Framing Surgical Decisions in Elderly Patients: Minimally Invasive Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Stage I Renal Cell Carcinoma at Mid-Term Follow-Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Study Groups and Surgical Approach
2.3. Variables and Outcomes
2.4. Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Analysis
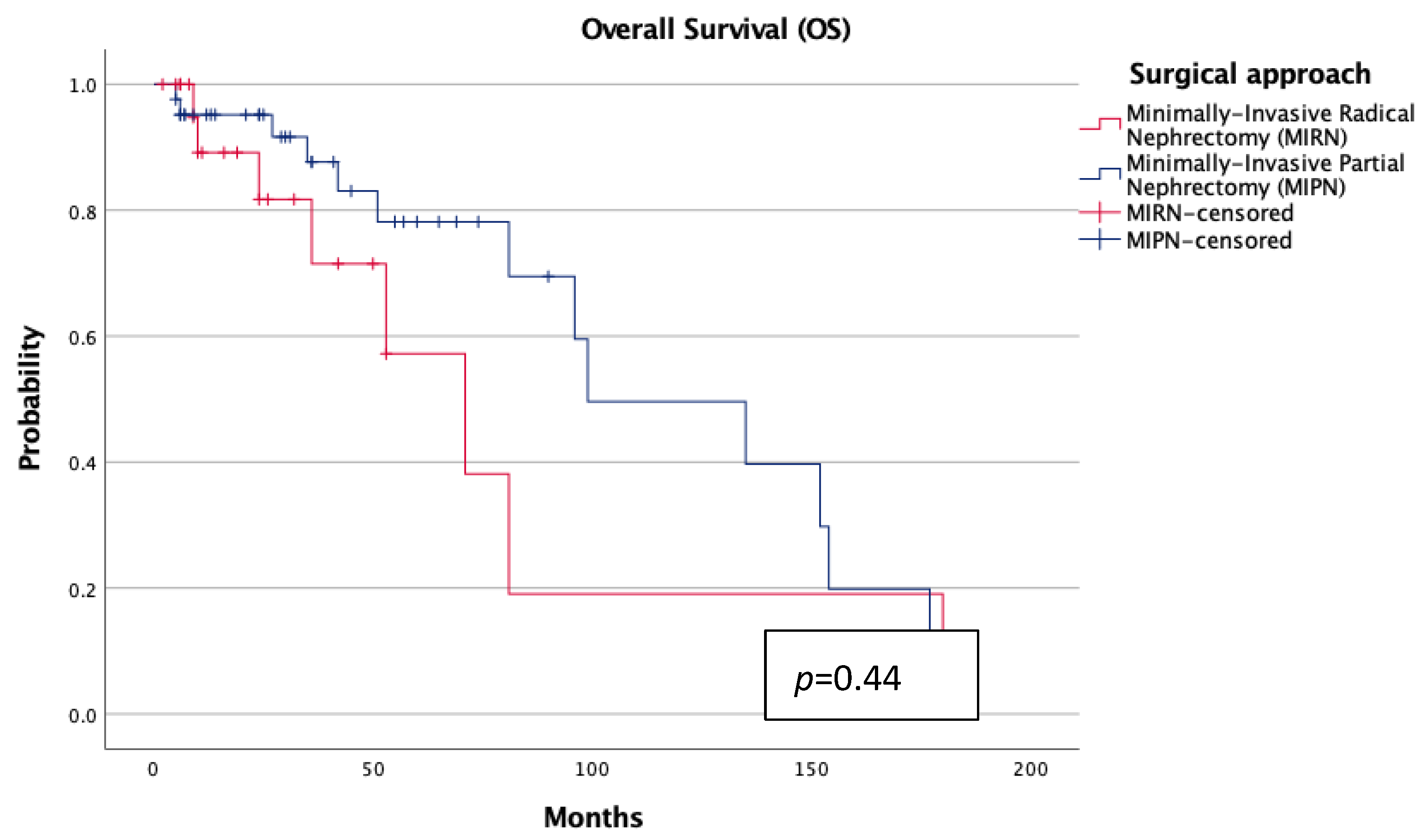
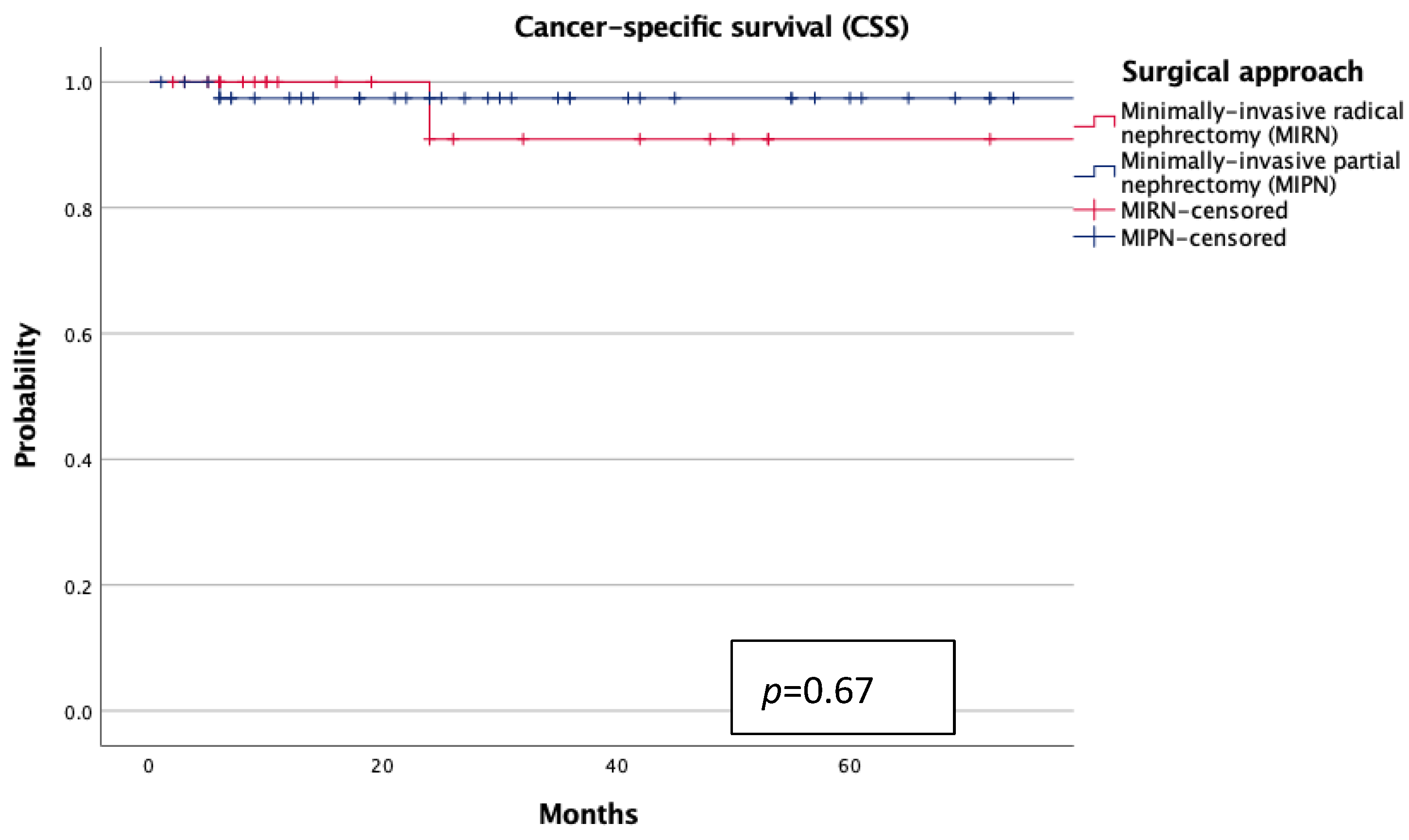
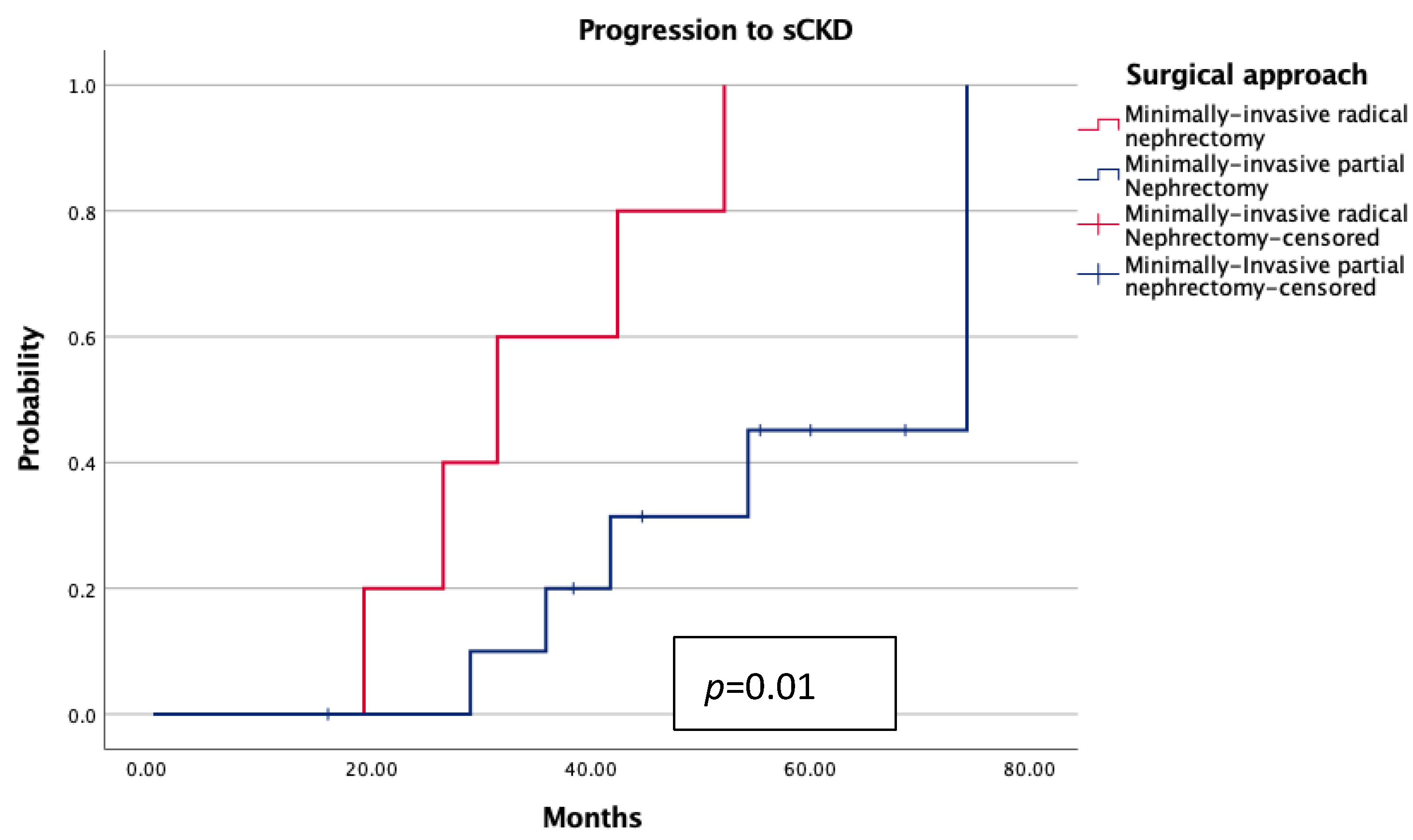
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| MIPN | minimally invasive partial nephrectomy |
| MIRN | minimally invasive radical nephrectomy |
| ccRCC | clear cell RCC |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| BMI | body mass index |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| LOS | length of hospital stay |
| IQR | interquartile ranges |
| sCKD | significant chronic kidney disease |
| ESRD | end-stage renal disease |
| OS | overall survival |
| CSS | cancer-specific survival |
References
- Quivy, A.; Daste, A.; Harbaoui, A.; Duc, S.; Bernhard, J.C.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Ravaud, A. Optimal management of renal cell carcinoma in the elderly: A review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongiat-Artus, P.; Paillaud, E.; Caillet, P.; Albrand, G.; Neuzillet, Y. Spécificités gériatriques du cancer du rein localisé [Geriatric specificities of localized renal cell carcinoma]. Prog. Urol. 2019, 29, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, A.; Testa, G.D.; Marandino, L.; Albiges, L.; Bex, A.; Capitanio, U.; Cappiello, I.; Masieri, L.; Mir, C.; Roupret, M.; et al. Frailty and Renal Cell Carcinoma: Integration of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment into Shared Decision-making. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2025, 8, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anceschi, U.; Brassetti, A.; Tuderti, G.; Consiglia Ferriero, M.; Minervini, A.; Mari, A.; Grosso, A.A.; Carini, M.; Capitanio, U.; Larcher, A.; et al. Risk factors for progression of chronic kidney disease after robotic partial nephrectomy in elderly patients: Results from a multi-institutional collaborative series. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 74, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.C.; Capitanio, U.; Bertolo, R.; Ouzaid, I.; Salagierski, M.; Kriegmair, M.; Volpe, A.; Jewett, M.A.S.; Kutikov, A.; Pierorazio, P.M.; et al. Role of Active Surveillance for Localized Small Renal Masses. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, D.C.; Finelli, A. Active Surveillance in Small Renal Masses in the Elderly: A Literature Review. Eur. Urol. Focus 2017, 3, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.G.; Ristau, B.T.; Ruth, K.; Jennings, R.; Ross, E.; Smaldone, M.C.; Chen, D.Y.T.; Viterbo, R.; Greenberg, R.E.; Kutikov, A.; et al. Active Surveillance for Localized Renal Masses: Tumor Growth, Delayed Intervention Rates, and >5-yr Clinical Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Izumi, K.; Naito, R.; Kadomoto, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Yaegashi, H.; Nohara, T.; Shigehara, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kadono, Y.; et al. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy and Cryoablation in Elderly Patients with Renal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Shan, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ding, X.; Wang, Z. Impact of thermal ablation/cryoablation treatment on prognosis among patients with kidney cancer: A SEER database-based cohort study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S.; Fujihara, A.; Hongo, F.; Shiraishi, T.; Ueda, T.; Narukawa, T.; Ohashi, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Hirota, T.; Yamada, K.; et al. Ten years of experience in percutaneous cryoablation for small renal masses in patients aged ≥ 80 years. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 109638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravi, C.A., on behalf of the Junior ERUS/Young Academic Urologist Working Group on Robot-Assisted Surgery; Dell’Oglio, P.; Pecoraro, A.; Khene, Z.-E.; Campi, R.; Diana, P.; Re, C.; Giulioni, C.; Tuna Beksac, A.; Bertolo, R.; et al. Surgical Experience and Functional Outcomes after Laparoscopic and Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy: Results from a Multi-Institutional Collaboration. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mir, M.C.; Pavan, N.; Capitanio, U.; Antonelli, A.; Derweesh, I.; Rodriguez-Faba, O.; Linares, E.; Takagi, T.; Rha, K.H.; Fiori, C.; et al. Partial versus radical nephrectomy in very elderly patients: A propensity score analysis of surgical, functional and oncologic outcomes (RESURGE project). World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfo, S.D.; Wu, Z.; Campi, R.; Bertolo, R.; Amparore, D.; Mari, A.; Verze, P.; Manfredi, C.; Franco, A.; Ditonno, F.; et al. Outcomes and Techniques of Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) for Renal Hilar Masses: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuderti, G.; Mastroianni, R.; Anceschi, U.; Bove, A.M.; Brassetti, A.; Ferriero, M.; Misuraca, L.; Guaglianone, S.; Costantini, M.; Torregiani, G.; et al. Assessing the Trade-off Between the Safety and Effectiveness of Off-clamp Robotic Partial Nephrectomy for Renal Masses with a High RENAL Score: A Propensity Score-matched Comparison of Perioperative and Functional Outcomes in a Multicenter Analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2023, 9, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, G.E.; Medina, L.G.; Gill, T.S.; Mendelsohn, A.; Husain, F.; Bhardwaj, L.; Artibani, W.; Sotelo, R.; Gill, I.S. Impact of Renal Hilar Control on Outcomes of Robotic Partial Nephrectomy: Systematic Review and Cumulative Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anceschi, U.; Flammia, R.S.; Mattevi, D.; Tufano, A.; Brassetti, A.; Ferriero, M.C.; Tuderti, G.; Misuraca, L.; Bove, A.M.; Mastroianni, R.; et al. External Validation of a Novel Comprehensive Trifecta System in Predicting Oncologic and Functional Outcomes of Partial Nephrectomy: Results of a Multicentric Series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajunen, H.; Veitonmäki, T.; Huhtala, H.; Nikkola, J.; Pöyhönen, A.; Murtola, T. Prognostic factors of renal cell cancer in elderly patients: A population-based cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anceschi, U.; Ferriero, M.C.; Tuderti, G.; Brassetti, A.; Bertolo, R.; Capitanio, U.; Larcher, A.; Garisto, J.; Antonelli, A.; Mottrie, A.; et al. Head to Head Impact of Margin, Ischemia, Complications, Score Versus a Novel Trifecta Score on Oncologic and Functional Outcomes After Robotic-assisted Partial Nephrectomy: Results of a Multicenter Series. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohada, Y.; Shikuma, H.; Goto, K.; Akiyama, K.; Kajiwara, M.; Matsuzaki, S.; Fujita, A.; Nishida, K.; Tasaka, R.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. Real-World Survival Outcomes of Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy: Cause-Specific and Time-Dependent Effects. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2025, 23, 102391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, G.; Shang, H.; Ding, B.; Sun, G.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Comparison of the oncological, perioperative and functional outcomes of partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for clinical T1b renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies. Asian J. Urol. 2021, 8, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, D.; Shou, J.; Li, C.; Xing, N. Efficacy and safety of surgery in renal carcinoma patients 75 years and older: A retrospective analysis. BMC Urol. 2022, 22, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Variable | MIPN (n = 51) Group A | MIRN (n = 26) Group B | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, median, IQR) | 81.9 (80.8–83.5) | 83 (80.6–84.5) | 0.23 |
| BMI (Kg/m2, median, IQR) | 26.4 (23.4–27.7) | 25.3 (22.8–28.4) | 0.81 |
| ASA score (n,%) 1–2 3–4 | 29 (56.9%) 22 (43.1%) | 17 (65.3%) 9 (34.7%) | 0.82 |
| Side (n,%) Right Left | 28 (54.9%) 23 (45.1%) | 7 (26.9%) 19 (73.1%) | 0.02 |
| Hypertension (n,%) | 29 (56.8%) | 14 (52%) | 0.72 |
| Diabetes (n,%) | 7 (13.7%) | 5 (19.2%) | 0.46 |
| Tumor size (mm, median, IQR) | 35 (25–45) | 50 (42.2–60) | 0.25 |
| RENAL score (median, IQR) | 7 (6–9) | 9 (8–9) | 0.01 |
| Solitary kidney (n,%) | 3 (5.8%) | - | - |
| Surgical approach (n,%) Laparoscopic Robotic | 16 (31.3%) 35 (68.7%) | 11 (42.3%) 15 (57.7%) | 0.34 |
| Reconstructive technique (n,%) Sutureless Renorraphy | 20 (39.2%) 31 (60.8%) | - - | - |
| Preoperative Hb (g/dL, median, IQR) | 13.4 (12.3–14.4) | 12.7 (12.2–14.3) | 0.52 |
| Preoperative eGFR (median, IQR) | 61.5 (54.5–77–5) | 54 (39.5–64.5) | 0.62 |
| LOS (days, median, IQR) | 2 (2–5) | 3.5 (2–6) | 0.45 |
