The Role of miRNAs as Predictors of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy Toxicity in Children: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
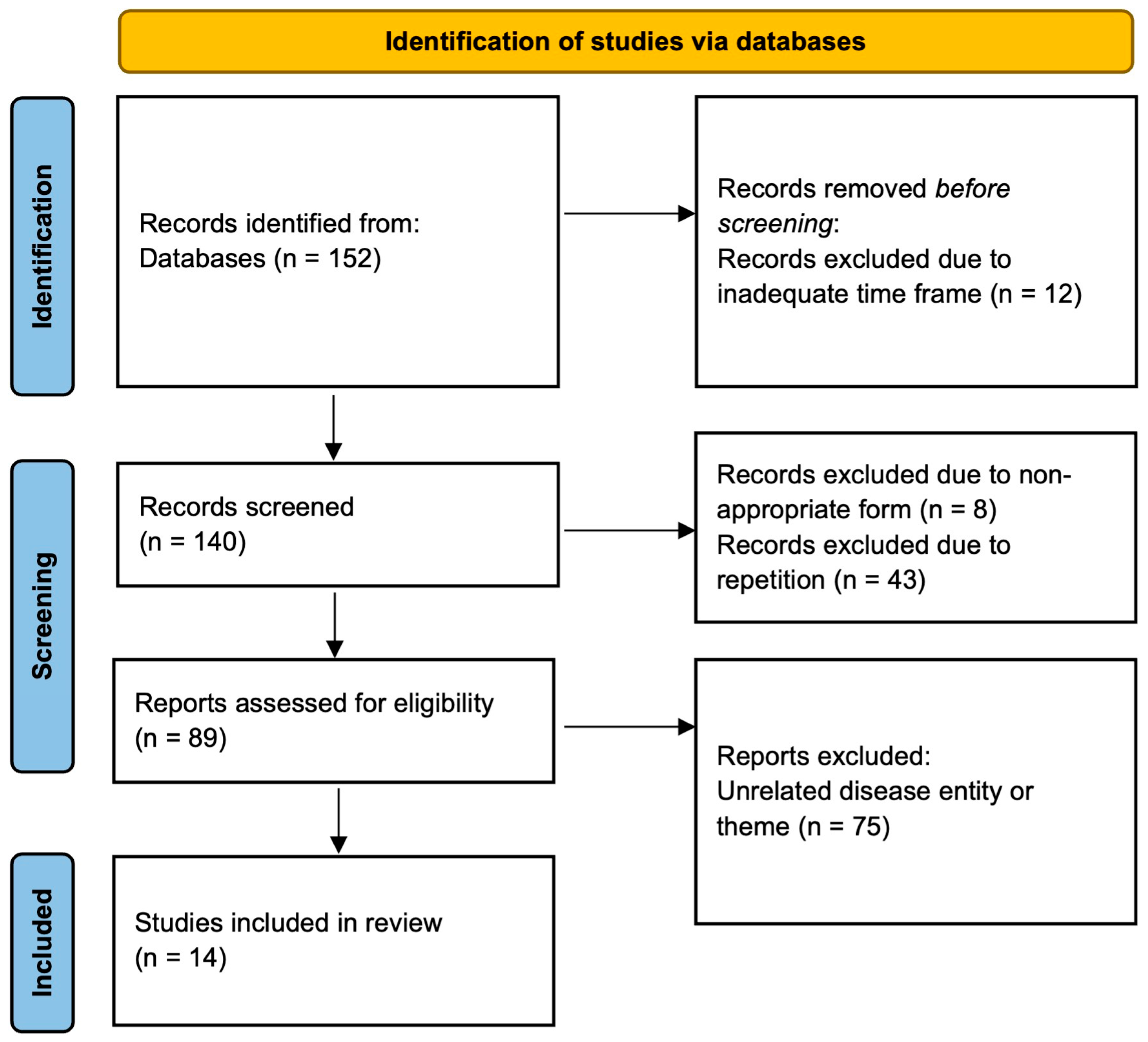
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Mucositis
3.2. Gastrointestinal Toxicity
3.3. Hepatic Toxicity
3.4. Cardiotoxicity
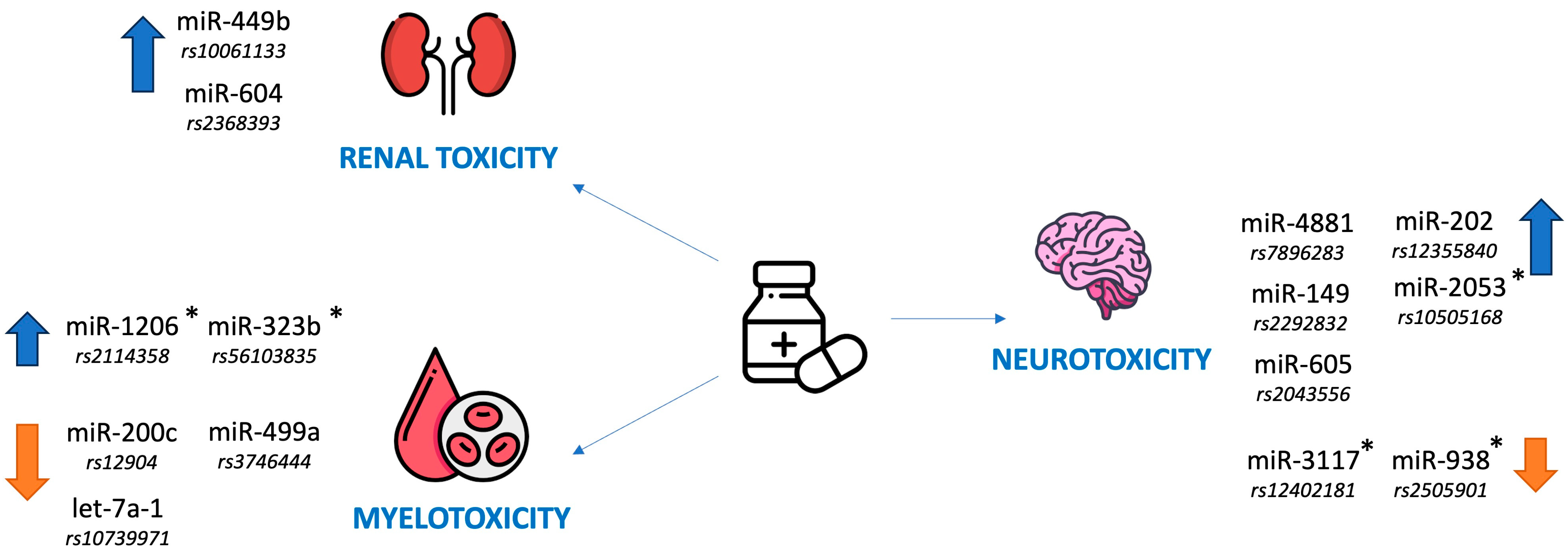
3.5. Renal Toxicity
3.6. Myelotoxicity
3.7. Neurotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| TRC | Treatment-related complications |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
References
- Ding, F.; Deng, L.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, J. Analysis of global trends in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children aged 0–5 years from 1990 to 2021. Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1542649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpa, Q.L.; Akahara, P.C.; Anderson, A.M.; Adekoya, O.O.; Ajayi, O.O.; Alabi, P.O.; Okobi, O.E.; Jaiyeola, O.; Ekanem, M.S. A Review of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) in the Pediatric Population: Evaluating Current Trends and Changes in Guidelines in the Past Decade. Cureus 2023, 15, e49930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, X.; Yang, L. Global, regional, and national burden of children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from 1990 to 2021: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1525751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Makimoto, A.; Yuza, Y. Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Historical Perspective. Cancers 2024, 16, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewska, M.; Kośmider, K.; Bednarz, K.; Ostapińska, K.; Lejman, M.; Zawitkowska, J. Recent Advances in Treatment Options for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, A.P.; Koç, B.; Zülfikar, B. Acute Complications and Survival Analysis of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A 15-year Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e39–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, U.M.; Tekkesin, F.; Koc, B.S.; Aydogdu, S.; Asarcikli, F.; Kilic, S.C. Acute complications observed during intensive chemotherapy in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Single-center experience. North. Clin. Istanb. 2023, 10, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVine, A.; Landier, W.; Hudson, M.M.; Constine, L.S.; Bhatia, S.; Armenian, S.H.; Gramatges, M.M.; Chow, E.J.; Friedman, D.N.; Ehrhardt, M.J. The Children’s Oncology Group Long-Term Follow-Up Guidelines for Survivors of Childhood, Adolescent, and Young Adult Cancers: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2025, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, R. Late renal toxicity of treatment for childhood malignancy: Risk factors, long-term outcomes, and surveillance. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renbarger, J.L.; McCammack, K.C.; Rouse, C.E.; Hall, S.D. Effect of race on vincristine-associated neurotoxicity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, R.R.; Cole, P.D. Pharmacogenetic Predictors of Treatment-Related Toxicity Among Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2017, 12, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egnell, C.; Heyman, M.; Jónsson, Ó.G.; Raja, R.A.; Niinimäki, R.; Albertsen, B.K.; Schmiegelow, K.; Stabell, N.; Vaitkeviciene, G.; Lepik, K.; et al. Obesity as a predictor of treatment-related toxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, C.C.; Rawlins, Y.A.; Oberley, M.J.; Bhojwani, D.; Orgel, E. Predictors of hepatotoxicity and pancreatitis in children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated according to contemporary regimens. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athale, U.H.; Flamand, Y.; Blonquist, T.; Stevenson, K.E.; Spira, M.; Asselin, B.L.; Clavell, L.A.; Cole, P.D.; Kelly, K.M.; Laverdiere, C.; et al. Predictors of thrombosis in children receiving therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium trial 05-001. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vang, S.I.; Schmiegelow, K.; Frandsen, T.; Rosthøj, S.; Nersting, J. Mercaptopurine metabolite levels are predictors of bone marrow toxicity following high-dose methotrexate therapy of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 75, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.D.; Bernhardt, M.B.; Zobeck, M.C.; Taylor, O.A.; Gramatges, M.M.; Schafer, E.S.; Lupo, P.J.; Rabin, K.R.; Scheurer, M.E.; Brown, A.L. Ethnic-specific predictors of neurotoxicity among patients with pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia after high-dose methotrexate. Cancer 2023, 129, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitura-Lesiuk, M.M.; Dubaj, M.; Dembowska, A.; Bigosiński, K.; Raniewicz, M. Hyperleukocytosis in Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Demographic and Clinical Characteristics. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.C. Great potential of miRNAs as predictive and prognostic markers for cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpa, V.; Kalinderi, K.; Fidani, L.; Tragiannidis, A. Association of microRNA Polymorphisms with Toxicities Induced by Methotrexate in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umerez, M.; Garcia-Obregon, S.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Astigarraga, I.; Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Garcia-Orad, A. Role of miRNAs in treatment response and toxicity of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics 2018, 19, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Guo, H.L.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, W.-R.; Li, Y.-M.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.-R.; et al. Vincristine-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Genetic Variation as a Potential Risk Factor. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 771487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Garcia-Obregon, S.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Astigarraga, I.; Garcia-Orad, A. miRNA deregulation in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A systematic review. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobbelaar, C.; Ford, A.M. The Role of MicroRNA in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Challenges for Diagnosis and Therapy. J. Oncol. 2019, 13, 8941471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, E.S.; Ismawati, N.D.S.; Ruslin, M. Prevalence and risk factors of oral mucositis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Dr. Soetomo Hospital Surabaya Indonesia. Enfermería Clínica 2020, 30, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, I.L.A.; Limeira, R.R.T.; Dias de Castro, R.; Ferreti Bonan, P.R.; Valença, A.M.G. Oral Mucositis in Pediatric Patients in Treatment for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.S.; Khan, S.D. Management of oral mucositis in children. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar]
