Perfusion Enhancement via Continuous Brachial Plexus Block to Prevent Vascular Insufficiency in Replanted Digits: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Randomization
2.3. Anesthetic Protocol and Interventions
2.4. Postoperative Management
2.5. Primary and Secondary Study Outcomes
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Sample Size Calculation
2.8. Ethical Approval
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Baseline Data
3.2. Digital Skin Temperature
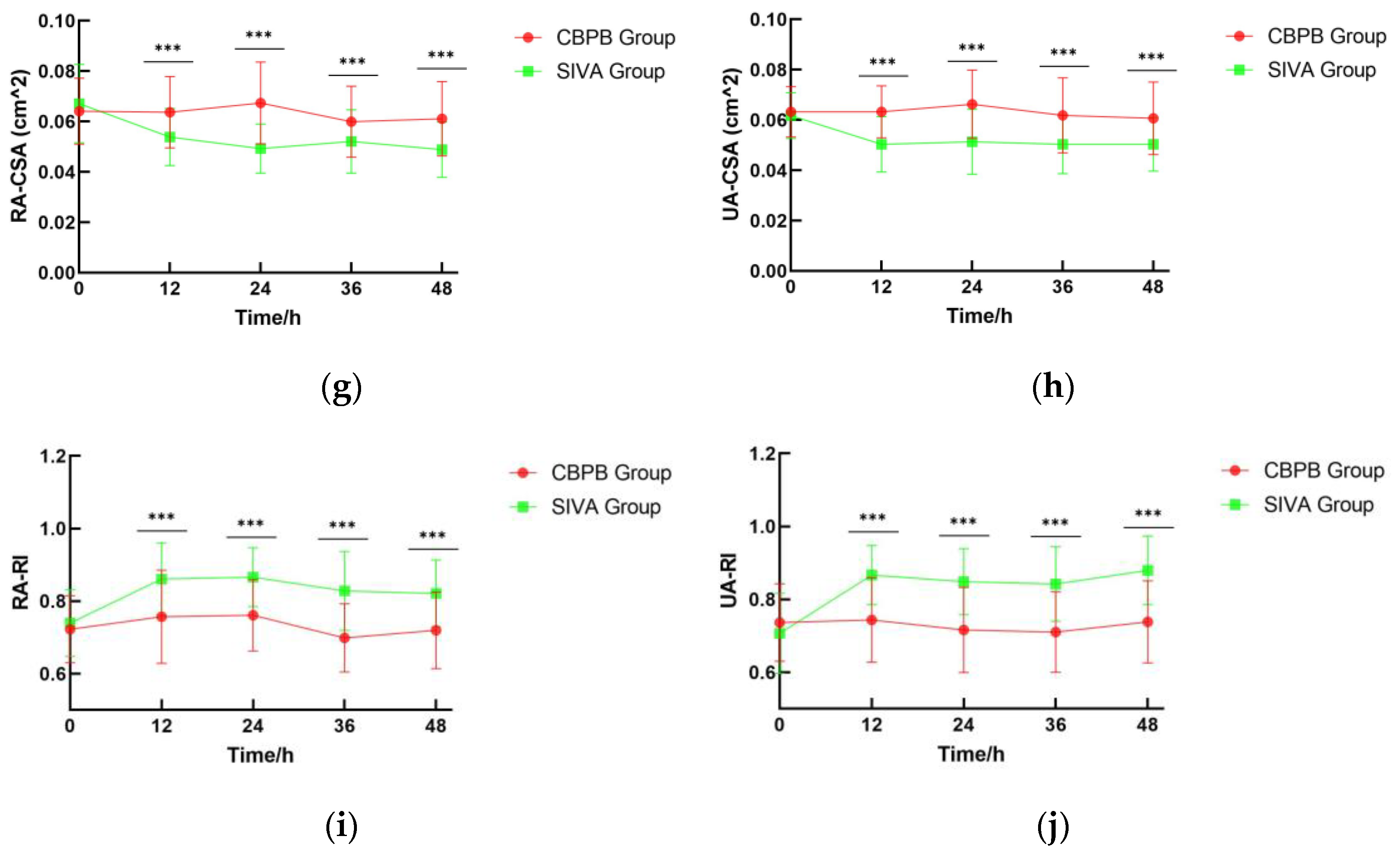
3.3. RA-UA VFR
3.4. VAS
3.5. Postoperative Incidence of Vascular Insufficiency
3.6. 7-Day Survival Rate
3.7. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SIVA | Systemic Intravenous Analgesia |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| CBPB | Continuous Brachial Plexus Block |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologist |
| BPB | Brachial Plexus Blockade |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| LMWH | Low Molecular Weight Heparin |
| APTT | Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time |
| VFR | Volumetric Flow Rate |
| RA-UA VFR | the combined Volumetric Flow Rate of the Radial Artery and Ulnar Artery |
| RA | Radial Artery |
| UA | Ulnar Artery |
| CSA | Cross-Sectional Area |
| TAMV | Time-Averaged Mean Velocity |
| RI | Resistance Index |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| GEE | Generalized Estimating EquationsLast |
| LOCF | Observation Carried Forward |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| MCID | Minimal Clinically Important Difference |
References
