The Combination of Atrial Fibrillation and Occlusion Site Predicts In Situ Atherosclerotic Thrombosis in Basilar Artery Occlusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Classification of the Stroke Mechanism
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Univariable and Multivariable Analyses of Potential Factors for BAO Due to ISAT
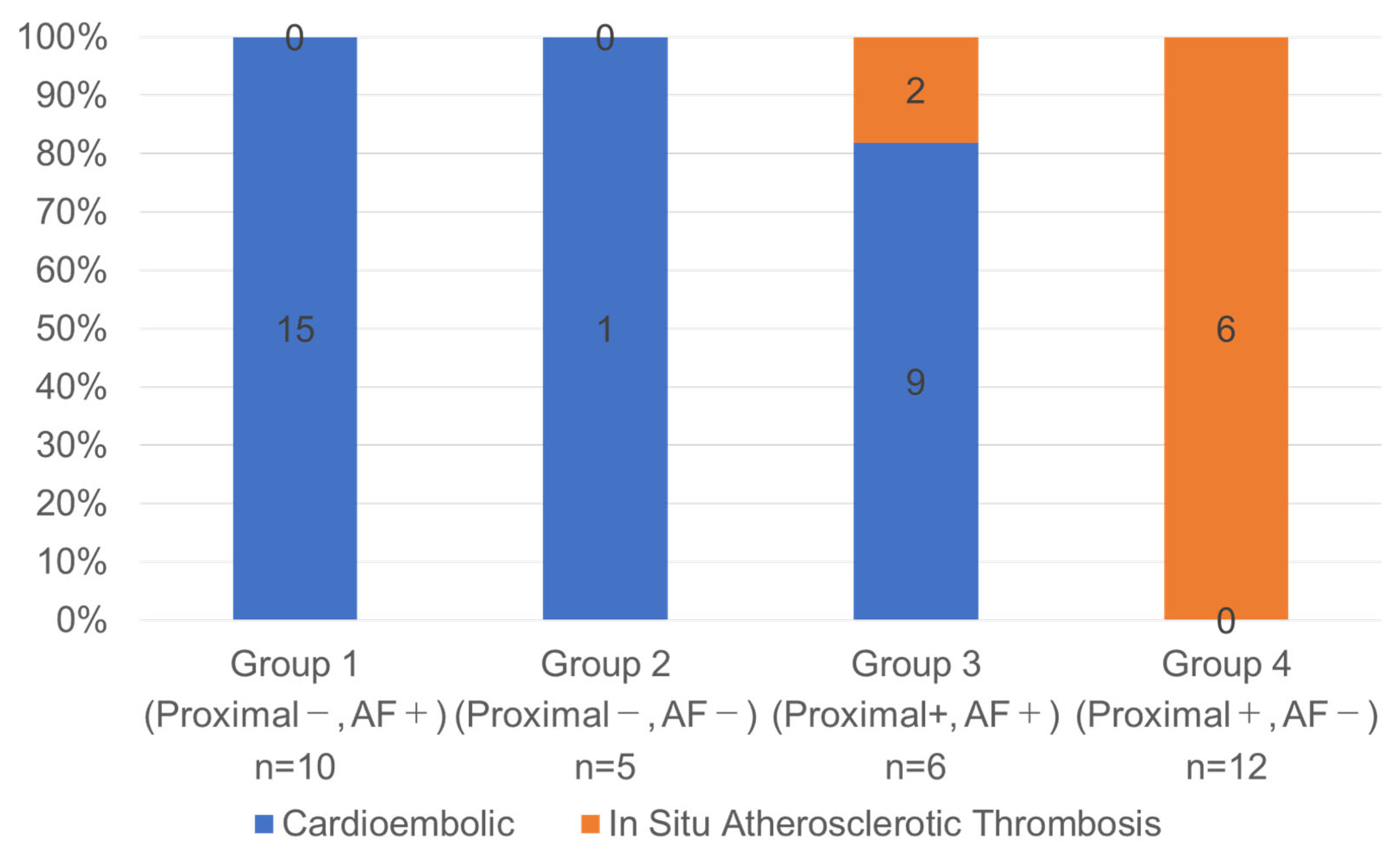
3.3. Classifications Based on the Combination of AF Status and the Presence of Proximal Occlusion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| BAO | basilar-artery occlusion |
| CE | cardioembolic |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| EVT | endovascular treatment |
| HAS | hyperdense artery sign |
| HT | hypertension |
| ISAT | in situ atherosclerotic thrombosis |
| LVO | large vessel occlusion |
| MRA | magnetic resonance angiography |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| pc-ASPECTS | posterior circulation Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score |
References
- Smith, W.S.; Lev, M.H.; English, J.D.; Camargo, E.C.; Chou, M.; Johnston, S.C.; Gonzalez, G.; Schaefer, P.W.; Dillon, W.P.; Koroshetz, W.J.; et al. Significance of large vessel intracranial occlusion causing acute ischemic stroke and TIA. Stroke 2009, 40, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsberg, P.J.; Sairanen, T.; Nagel, S.; Salonen, O.; Silvennoinen, H.; Strbian, D. Recanalization treatments in basilar artery occlusion-Systematic analysis. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 1, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Strbian, D. Endovascular Therapy for Stroke due to Basilar Artery Occlusion: A BASIC Challenge at BEST. Stroke 2021, 52, 3410–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovin, T.G.; Li, C.; Wu, L.; Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Jiang, C.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Z.; Song, C.; Chen, W.; et al. Trial of Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke Due to Basilar-Artery Occlusion. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Nogueira, R.G.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, H.; Yuan, G.; Wen, C.; Zhou, P.; Chen, W.; Zeng, G.; et al. Trial of Endovascular Treatment of Acute Basilar-Artery Occlusion. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Raynald; Tong, X.; Gao, F.; Deng, Y.; Ma, G.; Ma, N.; Mo, D.; Song, L.; Liu, L.; et al. Analysis of Treatment Outcome After Endovascular Treatment in Different Pathological Subtypes of Basilar Artery Occlusion: A Single Center Experience. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, G.; Zeng, H.; Yu, Y.; Yue, F.; Ke, Y.; Yan, Z.; Pu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; et al. Endovascular treatment for acute basilar artery occlusion due to different stroke etiologies of large artery atherosclerosis and cardioembolism. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierzwa, A.T.; Al Kasab, S.; Nelson, A.; Gutierrez, S.O.; Vivanco-Suarez, J.; Farooqui, M.; Jadhav, A.P.; Desai, S.; Toth, G.; Alrohimi, A.; et al. Thrombectomy Outcomes in Acute Basilar Artery Occlusions Due to Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease. Neurosurgery 2024, 95, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Nguyen, T.N.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Xia, H.; Long, C.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, F.; He, B.; et al. Effect of Stroke Etiology on Endovascular Treatment for Acute Basilar-Artery Occlusion: A Post Hoc Analysis of the ATTENTION Randomized Trial. Stroke 2024, 55, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychogios, M.; Brehm, A.; López-Cancio, E.; De Marchis, G.M.; Meseguer, E.; Katsanos, A.H.; Kremer, C.; Sporns, P.; Zedde, M.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. European Stroke Organisation guidelines on treatment of patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, III–IV. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Havenon, A.; Zaidat, O.O.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Nguyen, T.N.; Bangad, A.; Abbasi, M.; Anadani, M.; Almallouhi, E.; Chatterjee, R.; Mazighi, M.; et al. Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke due to Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease: Identification, Medical and Interventional Treatment, and Outcomes. Stroke 2023, 54, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Baek, B.; Kim, G.; Kim, J.; Park, M. Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion: Differences in Characteristics and Outcomes after Endovascular Therapy between Patients with and without Underlying Severe Atherosclerotic Stenosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, C.K.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D.J. Mechanical Thrombectomy in Subtypes of Basilar Artery Occlusion: Relationship to Recanalization Rate and Clinical Outcome. Radiology 2019, 291, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Higashida, R.T. Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion: Latest Findings and Critical Thinking on Future Study Design. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutke, M.A.; Potreck, A.; Schmitt, N.; Seker, F.; Ringleb, P.A.; Nagel, S.; Möhlenbruch, M.A.; Bendszus, M.; Weyland, C.S.; Jesser, J. Exact Basilar Artery Occlusion Location Indicates Stroke Etiology and Recanalization Success in Patients Eligible for Endovascular Stroke Treatment. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2023, 33, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tung, T.-H.; He, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Du, W.; Li, C.; et al. A simple score to predict atherosclerotic or embolic intracranial large-vessel occlusion stroke before endovascular treatment. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 137, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Qin, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, W. Development and internal-external validation of the ATHE Scale: Predicting acute large vessel occlusion due to underlying intracranial atherosclerosis prior to endovascular treatment. J Neurosurg. 2024, 141, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, M.; Wu, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, K.; Yang, Q.; Cai, H.; Ji, Y.; Lv, Q.; Yang, D.; et al. A Pre-Interventional Scale to Predict in situ Atherosclerotic Thrombosis in Acute Vertebrobasilar Artery Occlusion Patients. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 648081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, K.; Nour, M.; Tateshima, S.; Jahan, R.; Duckwiler, G.; Saver, J.; Szeder, V. Posterior Circulation Thrombectomy-pc-ASPECT Score Applied to Preintervention Magnetic Resonance Imaging Can Accurately Predict Functional Outcome. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, e566–e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebeskind, D.S.; Sanossian, N.; Yong, W.H.; Starkman, S.; Tsang, M.P.; Moya, A.L.; Zheng, D.D.; Abolian, A.M.; Kim, D.; Ali, L.K.; et al. CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, D.T., 3rd; Moran, C.J.; Akins, P.T.; Angtuaco, E.E.; Diringer, M.N. Relationship between clot location and outcome after basilar artery thrombolysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1997, 18, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wake-Buck, A.K.; Gatenby, J.C.; Gore, J.C. Hemodynamic characteristics of the vertebrobasilar system analyzed using MRI-based models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Koh, S.-H.; Heo, S.H.; Chang, D.-I. Basilar Artery Plaque and Pontine Infarction Location and Vascular Geometry. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. The Longitudinal Distribution and Stability of Curved Basilar Artery Plaque: A Study Based on HR-MRI. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2021, 28, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, J.; Huang, R.