Serum Granulin Concentrations Are Elevated in Prediabetes and Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
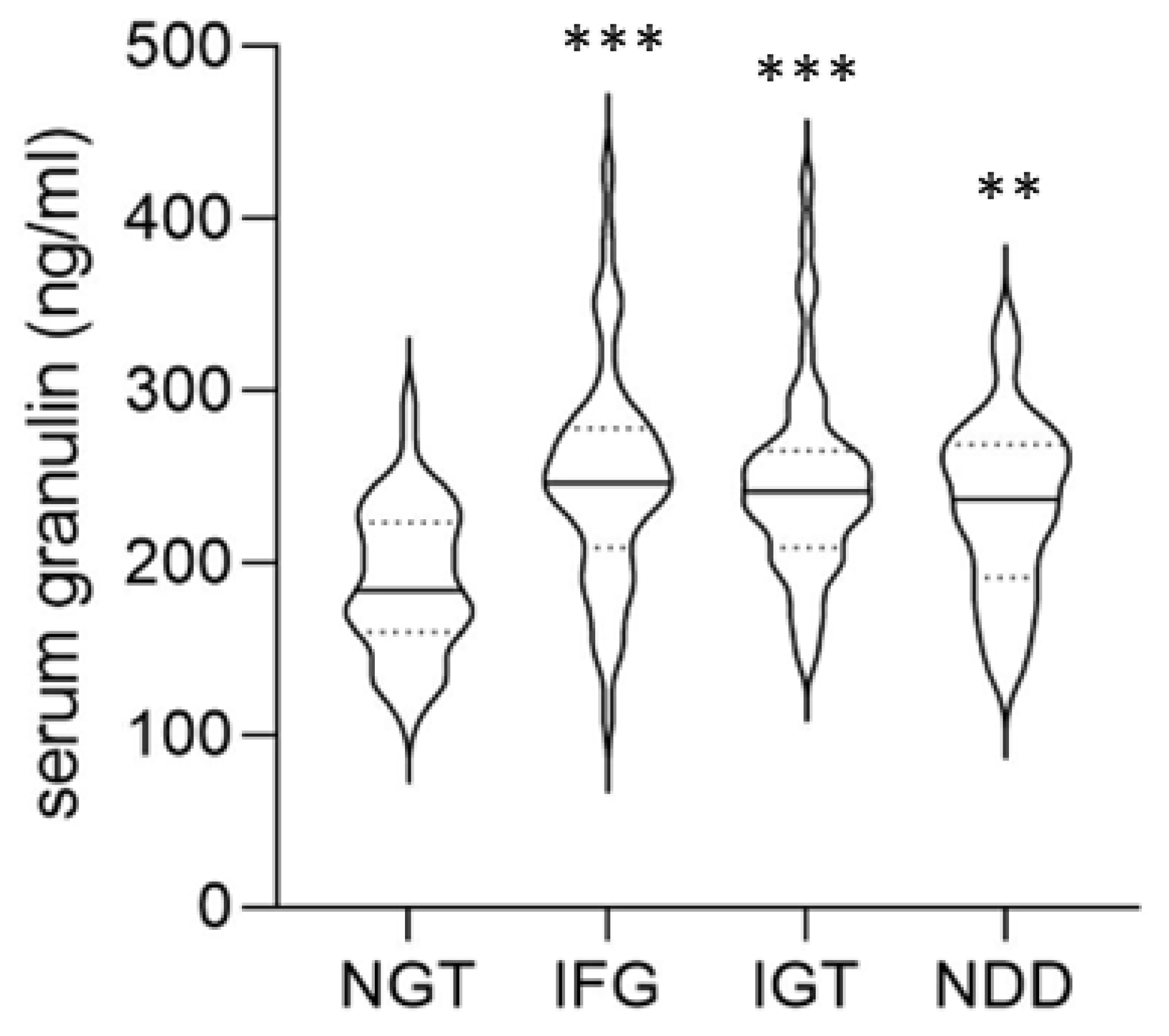
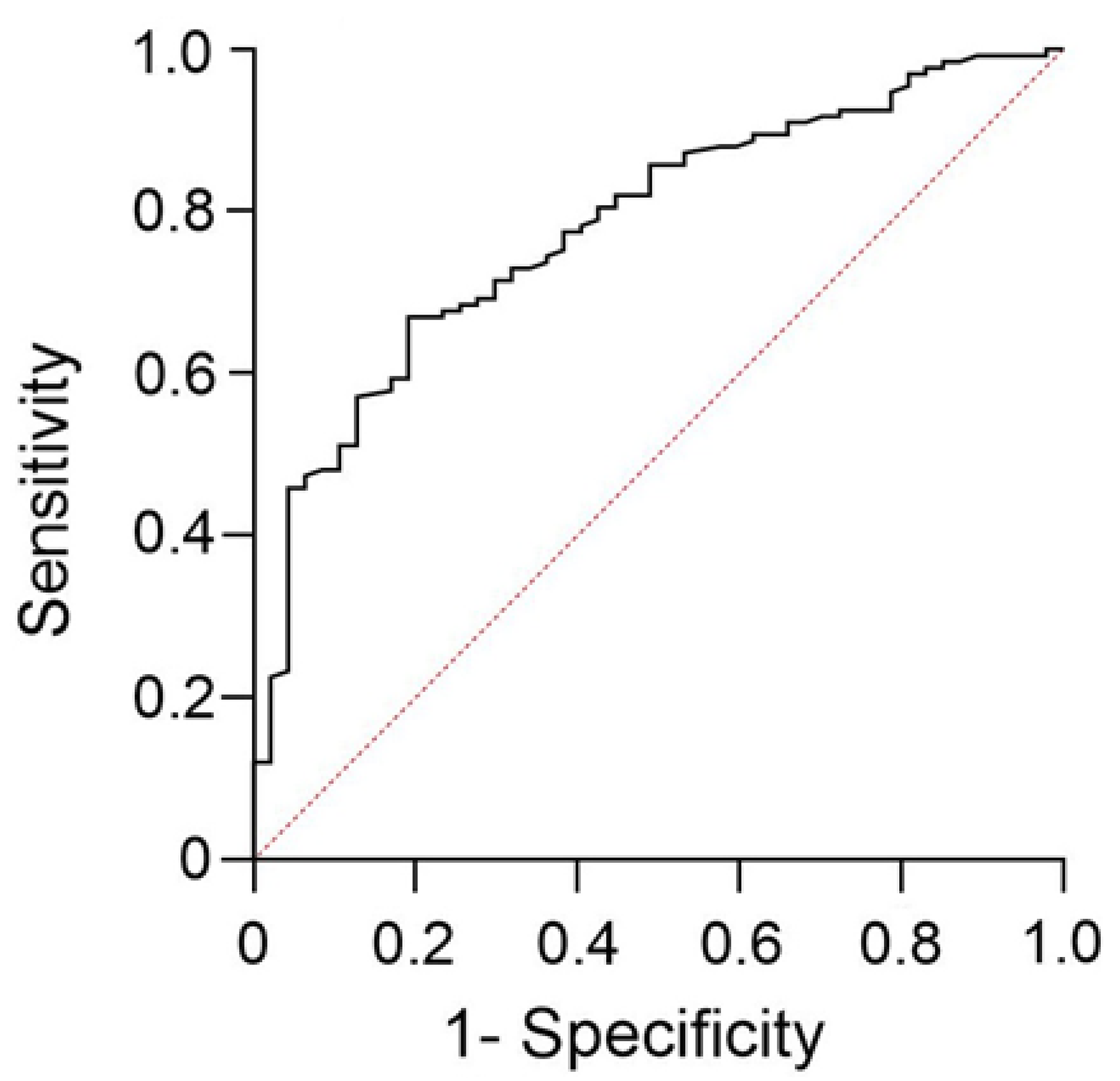
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, M.J.; Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.R. Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: Early detection should be focused. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafidh, K.; Malek, R.; Al-Rubeaan, K.; Kok, A.; Bayram, F.; Echtay, A.; Rajadhyaksha, V.; Hadaoui, A. Prevalence and risk factors of vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results from discover Middle East and Africa cohort. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 940309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, S. Vascular complications of diabetes: A narrative review. Medicine 2023, 102, e35285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.S.; Januszewski, A.S.; O’cOnnell, R.; Fulcher, G.; Scott, R.; Kesaniemi, A.; Wu, L.; Colagiuri, S.; Keech, A.; Jenkins, A.J. Long-Term Glycemic Variability and Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes: Post Hoc Analysis of the FIELD Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3638–e3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, T.; Hibler, E.; Walts, Z.L.; Giurini, L.; Steinwandel, M.; Lipworth, L.; Murff, H.J.; Zheng, W.; Andersen, S.W. Associations of diabetes and mortality among colorectal cancer patients from the Southern Community Cohort Study. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.; Koo, D.J.; Lee, W.Y. Insulin Resistance, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical and Experimental Perspective. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Selvin, E. Prediabetes and What It Means: The Epidemiological Evidence. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 2021, 42, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Early, K.B.; Bruemmer, D.; Ebekozien, O.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48, S27–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E.; Roberts, S.; Oke, J.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Normansell, R.; Greenhalgh, T. Efficacy and effectiveness of screen and treat policies in prevention of type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of screening tests and interventions. BMJ 2017, 356, i6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundholm, M.D.; Emanuele, M.A.; Ashraf, A.; Nadeem, S. Applications and pitfalls of hemoglobin A1C and alternative methods of glycemic monitoring. