Alterations in the Myokine Concentrations in Relation to Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances Correlations
4. Roles of Selected Myokines in Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances
4.1. Irisin
4.2. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
4.3. Meteorin-like Protein (Metrnl)
4.4. FGF-21
4.5. Interleukins
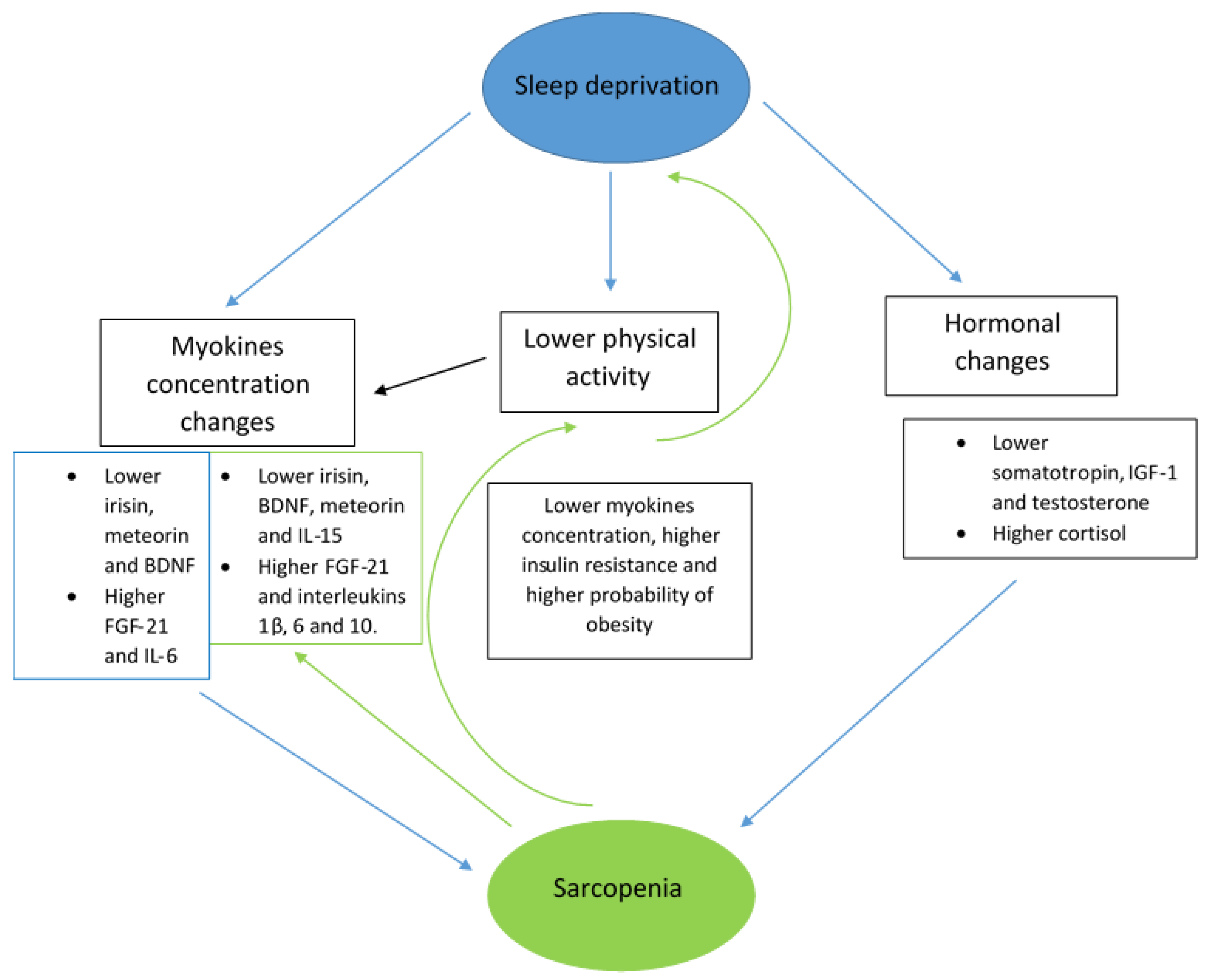
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Future Research Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishikawa, H.; Fukunishi, S.; Asai, A.; Yokohama, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; Higuchi, K. Pathophysiology and mechanisms of primary sarcopenia (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Balntzi, V.; Gray, S.R.; Lara, J.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deschenes, M.R. Effects of aging on muscle fibre type and size. Sports Med. 2004, 34, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournadre, A.; Vial, G.; Capel, F.; Soubrier, M.; Boirie, Y. Sarcopenia. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzuya, M. Drug-related sarcopenia as a secondary sarcopenia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, M.; Cappellesso, F.; Amorim, R.; Serneels, J.; Virga, F.; Eelen, G.; Carobbio, S.; Rincon, M.Y.; Maechler, P.; De Bock, K.; et al. Macrophage-derived glutamine boosts satellite cells and muscle regeneration. Nature 2020, 587, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, H.; Kusumoto, D.; Hashimoto, H.; Yuasa, S. Stem cell aging in skeletal muscle regeneration and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Charville, G.W.; Cheung, T.H.; Yoo, B.; Santos, P.J.; Schroeder, M.; Rando, T.A. Impaired notch signaling leads to a decrease in p53 activity and mitotic catastrophe in aged muscle stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 544–556.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, D.; Bartlett, D.B.; Patel, H.P.; Roberts, H.C. Understanding how we age: Insights into inflammaging. Longev. Heal. 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Flato, U.A.P.; Tofano, R.J.; Goulart, R.d.A.; Guiguer, E.L.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Buchaim, D.V.; Araújo, A.C.; Buchaim, R.L.; Reina, F.T.R.; et al. Physical Exercise and Myokines: Relationships with Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scisciola, L.; Fontanella, R.A.; Surina; Cataldo, V.; Paolisso, G.; Barbieri, M. Sarcopenia and Cognitive Function: Role of My-okines in Muscle Brain Cross-Talk. Life 2021, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arosio, B.; Calvani, R.; Ferri, E.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Carandina, A.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V.; Marzetti, E.; Picca, A. Sarcopenia and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: Targeting the Muscle–Brain Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ye, R.; Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Xie, J.; Li, P. Association between sleep traits and sarcopenia-related traits: A two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Peng, W.; Jia, B.; Lin, P.; Yang, Z. Longitudinal association of sleep duration with possible sarcopenia: Evidence from CHARLS. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e079237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shibuki, T.; Iida, M.; Harada, S.; Kato, S.; Kuwabara, K.; Hirata, A.; Sata, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Osawa, Y.; Okamura, T.; et al. The association between sleep parameters and sarcopenia in Japanese community-dwelling older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 109, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Dong, B.; Yang, M. Association between sleep duration and sarcopenia among community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2017, 96, e6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chen, H.-C. The relationship of sleep duration with obesity and sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults. Gerontology 2015, 61, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Niu, R.; Lu, W.; Zeng, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, C. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with increased risk of early-onset sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity: Results from NHANES 2015–2018. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szlejf, C.; Suemoto, C.; Drager, L.; Griep, R.; Fonseca, M.; Diniz, M.; Lotufo, P.; Benseãor, I. Association of sleep disturbances with sarcopenia and its defining components: The ELSA-Brasil study. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xue, Z.; Song, S.; Hu, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Risk of Sarcopenia and Osteoporosis in Elderly Male Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Densitom. 2024, 27, 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, D.A.; Park, K.M. Sarcopenia in patients with isolated rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Sleep Med. 2024, 114, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, A.G.; Kaya, D.; Dost, F.S.; Ontan, M.S.; Isik, A.T. Sarcopenia Seems to Be Common in Older Patients With Restless Legs Syndrome. J. Cachex- Sarcopenia Muscle 2025, 16, e13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nagaura, Y.; Kondo, H.; Nagayoshi, M.; Maeda, T. Sarcopenia is associated with insomnia in Japanese older adults: A cross-sectional study of data from the Nagasaki Islands study. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Soysal, P.; Smith, L.; Tan, S.G.; Capar, E.; Veronese, N.; Yang, L. Excessive daytime sleepiness is associated with an increased frequency of falls and sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovezan, R.D.; Abucham, J.; dos Santos, R.V.T.; Mello, M.T.; Tufik, S.; Poyares, D. The impact of sleep on age-related sarcopenia: Possible connections and clinical implications. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 23, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, R.; Ohashi, Y.; Ozaki, A. Sleep disturbances in adults with frailty and sarcopenia. Qual. Ageing Older Adults 2020, 21, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-S.; Kim, H.C.; Zhang, D.; Yeom, H.; Lim, S.-K. The novel myokine irisin: Clinical implications and potential role as a biomarker for sarcopenia in postmenopausal women. Endocrine 2019, 64, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Park, K.; Kim, N.; Kong, I.D. Circulating irisin levels as a predictive biomarker for sarcopenia: A cross-sectional community-based study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S.; Iino, N.; Koda, R.; Narita, I.; Kaneko, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with sarcopenia and frailty in Japanese hemodialysis patients. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2021, 21, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-M.; Yan, J.-J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lu, X.; Shen, Z.-K.; Xu, J.-S.; Gao, W. Low serum Metrnl levels are associated with increased risk of sarcopenia in the older adults. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 15, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Soytas, R.B.; Suzan, V.; Arman, P.; Gedik, T.E.; Unal, D.; Cengiz, M.; Bolayirli, I.M.; Erdincler, D.S.; Doventas, A.; Yavuzer, H. Association of FGF-19 and FGF-21 levels with primary sarcopenia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2021, 21, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, A.; Silay, K.; Balik, A.R.; Avcioğlu, G.; Aydin, A.S. The relationship between plasma interleukin-15 levels and sarcopenia in outpatient older people. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H.; Kai, H.; Shibata, R.; Niiyama, H.; Nishiyama, Y.; Murohara, T.; Yoshida, N.; Katoh, A.; Ikeda, H.; Mogi, M. New diagnostic index for sarcopenia in patients with cardiovascular diseases. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Jang, H.Y.; Ahn, J.M.; Hwang, S.H.; Chung, J.W.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J.-W.; Jang, E.S.; Choi, G.H.; Jeong, S.-H. The association of the serum levels of myostatin, follistatin, and interleukin-6 with sarcopenia, and their impacts on survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, A.-L.; Hu, H.-Y.; Rong, Y.-D.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhou, X.