Potential of Kidney Exchange Programs (KEPs) in Japan for Donor-Specific Antibody-Positive Kidney Transplants: A Questionnaire Survey on KEPs and a Multi-Institutional Study Conducting Virtual Cross-Matching Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- While recent advances in transplantation technology have improved the outcomes of kidney transplantation under these conditions, many transplant specialists believe that there is never such a great medical necessity that would require donor exchange to perform transplantation.
- (2)
- This is based on the intention to donate one’s own organs for the benefit of one’s relatives and does not violate the ethical guidelines of the Japan Society for Transplantation.
- (3)
- Donor exchange kidney transplantation involves major medical and ethical issues and should be conducted under the ethical review of each facility on a case-by-case basis. Therefore, donor exchange kidney transplantation should not be promoted through social systems such as donor exchange networks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research to Identify the Need for a KEP (Primary Research)
- The “immunological” criteria precluding kidney transplantation.
- Number of living-donor kidney transplants abandoned for “immunological” reasons over the last decade (2012–2021) and the underlying causes.
- What policy would be preferred in cases of abandonment mentioned in point 2 above?
- Do you think that a KEP for highly sensitive cases is necessary in Japan?
- “Immunological” scope of transplant eligibility if a KEP is established in Japan.
- Problems with KEPs.
- “Ethical” preoperative preparation for KEPs.
- “Transplant surgery method” in KEPs.
2.2. Simulation of Virtual Cross-Matching Through Multi-Institutional Collaboration (Secondary Research)
2.3. Example of Virtual Cross-Matching
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
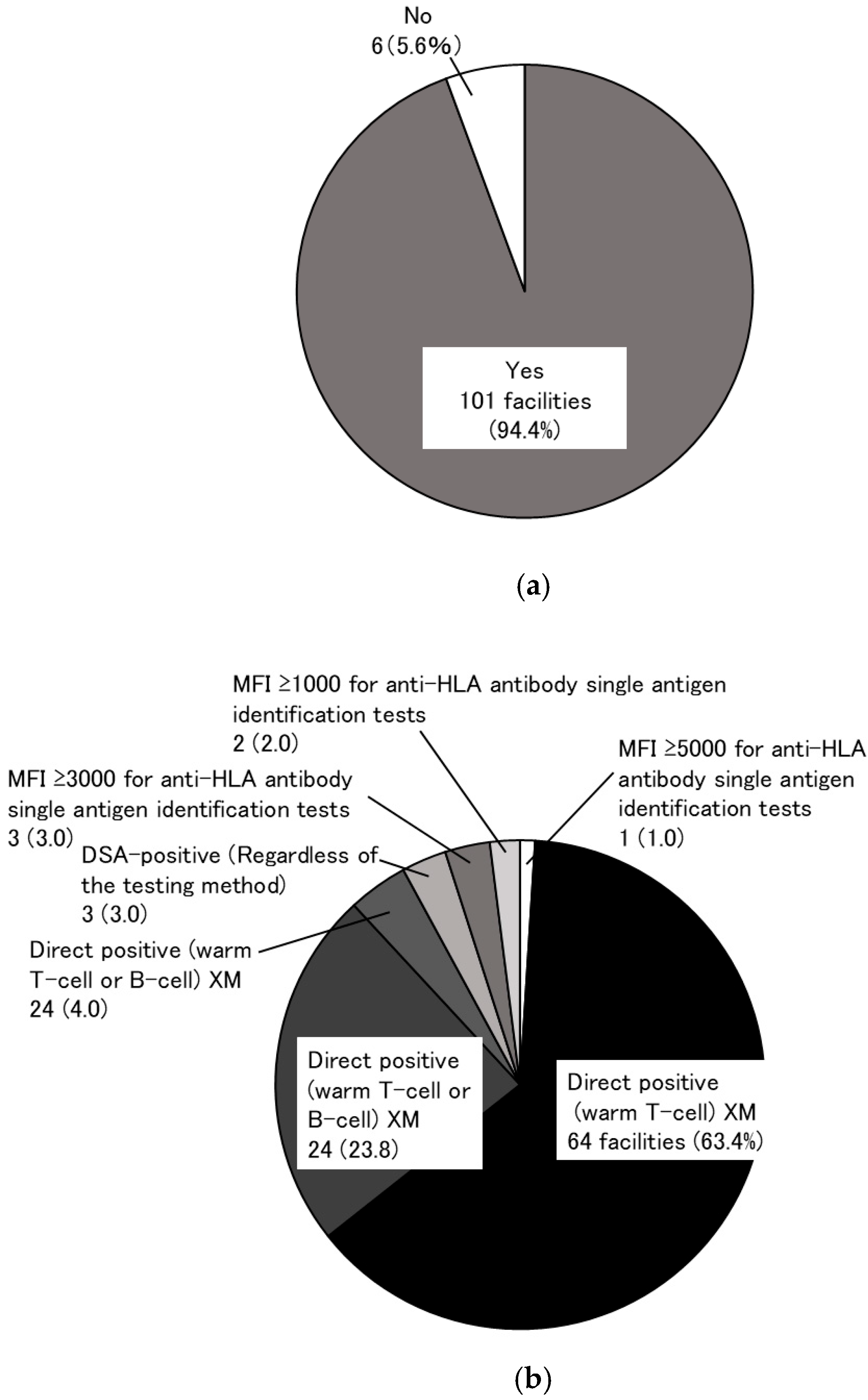
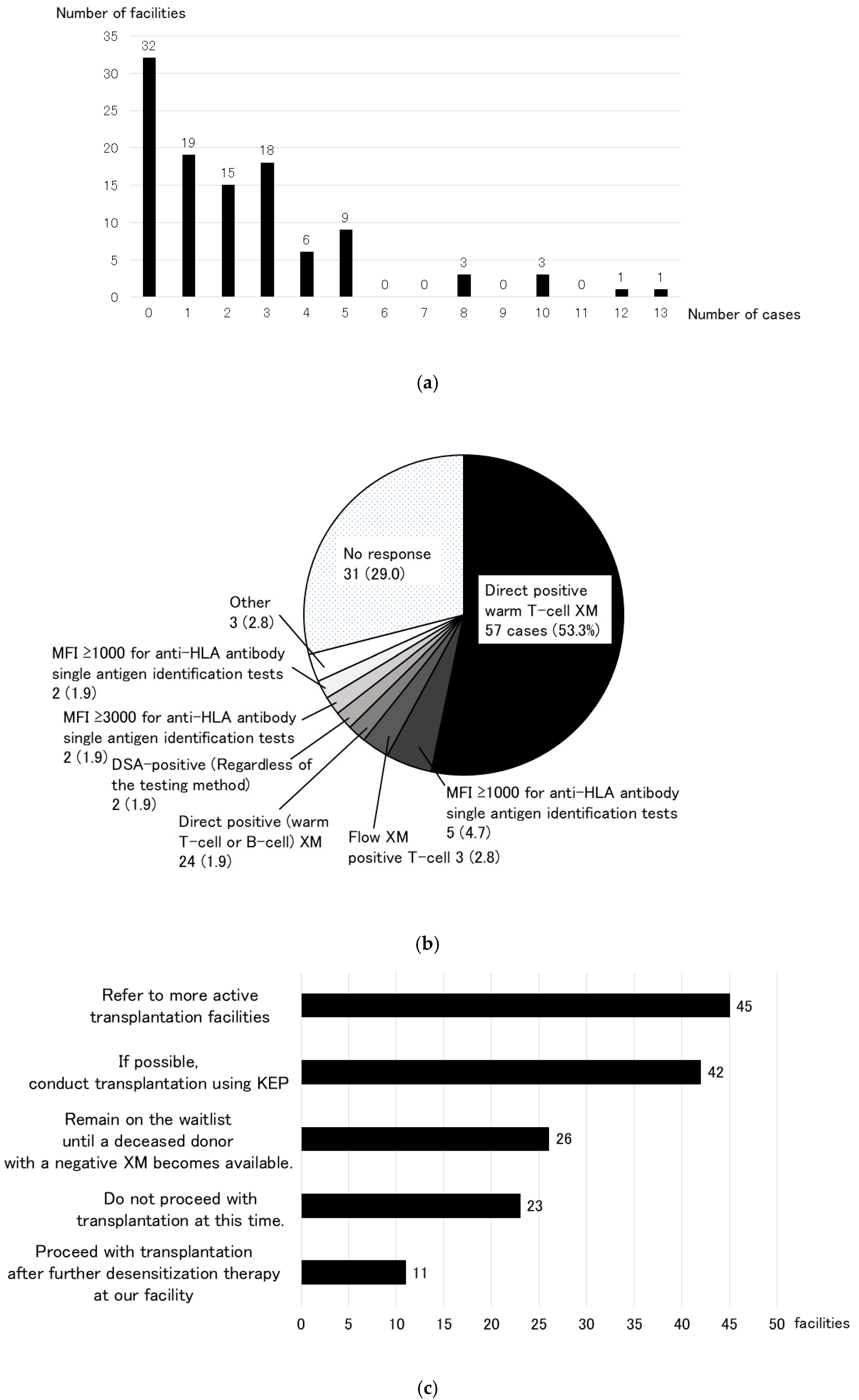
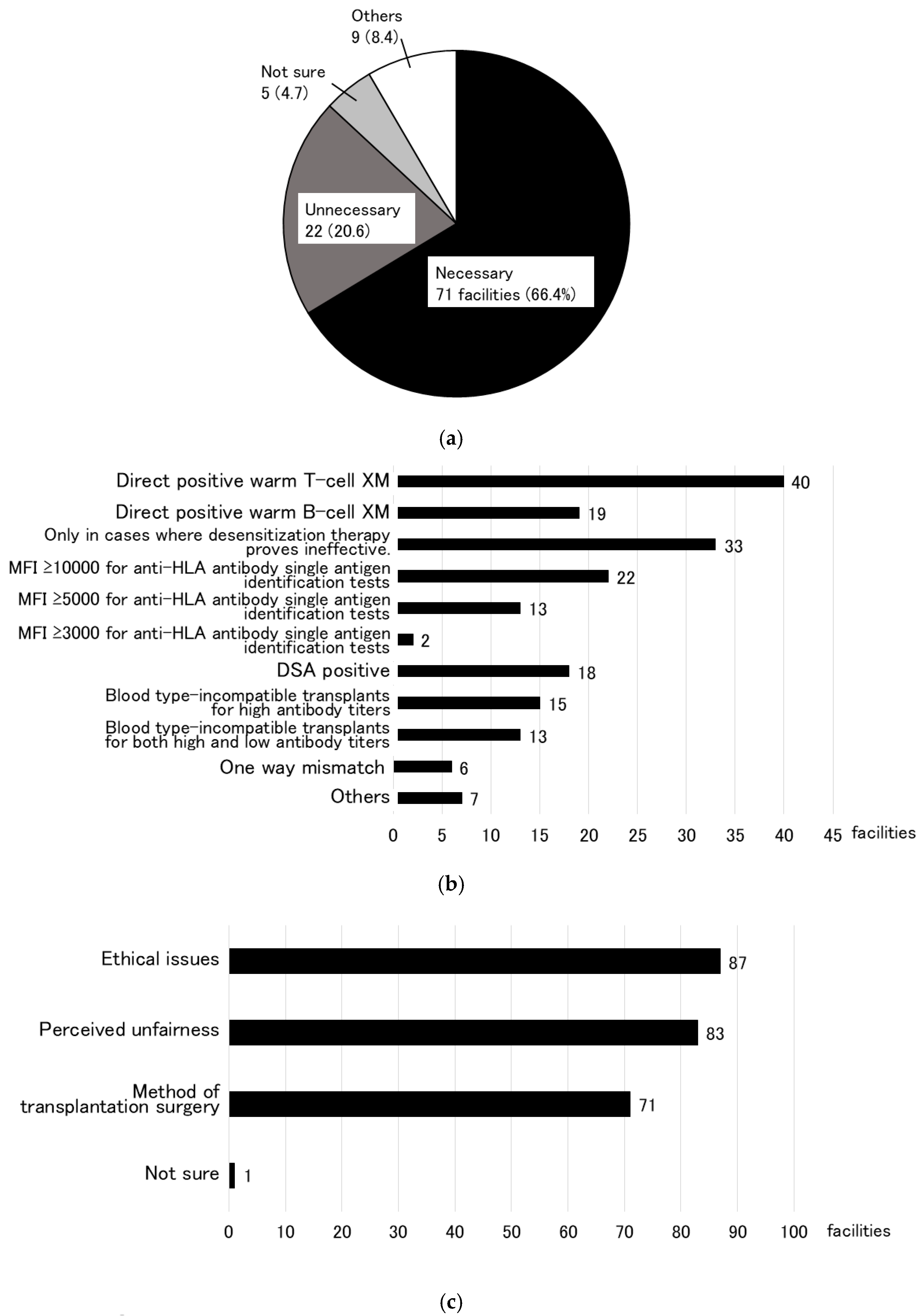
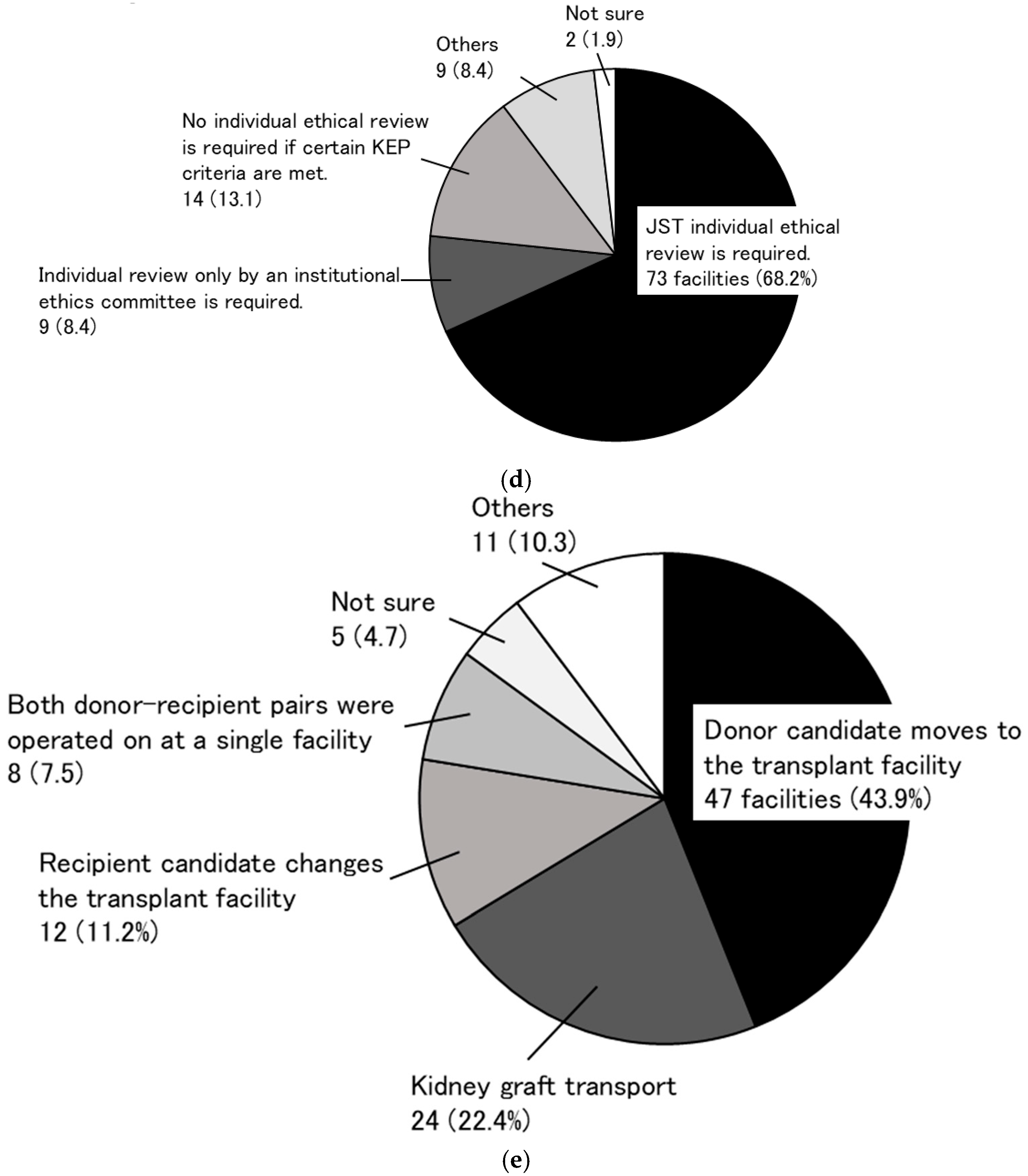
3.1. Research to Identify the Need for a KEP (Primary Research)
3.2. Simulation Using Virtual Cross-Matching (Secondary Research)
3.2.1. Donor Candidate Background
3.2.2. Recipient Candidate Background
3.2.3. Simulation 1
3.2.4. Simulation 2
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSA | donor-specific antibody |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| KEP | kidney exchange program |
| N/A | not available |
