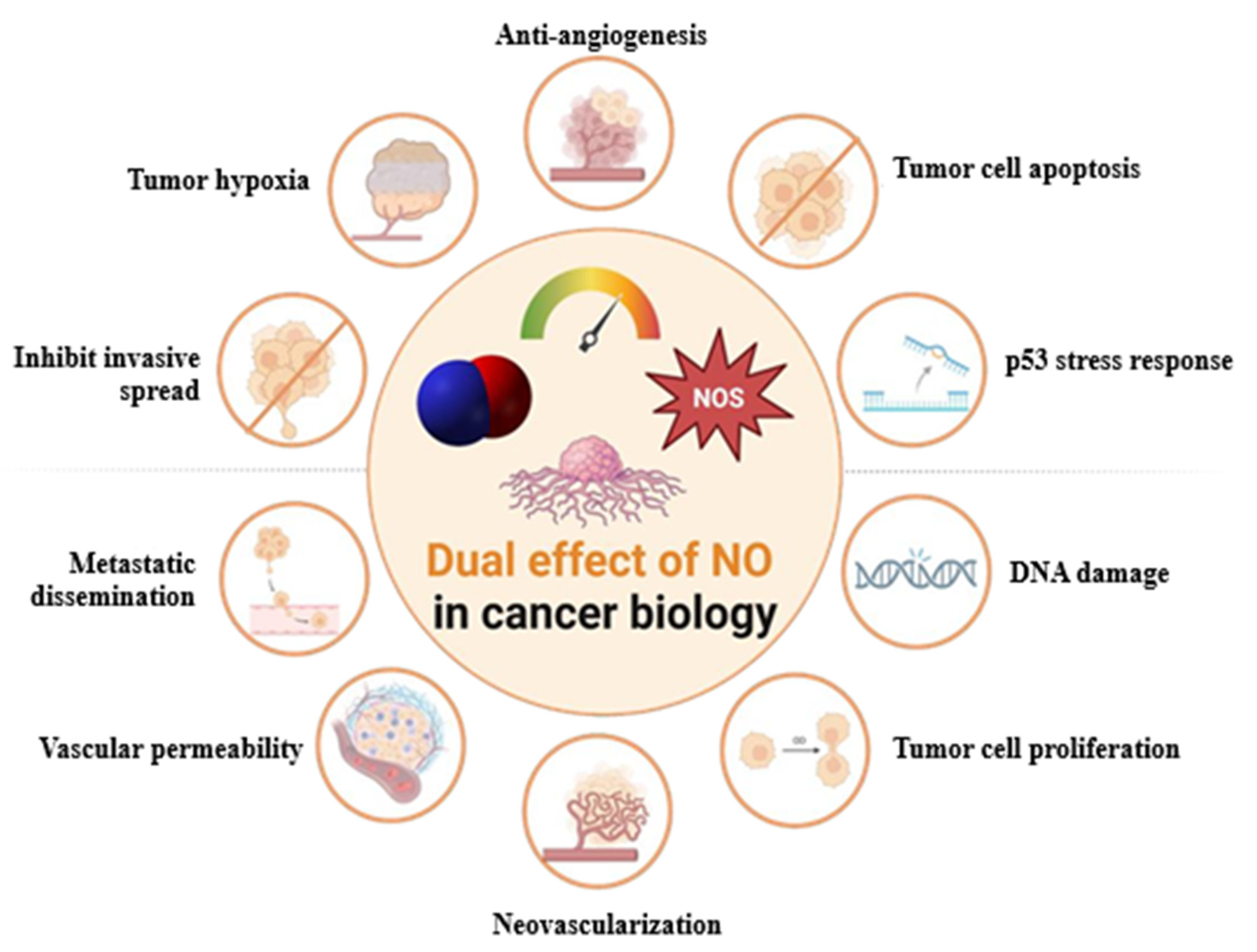
1.2. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Lung Cancer: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Potential, and Challenges
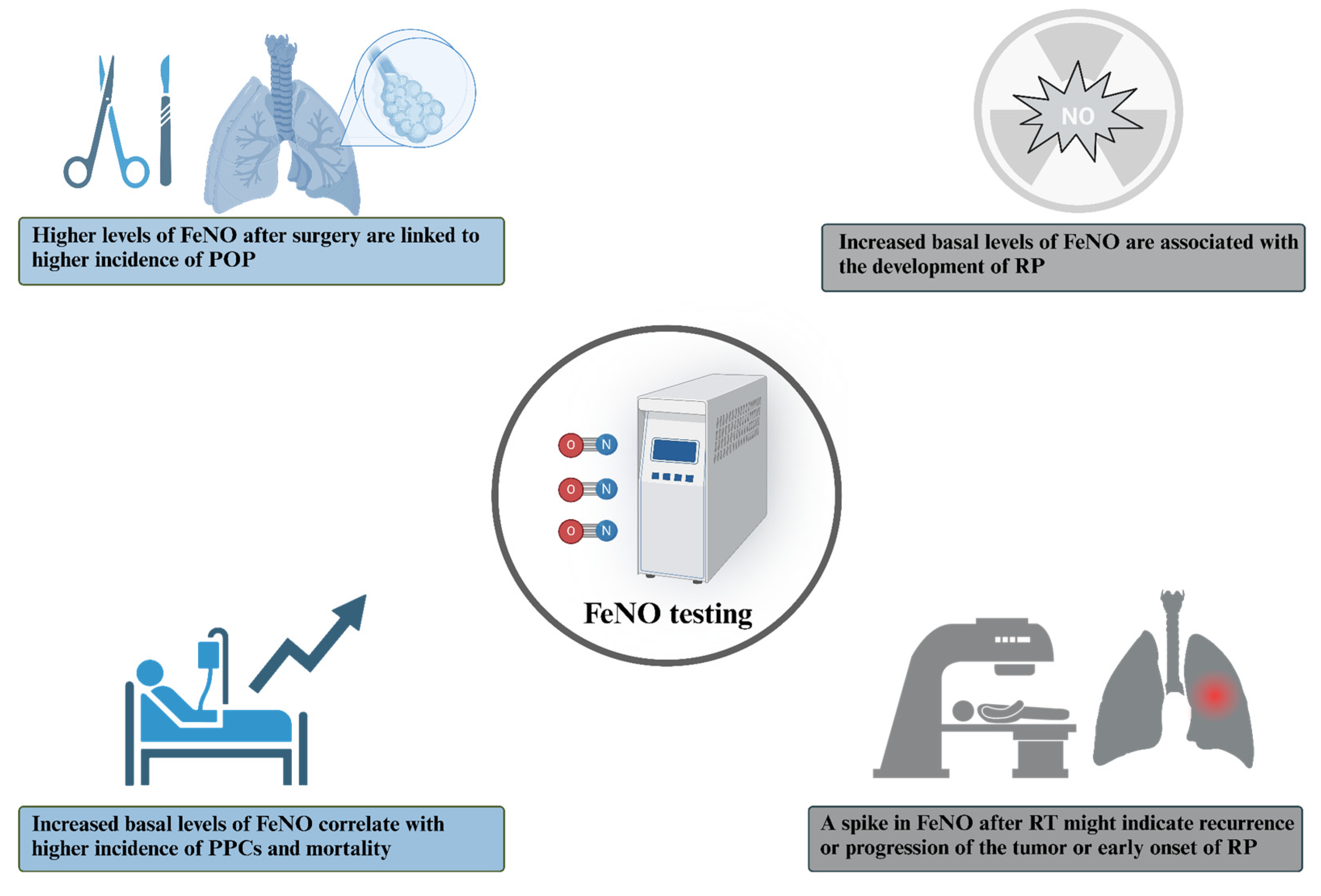
2. FeNO as a Biomarker of Treatment Response
2.1. Surgery
2.2. Radiotherapy
2.3. Chemotherapy
2.4. Immune Checkpoint-Inhibitors
2.5. Limitations and Confounding Factors
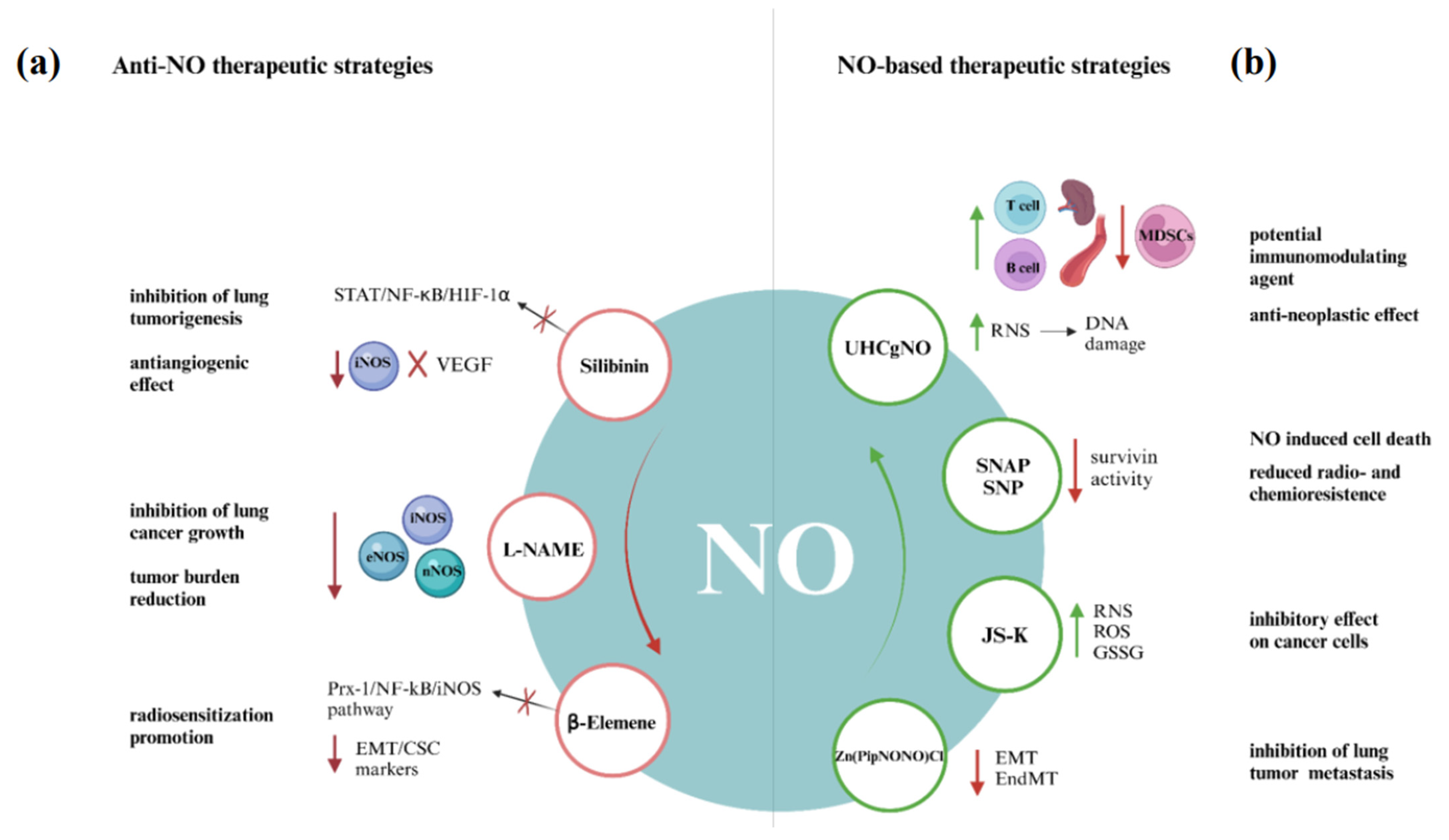
3. NO-Centered Therapeutic Approaches in Lung Cancer
3.1. Anti-NO Therapeutic Strategies
3.2. NO-Based Therapeutic Strategies
4. Future Directions and Conclusion Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Antigen-presenting cell |
| CHT | Chemotherapy |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DDS | Drug delivery system |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| FeNO | Fractional exhaled nitric oxide |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GSSG | Glutathione disulfide |
| L-NAME | NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| NSCLC | Non small cell lung cancer |
| POP | Postoperative pneumonia |
| PTX | Paclitaxel |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RP | Radiation pneumonitis |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| SNAP | S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penicillamine |
| SNP | Sodium nitroprusside |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| UHCgNO | Ultra-high concentration gaseous NO |
References
- Andrabi, S.M.; Sharma, N.S.; Karan, A.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Cordon, B.; Ma, B.; Xie, J. Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.A.; Do, H.T.; Miley, G.P.; Silverman, R.B. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase: Regulation, Structure, and Inhibition. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 158–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, D.; Kashiwagi, S.; Jain, R.K. The Role of Nitric Oxide in Tumour Progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, P.K.; Orucevic, A. Role of Nitric Oxide in Tumor Progression: Lessons from Experimental Tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998, 17, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, A.J.; Sullivan, F.J.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. The Yin and Yang of Nitric Oxide in Cancer Progression. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridnour, L.A.; Thomas, D.D.; Donzelli, S.; Espey, M.G.; Roberts, D.D.; Wink, D.A.; Isenberg, J.S. The Biphasic Nature of Nitric Oxide Responses in Tumor Biology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.P. Environment and Cancer: Who Are Susceptible? Science 1997, 278, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, J.; Shiraishi, K.; Kohno, T. Genetic Basis for Susceptibility to Lung Cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 109, pp. 51–72. ISBN 978-0-12-380890-5. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, E.A.; Sikora, A.G.; Ekmekcioglu, S. Molecular Pathways: Inflammation-Associated Nitric-Oxide Production as a Cancer-Supporting Redox Mechanism and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5557–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.W.; Cummings, K.M. Tobacco and Lung Cancer: Risks, Trends, and Outcomes in Patients with Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2013, 33, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, W.A.; Stone, K. Oxidants in Cigarette Smoke Radicals, Hydrogen Peroxide, Peroxynitrate, and Peroxynitritea. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 686, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zi, Y.; Yu, H.; Lan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ren, C.; Liao, K.; Chen, H. Cigarette Smoke Induces the ROS Accumulation and iNOS Activation through Deactivation of Nrf-2/SIRT3 Axis to Mediate the Human Bronchial Epithelium Ferroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 200, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimian Rizi, B.; Achreja, A.; Nagrath, D. Nitric Oxide: The Forgotten Child of Tumor Metabolism. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimoradi, H.; Greish, K.; Gamble, A.B.; Giles, G.I. Controlled Delivery of Nitric Oxide for Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellary, A.; Nowak, C.; Iwanicki, I.; Flores-Guzman, F.; Wu, L.; Kandel, J.J.; Laetsch, T.W.; Bleris, L.; Hernandez, S.L.; Sirsi, S.R. Non-Viral Nitric Oxide-Based Gene Therapy Improves Perfusion and Liposomal Doxorubicin Sonopermeation in Neuroblastoma Models. Theranostics 2023, 13, 3402–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Higashiyama, M.; Kuriyama, K.; Sasaki, A.; Mukai, M.; Shinkai, K.; Horai, T.; Matsuda, H.; Akedo, H. NG-Nitro-L-arginine Methyl Ester Inhibits Bone Metastasis after Modified Intracardiac Injection of Human Breast Cancer Cells in a Nude Mouse Model. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1997, 88, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavida, B.; Baritaki, S.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Vega, M.I.; Jazirehi, A.R.; Berenson, J. Nitric Oxide Donors Are a New Class of Anti-Cancer Therapeutics for the Reversal of Resistance and Inhibition of Metastasis. In Nitric Oxide (NO) and Cancer; Bonavida, B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 459–477. ISBN 978-1-4419-1431-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mocellin, S.; Bronte, V.; Nitti, D. Nitric Oxide, a Double Edged Sword in Cancer Biology: Searching for Therapeutic Opportunities. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Mansur, A.H.; Brightling, C.E. Clinical Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Severe Asthma Management. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pianigiani, T.; Alderighi, L.; Meocci, M.; Messina, M.; Perea, B.; Luzzi, S.; Bergantini, L.; D’Alessandro, M.; Refini, R.M.; Bargagli, E.; et al. Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, P.; Bargagli, E.; Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Pieroni, M.; Fontana, G.A.; Sestini, P.; Refini, R.M. Extended Exhaled Nitric Oxide Analysis in Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yin, D.; Wang, S.; Huang, K. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Is Associated with the Severity of Stable COPD. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 17, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.M.; Ridnour, L.A.; McGinity, C.L.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Wink, D.A. Nitric Oxide and Cancer: When to Give and When to Take Away? Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 15941–15947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, J.; Vedenko, A.; Rosete, O.; Shah, K.; Goldstein, G.; Hare, J.M.; Ramasamy, R.; Arora, H. Current Advances of Nitric Oxide in Cancer and Anticancer Therapeutics. Vaccines 2021, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.H.; Dervan, E.; Bhattacharyya, D.D.; McAuliffe, J.D.; Miranda, K.M.; Glynn, S.A. The Role of Nitric Oxide in Cancer: Master Regulator or NOt? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Łukasiewicz, H.; Samulak, D.; Piekarska, E.; Kołaciński, R.; Romanowicz, H. Lung Cancer—Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Treatment and Molecular Aspect (Review of Literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Su, L.; Tang, X. The Regulation of Nitric Oxide in Tumor Progression and Therapy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520905985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebe, S.; Leigh, J.; Henderson, D.W.; Nurminen, M. Asbestos, Smoking and Lung Cancer: An Update. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 17, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, B.K. Can Nitric Oxide-Based Therapy Be Improved for the Treatment of Cancers? A Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavida, B. Sensitizing Activities of Nitric Oxide Donors for Cancer Resistance to Anticancer Therapeutic Drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 176, 113913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yoon, B.; Dey, A.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Park, J.H. Recent Progress in Nitric Oxide-Generating Nanomedicine for Cancer Therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 352, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ye, S. Nitric Oxide in Occurrence, Progress and Therapy of Lung Cancer: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Xue, T.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z. Comparing the Utility of Lung Function Parameters and Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Predicting Lung Cancer. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2024, 41, e2024065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Hayashi, K.; Kaku, R.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Oshio, Y.; Hanaoka, J. Impact of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide on the Outcomes of Lung Resection Surgery: A Prospective Study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 2663–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Gu, M.-Q.; He, J.-T.; Wang, X. Perioperative Exhaled Nitric Oxide as an Indicator for Postoperative Pneumonia in Surgical Lung Cancer Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on 183 Cases. Can. Respir. J. 2022, 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Yu, G.; Tu, X. Preoperative Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Is a Risk and Predictive Factor of Postoperative Cough for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käsmann, L.; Dietrich, A.; Staab-Weijnitz, C.A.; Manapov, F.; Behr, J.; Rimner, A.; Jeremic, B.; Senan, S.; De Ruysscher, D.; Lauber, K.; et al. Radiation-Induced Lung Toxicity—Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pathogenesis, Management, and Literature Review. Radiat. Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2020, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voruganti Maddali, I.S.; Cunningham, C.; McLeod, L.; Bahig, H.; Chaudhuri, N.; Chua, K.L.M.; Evison, M.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Franks, K.; Harden, S.; et al. Optimal Management of Radiation Pneumonitis: Findings of an International Delphi Consensus Study. Lung Cancer 2024, 192, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.F.; Iocolano, M.; Leeman, J.; Imber, B.S.; Wild, A.T.; Offin, M.; Chaft, J.E.; Huang, J.; Rimner, A.; Wu, A.J.; et al. Clinical and Dosimetric Predictors of Radiation Pneumonitis in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Postoperative Radiation Therapy. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 11, e52–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moré, J.M.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Chung, M.P.; Wynne, J.F.; Shorter, J.H.; Nelson, D.D.; Hanlon, A.L.; Burmeister, R.; Banos, P.; Maxim, P.G.; et al. Feasibility and Potential Utility of Multicomponent Exhaled Breath Analysis for Predicting Development of Radiation Pneumonitis After Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, M.R.; Wazni, M.W.; Martinez, J.; McAleer, M.F.; Guerrero, T. Exhaled Nitric Oxide Predicts Radiation Pneumonitis in Esophageal and Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Thoracic Radiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 101, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, I.; Noel, G.; Jeung, M.-Y.; Meyer, N.; Oswald-Mammosser, M.; Urban-Kraemer, E.; Schumacher, C.; Geny, B.; Quoix, E.; Charloux, A. Can Exhaled NO Fraction Predict Radiotherapy-Induced Lung Toxicity in Lung Cancer Patients? Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szejniuk, W.M.; Nielsen, M.S.; Brønnum, D.; Takács-Szabó, Z.; Weinreich, U.M.; Pilegaard Thomsen, L.; Bøgsted, M.; Jensen, I.; McCulloch, T.; Falkmer, U.G.; et al. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide as a Potential Biomarker for Radiation Pneumonitis in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Pilot Study. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 19, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; Von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus Docetaxel in Patients with Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (OAK): A Phase 3, Open-Label, Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus Docetaxel for Patients with Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (POPLAR): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Hushmandi, K.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Torabi, S.M.R.; Ranjbar, A.; SeyedSaleh, S.; Sharifzadeh, S.O.; Khan, H.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; et al. Elucidating Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Cisplatin Chemotherapy: A Focus on Molecular Pathways and Possible Therapeutic Strategies. Molecules 2021, 26, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.N.; Gupta, A.; Srivastava, S.; Natu, S.M.; Mittal, B.; Negi, M.P.S.; Prasad, R. Cisplatin Combination Chemotherapy Induces Oxidative Stress in Advance Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2010, 11, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wewel, A.R.; Crusius, J.A.M.; Gatzemeier, U.; Heckmayr, M.; Becher, G.; Magnussen, H.; Jörres, R.A.; Holz, O. Time Course of Exhaled Hydrogen Peroxide and Nitric Oxide during Chemotherapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Liu, W.; Pu, J.; Feng, T.; Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Kai, J. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide in checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis: A case report and literature review. Immunotherapy 2022, 14, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Saito, J.; Kubota, S.; Ikeda, M.; Rikimaru, M.; Yamada, R.; Kumanaka, T.; Tanaka, R.; Kazama, K.; Saito, K.; et al. Successful management of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia triggered by immune checkpoint inhibitor: A case report and literature review. Front Immunol. 2025, 22, 1615531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Endo, M.; Komatsu, M.; Ishiguro, Y.; Murata, Y.; Yatera, K. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap in patient with adenocarcinoma. Respirol Case Rep. 2023, 11, e01222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Asada, K.; Shirai, T.; Torii, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Kusafuka, K. Eosinophilic airway inflammation and eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis during nivolumab and ipilimumab. Respirol Case Rep. 2020, 8, e00638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, T.; Huang, D.; Fu, Z.; Ma, S.; Lin, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Construction of a checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonia diagnostic model based on exhaled nitric oxide: A prospective observational study. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025, 14, 1740–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.; Bafadhel, M.; Beasley, R.; Bel, E.H.; Faner, R.; Gibson, P.G.; Louis, R.; McDonald, V.M.; Sterk, P.J.; Thomas, M.; et al. Precision Medicine in Airway Diseases: Moving to Clinical Practice. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, J.F.; Jain, N. Exhaled Nitric Oxide to Predict Corticosteroid Responsiveness and Reduce Asthma Exacerbation Rates. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragnoli, B.; Radaeli, A.; Pochetti, P.; Kette, S.; Morjaria, J.; Malerba, M. Fractional Nitric Oxide Measurement in Exhaled Air (FeNO): Perspectives in the Management of Respiratory Diseases. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2023, 14, 20406223231190480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, S.P.; Linn, W.S.; Berhane, K.; Rappaport, E.B.; Salam, M.T.; Zhang, Y.; Gilliland, F.D. Estimation of Parameters in the Two-Compartment Model for Exhaled Nitric Oxide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtimäki, L.; Turjanmaa, V.; Kankaanranta, H.; Saarelainen, S.; Hahtola, P.; Moilanen, E. Increased Bronchial Nitric Oxide Production in Patients with Asthma Measured with a Novel Method of Different Exhalation Flow Rates. Ann. Med. 2000, 32, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskakis, E.; Vergadi, E.; Chatzimichael, A.; Bush, A. The Role of Flow-Independent Exhaled Nitric Oxide Parameters in the Assessment of Airway Diseases. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Shiratori, T.; Oshio, Y.; Hanaoka, J. Clinicopathological Study of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Dynamics and Intratumoral Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Primary Lung Cancer Patients. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 4694–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdura, S.; Cuyàs, E.; Ruiz-Torres, V.; Micol, V.; Joven, J.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Menendez, J.A. Lung Cancer Management with Silibinin: A Historical and Translational Perspective. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, K.; Dwyer-Nield, L.D.; Serkova, N.J.; Hasebroock, K.M.; Tyagi, A.; Raina, K.; Singh, R.P.; Malkinson, A.M.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Prevents Lung Tumorigenesis in Wild-Type but Not in iNOS−/− Mice: Potential of Real-Time Micro-CT in Lung Cancer Chemoprevention Studies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittezhath, M.; Deep, G.; Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Inhibits Cytokine-Induced Signaling Cascades and down-Regulates Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Human Lung Carcinoma A549 Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershing, N.L.K.; Yang, C.-F.J.; Xu, M.; Counter, C.M. Treatment with the Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor L-NAME Provides a Survival Advantage in a Mouse Model of Kras. Mutation-Positive, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42385–42392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javrushyan, H.; Ginovyan, M.; Harutyunyan, T.; Gevorgyan, S.; Karabekian, Z.; Maloyan, A.; Avtandilyan, N. Elucidating the Impact of Hypericum Alpestre Extract and L-NAME on the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in A549 Lung Adenocarcinoma and MDA-MB-231 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0303736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Yao, C.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Ye, X.-Y.; Bai, R.; Xie, T. Anti-Tumor Drug Discovery Based on Natural Product β-Elemene: Anti-Tumor Mechanisms and Structural Modification. Molecules 2021, 26, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, R.; Deng, W.; Zou, L.; Liu, J. β-Elemene Enhances Radiosensitivity in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Inhibiting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cell Traits via Prx-1/NF-kB/iNOS Signaling Pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 2575–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.; Parveen, S.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Hirad, A.H.; Subarkhan, M.M.; Dhanapal, S.; Kalaiarasi, G. Palladium(II) Complexes Containing Andrographolide Appended N,O Heterocyclic Chelators: Investigation of Anti-Oxidant, Anti-Cancer and Apoptotic Activities. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2025, 265, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, V.; Filippelli, A.; Bacchella, C.; Monzani, E.; Morbidelli, L. The Nitric Oxide Donor [Zn(PipNONO)Cl] Exhibits Antitumor Activity through Inhibition of Epithelial and Endothelial Mesenchymal Transitions. Cancers 2022, 14, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confino, H.; Dirbas, F.M.; Goldshtein, M.; Yarkoni, S.; Kalaora, R.; Hatan, M.; Puyesky, S.; Levi, Y.; Malka, L.; Johnson, M.; et al. Gaseous Nitric Oxide Tumor Ablation Induces an Anti-Tumor Abscopal Effect. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachimatla, A.G.; Fenstermaker, R.; Ciesielski, M.; Yendamuri, S. Survivin in Lung Cancer: A Potential Target for Therapy and Prevention—A Narrative Review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.-I.; Kuo, P.-C.; Hsu, T.-S. Down-Regulation of Survivin in Nitric Oxide-Induced Cell Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis of the Human Lung Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20267–20276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciag, A.E.; Chakrapani, H.; Saavedra, J.E.; Morris, N.L.; Holland, R.J.; Kosak, K.M.; Shami, P.J.; Anderson, L.M.; Keefer, L.K. The Nitric Oxide Prodrug JS-K Is Effective against Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo: Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Shan, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Huang, P.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhang, S. Nitric Oxide-Driven Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Treatment. J. Control. Release 2023, 362, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Asghar, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, S.; Niu, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Y. Recent Advances in Diverse Nanosystems for Nitric Oxide Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 1498–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabie, J.A.; Keefer, L.K. Chemistry of the Nitric Oxide-Releasing Diazeniumdiolate (“Nitrosohydroxylamine”) Functional Group and Its Oxygen-Substituted Derivatives. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; He, Q.; et al. Glucose-Responsive Sequential Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide and Nitric Oxide for Synergistic Cancer Starving-Like/Gas Therapy. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, Q.; Yu, S.; Akhavan, B. Poly Ethylene Glycol (PEG)-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfili, L.; Gong, C.; Lombardi, F.; Cifone, M.G.; Eleuteri, A.M. Strategic Modification of Gut Microbiota through Oral Bacteriotherapy Influences Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α: Therapeutic Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemmerich, D.; Ramajayam, K.K.; Newton, D.A. Review of the Delivery Kinetics of Thermosensitive Liposomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, L.-A.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-S. Heat-Activated Sustaining Nitric Oxide Release from Zwitterionic Diazeniumdiolate Loaded in Thermo-Sensitive Liposomes. Nitric Oxide 2010, 23, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Zhong, X. NIR-Triggered NO Production Combined with Photodynamic Therapy for Tumor Treatment. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2024, 49, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, W.A.; Fahey, M.J.; Korytowski, W. Multiple Means by Which Nitric Oxide Can Antagonize Photodynamic Therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2754–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Anuraga, G.; Chang, C.-P.; Weng, T.-Y.; Hsu, H.-P.; Ta, H.D.K.; Su, P.-F.; Chiu, P.-H.; Yang, S.-J.; Chen, F.