Age-Dependent Clinical Relevance of Lipoprotein(a): A Comprehensive Review from Childhood to Adulthood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biology and Genetics of Lipoprotein(a)
3. Lp(a) Expression and Measurement Over the Lifespan
3.1. Children and Adolescents
3.2. Adults and Elders
3.3. Population Variations
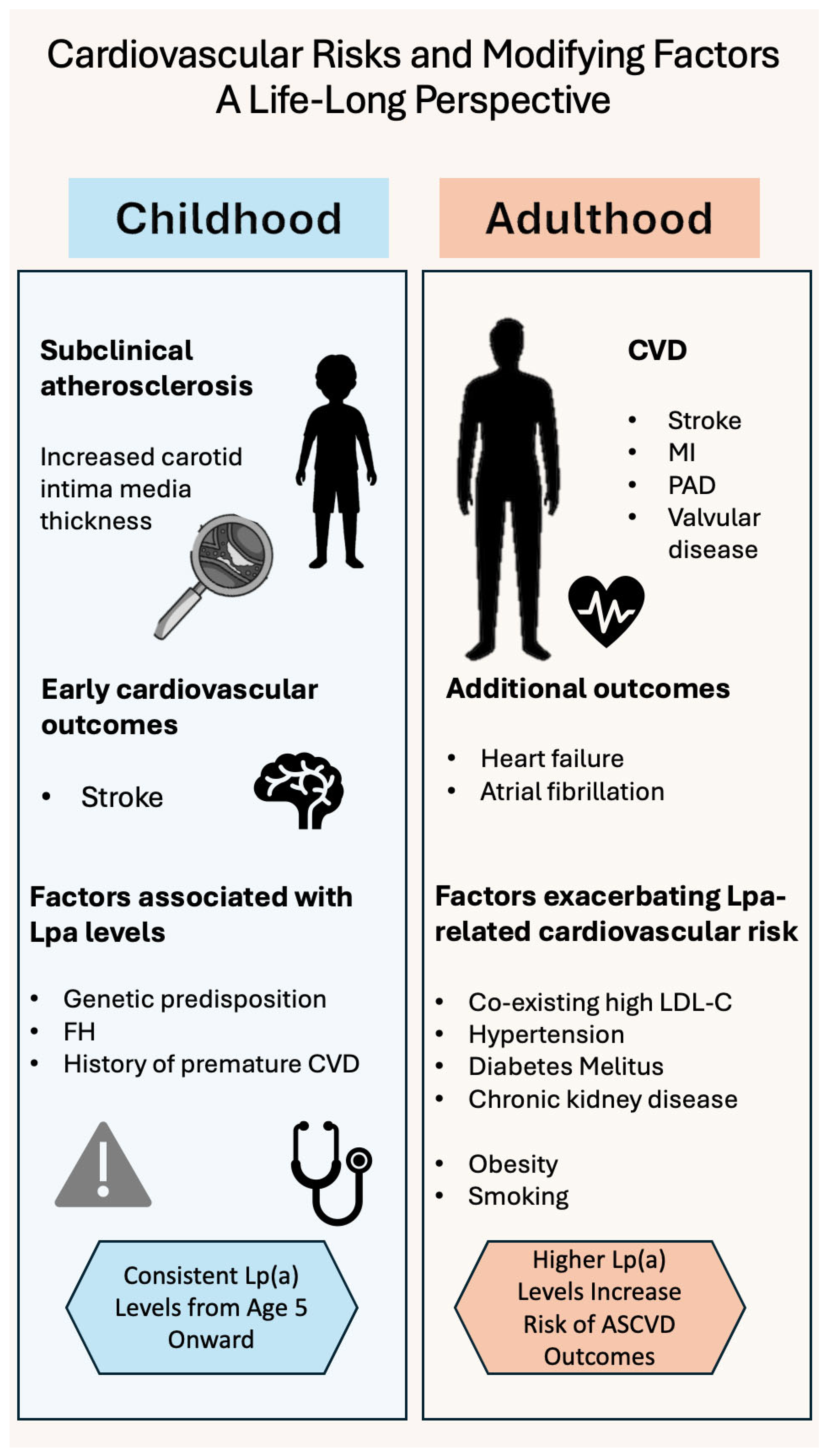
4. Risk-Stratification According to Age
4.1. Children and Adolescents
4.2. Adults
4.3. Elders
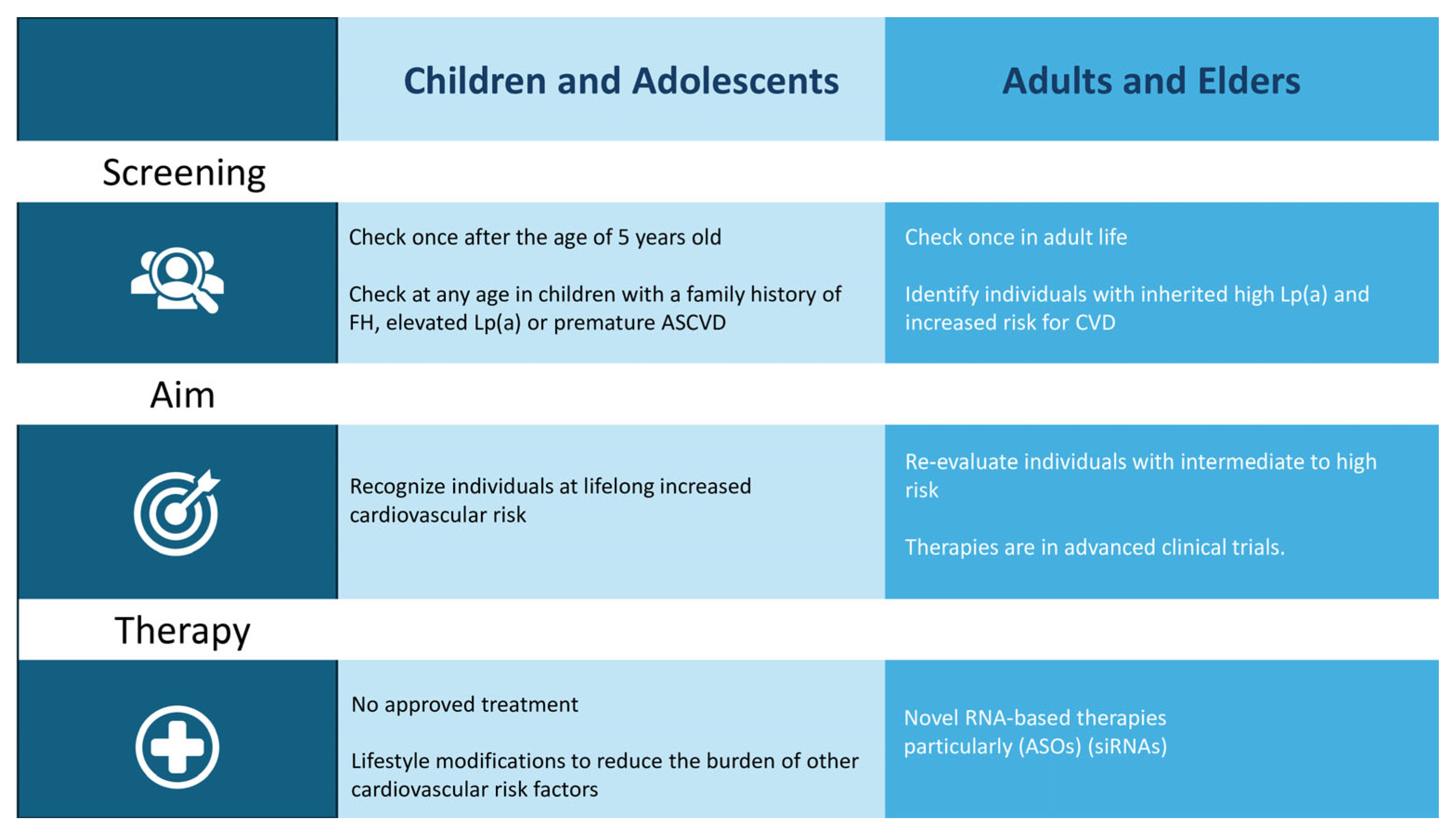
5. Screening
5.1. Children and Adolescents
5.2. Adults and Elders
6. Therapy
6.1. Lifestyle Modifications and Current Pharmacological Options
6.2. Novel Treatments
6.3. Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
6.4. Small Interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
6.5. Oral Therapy—Muvalaplin
6.6. Future Directions—Gene Editing
7. Limitations of Current Literature
8. Gaps in Evidence—Future Directions
8.1. Children and Adolescents
8.2. Elders
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein(a) |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease |
| FH | Familial Hypercholesterolemia |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| ApoB | Apolipoprotein B100 |
| ApoA | Apolipoprotein A |
| KIV | Kringle IV |
| CNVs | Copy Number Variations |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| SNPs | Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| FMD | Flow-Mediated Dilation |
| IMT | Intima-Media Thickness |
| PWV | Pulse Wave Velocity |
| SEVR | Subendocardial Viability Ratio |
| ART | Assisted Reproductive Technologies |
| AVS | Aortic Valve Stenosis |
| PCSK9is | Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin type 9 Inhibitors |
| ASOs | Antisense Oligonucleotides |
| siRNAs | Small Interfering RNAs |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
References
- Kostner, K.M.; Kostner, G.M. Lipoprotein(a): A historical appraisal. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 58, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Ference, B.A.; Arsenault, B.J.; Berglund, L.; Dweck, M.R.; Koschinsky, M.; Lambert, G.; Mach, F.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and aortic stenosis: A European Atherosclerosis Society consensus statement. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3925–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G. Consensus and guidelines on lipoprotein(a)—Seeing the forest through the trees. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2022, 33, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrington, P. Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic heart disease and familial hypercholesterolaemia. Br. J. Cardiol. 2024, 31 (Suppl. 1), S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. In Endotext; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Sheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lu, L.; Jin, W. Copy number variation of the Lipoprotein(a) (LPA) gene is associated with coronary artery disease in a southern Han Chinese population. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 3669. [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg, F. Lipoprotein(a): From Causality to Treatment. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2024, 26, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Björnson, E.; Wang, X.; Ζhang, B.; Xu, C.; Guan, Y.; Xiang, S.; Borén, J.; Hao, X.; Chen, J. Distinct lipoprotein contributions to valvular heart disease: Insights from genetic analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 431, 133218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simantiris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Papastamos, C.; Benetos, G.; Koumallos, N.