Circulating miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer: A Two-Phase Plasma-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Pancreatic Cancer Patients
3.2. Biochemical Alterations and Tumor Pathological Features
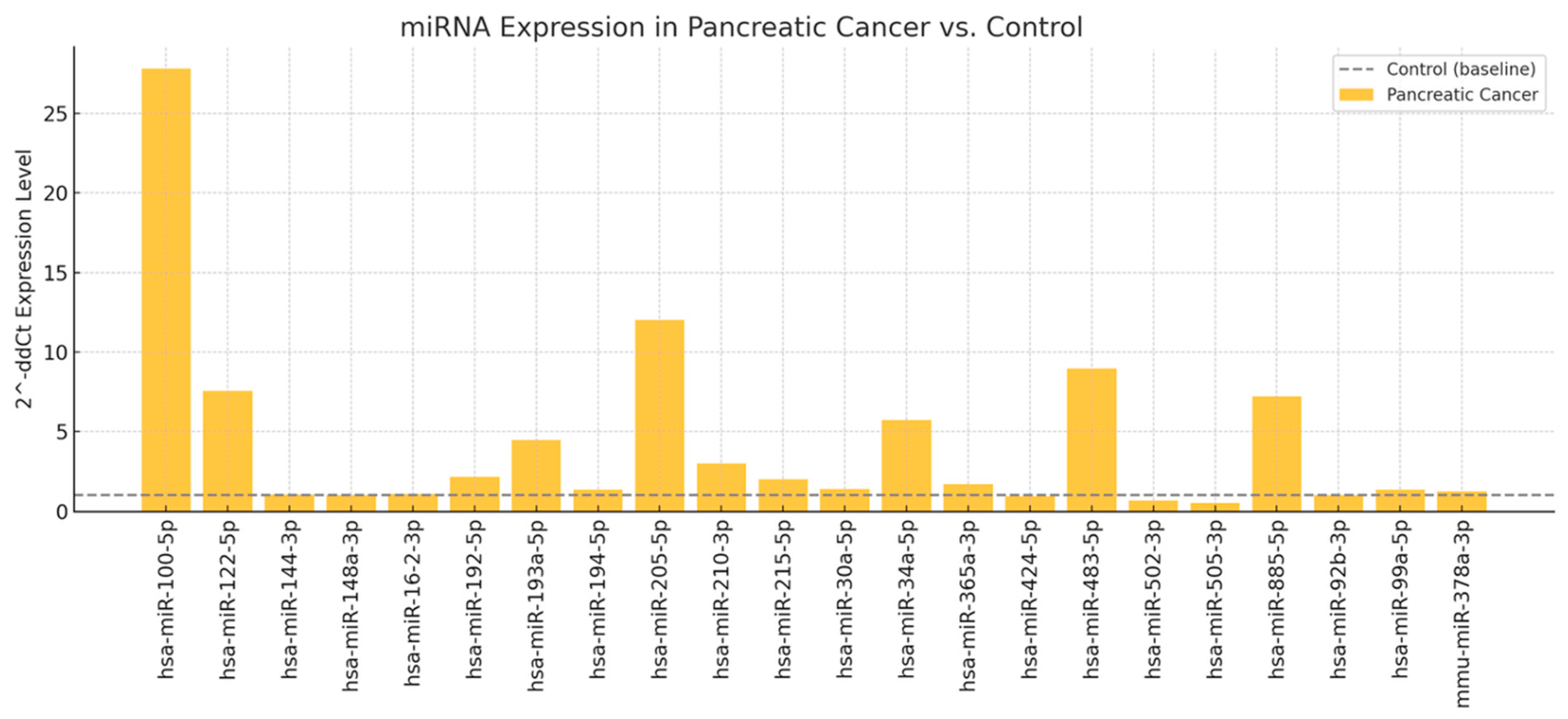
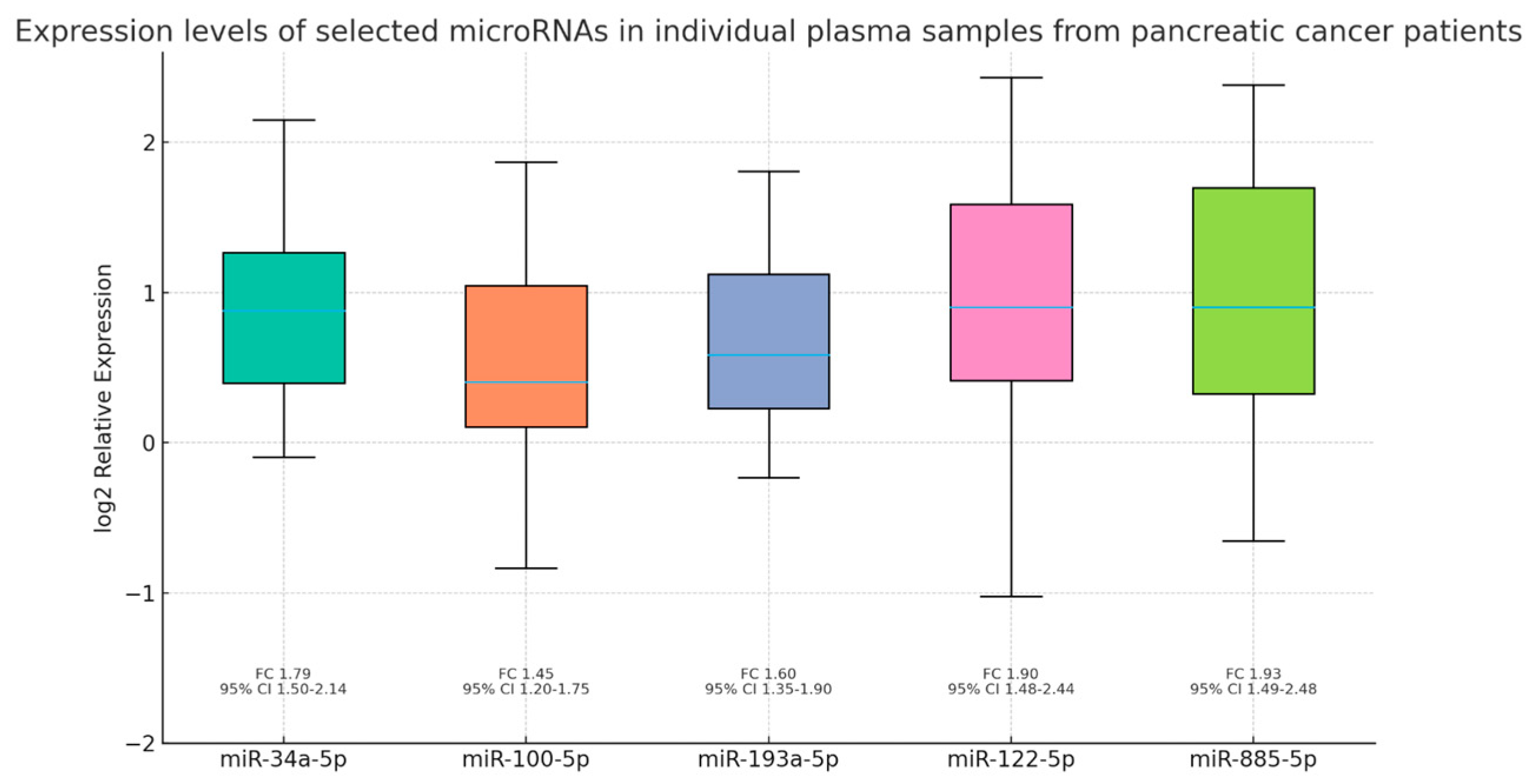
3.3. Differential Expression and Validation of Circulating miRNAs
4. Discussion
4.1. Patient Characteristics
4.2. Validation of Circulating miRNAs
4.3. Comparison with Literature
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawat, M.; Kadian, K.; Gupta, Y.; Kumar, A.; Chain, P.S.G.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Kumar, S.; Parasher, G. MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer: From biology to therapeutic potential. Genes 2019, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V.; The, C. Elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoud, A.Z.; Mulholland, E.J.; Cole, G.; McCarthy, H.O. MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer: Biomarkers, prognostic and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimasa, S.; Peter, J.M. Epigenetic Activation of Tumor Suppressor MicroRNAs in Human Cancer Cells. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2220–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.; Kupcinskas, J. MicroRNAs as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer: Current insights