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 34, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Kumar Mandal, A. Interference of hemoglobin variants in HbA(1c) quantification. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 539, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, J.L.; Mackenzie, I.R. Progranulin: Normal function and role in neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolczuk, A.; Bełtowski, J. Progranulin, a New Adipokine at the Crossroads of Metabolic Syndrome, Diabetes, Dyslipidemia and Hypertension. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Mita, A.; Minami, K.; Hosooka, T.; Kitazawa, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tamori, Y.; Yokoi, N.; Watanabe, M.; Matsuo, E.; et al. PGRN is a key adipokine mediating high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity through IL-6 in adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, K.W.; Shin, S.; Jang, W.H.; Byeon, J.; Oh, Y.R.; Kim, S.J.; Park, J.W.; Kang, G.M.; et al. Extracellular Cleavage of Microglia-Derived Progranulin Promotes Diet-Induced Obesity. Diabetes 2024, 73, 2009–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H.; Wu, S. Progranulin induces adipose insulin resistance and autophagic imbalance via TNFR1 in mice. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 55, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, B.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Zang, W.; Wu, S.; Sun, H. Circulating PGRN is significantly associated with systemic insulin sensitivity and autophagic activity in metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3493–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Park, C.B.; Kim, H.K.; Jang, W.H.; Min, S.H.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, M.S. Macrophage-Specific Progranulin Deficiency Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity through the Inhibition of Hypothalamic and Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Diabetes Metab. J. 2025, 49, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.F. Prevalence of obesity in Taiwan. Obes. Rev. 2005, 6, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappan, N.; Awosika, A.O.; Rehman, A. Dyslipidemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Pang, Z.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Ning, F.; Qiao, Q. Performance of an A1C and fasting capillary blood glucose test for screening newly diagnosed diabetes and pre-diabetes defined by an oral glucose tolerance test in Qingdao, China. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, C.