| s-Cre | serum creatinine level |
| XM | cross-match |
References
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2023 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2024, 59, 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Harano, M.; Tanabe, K.; Tokumoto, T.; Ishikawa, N.; Shimizu, T.; Shimmura, H.; Yagisawa, T.; Fuchinoue, S.; Nakajima, I.; Toma, H. Long-term results of kidney transplantation in preformed antibody-positive highly sensitized recipients. Transpl. Proc. 1999, 31, 2863–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Tahara, H.; Ohira, M.; Ishiyama, K.; Tashiro, H.; Ohdan, H. A phased desensitization protocol with rituximab and bortezomib for highly sensitized kidney transplant candidates. Transpl. Direct. 2015, 1, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inui, M.; Miyazato, T.; Furusawa, M.; Okumi, M.; Omoto, K.; Ishida, H.; Tanabe, K. Successful kidney transplantation after stepwise desensitization using rituximab and bortezomib in a highly HLA-sensitized and ABO incompatible high titer patient. Transpl. Direct. 2016, 2, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Unagami, K.; Omoto, K.; Kanzawa, T.; Tanabe, K. Desensitization regimen consisting of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis, and rituximab (an Anti-Cd20 Antibody), without eculizumab and/or bortezomib, in 41 highly sensitized kidney transplant recipients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 19, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, J.; Machida, Y.; Iwai, T.; Naganuma, T.; Kitamoto, K.; Iguchi, T.; Maeda, S.; Kamada, Y.; Kuwabara, N.; Kim, T. Desensitization protocol in highly HLA-sensitized and abo-incompatible high titer kidney transplantation. Transpl. Proc. 2010, 42, 3998–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.C.; Bhandari, T.R.; Adhikari, R.; Baral, H.; Verma, R.K.; Shrestha, K.K. Living donor kidney paired exchange: An observational study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 78, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, M.; Kal-van Gestel, J.A.; Roelen, D.; Betjes, M.G.H.; de Weerd, A.E.; Reinders, M.E.J.; van de Wetering, J.; Kho, M.M.L.; Glorie, K.; Roodnat, J.I. Increasing Kidney-exchange options within the existing living donor pool with CIAT: A pilot implementation study. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duus Weinreich, I.; Andersson, T.; Birna Andrésdóttir, M.; Bengtsson, M.; Biglarnia, A.; Bistrup, C.; Boulland, L.; Bruunsgaard, H.; Helanterä, I.; Kölvald, K. Scandiatransplant exchange program (STEP): Development and results from an international kidney exchange program. Transplant. Direct 2023, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flechner, S.M.; Thomas, A.G.; Ronin, M.; Veale, J.L.; Leeser, D.B.; Kapur, S.; Peipert, J.D.; Segev, D.L.; Henderson, M.L.; Shaffer, A.A. The first 9 years of kidney paired donation through the national kidney registry: Characteristics of donors and recipients compared with national live donor transplant registries. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorie, K.; Xiao, G.; van de Klundert, J. The health value of kidney exchange and altruistic donation. Value Health 2022, 25, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, A.; Najafi, M.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Fathi, M. Equity or equality? Which approach brings more satisfaction in a kidney-exchange chain? J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Pestana, J.; Abbud-Filho, M.; Garcia, V.D.; Foresto, R.D.; Requião-Moura, L.R. Paired kidney donation: Are we going beyond reasonable limits in living-donor transplantation? Braz. J. Nephrol. 2022, 44, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, G.R.; Cooper, M.; Verbesey, J.; Veale, J.L.; Ronin, M.; Irish, W.; Waterman, A.D.; Flechner, S.M.; Leeser, D.B. Risk aversion in the use of complex kidneys in paired exchange programs: Opportunities for even more transplants? Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 22, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakazawa, E.; Takimoto, Y.; Akabayashi, A. The current situation of paired kidney exchange in the world and its future perspectives in Japan: Through a systematic review of literatures. J. Jpn. Assoc. Bioethics. 2018, 28, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- The Japan Society for Transplantation Website. Available online: https://www.asas.or.jp/jst (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Garcia, K.K.S.; Abrahão, A.A. Research development using REDCap software. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2021, 27, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REDCap Website. Available online: https://projectredcap.org (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2012 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2013, 48, 346–360.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2013 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2014, 49, 240–260.