Uric Acid to Platelet Ratio (UAPR) and Its Link to Lipid Abnormalities: Findings from a Large Cohort Study in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
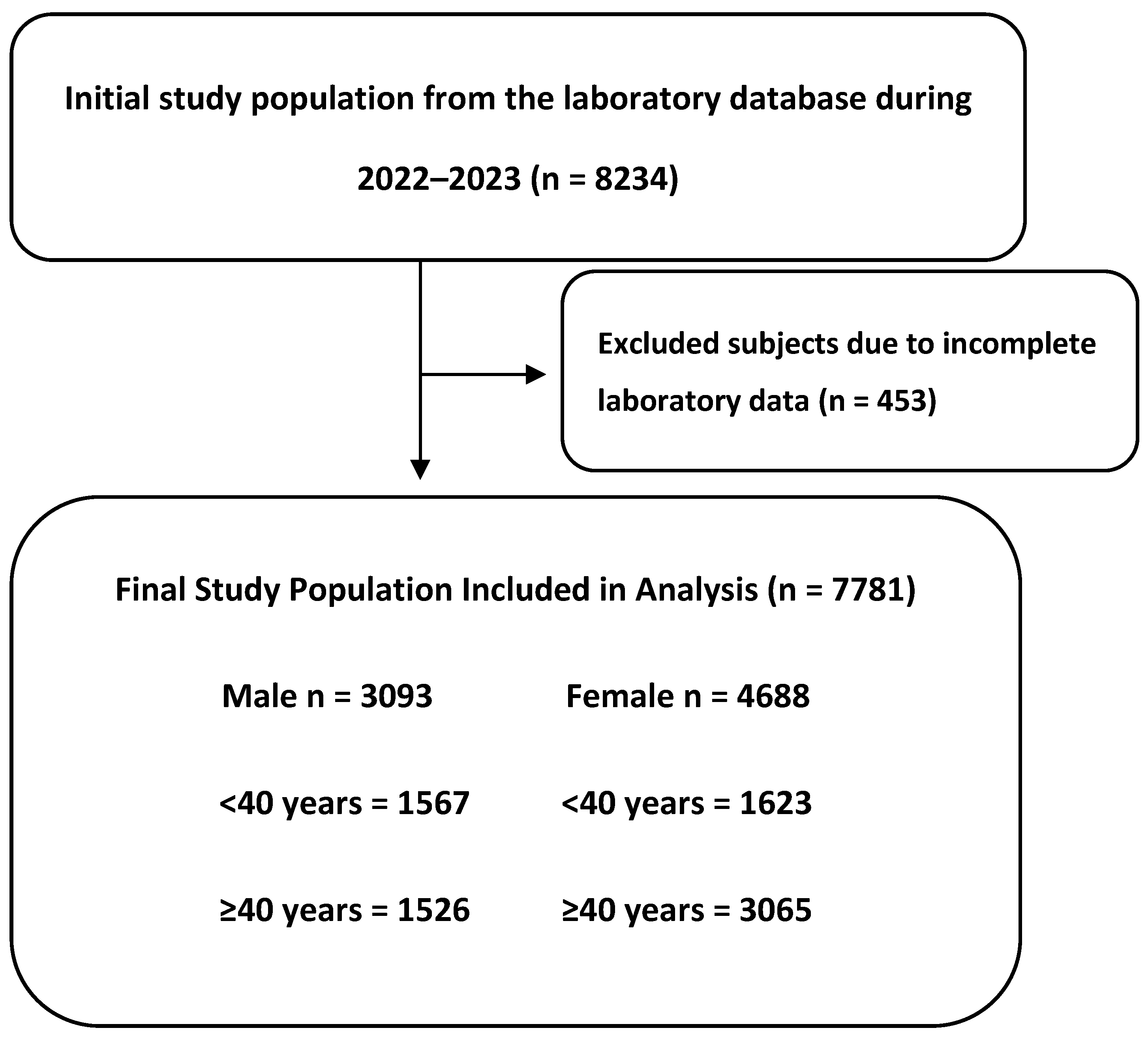
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Biochemical Features of the Included Subjects
3.2. Prevalence of Lipid Abnormalities and Its Derived Ratios in Males and Females
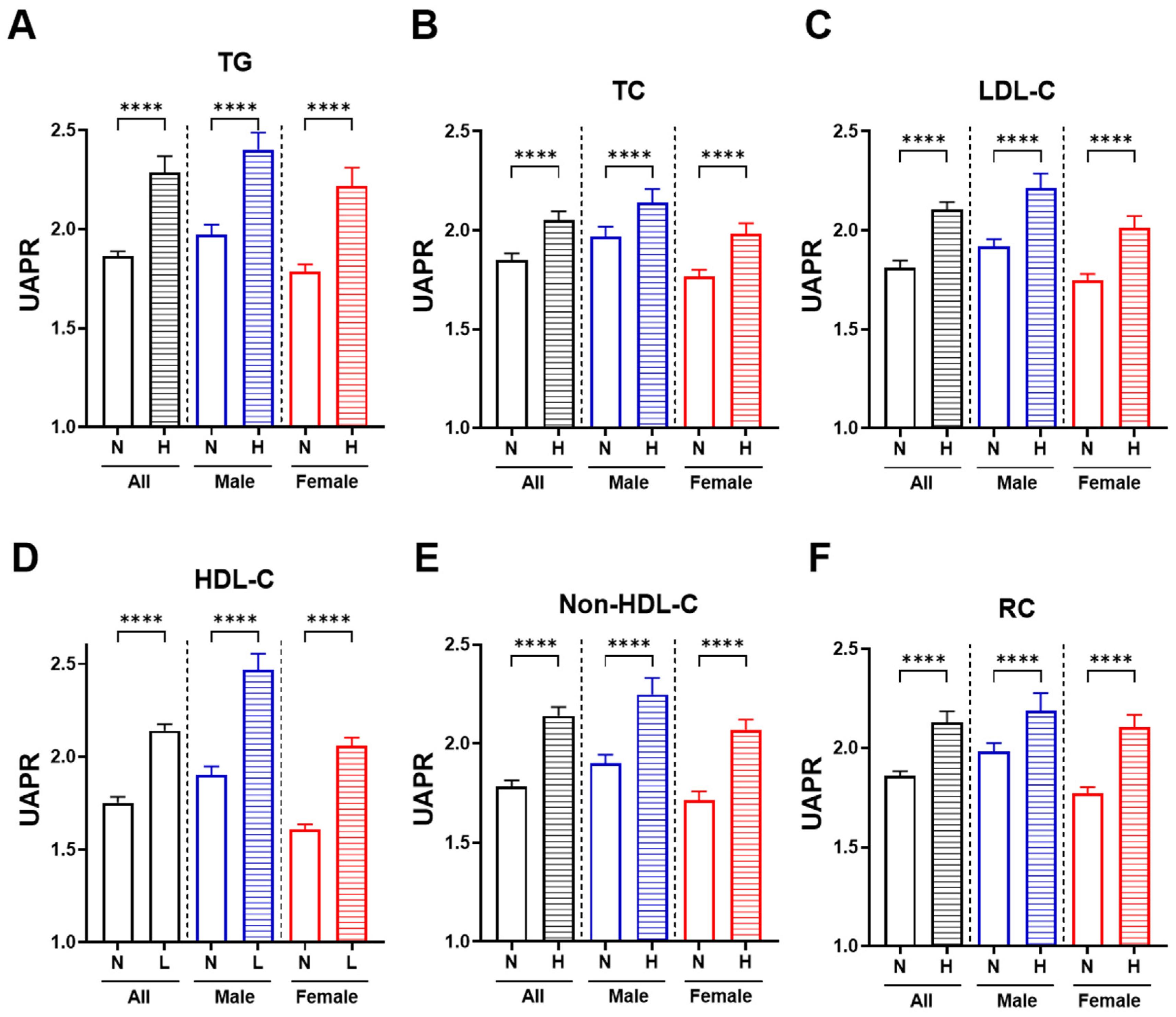
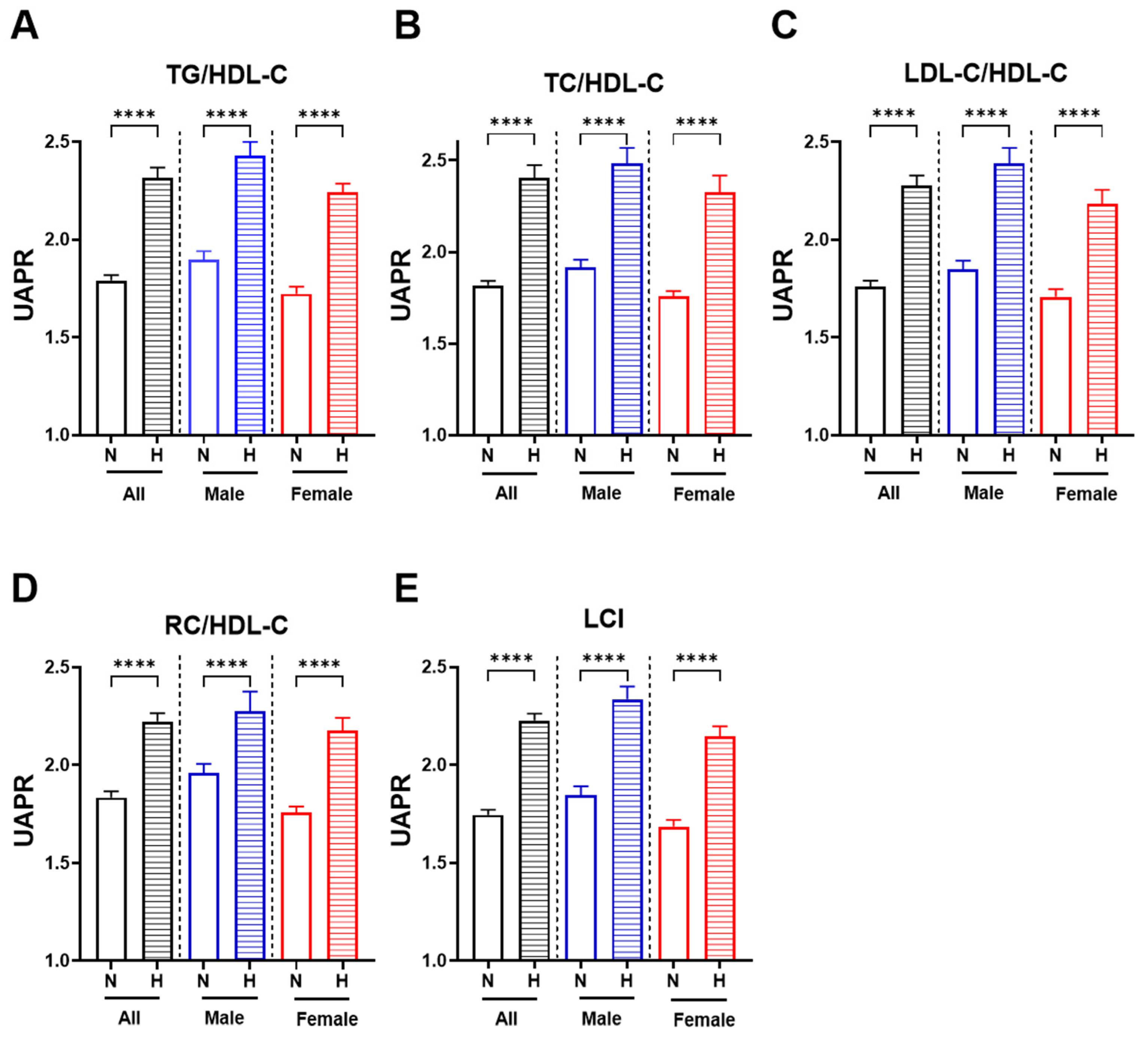
3.3. Higher UAPR Levels Exhibited Adverse Changes in Lipid Profile and Ratios
3.4. Subjects with Aberrant Lipid Parameters and Ratios Exhibit a Significant Increase in UAPR
3.5. Significant Associations Between UAPR and Both Conventional Lipid Markers and Ratios
3.6. Univariate and Multivariable Regression Analyses of UAPR with Lipid Parameters
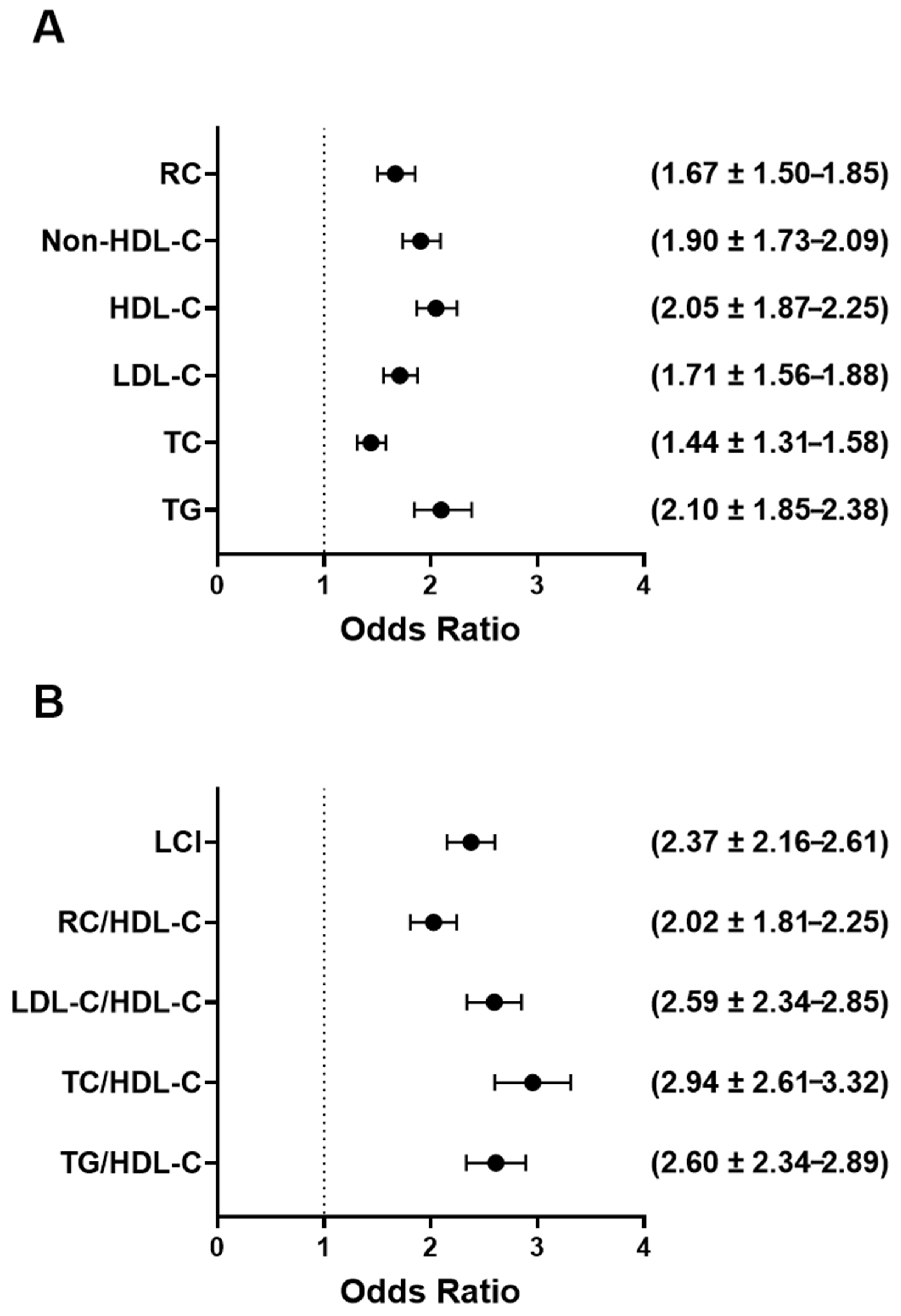
3.7. Higher UAPR Values Are Linked to Greater Odds of Dyslipidemia and Atherogenic Lipid Ratios
3.8. Subjects with High UAPR Exhibited a Higher Prevalence of Lipid Abnormalities
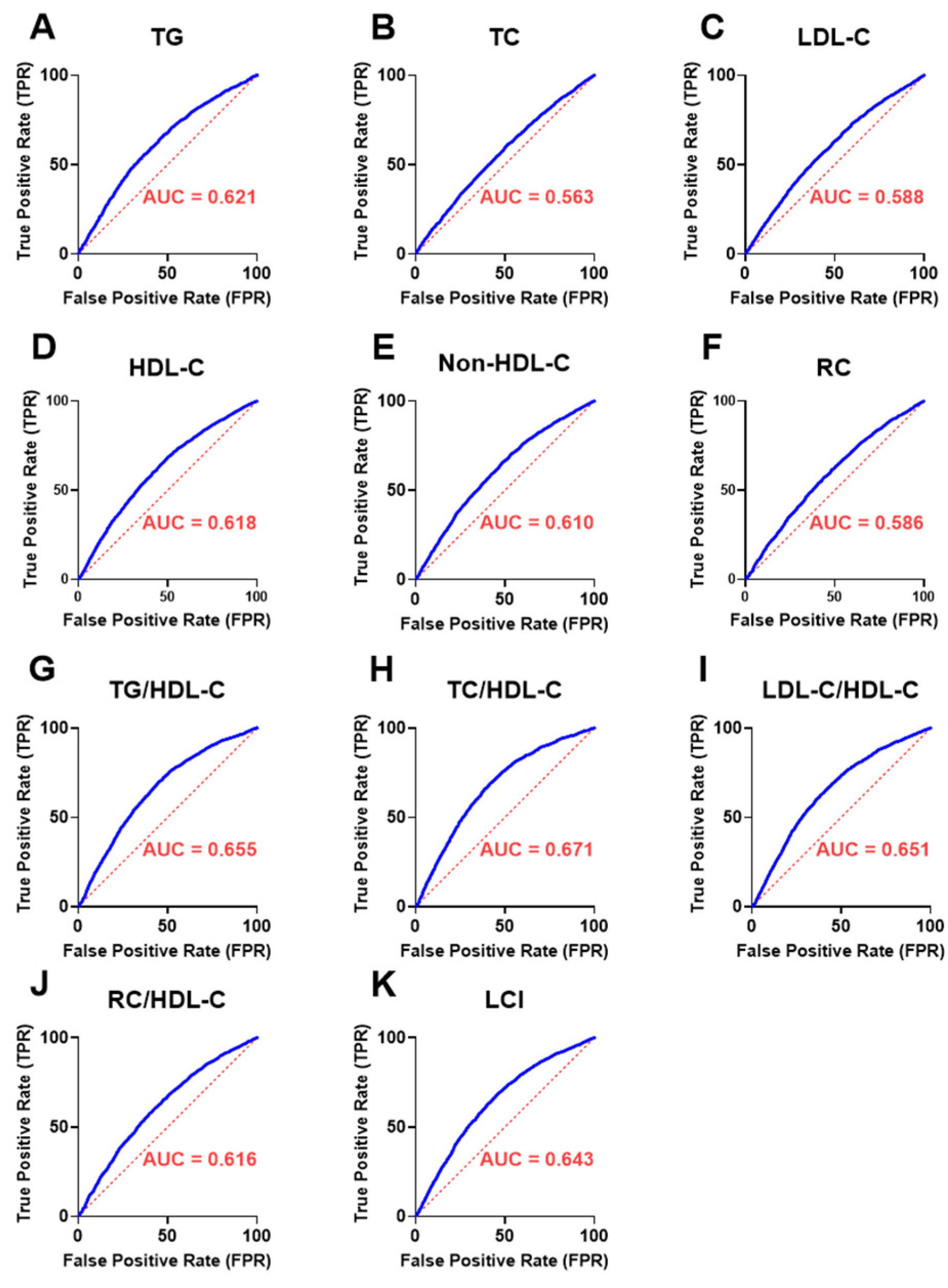
3.9. Discriminatory Performance of UAPR in Detecting Abnormal Lipid Parameters and Ratios
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malekmohammad, K.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Role of lipid accumulation and inflammation in atherosclerosis: Focus on molecular and cellular mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 707529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.P.; Whelton, S.P.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Mcevoy, J.W. Dyslipidemia. In Hypertension: A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, S.; Koyama, T.; Kuriyama, N.; Ozaki, E.; Uehara, R. The Association of Daily Physical Activity Behaviors with Visceral Fat. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 14, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 522637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Guo, Z.K.; Johnson, C.M.; Hensrud, D.D.; Jensen, M.D. Splanchnic lipolysis in human obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Vachher, M.; Arora, T.; Kumar, B.; Burman, A. Visceral fat: A key mediator of NAFLD development and progression. Hum. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 33, 200210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, D.; Macias, E.; Zarini, S.; Garfield, A.; Zemski Berry, K.; Gerszten, R.; Schoen, J.; Cree-Green, M.; Bergman, B.C. Quantifying the inflammatory secretome of human intermuscular adipose tissue. Physiol. Rep. 2022, 10, e15424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmaoğullari, S.; Tepe, D.; Uçaktürk, S.A.; Kara, F.K.; Demirel, F. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated factors in obese children and adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 7, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovsepian, S.; Kelishadi, R.; Djalalinia, S.; Farzadfar, F.; Naderimagham, S.; Qorbani, M. Prevalence of dyslipidemia in Iranian children and adolescents: A systematic review. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perak, A.M.; Ning, H.; Kit, B.K.; De Ferranti, S.D.; Van Horn, L.V.; Wilkins, J.T.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M. Trends in Levels of Lipids and Apolipoprotein B in US Youths Aged 6 to 19 Years, 1999–2016. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 321, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Yassin, M.S.; Baharudin, N.; Abdul-Razak, S.; Ramli, A.S.; Lai, N.M. Global prevalence of dyslipidaemia in adult populations: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e049662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enani, S.; Bahijri, S.; Malibary, M.; Jambi, H.; Eldakhakhny, B.; Al-Ahmadi, J.; Al Raddadi, R.; Ajabnoor, G.; Boraie, A.; Tuomilehto, J. The association between dyslipidemia, dietary habits and other lifestyle indicators among non-diabetic attendees of primary health care centers in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaheb, R.A.; Altemani, A.H. Prevalence and associated factors of dyslipidemia among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 4033–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Alasnag, M.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Al-Bassam, T.; Saeed, K.; Yazıcıoğlu, M.; Shabana, A. Patient journey for hypertension and dyslipidemia in Saudi Arabia: Highlighting the evidence gaps. Arch. Public Health 2023, 81, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Wei, P.; Suzauddula, M.; Nime, I.; Feroz, F.; Acharjee, M.; Pan, F. The interplay of factors in metabolic syndrome: Understanding its roots and complexity. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Tsukui, D.; Kono, H. Uric acid in inflammation and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Urrutia, R.; Kubes, P. Platelets: Bridging hemostasis, inflammation, and immunity. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2013, 35, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herter, J.M.; Rossaint, J.; Zarbock, A. Platelets in inflammation and immunity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, L.; Zhang, D.; Deng, C.; Wang, D.; Chen, R.; Chen, G.; et al. Association between uric acid and risk of venous thromboembolism in East Asian populations: A cohort and Mendelian randomization study. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2023, 39, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Merriman, T.R.; Stamp, L.K. Gout. Lancet 2016, 388, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Dong, B.; Geng, Z.; Xu, L. Excess Uric Acid Induces Gouty Nephropathy Through Crystal Formation: A Review of Recent Insights. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 911968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ridi, R.; Tallima, H. Physiological functions and pathogenic potential of uric acid: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Quintana, E.; Tugores, A.; Rodríguez-González, F. Serum uric acid levels and cardiovascular disease: The Gordian knot. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E1462–E1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.L.; Pei, D.; Lue, K.H.; Chen, Y.L. Uric acid levels can predict metabolic syndrome and hypertension in adolescents: A 10-year longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.K.; Ford, E.S.; Li, C.; Curhan, G. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with gout: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis Care Res. 2007, 57, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Schaft, N.; Brahimaj, A.; Wen, K.X.; Franco, O.H.; Dehghan, A. The association between serum uric acid and the incidence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Rotterdam Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Gu, Y. Correlation between serum uric acid level and central body fat distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 2521–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.S.; Lu, T.M.; Chen, C.H.; Guo, B.C.; Hsu, C.P. Hyperuricemia induces endothelial dysfunction and accelerates atherosclerosis by disturbing the asymmetric dimethylarginine/dimethylarginine dimethylaminotransferase 2 pathway. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Xu, H.; Sun, Q.; Yu, X.; Chen, W.; Wei, H.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, W. The role of oxidative stress in hyperuricemia and xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) inhibitors. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1470380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zong, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Xie, L.; Yang, B.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Gao, J. Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, B.; Yuan, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G. Associations of Platelet Count with Inflammation and Response to Anti-TNF-α Therapy in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 559593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, X.; Gao, W. Role of platelet biomarkers in inflammatory response. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshuweishi, Y.; Abudawood, A.; Alfayez, D.; Almufarrih, A.A.; Alanazi, F.; Alshuweishi, F.A.; Almuqrin, A.M. Platelet/High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio (PHR) Predicts Type 2 Diabetes in Obese Patients: A Retrospective Study. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, B.; Piackova, E.; Haller, P.M.; Andric, T.; Kahl, B.; Christ, G.; Geppert, A.; Wojta, J.; Huber, K. Increased platelet reactivity in dyslipidemic patients with coronary artery disease on dual anti-platelet therapy. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Hua, Y. The association of platelet to white blood cell ratio with diabetes: A nationwide survey in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1418583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y. The association of the platelet/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with self-reported stroke and cardiovascular mortality: A population-based observational study. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosak, K.; Sauer, A.; Meeusen, J. Clinical Update: Ceramides As Novel Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Nurse Pract. 2024, 20, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Palaiopanos, K.; Björkbacka, H.; Peters, A.; de Lemos, J.A.; Seshadri, S.; Dichgans, M.; Georgakis, M.K. Circulating interleukin-6 levels and incident ischemic stroke. Neurology 2022, 98, E1002–E1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejenie, T.A.; Abebe, E.C.; Mengstie, M.A.; Seid, M.A.; Gebeyehu, N.A.; Adella, G.A.; Kassie, G.A.; Gebrekidan, A.Y.; Gesese, M.M.; Tegegne, K.D.; et al. Dyslipidemia and serum cystatin C levels as biomarker of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1124367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfhili, M.A.; Alsughayyir, J.; Basudan, A.; Alfaifi, M.; Awan, Z.A.; Algethami, M.R.; Al-Sheikh, Y.A. Reduced platelet-lymphocyte ratio in a Saudi population with impaired fasting glycemia and hyperglycemia. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfhili, M.A.; Alotaibi, G.A.; Alfaifi, M.; Almoghrabi, Y.; Alsughayyir, J. Association of Platelet-Monocyte Ratio with Dyslipidemia in Saudi Arabia: A Large, Population-Based Study. Life 2023, 13, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Sun, L. The correlation of retinol-binding protein-4 and lipoprotein combine index with the prevalence and diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome. Heart Vessel. 2020, 35, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, A.D. Cholesterol levels. Nursing 2010, 40, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, R.; Martin, S.S.; Michos, E.D.; Lamba, I.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Saeed, A.; Lima, J.; Puri, R.; Nomura, S.; Tsai, M.; et al. Remnant cholesterol predicts cardiovascular disease beyond LDL and ApoB: A primary prevention study. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4324–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Jee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jin, S.M.; Suh, S.; Bae, J.C.; Kim, S.W.; Chung, J.H.; Min, Y.K.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Non-HDL-cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol is a better predictor of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance than apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Tian, N.; Xu, Q.; Zhan, X.; Peng, F.; Wang, X.; Su, N.; Feng, X.; Tang, X.; et al. Association of the remnant cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Yoo, W.; Alesh, I.; Mahajan, N.; Mirowska, K.K.; Mewada, A.; Kahn, J.; Afonso, L.; Williams, K.A.; Flack, J.M. Effect of long-term exposure to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol beginning early in life on the risk of coronary heart disease: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Ration. Pharmacother. Cardiol. 