-Z. A study on relationship between elderly sarcopenia and inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Hwang, H.; Kim, S.-K.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Bang, H.; Kwon, E.-S.; Lee, K.-P.; Chung, S.G.; Kwon, K.-S. Prediction of sarcopenia using a combination of multiple serum biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamijo, Y.; Kanda, E.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yoshida, M. Sarcopenia and frailty in PD: Impact on mortality, malnutrition, and inflammation. Perit. Dial. Int. J. Int. Soc. Perit. Dial. 2018, 38, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, R.M.; Mohamed, M.E.; Hammam, N.; El Fetoh, N.A.; Rashed, A.M.; Furst, D.E. Preliminary study of the association of serum irisin levels with poor sleep quality in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sleep Med. 2020, 67, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, D.; Cai, S. Association of serum irisin concentrations with the presence and severity of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 31, e22077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mikoteit, T.; Brand, S.; Eckert, A.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Beck, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a biomarker for subjective insomnia but not objectively assessable poor sleep continuity. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 110, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Kong, J. Correlation of serum meteorin-like concentration with the presence and severity of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 56, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaño Riera, M.; Santiago Sáez, A.; García Martín, Á.; Gómez Serrano, M.; Minoretti, P. Relation of Sleep Quality to a Panel of Plasma Cardiometabolic Markers in Airline Pilots: A Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e51650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stahl, S.T.; Smagula, S.F.; Rodakowski, J.; Dew, M.A.; Karp, J.F.; Albert, S.M.; Butters, M.; Gildengers, A.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd. Subjective Sleep Quality and Trajectories of Interleukin-6 in Older Adults. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 29, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fiedorczuk, P.; Olszewska, E.; Polecka, A.; Walasek, M.; Mroczko, B.; Kulczyńska-Przybik, A. Investigating the Role of Serum and Plasma IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-alpha, CRP, and S100B Concentrations in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, S.; Cui, F.; Ning, K.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Wang, D.; Xu, H. Role of irisin in physiology and pathology. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 962968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, D.; Müller, U.; Scheuermann, K.; Friebe, D.; Gesing, J.; Bielitz, J.; Erbs, S.; Landgraf, K.; Wagner, I.V.; Kiess, W.; et al. Serum Irisin Levels Are Regulated by Acute Strenuous Exercise. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsetti, I.; Palmini, G.; Donati, S.; Aurilia, C.; Iantomasi, T.; Brandi, M.L. Irisin and Its Role in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Jia, H. Circulating irisin levels in patients with sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 16, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, C.; Li, R.; Ma, Y.; Tang, X. Association between serum irisin concentrations and sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, A.; Sahin, M.; Tuzun, D.; Kurutas, E.B.; Ulgen, C.; Bozkus, O.; Gul, K. Irisin is a predictor of sarcopenic obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine 2021, 100, e26529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baek, J.Y.; Jang, I.-Y.; Jung, H.-W.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, E.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, E.; Kim, B.-J. Serum irisin level is independent of sarcopenia and related muscle parameters in older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 162, 111744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, H.; Guan, J.; Yi, H.; Zou, J. Association of the serum irisin level with obstructive sleep apnea: A body mass index- and physical activity-matched study. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazlıoğlu, N.; Uysal, P.; Durmus, S.; Yurt, S.; Gelisgen, R.; Uzun, H. Significance of Plasma Irisin, Adiponectin, and Retinol Binding Protein-4 Levels as Biomarkers for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Severity. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yildiz, H.; Alp, H.H. The role of irisin in predicting obstructive sleep apnea severity among obese individuals: A comparative analysis. Sleep Breath. 2024, 28, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carroll, J.E. Sleep Disturbance, Sleep Duration, and Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies and Experimental Sleep Deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jaspan, V.N.; Greenberg, G.S.; Parihar, S.; Park, C.M.; Somers, V.K.; Shapiro, M.D.; Lavie, C.J.; Virani, S.S.; Slipczuk, L. The Role of Sleep in Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2024, 26, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Faraguna, U.; Vyazovskiy, V.V.; Nelson, A.B.; Tononi, G.; Cirelli, C. A causal role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the homeostatic regulation of sleep. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4088–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, K.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Eckert, A. BDNF in sleep, insomnia, and sleep deprivation. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElGrawani, W.; Sun, G.; Kliem, F.P.; Sennhauser, S.; Pierre-Ferrer, S.; Rosi-Andersen, A.; Boccalaro, I.; Bethge, P.; Heo, W.D.; Helmchen, F.; et al. BDNF-TrkB signaling orchestrates the buildup process of local sleep. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muheim, C.M.; Singletary, K.G.; Frank, M.G. A chemical-genetic investigation of BDNF-NtrkB signaling in mammalian sleep. Sleep 2021, 45, zsab237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roh, E.; Hwang, S.Y.; Song, E.; Park, M.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Kim, M.; Won, C.W.; Choi, K.M. Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karim, A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Muhammad, T.; Qaisar, R. Evaluation of Sarcopenia Using Biomarkers of the Neuromuscular Junction in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.; Muhammad, T.; Qaisar, R. Prediction of Sarcopenia Using Multiple Biomarkers of Neuromuscular Junction Degeneration in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nakano, I.; Kinugawa, S.; Hori, H.; Fukushima, A.; Yokota, T.; Takada, S.; Kakutani, N.; Obata, Y.; Yamanashi, K.; Anzai, T. Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels Are Associated with Skeletal Muscle Function but Not with Muscle Mass in Patients with Heart Failure. Int. Heart J. 2020, 61, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, J.; Motanova, E.; Narici, M.V.; Boreham, C.; De Vito, G. Plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentrations are elevated in community-dwelling adults with sarcopenia. Age Ageing 2025, 54, afaf024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rao, R.R.; Long, J.Z.; White, J.P.; Svensson, K.J.; Lou, J.; Lokurkar, I.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Ruas, J.L.; Wrann, C.D.; Lo, J.C.; et al. Meteorin-like is a hormone that regulates immune-adipose interactions to increase beige fat thermogenesis. Cell 2014, 157, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomarasca, M.; Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G. Myokines: The endocrine coupling of skeletal muscle and bone. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 94, 155–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potthoff, M.J.; Inagaki, T.; Satapati, S.; Ding, X.; He, T.; Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Finck, B.N.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A.; et al. FGF21 induces PGC-1α and regulates carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism during the adaptive starvation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10853–10858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.