Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Stillen® and Rebamipide in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outcomes
2.2. Data Collection Methods
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.6. Grading of the Certainty of Evidence
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Efficacy Outcomes
3.2.1. Primary Analysis
Improvement Rate
Cure Rate
3.2.2. Secondary Analysis
Improvement Rate
Cure Rate
3.3. Safety Outcomes
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.5. Assumptions of NMA and Study Quality
3.6. GRADE Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| H2RAs | Histamine H2 Receptor Antagonists |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PPIs | Proton pump inhibitors |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| FAS | Full analysis set |
| PPS | Per-protocol set |
| ACG | American College of Gastroenterology |
| APAGE | Asian Pacific Association of Gastroenterology |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| NMA | Network Meta-Analysis |
| EGD | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy |
| AE | Adverse event |
| SAE | Serious adverse event |
| ADR | Adverse drug reaction |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| RISS | Research Information Sharing Service |
| KoreaMed | Korean medical literature database |
| ICTRP | International Clinical Trials Registry Platform |
| CoE | Certainty of evidence |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation |
| CKD-495 | Component extracted from Cinnamomum cassia |
| RD | Risk difference |
| IPD | Individual patient data |
References
- Laine, L.; Cohen, H.; Sloane, R.; Marin-Sorensen, M.; Weinstein, W.M. Interobserver agreement and predictive value of endoscopic findings for H. pylori and gastritis in normal volunteers. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 42, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cw, H. Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Kusters, J.G.; Van Vliet, A.H.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.E.; Holt, R.J. Cardiovascular risk with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Clinical implications. Drug Saf. 2014, 37, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A.; Chan, F.K. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2017, 390, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, F.L.; Chan, F.K.; Quigley, E.M.; Gastroenterology, P.P.C.o.t.A.C.o. Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 728–738. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, P.O.; Dunbar, K.B.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.H.; Greer, K.B.; Yadlapati, R.; Spechler, S.J. ACG clinical guideline for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedberg, D.E.; Kim, L.S.; Yang, Y.-X. The risks and benefits of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: Expert review and best practice advice from the American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, S.J.; Howell, M.D.; Ngo, L.H.; Marcantonio, E.R. Acid-suppressive medication use and the risk for hospital-acquired pneumonia. JAMA 2009, 301, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, L.; Ahnen, D.; Mcclain, C.; Solcia, E.; Walsh, H. Potential gastrointestinal effects of long-term acid suppression with proton pump inhibitors. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsky, A.; Gupta, K.; Lawler, E.V.; Fonda, J.R.; Hermos, J.A. Proton pump inhibitors and risk for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehested, T.S.; Gerds, T.A.; Fosbøl, E.L.; Hansen, P.W.; Charlot, M.G.; Carlson, N.; Hlatky, M.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.H. Long-term use of proton pump inhibitors, dose–response relationship and associated risk of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLaren, R.; Reynolds, P.M.; Allen, R.R. Histamine-2 receptor antagonists vs proton pump inhibitors on gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage and infectious complications in the intensive care unit. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Bertz, R.; Ren, S.; Boulton, D.W.; Någård, M. A systematic review of gastric acid-reducing agent-mediated drug–drug interactions with orally administered medications. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRorie, J.W.; Kirby, J.A.; Miner, P.B. Histamine2-receptor antagonists: Rapid development of tachyphylaxis with repeat dosing. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, S.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Ryu, J.S.; Choi, M.G.; Shin, D.W.; Ahn, B.O. DA-9601 for erosive gastritis: Results of a double-blind placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, M.