2013, 9, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement fromthe European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holven, K.B.; Roeters van Lennep, J. Sex differences in lipids: A life course approach. Atherosclerosis 2023, 384, 117270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, G.; Pintaudi, B.; Giorda, C.; Lucisano, G.; Nicolucci, A.; Cristofaro, M.R.; Suraci, C.; Mulas, M.F.; Napoli, A.; Rossi, M.C.; et al. Age- and gender-related differences in LDL-cholesterol management in outpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 957105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Rodriguez, F.; Yeh, R.W.; Wadhera, R.K. Trends in Lipid Concentrations and Lipid Control among US Adults, 2007–2018. JAMA 2022, 328, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Rahman, S.; Islam, S.; Haque, T.; Molla, N.H.; Sumon, A.H.; Kathak, R.R.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Islam, F.; Mohanto, N.C.; et al. The relationship between serum uric acid and lipid profile in Bangladeshi adults. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M.; Salvagno, G.L.; Targher, G.; Guidi, G.C. Epidemiological association between uric acid concentration in plasma, lipoprotein(a), and the traditional lipid profile. Clin. Cardiol. 2010, 33, E76–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Du, G.L.; Song, N.; Ma, Y.T.; Li, X.M.; Gao, X.M.; Yang, Y.N. Hyperuricemia and its association with adiposity and dyslipidemia in Northwest China: Results from cardiovascular risk survey in Xinjiang (CRS 2008-2012). Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.C.; Wang, C.C.; Kao, T.W.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, W.L. Relationship between hyperuricemia and lipid profiles in us adults. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 127596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Seo, J.; Yang, S. Association between dyslipidemia and serum uric acid levels in Korean adults: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–2017. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 228684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaql, A.B.; Almousa, A.I.; Alonazi, F.S. Association between Uric Acid Levels and Lipid Profiles in Adult Population of Alkharj City. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 71, 3648–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Nishizawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Fukata, T.; Mizushima, T.; Furuno, M.; Bamba, T.; Tsushima, Y.; Fujishima, Y.; Kita, S.; et al. Hypoxanthine Secretion from Human Adipose Tissue and its Increase in Hypoxia. Obesity 2018, 26, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chang, X.; Bian, N.; An, Y.; Liu, J.; Leng, S.; Wang, G. Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance Is Positively Associated With Serum Uric Acid Levels and Hyperuricemia in Northern Chinese Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 835154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, Y.; Nishizawa, H.; Tochino, Y.; Nakatsuji, H.; Sekimoto, R.; Nagao, H.; Shirakura, T.; Kato, K.; Imaizumi, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Uric acid secretion from adipose tissue and its increase