-W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.A.; Jang, I.-Y.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Yi, H.-S.; Lee, E.; et al. Association between serum FGF21 level and sarcopenia in older adults. Bone 2021, 145, 115877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; He, X.; Deng, X.-Y.; Yan, J.-L. Exploring the correlation between serum fibroblast growth factor-21 levels and Sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L. The Associations of Serum Levels of Irisin and FGF21 with Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oflazoglu, U.; Caglar, S.; Yılmaz, H.E.; Önal, H.T.; Varol, U.; Salman, T.; Yildiz, Y.; Unal, S.; Guc, Z.G.; Kucukzeybek, Y.; et al. The relationship between sarcopenia detected in newly diagnosed colorectal cancer patients and FGF21, irisin and CRP levels. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-W.; Yu, K.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Li, G.-X.; Jiang, L.-J.; Yu, S.-L.; Xu, L.-Y.; Liu, R.-J.; Guo, Z.-J.; Xie, H.-Y.; et al. Circulating factors associated with sarcopenia during ageing and after intensive lifestyle intervention. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, D.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zuo, J.; Zeng, C.; Mamtawla, G.; Huang, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Liver-secreted FGF21 induces sarcopenia by inhibiting satellite cell myogenesis via klotho beta in decompensated cirrhosis. Redox Biol. 2024, 76, 103333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandão, L.E.M.; Espes, D.; Westholm, J.O.; Martikainen, T.; Westerlund, N.; Lampola, L.; Popa, A.; Vogel, H.; Schürmann, A.; Dickson, S.L.; et al. Acute sleep loss alters circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 levels in humans: A randomised crossover trial. J. Sleep Res. 2022, 31, e13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zou, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Guan, J.; Yi, H.; Liu, S.; Yin, S. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is an independent predictor of prevalent and incident obstructive sleep apnea. iScience 2023, 26, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookout, A.L.; de Groot, M.H.M.; Owen, B.M.; Lee, S.; Gautron, L.; Lawrence, H.L.; Ding, X.; Elmquist, J.K.; Takahashi, J.S.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. FGF21 regulates metabolism and circadian behavior by acting on the nervous system. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, M.; Burgler, S.; Crameri, R.; Eiwegger, T.; Fujita, H.; Gomez, E.; Klunker, S.; Meyer, N.; O’Mahony, L.; Palomares, O.; et al. Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferon-γ: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 701–721.e70, Erratum in J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Duan, W.; Xu, P.; Lin, T.; Xiang, Q.; Dong, B.; Ge, N.; Yue, J. Exploring the impact of interleukins on sarcopenia development: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 193, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-J.; Chao, Y.-J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wang, H.-C.; Tung, H.-L.; Lin, J.-T.; Shan, Y.-S. Elevated Serum Interleukin-8 Level Correlates with Cancer-Related Cachexia and Sarcopenia: An Indicator for Pancreatic Cancer Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, C.T.; Quinn, L.S. Sarcopenia, obesity, and natural killer cell immune senescence in aging: Altered cytokine levels as a common mechanism. Aging 2012, 4, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohleder, N.; Aringer, M.; Boentert, M. Role of interleukin-6 in stress, sleep, and fatigue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1261, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, R.; Ren, X.; He, J. Interleukin-8 concentrations in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10666–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, Y.; Gu, K.; Meng, C.