- López-López, E.; Gutiérrez-Camino, Á.; Piñán, M.Á.; Sánchez-Toledo, J.; Uriz, J.J.; Ballesteros, J.; García-Miguel, P.; Navajas, A.; García-Orad, Á. Pharmacogenetics of microRNAs and microRNAs biogenesis machinery in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Zeng, H.; Mai, H.; Chen, Z. Impact of microRNA polymorphisms on high-dose methotrexate-related hematological toxicities in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1153767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberianpour, S.; Abkhooie, L. MiR-1307: A comprehensive review of its role in various cancer. Gene Rep. 2021, 25, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Oosterom, N.; den Hoed, M.A.H.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Pluijm, S.M.; Pieters, R.; de Jonge, R.; Tissing, W.J.; Heil, S.G.; et al. The miR-1206 microRNA variant is associated with methotrexate-induced oral mucositis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2017, 27, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Camino, Á.; Umerez, M.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Santos-Zorrozua, B.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; de Andoin, N.G.; Garcia-Orad, A. Involvement of miRNA Polymorphism in Mucositis Development in Childhood Acute lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment. Pharmacogenomics 2018, 19, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yu, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, W.; Fang, L.; Liu, Z. Blockade of PLD2 Ameliorates Intestinal Mucosal Inflammation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 2543070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Menezes, E.; de Moraes, F.C.A.; de Nazaré Cohen-Paes, A.; Wanderley, A.V.; Pereira, E.E.B.; Pastana, L.F.; Modesto, A.A.C.; de Assumpção, P.P.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Dos Santos, S.E.B.; et al. Influence of Genetic Variations in miRNA and Genes Encoding Proteins in the miRNA Synthesis Complex on Toxicity of the Treatment of Pediatric B-Cell ALL in the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wan, C. Toll-like receptor 4 plays a vital role in irritable bowel syndrome: A scoping review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1490653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Hua, H.; Liu, L.; Mao, Y.; Wang, R. Interactions between toll-like receptors signaling pathway and gut microbiota in host homeostasis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xu, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.Q.; Miao, L.; Deng, X. Aprepitant Inhibits JNK and p38/MAPK to Attenuate Inflammation and Suppresses Inflammatory Pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 811584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Miao, R.-R. Relationship between the efficacy and adverse effects of methotrexate and gene polymorphism. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2024, 25, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, Z.L.; Vang, J.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Oosterom, N.; Mikkelsen, T.; Ramsey, L.B. Systematic Review of Pharmacogenetic Factors That Influence High-Dose Methotrexate Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Malignancies. Cancers 2021, 13, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.P.; de Carvalho, D.C.; Wanderley, A.V.; Fernandes, S.M.; Rodrigues, J.C.G.; Cohen-Paes, A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Mello, F.A.R.; Pastana, L.F.; Vinagre, L.W.M.S.; et al. Influence of variants of the drosha, mir499a, and mir938 genes on susceptibility to acute lymphoblastic leukemia in an admixed population from the brazilian amazon. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 8216–8224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, X.; He, Q.; Zhong, W.; Wu, Q. miR-938rs2505901 T>C polymorphism increases Hirschsprung disease risk: A case-control study of Chinese children. Pers. Med. 2021, 18, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, H.; Hossain, B.; Siddiqua, T.; Kabir, M.; Noor, Z.; Ahmed, M.; Haque, R. Fecal MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Screening and Diagnosis of Intestinal Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Palacios, D.; Organista-Nava, J.; Balandrán, J.C.; Alarcón-Romero, L.d.C.; Zubillaga-Guerrero, M.I.; Illades-Aguiar, B.; Rivas-Alarcón, A.A.; Diaz-Lucas, J.J.; Gómez-Gómez, Y.