in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27138–27149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzatti, A.J.; Toth, P.P. New perspectives on atherogenic dyslipidaemia and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 15, e04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, T.T.; Foresto-Neto, O.; Camara, N.O.S. The role of uric acid in inflammasome-mediated kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Bartsch, L.A.; Castillo-Rodriguez, E.; Fernandez-Prado, R.; Kanbay, M.; Ortiz, A. Potential Dangers of Serum Urate-Lowering Therapy. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiao, R. Pyroptosis in platelets: Thrombocytopenia and inflammation. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Bravo, G.; Annarapu, G.; Carmona, E.; Nawarskas, J.; Clark, R.; Novelli, E.; Mota Alvidrez, R.I. Platelets in Thrombosis and Atherosclerosis: A Double-Edged Sword. Am. J. Pathol. 2024, 194, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQueen, M.J.; Hawken, S.; Wang, X.; Ounpuu, S.; Sniderman, A.; Probstfield, J.; Steyn, K.; Sanderson, J.E.; Hasani, M.; Volkova, E.; et al. Lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins as risk markers of myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): A case-control study. Lancet 2008, 372, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walldius, G.; Jungner, I.; Holme, I.; Aastveit, A.H.; Kolar, W.; Steiner, E. High apolipoprotein B, low apolipoprotein A-I, and improvement in the prediction of fatal myocardial infarction (AMORIS study): A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 358, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhong, Y.; Kuang, C.; Liao, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Q. Lipoprotein ratios are better than conventional lipid parameters in predicting arterial stiffness in young men. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, N.; Nosrati, M.; Koochackpoor, G.; Aghasizadeh, M.; Bahari, H.; Namdar, H.B.; Afkhami, N.; Darban, R.A.; Azarian, F.; Ferns, G.A.; et al. The association between hyperuricemia and insulin resistance surrogates, dietary- and lifestyle insulin resistance indices in an Iranian population: MASHAD cohort study. Nutr. J. 2024, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsans, J.; Kauppi, J.; Rantalaiho, V.; Kerola, A.; Hakkarainen, K.; Lehto, T.; Kautiainen, H.; Kauppi, M. Serum Uric Acid Is Associated with Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetic Subjects. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, G. Effects of antidiabetic drugs on the level of serum uric acid in patients who have type 2 diabetes. Saudi Med. J. 2025, 46, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asma Sakalli, A.; Küçükerdem, H.S.; Aygün, O. What is the relationship between serum uric acid level and insulin resistance?: A case-control study. Medicine 2023, 102, E36732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Median (±IQR) |
|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 37 (32–46) |