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yan, D.; Li, D.; Pei, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Relationship between sleep and serum inflammatory factors in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 329, 115528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.; Huang, H. Inflammation and aging: Signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dattilo, M.; Antunes, H.; Medeiros, A.; Neto, M.M.; Souza, H.; Tufik, S.; de Mello, M. Sleep and muscle recovery: Endocrinological and molecular basis for a new and promising hypothesis. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 77, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopidis, K.; Dionyssiotis, Y. Effects of sleep deprivation on sarcopenia and obesity: A narrative review of randomized controlled and crossover trials. J. Frailty Sarcopenia Falls 2021, 6, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| No. | Title and Authors | Country | Study Population | Sarcopenia Parameters/ Diagnostic Criteria (1–11) | Main Findings | Study Design | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Age | Gender | Sleep Disturbances Parameters (12–18) | |||||
| Sarcopenia-related studies | ||||||||
| 1. | Park H.S. et al. [29] | South Korea | 153 + 147 in control group | 60+ | Females | Quadriceps cross-sectional area, bone mineral density, liver attenuation in CT; muscle strength and physical performance were evaluated by handgrip test and short physical performance battery, respectively. | Circulating irisin was significantly lower in the sarcopenia group. Positive correlation with quadriceps cross-sectional area and liver attenuation was observed. | Cross-sectional |
| 2. | Chang J.S. et al. [30] | South Korea | 715 | 18–90 | Females and males | Skeletal muscle mass defined as the sum of appendicular lean mass from all four limbs and adjusted for height squared in meters. Handgrip strength measured by a dynamometer. | Circulating irisin levels were correlated with appendicular lean mass/height2 and handgrip strength in both sexes (all p < 0.01). The mean circulating irisin levels were lower in the sarcopenia group than in the control group. | Cross-sectional |
| 3. | Miyazaki S. et al. [31] | Japan | 20 | 65+ | Females and males | Handgrip strength, 6 m walk test, Short Physical Performance Battery, 5-times chair stand test | BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor) serum levels are significantly lower among patients with sarcopenia and frailty. | Cross-sectional |
| 4. | Wang Z.Y. et al. [32] | China | 772 | 65+ | Females and males | Muscle mass measured by bioimpedance analysis; grip strength measured by dynamometer; appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; 6 m walk test | Patients with sarcopenia had significantly lower Metrnl serum levels than healthy controls. | Cross-sectional |
| 5. | Bag Soytas R. et al. [33] | Turkey | 88 | 65+ | Females and males | Sarcopenia was determined by handgrip strength (HGS), bioelectrical impedance analysis and 6 m walk test. | Study revealed a positive correlation with the 6 min walk test and inverse correlation with the handgrip strength. Study indicate higher FGF-21 serum levels among sarcopenic patients than healthy controls. | Cross-sectional |
| 6, | Yalcin A. et al. [34] | Turkey | 160 | 65+ | Females and males | Skeletal muscle mass was measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). Handgrip strength was measured using a handheld digital dynamometer. Muscle function by 4 m gait speed. Sarcopenia was diagnosed according to the EWGSOP (European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People) criteria. | Study showed lower IL-15 levels among sarcopenic patients. | Cross-sectional |
| 7. | Harada H. et al. [35] | Japan | 132 | 27–93 | Females and males | Sarcopenia was determined by AWGS (Asian Working Group on Sarcopenia) diagnosis criteria. | Serum levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in sarcopenic than in non-sarcopenic patients. | Retrospective |
| 8. | Choi K. et al. [36] | Korea | 238 | 60+ | Females and males | Sarcopenia was determined by Psoas Muscle Index. | Serum levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in sarcopenic than in non-sarcopenic patients. | Prospective cohort |