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2014 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2015, 50, 138–155.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2015 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2016, 51, 124–144.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2016 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2017, 52, 113–133.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2017 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2018, 53, 89–108.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2018 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2019, 54, 61–80.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2019 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2020, 55, 225–243.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2020 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2021, 56, 195–216.
- Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation and the Japan Spciety for Transplantation. Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2021 and Follow-up Survey. Jpn. J. Transplant. 2022, 57, 199–219.
- HLA Laboratory Website. Available online: https://hla.or.jp/med/kensa/pdf/cross_reactive_map.pdf H (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Saito, K. Present status of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in Japan. Xenotransplantation 2006, 13, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flechner, S.M.; Leeser, D.; Pelletier, R.; Morgievich, M.; Miller, K.; Thompson, L.; McGuire, S.; Sinacore, J.; Hil, G. The incorporation of an advanced donation program into kidney paired exchange: Initial experience of the national kidney registry. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 2712–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmonico, F.L.; Morrissey, P.E.; Lipkowitz, G.S.; Stoff, J.S.; Himmelfarb, J.; Harmon, W.; Pavlakis, M.; Mah, H.; Goguen, J.; Luskin, R. Donor kidney exchanges. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeser, D.B.; Thomas, A.G.; Shaffer, A.A.; Veale, J.L.; Massie, A.B.; Cooper, M.; Kapur, S.; Turgeon, N.; Segev, D.L.; Waterman, A.D. Patient and kidney allograft survival with national kidney paired donation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, J.L.; Capron, A.M.; Nassiri, N.; Danovitch, G.; Gritsch, H.A.; Waterman, A.; Del Pizzo, J.; Hu, J.C.; Pycia, M.; McGuire, S.; et al. Vouchers for Future Kidney Transplants to Overcome “Chronological Incompatibility” Between Living Donors and Recipients. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2115–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashlagi, I.; Gilchrist, D.S.; Roth, A.E.; Rees, M.A. Nonsimultaneous chains and dominos in kidney- paired donation-revisited. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Allen, J.E.; Fuggle, S.V.; Bradley, J.A.; Rudge, C. Early experience of paired living kidney donation in the United Kingdom. Transplantation 2008, 86, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klerk, M.; Van Der Deijl, W.M.; Witvliet, M.D.; Haase-Kromwijk, B.J.J.M.; Claas, F.H.J.; Weimar, W. The optimal chain length for kidney paired exchanges: An analysis of the dutch program. Transpl. Int. 2010, 23, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klerk, M.; Keizer, K.M.; Claas, F.H.J.; Witvliet, M.; Haase-Kromwijk, B.J.J.M.; Willem, W. The Dutch national living donor kidney exchange program. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2302–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, P.; Haase-Kromwijk, B.; Andersson, T.; Ásgeirsson, E.I.; Baltesová, T.; Boletis, I.; Bolotinha, C.; Bond, G.; Böhmig, G.; Burnapp, L. Building kidney exchange programmes in Europe—An overview of exchange practice and activities. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Laar, S.C.; de Weerd, A.E.; Bemelman, F.J.; Idu, M.M.; de Vries, A.P.J.; Alwayn, I.P.J.; Berger, S.P.; Pol, R.A.; van Zuilen, A.D.; Toorop, R.J. Favorable living donor kidney transplantation outcomes within a national kidney exchange program. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2025, 20, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Hughes, P.D.; Cohney, S.J.; Woodroffe, C.; Fidler, S.; D’Orsogna, L. ABO-incompatible matching significantly enhances transplant rates in kidney paired donation. Transplantation 2013, 96, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.A.; Kausman, J.Y. ABO-incompatible, paired kidney exchange transplantation in a highly sensitized patient with donor-specific antibodies. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1541–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, J.; Machado, D.J.d.B.; David-Neto, E. Increasing transplantability in brazil: Time to discuss kidney paired donation. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2022, 44, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Sethi, S.; Bansal, S.; Jain, M.; Sharma, R.; Phanish, M.; Duggal, R.; Ahlawat, R.; Kher, V. Paired kidney exchange transplantation: Maximizing the donor pool. Indian J. Nephrol. 