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Hanley, A.J.; Rewers, M.J.; Karter, A.J.; Haffner, S.M. A1C between 5.7 and 6.4% as a marker for identifying pre-diabetes, insulin sensitivity and secretion, and cardiovascular risk factors: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorcely, B.; Katz, K.; Jagannathan, R.; Chiang, S.S.; Oluwadare, B.; Goldberg, I.J.; Bergman, M. Novel biomarkers for prediabetes, diabetes, and associated complications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Martínez, M.; González-González, M.; Martagón, A.J.; Hlavinka, V.; Willson, R.C.; Rito-Palomares, M. Recent Developments in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Screening of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diab Rep. 2022, 22, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; You, L.; Li, F.; Chen, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xuan, W.; Sun, K.; Lao, G.; et al. The association of adiponectin with risk of pre-diabetes and diabetes in different subgroups: Cluster analysis of a general population in south China. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Koh, W.P.; Jensen, M.K.; Yuan, J.M.; Pan, A. Plasma Fetuin-A Levels and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Chinese Population: A Nested Case-Control Study. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafaei, A.; Marjani, A.; Khoshnia, M. Serum Progranulin Levels in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 54, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Deng, H.; Hu, Z. Plasma progranulin concentrations are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity and correlated with insulin resistance. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 360190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.S.; Mahran, N.A.; Hegazy, M.G.A. Assessment of the association of serum progranulin with autophagy in diabetic patients. Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönjes, A.; Fasshauer, M.; Kratzsch, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokine pattern in subjects with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in comparison to normal glucose tolerance and diabetes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, B.S.; Bang, S.I.; Klöting, N.; Park, J.W.; Lee, N.; Oh, J.E.; Pi, K.B.; Lee, T.H.; Ruschke, K.; Fasshauer, M.; et al. Serum progranulin concentrations may be associated with macrophage infiltration into omental adipose tissue. Diabetes 2009, 58, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakoshi, M.; Gohda, T.; Sakuma, H.; Shibata, T.; Adachi, E.; Kishida, C.; Ichikawa, S.; Koshida, T.; Kamei, N.; Suzuki, Y. Progranulin and Its Receptor Predict Kidney Function Decline