The Efficacy and Safety of Deferasirox Monotherapy as a Second-Line Treatment in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Iron Overload
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target Patients and Study Design
2.2. Efficacy Assessments
2.3. Adverse Event Assessments
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
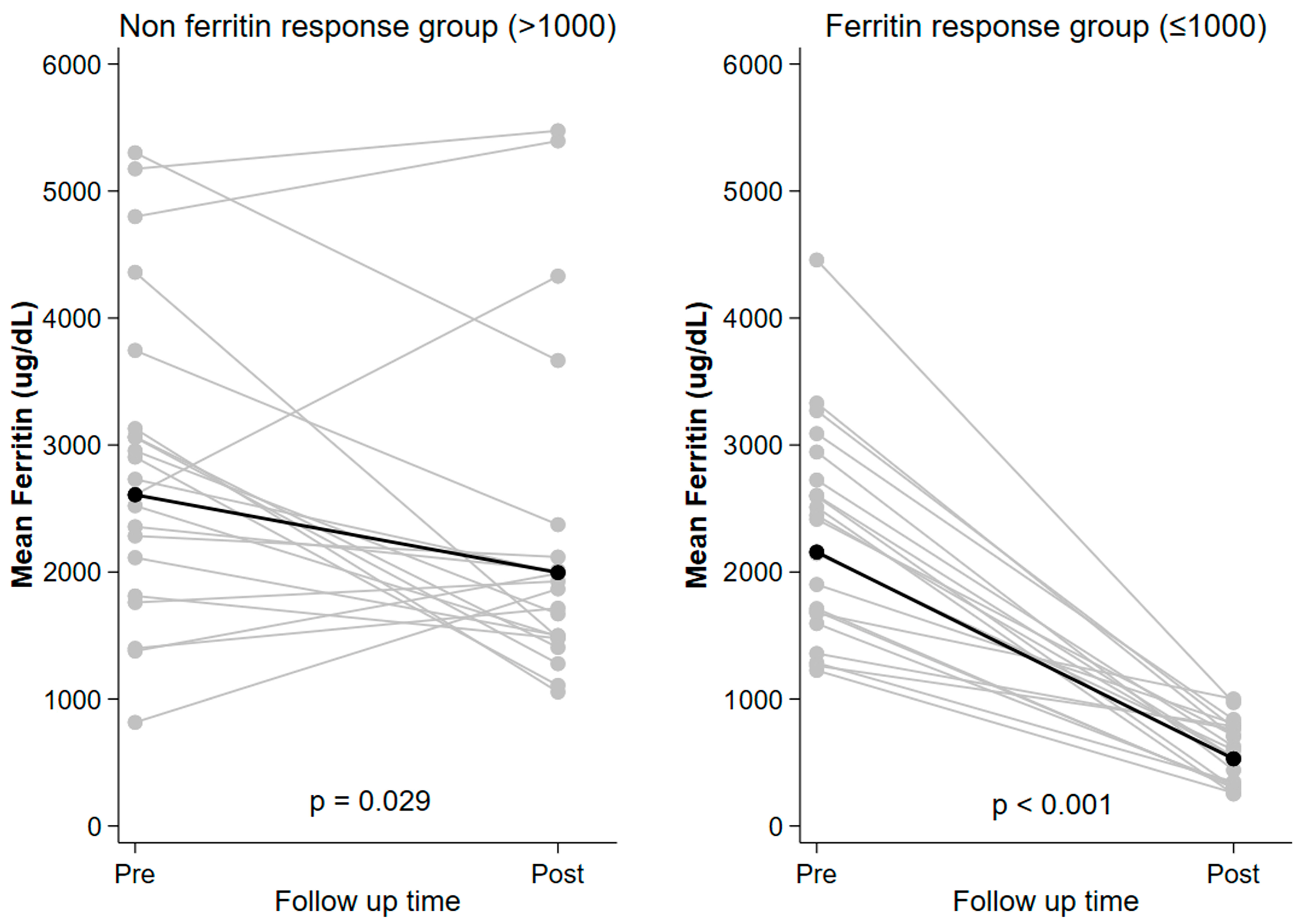
3.2. Efficacy of Deferasirox
3.3. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFX | deferasirox |
| SF | serum ferritin |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| DLP | Dyslipidemia |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| TDT | transfusion-dependent thalassemia |
| NLEM | National List of Essential Medicines |
| TIF | Thalassemia International Federation |
| DFP | Deferiprone |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| LIC | liver iron concentration |
| OR | odds ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
References
- Panich, V.; Pornpatkul, M.; Sriroongrueng, W. The problem of thalassemia in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1992, 23 (Suppl. S2), 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Farmakis, D.; Porter, J.; Taher, A.; Domenica Cappellini, M.; Angastiniotis, M.; Eleftheriou, A. 2021 Thalassaemia International Federation Guidelines for the Management of Transfusion-dependent Thalassemia. Hemasphere 2022, 6, e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remacha, A.; Sanz, C.; Contreras, E.; De Heredia, C.D.; Grifols, J.R.; Lozano, M.; Nuñez, G.M.; Salinas, R.; Corral, M.; Villegas, A. Guidelines on haemovigilance of post-transfusional iron overload. Blood Transfus. 2013, 11, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.T.; Saliba, A.N. Iron overload in thalassemia: Different organs at different rates. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2017, 2017, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittenham, G.M. Iron-chelating therapy for transfusional iron overload. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarra, N.; Shanaki, M.; Ehteram, H.; Nasiri, H.; Sahmani, M.; Saeidi, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Pourkarim, H.; Azad, M. A Review on Iron Chelators in Treatment of Iron Overload Syndromes. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Victor Hoffbrand, A. Deferiprone therapy for transfusional iron overload. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2005, 18, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, E.J. Oral chelators deferasirox and deferiprone for transfusional iron overload in thalassemia major: New data, new questions. Blood 2006, 107, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Taher, A. Deferasirox (Exjade) for the treatment of iron overload. Acta Haematol. 2009, 122, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanello, R.; Piga, A.; Forni, G.L.; Bertrand, Y.; Foschini, M.L.; Bordone, E.; Leoni, G.; Lavagetto, A.; Zappu, A.; Longo, F.; et al. Phase II clinical evaluation of deferasirox, a once-daily oral chelating agent, in pediatric patients with beta-thalassemia major. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Cohen, A.; Piga, A.; Bejaoui, M.; Perrotta, S.; Agaoglu, L.; Aydinok, Y.; Kattamis, A.; Kilinc, Y.; Porter, J.; et al. A phase 3 study of deferasirox (ICL670), a once-daily oral iron chelator, in patients with beta-thalassemia. Blood 2006, 107, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, A.; El-Beshlawy, A.; Elalfy, M.S.; Al Zir, K.; Daar, S.; Habr, D.; Kriemler-Krahn, U.; Hmissi, A.; Al Jefri, A. Efficacy and safety of deferasirox, an oral iron chelator, in heavily iron-overloaded patients with beta-thalassaemia: The ESCALATOR study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 82, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.; Cappellini, M.D.; Vichinsky, E.; Galanello, R.; Piga, A.; Lawniczek, T.; Clark, J.; Habr, D.; Porter, J.B. Efficacy and safety of deferasirox doses of >30 mg/kg per d in patients with transfusion-dependent anaemia and iron overload. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 147, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; Ohyashiki, K.; Urabe, A.; Hata, T.; Nakao, S.; Ozawa, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Kato, J.; Tatsumi, Y.; Mori, H.; et al. A safety, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic investigation of deferasirox (Exjade, ICL670) in patients with transfusion-dependent anemias and iron-overload: A Phase I study in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2008, 88, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet-Brown, E.; Olivieri, N.F.; Giardina, P.J.; Grady, R.W.; Neufeld, E.J.; Séchaud, R.; Krebs-Brown, A.J.; Anderson, J.R.; Alberti, D.; Sizer, K.C.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of ICL670 in iron-loaded patients with thalassaemia: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, A.; Galanello, R.; Forni, G.L.; Cappellini, M.D.; Origa, R.; Zappu, A.; Donato, G.; Bordone, E.; Lavagetto, A.; Zanaboni, L.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of deferasirox (Exjade, ICL670), a once-daily, orally-administered iron chelator, in comparison to deferoxamine in thalassemia patients with transfusional iron overload. Haematologica 2006, 91, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Grangé, S.; Bertrand, D.M.; Guerrot, D.; Eas, F.; Godin, M. Acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome due to deferasirox. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2376–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, C.T.; Talaulikar, G.S.; Falk, M.C.; Clayton, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Brown, M. Acute interstitial nephritis secondary to deferasirox causing acute renal injury needing short-term dialysis. Nephrology 2010, 15, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, N.; Elramah, M.; Vats, H.; Zhong, W.; Chan, M.R. A case report of deferasirox-induced kidney injury and Fanconi syndrome. Wmj 2013, 112, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chuansumrit, A.; Songdej, D.; Sirachainan, N.; Kadegasem, P.; Saisawat, P.; Sungkarat, W.; Kempka, K.; Tungbubpha, N. Efficacy and Safety of a Dispersible Tablet of GPO-Deferasirox Monotherapy among Children with Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia and Iron Overload. Hemoglobin 2024, 48, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittipoom, T.; Tantiworawit, A.; Punnachet, T.; Hantrakun, N.; Piriyakhuntorn, P.