-G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.K.; Am Song, G.; Rhee, P.-L.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kang, D.-H.; Lee, Y.C. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of DA-9601 versus its new formulation, DA-5204, in patients with gastritis: Phase III, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, M.W.; Kim, A.; Lee, S.G. DA-9601 has protective effects comparable to those of proton pump inhibitor and rebamipide against nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-induced upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide study using Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database. Medicine 2024, 103, e38801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kak, M. Rebamipide in gastric mucosal protection and healing: An Asian perspective. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 16, 101753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-W.; Choi, M.-G.; Seol, S.-Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, T.-N.; Choi, S.-C.; Kim, H.-S. Efficacy and Safety of Albis (R) in Acute and Chronic Patients with Gastritis: A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Randomized Multi-center Study. Korean J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 42, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.H.; Lee, H.L.; Joo, M.K.; Park, H.J.; Jung, S.W.; Lee, O.-J.; Kim, H.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, J.W. Efficacy and safety of rebamipide versus its new formulation, AD-203, in patients with erosive gastritis: A randomized, double-blind, active control, noninferiority, multicenter, phase 3 study. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-J.; Choi, M.-G.; Choi, H.; PARK, J.-M.; OH, J.-H.; JEON, E.-J.; LEE, B.-I.; LEE, I.-S.; KIM, S.-W.; CHOI, S.-W. Single blinded, randomized, active drug comparative, multi-center study to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of gliptide (R) tab (sulglycotide 200 mg) in gastritis patients; phase IV study. Korean J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 35, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.-J.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, O.Y.; Kim, J.J. Therapeutic Efficacy of Gliptide (Sulglycotide 200 mg): A Double Blinded, Randomized, Active Drug Comparative, Multicenter Study. Korean J. Helicobacter Up. Gastrointest. Res. 2013, 13, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, O.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, K.S.; Park, J.J.; Park, M.I.; Song, G.A.; Lee, D.H.; Jung, H.; Kim, S.K. A Phase 2, Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of CKD-495 in Patients with Acute and Chronic Gastritis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 2025, 2702089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, S.K.; Chun, H.J.; Am Song, G.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, T.N. Efficacy and safety of CKD-495 in acute and chronic gastritis: A Phase III superiority clinical trial. Medicine 2023, 102, e35926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutron, I.; Page, M.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Lundh, A.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Group, C.B.M. Considering bias and conflicts of interest among the included studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Cochrane: London, UK, 2019; pp. 177–204. [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadrani, M.; Eltahir, H.M.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Abouzied, M.M. Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Malaria Preventive Measures in Pregnant Women with a Focus on HIV Status: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, J.L. Measures of effect size for categorical data. Handb. Res. Synth. 1994, 247, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, F.; Freedland, K.; Carney, R.; De Jonge, P.; Dickens, C.; Pedersen, S.; Sorensen, J.; Dempster, M. Network meta-analysis of randomised trials of pharmacological, psychotherapeutic, exercise and collaborative care interventions for depressive symptoms in patients with coronary artery disease: Hybrid systematic review of systematic reviews protocol. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Kim, J.I. A Multicenter, Active-Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy of 4-Week Treatment with Stillen in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01817556?cond=NCT01817556&rank=1 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Guidelines for Submitting Data for Each Stage of Indirect Comparisons in Clinical Utility Assessment; The Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service: Wonju-si, Republic of Korea, 2014.
