New Trends in Airway Management During Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conventional Oxygen Therapy
3. High-Flow Nasal Oxygen
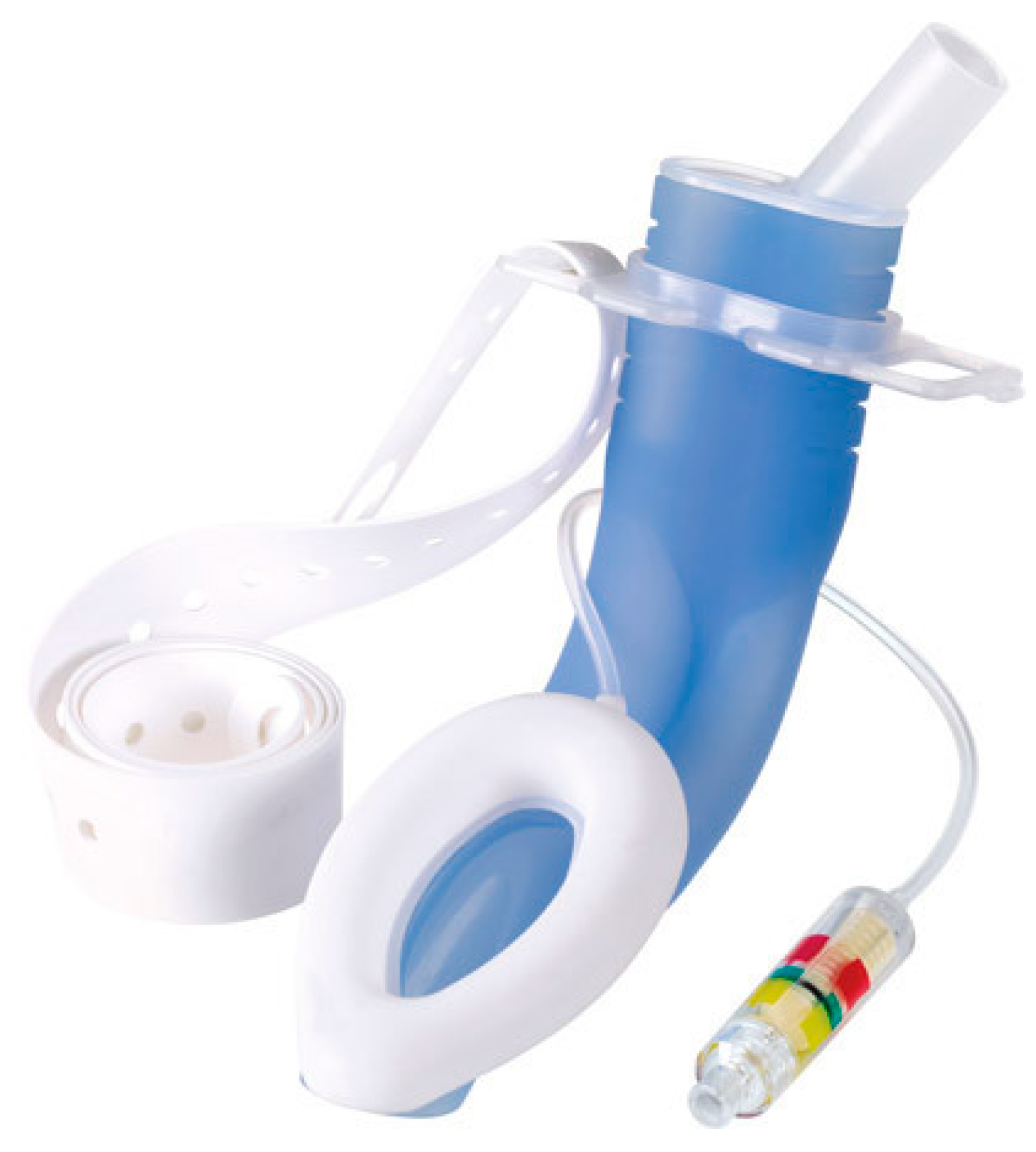
4. Supraglottic Devices
5. Endotracheal Intubation
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologist |
| ASGE | American Society for Gastroenterology Endoscopy |
| BMI | body mass index |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| COT | conventional oxygen therapy |
| ERCP | endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography |
| Et | end-tidal |
| ETI | endotracheal intubation |
| GA | general anesthesia |
| HFNO | high flow nasal oxygen |
| LMA | laryngeal mask airway |
| MAC | monitored anesthesia care |
| OSAS | obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| PEEP | positive end-expiratory pressure |
| SGAs | supraglottic devices |
References
- Goudra, B.; Singh, P.M. Airway Management During Upper GI Endoscopic Procedures: State of the Art Review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, B.; Karamchandani, K. Management of anesthetic complications outside the operating room. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2023, 36, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.C.; Mönkemüller, K. Anesthesia for complex endoscopy: A new paradigm. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, O.S. Sedation for routine gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures: A review on efficacy, safety, efficiency, cost and satisfaction. Intest. Res. 2017, 15, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, F.; Giarratano, A.; Giaccone, P.; De Robertis, E.; Monzani, R.; Rossi, M.; Tritapepe, L.; Pasquale, L.; Conigliaro, R.; Fanti, L.; et al. Analgo-Sedazione In Endoscopia Digestiva: Verso un Approccio Multidisciplinare per la Qualità e la Sicurezza: La Posizione Inter-Societaria SIAAR- TI-SIED per un Percorso di Buona Pratica Clinica. Available online: https://www.siaarti.it/news/338126 (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Janik, L.S.; Stamper, S.; Vender, J.S.; Troianos, C.A. Pro-Con Debate: Monitored Anesthesia Care Versus General Endotracheal Anesthesia for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. Anesth. Analg. 2022, 134, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimaraghi, O.; Bilal, M.; Amornyotin, S.; Arain, M.; Behrends, M.; Berzin, T.M.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Choice, C.; Fassbender, P.; Sawhney, M.S.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the perioperative management of patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 130, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, S.J.; Absalom, A.R. Consensus guidelines, Delphi methods, and evidence around anaesthetic technique for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 131, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, G. Comparing sedation protocols for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A retrospective study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Chen, T.; Shi, D.; Qiao, Y.; Liao, X. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Anesthetic and Sedative Regimens for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Network Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. 2025, 43, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, M.; Kamal, M.A.; Abuelazm, M.; Yousaf, A.; Abdelazeem, B. Meta-analysis comparing the efficiency of high-flow nasal cannula versus low-flow nasal cannula in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Proc. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. 2022, 35, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, K.B.; Carlson, R.; Arnold, B.; Nguyen, L.; Lee, J.; Weston, B.; Hernandez, M.; Feng, L.; Syed, T.; Hagberg, C. Safety of the LMA®Gastro™ for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, H.; Senturk, H.; Calim, M.; Daskaya, H.; Guney, I.A.; Karaaslan, K. Comparison of LMA®® Gastro™ airway and gastrolaryngeal tube in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A prospective randomized observational trial. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021, 87, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A.; Dhindsa, B.S.; Saghir, S.M.; Ramai, D.; Chandan, S.; Mashiana, H.; Bhogal, N.; Sayles, H.; Bhat, I.; Singh, S. Choice of sedation in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: Is monitored anesthesia care as safe as general anesthesia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, F.C.; Agnihotri, A.; Grabitz, S.D.; Santer, P.; Nabel, S.; Tran, T.; Berzin, T.M.; Sundar, E.; Xu, X.; Sawhney, M.S.; et al. Outcomes after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with general anaesthesia versus sedation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, A.J.; Sanders, D.S.; Hopper, A.; Kurien, M.; Sidhu, R. How does tolerability of double balloon enteroscopy compare to other forms of endoscopy? Frontline Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, D.A.; Donnelly, M.T.; Smith, K.S.; Riley, S.A. Factors associated with abdominal discomfort during colonoscopy: A prospective analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagaito, Y.; Isono, S.; Nishino, T. Upper airway reflexes during a combination of propofol and fentanyl anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1998, 88, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.C.; Park, C.H.; Shin, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Min, K.T. A comparison of sedation protocols for gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: Moderate sedation with analgesic supplementation vs analgesia targeted light sedation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Yuan, F.; Ma, X.; Qu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Incidence rates, risk factors, and outcomes of aspiration pneumonia after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Farooq, P.; Zwilling, K.; Patel, D.; Siddiqui, A.A. Efficacy and Safety of Propofol-Mediated Sedation for Outpatient Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.L.; Nickel, K.B.; Olsen, M.A.; Vargo, J.J.; Kushnir, V.M. Type of sedation and the need for unplanned interventions during ERCP: Analysis of the clinical outcomes research initiative national endoscopic database (CORI-NED). Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019, 11, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enestvedt, B.K.; Eisen, G.M.; Holub, J.; Lieberman, D.A. Is the American Society of Anesthesiologists classification useful in risk stratification for endoscopic procedures? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 77, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.D.; Bown, S.; Morden, A.; Coady, T.; Logan, R.F. Prevention of hypoxaemia during upper-gastrointestinal endoscopy by means of oxygen via nasal cannulae. Lancet 1987, 1, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagappa, M.; Patra, J.; Wong, J.; Subramani, Y.; Singh, M.; Ho, G.; Wong, D.; Chung, F. Association of STOP-Bang Questionnaire as a Screening Tool for Sleep Apnea and Postoperative Complications: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-analysis of Prospective and Retrospective Cohort Studies. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, C.E.; Rice, A.N.; Broome, M.E.; Silva, S.G.; Muckler, V.C. Nasal Ventilation Mask for Prevention of Upper Airway Obstruction in Patients With Obesity or Obstructive Sleep Apnea. AANA J. 2019, 87, 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- Qadeer, M.A.; Vargo, J.J.; Dumot, J.A.; Lopez, R.; Trolli, P.A.; Stevens, T.; Parsi, M.A.; Sanaka, M.R.; Zuccaro, G. Capnographic monitoring of respiratory activity improves safety of sedation for endoscopic cholangiopancreatography and ultrasonography. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1568–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, Y.; Iwasaki, E.; Masaoka, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Seino, T.; Katayama, T.; Minami, K.; Tamagawa, H.; Machida, Y.; et al. Novel mainstream capnometer system is safe and feasible even under CO2 insufflation during ERCP-related procedure: A pilot study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Welte, M.; Welte, C.; Albert, J.; Meckbach, Y.; Herrmann, E.; Kannengiesser, M.; Trojan, J.; Filmann, N.; Schroeter, H.; et al. Capnographic monitoring of propofol-based sedation during colonoscopy. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, A.; Kreuzmayr, A.; Manner, H.; Koop, H.; Lorenz, A.; Schaefer, C.; Plauth, M.; Jetschmann, J.-U.; von Tirpitz, C. Acute sedation-associated complications in GI endoscopy (ProSed 2 Study): Results from the prospective multicentre electronic registry of sedation-associated complications. Gut 2019, 68, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.M.; Mason, K.P.; Krauss, B.S. Pulmonary aspiration during procedural sedation: A comprehensive systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Early, D.S.; Lightdale, J.R.; Vargo, J.J.; Acosta, R.D.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Chathadi, K.V.; Evans, J.A.; Fisher, D.A.; Fonkalsrud, L.; et al. Guidelines for sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbtani, Y.B.; Summerlee, R.J.; Yang, D.; An, Q.; Suarez, A.; Williamson, J.B.; Shrode, C.W.; Gupte, A.R.; Chauhan, S.S.; Draganov, P.V.; et al. Impact of Endotracheal Intubation on Interventional Endoscopy Unit Efficiency Metrics at a Tertiary Academic Medical Center. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melita, G.; Tripodi, V.F.; Pallio, S.; Shahini, E.; Vitello, A.; Sinagra, E.; Facciorusso, A.; Mazzeo, A.T.; Choudhury, A.; Dhar, J.; et al. Moderate Sedation or Deep Sedation for ERCP: What Are the Preferences in the Literature? Life 2024, 14, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhu, N.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. A prospective, randomized, single-blinded study comparing the efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024, 24, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gu, C. Effectiveness of single loading dose of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol for deep sedation of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in elderly patients: A prospective randomized study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassoulaki, A.; Iatrelli, I.; Vezakis, A.; Polydorou, A. Deep sedation for endoscopic cholangiopancreatography with or without pre or intraprocedural opioids: A double-blind randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 32, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Sun, M.; Miao, M.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cong, X.; Zhang, J. High flow nasal cannula for patients undergoing bronchoscopy and gastrointestinal endoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 949614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvenkatarajan, V.; Dharmalingam, A.; Arenas, G.; Arenas, G.; Wahba, M.; Liu, W.-M.; Zaw, Y.; Steiner, R.; Tran, A.; Currie, J. Effect of high-flow vs. low-flow nasal plus mouthguard oxygen therapy on hypoxaemia during sedation: A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Anaesthesia 2022, 77, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeffi, M.A.; Petrick, K.M.; Magder, L.; Greenwald, B.D.; Darwin, P.; Goldberg, E.M.; Bigeleisen, P.; Chow, J.H.; Anders, M.; Boyd, C.; et al. High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen in Patients Having Anesthesia for Advanced Esophagogastroduodenoscopy: HIFLOW-ENDO, a Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; He, X.X.; Chen, Y.P.; Yang, S. The effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula during sedated digestive endoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Cha, B.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Han, J.-H.; Park, M.H.; Yang, C. Impact of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygenation on the Prevention of Hypoxia During Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in Elderly Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 4154–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nay, M.A.; Fromont, L.; Eugene, A.; Marcueyz, J.-L.; Mfam, W.-S.; Baert, O.; Remerand, F.; Ravry, C.; Auvet, A. Thierry Boulain High-flow nasal oxygenation or standard oxygenation for gastrointestinal endoscopy with sedation in patients at risk of hypoxaemia: A multicentre randomised controlled trial (ODEPHI trial). Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 127, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuse, T.; Sawase, H.; Ozawa, E.; Nagata, K.; Komatsu, N.; Sanuki, T.; Kurata, S.; Mishima, G.; Hosogaya, N.; Nakashima, S.; et al. Study on prevention of hypercapnia by nasal high flow in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography during intravenous anesthesia. Medicine 2020, 99, e20036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, E.; Lam, K.; Behringer, E.; Chan, V.; Bozak, D.; Mitsakakis, N.; Perlas, A. High-flow nasal oxygen does not increase the volume of gastric secretions during spontaneous ventilation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, e75–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lian, Y.; Li, W.X. Airway Complications during and after General Anesthesia: A Comparison, Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Using Flexible Laryngeal Mask Airways and Endotracheal Tubes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A.; Cook, T.M.; Smith, A.F.; Lewis, S.R.; Reed, S.S. Supraglottic airway devices versus tracheal intubation for airway management during general anaesthesia in obese patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD010105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martindale, S.J. Anaesthetic considerations during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2006, 34, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmutz, A.; Loeffler, T.; Schmidt, A.; Goebel, U. LMA Gastro™ airway is feasible during upper gastrointestinal interventional endoscopic procedures in high risk patients: A single-center observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.L.; Wilson, S.R.; Burgoyne, L.L.; Endlich, Y. LMA®® Gastro™: A paediatric experience. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2021, 49, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polese, L.; Giugliano, E.; Valmasoni, M. Patient Position in Operative Endoscopy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, K.S.; Petersen, J.T.; Pedersen, N.A.; Rovsing, L. Self-positioning followed by induction of anaesthesia and insertion of a laryngeal mask airway versus endotracheal intubation and subsequent positioning for spinal surgery in the prone position: A randomised clinical trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 31, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Sreevastava, D.K.; Dwivedi, D.; Gadgi, S.; Sud, S.; Dudeja, P. A Comparison of Stress Response between Insertion of Gastro-laryngeal Tube and Endotracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Procedures for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. Anesth. Essays Res. 2019, 13, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengre, A.; Haldar, R.; Kannaujia, A.K.; Singh, N.; Mohindra, S.; Mishra, P. Outcomes and evaluation of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography via Gastro-Laryngeal Tube in adult patients: A prospective randomised control study. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2023, 20, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terblanche, N.C.S.; Middleton, C.; Choi-Lundberg, D.L.; Skinner, M. Efficacy of a new dual channel laryngeal mask airway, the LMA®®Gastro™ Airway, for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: A prospective observational study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.H.; Wei, P.; Yuan, W.; Ruan, W.Q.; Li, X.; Song, J.G. Case series of tracheal extubation in prone position after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography general anesthesia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 6092–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.H.; Wei, P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, H.; Yuan, L.; et al. Safety of prone emergence from general endotracheal anesthesia in patients undergoing ERCP: A randomized controlled trial. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzanbagi, A.B.; Jilani, T.L.; Qureshi, L.A.