| 9. | Bian A.L. et al. [37] | China | 441 | 60+ | Females and males | Sarcopenia was determined by EWGSOP diagnostic criteria. | Serum levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in sarcopenic than in non-sarcopenic patients. | Cross-sectional |
| 10. | Kwak Y. et al. [38] | Korea | 96 | 60+ | Females and males | Sarcopenia was determined by AWGS diagnostic criteria. | Serum levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in sarcopenic than in non-sarcopenic patients. | Prospective longitudinal |
| 11. | Kamijo Y. et al. [39] | Japan | 119 | 66+ | Females and males | Sarcopenia was determined by AWGS diagnostic criteria. | Serum levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in sarcopenic than in non-sarcopenic patients. | Prospective cohort |
| Sleep-disturbance-related studies | ||||||||
| 12. | Gamal R.M. et al. [40] | Egypt | 58 RA patients + 30 in control group | 18–71 | Females and males | Sleep quality was measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. | Irisin levels were lower in RA patients with poor sleep quality compared to RA patients with good sleep quality and healthy controls. | Cross-sectional |
| 13. | Li Y. et al. [41] | China | 165 + 98 in control group | 54 ± 6 | Males | Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) diagnosed through polysomnography. | OSA patients have lower irisin levels than healthy individuals. Among OSA patients, there were significantly lower irisin levels in severe OSA compared to moderate and mild. | Cross-sectional |
| 14. | Mikoteit T. et al. [42] | Switzerland | 60 + 30 in control group | 18–65 | Females and males | Total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency (ratio of TST to time in bed), sleep onset latency (SOL), number of awakenings, wake-time after sleep onset, sleep architecture measures measured from EEG (electroencephalogram) records. | Patients suffering from insomnia have significantly lower BDNF levels than healthy controls. | Case-control |
| 15. | Sun H. et al. [43] | China | 207 + 106 in control group | 54 ± 6 | Males | OSA diagnosed through polysomnography. | OSA patients had significantly lower serum concentration of the meteorin-like protein than healthy controls, and among OSA patients, a higher severity of disease was associated with lower concentrations of meteorin. | Cross-sectional |
| 16. | Liaño Riera M. et al. [44] | Spain | 117 | 41 ± 6 | Males | Sleep quality was measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. | The study demonstrated that sleep disturbances among airline pilots are correlated with significantly higher levels of FGF-21 and GDF-15 as well as lower levels of adiponectin. | Cross-sectional |
| 17. | Stahl S.T. et al. [45] | USA | 195 | 60+ | Females and males | Sleep quality was measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. | Older adults with worse sleep quality often have chronically high levels of IL-6. | Longitudinal |
| 18. | Fiedorczuk P. et al. [46] | Poland | 80 | 20–65 | Females and males | OSA diagnosed through polysomnography. | There are increased IL-6 and IL-8 levels among obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients. | Case-control |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knapik, M.; Kuna, J.; Chmielewski, G.; Jaśkiewicz, Ł.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M. Alterations in the Myokine Concentrations in Relation to Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186527
Knapik M, Kuna J, Chmielewski G, Jaśkiewicz Ł, Krajewska-Włodarczyk M. Alterations in the Myokine Concentrations in Relation to Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186527
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnapik, Michalina, Jakub Kuna, Grzegorz Chmielewski, Łukasz Jaśkiewicz, and Magdalena Krajewska-Włodarczyk. 2025. "Alterations in the Myokine Concentrations in Relation to Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances: A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186527
APA StyleKnapik, M., Kuna, J., Chmielewski, G., Jaśkiewicz, Ł., & Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M. (2025). Alterations in the Myokine Concentrations in Relation to Sarcopenia and Sleep Disturbances: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186527