in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 849457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, D.; Kamenov, Z.; Hristova, J.; Gateva, A.T. Levels of DEFA1, Progranulin, and NRG4 in Patients with Autonomic Neuropathy: Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albeltagy, E.S.; Hammour, A.E.; Albeltagy, S.A. Potential value of serum Progranulin as a biomarker for the presence and severity of micro vascular complications among Egyptian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2019, 18, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waluga-Kozlowska, E.; Kuznik-Trocha, K.; Komosinska-Vassev, K.; Olczyk, P.; Jura-Poltorak, A.; Winsz-Szczotka, K.; Telega, A.; Ivanova, D.; Strzoda, W.; Zimmermann, A.; et al. Progranulin and chemerin plasma level in obese patients with type 2 diabetes treated with a long-acting insulin analogue and premixed insulin analogue. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 72, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | NGT | IFG | IGT | NDD | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 47 | 45 | 48 | 40 | -- |
| Age (years) | 61.0 ± 11.0 | 62.1 ± 12.8 | 62.7 ± 12.0 | 61.9 ± 12.1 | 0.928 |
| Sex (F/M) | 18/29 | 17/28 | 19/29 | 15/25 | 0.997 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.9 ± 2.8 | 23.8 ± 3.5 | 23.8 ± 3.2 | 23.5 ± 2.8 | 0.455 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 124.1 ± 17.2 | 127.3 ± 16.3 | 127.8 ± 16.1 | 128.6 ± 20.3 | 0.639 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 72.6 ± 9.4 | 73.0 ± 11.3 | 73.2 ± 9.8 | 75.3 ± 11.0 | 0.643 |
| ALT (U/L) | 23.4 ± 9.7 | 31.3 ± 24.6 | 21.8 ± 8.6 | 26.8 ± 20.4 | 0.042 |
| AST (U/L) | 25.9 ± 6.5 | 27.8 ± 16.7 | 23.8 ± 4.9 | 26.3 ± 11.7 | 0.351 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 75.80 ± 15.17 | 85.65 ± 21.88 | 79.38 ± 17.35 | 73.59 ± 18.82 | 0.015 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 2.9 ± 4.5 | 4.4 ± 7.3 | 2.9 ± 4.6 | 6.7 ± 9.4 | 0.023 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.27 ± 1.04 | 5.26 ± 0.93 | 5.24 ± 0.99 | 5.41 ± 1.25 | 0.882 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.10 ± 0.45 | 1.27 ± 0.64 | 1.31 ± 0.73 | 1.46 ± 0.75 | 0.086 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.53 ± 0.43 | 1.34 ± 0.40 | 1.34 ± 0.39 | 1.32 ± 0.28 | 0.027 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.23 ± 0.99 | 3.34 ± 0.78 | 3.29 ± 0.90 | 3.42 ± 1.04 | 0.820 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 4.79 ± 0.40 | 5.83 ± 0.27 | 4.84 ± 0.55 | 7.17 ± 3.42 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.46 ± 0.31 | 0.68 ± 0.37 | 0.55 ± 0.44 | 0.78 ± 0.79 | 0.025 |