- Fufa, D.T.; Calfee, R.P.; Wall, L.B.; Zeng, W.; Goldfarb, C.A. Digit replantation: Experience of two U.S. academic level-I trauma centers. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchell, A.C.; Sandre, A.R.; McRae, M.; Farrokhyar, F.; Avram, R. The success of salvage procedures for failing digital replants: A retrospective cohort study. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wen, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhu, H. Reconstruction of circulation in the fingertip without vein repair in zone I replantation. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2008, 33, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Scott, F.; Ipaktchi, K.R.; Lauder, A. Postoperative digit and hand replantation protocols: A review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, e732–e742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, J.C.; Mao, J. Opioid therapy for chronic pain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, E.; Ozturk, S.; Isik, S.; Zor, F. Continuous brachial plexus blockade for digital replantations and toe-to-hand transfers. Reg. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2005, 30, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karmakar, M.K.; Li, X.; Kwok, W.H.; Ngan Kee, W.D. Regional hemodynamic changes after an axillary brachial plexus block: A pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasound study. Reg. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2012, 37, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.; Amr, A.; Schaller, H.E.; Rothenberger, J. Skin perfusion changes within 12 h after axillary plexus block. Eur. Surg. Res. 2017, 58, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, S.P.; Maggard, B.D.; Hines, K.M. Prolonged continuous infraclavicular brachial plexus perineural infusion following replantation of a mid-humeral amputation. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2050313X18823094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.J.; Durning, S.J.; Stevens, S.D.; Lowery, D.R. Regional anesthesia in the setting of arm replantation: A case report. A A Pract. 2018, 11, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Huang, S.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Z. Is Prolonged Use of Antibiotic Prophylaxis and Postoperative Antithrombotic and Antispasmodic Treatments Necessary After Digit Replantation or Revascularization? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2023, 481, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standring, S. (Ed.) Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 42nd ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; p. 862. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, D.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Q.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y. Blood flow changes in the forearm arteries after ultrasound-guided costoclavicular brachial plexus blocks: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosselmann, T.; Kolbenschlag, J.; Goertz, O.; Daigeler, A.; Behr, B.; Kapalschinski, N. Improvement of superficial and deep cutaneous microcirculation due to axillary plexus anesthesia impaired by smoking. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.M.; Ferrige, A.G.; Moncada, S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 1987, 327, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dieussaert, E.; Baets, R. Miniaturization of laser Doppler vibrometers—A review. Sensors 2022, 22, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, B.B.; Bagavathiappan, S.; Jayakumar, T.; Philip, J. Medical applications of infrared thermography: A review. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, E.D.; Chung, K.C. Replantation of finger avulsion injuries: A systematic review of survival and functional outcomes. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2011, 36, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchum, L.D. Pharmacological alterations in the clotting mechanism: Use in microvascular surgery. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1978, 3, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.I. Low-molecular-weight heparins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallali, N. Dextrans in microsurgery: A review. Microsurgery 2003, 23, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, W.S.; Westein, E.; Tovar-Lopez, F.J.; Tolouei, E.; Mitchell, A.; Fu, J.; Carberry, J.; Fouras, A.; Jackson, S.P. A shear gradient-dependent platelet aggregation mechanism drives thrombus formation. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierings, R.; van den Eijnden, M.; van Gorp, R.M.; van der Meer, D.L.; Hennekam, M.; van Buul, J.D.; de Vries, C.J.M.; Kruithof, B.P.T.; Mul, E.; Voorberg, J.; et al. The interplay between shear stress and α-adrenergic signaling in endothelial von Willebrand factor release. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wei, L.; Liang, B.; Hou, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y. Nonsurgical factors of digital replantation and survival rate: A meta-analysis. Indian J. Orthop. 2015, 49, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, A.U.; El-Beheiry, H.; Ramlogan, R.; Graham, B.; von Schroeder, H.P.; Tumber, P.S. Continuous infraclavicular brachial plexus blockade: Effect on survival of replanted digits. Hand Surg. 2013, 18, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P., Jr.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, R.M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, P.S.; Myles, D.B.; Gallagher, W.; Boyd, D.; Chester, K.; Hannah, L. Measuring acute postoperative pain using the visual analog scale: The minimal clinically important difference and patient acceptable symptom state. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Kamiya, Y. Distance of catheter tip dislocation in continuous interscalene brachial plexus block. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyyalamudi, V.; Langley, N.R.; Harbell, M.W.; Kim, S.E.; Hoyt, J.W.; Kim, R. Evaluating the spread of costoclavicular brachial plexus block: An anatomical study. Reg. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2021, 46, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.T.; Wang, S.H.; Chi, C.C. Low molecular weight heparin for prevention of microvascular occlusion in digital replantation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 4, CD009894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaterian, A.; Rajaii, R.; Kanack, M.; Evans, G.R.D.; Leis, A. Predictors of digit survival following replantation: Quantitative review and meta-analysis. J. Hand Microsurg. 