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Tashkandi, A.M.S.; Elshrief, E.E.A.; Khan, M.S.; Abdelhalim, M.A.H.; Zahrani, S.A.; Mohamed, W.M.K.; et al. Randomized trial comparing general anesthesia with anesthesiologist-administered deep sedation for ERCP in average-risk patients. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 96, 983–990.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.L.; Mullady, D.K.; Lang, G.D.; Das, K.K.; Hovis, R.M.; Patel, R.S.; Hollander, T.G.; Elsner, J.; Ifune, C.; Kushnir, V.M. A randomized controlled trial evaluating general endotracheal anesthesia versus monitored anesthesia care and the incidence of sedation-related adverse events during ERCP in high-risk patients. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Cao, X. Safety and efficacy of remifentanil-propofol combination on “muscle relaxant-free” general anesthesia for therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 5292–5303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cummings, L.C.; Liang, C.; Mascha, E.J.; Saager, L.; Smith, Z.L.; Bhavani, S.; Vargo, J.J.; Cummings, K.C. Incidence of sedation-related adverse events during ERCP with anesthesia assistance: A multicenter observational study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 96, 269–281.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, T.R.; Hathorn, K.E.; Creighton, D.W.; AlSamman, M.A.; Thompson, C.C. Safety and sedation-associated adverse event reporting among patients undergoing endoscopic cholangiopancreatography: A comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 6977–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.M.; Kuo, C.M.; Lu, L.S.; Wu, C.-K.; Tsai, C.-E.; Kuo, M.-T.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Tai, W.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-H.; et al. A comparison between non-sedation and general endotracheal anesthesia for retrograde endoscopic common bile duct stone removal: A tertiary center experience. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M.T.; Angelotti, T.; Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S. Prospective randomized comparison of endoscopist-facilitated endotracheal intubation and standard intubation for ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 98, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosenz, J.; Lang, R.P.; Bernhofer, S.; Maieron, A. A prospective study on incidence of desaturations in ERCP with non-anesthesiologist sedation and adverse event awareness of endoscopists. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study (Ref), Year | Design | Main Topic | Population Studied | Outcomes | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang N et al. [9], 2024 | Observational retrospective study | Pharmacological strategy | 600 patients undergoing ERCP divided into four groups:
| Hemodynamic parameters, sedation level, recovery time, and procedure-related complications. | Pro-Dex protocol offers superior sedation quality, faster recovery, and fewer complications compared to other protocols during ERCP. No significant differences in the incidence of ERCP-related adverse events, hypotension, or bradycardia among the four groups. |
| Liu Y et al. [10], 2025 | Meta-analysis | Pharmacological strategy | 42 RCTs comparing patients undergoing ERCP with various drug combinations. | Procedure time, patient satisfaction, SpO2, incidence of SpO2 < 90%, and adverse events. | Combination approaches—particularly propofol with oxycodone or dexmedetomidine plus fentanyl—appear to offer an optimal balance of procedural efficiency, patient satisfaction, and a safer oxygenation profile. |
| Gamal et al. [11], 2022 | Meta-analysis | HFNO | 3 RCTs with 390 patients:
| Incidence of hypoxia, lowest SpO2, adverse events. | HFNO reduced the incidence of hypoxia in patients undergoing ERCP, provided a higher mean lowest oxygen saturation, and a lower need for airway interventions. |