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Qiu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, L. High-risk features of basilar artery atherosclerotic plaque. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1019036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Mei, L.; Zhang, C.; Xia, J.; Chen, H.; Qu, X.; Wu, J. Vessel wall imaging of vertebrobasilar artery configurations associated with posterior circulation infarction and high-risk atherosclerotic plaques. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | ISAT (n = 8) | CE (n = 25) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient demographics | |||
| Age (years) | 78 ± 11 | 83 ± 7.9 | 0.35 |
| Male | 4 (50) | 8 (32) | 0.42 |
| Risk factor | |||
| Hypertension | 8 (100) | 18 (72) | 0.15 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 5 (63) | 13 (52) | 0.70 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2 (25) | 13 (52) | 0.24 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0 (0) | 16 (64) | 0.003 |
| Smoking history (past or current) | 4 (50) | 11 (44) | 1.0 |
| History of ischemic stroke | 1 (13) | 6 (24) | 0.65 |
| Clinical manifestation | |||
| Symptom progression | 4 (50) | 5 (20) | 0.17 |
| Presence of coma on admission | 2 (25) | 14 (56) | 0.22 |
| Baseline NIHSS score | 14 ± 9.8 | 26 ± 13 | 0.033 |
| Radiological characteristics | |||
| Occlusion site | <0.001 | ||
| Proximal | 6 (75) | 1 (4) | |
| Middle | 2 (25) | 9 (36) | |
| Distal | 0 (0) | 15 (60) | |
| Hyperdense artery sign | 5 (63) | 22 (88) | 0.14 |
| pc-ASPECTS | 6.4 ± 2.3 | 6.7 ± 1.7 | 1.0 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age | 0.95 (0.86–1.03) | 0.216 | ||
| Male | 0.49 (0.10–2.32) | 0.359 | ||
| Hypertension | 6.89 (0.69–932.94) | 0.112 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.36 (0.06–1.71) | 0.203 | ||
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.46 (0.32–7.46) | 0.632 | ||
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.03 (0.00–0.32) | 0.001 | 0.03 (0.00–0.56) | 0.014 |
| Smoking history | 1.26 (0.27–5.96) | 0.765 | ||
| Symptom progression | 4.00 (0.73–21.8) | 0.109 | ||
| Presence of coma on admission | 0.26 (0.04–1.56) | 0.141 | ||
| Baseline NIHSS score | 0.94 (0.87–1.00) | 0.067 | ||
| Hyperdense artery sign | 0.24 (0.04–1.44) | 0.117 | ||
| pc-ASPECTs | 0.91 (0.60–1.40) | 0.649 | ||
| Occlusion site (distal/middle) | 0.02 (0.00–0.17) | <0.001 | 0.02 (0.00–0.27) | 0.001 |
| Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | PPV, % | NPV, % | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrial fibrillation | 100 | 64 | 47 | 100 | 0.820 |
| Proximal occlusion | 75 | 96 | 86 | 82 | 0.855 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hashimoto, Y.; Ikawa, F.; Kawano, R.; Hidaka, T.; Inoue, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Horie, N. The Combination of Atrial Fibrillation and Occlusion Site Predicts In Situ Atherosclerotic Thrombosis in Basilar Artery Occlusion. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186384
Hashimoto Y, Ikawa F, Kawano R, Hidaka T, Inoue Y, Yamamoto Y, Horie N. The Combination of Atrial Fibrillation and Occlusion Site Predicts In Situ Atherosclerotic Thrombosis in Basilar Artery Occlusion. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186384
Chicago/Turabian StyleHashimoto, Yukishige, Fusao Ikawa, Reo Kawano, Toshikazu Hidaka, Yusuke Inoue, Yusuke Yamamoto, and Nobutaka Horie. 2025. "The Combination of Atrial Fibrillation and Occlusion Site Predicts In Situ Atherosclerotic Thrombosis in Basilar Artery Occlusion" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186384
APA StyleHashimoto, Y., Ikawa, F., Kawano, R., Hidaka, T., Inoue, Y., Yamamoto, Y., & Horie, N. (2025). The Combination of Atrial Fibrillation and Occlusion Site Predicts In Situ Atherosclerotic Thrombosis in Basilar Artery Occlusion. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186384