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | Standard β | p-Value | Adjusted R Square | β (95% CI) | Standard β | p-Value | Adjusted R Square | β (95% CI) | Standard β | p-Value | Adjusted R Square | |
| Age | −0.592 (−1.455, 0.271) | −0.186 | 0.177 | 0.042 | −0.519 (−1.313, 0.275) | −0.107 | 0.199 | 0.190 | −0.566 (−1.358, 0.225) | −0.117 | 0.159 | 0.203 |
| sex | −21.623 (−45.056, 1.809) | −0.122 | 0.070 | −18.131 (−39.717, 3.454) | −0.156 | 0.099 | −15.915 (−37.481, 5.652) | −0.137 | 0.147 | |||
| ALT | 0.394 (−0.127, 0.916) | 0.119 | 0.138 | 0.343 (−0.137, 0.823) | 0.104 | 0.160 | 0.350 (−0.131, 0.832) | 0.106 | 0.152 | |||
| Creatinine | 0.559 (−0.088, 1.205) | 0.175 | 0.090 | 0.425 (−0.172, 1.022) | 0.133 | 0.161 | 0.308 (−0.295, 0.912) | 0.097 | 0.314 | |||
| Hypertension | 5.711 (−12.934, 24.357) | 0.605 | 0.545 | 2.836 (−14.342, 20.014) | 0.025 | 0.745 | 4.434 (−12.685, 21.563) | 0.039 | 0.610 | |||
| hs-CRP | 0.651 (−0.766, 2.068) | 0.907 | 0.366 | 0.352 (−0.956, 1.659) | 0.041 | 0.596 | 0.642 (−0.686, 1.970) | 0.074 | 0.341 | |||
| Dyslipidemia | −10.995 (−36.940, 14.949) | −0.837 | 0.404 | −6.903 (−30.808, 17.001) | −0.043 | 0.569 | −6.944 (−30.690, 16.801) | −0.043 | 0.564 | |||
| Obesity | 29.680 (1.494, 57.865) | 0.164 | 0.039 | 21.624 (−4.461, 47.710) | 0.119 | 0.104 | 20.689 (−5.232, 46.609) | 0.114 | 0.117 | |||
| Glycemic status | -- | -- | 48.779 (30.980, 66.578) | 0.390 | <0.001 | -- | -- | |||||
| IFG vs. NGT | -- | -- | -- | -- | 55.922 (32.102, 79.743) | 0.387 | <0.001 | |||||
| IGT vs. NGT | -- | -- | -- | -- | 56.012 (34.986, 77.039) | 0.447 | <0.001 | |||||
| NDD vs. NGT | -- | -- | -- | -- | 34.000 (11.605, 56.395) | 0.256 | 0.003 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, Y.-H.; Kao, Y.; Chan, K.C.; Chou, H.-W.; Liang, Y.-C.; Wu, H.-T.; Ou, H.-Y. Serum Granulin Concentrations Are Elevated in Prediabetes and Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186566
Chou Y-H, Kao Y, Chan KC, Chou H-W, Liang Y-C, Wu H-T, Ou H-Y. Serum Granulin Concentrations Are Elevated in Prediabetes and Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186566
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Yu-Hsuan, Yuan Kao, Ka Chon Chan, Hsuan-Wen Chou, Yu-Cheng Liang, Hung-Tsung Wu, and Horng-Yih Ou. 2025. "Serum Granulin Concentrations Are Elevated in Prediabetes and Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186566
APA StyleChou, Y.-H., Kao, Y., Chan, K. C., Chou, H.-W., Liang, Y.-C., Wu, H.-T., & Ou, H.-Y. (2025). Serum Granulin Concentrations Are Elevated in Prediabetes and Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186566