- Guidelines for Economic Evaluation of Pharmaceuticals; The Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service: Wonju-si, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Cho, S.W. Phase 2b Multi-Center Clinical Trial to Clarify the Efficacy and Target Population of DA9601 in Patients with Acute and Chronic Gastritis, and to Determine the Optimal Clinical Dosage and Administration. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT07139886?cond=NCT07139886&rank=1 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Kim, J.-H.; Yoon, Y.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Yoon, Y.B.; Ryu, J.K.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, N.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, G.R.; Kim, J.W. Therapeutic Efficacy of Gliptide (Sulglycotide) on Gastritis—A Single Blind, Randomized, Active Drug Comparative, Multi-center, Phase IV Study. Korean J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 35, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Naito, Y. The role of neutrophils and inflammation in gastric mucosal injury. Free Radic. Res. 2000, 33, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.B.; Cheon, S.A.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, O.K.; Ko, S.T.; Yu, K.J.; Shin, D.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Sohn, M.H. General Pharmacology of Artemisia Extract Powder, DA-9601. J. Appl. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 4, 174–183. [Google Scholar]


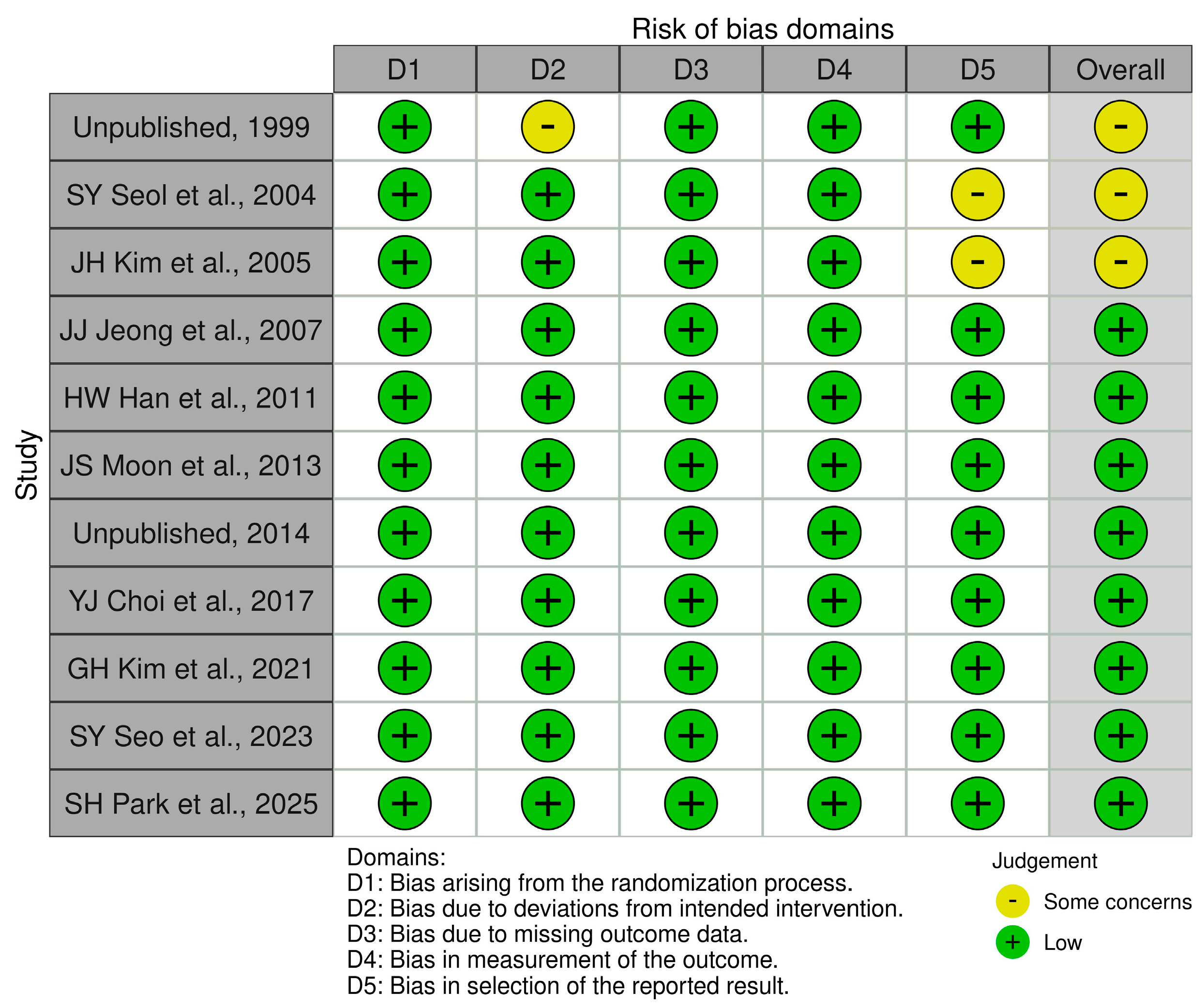
| Study ID | Study Arms | Study Design | Phase | n | Sex (Male), (%) | Age (Years), Mean ± SD | Treatment Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unpublished, 1999 [35] | Placebo, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 120 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | II | 176 | 101 (57.4) | 45.9 ± 11.30 | 2 weeks |
| SY Seol et al., 2004 [17] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 120 mg, 3 times/day, Cetraxate 200 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | III | 512 | 253 (49.4) | 45.7 ± 11.56 | 2 weeks |
| HW Han et al., 2011 [21] | Albis® a 1 tab, 2 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg 3, times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | II | 229 | 118 (51.5) | 44.6 ± 10.20 | 2 weeks |
| YJ Choi et al., 2017 [18] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 90 mg, 2 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | III | 434 | 167 (38.5) | 45.7 ± 13.05 | 2 weeks |
| GH Kim et al., 2021 [22] | Rebamipide 150 mg, 2 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | III | 454 | 187 (41.2) | 47.0 ± 12.20 | 2 weeks |
| SY Seo et al., 2023 [26] | CKD-495 75 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | III | 220 | 85 (38.6) | 48.1 ± 13.20 | 2 weeks |
| SH Park et al., 2025 [25] | Placebo, CKD-495 75 mg, 3 times/day, CKD-495 150 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | II | 233 | 122 (52.7) | 48.6 ± 16.40 | 2 weeks |