2015, 25, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kute, V.B.; Patel, H.V.; Shah, P.R.; Modi, P.R.; Shah, V.R.; Rizvi, S.J.; Pal, B.C.; Shah, P.S.; Modi, M.P.; Butala, B.P. Impact of single centre kidney paired donation transplantation to increase donor pool in India: A cohort study. Transpl. Int. 2017, 30, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeser, D.B.; Aull, M.J.; Afaneh, C.; Dadhania, D.; Charlton, M.; Walker, J.K.; Hartono, C.; Serur, D.; Del Pizzo, J.J.; Kapur, S. Living donor kidney paired donation transplantation: Experience as a founding member center of the national kidney registry. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, M.; Tekin, S.; Yücetin, L.; Şengül, A.; Demirbas, A. Comparison of paired exchange kidney transplantations with living related kidney transplantations. Transpl. Proc. 2012, 44, 1626–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kher, V.; Jha, P.K. Paired kidney exchange transplantation—pushing the boundaries. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, I.R.; Roth, A.E.; Rees, M.A. Living kidney donor transplantation and global kidney exchange. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 20, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozek, D.N.; Dunn, T.B.; Kuhr, C.S.; Marsh, C.L.; Rogers, J.; Rees, S.E.; Basagoitia, L.; Brunner, R.J.; Roth, A.E.; Ekwenna, O. complete chain of the first global kidney exchange transplant and 3-yr follow-up. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurt, F.G.; Ewert, L.; Mertens, P.R.; Haller, H.; Schmidt, B.M.W.; Chatzikyrkou, C. Clinical outcomes after ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2019, 393, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, N.; Ito, T.; Kurihara, K.; Hiratsuka, I.; Shibata, M.; Suzuki, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Kenmochi, T. Impact of B cell depletion on COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients. Viruses 2023, 15, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

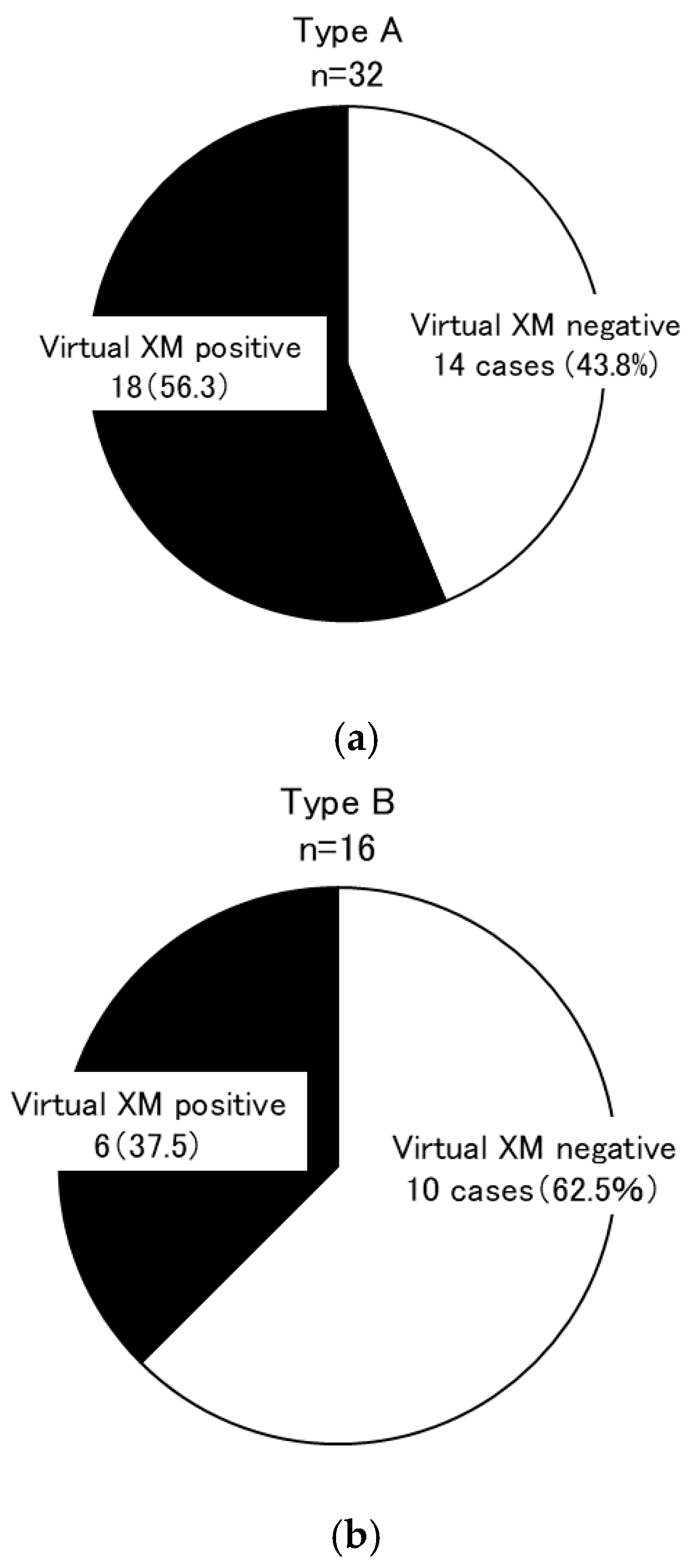
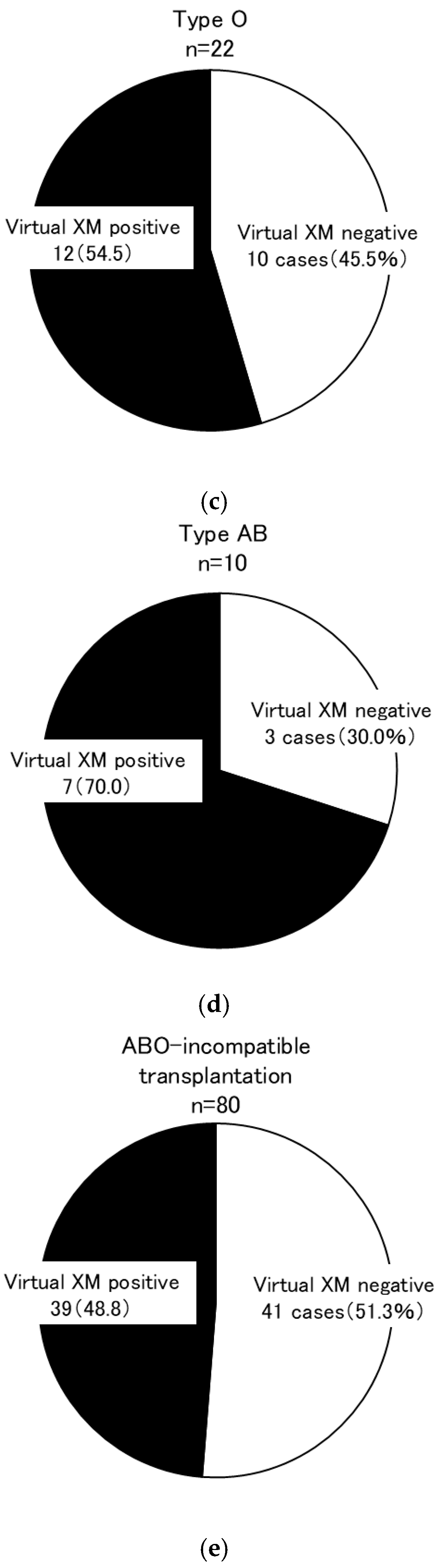
| Group | Overall Secondary Research Enrollment | Virtual Cross-Match Group | Excluded Group | p-Value * | Living Kidney Transplantation (2012–2021) | p-Value ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 117 | 80 | 37 | 14,354 | |||
| Age (years) | 56.5 ± 12.1 | 56.3 ± 11.0 | 56.9 ± 14.5 | 0.815 | 58.0 | N/A | |
| Age distribution | 20–29 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.026 | 128 | 0.138 |