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A. The Role of miRNAs in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapse and the Associated Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidowicz, E.; Bartoszewicz, N.; Czyżewski, K.; Cisek, J.; Dąbrowska, A.; Dębski, R.; Dziedzic, M.; Ewertowska, M.; Grześk, E.; Jatczak-Gaca, A.; et al. Acute non-hematological toxicity of intensive chemotherapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Acta Haematol. Pol. 2020, 51, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Umerez, M.; Santos, B.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; de Andoin, N.G.; Sastre, A.; Navajas, A.; Astigarraga, I.; Garcia-Orad, A. Pharmacoepigenetics in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Involvement of miRNA polymorphisms in hepatotoxicity. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fernandez, C.A.; Smith, C.; Yang, W.; Cheng, C.; Panetta, J.; Kornegay, N.; Liu, C.; Ramsey, L.; Karol, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Study Links PNPLA3 Variant With Elevated Hepatic Transaminase After Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.E.; Mikael, L.G.; Leung, K.Y.; Lévesque, N.; Deng, L.; Wu, Q.; Malysheva, O.V.; Best, A.; A Caudill, M.; DE Greene, N.; et al. High folic acid consumption leads to pseudo-MTHFR deficiency, altered lipid metabolism, and liver injury in mice. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Adam, H.; Hailu, D.; Engidawork, E.; Howe, R.; Abula, T.; Coenen, M.J.H. Genetic variants of genes involved in thiopurine metabolism pathway are associated with 6-mercaptopurine toxicity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients from Ethiopia. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1159307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, M.A.; Kazemi, A.; Zaker, F.; Faranoush, M.; Rezvany, M.R. Effects of Reduced Mir-24 Expression on Plasma Methotrexate Levels, Therapy-Related Toxicities, and Patient Outcomes in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 8, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Organista-Nava, J.; Gómez-Gómez, Y.; Illades-Aguiar, B.; Del Carmen Alarcón-Romero, L.; Saavedra-Herrera, M.V.; Rivera-Ramírez, A.B.; Garzón-Barrientos, V.H.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A. High miR-24 expression is associated with risk of relapse and poor survival in acute leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Lu, J.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Neilly, M.B.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19971–19976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.J.; Humeniuk, R.; Mishra, P.J.; Longo-Sorbello, G.S.; Banerjee, D.; Bertino, J.R. A miR-24 microRNA binding-site polymorphism in dihydrofolate reductase gene leads to methotrexate resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13513–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Kluiver, J.; Koerts, J.; de Jong, D.; Rutgers, B.; Razak, F.R.A.; Terpstra, M.; Plaat, B.E.; Nolte, I.M.; Diepstra, A.; et al. miR-24-3p Is Overexpressed in Hodgkin Lymphoma and Protects Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells from Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.D.; Bates, J.E.; Kinahan, K.E.; Leger, K.J.; Mulrooney, D.A.; Narayan, H.K.; Ness, K.; Okwuosa, T.M.; Rainusso, N.C.; Steinberger, J.; et al. Cardiovascular Toxicity in Patients Treated for Childhood Cancer: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2025, 151, e926–e943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazăr, D.R.; Farcaş, A.D.; Blag, C.; Neaga, A.; Zdrenghea, M.T.; Căinap, C.; Lazăr, F.L.; Stef, A.; Căinap, S.S. Cardiotoxicity: A Major Setback in Childhood Leukemia Treatment. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8828410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, L.; Savarese, M.; Munno, C.; Mirabelli, P.; Ragno, P.; Leone, O.; Alfieri, M. Circulating Biomarkers for Monitoring Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Children. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, K.J.; Leonard, D.; Nielson, D.; de Lemos, J.A.; Mammen, P.P.; Winick, N.J. Circulating microRNAs: Potential Markers of Cardiotoxicity in Children and Young Adults Treated With Anthracycline Chemotherapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengatapathy, K.; Velu Ramesh, R.; Rajappa, M.; Kulkarni, S.; Hanifa, M. Role of serum microRNA-499 as a diagnostic marker in acute myocardial infarction. Cor Vasa 2019, 61, e272–e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hou, H.; Shao, W.; Huang, D.; Hao, Z.; Xue, H.; Ye, Y. miRNA-29 aggravates myocardial infarction via inhibiting the PI3K/mTOR/HIF1α/VEGF pathway. Aging 2022, 14, 3129–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.F.; Li, V.W.; Lai, C.T.; Shin, V.Y.; Keung, W.; Cheuk, D.K.; Kwong, A.; Li, R.A.; Chan, G.C. Circulating high-sensitivity troponin T and microRNAs as markers of myocardial damage during childhood leukaemia treatment. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, V.O.; Ferreira, L.R.; Ayub-Ferreira, S.M.; Ávila, M.S.; Brandão, S.M.; Cruz, F.D.; Santos, M.H.; Cruz, C.B.; Alves, M.S.; Issa, V.S.; et al. Circulating miR-1 as a potential biomarker of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 6994–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boen, H.M.; Cherubin, M.; Franssen, C.; Gevaert, A.B.; Witvrouwen, I.; Bosman, M.; Guns, P.J.; Heidbuchel, H.; Loeys, B.; Alaerts, M.; et al. Circulating MicroRNA as Biomarkers of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2024, 6, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wan, X.; Schwieterman, N.; Cavus, O.; Kacira, E.; Xu, X.; Laurita, K.R.; Wold, L.E.; Hund, T.J.; Mohler, P.J.; et al. MicroRNA-1 Deficiency Is a Primary Etiological Factor Disrupting Cardiac Contractility and Electrophysiological Homeostasis. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatmen, K.E.; Toro-Salazar, O.H.; Hauser, K.; Zellars, K.N.; Mason, K.C.; Hor, K.; Gillan, E.; Zeiss, C.J.; Gatti, D.M.; Spinale, F.G. Identification of a novel microRNA profile in pediatric patients with cancer treated with anthracycline chemotherapy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H1443–H1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadi, K.; Thomaidis, N.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Toutouzas, K.; Gikas, E.; Kelaidi, C.; Polychronopoulou, S. Prognostic Factors for Cardiotoxicity among Children with Cancer: Definition, Causes, and Diagnosis with Omics Technologies. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petgrave, Y.; Selukar, S.; Epperly, R.; Naik, S.; Santos, N.D.; Triplett, B.M.; Gottschalk, S.; Bissler, J.; Talleur, A.C. Acute kidney injury following treatment with CD19-specific CAR T-cell therapy in children, adolescent, and young adult patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, W.; Li, Y.; Getz, K.; Cao, L.; Krause, E.; Ramos, M.; Lee, J.; Gramatges, M.M.; Rabin, K.R.; Scheurer, M.E.; et al. Acute and chronic kidney injury during therapy for pediatric acute leukemia: A report from the Leukemia Electronic Abstraction of Records Network (LEARN). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Xie, W.; Yang, X.; Xia, N.; Yang, K. Inhibiting microRNA-449 Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Injury in NRK-52E Cells Possibly via Regulating the SIRT1/P53/BAX Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Chu, P.H. MicroRNAs in acute kidney injury. Hum. Genom. 