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. Lipoprotein(a) and inflammation- pathophysiological links and clinical implications for cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2023, 17, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K.E.; Kraaijenhof, J.M.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Nurmohamed, N.S.; Kroon, J. Lipoprotein(a): An underestimated inflammatory mastermind. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Ma, T.Y.; Huang, K.; Lu, S.J.; Zhong, J.H.; Li, J.J. Lipoprotein(a)-Related Inflammatory Imbalance: A Novel Horizon for the Development of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2024, 26, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, M.; Orlando, A.; Tassistro, E.; Torresani, E.; Lieti, G.; Patti, I.; Colombrita, C.; Bulgarelli, I.; Antolini, L.; Parati, G.; et al. Is lipoprotein(a) measurement important for cardiovascular risk stratification in children and adolescents? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2024, 50, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pac-Kozuchowska, E.; Krawiec, P.; Grywalska, E. Selected risk factors for atherosclerosis in children and their parents with positive family history of premature cardiovascular diseases: A prospective study. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simony, S.B.; Mortensen, M.B.; Langsted, A.; Afzal, S.; Kamstrup, P.R.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Sex differences of lipoprotein(a) levels and associated risk of morbidity and mortality by age: The Copenhagen General Population Study. Atherosclerosis 2022, 355, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Prasad, A.; Choi, Y.S.; Xing, C.; Clopton, P.; Witztum, J.L.; Tsimikas, S. The LPA gene, ethnicity and cardiovascular events. Circulation 2016, 135, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenson, G.S. Bogalusa Heart Study: A long-term community study of a rural biracial (Black/White) population. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2001, 322, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayum, O.; Alshami, N.; Ibezim, C.F.; Reid, K.J.; Noel-MacDonnell, J.R.; Raghuveer, G. Lipoprotein(a): Examination of Cardiovascular Risk in a Pediatric Referral Population. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2018, 39, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammanco, A.; Noto, D.; Nardi, E.; Gagliardo, C.M.; Scrimali, C.; Brucato, F.; Spina, R.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Caldarella, R.; Ciaccio, Μ.; et al. Do genetically determined very high and very low LDL levels contribute to Lp(a) plasma concentration? Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 35, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, L.M.; Wiegman, A.; van Gemert, R.L.A.; Hutten, B.A.; Klaassen, I.L.M. The association between lipoprotein(a) levels and ischemic stroke in children: A case-control study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2024, 71, e31236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, A.H.; Lange, K.S.; Leonards, C.O.; Siegerink, B.; Doehner, W.; Landmesser, U.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Endres, M.; Ebinger, M. Lipoprotein(a) as a risk factor for ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawacki, A.W.; Dodge, A.; Woo, K.M.; Ralphe, J.C.; Peterson, A.L. In pediatric familial hypercholesterolemia, lipoprotein(a) is more predictive than LDL-C for early onset of cardiovascular disease in family members. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederiva, C.; Capra, M.E.; Biasucci, G.; Banderali, G.; Fabrizi, E.; Gazzotti, M.; Casula, M.; Catapano, A.L. Lipoprotein(a) and family history for cardiovascular disease in paediatric patients: A new frontier in cardiovascular risk stratification. Data from the LIPIGEN paediatric group. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitakari, O.; Kartiosuo, N.; Pahkala, K.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Bazzano, L.A.; Chen, W.; Urbina, E.M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Sinaiko, A.; Steinberger, J.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Youth and Prediction of Major Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adulthood. Circulation 2023, 147, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, K.E.; Celermajer, D.S.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Hatcher, G.; Betteridge, D.J.; Deanfield, J.E. Impairment of endothelium-dependent dilation is an early event in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and is related to the lipoprotein(a) level. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapinleimu, J.; Raitakari, O.T.; Lapinleimu, H.; Pahkala, K.; Rönnemaa, T.; Simell, O.G.; Viikari, J.S.A. High Lipoprotein(a) Concentrations Are Associated with Impaired Endothelial Function in Children. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 947–952.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, L.M.; Wiegman, A.; Kroon, J.; Tsimikas, S.; Yeang, C.; Peletier, M.C.; Revers, A.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Hutten, B.A. Lipoprotein(a) and carotid intima-media thickness in children with familial hypercholesterolaemia in the Netherlands: A 20-year follow-up study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helk, O.; Böck, A.; Stefanutti, C.; Widhalm, K. Lp(a) does not affect intima media thickness in hypercholesterolemic children -a retrospective cross sectional study. Atheroscler. Plus 2022, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimäki, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Juonala, M.; Kähönen, M.; Kettunen, J.; Loo, B.M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Viikari, J.; Raitakari, O.T. Conventional and Mendelian randomization analyses suggest no association between lipoprotein(a) and early atherosclerosis: The Young Finns Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bosch, S.E.; Boer, L.M.D.; Revers, A.; Schrauben, E.M.; Ooij, P.V.; Nederveen, A.J.; Corpeleijn, W.E.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Wiegman, A.; Hutten, B.A. Association Between Lipoprotein(a) and Arterial Stiffness in Young Adults with Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou-Legbelou, K.; Triantafyllou, A.; Vampertzi, O.; Koletsos, N.; Douma, S.; Papadopoulou-Alataki, E. Similar Myocardial Perfusion and Vascular Stiffness in Children and Adolescents with High Lipoprotein(a) Levels, in Comparison with Healthy Controls. Pulse 2021, 9, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Moran, M.; Gamboa-Gómez, C.I.; Preza-Rodríguez, L.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Lipoprotein(a) and Hyperinsulinemia in Healthy Normal-weight, Prepubertal Mexican Children. Endocr. Res. 2021, 46, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacopoulou, F.; Apostolaki, D.; Mantzou, A.; Doulgeraki, A.; Pałasz, A.; Tsimaris, P.; Koniari, E.; Efthymiou, V. Serum Spexin is Correlated with Lipoprotein(a) and Androgens in Female Adolescents. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberhoffer, F.S.; Langer, M.; Li, P.; Sciuk, F.; Kramer, M.; Kolbinger, B.; Jakob, A.; Rogenhofer, N.; Dalla-Pozza; Thaler, C.; et al. Vascular function in a cohort of children, adolescents and young adults conceived through assisted reproductive technologies—Results from the Munich heARTerY-study. Transl. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Moran, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Low birthweight and elevated levels of lipoprotein(a) in prepubertal children. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2014, 50, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, R.W.; Ford, C.E.; Simpson, L.M.; Walldius, G.; Jungner, I.; Folsom, A.R.; Chambless, L.; Panagiotakos, D.; Pitsavos, C.; Chrysohoou, C.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) Concentration and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke, and Nonvascular Mortality. JAMA 2009, 302, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsis, A.; Myrianthefs, M.; Sokratous, S.; Karmioti, G.; Kyriakou, M.; Drakomathioulakis, M.; Tzikas, S.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Karagiannidis, E.; Nasoufidou, A.; et al. Emerging Therapeutic Targets for Acute Coronary Syndromes: Novel Advancements and Future Directions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Acerbo, V.; Scialla, F.; De Michele, G.; Panico, D.; Porcelli, G.; de Sio, V.; Capolongo, A.; Sperlongano, S.; Ruggiero, A.; et al. Role of LipoprotEin(a) in CardiovascuLar diseases and premature acute coronary syndromes (RELACS study): Impact of Lipoprotein(a) levels on the premature coronary event and the severity of coronary artery disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 35, 103843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Wright, N.; Lin, K.; Yu, C.; Walters, R.G.; Lv, J.; Hill, M.; Kartsonaki, C.; Millwood, I.Y.; Bennett, D.A.; et al. Causal Relevance of Lp(a) for Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke Types in East Asian and European Ancestry Populations: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Circulation 2025, 151, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Shi, Q.; Fang, L.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J. Persistent lipoprotein(a) exposure and its association with clinical outcomes after acute myocardial infarction: A longitudinal cohort study. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2454975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.P.; Wang, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ng, K.; Kathiresan, S.; Khera, A.V. Lp(a) (Lipoprotein[a]) Concentrations and Incident Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease New Insights from a Large National Biobank. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, T.; Shah, N.P.; Giamberardino, S.N.; Kwee, L.C.; Voora, D.; McGarrah, R.W.; Ferencik, M.; Lu, M.T.; Kraus, W.E.; Foldyna, B.; et al. Association Between Lipoprotein(a) and Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease and High-Risk Plaque: Insights From the PROMISE Trial. Am. J. Cardiol. 2024, 231, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.L.; Garg, P.K.; Guan, W.; Tsai, M.Y.; Criqui, M.H.; Tsimikas, S.; Bhatia, H.S. Lipoprotein(a) and coronary artery calcium in comparison with other lipid biomarkers: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2023, 17, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouvari, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Yannakoulia, M.