Heart Failure and Stroke: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
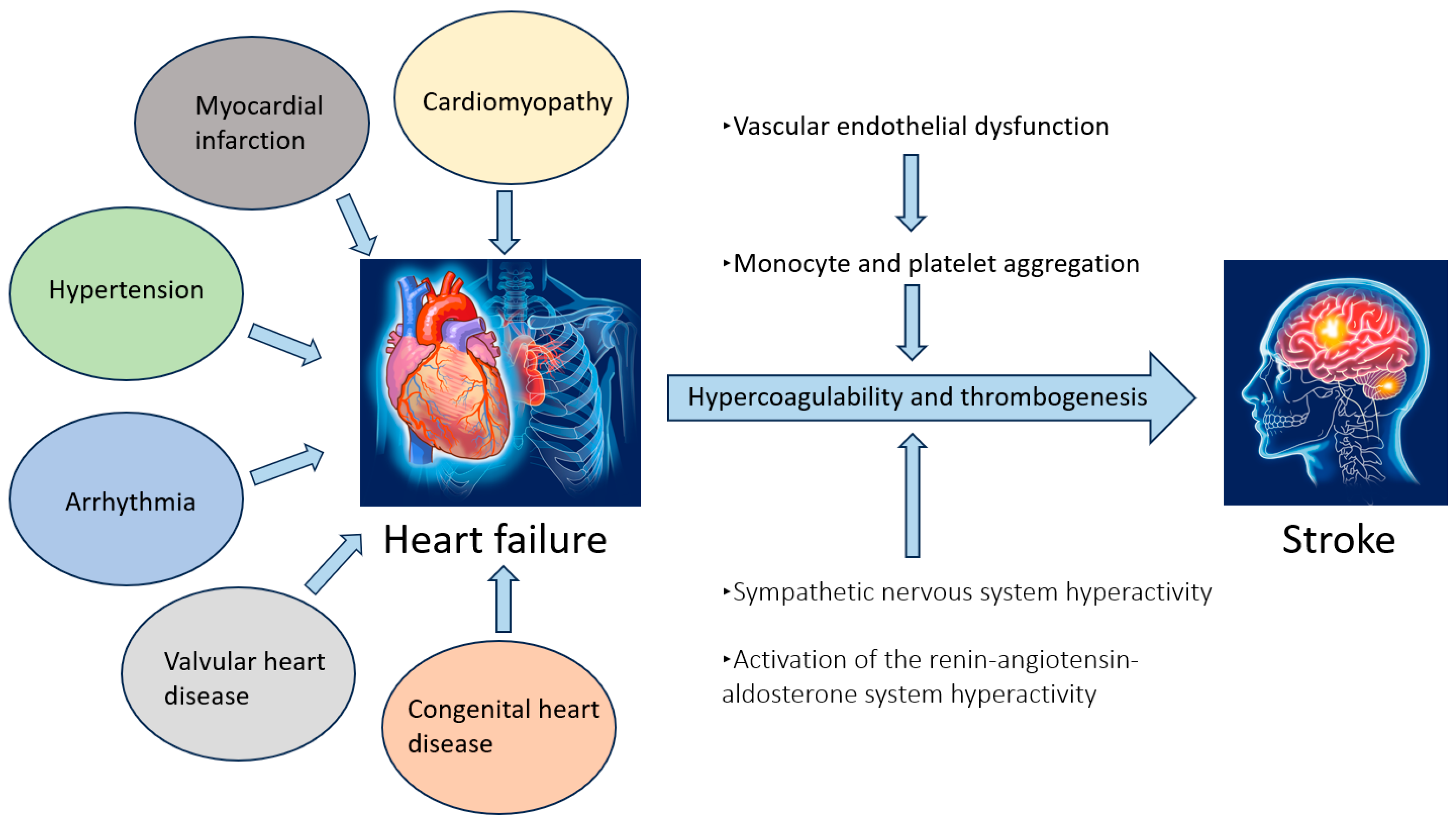
2. Mechanism of Heart Failure
3. Epidemiology of Heart Failure
4. Epidemiology of Heart Failure and Stroke
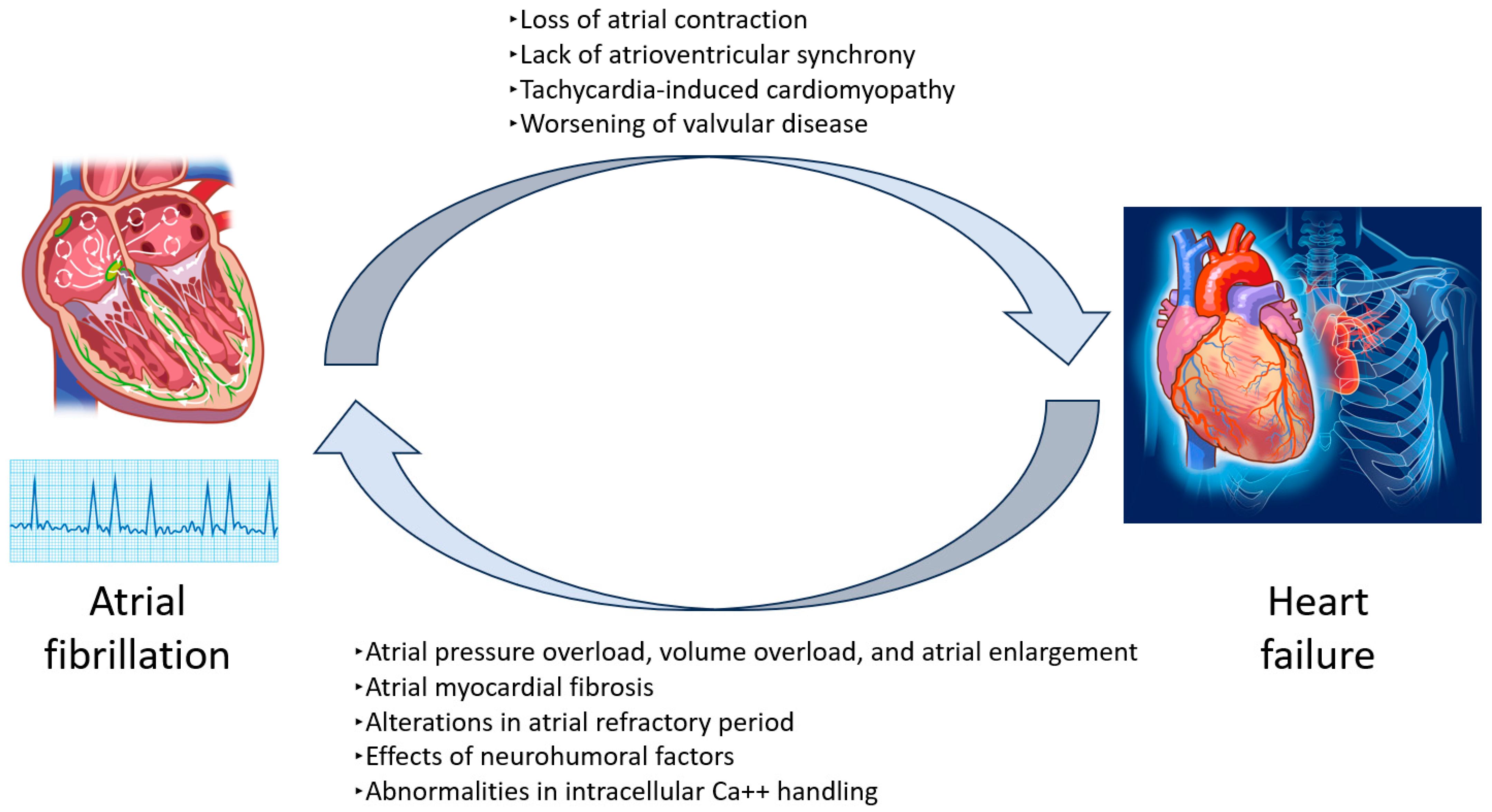
5. Pathophysiological Link Between Heart Failure and Stroke
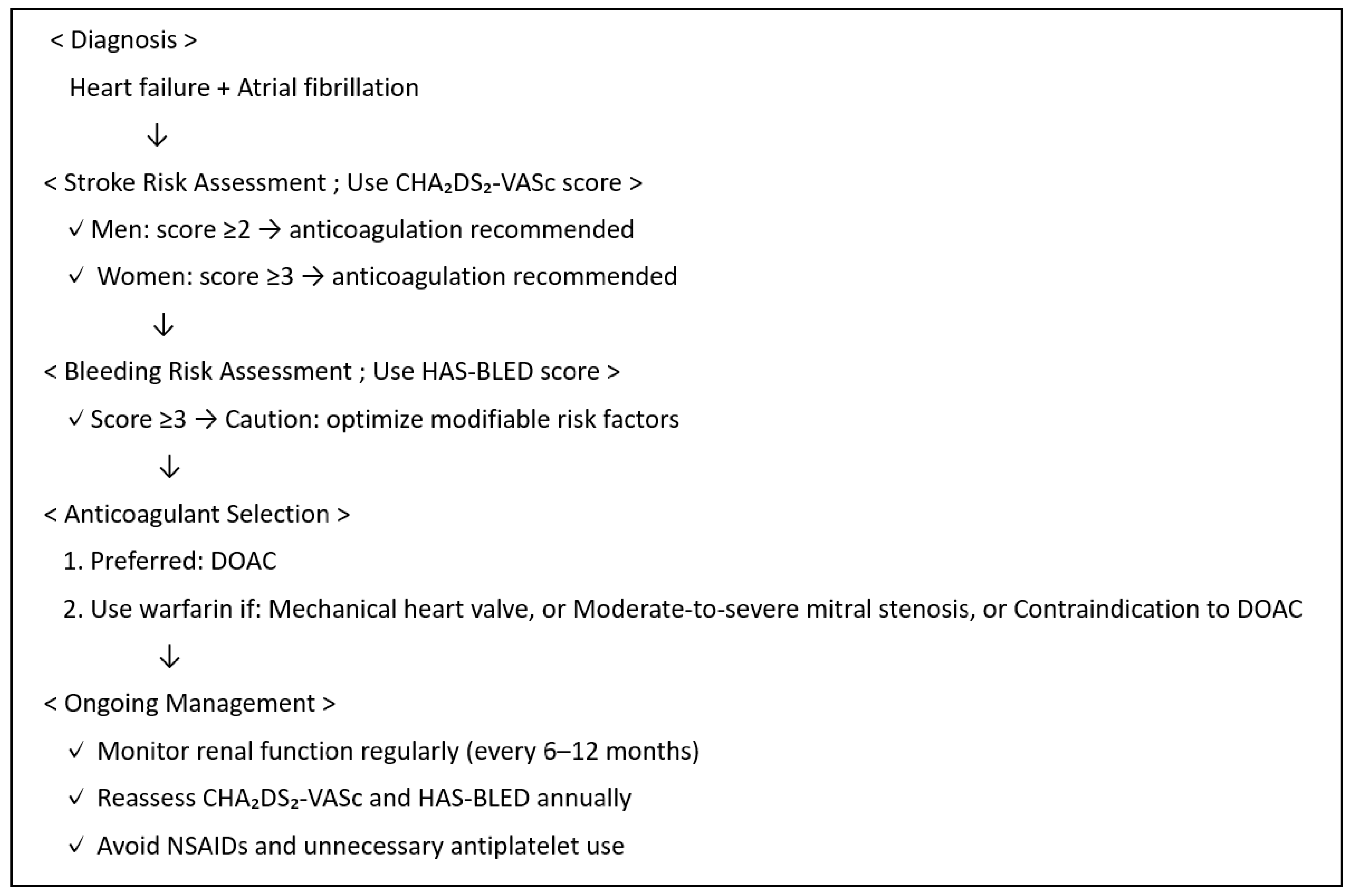
6. Risk Factors and Predictive Models for Stroke
7. Clinical Outcomes and Prognosis After Ischemic Stroke
8. Management and Treatment Strategies
8.1. Pharmacological Therapies for Heart Failure
8.2. Pharmacological Therapies for Atrial Fibrillation
8.3. Non-Pharmacological Therapies for Heart Failure
8.4. Stroke Management in Patients with Heart Failure
9. Future Directions and Research Gaps
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, K.K.; Pinsky, J.L.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. The epidemiology of heart failure: The Framingham Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22, A6–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Böhm, M.; Butler, J.; et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: A report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 387–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaeian, B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Sakata, Y.; Nochioka, K.; Miura, M.; Abe, R.; Kasahara, S.; Sato, M.; Aoyanagi, H.; Fujihashi, T.; Yamanaka, S.; et al. Risk of de-novo heart failure and competing risk in asymptomatic patients with structural heart diseases. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 307, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Larson, M.G.; Leip, E.P.; Beiser, A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Kannel, W.B.; Murabito, J.M.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2002, 106, 3068–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimokawa, H.; Miura, M.; Nochioka, K.; Sakata, Y. Heart failure as a general pandemic in Asia. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.K.; Anderson, K.M.; Kannel, W.B.; Grossman, W.; Levy, D. Survival after the onset of congestive heart failure in Framingham Heart Study subjects. Circulation 1993, 88, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, H.; Kronmal, R.; Bluemke, D.A.; Olson, J.; Shea, S.; Liu, K.; Burke, G.L.; Lima, J.A. Differences in the incidence of congestive heart failure by ethnicity: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, M.; Tezuka, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Hamatani, Y.; Takagi, D.; An, Y.; Unoki, T.; Ishii, M.; Masunaga, N.; Esato, M.; et al. Incidence and Risk Factors of Stroke or Systemic Embolism in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure- The Fushimi AF Registry. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.P.; Kinugawa, K. Globe is Still Heterogenous from the Perspective of Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail 2022, 28, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelborg, K.; Szépligeti, S.; Sundbøll, J.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Henderson, V.W.; Ording, A.; Pedersen, L.; Sørensen, H.T. Risk of Stroke in Patients with Heart Failure: A Population-Based 30-Year Cohort Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khadra, A.S.; Salem, D.N.; Rand, W.M.; Udelson, J.E.; Smith, J.J.; Konstam, M.A. Antiplatelet agents and survival: A cohort analysis from the Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction (SOLVD) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedberg, K.; Kjekshus, J. CONSENSUS Trial Study Group. Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. Results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Barkhudaryan, A.; Doehner, W.; Scherbakov, N. Ischemic Stroke and Heart Failure: Facts and Numbers. An Update. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahim, A.H.; Perez, A.C.; MacIsaac, R.L.; Jhund, P.S.; Claggett, B.L.; Carson, P.E.; Komajda, M.; McKelvie, R.S.; Zile, M.R.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Risk of Stroke in Chronic Heart Failure Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction, but without Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of the CHARM-Preserved and I-Preserve Trials. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahim, A.H.; Perez, A.C.; Fulton, R.L.; Jhund, P.S.; Latini, R.; Tognoni, G.; Wikstrand, J.; Kjekshus, J.; Lip, G.Y.; Maggioni, A.P.; et al. Risk of Stroke in Chronic Heart Failure Patients Without Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of the Controlled Rosuvastatin in Multinational Trial Heart Failure (CORONA) and the Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell’Insufficienza Cardiaca-Heart Failure (GISSI-HF) Trials. Circulation 2015, 131, 1486–1494; discussion 1494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Kim, J.; Park, J.J.; Oh, I.Y.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Choi, D.J. Risk of stroke in congestive heart failure with and without atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 248, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinugawa, T.; Kato, M.; Ogino, K.; Igawa, O.; Hisatome, I.; Shigemasa, C.; Nohara, R. Neurohormonal determinants of peak oxygen uptake in patients with chronic heart failure. Jpn. Heart J. 2003, 44, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, A.; Andrade, A.; Azevedo, E.; Gomes, F.; Araújo, J.P.; Castro, P. Neurovascular Coupling Impairment in Heart Failure with Reduction Ejection Fraction. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Howard, S.C.; Dolan, E.; O’Brien, E.; Dobson, J.; Dahlöf, B.; Sever, P.S.; Poulter, N.R. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010, 375, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, E.J. Heart Failure as a Risk Factor for Stroke. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaber, N.N.; Mattash, Z.A.; Alshoabi, S.A.; Alhazmi, F.H. The prevalence of left ventricular thrombus among patients with low ejection fraction by trans-thoracic echocardiography. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Kim, S.; Moore, C.; Thomas, L.; Gersh, B.; Allen, L.A.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Hylek, E.; Peterson, E.D.; et al. Predictors and Prognostic Implications of Incident Heart Failure in Patients with Prevalent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vaziri, S.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Wolf, P.A. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA 1994, 271, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanakrishnan, R.; Wang, N.; Larson, M.G.; Magnani, J.W.; McManus, D.D.