Abstract
Background/Objectives: Swallowing disorder(s), or oropharyngeal dysphagia (OPD), are very common in children with cerebral palsy (CP) and pose a significant risk to their health. Behavioural interventions are frequently recommended when targeting OPD in children with CP; however, their efficacy has yet to be determined. This systematic review aimed to synthesise the current evidence for behavioural interventions in the treatment of OPD in children with CP. Methods: A comprehensive search in six databases in October 2024 sought studies that (1) included participants aged 0–18 years with a diagnosis of CP and OPD; (2) utilised and described a behavioural intervention for OPD; and (3) used a randomised controlled trial (RCT) experimental design. Three reviewers independently extracted the data, and results were tabulated. The Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias (ROB-2) tool was used to determine the methodological quality of eligible articles. Results: From an initial yield of 2083 papers, 99 full-text studies were screened for eligibility. Seven RCTs involving 329 participants aged 9.5 months (SD = 2.03) to 10.6 yrs were included. CP description varied. Most studies used a combination of behavioural interventions to treat OPD (n = 6), and oral sensorimotor treatment was the most frequently utilised treatment (n = 4). Positive outcomes were reported in all (n = 7); however, there was high risk of bias in five studies. Conclusions: The use of behavioural interventions to treat OPD in children with CP continues to be supported by low-level evidence. Rigorously designed RCTs with larger samples of children with CP and OPD are needed to evaluate the true effects of behavioural interventions across the developmental phase of childhood. Importantly, consistency in describing and reporting baseline analysis of swallowing and OPD; together with treatment-component data, is a priority in future research.
1. Introduction
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a permanent, lifelong condition which describes a spectrum of motor impairments caused by a non-progressive brain injury during the early developmental period [1]. CP is the most common cause of childhood-onset disability, with a prevalence range of 1.6 per 1000 live births for high-income countries and 3.4 per 1000 live births in low-income countries [2]. The presenting motor impairments, which are core to CP, are frequently accompanied by sensory, perceptual, cognitive, communication, and behavioural difficulties, and secondary musculoskeletal disorders [3,4,5]. Due to a complex interplay of aetiological factors, motoric dysfunction, and associated comorbid features, there is significant heterogeneity in the profiles of children with CP [6].
Oropharyngeal dysphagia (OPD), or swallowing disorder, is a frequently occurring comorbidity in people with CP, with a reported pooled prevalence estimate of 50.4% [7]. Prevalence estimates are higher in children with CP, with reported ranges varying from 60 to 90% [8,9,10]. With a diagnosis of OPD in children with CP, the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing are often affected [11]. The oral phase involves two discrete events: Oral preparation, where the food/fluid material is manipulated adequately and formed into a cohesive bolus. Once complete, the tongue elevates to propel the bolus posteriorly until the pharyngeal swallow, and next phase, is initiated [12]. The pharyngeal phase involves directing the bolus into the oesophagus whilst protecting the airway from aspiration [13].
Common features of OPD in children with CP include poor lip closure, tongue thrusting, masticatory inefficiency, choking, and aspiration [14,15]. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease is also common in CP and can further exacerbate feeding difficulties by causing discomfort and complicating the feeding process [16]. The implications of OPD in CP are often serious, potentially leading to malnutrition and underdevelopment, significant pulmonary compromise, and prolonged stressful mealtimes [17]. Despite high prevalence rates and the evident serious health repercussions for children with CP who present with swallowing impairments, effective treatments to optimise swallowing function and reduce the impact of OPD are lacking [18].
Behavioural interventions are frequently recommended to treat OPD in children with CP [19]. However, previous research highlights conflicting findings regarding treatment effectiveness in the context of poorly designed quasi-experimental research conducted with small samples [20,21]. Traditionally, a host of behavioural interventions including reinforcement, modelling, or shaping can be used by clinicians to modify a desirable or undesirable behaviour [22]. Behavioural interventions for OPD can be further divided into interventions that target compensation and skill training [23]. Compensatory techniques prioritise safety, adapting to or compensating for a deficit in functioning [24], while skill training aims for the individual to acquire new, more advanced skills to increase their independence [25,26], which can lead to long-term change in swallowing. Skill training can be further broken down into direct and indirect training. Direct interventions involve the use of food or fluid items and are goal-oriented task-specific behavioural techniques that optimise skill acquisition, often by harnessing neuroplasticity, e.g., increasing flow rate using faster-flow bottle nipples, and incremental increases to more challenging textures for improved acceptability of foods and improved chewing ability [23,27]. Indirect skill training uses non-nutritive stimuli to increase the resistance and strength of targeted muscles [28,29], e.g., non-nutritive sucking on a pacifier, and oral motor resistance exercises with chewy tubes.
In the current study, the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) [30] was used as the conceptual framework. The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health conceptualises a person’s level of ‘functioning’ as a dynamic interaction between health conditions, environmental factors, and personal factors. Functioning includes two parts related to (1) body functions and structures, which describe the anatomy and physiology/psychology of the human body; and (2) activity and participation, which describe the individuals’ current functional level related to skills like mobility, self-care communication, and learning [31].