2018, 10, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Yanagibayashi, S.; Koshima, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Iida, T. The effect of smoking on necrosis rate in digital replantation and revascularization with prostaglandin E1 therapy: A retrospective study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
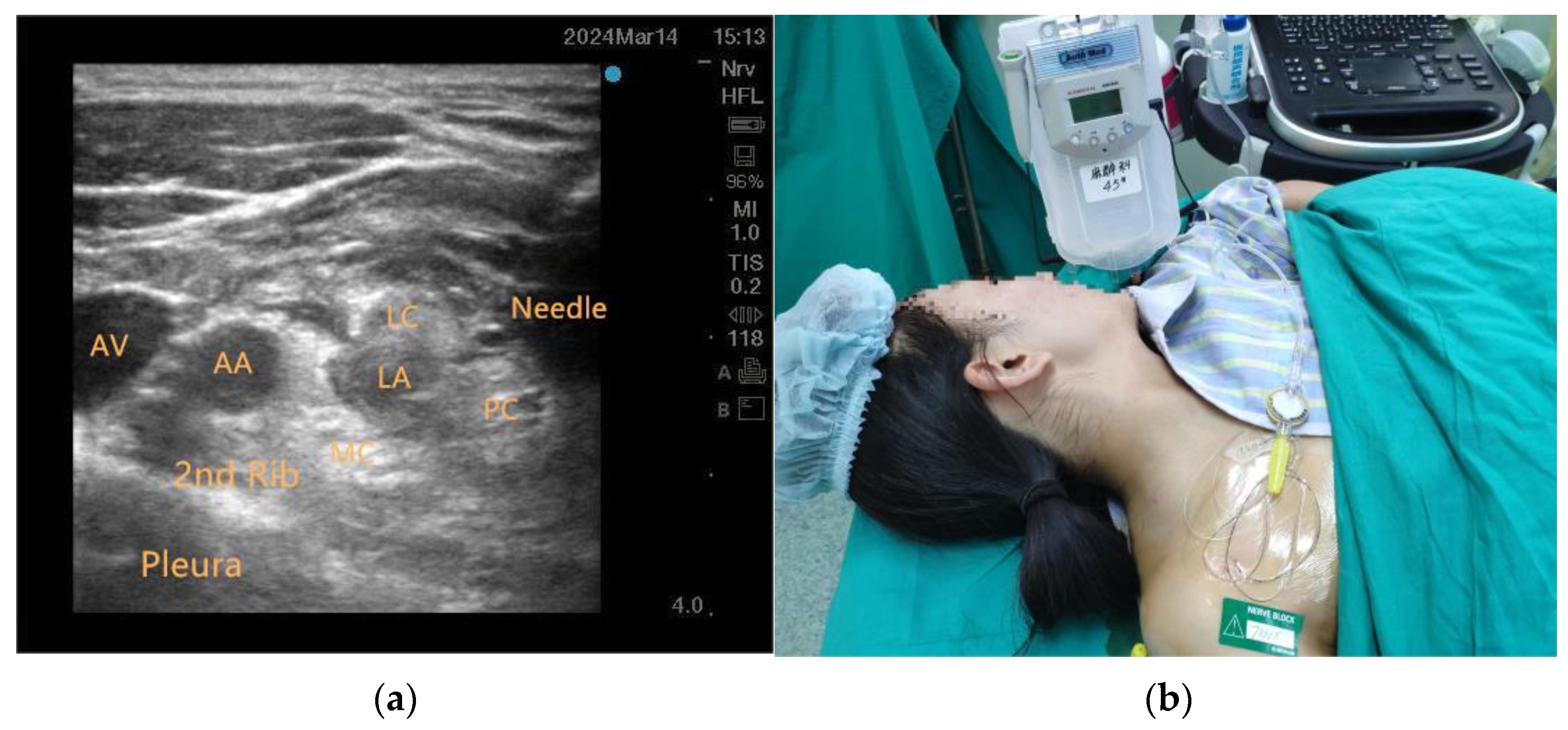
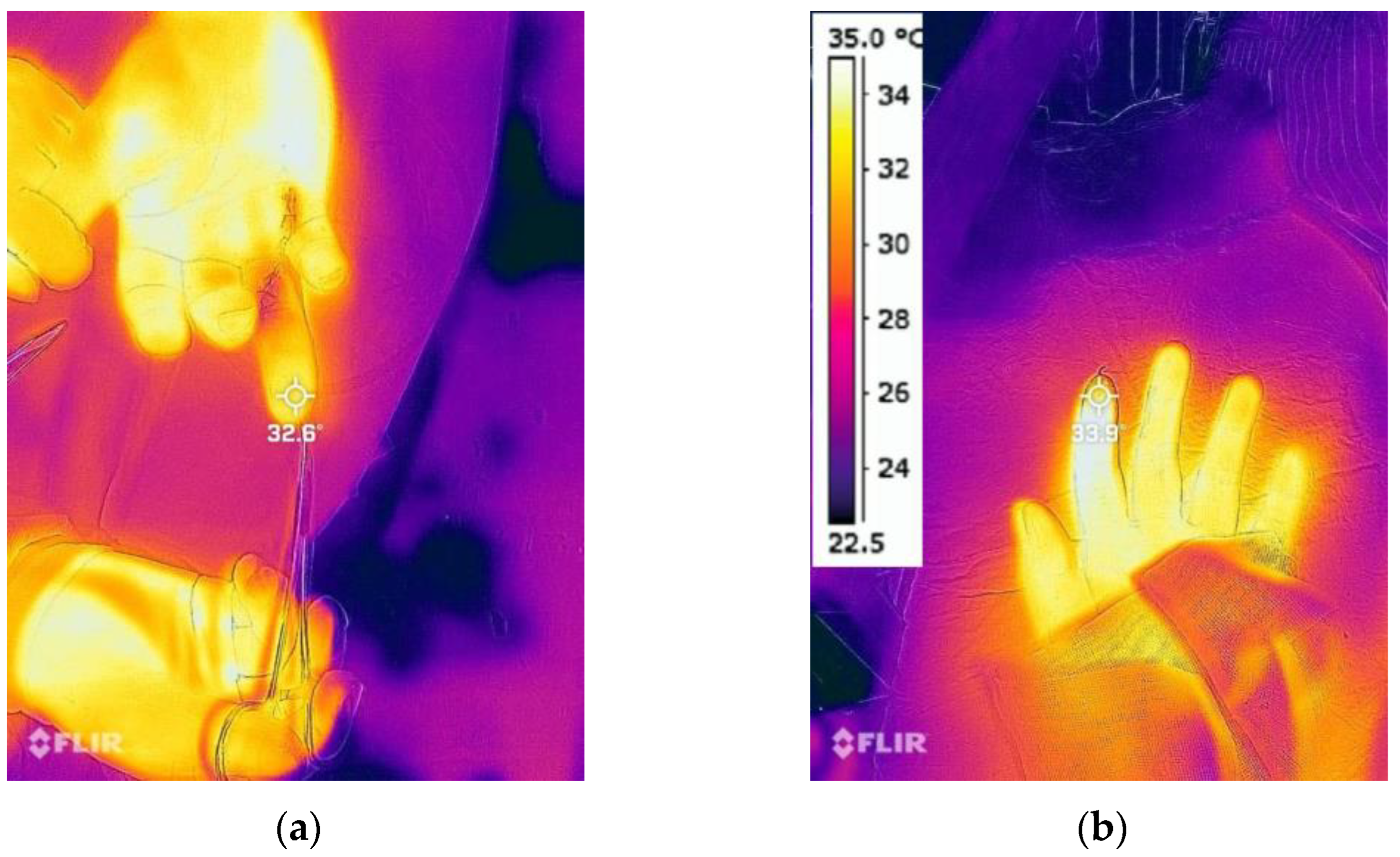
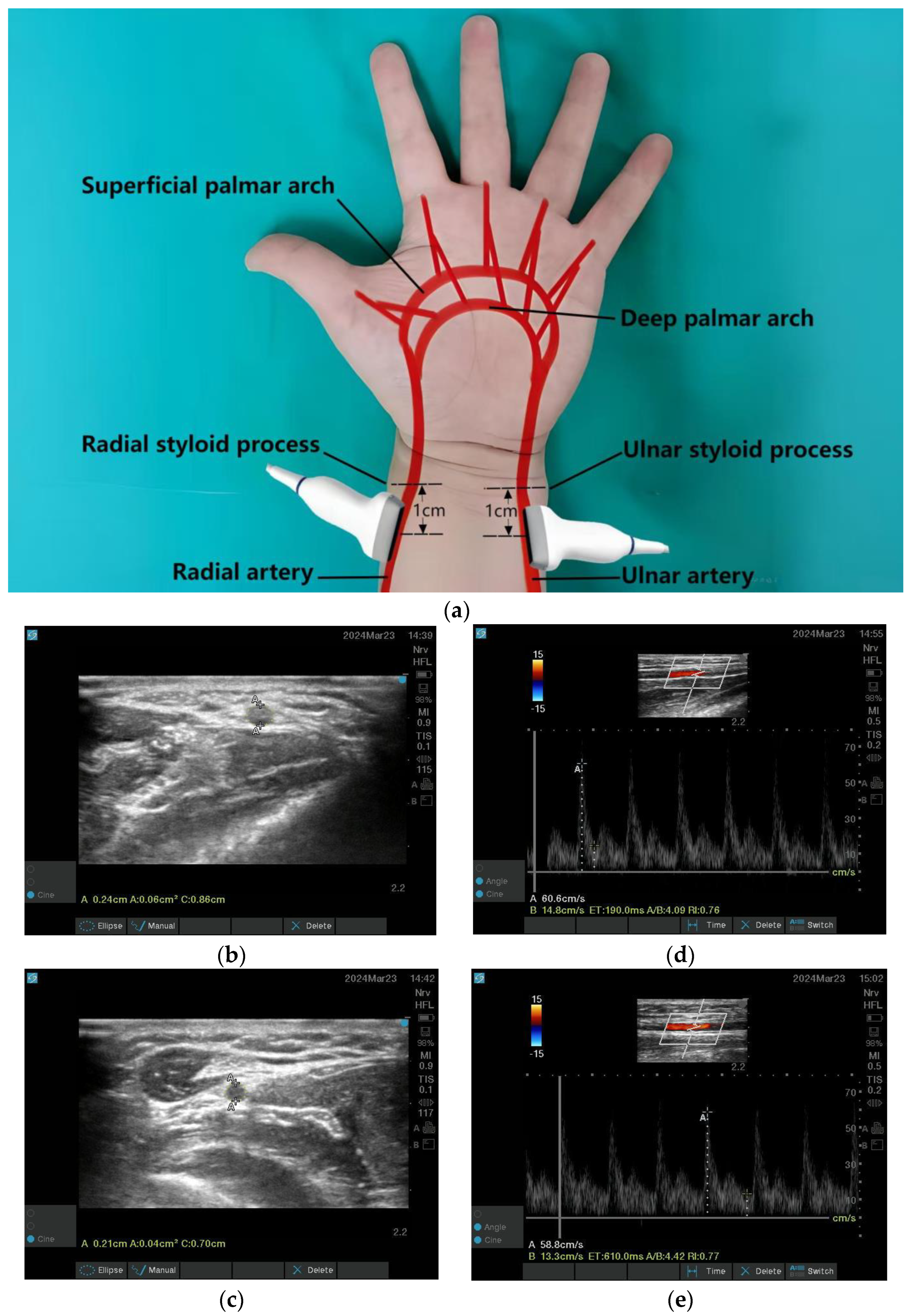

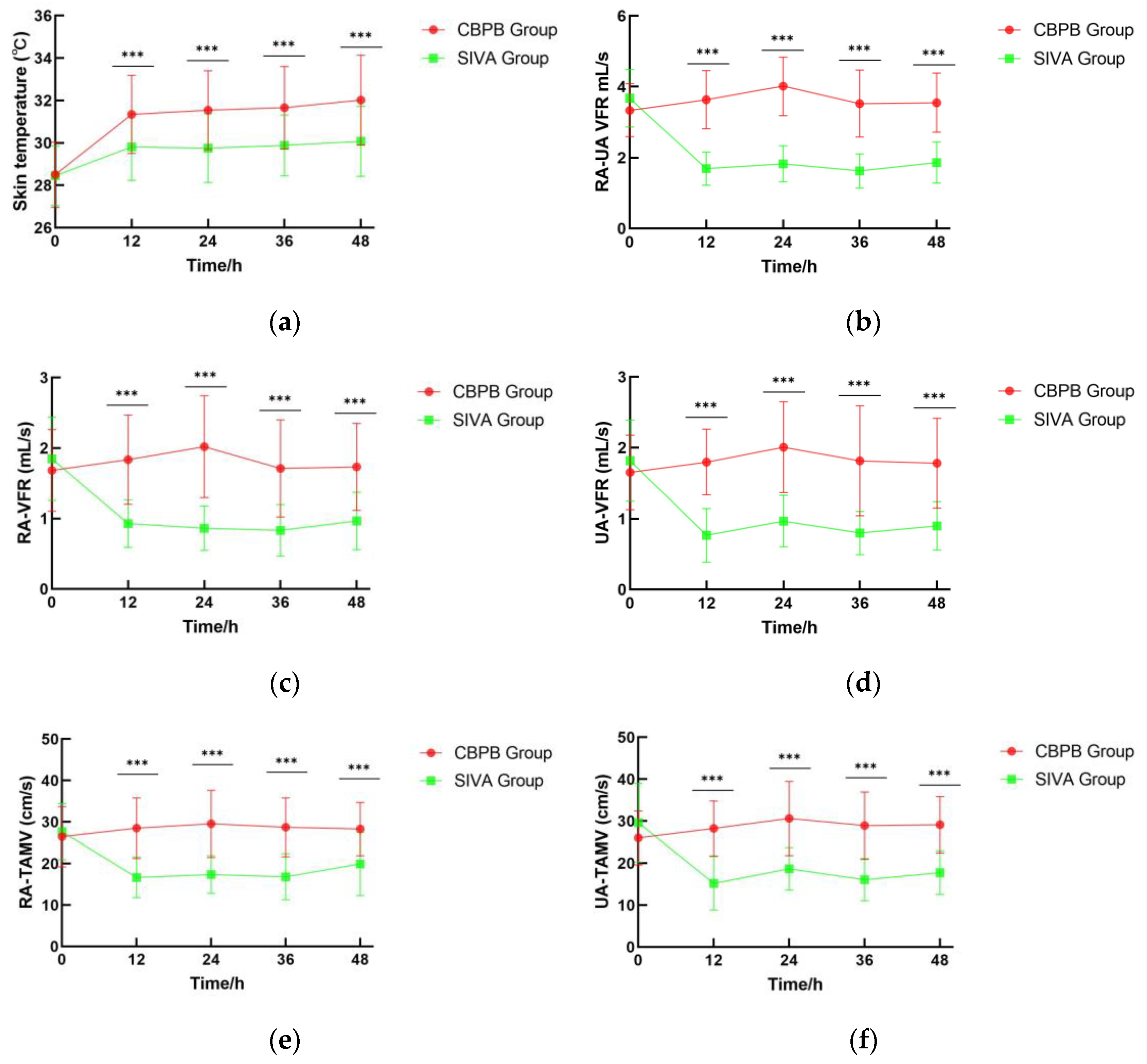
| Variables | Total (n = 55, 71 Digits) | CBPB (n = 27, 36 Digits) | SIVA (n = 28, 35 Digits) | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), years | 34 (11) | 34 (11) | 34 (12) | 0.873 |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 43 (78) | 21 (78) | 22 (79) | 1.000 |
| Female | 12 (22) | 6 (22) | 6 (21) | 1.000 |
| ASA, n (%) | ||||
| I | 25 (45) | 11 (41) | 14 (50) | 0.181 |
| II | 30 (55) | 16 (59) | 14 (50) | 0.150 |
| BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 24 (1.1) | 24 (1.2) | 24 (0.93) | 0.807 |
| Type of injury, n (%) | ||||
| Cut | 43/71 (61) | 19/36 (53) | 24/35 (69) | 0.174 |
| Crushed/Avulsion | 28/71 (39) | 17/36 (47) | 11/35 (31) | 0.174 |
| Ischemic time † (SD), hours | 6.2 (2.6) | 6.5 (2.8) | 5.9 (2.4) | 0.408 |
| Operation time (SD), hours | 4.3 (1.5) | 4.5 (1.5) | 4.2 (1.4) | 0.830 |
| Time Point (h) | β (°C) | 95% CI | Wald χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 1.5 | 2.2 to 0.73 | 15.09 | <0.001 |