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; Cheng, S.; Vasan, R.S.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Begets Heart Failure and Vice Versa: Temporal Associations and Differences in Preserved Versus Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2016, 133, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnussen, C.; Niiranen, T.J.; Ojeda, F.M.; Gianfagna, F.; Blankenberg, S.; Njølstad, I.; Vartiainen, E.; Sans, S.; Pasterkamp, G.; Hughes, M.; et al. BiomarCaRE Consortium. Sex Differences and Similarities in Atrial Fibrillation Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Mortality in Community Cohorts: Results from the BiomarCaRE Consortium (Biomarker for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Europe). Circulation 2017, 136, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewland, T.A.; Olgin, J.E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Marcus, G.M. Incident atrial fibrillation among Asians, Hispanics, blacks, and whites. Circulation 2013, 128, 2470–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, M.F.; Tucker, N.R.; Lunetta, K.L.; Ozaki, K.; Smith, J.G.; Trompet, S.; Bis, J.C.; Lin, H.; Chung, M.K.; Nielsen, J.B.; et al. Integrating genetic, transcriptional, and functional analyses to identify 5 novel genes for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 130, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.K.; Takahashi, A.; Ebana, Y.; Ozaki, K.; Christophersen, I.E.; Ellinor, P.T.; AFGen Consortium; Ogishima, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Satoh, M.; et al. Identification of six new genetic loci associated with atrial fibrillation in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, B.F.; Waterman, A.D.; Shannon, W.; Boechler, M.; Rich, M.W.; Radford, M.J. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: Results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2001, 285, 2864–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Heart Rhythm Association; European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery; Camm, A.J.; Kirchhof, P.; Lip, G.Y.; Schotten, U.; Savelieva, I.; Ernst, S.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Al-Attar, N.; et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: The Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2369–2429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okumura, K.; Tomita, H.; Nakai, M.; Kodani, E.; Akao, M.; Suzuki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Sawano, M.; Goya, M.; Yamashita, T.; et al. A Novel Risk Stratification System for Ischemic Stroke in Japanese Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2021, 85, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, C.; Ling, A.Y.; Crawford, M.H.; Zhao, S.X.; Shah, N.H. A Clinical Score for Predicting Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Cryptogenic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Cardiology 2017, 138, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, B.; Chang, A.D.; Hemendinger, M.; Dakay, K.; Cutting, S.; Burton, T.; Mac Grory, B.; Narwal, P.; Song, C.; Chu, A.; et al. A Simple Score That Predicts Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation on Outpatient Cardiac Monitoring after Embolic Stroke of Unknown Source. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, T.; Suda, S.; Morimoto, M.; Tsuboi, Y.; Sonoda, T.; Sonoda, K.; Koga, M.; Ihara, M.; Iguchi, Y.; Murakami, H.; et al. Atrial fibrillation detection in cryptogenic stroke and a prediction score using imaging examination. J. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 473, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaard, L.; Gorst-Rasmussen, A.; Lane, D.A.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Larsen, T.B.; Lip, G.Y. Assessment of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score in Predicting Ischemic Stroke, Thromboembolism, and Death in Patients with Heart Failure with and Without Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2015, 314, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FFreudenberger, R.S.; Cheng, B.; Mann, D.L.; Thompson, J.L.; Sacco, R.L.; Buchsbaum, R.; Sanford, A.; Pullicino, P.M.; Levin, B.; Teerlink, J.R.; et al. The first prognostic model for stroke and death in patients with systolic heart failure. J. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Tullio, M.R.; Qian, M.; Thompson, J.L.; Labovitz, A.J.; Mann, D.L.; Sacco, R.L.; Pullicino, P.M.; Freudenberger, R.S.; Teerlink, J.R.; Graham, S.; et al. Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction and Risk of Stroke and Cardiac Events in Heart Failure: Data from the Warfarin Versus Aspirin in Reduced Ejection Fraction Trial. Stroke 2016, 47, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Girerd, N.; Gregson, J.; Latar, I.; Sharma, A.; Pfeffer, M.A.; McMurray, J.J.; Abdul-Rahim, A.H.; Pitt, B.; Dickstein, K.; et al. Stroke Risk in Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction After Myocardial Infarction Without Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, B.J.R.; Harrison, S.L.; Hill, A.; Underhill, P.; Lane, D.A.; Lip, G.Y.H. Stroke-Heart Syndrome: Incidence and Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Complications Following Stroke. Stroke 2022, 53, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehner, W.; Böhm, M.; Boriani, G.; Christersson, C.; Coats, A.J.; Haeusler, K.G.; Jones, I.D.; Lip, G.Y.; Metra, M.; Ntaios, G.; et al. Interaction of heart failure and stroke: A clinical consensus statement of the ESC Council on Stroke, the Heart Failure Association (HFA) and the ESC Working Group on Thrombosis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 2107–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.; MacGregor, L.; Lees, K.R.; Diener, H.-C.; Hacke, W.; Davis, S.; VISTA Investigators. Predictors of early cardiac morbidity and mortality after ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007, 38, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Yeh, C.-C.; Sung, L.-C.; Hu, C.-J.; Cherng, Y.-G.; Chen, T.-L.; Liao, C.-C. Long-Term Risk of Stroke and Poststroke Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure: Two Nationwide Studies. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 12, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennfält, S.; Pihlsgård, M.; Petersson, J.; Norrving, B.; Ullberg, T. Long-term outcome after ischemic stroke in relation to comorbidity—An observational study from the Swedish Stroke Register (Riksstroke). Eur. Stroke J. 2020, 5, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Kondo, T.; Butt, J.H.; Abraham, W.T.; Anand, I.S.; Desai, A.S.; Køber, L.; Packer, M.