Given the paucity of high-quality evidence in relation to interventions for children with CP, this systematic review aimed to determine the effects of behavioural interventions in children with CP based only on the highest level of evidence (randomised controlled trials (RCTs)). Behavioural interventions that targeted a behaviour related to feeding, eating, drinking, and/or swallowing and which were delivered by a professional dysphagia expert were the focus of this review. Dysphagia experts could include the disciplines of speech and language pathologists, occupational therapists, or physiotherapists but could also incorporate other wider discipline groups relevant to this study’s health service/system. Surgical, pharmacological measures and neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) to treat OPD were considered outside the scope of this review.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review was designed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [32]. Covidence (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia) was utilised as the primary platform for screening and inclusion of studies, facilitating an efficient and organised review process.
2.1. Information Sources
To identify studies, literature searches were conducted on 13th Oct 2024 across six electronic databases: CINAHL, Cochrane, Embase, MEDLINE, PsycINFO, and Scopus. Publication dates ranged from 1980 to October 2024. Two reviewers (S.M., So.M.) also completed a hand search of reference lists in eligible full-text articles.
2.2. Search Strategy
The creation of a structured and comprehensive search strategy was guided by the PICO framework [33]. Electronic search strategies were completed in all six electronic databases using free text and specific subheadings (i.e., MeSH and Thesaurus terms). Four strings of terms were combined for ‘cerebral palsy’, ‘swallow* disorder’ OR ‘feed* difficult*’ OR ‘feed* disorder’, ‘child’, ‘behavioural intervention’, and associated subject headings. All of the retrieved articles were imported into the reference management software Endnote 20 and then exported into Covidence for screening and management.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Studies were eligible if they (i) included participants aged 0–18 yrs, (ii) required a diagnosis of CP and OPD, (iii) involved delivery of a behavioural intervention that focussed on feeding, eating, drinking, and/or swallowing skills/impairment (OPD), (iv) provided a description of the intervention related to contents and dosage, and (v) clearly referred to using a randomised controlled trial (RCT) design in the title or abstract. Exclusion criteria included (i) lack of clarity as to whether the participant had CP and/or OPD, (ii) provision of an intervention name but not a description of the treatment components (content and dosage), and (iii) papers published before 1980 (due to advances in research methodological practices).
2.4. Data Collection Process
A data extraction tool was developed using Excel, then trialled and further modified to create a final robust data extraction form. Three reviewers (B.M.A., M.M., S.M.) independently used this template to extract and tabulate the data on the following variables: purpose/aim of study, age and sex of participants, total number of participants, motoric description of CP, intervention description, outcome measures, and treatment outcomes. Turkstra’s framework [34] was used to describe the treatment components of the intervention. The target behaviour/target(s) was defined as the specific aspect of functioning selected and intended to change as a result of the treatment; active ingredients are specific clinician-directed actions taken to affect a change in the target behaviour; and the mechanism of action is the hypothesised means in which the treatment is intended to exert its effects [34,35]. Primary outcomes of interest related to feeding, eating, drinking, and/or swallowing. During data collection, data points across all studies were extracted.
2.5. Data, Items, and Synthesis of Results
Two reviewers (S.M., So.M.) independently applied the selection criteria initially to titles and abstracts, and then original articles, to assess for eligibility. To ensure rating accuracy, three group sessions were held and attended by four team members (C.-A.M., M.M., S.M., So.M.) to discuss the ratings of fifty randomly selected records to achieve consensus before rating the remaining abstracts. Any differences in opinion regarding inclusion were mostly resolved through consensus by two team members (S.M., So.M.). A third member of the research team (M.M. or C.-A.M.) was consulted if disagreement occurred, until a final decision regarding inclusion was reached. To ensure a comprehensive search strategy, the criterion of an RCT was not applied until the stage of full-text screening. The risk-of-bias assessment was performed at a study level; with the Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias tool (ROB-2) [36] used by two independent researchers (M.M., B.McA.) to assess the methodological quality of the included studies. There was 100% agreement across each of the five domains, and consensus was therefore reached without the need to involve a third party. The main summary measures for assessing treatment outcomes were effect sizes and significance of findings. A meta-analysis could not be performed, due to ineligibility of included studies, and a narrative method was therefore used to synthesise the data for the key study variables, study quality, and risk of bias. Tabular and graphical formats were used in the reporting of the results.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
An initial yield of 2083 studies was retrieved across six databases (CINAHL (n = 17), Cochrane (n = 18), Embase (n = 880), MEDLINE (n = 39), PsychINFO (n = 8), and Scopus (n = 1121)). After removal of duplicate titles and abstracts, a total of 1913 records remained. Following title and abstract screening, 79 original articles were identified, and the full-text records were examined to verify that they met all inclusion criteria. A further six studies were identified from hand searching of these full-text records and were sourced to assess eligibility. Finally, seven RCTs published since 2017 were included. Figure 1 presents the PRISMA flow diagram.