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Hantrakool, S.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Rattarittamrong, E.; Norasetthada, L.; et al. The Long-Term Efficacy of Deferiprone in Thalassemia Patients with Iron Overload: Real-World Data from the Registry Database. Hemoglobin 2022, 46, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin Ersoy, G.; Ayçiçek, A.; Odaman Al, I.; Bayram, C.; Arslantaş, E.; Özdemir, G.N.; Uysalol, E.P.; Şalcıoğlu, Z.; Akıcı, F.; Aydoğan, G. Safety and efficacy of deferasirox in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia: A 4-year single-center experience. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 38, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeotti, L.; Ceccherini, F.; Fucile, C.; Marini, V.; Di Paolo, A.; Maximova, N.; Mattioli, F. Evaluation of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Deferasirox in Pediatric Patients. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kloub, M.I.; MA, A.B.; Al Khawaldeh, O.A.; Al Tawarah, Y.M.; Froelicher, E.S. Predictors of non-adherence to follow-up visits and deferasirox chelation therapy among jordanian adolescents with Thalassemia major. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 31, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origa, R.; Cazzola, M.; Mereu, E.; Danjou, F.; Barella, S.; Giagu, N.; Galanello, R.; Swinkels, D.W. Differences in the erythropoiesis-hepcidin-iron store axis between hemoglobin H disease and β-thalassemia intermedia. Haematologica 2015, 100, e169–e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 42) |
|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 35.5 (13–57) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 22 (52.38%) |
| Female | 20 (47.62%) |
| Underlying disease, n (%) | |
| No other underlying disease | 29 (69.05%) |
| DM | 1 (2.38%) |
| HTN | 2 (4.76%) |
| DLP | 1 (2.38%) |
| Thalassemia type, n (%) | |
| Alpha thalassemia | 11 (26.19%) |
| Hb H disease | 10 (90.91%) |
| Hb H/CS | 1 (9.09) |
| Beta thalassemia | 31 (73.81%) |
| Beta thalassemia/Hb E | 19 (61.29%) |
| Beta thalassemia major | 12 (38.71%) |
| Splenectomy, n (%) | 12 (28.57%) |
| Number of transfusions, median (IQR), unit/month | 0.75 (0.5–1) |
| Previous iron chelator, n (%) | |
| Deferoxamine monotherapy | 14 (33.33%) |
| Deferiprone monotherapy | 27 (64.29%) |
| Deferoxamine + Deferiprone | 1 (2.38%) |
| Baseline SF, median (range), ng/mL | 2516 (1712–3065) |
| Pretransfusion Hb, mean ± SD, g/dL | 8.130 ± 1.600 |
| Maximum dose of DFX, median (range), mg/kg/day | 27.19 (21.73–32.37) |
| Parameters | Total (n = 42) | Ferritin Response Group [n, (%)] | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 22 | 11 (50.00%) | 1 | 0.29–3.41 | 1.000 | |||