| 30–39 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 672 | |||
| 40–49 | 20 | 16 | 4 | 2314 | |||
| 50–59 | 38 | 31 | 7 | 4003 | |||
| 60–69 | 39 | 20 | 19 | 4862 | |||
| 70–79 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 1919 | |||
| 80- | 2 | 1 | 1 | 75 | |||
| Sex (male/female) | 81:35 | 58:22 | 23:13 | 0.386 | 5213:9141 | <0.001 | |
| Relationship (spouse(husband/wife)/parent/sibling/other) | 81(70:11):17:13:6 | 59(51:8):11:6:4 | 22(19:3):6:7:2 | 0.131 | 5589:4885:1433:2447 | <0.001 | |
| Hypertension (yes/no) | 20:89 | 17:61 | 3:28 | 0.018 | 2481:9202 | 0.890 | |
| Diabetes mellitus (yes/no) | 10:101 | 9:69 | 1:32 | 0.058 | 568:11,109 | 0.014 | |
| s-Cre (mg/dL) | 0.85 ± 0.62 | 0.82 ± 0.14 | 0.93 ± 1.15 | 0.430 | 0.70 | N/A | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 74.4 ± 14.5 | 72.6 ± 12.3 | 78.3 ± 18.4 | 0.074 | N/A | N/A | |
| Overall Secondary Research Enrollment | Virtual Cross-Match Group | Excluded Group | p Value * | Living Kidney Transplantation (2012–2021) | p Value ** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 117 | 80 | 37 | 14,354 | ||||
| Age (years) | 52.1 ± 10.6 | 51.2 ± 10.7 | 53.9 ± 10.3 | 0.201 | 47.2 | N/A | |
| Age distribution | 0–9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.166 | 252 | 1.000 |
| 10–19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 430 | |||
| 20–29 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1156 | |||
| 30–39 | 18 | 10 | 8 | 2388 | |||
| 40–49 | 27 | 23 | 4 | 3415 | |||
| 50–59 | 46 | 31 | 15 | 3199 | |||
| 60–69 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 2922 | |||
| 70- | 0 | 0 | 0 | 592 | |||
| Sex (male/female) | 22:95 | 15:65 | 7:30 | 1.000 | 9192:5162 | <0.001 | |
| Blood type (compatible/incompatible) | 65:49 | 45:35 | 20:14 | 0.839 | 8671:4033 | 0.029 | |
| HLA mismatch | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0.024 | 535 | 0.024 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 682 | |||
| 2 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 2099 | |||
| 3 | 30 | 17 | 13 | 3458 | |||
| 4 | 20 | 16 | 4 | 1607 | |||
| 5 | 41 | 30 | 11 | 1743 | |||
| 6 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 953 | |||
| Direct XM T warm (positive/negative) | 50:54 | 32:39 | 18:15 | 0.669 | 81:11,248 | <0.001 | |
| Direct XM B warm (positive/negative) | 58:39 | 37:30 | 21:9 | 0.044 | 265:11,007 | <0.001 | |
| Flow XM T (positive/negative) | 86:21 | 61:14 | 25:7 | 0.717 | 501:11,026 | <0.001 | |
