Prognostic Role of the Naples Score in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Missed Opportunity in Inflammation-Based Stratification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collection and Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Naples Prognostic Score Assessment
2.4. Outcome Definition
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Comparison Between Risk Groups
3.3. Overall Survival Analysis
3.4. Univariate Cox Regression Analysis
3.5. Multivariate Cox Regression Analysis
3.5.1. Model 1—Prognostic Impact of the Composite NPS
3.5.2. Model 2—Prognostic Role of Individual NPS Components
3.6. Exploratory Analysis Based on the Original NPS Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCLC | Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| ES-SCLC | Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| NPS | Naples Prognostic Score |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| LMR | Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio |
| ECOG PS | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status |
| PCI | Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| TAM | Tumor-Associated Macrophages |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| ORCID | Open Researcher and Contributor ID |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| MD | Medical Doctor |
References
- Matera, R.; Chiang, A. What Is New in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 37, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Vaccarella, S.; Morgan, E.; Li, M.; Etxeberria, J.; Chokunonga, E.; Manraj, S.S.; Kamate, B.; Omonisi, A.; Bray, F. Global variations in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype in 2020: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Chiang, A.C. Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2025, 333, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Sugawara, S.; Kao, S.; Hochmair, M.; Huemer, F.; de Castro, G.; Havel, L.; Caro, R.B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. Five-year survival in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer treated with atezolizumab in the Phase III IMpower133 study and the Phase III IMbrella A extension study. Lung Cancer 2024, 196, 107924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, K.; Watanabe, K.; Seike, M.; Hosomi, Y. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide chemotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A retrospective real-world study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamakawa, Y.; Hirahara, A.; Hayashi, A.; Ito, K.; Shinohara, H.; Shiba, A.; Higashi, Y.; Aga, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with small-cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, M.K.; Mix, M.D.; Wang, X.; Jaszewski, B.; Foster, N.; Masters, G.A.; Laurie, F.; Smith, K.; Razavian, N.B.; Alden, R.S.; et al. Prognostic Factors in Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of CALGB 30610-RTOG 0538. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2440673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Liu, X.; Ji, W.; Zheng, K.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Guan, M.; et al. Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Nutrition in Patients with Various Types of Malignant Tumors: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; Mcnamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Sonpavde, G.; Knox, J.J.; Tran, B.; et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kawada, K.; Obama, K. Inflammation-Related Biomarkers for the Prediction of Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, M.; Xia, C.; Feng, W. Prognostic value of inflammatory markers NLR, PLR, and LMR in gastric cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1408700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, M.J.; Morrison, D.S.; Talwar, D.; Balmer, S.M.; Fletcher, C.D.; O’rEilly, D.S.; Foulis, A.K.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. A comparison of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with cancer. A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, G.; Lieto, E.; Auricchio, A.; Cardella, F.; Mabilia, A.; Podzemny, V.; Castellano, P.; Orditura, M.; Napolitano, V. Naples Prognostic Score, Based on Nutritional and Inflammatory Status, is an Independent Predictor of Long-term Outcome in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2017, 60, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.M.; Ren, J.J.; Yu, N.; Xu, J.Y.; Chen, G.C.; Li, X.; Li, D.P.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.N.; Zhang, Y.S.; et al. The prognostic value of the Naples prognostic score for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulturk, I.; Yilmaz, M.; Tacar, S.Y.; Bakkaloglu, O.K.; Sonmezoz, G.B.; Erdal, G.S.; Ozmen, A.; Tural, D. Naples prognostic score may predict overall survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2024, 20, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, G.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, B.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z. Naples Prognostic Score as a Novel Prognostic Prediction Tool for Resectable Locally Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Neoadjuvant Therapy. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 4843–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitmez, M.; Ekingen, E.; Zaman, S. Predictive Value of the Naples Prognostic Score for One-Year Mortality in NSTEMI Patients Undergoing Selective PCI. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.; Cao, S.; Han, Z.; Kong, L.; Ren, D. Naples Prognostic Score is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer and Nomogram Predictive Model Established. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3719–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Ji, S. Assessment of Naples prognostic score in predicting survival for small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2242254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Wellenstein, M.D.; de Visser, K.E. Neutrophils in cancer: Neutral no more. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, T.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, X. Prognostic value of pre-treatment Naples prognostic score (NPS) in patients with osteosarcoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekes, E.M.; Schweighofer, B.; Kupriyanova, T.A.; Zajac, E.; Ardi, V.C.; Quigley, J.P.; Deryugina, E.I. Tumor-recruited neutrophils and neutrophil TIMP-free MMP-9 regulate coordinately the levels of tumor angiogenesis and efficiency of malignant cell intravasation. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Choi, S.H. Tumor-associated macrophages in cancer: Recent advancements in cancer nanoimmunotherapies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasaudi, A.S.; Dolan, R.D.; Edwards, C.A.; McMillan, D.C. Hypoalbuminemia Reflects Nutritional Risk, Body Composition and Systemic Inflammation and Is Independently Associated with Survival in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecci, F.; Cantini, L.; Cognigni, V.; Perrone, F.; Mazzaschi, G.; Agostinelli, V.; Mentrasti, G.; Favari, E.; Maffezzoli, M.; Cortellini, A.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Blood Lipid Profile in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Oncologist 2024, 29, e372–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Lu, W.; Cheng, J.; Dai, M.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, D.D.; Fu, T.W.; Ye, T.W.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, C.W.; et al. Naples Prognostic Score is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients Undergoing Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Deng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, F.; Xue, Y.; Qin, L.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; et al. Modified Naples prognostic score for evaluating the prognosis of patients with obstructive colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lv, L.; Zhao, F.; Mei, X.; Zhou, H.; Yu, F. The value of the preoperative Naples prognostic score in predicting prognosis in gallbladder cancer surgery patients. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, M.; Zhu, J.; Gu, R.; Yang, B.; Ji, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, K. Prognostic value of Naples Prognostic Score in locally advanced cervical cancer patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Biomol. Biomed. 2025, 25, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Li, J.; Ji, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ji, S. Naples Prognostic Score as an Independent Predictor of Survival Outcomes for Resected Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients After Neoadjuvant Treatment. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Duan, G. Clinical Significance of Preoperative Naples Prognostic Score in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221129447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Niu, L.; Shi, W.X.; Li, X.Y.; Shen, L. Naples prognostic score as a predictor of outcomes in lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 8144–8153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peker, P.; Geçgel, A.; Düşgün, A.; Özkan, O.; Bozkurt Duman, B. Prognostic Power of the Naples Score in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Can Inflammation and Nutrition Predict Survival? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
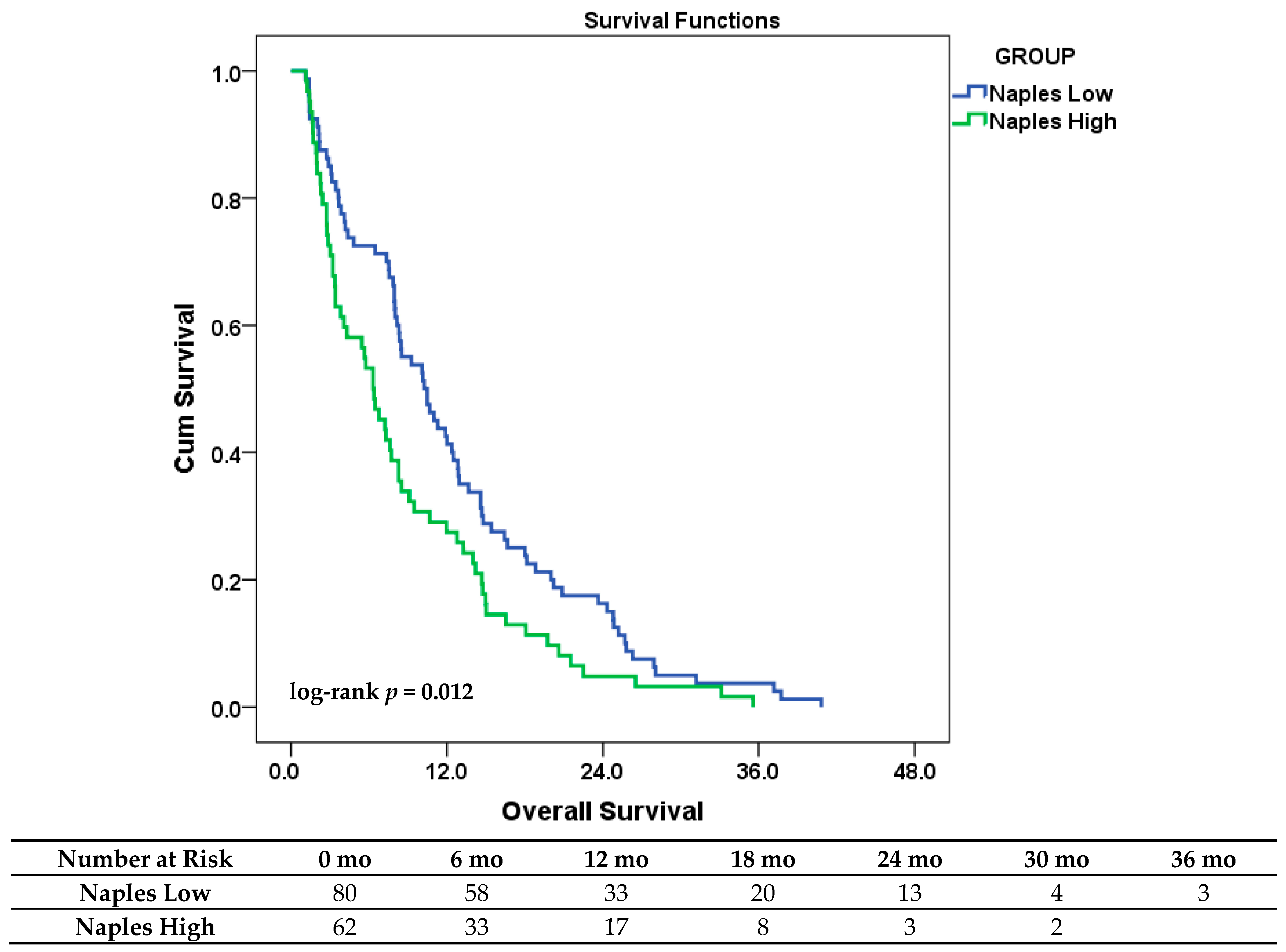
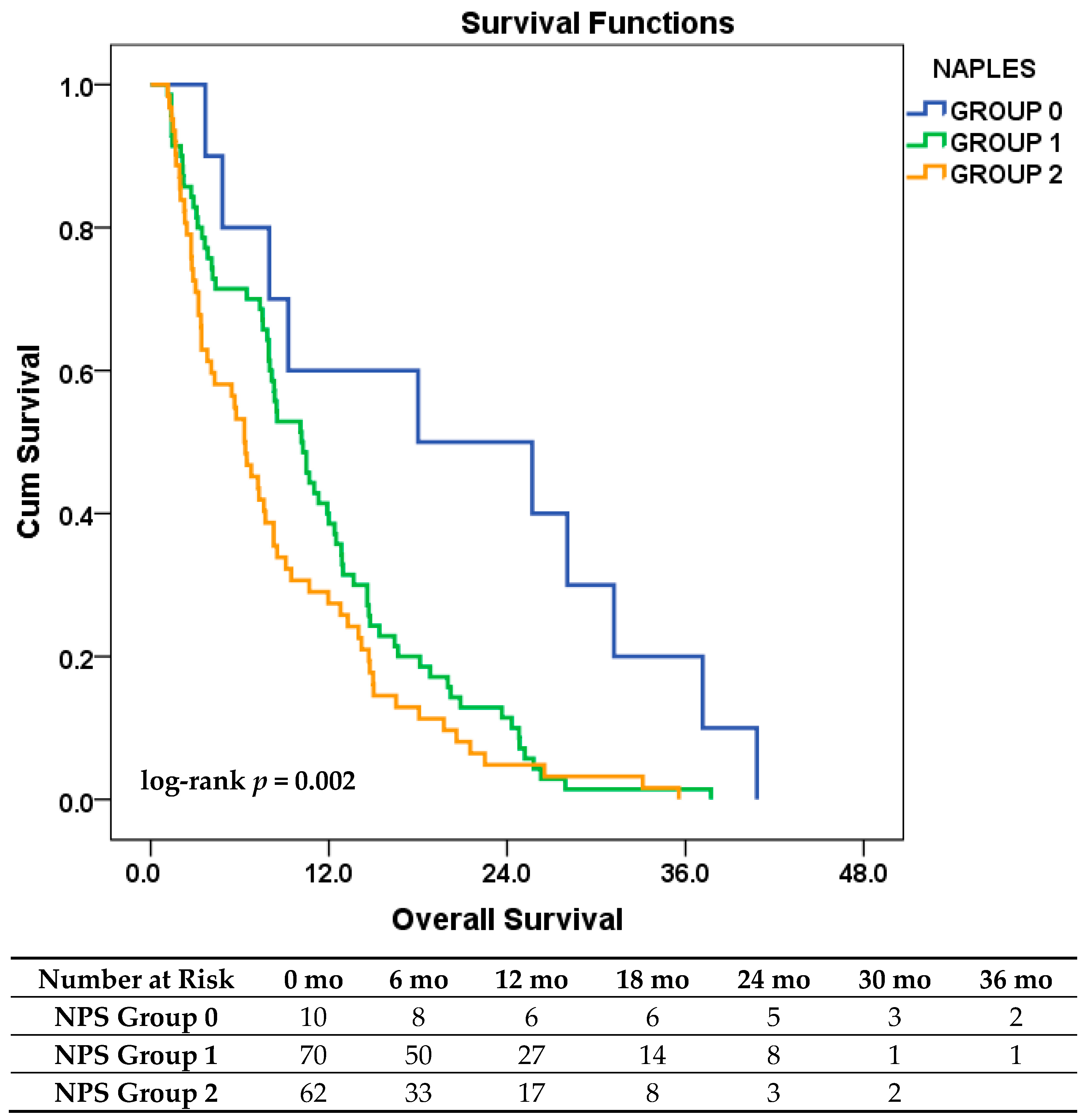
| Clinical Variable | Category | Total (n, %) | Low-Risk Group | High-Risk Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <65 years | 95 (66.9%) | 56 (70.0%) | 39 (62.9%) | 0.472 |
| ≥65 years | 47 (33.1%) | 24 (30.0%) | 23 (37.1%) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0 | 91 (64.1%) | 58 (72.5%) | 33 (53.2%) | 0.018 |
| ≥1 | 51 (35.9%) | 22 (27.5%) | 29 (46.8%) | ||
| Sex | Female | 11 (7.7%) | 5 (6.3%) | 6 (9.7%) | 0.449 |
| Male | 131 (92.3%) | 75 (93.8%) | 56 (90.3%) | ||
| Smoking Status | Non-current smoker | 34 (23.9%) | 17 (21.3%) | 17 (27.4%) | 0.393 |
| Current smoker | 108 (76.1%) | 63 (78.8%) | 45 (72.6%) | ||
| Comorbidity | Absent | 72 (50.7%) | 41 (51.2%) | 31 (50.0%) | 0.883 |
| Present | 70 (49.3%) | 39 (48.8%) | 31 (50.0%) | ||
| Stage at Diagnosis | Limited disease | 39 (27.5%) | 23 (28.7%) | 16 (25.8%) | 0.697 |
| Extensive disease | 103 (72.5%) | 57 (71.3%) | 46 (74.2%) | ||
| PCI | Not administered | 107 (75.4%) | 56 (70.0%) | 51 (82.3%) | 0.093 |
| Administered | 35 (24.6%) | 24 (30.0%) | 11 (17.7%) | ||
| Number of Metastatic Sites | Single site | 45 (31.7%) | 25 (31.3%) | 20 (32.3%) | 0.898 |
| ≥2 sites | 97 (68.3%) | 55 (68.8%) | 42 (67.7%) | ||
| Brain Metastasis | Absent | 102 (71.8%) | 57 (71.3%) | 45 (72.6%) | 0.861 |
| Present | 40 (28.2%) | 23 (28.7%) | 17 (27.4%) | ||
| Bone Metastasis | Absent | 71 (50.0%) | 44 (55.0%) | 27 (43.5%) | 0.176 |
| Present | 71 (50.0%) | 36 (45.0%) | 35 (56.5%) | ||
| Liver Metastasis | Absent | 105 (73.9%) | 61 (76.3%) | 44 (71.0%) | 0.477 |
| Present | 37 (26.1%) | 19 (23.8%) | 18 (29.0%) | ||
| Lung Metastasis | Absent | 117 (82.4%) | 67 (83.8%) | 50 (80.6%) | 0.630 |
| Present | 25 (17.6%) | 13 (16.3%) | 12 (19.4%) | ||
| Adrenal Metastasis | Absent | 109 (76.8%) | 61 (76.3%) | 48 (77.4%) | 0.870 |
| Present | 33 (23.2%) | 19 (23.8%) | 14 (22.6%) |
| Clinical Variable | Category | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Reference Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ≥65 years | 1.35 (0.94–1.92) | 0.101 | <65 years |
| ECOG PS | ECOG ≥ 1 | 1.43 (1.01–2.03) | 0.047 | ECOG 0 |
| Sex | Male | 0.98 (0.53–1.83) | 0.957 | Female |
| Smoking Status | Current smoker | 1.05 (0.71–1.55) | 0.809 | Non-current smoker |
| Comorbidity | Present | 1.26 (0.91–1.76) | 0.168 | Absent |
| Stage at Diagnosis | De novo | 0.93 (0.65–1.34) | 0.681 | Relapsed |