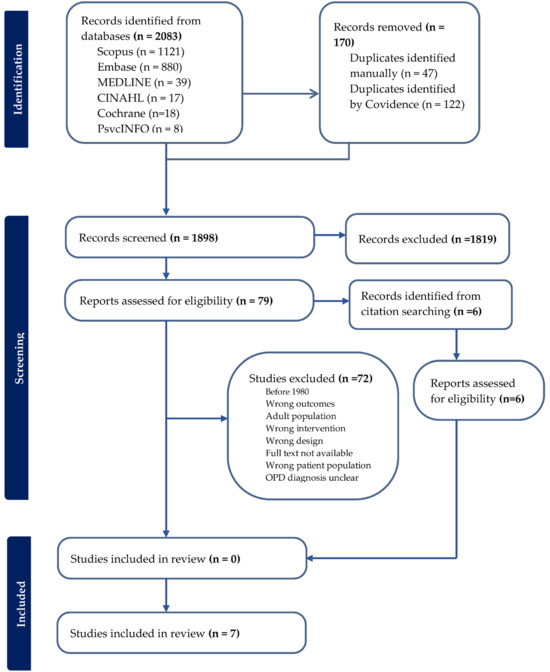
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the reviewing process according to PRISMA.
3.2. Description of Studies
All seven included studies are described in detail in Table 1 and Table 2 [37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Three studies had a total sample greater than 50 participants, while four studies had fewer than 40 participants in their sample. In Table 1, information on the study characteristics is presented and includes a definition of OPD, tools/methods used to diagnose OPD, reporting of OPD severity, reported description of participants in the sample, and the intervention group types. A description of participants’ ages, sex, and CP is provided for all study groups in Table 1. Detailed information is provided in Table 2 on the treatment components: the intervention, target behaviour, mechanism of action, primary outcomes of interest, outcome measures, and all treatment outcomes reported in each included study.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of studies on behavioural interventions for children with CP with oropharyngeal dysphagia.

Table 2.
Outcome of behavioural interventions for children with CP and oropharyngeal dysphagia.
3.2.1. Participants (See Table 1)
The seven included studies involved a total of 329 participants with CP (Males, n = 182; Females, n = 147) who received a type of behavioural intervention to treat their OPD (see Table 1). The participants’ age group ranged from age 9.5 months (SD = 2.03) to 10.6 yrs, with no studies focussed on adolescence. A description of CP was not reported in two studies and there was variability in methods of description across studies (GMFCS level, topography, nature of pathological impairment, etc.). Spastic quadriplegia was the most frequently reported CP sub-classification (n = 64), followed by hemiplegia (n = 20).
3.2.2. Outcomes and Outcome Measures (See Table 1 and Table 2)
There were a range of outcomes and outcome measures [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58] reported across the seven studies. Sixteen outcomes targeted a body functions and structures (BFS) level of functioning in six studies, and six activity-level outcomes were targeted in five studies. None of the studies assessed outcomes related to participation. Three studies included a quality of life-related outcome. Outcomes targeting a BFS level focussed largely on either the oral preparatory or oral phases of swallowing, e.g., lip and tongue movements. Other primary-related BFS-level outcomes included drooling, weight, physical growth, and negative aspects of functioning related to swallowing, e.g., vomiting. Activity-level outcomes included those primarily focussed on the tasks of feeding, eating, chewing, drinking, and/or swallowing. A range of outcome measures were employed to measure treatment effects in the studies (see Table 1). The most frequently used outcome measures were the Schedule of Oral Motor Assessment (n = 3) and the Oral Motor Assessment Scale (n = 2) [49,53].
3.2.3. Behavioural Intervention Groups (Table 1)
Each study included a comparison group that received an alternative treatment targeting their OPD. Terms used to describe the comparison included traditional or conventional therapy, sham treatment, or standard care.
3.2.4. Interventions and Treatment Components (Table 2)
Most studies used a combination of behavioural interventions to treat OPD (n = 6). Four of the seven studies used a combination of compensatory, direct, and indirect skills training. Five studies used direct skill training techniques. Oral sensorimotor therapy (OSMT)), used interchangeably with the terms oral motor therapy and oral sensorimotor stimulation, was the most frequently trialled intervention (n = 4), followed by a form of neurodevelopmental treatment (NDT) (n = 2). Three studies reported embedding traditional behavioural techniques of reinforcement through verbal and visual means. The active ingredients including the content and dosage information were largely well described, and the setting information was provided for each study. The latter included university clinic, hospital, outpatient department, and home/telehealth/online settings. The target behaviour was not clearly outlined in three studies, and the mechanism of action was not mentioned in two studies. No study reported treatment fidelity.
3.3. Methodological Quality
The methodological quality of the included RCTs was assessed using the ROB-2 tool [36]. Table 3 and Figure 2 present the risk-of-bias summary per domain for individual studies and for all included studies. Only two studies showed a low risk of bias overall, with one domain having some concerns; five studies were deemed at high risk of bias as they each had a rating of at least two domains for ‘high bias’. In five studies, there was either unclear or absent reporting regarding allocation concealment or a lack of reporting on the random sequence generation method, indicating a higher selection bias. Blinding of participants and personnel was also absent or not clearly reported in five studies. Blinding of outcome assessment was not reported in two studies, potentially leading to increased detection bias. While two pilot RCTs had an overall low risk of bias, both studies had fewer than 10 participants in each of the respective experimental and control groups, indicating that a meta-analysis would not yield reliable results [59,60].