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Critselis, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Pitsavos, C. Transition from metabolically benign to metabolically unhealthy obesity and 10-year cardiovascular disease incidence: The ATTICA cohort study. Metabolism 2019, 93, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Zu, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, Y.; Shen, D.; Ma, Y.; Fu, J.; Du, J.; Yu, C.; Lv, J.; et al. Prevalence of Elevated Lipoprotein(a) and its Association With Subclinical Atherosclerosis in 2.9 Million Chinese Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2025, 85, 1979–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelidis, P.; Oikonomou, E.; Lampsas, S.; Zakynthinos, G.E.; Lysandrou, A.; Kalogeras, K.; Katsianos, E.; Theofilis, P.; Siasos, G.; Vavuranakis, M.A.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and calcific aortic valve disease initiation and progression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.J.; Xia, T.L.; Chen, G.C.; Yang, J.; Li, F.R. Lipoprotein(a), family history of cardiovascular disease, and incidence of heart failure. J. Lipid Res. 2023, 64, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamstrup, P.R.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated lipoprotein(a) levels, LPA risk genotypes, and increased risk of heart failure in the general population. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Baars, D.P.; Aggarwal, K.; Desai, R.; Singh, D.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.J. Association between Lipoprotein(a) and risk of heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Mendelian randomization studies. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Chong, M.; Narula, S.; Perrot, N.; Conen, D.; Roberts, J.D.; Thériault, S.; Bossé, Y.; Lanktree, M.B.; Pigeyre, M.; et al. Elevated Lipoprotein(a) and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: An Observational and Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaw, A.; Murray, H.M.; Brown, E.A. Plasma lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] concentrations and cardiovascular events in the elderly: Evidence from the prospective study of pravastatin in the elderly at risk (PROSPER). Atherosclerosis 2005, 180, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyo, A.A.; Thach, C.; Tracy, R. Lp(a) Lipoprotein, Vascular Disease, and Mortality in the Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.H.; Jin, J.L.; Yan, X.N.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.J. Lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular death in oldest-old (≥80 years) patients with acute myocardial infarction: A prospective cohort study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 312, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli-Leonard, F.; Turner, M.E.; Zimmer, J.; Chapurlat, R.; Pham, T.; Aikawa, M.; Pradhan, A.D.; Szulc, P.; Aikawa, E. Elevated lipoprotein(a) as a predictor for coronary events in older men. J. Lipid Res. 2022, 63, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, L.A.; Simons, J.; Friedlander, Y.; McCallum, J. LDL-cholesterol Predicts a First CHD Event in Senior Citizens, Especially So in Those With Elevated Lipoprotein(a): Dubbo Study of the Elderly. Heart Lung Circ. 2018, 27, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Adiels, M.; Taskinen, M.R.; Burgess, S.; Chapman, M.J.; Packard, C.J.; Βorén, J. Lipoprotein(a) Is Markedly More Atherogenic Than LDL: An Apolipoprotein B-Based