and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3313–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sarkar, F.H. MicroRNA targeted therapeutic approach for pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Hu, L.; Badehnoosh, B. MicroRNA-1303 in cancer pathogenesis and therapy: Clinical implications for biomarker development and targeted treatment strategies. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Kenoki, O.; Kazuhiro, M.; Norihiro, S.; Tadashi, K.; Hayato, F.; Kouhei, N.; Masao, T. MicroRNA, hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but increases cell proliferation. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.J.; Gusev, Y.; Jiang, J.; Nuovo, G.J.; Lerner, M.R.; Frankel, W.L.; Morgan, D.L.; Postier, R.G.; Brackett, D.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.H.; Park, I.Y. MicroRNA expression profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from surgical pancreatic cancer specimens. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2014, 87, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahovac, J.; Duric, A.; Tanic, M.; Krivokuca, A. Sex-Related Differences in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Progression and Response to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.M.; Turk, T.; Al-Husseini, M.J.; Abdel-Rahman, O. Trends in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Incidence and Mortality in the United States in the Last Four Decades; a SEER-Based Study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, S.; Abboud, Y.; Oh, J.; Samaan, J.S.; Nissen, N.N.; Lu, S.C.; Lo, S.K. Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer by Age and Sex in the US 2000–2008. JAMA 2021, 326, 2075–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshayedi, N.; Escobedo, A.L.; Thomassian, S.; Osipov, A.; Hendifar, A.E. Race, sex, age, and geographic disparities in pancreatic cancer incidence. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, G.; Ionescu, V.A.; Moldovan, H.; Diaconu, C.C. Clinical and Biological Data in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer vs. Chronic Pancreatitis—A Single Center Comparative Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunovsky, L.; Dite, P.; Jabandziev, P.; Dolina, J.; Vaculova, J.; Blaho, M.; Bojkova, M.; Dvorackova, J.; Uvirova, M.; Kala, Z.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and other bacteria in pancreatic cancer and autoimmune pancreatitis. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, G.; Bungau, S.; Ilie, M.; Behl, T.; Vesa, C.M.; Brisc, C.; Bacalbasa, N.; Turi, V.; Costache, R.S.; Diaconu, C.C. Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer: The Key for Survival. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.D.; Canto, M.I.; Jaffee, E.M.; Simeone, D.M. Pancreatic Cancer: Pathogenesis, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Gastroenterology 2023, 163, 386–402.