| Flow XM B (positive/negative) | 102:2 | 73:0 | 29:2 | 0.083 | 990:10,147 | <0.001 | |
| Flow PRA class1 | 0–less than 20% | 9 | 6 | 3 | 0.847 | 5276 | <0.001 |
| 20–less than 40% | 6 | 3 | 3 | 180 | |||
| 40–less than 60% | 8 | 6 | 2 | 113 | |||
| 60–less than 80% | 9 | 7 | 2 | 70 | |||
| 80–100% | 17 | 12 | 5 | 66 | |||
| Flow PRA class2 | 0–less than 20% | 13 | 12 | 1 | 0.101 | 5334 | <0.001 |
| 20–less than 40% | 2 | 2 | 0 | 134 | |||
| 40–less than 60% | 9 | 6 | 3 | 72 | |||
| 60–less than 80% | 6 | 6 | 3 | 60 | |||
| 80–100% | 15 | 7 | 8 | 66 | |||
| DSA (positive/negative) | 117:0 | 80:0 | 37:0 | 1.000 | 777:5837 | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ito, T.; Ito, M.; Aida, N.; Kurihara, K.; Terao, A.; Watarai, Y.; Saito, M.; Kaku, K.; Ishii, D.; Sekiguchi, S.; et al. Potential of Kidney Exchange Programs (KEPs) in Japan for Donor-Specific Antibody-Positive Kidney Transplants: A Questionnaire Survey on KEPs and a Multi-Institutional Study Conducting Virtual Cross-Matching Simulations. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176122
Ito T, Ito M, Aida N, Kurihara K, Terao A, Watarai Y, Saito M, Kaku K, Ishii D, Sekiguchi S, et al. Potential of Kidney Exchange Programs (KEPs) in Japan for Donor-Specific Antibody-Positive Kidney Transplants: A Questionnaire Survey on KEPs and a Multi-Institutional Study Conducting Virtual Cross-Matching Simulations. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176122
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Taihei, Miki Ito, Naohiro Aida, Kei Kurihara, Akihiro Terao, Yoshihiko Watarai, Mitsuru Saito, Keizo Kaku, Daisuke Ishii, Satoshi Sekiguchi, and et al. 2025. "Potential of Kidney Exchange Programs (KEPs) in Japan for Donor-Specific Antibody-Positive Kidney Transplants: A Questionnaire Survey on KEPs and a Multi-Institutional Study Conducting Virtual Cross-Matching Simulations" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176122
APA StyleIto, T., Ito, M., Aida, N., Kurihara, K., Terao, A., Watarai, Y., Saito, M., Kaku, K., Ishii, D., Sekiguchi, S., Yoneda, T., Unagami, K., Tasaki, M., Iwamoto, H., Araki, M., Takahashi, K., Yamanaka, K., Sugimoto, M., Nishikawa, K., ... Kenmochi, T. (2025). Potential of Kidney Exchange Programs (KEPs) in Japan for Donor-Specific Antibody-Positive Kidney Transplants: A Questionnaire Survey on KEPs and a Multi-Institutional Study Conducting Virtual Cross-Matching Simulations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176122