Table 3.
ROB-2 summary table.
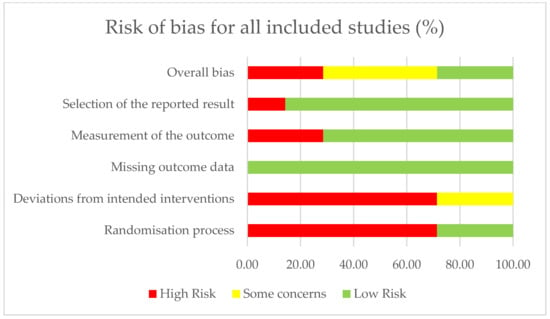
Figure 2.
Risk of bias summary for all included studies (n = 7) in accordance with ROB-2.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to determine the effectiveness of behavioural interventions in the treatment of OPD in children with CP.
4.1. Lack of Robust RCTs
Considering the serious impact of OPD on the health and quality of life of individual children with CP, the small number of high-quality RCTs being undertaken is a cause for concern. RCTs and systematic reviews of such trials provide the most reliable evidence about the effects of healthcare treatments [61]. In total, seven behavioural RCTs in the paediatric population of CP, which involved a total of 329 participants, were identified. Our review highlighted that there was considerable clinical heterogeneity amongst the seven included RCTs, which limits the ability to generalise the findings to a real-world context [62]. Clinical heterogeneity can be viewed as differences in participant characteristics, outcome measures, and intervention characteristics, including dose [63]. We found omitted or variable participant baseline data, in relation to CP sub-classification and/or OPD severity, which may have affected the participants’ intervention responses, and therefore, the study outcomes [64]. In addition, the variability in outcome measures used across studies, e.g., related to trunk control vs. oral phase of swallowing, makes it difficult to directly compare treatment results [65]. Whilst we found that mostly treatment combinations of compensatory and skills training occurred across studies, the individual interventions within these combinations, and by extension, their active ingredients, varied, e.g., chewing therapy vs. action observation therapy. Variations in active ingredients infer a different set of treatment components were used [34], and the treatments therefore are not directly comparable. Dosage was also set at different intensities across intervention studies, e.g., number of exercise trials vs. number of weeks. Poor fidelity reporting further complicates our understanding of dosage, as potential variations in intervention delivery can affect the participants’ exposure to the treatment components or dose [64,66]. The collective variability across participants, treatment components, and outcome measures significantly influences the reliability of the treatment effect [62,67] and does not allow for the generalisability of findings [68].
The clinical heterogeneity found in this review is further compounded by the high risk of bias found in five studies. A hallmark characteristic of an RCT design is random allocation and blinding [60]. However, only two studies included sufficient reporting on the processes of randomisation and blinding. Two studies also had a high risk of bias for outcome measurement, thus undermining the ability to draw causal inferences regarding the intervention’s true effects [60]. The two pilot RCTs that demonstrated overall low-level bias are a promising indication that high standards can be achieved; however, the inclusion of larger samples and increased consistency in reporting are needed to facilitate the conduct of a meta-analysis.
4.2. Progress in the Research Field of OPD in CP
Of note, the seven included studies in this review were published in the past eight years, providing contemporary studies from which to draw evidence; however, this still strongly suggests that treatment for OPD in paediatric CP is an under-researched area. Whilst outcomes in the seven studies focused on impaired BFS-level outcomes, a positive was that five studies outlined how activity-level outcomes were targeted, focusing on more global aspects of functioning related to swallowing. Previous research has highlighted a predominant focus on compensatory methods when implementing behavioural methods to treat OPD in children with CP, largely addressing impairment-level outcomes [21]. It is encouraging that direct skill training was the primary focus in five studies, and in four of the seven studies, a combination of skill training and compensatory behavioural techniques was used. The latter is important as it aligns with best-practice principles when developing effective behavioural interventions [69]. OPD is a complex behaviour; therefore, a single intervention approach used in isolation is unlikely to produce a significant change in behaviour. In our review, we found that the active ingredients of the interventions were largely well-reported. Reporting this detailed information on content and dosage allows a greater opportunity to test how treatment components are linked to the mechanism of action(s), which is a prelude to evaluating clinical significance [70]. Importantly, five studies used a patient-reported outcome measure or quality-of-life measure, and three studies utilised a test to determine effect sizes in order to help ascertain clinical significance [71].