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Mei, W.; Zheng, Z.; Cao, F.; Liang, K.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Li, F. Exosomes secreted from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth by transferring miR-100-5p. Tissue Cell 2021, 73, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviani, S.; Stebbing, J.; Frampton, A.E.; Zagorac, S.; Krell, J.; de Giorgio, A.; Trabulo, S.M.; Nguyen, V.T.M.; Magnani, L.; Fent, H.; et al. TGF-β induces miR-100 and miR-125b but blocks let-7a through LIN28B controlling PDAC progression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, T.; Gioffreda, D.; Fontana, A.; Biagini, T.; Carella, M.; Palumbo, O.; Maiello, E.; Bazzocchi, F.; Andriulli, A.; Tavano, F. Clinical Significance of Circulating miR-1273g-3p and miR-122-5p in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, M. MicroRNA-122-5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting CCNG1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganepola, G.A.; Rutledge, J.R.; Suman, P.; Yiengpruksawan, A.; Chang, D.H. Novel blood-based microRNA biomarker panel for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Sastre, A.; Lubeseder-Martellato, C.; Engleiner, T.; Steiger, K.; Zhong, S.; Desztics, J.; Ollinger, R.; Rad, R.; Schmid, R.M.; Hermeking, H.; et al. Mir34a constrains pancreatic carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, Y.S. miR-34a inhibits pancreatic cancer