| Perioperative Complications (n, detail, %) Clavien I–II Clavien III–V | 3 (5.8%) 3 (2 Ileus, 1 Fever) - | 3 (11.5%) 3 (Anemia) | 0.54 |
| Perioperative transfusions (n,%) | - | 3 (11.5%) | 0.01 |
| 30-days readmission (n,%) | - | - | - |
| 90-days readmission (n,%) | - | - | - |
| pT stage (n,%) pT1a pT1b | 32 (62.7%) 19 (37.3%) | 6 (23%) 20 (77%) | 0.01 |
| Surgical margin status (n,%) | - | - | - |
| Median follow-up (months, median, IQR) | 36 (13.7–70.2) | 21.5 (9–48) | 0.15 |
| eGFR follow-up (median, IQR) | 48 (38.8–64.2) | 30.9 (27.2–39.6) | 0.01 |
| ESRD (n,%) | 1 | 2 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anceschi, U.; Tufano, A.; Flammia, R.S.; Bologna, E.; Mastroianni, R.; Licari, L.C.; Brassetti, A.; Ferriero, M.C.; Bove, A.M.; Tuderti, G.; et al. Framing Surgical Decisions in Elderly Patients: Minimally Invasive Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Stage I Renal Cell Carcinoma at Mid-Term Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186634
Anceschi U, Tufano A, Flammia RS, Bologna E, Mastroianni R, Licari LC, Brassetti A, Ferriero MC, Bove AM, Tuderti G, et al. Framing Surgical Decisions in Elderly Patients: Minimally Invasive Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Stage I Renal Cell Carcinoma at Mid-Term Follow-Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186634
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnceschi, Umberto, Antonio Tufano, Rocco Simone Flammia, Eugenio Bologna, Riccardo Mastroianni, Leslie Claire Licari, Aldo Brassetti, Maria Consiglia Ferriero, Alfredo Maria Bove, Gabriele Tuderti, and et al. 2025. "Framing Surgical Decisions in Elderly Patients: Minimally Invasive Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Stage I Renal Cell Carcinoma at Mid-Term Follow-Up" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186634
APA StyleAnceschi, U., Tufano, A., Flammia, R. S., Bologna, E., Mastroianni, R., Licari, L. C., Brassetti, A., Ferriero, M. C., Bove, A. M., Tuderti, G., D’Annunzio, S., Iori, M., Cartolano, S., Pula, M., Leonardo, C., & Simone, G. (2025). Framing Surgical Decisions in Elderly Patients: Minimally Invasive Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Stage I Renal Cell Carcinoma at Mid-Term Follow-Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186634