| Female | 20 | 10 (50.00%) | Reference | |||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| Adult | 30 | 19 (63.33%) | 8.64 | 1.56–47.78 | 0.013 | 7.13 | 1.05–48.49 | 0.045 |
| Pediatrics | 12 | 2 (16.67%) | Reference | |||||
| Thalassemia type | ||||||||
| Alpha thalassemia | 11 | 9 (81.82%) | 7.12 | 1.28–39.58 | 0.025 | 4.46 | 0.79–25.27 | 0.091 |
| Beta thalassemia | 31 | 12 (38.71%) | Reference | |||||
| Splenectomy | ||||||||
| Intact spleen | 30 | 16 (53.33%) | 1.6 | 0.41–6.29 | 0.501 | |||
| Splenectomized | 12 | 5 (41.67%) | Reference | |||||
| Reasons for switching to DFX | ||||||||
| Cannot response target SF | 29 | 14 (48.28%) | 1.25 | 0.33–4.63 | 0.738 | |||
| Exhibiting adverse events | 13 | 7 (53.85%) | Reference | |||||
| Initial serum ferritin (ng/mL) | 0.99 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.083 | 0.93 | 0.87–1.00 | 0.039 | ||
| Starting dose of DFX | ||||||||
| <20 mg/kg/day | 19 | 12 (63.16%) | 2.66 | 0.75–9.48 | 0.130 | |||
| ≥20 mg/kg/day | 23 | 9 (39.13%) | Reference | |||||
| Pre-transfusion Hb | ||||||||
| <7 g/dL | 10 | 4 (40.00%) | Reference | |||||
| ≥7 g/dL | 32 | 17 (53.12%) | 1.70 | 0.39–7.32 | 0.476 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pongamnuaykrit, M.; Tantiworawit, A.; Niprapan, P.; Punnachet, T.; Hantrakun, N.; Piriyakhuntorn, P.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Hantrakool, S.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Rattarittamrong, E.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Deferasirox Monotherapy as a Second-Line Treatment in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Iron Overload. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176212
Pongamnuaykrit M, Tantiworawit A, Niprapan P, Punnachet T, Hantrakun N, Piriyakhuntorn P, Rattanathammethee T, Hantrakool S, Chai-Adisaksopha C, Rattarittamrong E, et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Deferasirox Monotherapy as a Second-Line Treatment in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Iron Overload. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176212
Chicago/Turabian StylePongamnuaykrit, Manatchaya, Adisak Tantiworawit, Piangrawee Niprapan, Teerachat Punnachet, Nonthakorn Hantrakun, Pokpong Piriyakhuntorn, Thanawat Rattanathammethee, Sasinee Hantrakool, Chatree Chai-Adisaksopha, Ekarat Rattarittamrong, and et al. 2025. "The Efficacy and Safety of Deferasirox Monotherapy as a Second-Line Treatment in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Iron Overload" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176212
APA StylePongamnuaykrit, M., Tantiworawit, A., Niprapan, P., Punnachet, T., Hantrakun, N., Piriyakhuntorn, P., Rattanathammethee, T., Hantrakool, S., Chai-Adisaksopha, C., Rattarittamrong, E., Norasetthada, L., & Charoenkwan, P. (2025). The Efficacy and Safety of Deferasirox Monotherapy as a Second-Line Treatment in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Iron Overload. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176212