| Sex (female), % | 60.25 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.2 (13–15.6) |
| Red Cell Count (×1012/μL) | 5.24 (4.86–5.67) |
| Total Leukocytic Count (×109/μL) | 5.65 (4.57–6.97) |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | 92 (86–99) |
| Glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) % | 5.3 (5.1–5.3) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.70 (0.60–0.85) |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 22 (16–27) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 93 (70–127) |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 187 (165–209) |
| Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 120 (99–141) |
| High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 47 (41–55) |
| Non-HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 137 (115–161) |
| Remnant Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 16 (10–23) |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (U/L) | 18 (13–27) |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (U/L) | 18 (15–23) |
| Albumin in Serum (g/dL) | 4.2 (4–4.5) |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (mm/h) | 8 (5–15) |
| 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (ng/mL) | 14.3 (9.9–21.9) |
| Lipid Abnormality | Overall Prevalence (%) | Male Prevalence (%) | Female Prevalence (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High TG | 14.59 | 15.71 | 13.84 | 0.0243 |
| High TC | 35.5 | 35.92 | 35.22 | 0.5423 |
| High LDL-C | 37.55 | 39.73 | 36.11 | 0.0014 |
| Low HDL-C | 42.22 | 23.63 | 54.5 | <0.0001 |
| High Non-HDL-C | 36.7 | 38.96 | 35.22 | 0.0009 |
| High RC | 23.34 | 23.5 | 23.23 | 0.7999 |
| High TG/HDL-C Ratio | 23.99 | 25.93 | 22.72 | 0.0013 |
| High TC/HDL-C Ratio | 17.75 | 20.21 | 16.13 | <0.0001 |
| High LDL-C/HDL-C Ratio | 30.9 | 34.46 | 28.54 | <0.0001 |
| High RC/HDL-C Ratio | 22.3 | 23.08 | 21.78 | 0.1849 |
| High LCI | 36.49 | 39.8 | 34.3 | <0.0001 |
| Lipid Parameters and Ratios | T1 | T2 | T3 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG | 82 (63–110) | 94.5 (71–127) | 106 (78–142.3) | <0.0001 |
| TC | 204 (164–183) | 208 (165–187.5) | 214.3 (165–191) | <0.0001 |
| LDL-C | 97 (114–133) | 100 (120.5–141) | 102 (126–147) | <0.0001 |
| HDL-C | 45 (52–60) | 41 (47–55) | 37 (43–51) | <0.0001 |
| Non-HDL-C | 129 (111–150) | 138 (117–160) | 146 (120–170) | <0.0001 |
| RC | 14 (9–20) | 16 (10–23) | 18 (12–25) | <0.0001 |
| TG/HDL-C | 1.60 (1.11–2.27) | 2.00 (1.38–2.91) | 2.42 (1.66–3.56) | <0.0001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.19 (1.73–2.75) | 2.53 (1.98–3.13) | 2.86 (2.23–3.54) | <0.0001 |
| TC-C/HDL-C | 3.49 (2.96–4.14) | 3.90 (3.27–4.63) | 4.31 (3.58–5.13) | <0.0001 |
| RC/HDL-C | 0.26 (0.16–0.43) | 0.33 (0.2–0.53) | 0.41 (0.25–0.64) | <0.0001 |
| LCI | 9.65 (5.76–15.9) | 13.01 (7.55–21.91) | 16.96 (9.30–28.57) | <0.0001 |
| Lipid Marker | r (q-Values a) | Lipid Ratio | r (q-Values) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TG | 0.226 (<0.0001) | TG/HDL-C | 0.298 (<0.0001) |
| TC | 0.074 (<0.0001) | TC/HDL-C | 0.302 (<0.0001) |