progression through Snail1-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition and the Notch signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 28232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamony, M.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Ge, L.; Sojitra, P.; Bapana, S.; Norton, J.A.; Gondi, C.S. Circular dumbbell miR-34a-3p and −5p suppresses pancreatic tumor cell-induced angiogenesis and activates macrophages. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Deng, S.; Ni, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Pan, Y. miR-193a-5p promotes pancreatic cancer cell metastasis through SRSF6-mediated alternative splicing of OGDHL and ECM. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 38–59. [Google Scholar]
- Vila-Navarro, E.; Fernandez-Castaner, E.; Rovira-Rigau, M.; Raimondi, G.; Vila-Casadesus, M.; Lozano, J.J.; Soubeyran, P.; Iovanna, J.; Castells, A.; Fillat, C.; et al. MiR-93 is related to poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer and promotes tumor progression by targeting microtubule dynamics. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasani, F.; Masrour, M.; Khamaki, S.; Jazi, K.; Hosseini, S.; Heidarpour, H.; Namazee, M. Diagnostic and Prognostic Accuracy of MiRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadjim, R.; An, T.; Cui, J. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Advances in Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
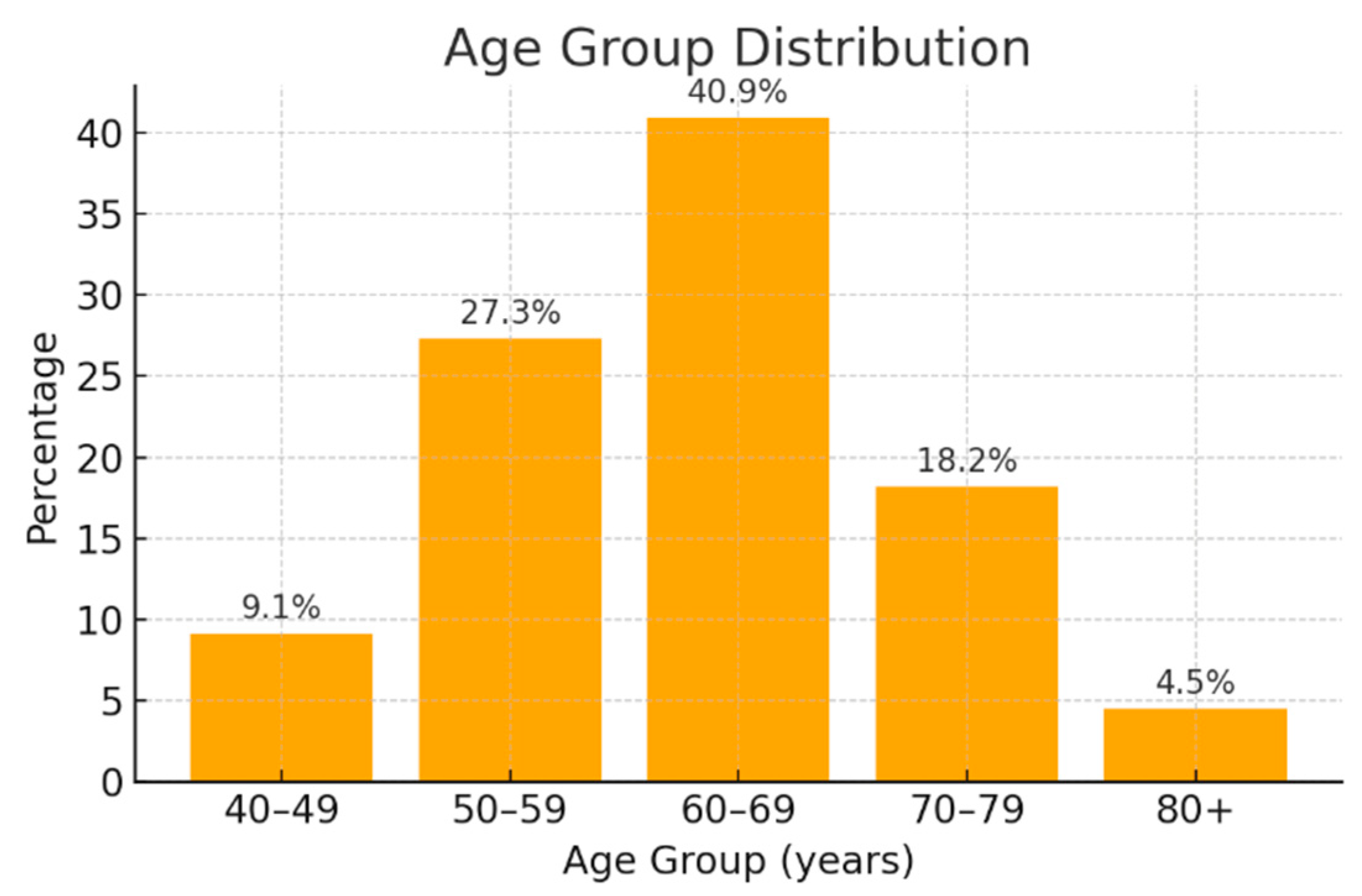
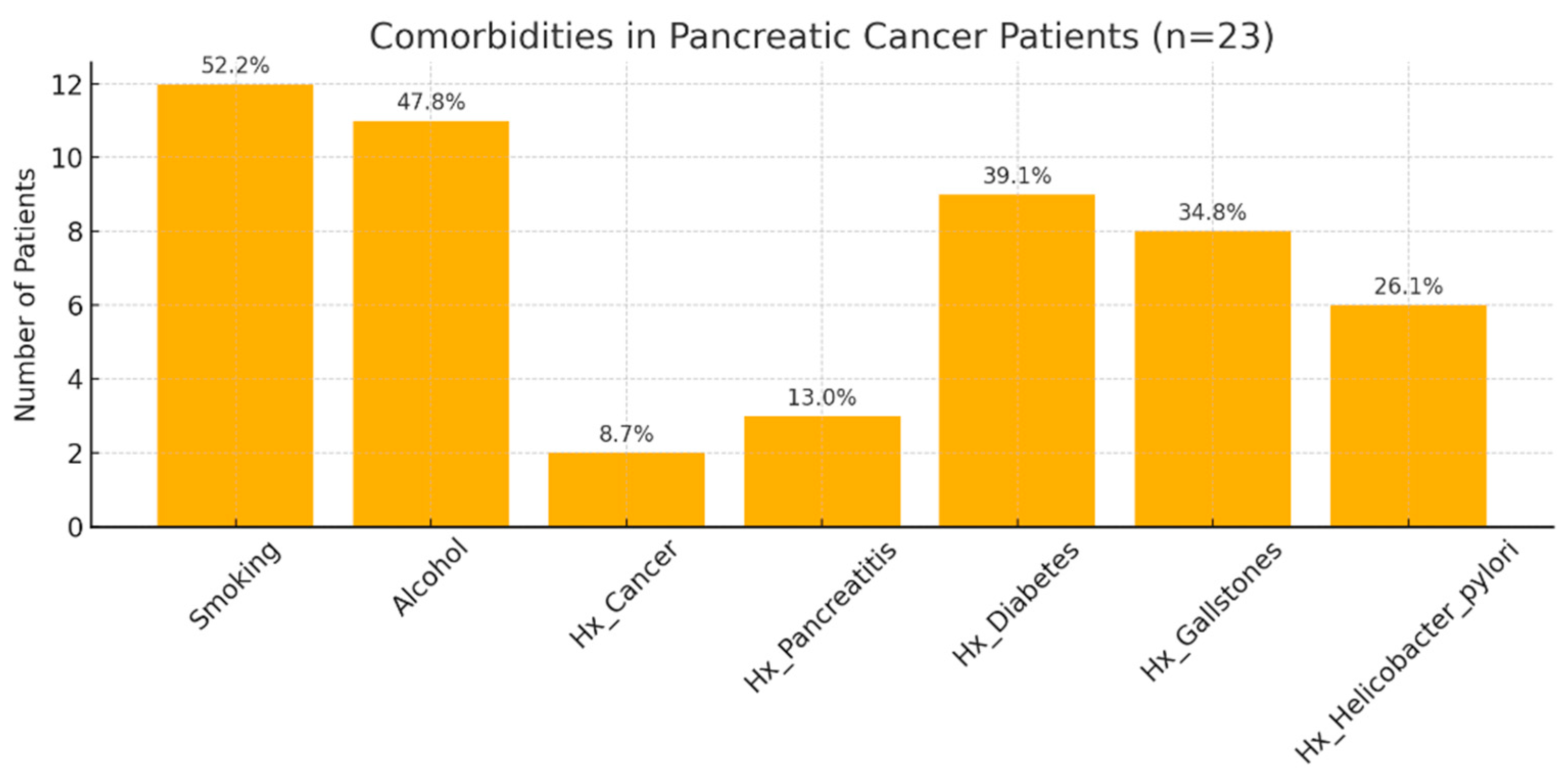
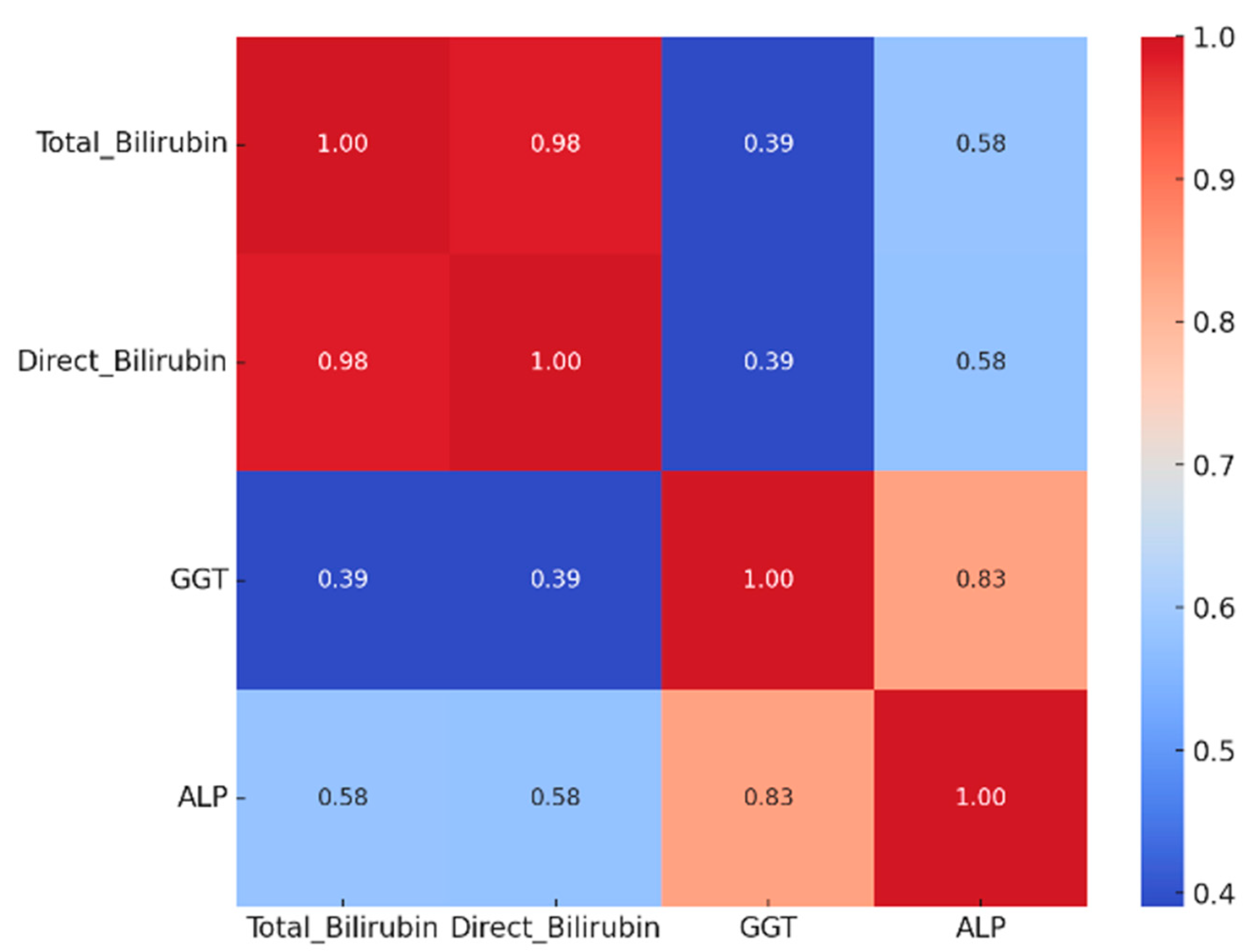
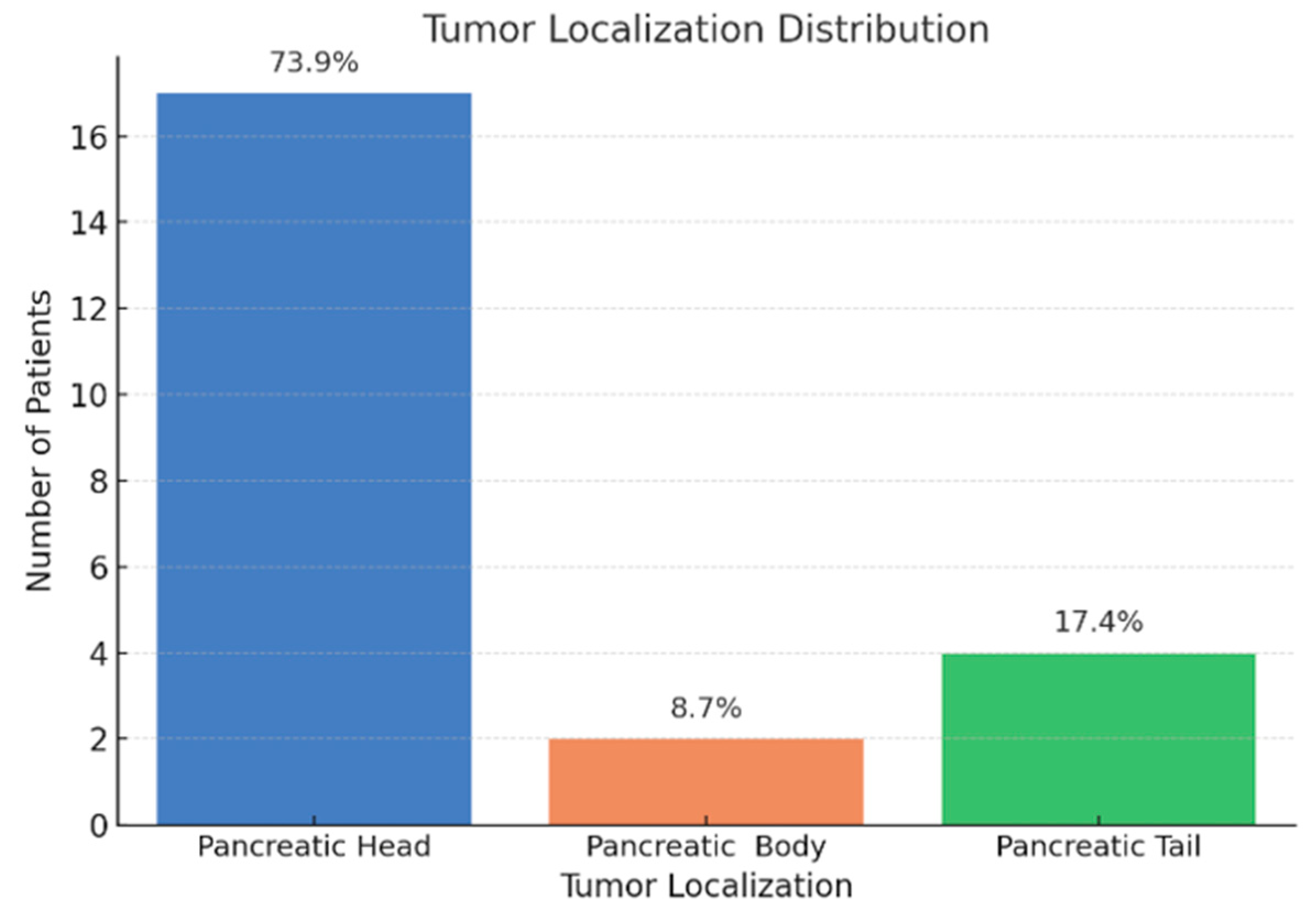

| Biological Marker | Mean | Std | Min | 25% | 50% | 75% | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 12.11 | 1.53 | 8.5 | 11.25 | 12.22 | 13.1 | 14.7 |
| White blood cells | 7985.65 | 3119.04 | 3720.0 | 5455.0 | 7010.0 | 9605.0 | 15,300.0 |
| Platelets | 263,695.65 | 90,904.13 | 89,800.0 | 205,800.0 | 242,000.0 | 317,500.0 | 428,000.0 |
| Glucose | 118.7 | 35.03 | 78.0 | 101.0 | 115.0 | 126.5 | 247.0 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 218.13 | 225.36 | 17.0 | 35.5 | 156.0 | 256.0 | 724.0 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 284.22 | 333.0 | 15.0 | 53.0 | 125.0 | 467.5 | 1039.0 |
| Amylase | 115.33 | 125.01 | 10.6 | 43.5 | 52.0 | 153.5 | 519.0 |
| Lipase | 437.8 | 684.96 | 7.0 | 61.2 | 88.5 | 515.75 | 2811.0 |
| Total Bilirubin | 10.39 | 12.16 | 0.43 | 1.12 | 4.2 | 18.12 | 40.29 |
| Direct Bilirubin | 7.97 | 9.78 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 3.08 | 14.34 | 29.0 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase | 674.04 | 861.81 | 10.0 | 131.0 | 256.0 | 849.0 | 3086.0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 426.49 | 336.99 | 50.28 | 183.5 | 324.0 | 610.5 | 1225.0 |
| Cholesterol | 188.3 | 60.06 | 120.0 | 136.4 | 183.0 | 223.5 | 355.0 |