2016, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosdiana, D.S.; Setiabudy, R.; Andalusia, R.; Gatot, D.; Louisa, M.; Bardosono, S.; Instiaty, I. TPMT Genetic Variability and Its Association with Hematotoxicity in Indonesian Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Maintenance Therapy. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Shim, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, N.; Ha, J.S. The Effect of NUDT15, TPMT, APEX1, and ITPA Genetic Variations on Mercaptopurine Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Children 2021, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Adam, H.; Hailu, D.; Coenen, M.J.H.; Howe, R.; Abula, T. Incidence and determinants of hematotoxicity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia children who received 6-mercaptopurine based maintenance therapy in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Peng, D.; Dhakal, D.P. Risk factors for hematological toxicity of chemotherapy for bone and soft tissue sarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Z.; Kar, Y.; Turhan, A.; Bör, Ö. Assessment of Hematological Toxicity in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Receiving Treatment with ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol. Open Access Libr. J. 2017, 4, 78829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawitkowska, J.; Lejman, M.; Zaucha-Prażmo, A.; Drabko, K.; Płonowski, M.; Bulsa, J.; Romiszewski, M.; Mizia-Malarz, A.; Kołtan, A.; Derwich, K.; et al. Grade 3 and 4 Toxicity Profiles During Therapy of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, B.; Åsberg, A.; Heyman, M.; Kanerva, J.; Harila-Saari, A.; Hasle, H.; Söderhäll, S.; Jónsson, Ó.G.; Lydersen, S.; Schmiegelow, K.; et al. Risk factors for treatment related mortality in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantararoungtong, T.; Wiwattanakul, S.; Tiyasirichokchai, R.; Prommas, S.; Sukprasong, R.; Koomdee, N.; Jinda, P.; Rachanakul, J.; Nuntharadthanaphong, N.; Pakakasama, S.; et al. TPMT*3C as a Predictor of 6-Mercaptopurine-Induced Myelotoxicity in Thai Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodousi, E.S.; Rahgozar, S. MicroRNA-326 and microRNA-200c: Two novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6024–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Piñan, M.A.; Garcia-Miguel, P.; Sanchez-Toledo, J.; Carbone Bañeres, A.; Uriz, J.; Navajas, A.; Garcia-Orad, A. Noncoding RNA-related polymorphisms in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia susceptibility. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Jiang, C.; Liu, H.; Hao, W.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Qian, J.; Qian, M.; Zhang, H. Down-Regulated FOXO1 in Refractory/Relapse Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 579673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudd, T.W., Jr.; Lu, C.; Klement, J.D.; Liu, K. MS4A1 expression and function in T cells in the colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment. Cell. Immunol. 2021, 360, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Hu, B.F.; Xu, X.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, S.S.; Tang, Y.M. Clinical features and prognostic impact of TCF3-PBX1 in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A single-center retrospective study of 837 patients from China. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2021, 45, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, I.; Kyriakidis, K.; Tsezou, A. MicroRNAs and the Diagnosis of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Re-Analysis with Novel Small RNA-Seq Tools. Cancers 2022, 14, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazarlou, F.; Kadkhoda, S.