| Hagan KB et al. [12], 2020 | Prospective observational study | Supraglottic devices | 30 patients undergoing ERCP with an LMA® Gastro™ placement | Number of attempts and time to successful SGA placement, vital signs, SpO2, median end-tidal CO2, practitioner satisfaction, and any complications. | LMA® Gastro™ is a safe alternative airway for ERCP, with high placement success (96–97%), excellent procedural completion rates (93–98%), maintained oxygenation (SpO2 ≥ 95%), median end-tidal CO2 of 35 mmHg, high practitioner satisfaction, and only minor, transient postoperative complications. |
| Uysal H et al. [13], 2021 | Randomized controlled trial | Supraglottic devices | 83 patients undergoing ERCP divided into two groups:
| Oropharyngeal leak pressure and supraglottic devices-related adverse events. | Oropharyngeal leak pressure and complication rate were lower in the LMA group. |
| Dhaliwal A et al. [14], 2021 | Meta-analysis | MAC vs. GA with endotracheal intubation | 21 studies with a total of 11,592 patients undergoing ERCP under MAC or GA. | Adverse events, duration of the procedure, recovery time, ERCP cannulation rates, and conversion rate of MAC to GA. | No statistically significant differences between the two groups. The mean duration of the procedure was longer in the MAC group, but the mean recovery time was shorter. |
| Althoff FC et al. [15], 2021 | Observational retrospective study | MAC vs. GA with endotracheal intubation | 17,538 patients undergoing ERCP | Adverse discharge (in-hospital mortality or new discharge to a nursing facility), intraoperative adverse events, 30- and 90-day mortality, length of stay, hospital charges, postoperative acute kidney injury and pneumonia within 30 days. | Sedation was associated with reduced adverse discharge, intraoperative hypotension, and lower length of stay. |
| ASGE Levels | Procedures | Estimate Duration |
|---|---|---|
| I Diagnostic ERCP or simple therapeutic maneuvers | Deep cannulation of the duct of interest, main papilla, or sampling; biliary stent removal or exchange. | <30 min |
| II Standard therapeutic interventions with moderate complexity | Biliary stone extraction ≤ 10 mm; treatment of biliary leaks; treatment of extrahepatic strictures (benign or malignant); placement of prophylactic pancreatic stents. | 30–60 min |
| III Advanced therapeutic procedures or multiple interventions | Biliary stone extraction ≥ 10 mm; minor papilla cannulation in divisum and therapy; removal of internally migrated biliary stents; intraductal imaging, biopsy, or fine-needle aspiration; management of acute or recurrent pancreatitis; treatment of pancreatic strictures; removal of pancreatic stones that are mobile and ≤5 mm; treatment of hilar tumors; treatment of benign biliary strictures, hilum, and above; management of suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (with or without manometry). | >60 min |
| IV Highly complex or high-risk interventions | Removal of internally migrated pancreatic stents; removal of pancreatic stones that are impacted and/or ≥5 mm; removal of intrahepatic stones; pseudocyst drainage or necrosectomy; ampullectomy; ERCP after a Whipple procedure or Roux-en-Y bariatric surgery. | >60 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maiellare, F.; Sbaraglia, F.; Del Vicario, M.; Fattore, R.; Ferrone, G.; Lucente, M.; Piersanti, A.; Posa, D.; Spinazzola, G.; De Padova, D.; et al. New Trends in Airway Management During Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165905
Maiellare F, Sbaraglia F, Del Vicario M, Fattore R, Ferrone G, Lucente M, Piersanti A, Posa D, Spinazzola G, De Padova D, et al. New Trends in Airway Management During Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165905
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaiellare, Federica, Fabio Sbaraglia, Miryam Del Vicario, Riccardo Fattore, Giuliano Ferrone, Monica Lucente, Alessandra Piersanti, Domenico Posa, Giorgia Spinazzola, Daniele De Padova, and et al. 2025. "New Trends in Airway Management During Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165905
APA StyleMaiellare, F., Sbaraglia, F., Del Vicario, M., Fattore, R., Ferrone, G., Lucente, M., Piersanti, A., Posa, D., Spinazzola, G., De Padova, D., Malatesta, C., Memoli, C., & Rossi, M. (2025). New Trends in Airway Management During Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165905