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Rouleau, J.L.; et al. Stroke in patients with heart failure and reduced or preserved ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2998–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e263–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, C.; Kernan, W.N.; Sharrief, A.Z.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cole, J.W.; Cornwell, W.K.; Cosby-Gaither, C.; Doyle, S.; Goldstein, L.B.; Lennon, O.; et al. Guideline for the Primary Prevention of Stroke: A Guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2024, 55, e344–e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S. Medical Management of Acute Stroke based on Japan Stroke Society Guidelines and the Japan Stroke Data Bank. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2024, 31, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Minematsu, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Japan Multicenter Stroke Investigators’ Collaboration (J-MUSIC). Atrial fibrillation as a predictive factor for severe stroke and early death in 15,831 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Tsutsui, K.; Nakano, S.; Hayashi, T.; Suda, S. Cardioembolic Stroke: Past Advancements, Current Challenges, and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.A.; Chae, C.U.; Kim, E.; Moorthy, M.V.; Conen, D.; Sandhu, R.K.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.-M.; Albert, C.M. Modifiable Risk Factors for Incident Heart Failure in Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishii, M.; Iguchi, M.; Masunaga, N.; Esato, M.; Tsuji, H.; Wada, H.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Causes of death in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation: The Fushimi Atrial Fibrillation Registry. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2019, 5, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Bristow, M.R.; Cohn, J.N.; Colucci, W.S.; Fowler, M.B.; Gilbert, E.M.; Shusterman, N.H. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechat, P.; Brunhuber, K.W.; Hofmann, R.; Kuhn, P.; Nesser, H.J.; Slany, J.; Weihs, W.; Wiedermann, C.; Wimmer, H.; Mieghem, W.; et al. The Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II (CIBIS-II): A randomised trial. Lancet 1999, 353, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Zannad, F.; Remme, W.J.; Cody, R.; Castaigne, A.; Perez, A.; Palensky, J.; Wittes, J. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.L.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.P.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Januzzi, J.L. Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauersachs, J. Heart failure drug treatment: The fantastic four. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; Jhund, P.S.; Cunningham, J.W.; Ferreira, J.P.; Zannad, F.; Packer, M.; Fonarow, G.C.