| 24 | 1.7 | 2.5 to 1.0 | 21.39 | <0.001 |
| 36 | 1.7 | 2.5 to 0.97 | 20.25 | <0.001 |
| 48 | 1.9 | 2.7 to 1.1 | 21.69 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Total (n = 55, 71 Digits) | CBPB (n = 27, 36 Digits) | SIVA (n = 28, 35 Digits) | p Value 1 | p Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascular insufficiency incidence | 13/71(18) | 3/36(8.3) | 10/35(29) | 0.028 | 0.048 |
| Secondary revascularization | 9/71(13) | 1/36(2.8) | 8/35(23) | 0.014 | 0.036 |
| Survival rate | 67/71(94) | 35/36(97) | 32/35(91) | 0.329 | 0.290 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Xie, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, T. Perfusion Enhancement via Continuous Brachial Plexus Block to Prevent Vascular Insufficiency in Replanted Digits: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186591
Xu Y, Xie F, Wang Y, Chen J, Liu S, Xu T. Perfusion Enhancement via Continuous Brachial Plexus Block to Prevent Vascular Insufficiency in Replanted Digits: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186591
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yang, Fang Xie, Yan Wang, Jie Chen, Shenghe Liu, and Tao Xu. 2025. "Perfusion Enhancement via Continuous Brachial Plexus Block to Prevent Vascular Insufficiency in Replanted Digits: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186591
APA StyleXu, Y., Xie, F., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Liu, S., & Xu, T. (2025). Perfusion Enhancement via Continuous Brachial Plexus Block to Prevent Vascular Insufficiency in Replanted Digits: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186591