Genetic Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Zhou, L. Correlation analysis between serum Lipoprotein(a) and the incidence of aortic valve sclerosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 19318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milionis, H.J.; Filippatos, T.D.; Loukas, T.; Bairaktari, E.T.; Tselepis, A.D.; Elisaf, M.S. Serum lipoprotein(a) levels and apolipoprotein(a) isoform size and risk for first-ever acute ischaemic nonembolic stroke in elderly individuals. Atherosclerosis 2006, 187, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, M.; Clarke, S.L. The Value of Measuring Lipoprotein(a) in Children. Circulation 2023, 147, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, e285–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCORE2 Working Group and ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2 risk prediction algorithms: New models to estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2439–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Roger Blumenthal, C.-C.S.; Michelle Albert, C.-C.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; William McEvoy, J.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1376–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, L.M.; Wiegman, A.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Hutten, B.A. Pharmacotherapy for children with elevated levels of lipoprotein(a): Future directions. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, F.; Sun, J.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Gill, D.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C.; Yuan, S.; Li, X. Factorial Mendelian randomization of Lipoprotein(a) lowering, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering, and lifestyle improvements: Joint associations with cardiovascular risk. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2025, 54, dyaf020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Gordts, P.L.S.M.; Nora, C.; Yeang, C.; Witztum, J.L. Statin therapy increases lipoprotein(a) levels. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, F.B.; Cha, S.W.; Linnaeus Louisse, C.; Carado, G.P.; Magalong, J.V.; Tang, V.A.; Enriquez, M.G.; Gulati, M.; Enkhmaa, B.; Pagidipati, N.; et al. Impact of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors on Lipoprotein(a): A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Randomized Controlled Trials. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebkar, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Ferretti, G.; Cicero, A.F.G. Effect of extended-release niacin on plasma lipoprotein(a) levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1664–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasoufidou, A.; Stachteas, P.; Karakasis, P.; Kofos, C.; Karagiannidis, E.; Klisic, A.; Popovic, D.S.; Koufakis, T.; Fragakis, N.; Patoulias, D. Treatment options for heart failure in individuals with overweight or obesity: A review. Future Cardiol. 2025, 21, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytyçi, I.; Bytyqi, S.; Lewek, J.; Surma, S.; Bajraktari, G.; Henein, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Al-Khnifsawi, M.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Pećin, I.; et al. Management of children with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia worldwide: A meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. Open 2025, 5, oeaf001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijman, M.D.; Kusters, D.M.; Groothoff, J.W.; Arbeiter, K.; Dann, E.J.; de Boer, L.M.