| JJ Jeong et al., 2007 [23] | Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | Single-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | IV | 73 | 23 (31.5) | 49.7 ± 10.00 | 3 weeks |
| JH Kim et al., 2005 [36] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day | Single-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | IV | 150 | 66 (44.0) | 52.7 ± 11.40 | 4 weeks |
| JS Moon et al., 2013 [24] | Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | UK | 197 | 66 (33.5) | 49.9 ± 12.40 | 4 weeks |
| Unpublished, 2014 [32] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | Double-blind, Randomized, Multi-center trial | IV | 266 | 103 (38.7) | 42.4 ± 12.19 | 4 weeks |
| Study ID | Study Arms | N1, N2 | Improvement n1 (%), n2 (%) | Cure n1 (%), n2 (%) | |||
| Unpublished, 1999 [35] | Placebo, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 120 mg, 3 times/day | 50, 42 52, 44 49, 39 | 8 (16.00), 6 (14.30) 25 (48.10), 22 (50.00) 17 (34.70), 14 (35.90) | N/A, N/A N/A, N/A N/A, N/A | |||
| SY Seol et al., 2004 [17] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 120 mg, 3 times/day, Cetrarate 200 mg, 3 times/day | 186, 171 140, 120 186, 166 | 118 (63.40), 115 (67.30) 81 (57.90), 78 (65.00) 83 (44.60), 77 (46.40) | 97 (52.20), 95 (55.60) 72 (51.40), 69 (57.50) 65 (35.00), 59 (35.50) | |||
| HW Han et al., 2011 [21] | Albis® 1 tab, 2 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day | 116, 87 113, 96 | 41 (35.30), 37 (42.50) 39 (34.50), 38 (39.60) | 32 (27.60), 28 (32.20) 31 (27.40), 30 (31.30) | |||
| YJ Choi et al., 2017 [18] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 90 mg, 2 times/day | 212, 199 209, 197 | 90 (42.50), 86 (43.20) 88 (42.10), 82 (41.60) | 79 (37.30), 75 (37.70) 78 (37.30), 73 (37.10) | |||
| GH Kim et al., 2021 [22] | Rebamipide 150 mg, 2 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 229, 224 224, 216 | 91 (39.70), 88 (39.30) 98 (43.80), 94 (43.70) | 79 (34.50), 76 (33.90) 80 (35.70), 77 (35.80) | |||
| SY Seo et al., 2023 [26] | CKD-495 75 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day | 111, 109 109, 102 | 62 (55.86), 60 (54.63) 43 (39.45), 39 (38.24) | N/A, N/A N/A, N/A | |||
| SH Park et al., 2025 [25] | Placebo, CKD-495 75 mg, 3 times/day, CKD-495 150 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 47, 45 52, 48 44, 41 48, 43 42, 38 | 21 (45.00), 20 (44.44) 38 (73.00), 36 (75.00) 18 (41.00), 15 (36.59) 25 (52.00), 22 (51.16) 20 (48.00), 19 (50.00) | 20 (43.00), 19 (42.00) 36 (69.00), 34 (71.00) 18 (41.00), 15 (37.00) 21 (44.00), 18 (42.00) 17 (41.00), 16 (42.00) | |||
| JJ Jeong et al., 2007 [23] | Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 36, 27 37, 32 | 18 (50.00), 17 (63.00) 20 (54.10), 20 (62.50) | 8 (22.20), 8 (29.60) 8 (21.60), 7 (21.60) | |||
| JH Kim et al., 2005 [36] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day | 74, 56 76, 59 | 24 (32.40), 22 (39.30) 29 (38.20), 28 (47.50) | 15 (20.30), 15 (26.80) 19 (25.00), 19 (32.20) | |||