| LDL-C | 0.131 (<0.0001) | LDL-C/HDL-C | 0.284 (<0.0001) |
| HDL-C | −0.314 (<0.0001) | RC/HDL-C | 0.242 (<0.0001) |
| Non-HDL-C | 0.180 (<0.0001) | LCI | 0.260 (<0.0001) |
| RC | 0.182 (<0.0001) |
| Lipid Parameter | Univariate β (95% CI) | p Value | Multivariable β (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG | 0.15 (0.12–0.18) | <0.0001 | 0.14 (0.11–0.18) | <0.0001 |
| TC | −0.01 (−0.02–0.01) | 0.0004 | −0.01 (−0.03–0.01) | 0.42 |
| LDL-C | 0.01 (0.00–0.02) | 0.0227 | 0.01 (−0.02–0.03) | 0.589 |
| HDL-C | −0.13 (−0.16–0.10) | <0.0001 | −0.12 (−0.15–0.08) | <0.0001 |
| non-HDL-C | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | <0.0001 | 0.01 (−0.01–0.04) | 0.381 |
| RC | 0.17 (0.14–0.20) | <0.0001 | −0.01 (−0.47–0.44) | 0.9613 |
| Lipid Parameters and Ratios | N-UAPR (%) | H-UAPR (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triglycerides (TG) | <150 | 89.31 | 79.93 |
| ≥150 | 10.69 | 20.07 | |
| TG/HDL-C Ratio | <3 | 83.31 | 65.74 |
| ≥3 | 16.69 | 34.26 | |
| Total Cholesterol (TC) | <200 | 67.98 | 59.62 |
| ≥200 | 32.02 | 40.38 | |
| TC/HDL-C Ratio | <5 | 88.83 | 73.01 |
| ≥5 | 11.17 | 26.99 | |
| LDL-C | <130 | 67.69 | 55.07 |
| ≥130 | 32.31 | 44.93 | |
| LDL-C/HDL-C Ratio | <3 | 77.57 | 57.2 |
| ≥3 | 22.43 | 42.8 | |
| HDL-C | ≥40 in males, ≥50 in females | 65.03 | 47.59 |
| <40 in males, <50 in females | 34.97 | 52.41 | |
| Non-HDL-C | <150 | 69.54 | 54.51 |
| ≥150 | 30.46 | 45.49 | |
| Remnant Cholesterol (RC) | ≤23 | 80.51 | 71.24 |
| >23 | 19.49 | 28.76 | |
| RC/HDL-C Ratio | <0.56 | 82.82 | 70.5 |
| ≥0.56 | 17.18 | 29.5 | |
| Lipoprotein Combine Index (LCI) | <16 | 71.83 | 51.82 |
| ≥16 | 28.17 | 48.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshuweishi, Y.; Izziddeen, L.; Alsaidan, M.; Alshuwayer, N.A.; Alshuweishi, F.A.; Basudan, A.M. Uric Acid to Platelet Ratio (UAPR) and Its Link to Lipid Abnormalities: Findings from a Large Cohort Study in Saudi Arabia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175952
Alshuweishi Y, Izziddeen L, Alsaidan M, Alshuwayer NA, Alshuweishi FA, Basudan AM. Uric Acid to Platelet Ratio (UAPR) and Its Link to Lipid Abnormalities: Findings from a Large Cohort Study in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):5952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175952
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshuweishi, Yazeed, Lama Izziddeen, Muath Alsaidan, Noha A. Alshuwayer, Faisal A. Alshuweishi, and Ahmed M. Basudan. 2025. "Uric Acid to Platelet Ratio (UAPR) and Its Link to Lipid Abnormalities: Findings from a Large Cohort Study in Saudi Arabia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 5952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175952
APA StyleAlshuweishi, Y., Izziddeen, L., Alsaidan, M., Alshuwayer, N. A., Alshuweishi, F. A., & Basudan, A. M. (2025). Uric Acid to Platelet Ratio (UAPR) and Its Link to Lipid Abnormalities: Findings from a Large Cohort Study in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 5952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175952