| PCI | Yes | 0.98 (0.67–1.45) | 0.935 | No PCI |
| Number of Metastatic Sites | ≥2 sites | 1.59 (1.11–2.29) | 0.012 | Single site |
| Brain Metastasis | Present | 1.38 (0.95–2.00) | 0.088 | Absent |
| Bone Metastasis | Present | 1.41 (1.01–1.98) | 0.044 | Absent |
| Liver Metastasis | Present | 1.08 (0.74–1.58) | 0.691 | Absent |
| Lung Metastasis | Present | 1.52 (0.98–2.33) | 0.061 | Absent |
| Adrenal Metastasis | Present | 0.97 (0.65–1.44) | 0.868 | Absent |
| NLR | High (≥cutoff) | 1.34 (0.95–1.89) | 0.098 | Low (<cutoff) |
| LMR | High (≥cutoff) | 1.62 (1.06–2.47) | 0.027 | Low (<cutoff) |
| Serum Cholesterol | High (≥cutoff) | 0.86 (0.57–1.30) | 0.475 | Low (<cutoff) |
| Serum Albumin | High (≥cutoff) | 1.44 (1.02–2.03) | 0.040 | Low (<cutoff) |
| NPS | High (3–4) | 1.54 (1.10–2.15) | 0.013 | Low (0–2) |
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| High NPS (3–4) | 1.45 (1.02–2.06) | 0.041 |
| Bone metastasis | 1.27 (0.88–1.82) | 0.203 |
| Brain metastasis | 1.23 (0.84–1.78) | 0.290 |
| Lung metastasis | 0.68 (0.43–1.08) | 0.100 |
| ECOG PS ≥ 1 | 1.19 (0.82–1.73) | 0.367 |
| Age ≥ 65 | 1.20 (0.83–1.73) | 0.329 |
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| LMR (High) | 1.65 (1.04–2.61) | 0.034 |
| Serum albumin (High) | 1.48 (1.03–2.11) | 0.033 |
| NLR (High) | 1.01 (0.69–1.49) | 0.954 |
| Bone metastasis | 1.30 (0.89–1.88) | 0.164 |
| Brain metastasis | 1.18 (0.80–1.73) | 0.408 |
| Lung metastasis | 0.71 (0.45–1.12) | 0.139 |
| ECOG PS ≥ 1 | 1.43 (0.97–2.11) | 0.068 |
| Age ≥ 65 | 1.11 (0.77–1.60) | 0.591 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akgül, F.; Gökmen, İ.; Bayrakçı, İ.; Divriklioğlu, D.; Akkuş, A.F.; Bakır Kahveci, G.; Aydın, T.İ.; Erdoğan, B. Prognostic Role of the Naples Score in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Missed Opportunity in Inflammation-Based Stratification. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165892
Akgül F, Gökmen İ, Bayrakçı İ, Divriklioğlu D, Akkuş AF, Bakır Kahveci G, Aydın Tİ, Erdoğan B. Prognostic Role of the Naples Score in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Missed Opportunity in Inflammation-Based Stratification. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165892
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkgül, Fahri, İvo Gökmen, İsmail Bayrakçı, Didem Divriklioğlu, Aysun Fatma Akkuş, Gizem Bakır Kahveci, Tayyip İlker Aydın, and Bülent Erdoğan. 2025. "Prognostic Role of the Naples Score in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Missed Opportunity in Inflammation-Based Stratification" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165892
APA StyleAkgül, F., Gökmen, İ., Bayrakçı, İ., Divriklioğlu, D., Akkuş, A. F., Bakır Kahveci, G., Aydın, T. İ., & Erdoğan, B. (2025). Prognostic Role of the Naples Score in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Missed Opportunity in Inflammation-Based Stratification. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165892