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D. Estimating lifetime benefits of comprehensive disease-modifying pharmacological therapies in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A comparative analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2020, 396, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M. How Should We Sequence the Treatments for Heart Failure and a Reduced Ejection Fraction?: A Redefinition of Evidence-Based Medicine. Circulation 2021, 143, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner–La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.; Martinez, F.; et al. Baseline Characteristics of Patients With HF With Mildly Reduced and Preserved Ejection Fraction: DELIVER Trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2022, 10, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voors, A.A. Novel Recommendations for the Treatment of Patients With Heart Failure: 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Heart Failure Guidelines. J. Card. Fail. 2023, 29, 1667–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Assmann, S.F.; Boineau, R.; Anand, I.S.; Claggett, B.; Clausell, N.; Desai, A.S.; Diaz, R.; Fleg, J.L.; et al. Spironolactone for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Anand, I.S.; Junbo Ge, D.P.; Lam, C.S.P.; Maggioni, A.P.; Martinez, F.; Packer, M.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Pieske, B.; et al. Angiotensin-Neprilysin Inhibition in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Chen, X.Q.; Xu, L.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Luo, B.H. SGLT2 inhibitors and atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis of 16 randomized controlled trials. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.N.; Duan, J.Y.; Yuan, M.Y.; Zhang, J.Y. Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors with Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke in Patients With and Without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, e145–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-H.; Chuang, S.-M.; Liu, S.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Chien, M.-N.; Leung, C.-H.; Liu, S.-J.; Shih, H.-M. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on stroke and its subtypes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantsila, E.; Lip, G.Y. Antiplatelet versus anticoagulation treatment for patients with heart failure in sinus rhythm. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 9, CD003333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, J.; Findlay, I.; Jafri, S.; Sutton, G.; Falk, R.; Bulpitt, C.; Prentice, C.; Ford, I.; Trainer, A.; Poole-Wilson, P. The Warfarin/Aspirin Study in Heart failure (WASH): A randomized trial comparing antithrombotic strategies for patients with heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2004, 148, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cokkinos, D.V.; Haralabopoulos, G.C.; Kostis, J.B.; Toutouzas, P.K.; HELAS investigators. Efficacy of antithrombotic therapy in chronic heart failure: The HELAS study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2006, 8, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massie, B.M.; Ammon, S.E.; Collins, J.F.; Krol, W.F.; Armstrong, P.W.; Cleland, J.G.; Ezekowitz, M.; Jafri, S.M.; O’Connor, C.M.; Schulman, K.A.; et al. Randomized trial of warfarin, aspirin, and clopidogrel in patients with chronic heart failure: The Warfarin and Antiplatelet Therapy in Chronic Heart Failure (WATCH) trial. Circulation 2009, 119, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Thompson, J.L.; Pullicino, P.M.; Levin, B.; Freudenberger, R.S.; Teerlink, J.R.; Ammon, S.E.; Graham, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Mann, D.L.; et al. Warfarin and aspirin in patients with heart failure and sinus rhythm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannad, F.; Anker, S.D.; Byra, W.M.; Cleland, J.G.; Fu, M.; Gheorghiade, M.; Lam, C.