4.3. What Are the Important Elements of a Behavioural Intervention in the Treatment of OPD in CP?
This review highlighted fundamental issues about implementing behavioural interventions to treat OPD in children with CP. First, a functional analysis of the baseline condition, that is, feeding, eating, drinking and/or swallowing skills, is needed to enhance our understanding of the primary aetiological factors of the child’s condition [72,73], in this case, OPD. In a novel contribution, our review highlighted a range of relevant tools used to assess OPD or OPD-related behaviour. However, the links between the identified individual impairments from those measures and their likely effects on swallowing function were not adequately described. Clearly identifying and reporting the antecedent behaviours and their consequences helps to hypothesise regarding potential causation, supporting the development of a more tailored evidence-based intervention [22,74]. For example, a child with CP and a GMFCS level V has poor head control secondary to when poorly positioning in his customised seating, leading to an increased frequency of mouth opening and loss of food/fluid. The antecedents are sub-optimal positioning and poor head control, leading to consequences of increased tongue thrusting, reduced lip closure, and increased delay in triggering pharyngeal swallow (which increases the risk of premature spillage into the airway and subsequent aspiration). We hypothesise that poor seating is a controlling variable and maintaining factor in decreasing performance at the oral preparatory and oral stages of swallowing, thus increasing the risk of aspiration. An occupational therapy referral for seating review is prompted; the child receives a new customised seating system and as a result has a more optimal position for safer and more effective swallowing.
As part of a functional analysis, sufficient information must be provided for the baseline characteristics of the individual participant data, including the diagnosis and severity of the condition to be identified. In our review, two of the seven studies [40,43] did not provide a CP description beyond diagnosis. Further, only two studies [38,42] used the EDACS tool [58] to describe levels of ability regarding safety and efficiency in eating, drinking and swallowing and no study reported baseline OPD severity. Reporting this additional information on CP and OPD diagnoses, and their severities, will facilitate increased accuracy in identifying antecedent behaviours, in turn, optimising chances of success in developing an effective functional behavioural treatment [22,72,73,74].
Clear reporting of the target behaviour of the intervention is needed in order to know which specific aspect of functioning is intended to change because of the treatment [34,74]. Our study highlighted that the target behaviour(s) of the intervention was not always clearly articulated in each study, separately from outcomes. Detailing an operational definition of the target behaviour outlines what is needed from the recipient of the intervention to signify that event [22,75], facilitating increased transparency and accuracy in the recording of that behaviour. Additionally, the mechanisms of action were not consistently reported across studies. Outlining the mechanisms of action(s) provides information on the intrapersonal processes that must change in order to achieve a clinical response [76]. Providing details regarding the target behaviours and mechanisms of actions can contribute to formulating a hypothesis as to how the treatment might be effective. Without this theory-driven approach, we cannot identify the key components that render the treatment effective [34,77].
The consistent reporting of treatment fidelity is of paramount importance as higher levels of treatment fidelity are associated with higher gains attributable to intervention [78]. As a positive, the largely well-reported active ingredients of behavioural interventions in the included studies ‘partly’ ensure treatment fidelity [75], but levels of adherence still need to be reported [79]. Finally, OPD is complex, with multiple determinants, thus warranting equally complex interventions with coordinated input across many different disciplines. Detailed information on intervention agent, e.g., discipline, and/or setting information was inconsistently reported across the RCTs. The provision of more detailed information on the involvement of the team, in addition to specifying the intervention agent and setting, will facilitate an enhanced understanding of how treatments might be effective if significant results are found.
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
This systematic review aimed to answer a specific focused clinical intervention question. Finding only seven RCTs despite a comprehensive systematic search in six databases is an indication that this is an under-researched area. While papers in all languages were included to minimise publication bias, four studies from Chinese journals could not be retrieved and these studies may have contained relevant experimental data. Data on race and ethnicity were not collected, which may reduce the generalisability of the findings. As we limited our focus to RCTs only, since these represent the highest level of evidence, other potentially relevant experimental research may have been excluded.
Future methodologically robust and larger RCTs that minimise clinical heterogeneity and provide detail on the functional analysis of OPD (to outline primary determinants) are urgently needed. Clearly describing the treatment components may also help to identify the critical components that underlie its efficacy [34,69], leading to advanced insights into how received treatment improves health [80]. The reporting of treatment fidelity is also a priority in future OPD-focused studies, to facilitate higher validity and translation into clinical practice [81]. Statistical testing alone is not sufficient to evaluate a clinically relevant effect. Standardised effect sizes are recommended when studies use different measurement scales to facilitate comparison between studies and foster completion of meta-analysis [82]. Collaboration between experts on how to support the implementation of such high-quality RCTs would help to accelerate progress. By taking these measures, transparency in research reporting will be facilitated and help to advance progress in the field.