-W.; et al. Repurposing Nitric Oxide Donating Drugs in Cancer Therapy through Immune Modulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munaweera, I.; Shi, Y.; Koneru, B.; Patel, A.; Dang, M.H.; Di Pasqua, A.J.; Balkus, K.J. Nitric Oxide- and Cisplatin-Releasing Silica Nanoparticles for Use against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 153, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Molaro, M.C.; Somma, F.; Battisegola, C.; Failla, M.; Lazzarato, L.; Chegaev, K.; Rolando, B.; Kopecka, J.; Ianaro, A.; et al. FS536, a Novel Nitric Oxide-Releasing Doxorubicin Hybrid, Reverts Multidrug Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells. J. Control. Release 2025, 382, 113732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qiu, C.-J.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Huang, R.; Pan, S.-J.; Tan, L. A Polymeric Vesicle System for Combined Lung Cancer Therapy through Chemotherapy and Vasculature Normalization. Biomater. Res. 2024, 28, 0117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, L.; Meng, R.; Yang, R.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Z.; Lyu, Y.; Huang, R.; Xue, F.; et al. Overcoming Radiation-Induced PD-L1 and COX-2 Upregulation by Nitric Oxide Gas Nanogenerator to Sensitize Radiotherapy of Lung Cancer. Biomaterials 2025, 321, 123335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.; et al. Anti-CD24 Antibody–Nitric Oxide Conjugate Selectively and Potently Suppresses Hepatic Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3395–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolli, R. Cardioprotective Function of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Role of Nitric Oxide in Myocardial Ischemia and Preconditioning: An Overview of a Decade of Research. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1897–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isoform | Descriptive Name | Molecular Weight (kD) | Gene Encoding and Position | Tissue | Expression | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOS-1 | neuronal NOS (nNOS) | 155 | NOS1 (12q24.2-31) | Neurons, skeletal muscle | Constitutive | Cytosol, endoplasmic reticulum, sarcolemma, postsynaptic densities, caveolae (caveolin 3) |
| NOS-2 | inducible NOS (iNOS) | 125 | NOS2 (17q11.2-12) | Macrophages, smooth muscle cells | Transcriptional induction | Phagosomes |
| NOS-3 | endothelial NOS (eNOS) | 135 | NOS3 (7q35-36) | Endothelial cells, neurons | Constitutive | Golgi apparatus, plasmalemmal caveolae |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pianigiani, T.; Dilroba, A.; Fanella, A.; Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Bargagli, E.; Cameli, P. From Prognostic Marker to Therapeutic Agent: The Role of Nitric Oxide in Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196801
Pianigiani T, Dilroba A, Fanella A, Bergantini L, d’Alessandro M, Bargagli E, Cameli P. From Prognostic Marker to Therapeutic Agent: The Role of Nitric Oxide in Lung Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196801
Chicago/Turabian StylePianigiani, Tommaso, Akter Dilroba, Asia Fanella, Laura Bergantini, Miriana d’Alessandro, Elena Bargagli, and Paolo Cameli. 2025. "From Prognostic Marker to Therapeutic Agent: The Role of Nitric Oxide in Lung Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196801
APA StylePianigiani, T., Dilroba, A., Fanella, A., Bergantini, L., d’Alessandro, M., Bargagli, E., & Cameli, P. (2025). From Prognostic Marker to Therapeutic Agent: The Role of Nitric Oxide in Lung Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196801