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Neaton, J.D.; Nessel, C.C.; et al. Rivaroxaban in Patients with Heart Failure, Sinus Rhythm, and Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, B.; Neaton, J.D.; Anker, S.D.; Byra, W.M.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Deng, H.; Fu, M.; La Police, D.A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Mehra, M.R.; et al. Association of Rivaroxaban with Thromboembolic Events in Patients With Heart Failure, Coronary Disease, and Sinus Rhythm: A Post Hoc Analysis of the COMMANDER HF Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Ave-zum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Špinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Lau, Y.C.; Senoo, K.; Lane, D.A.; Hong, K.; Lip, G.Y. Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) in patients with concomitant atrial fibrillation and heart failure: A systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M. Safety and efficacy of intravenous thrombolysis before mechanical thrombectomy in patients with atrial fibrillation. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Sievert, H.; Halperin, J.; Doshi, S.K.; Buchbinder, M.; Neuzil, P.; Huber, K.; Whisenant, B.; Kar, S.; Swarup, V.; et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure vs warfarin for atrial fibrillation: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 1988–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, R.; Healey, J.; Vincent, J.; Brady, K.; Teoh, K.; Royse, A.; Shah, P.; Guo, Y.; Alings, M.; Folkeringa, R.J.; et al. Rationale and design of the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Study (LAAOS) III. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 3, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belgaid, D.R.; Khan, Z.; Zaidi, M.; Hobbs, A. Prospective randomized evaluation of the watchman left atrial appendage closure device in patients with atrial fibrillation versus long-term warfarin therapy: The PREVAIL trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 219, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmancik, P.; Herman, D.; Neuzil, P.; Hala, P.; Taborsky, M.; Kala, P.; Poloczek, M.; Stasek, J.; Haman, L.; Branny, M.; et al. 4-Year Outcomes After Left Atrial Appendage Closure Versus Nonwarfarin Oral Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Carroll, J.D.; Thaler, D.E.; Smalling, R.W.; MacDonald, L.A.; Marks, D.S.; Tirschwell, D.L. Long-Term Outcomes of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Medical Therapy after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.-L.; Derumeaux, G.; Guillon, B.; Massardier, E.; Hosseini, H.; Mechtouff, L.; Arquizan, C.; Béjot, Y.; Vuillier, F.; Detante, O.; et al. CLOSE Investigators. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E.; Rhodes, J.F.; Andersen, G.; Iversen, H.K.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Settergren, M.; Sjöstrand, C.; Roine, R.O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Gore REDUCE Clinical Study Investigators. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J.G.M. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobita, T.; Nomura, S.; Fujita, T.; Morita, H.; Asano, Y.; Onoue, K.; Ito, M.; Imai, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Ko, T.; et al. Genetic basis of cardiomyopathy and the genotypes involved in prognosis and left ventricular reverse remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial Name | LVEF | Study Design | Intervention | Primary Outcome | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WASH | ≤35% | Open-label, randomized, control trial. | Warfarin vs. aspirin vs. no anti-platelet therapy | Composite outcome of death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke | No significant difference in the primary clinical outcome among the 3 groups |
| HELAS | ≤35% | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. | Warfarin vs. aspirin vs. placebo | Composite of non-fatal stroke, peripheral or pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, rehospitalization, worsening heart failure, and all-cause mortality | No significant difference in the primary clinical outcome among the 3 groups |
| WATCH | ≤35% | Double-blind, randomized trial. Double-dummy controlled for anti-platelet therapy or open-label warfarin. | Warfarin vs. aspirin vs. clopidogrel | Composite of all-cause mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke | No significant difference in the primary clinical outcome among the 3 groups |
| WARCEF | ≤35% | Double-blind, randomized, double-dummy controlled trial. | Warfarin vs. aspirin | Time to first event in a composite endpoint of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage or all-cause mortality | No difference between the 2 groups |
| COMMANDER-HF | ≤40% | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. | Rivaroxaban vs. placebo | Composite of all-cause mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke | No difference between the 2 groups |
| Trial Name | DOAC | Patient Population | Efficacy (Stroke/Systemic Embolism) (vs. Warfarin) | Major Bleeding Risk (vs. Warfarin) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE-LY | Dabigatran | Non-valvular AF, included HF | Superior (150 mg twice daily) | Similar overall; increased gastrointestinal bleeding at 150 mg dose | Two-dose comparison (110 mg and 150 mg) |
| ROCKET AF | Rivaroxaban | Non-valvular AF (CHADS2 score ≥ 2), included HF | Non-inferior | Similar overall; increased gastrointestinal bleeding | Once-daily dosing High-risk population |
| ARISTOTLE | Apixaban | Non-valvular AF, included HF | Superior | Lower major bleeding, including lower gastrointestinal bleeding | Once-daily dosing |
| ENGAGE AF | Edoxiaban | Non-valvular AF, included HF | Non-inferior | Lower major bleeding, especially lower gastrointestinal bleeding | Two doses tested (60 mg and 30 mg) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katano, T.; Mori, H.; Suda, S. Heart Failure and Stroke: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176044
Katano T, Mori H, Suda S. Heart Failure and Stroke: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176044
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatano, Takehiro, Hitoshi Mori, and Satoshi Suda. 2025. "Heart Failure and Stroke: A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176044
APA StyleKatano, T., Mori, H., & Suda, S. (2025). Heart Failure and Stroke: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176044