5. Conclusions
Progress in proving the effectiveness of behavioural interventions to treat OPD in children with CP is slow. Despite the serious health repercussions for children with CP and OPD, it remains the case that low-level evidence supports the use of behavioural interventions to treat OPD in children with CP. Rigorously designed RCTs with larger samples of children with CP and OPD are urgently needed, to evaluate the effectiveness of behavioural interventions across the developmental childhood phase. In future research, consistency in describing a functional analysis of swallowing in OPD together with reporting theoretical treatment component-related data and treatment fidelity is a priority.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, M.M.; methodology, M.M., C.-A.M., S.M. (Sarah Moran), and S.M. (Sophie Molloy); formal analysis, M.M., B.M. and S.M. (Sarah Moran); writing—original draft preparation, M.M. and S.M. (Sarah Moran), B.M.; writing—review and editing, M.M., C.-A.M. and B.M.; project administration, M.M. and C.-A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| AOT | Action Observation Training |
| babiEAT | baby intensive Early active Treatment |
| BPFAS | Behavioural Pediatrics Feeding Assessment Scale |
| CP | Cerebral Palsy |
| DSFS | Drooling Severity and Frequency Scale |
| FIPQ | Feeding Intervention Preferences Questionnaire |
| FOIS | Functional Oral Intake Scale |
| FOISi | Functional Oral Intake scale for Infants |
| FOMS | Feeding Oral Motor Scale |
| FS-IS | Feeding and Swallowing Impact Survey |
| FSIS | Feeding Swallowing Impact Scale |
| FuCT | Functional Chewing Training |
| GAS | Goal Attainment Scale |
| GMFM-88 | Gross Motor Function Measure-88 |
| IDDSI | International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative |
| ICF-CY | International Classification of Functioning-Children and Youth |
| KCPS | Karaduman Chewing Performance Scale |
| NCRT | Nutrition Related Caregiver Training |
| NDT-B | Neurodevelopmental Therapy Method-Bobath |
| OM | Oral Motor |
| OMAS | Oral Motor Assessment Scale |
| OMIS | Oral Motor Intervention Strategies |
| OMT | Oral Motor Therapy |
| OPD | Oropharyngeal Dysphagia |
| OSMS | Oral Sensorimotor Stimulation |
| Pedi-Eat | Pediatric Eating Assessment Tool, |
| PedsQL | Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory |
| PT | Physiotherapist |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| SATCo | Segmental Assessment of Trunk Control |
| SLP | Speech-Language Pathologist |
| SLT | Speech and Language Therapist |
| SOMA | Schedule for Oral Motor Assessment |
| TIS | Trunk Impairment Scale |
References
- Dan, B.; Rosenbaum, P.; Carr, L.; Gough, M.; Coughlan, J.; Nweke, N. Proposed updated description of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2025, 67, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, S.; Goldsmith, S.; Webb, A.; Ehlinger, V.; Hollung, S.J.; McConnell, K.; Arnaud, C.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Oskoui, M.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Global CP Prevalence Group. Global prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cans, C.; Dolk, H.; Platt, M.J.; Colver, A.; Prasauskiene, A.; Krageloh-Mann, I.; SCPE Collaborative Group. Recommendations from the SCPE collaborative group for defining and classifying cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 109, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe. Surveillance of cerebral palsy in Europe: A collaboration of cerebral palsy surveys and registers. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2000, 42, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Kopyta, I. Cerebral Palsy: Current Opinions on Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification and Treatment Options. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyer, R.; Cordier, R.; Kim, J.H.; Cocks, N.; Michou, E.; Wilkes-Gillan, S. Prevalence of drooling, swallowing, and feeding problems in cerebral palsy across the lifespan: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S.; Skuse, D.; Poblete, X. Prevalence of feeding problems and oral motor dysfunction in children with cerebral palsy: A community survey. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.; Kozlowski, A.M.; Girolami, P.A. Comparing behavioral treatment of feeding difficulties and tube dependence in children with cerebral palsy and autism spectrum disorder. NeuroRehabilitation 2017, 41, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfer, K.A.; Weir, K.A.; Bell, K.L.; Ware, R.S.; Davies, P.S.; Boyd, R.N. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in preschool children with cerebral palsy: Oral phase impairments. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 3469–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisel, E.G.; Tessier, M.J.; Lapierre, G.; Seldman, E.; Drouin, E.; Filion, G. Feeding management of children with severe cerebral palsy and eating impairment: An exploratory study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 37, 456–462. [Google Scholar]
- Panara, K.; Ramezanpour, A.E.; Padalia, D. Physiology, Swallowing. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, K.; Palmer, J.B. Anatomy and physiology of feeding and swallowing: Normal and abnormal. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 19, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisel, E.G.; Applegate-Ferrante, T.; Benson, J.E.; Bosma, J.F. Oral-motor skills following sensorimotor therapy in two groups of moderately dysphagic children with cerebral palsy: Aspiration vs nonaspiration. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1996, 23, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.B. Gastrointestinal disorders in children with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Hosp. Pediatr. 2015, 5, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, C.; Haak, P.; Himmelmann, K.; Krägeloh-Mann, I. Feeding-related challenges in children with cerebral palsy: Dysphagia, masticatory inefficiency, and malnutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Arvedson, J.C.; Brodsky, L.; Lefton-Greif, M.A. (Eds.) Pediatric Swallowing and Feeding: Assessment and Management, 3rd ed.; Plural Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arvedson, J.C. Feeding children with cerebral palsy and swallowing difficulties. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2013, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groher, M.E.; Crary, M.A. (Eds.) Dysphagia: Clinical Management in Adults and Children, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arvedson, J.; Clark, H.; Lazarus, C.; Schooling, T.; Frymark, T. The effects of oral-motor exercises on swallowing in children: An evidence-based systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, L.; Majnemer, A.; Darsaklis, V. Feeding Interventions for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Review of the Evidence. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2011, 31, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltenberger, R.G. Behavior Modification: Principles and Procedures, 6th ed.; Wadsworth Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khamis, A.; Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Tzannes, G.; Pettigrew, J.; Cowell, J.; Badawi, N. Motor Learning Feeding Interventions for Infants at Risk of Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2020, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A. Innovative Evidence-Based Assessment and Treatment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia and Communication Disorders in Infants and Young Children at High Risk of Cerebral Palsy. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Sydney, Camperdown, NSW, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fucile, S.; McFarland, D.H.; Gisel, E.G.; Lau, C. Oral and nonoral sensorimotor interventions facilitate suck-swallow-respiration functions and their coordination in preterm infants. Early Hum. Development. 2012, 88, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, Z.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Walshe, M. Oral stimulation for promoting oral feeding in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 9, CD009720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reche-Olmedo, L.; Torres-Collado, L.; Compañ-Gabucio, L.M.; Garcia-de-la-Hera, M. The Role of Occupational Therapy in Managing Food Selectivity of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review. Children 2021, 8, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvedson, J.C.; Brodsky, L. (Eds.) Pediatric Swallowing and Feeding: Assessment and Management; Whurr: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Engel-Hoek, L.; Harding, C.; van Gerven, M.; Cockerill, H. Pediatric feeding and swallowing rehabilitation: An overview. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 10, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). ICF: International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: Children and Youth Version: ICF-CY; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.; McKenzie, J.; Bossuyt, P.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.; Mulrow, C.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.; Akl, E.; Brennan, S.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frandsen, T.F.; Nielsen, M.F.B.; Lindhard, C.L.; Eriksen, M.B. Using the full PICO model as a search tool for systematic reviews resulted in lower recall for some PICO elements. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 127, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkstra, L.S.; Norman, R.; Whyte, J.; Dijkers, M.P.; Hart, T. Knowing What We’re Doing: Why Specification of Treatment Methods Is Critical for Evidence-Based Practice in Speech-Language Pathology. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2016, 25, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, T.; Tsaousides, T.; Zanca, J.M.; Whyte, J.; Packel, A.; Ferraro, M.; Dijkers, M.P. Toward a theory-driven classification of rehabilitation treatments. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95 (Suppl. 1), S33–S44.e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmonem, A.M.; Saad-Eldien, S.S.; Abd El-Nable, W.A. Effect of oral sensorimotor stimulation on oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with spastic cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, G.; Ejraei, N.; Turkdoğan, D.; Enver, N.; Öztürk, G.; Aktaş, G. The Effects of Neurodevelopmental Therapy on Feeding and Swallowing Activities in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaltun, M.S.; Umay, E.; Altindag, O.; Karaahmet, O.Z. Effectiveness of kinesiotape and sham kinesiotape application in children with cerebral palsy with dysphagia: A randomized controlled study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 69, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Badawi, N.; Morgan, C.; Novak, I. Baby Intensive Early Active Treatment (babiEAT): A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial of Feeding Therapy for Infants with Cerebral Palsy and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.; Butt, G.A.; Nasir, M.; Hassan, F. Effects of oral motor therapy in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 31, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhlesin, M.; Yadegari, F.; Noroozi, M.; Ravarian, A.; Ghoreishi, Z.S. Effect of action observation training on the oral phase of swallowing in children with cerebral palsy: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Logoped Phoniatr. Vocol. 2024, 49, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serel Aslan, S.; Demir, N.; Karaduman, A.A. Effect of a new treatment protocol called Functional Chewing Training on chewing function in children with cerebral palsy: A double-blind randomised controlled trial. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2017, 44, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.L.; Smith, I.M.; Duku, E.; Vaillancourt, T.; Szatmari, P.; Bryson, S.; Fombonne, E.; Volden, J.; Waddell, C.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; et al. Behavioral Pediatrics Feeding Assessment Scale in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Psychometrics and Associations With Child and Parent Variables. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2015, 40, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, P.; Saavedra, M.S.; Sofranac, M.M.; Jarvis, M.S.; Woollacott, M. Refinement, reliability and validity of the segmental assessment of trunk control (SATCo). Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2010, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A.Y. Evaluating chewing function: Expanding the dysphagia field using food oral processing and the IDDSI framework. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, M.A.; Mann, G.D.; Groher, M.E. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, A.; McIntyre, S.; Novak, I.; Lannin, N.; Lowe, K. A comparison of goal attainment scaling and the Canadian Occupational Performance Measure for paediatric rehabilitation research. Pediatr. Rehabil. 2006, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Lisa Ortega, A.; Ciamponi, A.L.; Mendes, F.M.; Santos, M.T. Assessment scale of the oral motor performance of children and adolescents with neurological damages. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 36, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefton-Greif, M.A.; Okelo, S.O.; Wright, J.M.; Collaco, J.M.; McGrath-Morrow, S.A.; Eakin, M.N. Impact of children’s feeding/swallowing problems: Validation of a new caregiver instrument. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.J.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Avery, L.M.; Lane, M. Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM-66 & GMFM-88) User’s Manual; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Serel Arslan, S.; Aydın, G.; Alemdaroğlu, I.; Tunca Yılmaz, Ö.; Karaduman, A.A. Reliability and validity of the Karaduman Chewing Performance Scale in paediatric neuromuscular diseases: A system for classification of chewing disorders. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skuse, D.; Stevenson, J.; Reilly, S.; Mathisen, B. Schedule for Oral-Motor Assessment (SOMA): Methods of Validation. Dysphagia 1995, 10, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Stonell, N.; Greenberg, J. Three treatment approaches and clinical factors in the reduction of drooling. Dysphagia 1988, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoyre, S.; Pados, B.; Park, J.; Estrem, H.; Hodges, E.; McComish, C.; Van Riper, M.; Murdoch, K. Development and content validation of the Pediatric Eating Assessment Tool (Pedi-EAT). Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2014, 23, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Seid, M.; Kurtin, P.S. PedsQL 4.0: Reliability and validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 generic core scales in healthy and patient populations. Med. Care 2001, 39, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyden, G.; Nieuwboer, A.; Mertin, J.; Preger, R.; Kiekens, C.; De Weerdt, W. The Trunk Impairment Scale: A new tool to measure motor impairment of the trunk after stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 2004, 18, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, D.; Mandy, A.; Pennington, L.; Hankins, M.; Morris, C. Development and reliability of a system to classify the eating and drinking ability of people with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.C.; Pigott, T.D.; Rothstein, H.R. How many studies do you need? A primer on statistical power for meta-analysis. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2010, 35, 215–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, G.M.; Dila, K.A.S.; Mohamed, M.Y.F.; Tam, D.N.H.; Kien, N.D.; Ahmed, A.M.; Huy, N.T. A step by step guide for conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis with simulation data. Trop. Med. Health 2019, 47, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susukida, R.; Crum, R.M.; Ebnesajjad, C.; Stuart, E.A.; Mojtabai, R. Generalizability of findings from randomized controlled trials: Application to the National Institute of Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network. Addiction 2017, 112, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chess, L.E.; Gagnier, J.J. Applicable or non-applicable: Investigations of clinical heterogeneity in systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2016, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhide, A.; Shah, P.S.; Acharya, G. A simplified guide to randomized controlled trials. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2018, 97, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.F.; Audrey, S.; Barker, M.; Bond, L.; Bonell, C.; Hardeman, W.; Moore, L.; O’Cathain, A.; Tinati, T.; Wight, D.; et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ 2015, 350, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellefson, M.R.; Oppenheimer, D.M. Is replication possible without fidelity? Psychol. Methods 2022, 28, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, D.L.; Stratford, P.W.; Bowman, D.H. Findings of extensive variation in the types of outcome measures used in hip and knee replacement clinical trials: A systematic review. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.; Egger, M.; Gluud, L.L.; Schulz, K.F.; Jüni, P.; Altman, D.G.; Gluud, C.; Martin, R.M.; Wood, A.J.; Sterne, J.A. Empirical evidence of bias in treatment effect estimates in controlled trials with different interventions and outcomes: Meta-epidemiological study. BMJ 2008, 336, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitlin, L.N. Behavioral Intervention Research: Designing, Evaluating, and Implementing; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tolin, D.F.; McKay, D.; Olatunji, B.O.; Abramowitz, J.S.; Otto, M.W. On the importance of identifying mechanisms and active ingredients of psychological treatments. Behav. Res. Ther. 2023, 170, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenny, S.; Abdelgawad, I. Statistical Significance. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Miltenberger, R.G.; Valbuena, D.; Sanchez, S. Functional Assessment of Challenging Behavior. Curr. Dev. Disord. Rep. 2019, 6, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, E.; Schlichenmeyer, K.; Dube, W. Functional analysis of problem behavior: A systematic approach for identifying idiosyncratic variables. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2015, 48, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, G. Theory and Practice of Counseling and Psychotherapy, 5th ed.; Brooks/Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- McInerney, M.S.; Reddihough, D.S.; Carding, P.N.; Swanton, R.; Walton, C.M.; Imms, C. Behavioural interventions to treat drooling in children with neurodisability: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, U.; Cratsley, K. Psychological mechanisms. In Encyclopedia of personality and individual differences; Zeigler-Hill, V., Shackelford, T.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, J.; Dijkers, M.P.; Hart, T.; Zanca, J.M.; Packel, A.; Ferraro, M.; Tsaousides, T. Development of a Theory-Driven Rehabilitation Treatment Taxonomy: Conceptual Issues. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, S24–S32.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinckley, J.J.; Douglas, N.F. Treatment fidelity: Its importance and reported frequency in aphasia treatment studies. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2013, 22, S279–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, R.L. The Risk-of-Bias in N-of-1 Trials (RoBiNT) Scale: An Expanded Manual for the Critical Appraisal of Single-Case Reports; John Walsh Centre for Rehabilitation Research: St Leonards, NSW, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, R.A.; Lipsey, M. The role of theory in rehabilitation assessment, treatment, and outcomes. In Improving Assessment in Rehabilitation and health; Glueckauf, R., Sechrest, L., Bond, G., McDonel, E., Eds.; Sage Publications, Inc.: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- Malmivaara, A. Generalizability of findings from systematic reviews and meta-analyses in the Leading General Medical Journals. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52, jrm00031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, S.; van den Akker, M.; Winkens, B. The importance of effect sizes. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2013, 20, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).