| JS Moon et al., 2013 [24] | Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 98, 88 99, 90 | 51 (52.00), 47 (53.40) 60 (60.60), 55 (61.61) | 43 (43.90), 40 (45.50) 53 (53.50), 48 (53.30) | |||
| Unpublished, 2014 [32] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 136, 115 126, 104 | 70 (51.50), 56 (48.70) 69 (54.80), 55 (52.90) | 67 (49.30), 57 (47.00) 66 (52.40), 52 (50.00) | |||
| Study ID | Study Arms | n | AE n (%) | ADR n (%) | GI disorder AE n (%) | GI disorder ADR n (%) | |
| Unpublished, 1999 [35] | Placebo, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 120 mg, 3 times/day | 60 60 56 | 4 (6.67) 1 (1.67) 0 (0.00) | 3 (5.00) 1 (1.67) 0 (0.00) | 4 (6.67) 1 (1.67) 0 (0.00) | 3 (5.00) 1 (1.67) 0 (0.00) | |
| SY Seol et al., 2004 [17] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 120 mg, 3 times/day, Cetraxate 200 mg, 3 times/day | 186 140 186 | 9 (4.84) 0 (0.00) 6 (3.23) | 9 (4.84) 0 (0.00) 5 (2.69) | 6 (3.23) 0 (0.00) 2 (1.08) | 6 (3.23) 0 (0.00) 2 (1.08) | |
| HW Han et al., 2011 [21] | Albis® 1 tab, 2 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day | 115 116 | 9 (7.83) 10 (8.62) | 1 (0.87) 4 (3.45) | N/A N/A | N/A N/A | |
| YJ Choi et al., 2017 [18] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 90 mg, 2 times/day | 217 215 | 19 (8.76) 18 (8.37) | 4 (1.84) 5 (2.33) | 11 (5.07) 11 (5.12) | 2 (0.92) 5 (2.33) | |
| GH Kim et al., 2021 [22] | Rebamipide 150 mg, 2 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 236 234 | 24 (10.17) 20 (8.55) | 17 (7.20) 12 (5.13) | N/A N/A | 4 (1.69) 3 (1.28) | |
| SY Seo et al., 2023 [26] | CKD-495 75 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day | 122 120 | 4 (3.28) 5 (4.17) | N/A N/A | N/A N/A | N/A N/A | |
| SH Park et al., 2025 [25] | Placebo, CKD-495 75 mg, 3 times/day, CKD-495 150 mg, 3 times/day, Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 48 54 58 48 45 | N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A | 2 (4.17) 3 (5.56) 4 (6.90) 3 (6.25) 4 (8.89) | N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A | 1 (2.08) 3 (5.56) 2 (3.45) 2 (4.17) 4 (8.89) | |
| JJ Jeong et al., 2007 [23] | Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 36 37 | 2 (5.56) 4 (10.81) | N/A N/A | 2 (5.56) 4 (10.81) | N/A N/A | |
| JH Kim et al., 2005 [36] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day | 74 76 | 8 (10.81) 15 (19.74) | N/A N/A | 8 (10.81) 10 (13.16) | N/A N/A | |
| JS Moon et al., 2013 [24] | Sulglycotide 200 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 100 102 | 11 (11.00) 12 (11.76) | 2 (2.00) 2 (1.96) | 4 (4.00) 2 (1.96) | 2 (2.00) 2 (1.96) | |
| Unpublished, 2014 [32] | Stillen® 60 mg, 3 times/day, Rebamipide 100 mg, 3 times/day | 137 129 | 18 (13.14) 19 (14.73) | 2 (1.46) 3 (2.33) | 13 (9.49) 9 (6.98) | 1 (0.73) 2 (1.55) | |
| Outcome | Treatment Duration | Analysis Set | OR | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improvement rate | 2 weeks | FAS | 1.11 | (0.88, 1.39) S_NE) |
| Improvement rate | 2 weeks | PPS | 1.09 | (0.85, 1.41) S_NE) |
| Improvement rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | FAS | 0.99 | (0.88, 1.10) S_NE) |