| Triglycerides | 166.61 | 102.03 | 67.0 | 112.5 | 133.0 | 171.5 | 485.0 |
| C-reactive protein | 30.67 | 13.63 | 0.93 | 23.0 | 32.0 | 40.06 | 56.0 |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 35.8 | 17.27 | 0.4 | 30.5 | 34.0 | 42.5 | 70.0 |
| Uric acid | 5.59 | 1.1 | 3.0 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 6.35 | 7.2 |
| Predictor | miR-34a-5p 95% CI 1 p Value Pearson r R2 | miR-100-5p 95% CI 1 p Value Pearson r R2 | miR-193a-5p 95% CI 1 p Value Pearson r R2 | miR-122-5p 95% CI 1 p Value Pearson r R2 | miR-885-5p 95% CI 1 p Value Pearson r R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor stage | 3.44–4.22 0.04 0.213 0.045 | 3.52–4.08 0.004 0.398 0.158 | 3.49–4.17 0.01 0.238 0.057 | 3.49–4.21 0.01 0.186 0.034 | 3.47–4.16 0.02 0.202 0.041 |
| Age | 0.03–0.01 0.40 −0.183 0.033 | 0.03–0.02 0.55 −0.130 0.017 | 0.03–0.01 0.56 −0.126 0.016 | 0.05–0.02 0.44 −0.166 0.028 | 0.04–0.02 0.56 −0.126 0.016 |
| Gender | 0.79–0.40 0.50 −0.146 0.021 | 0.91–0.34 0.35 −0.202 0.041 | 0.77–0.35 0.44 −0.167 0.028 | 0.89–0.81 0.92 −0.021 0.000 | 0.93–0.80 0.87 −0.036 0.001 |
| Smoking | 0.91–1.77 0.53 −0.203 0.041 | 0.97–1.64 0.22 −0.387 0.150 | 0.94–1.73 0.45 −0.248 0.062 | 0.95–1.78 0.62 −0.150 0.022 | 0.94–1.72 0.44 −0.249 0.062 |
| Alcohol consumption | 1.20–1.99 0.53 −0.064 0.004 | 1.35–1.99 0.81 −0.081 0.007 | 1.28–2.02 0.74 −0.036 0.001 | 1.19–1.94 0.37 −0.087 0.008 | 1.22–1.95 0.42 −0.124 0.015 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.33–2.17 0.36 0.085 0.007 | 1.34–2.02 0.47 −0.041 0.002 | 1.31–2.09 0.47 0.019 0.000 | 1.35–2.15 0.33 −0.029 0.001 | 1.32–2.10 0.44 −0.002 0.000 |
| Acute/Chronic pancreatitis | 1.60–2.22 0.60 0.137 0.019 | 1.63–2.13 0.67 0.115 0.013 | 1.65–2.21 0.44 0.176 0.031 | 1.68–2.26 0.29 0.230 0.053 | 1.62–2.20 0.49 0.161 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Bleotu, C.; Puiu, L.; Mambet, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Diaconu, C.C. Circulating miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer: A Two-Phase Plasma-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186430
Ionescu VA, Gheorghe G, Bleotu C, Puiu L, Mambet C, Diaconu CC, Diaconu CC. Circulating miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer: A Two-Phase Plasma-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186430
Chicago/Turabian StyleIonescu, Vlad Alexandru, Gina Gheorghe, Coralia Bleotu, Liliana Puiu, Cristina Mambet, Camelia Cristina Diaconu, and Carmen Cristina Diaconu. 2025. "Circulating miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer: A Two-Phase Plasma-Based Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186430
APA StyleIonescu, V. A., Gheorghe, G., Bleotu, C., Puiu, L., Mambet, C., Diaconu, C. C., & Diaconu, C. C. (2025). Circulating miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer: A Two-Phase Plasma-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186430