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Gallo, A.; Greber-Platzer, S.; Hartz, J.; et al. Clinical practice recommendations on lipoprotein apheresis for children with homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: An expert consensus statement from ERKNet and ESPN. Atherosclerosis 2024, 392, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianos, E.; Duell, P.B.; Toth, P.P.; Moriarty, P.M.; Thompson, G.R.; Brinton, E.A.; Hudgins, L.C.; Nametka, M.; Byrne, K.H.; Raghuveer, G.; et al. Lipoprotein Apheresis: Utility, Outcomes, and Implementation in Clinical Practice: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffa, M.B.; Koschinsky, M.L. Therapeutic Lowering of Lipoprotein(a). Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e002052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Ference, B.A.; Staley, J.R.; Freitag, D.F.; Mason, A.M.; Nielsen, S.F.; Willeit, P.; Young, R.; Surendran, P.; Karthikeyan, S.; et al. Association of LPA Variants With Risk of Coronary Disease and the Implications for Lipoprotein(a)-Lowering Therapies: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimikas, S.; Viney, N.J.; Hughes, S.G.; Singleton, W.; Graham, M.J.; Baker, B.F.; Burkey, J.L.; Yang, Q.; Marcovina, S.M.; Geary, R.S.; et al. Antisense therapy targeting apolipoprotein(a): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 study. Lancet 2015, 386, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Tardif, J.-C.; Baum, S.J.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Shapiro, M.D.; Stroes, E.S.; Moriarty, P.M.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) Reduction in Persons with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, L.; Nicholls, S.J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Landmesser, U.; Tsimikas, S.; Blaha, M.J.; Leitersdorf, E.; Lincoff, A.M.; Lesogor, A.; Manning, B.; et al. Design and Rationale of Lp(a)HORIZON Trial: Assessing the Effect of Lipoprotein(a) Lowering With Pelacarsen on Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients With CVD and Elevated Lp(a). Am. Heart J. 2025, 287, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Tsamoulis, D.; Gianniou, M.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Rallidis, L.S. Novel RNA-Based Therapies in the Management of Dyslipidemias. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Rosenson, R.S.; Gencer, B.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Park, J.G.; et al. Olpasiran lowering of lipoprotein(a) according to baseline levels: Insights from the OCEAN(a)-DOSE study. Eur. Heart J. 2025, 46, 1162–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Ni, W.; Shen, X.; Wang, Q.; Navar, A.M.; Nicholls, S.J.; Wolski, K.; Michael, L.; Haupt, A.; Krege, J.H.; et al. Lepodisiran—A Long-Duration Small Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a). N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wang, Q.; Nicholls, S.J.; Navar, A.M.; Ray, K.K.; Schwartz, G.G.; Szarek, M.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Troquay, R.; Dorresteijn, J.; et al. Zerlasiran—A Small-Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a): A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Details | A Study to Investigate the Effect of Lepodisiran on the Reduction of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Adults with Elevated Lipoprotein(a)—ACCLAIM-Lp(a) | ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06292013 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Nicholls, S.J.; Nissen, S.E.; Fleming, C.; Urva, S.; Suico, J.; Berg, P.H.; Linnebjerg, H.; Ruotolo, G.; Turner, P.K.; Michael, L.F. Muvalaplin, an Oral Small Molecule Inhibitor of Lipoprotein(a) Formation: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerfler, A.M.; Park, S.H.; Assini, J.M.; Youssef, A.; Saxena, L.; Yaseen, A.B.; De Giorgi, M.; Chuecos, M.; Hurley, A.E.; Li, A.; et al. LPA disruption with AAV-CRISPR potently lowers plasma apo(a) in transgenic mouse model: A proof-of-concept study. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 27, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials in Children. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/clinical-trials-registry-platform/clinical-trials-in-children (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Ethical Considerations for Clinical Trials on Medicinal Products Conducted with Minors Recommendations of the Expert Group on Clinical Trials for the Implementation of Regulation (EU) No 536/2014 on Clinical Trials on Medicinal Products for Human Use 2017. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/document/download/d721d6cb-687a-477f-b40f-8c7922e9ec9a_en (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Sbrana, F.; Dal Pino, B.; Corciulo, C.; Ripoli, A.; Bigazzi, F.; Sampietro, T. Pediatrics cascade screening in inherited dyslipidemias: A lipoprotein apheresis center experience. Endocrine 2025, 88, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age | Stroke | MI | CAD | Atherosclerosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Child | Bogalusa (n = 1587, cohort) [16] | Bogalusa [16] Zawacki et al. (n = 129, cohort) [21] LIPIGEN (n = 653 *, cohort) [22] | de Boer LM et al. (n = 214, cohort) [26] Young Finns (n = 2.080, cohort) [28] | |
| Adolescent | Zawacki et al. (n = 129, cohort) [21] LIPIGEN (n = 653 *, cohort) [22] | Young Finns (n = 3.596, cohort) [23] | ||
| Adult | Tipping (n = 174.111, meta-analysis) [35] | Tipping (n = 102.221, meta-analysis) [35] Wang (n = 1.131, cohort) [39] Patel (n = 460.506, Biobank) [40] | PROMISE (n = 1.185, secondary analysis of an RCT) [41] ATTICA (n = 3.042, cohort) [43] | Jackson (n= 5.597, cohort) [42] |
| Elder | PROSPER (n = =5732, cohort) [50] Ariyo (n= 5888, cohort) [51] Milionis (n = 328, case-control) [57] | Zhang (n = 1.008, cohort) [52] Bartoli (n = 755, cohort) [53] | Simons (n= 2.805, cohort) [54] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasoufidou, A.; Glava, A.; Mavridou, M.; Stachteas, P.; Karagiannidis, E.; Patoulias, D.; Kassimis, G.; Fragakis, N.; Kavga, M. Age-Dependent Clinical Relevance of Lipoprotein(a): A Comprehensive Review from Childhood to Adulthood. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176018
Nasoufidou A, Glava A, Mavridou M, Stachteas P, Karagiannidis E, Patoulias D, Kassimis G, Fragakis N, Kavga M. Age-Dependent Clinical Relevance of Lipoprotein(a): A Comprehensive Review from Childhood to Adulthood. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176018
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasoufidou, Athina, Agni Glava, Maria Mavridou, Panagiotis Stachteas, Efstratios Karagiannidis, Dimitrios Patoulias, George Kassimis, Nikolaos Fragakis, and Maria Kavga. 2025. "Age-Dependent Clinical Relevance of Lipoprotein(a): A Comprehensive Review from Childhood to Adulthood" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176018
APA StyleNasoufidou, A., Glava, A., Mavridou, M., Stachteas, P., Karagiannidis, E., Patoulias, D., Kassimis, G., Fragakis, N., & Kavga, M. (2025). Age-Dependent Clinical Relevance of Lipoprotein(a): A Comprehensive Review from Childhood to Adulthood. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176018