| Improvement rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | PPS | 0.98 | (0.87, 1.11) S_NE) |
| Cure rate | 2 weeks | FAS | 1.03 | (0.84, 1.26) NS_D) |
| Cure rate | 2 weeks | PPS | 1.00 | (0.81, 1.24) NS_D) |
| Cure rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | FAS | 0.96 | (0.88, 1.05) NS_D) |
| Cure rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | PPS | 0.96 | (0.87, 1.06) NS_D) |
| Outcome | Treatment Duration | Analysis Set | Stillen® | Rebamipide | RD | 95% CI for RD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improvement rate | 2 weeks | FAS | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.04 | (–0.05, 0.12) S_NE) |
| Improvement rate | 2 weeks | PPS | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.05 | (–0.04, 0.15) S_NE) |
| Improvement rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | FAS | 0.45 | 0.49 | –0.04 | (–0.139, 0.05) S_NE) |
| Improvement rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | PPS | 0.47 | 0.50 | –0.04 1) | (–0.138, 0.07) S_NE) |
| Cure rate | 2 weeks | FAS | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.04 2) | (–0.05, 0.13) NS_D) |
| Cure rate | 2 weeks | PPS | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.05 3) | (–0.04, 0.15) NS_D) |
| Cure rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | FAS | 0.38 | 0.40 | –0.02 | (–0.14, 0.11) NS_D) |
| Cure rate | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | PPS | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.01 4) | (–0.11, 0.12) NS_D) |
| Outcome | Treatment Duration | OR | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|
| AE | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | 0.96 | (0.89, 1.03) NS_D) |
| ADR | 2 weeks | 0.95 | (0.86, 1.05) NS_D) |
| ADR | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | 0.99 | (0.96, 1.02) NS_D) |
| GI disorder AE | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | 1.02 | (0.96, 1.08) NS_D) |
| GI disorder ADR | 2 weeks | 0.94 | (0.85, 1.04) NS_D) |
| GI disorder ADR | 2, 3, and 4 weeks | 0.98 | (0.94, 1.02) NS_D) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Lim, N.R.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Chung, W.C. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Stillen® and Rebamipide in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176209
Lee H, Lim NR, Kim S, Cho H, Chung WC. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Stillen® and Rebamipide in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176209
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyejoo, Na Rae Lim, Seonwoo Kim, Hyun Cho, and Woo Chul Chung. 2025. "Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Stillen® and Rebamipide in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176209
APA StyleLee, H., Lim, N. R., Kim, S., Cho, H., & Chung, W. C. (2025). Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Stillen® and Rebamipide in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176209