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Emerging role of let-7 family in the pathogenesis of hematological malignancies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, T.S.; Thorn, C.F.; Yang, J.J.; Ulrich, C.M.; French, D.; Zaza, G.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Marsh, S.; McLeod, H.L.; Giacomini, K.; et al. PharmGKB summary: Methotrexate pathway. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamari, D.; El-Khoury, H.; Saifi, O.; Muwakkit, S.A.; Zgheib, N.K. Implementation of Pharmacogenetics to Individualize Treatment Regimens for Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2020, 13, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkanen, R.; Aarnivala, H.; Pokka, T.; Niinimäki, R. Chemotherapy-related toxicities follow a typical pattern in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Acta Paediatr. 2024, 113, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjčec, I.; Rajačić, N.; Janjić, T.; Kukuruzović, M.; Jadrijević-Cvrlje, F.; Pavlović, M.; Roganović, J. Acute Neurotoxicity in Children Treated for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Lymphoblastic Lymphoma: A 10-Year Single-Centre Experience. Children 2024, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwa-Tytko, P.; Kaczmarska, A.; Lejman, M.; Zawitkowska, J. Neurotoxicity Associated with Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, M.K.; Marshall, G.M.; Barbaro, P.M.; Quinn, M.C.; George, C.; Mayoh, C.; Sutton, R.; Revesz, T.; Giles, J.E.; Barbaric, D.; et al. Methotrexate-related central neurotoxicity: Clinical characteristics, risk factors and genome-wide association study in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2022, 107, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Huang, L.T.; Yu, H.R.; Sheen, J.M. MicroRNA-155 modulates methotrexate-induced spatial memory impairment by disruption of the blood-brain barrier integrity. Brain Res. Bull. 2025, 222, 111240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suofu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Carlisle, D.L.; Friedlander, R.M. Mir-155 knockout protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury and hemorrhagic transformation. Neuroreport 2020, 31, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Camino, Á.; Umerez, M.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; García de Andoin, N.; Santos, B.; Sastre, A.; Echebarria-Barona, A.; Astigarraga, I.; Navajas, A.; Garcia-Orad, A. Mir-pharmacogenetics of Vincristine and peripheral neurotoxicity in childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenom. J. 2018, 18, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, S.; Kotur, N.; Stankovic, B.; Zukic, B.; Gasic, V.; Dokmanovic, L. Pharmacogenomic and Pharmacotranscriptomic Profiling of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Paving the Way to Personalized Treatment. Genes 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Guerrero, I.; Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Echebarria-Barona, A.; Astigarraga, I.; de Andoin, N.G.; Navajas, A.; Garcia-Orad, A. Variants in vincristine pharmacodynamic genes involved in neurotoxicity at induction phase in the therapy of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenom. J. 2019, 19, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Hu, J.; Ngo, F.Y.; Zhang, H.; He, L.; Huang, H.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Targeting TUBB2B inhibits triple-negative breast cancer growth and brain-metastatic colonization. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Q. miR-149 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity by targeting CDC42 and BCL2 in neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teertam, S.K.; Jha, S.; Prakash Babu, P. Up-regulation of Sirt1/miR-149-5p signaling may play a role in resveratrol induced protection against ischemia via p53 in rat brain. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egyed, B.; Kutszegi, N.; Sági, J.C.; Gézsi, A.; Rzepiel, A.; Visnovitz, T.; Lőrincz, P.; Müller, J.; Zombori, M.; Szalai, C.; et al. MicroRNA-181a as novel liquid biopsy marker of central nervous system involvement in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyed, B.; Horváth, A.; Semsei, Á.F.; Szalai, C.; Müller, J.; Erdélyi, D.J.; Kovács, G.T. Co-Detection of VEGF-A and Its Regulator, microRNA-181a, May Indicate Central Nervous System Involvement in Pediatric Leukemia. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W. Secretory miRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, P.; Ladame, S.; O’Hare, D. Molecular methods in electrochemical microRNA detection. Analyst 2018, 144, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalf, G.A.D. MicroRNAs: Circulating biomarkers for the early detection of imperceptible cancers via biosensor and machine-learning advances. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Research | Country | Study Group | Treatment | Phase | miRNA | Changes | Risk | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| López-López et al. (2014) [29] | Spain | N = 152 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Cons | miR-1206 | SNP rs2114358 | ↑ | SLCO1A2 ABCC2 ABCG2 |
| miR-2053 | SNP rs10505168 | ↑ | FPK PI3K/AKT | |||||
| miR-1307 | SNP rs7911488 | ↑ | BMPR2 MDM4 MCF7 Bcl2 | |||||
| miR-146a | SNP rs2910164 | ↑ | TRAF6 IRAK1 | |||||
| Gutierrez-Camino et al. (2017) [32] | Spain | N = 117 T-ALL B-ALL | DCOG ALL10 | Cons | miR-1206 | SNP rs2114358 | ↑ | SLCO1A2 ABCC2 ABCG2 |
| Gutierrez-Camino et al. (2018) [33] | Spain | N = 170 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-3683 | SNP rs6977967 | ↑ | SHMT1 ALDH5A1 |
| miR-1908 | SNP rs174561 | ↑ | - | |||||
| miR-4250a | SNP rs8078913 | ↑ | - | |||||
| miR-4268 | SNP rs4674470 | ↓ | NFKBIE CBR1 MTHFR MTR SLC46A PLD |
| Research | Country | Study Group | Treatment | Phase | miRNA | Changes | Risk | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIARRHEA | ||||||||
| López-López et al. (2014) [29] | Spain | N = 152 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-1307 | SNP rs7911488 | ↑ | FOXO3A SMYD4 TUSC5 ING5 |
| miR-423 | SNP rs6505162 | ↓ | RFVT3 SRF | |||||
| Gutierrez-Camino et al. (2018) [33] | Spain | N = 170 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-4751 | SNP rs8667 | ↑ | NDUSF2 SLC19A1 ERCC4 TLR |
| VOMITING | ||||||||
| López-López et al. (2014) [29] | Spain | N = 152 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Cons | miR-453 | SNP rs56103835 | ↑ | ABCC1 ABCB1 ABCC2 ABCC4 |
| Ind | miR-323b [synonym: miR-492] | SNP rs2289030 | ↑ | CD44 PTEN TIMP2 | ||||
| Gutierrez-Camino et al. (2018) [33] | Spain | N = 170 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-3117 | SNP rs12402181 | ↓ | ABCC1 PPAT SLC46A1 SLCO1A2 ABCC1 ALDH5A1 MAPK |
| GASTROINTESTINAL TOXICITY | ||||||||
| da Silva Menezes et al. (2022) [35] | Brazil | N = 77 B-ALL | ALL IC-BFM 2002 | - | miR-938 | SNP rs2505901 | ↓ | CXCL12 SMAD3 IL17A RBM5 |
| miR-323b | SNP rs56103835 | ↓ | ABCC1 ABCB1 ABCC2 ABCC4 | |||||
| Research | Country | Study Group | Treatment | Phase | miRNA | Changes | Risk | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| López-López et al. (2014) [29] | Spain | N = 152 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-300 | SNP rs12894467 | ↑ | ABCC1 ABCB1 ALDH5A1 |
| miR-577 | SNP rs34115976 | ↓ | HOXA1 WNT2B | |||||
| Gutierrez-Camino et al. (2018) [46] | Spain | N = 179 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Cons | miR-1208 | SNP rs264881 | ↓ | DHFR MTHFR MTR SLCO1A2 SLC46A1 |
| Esmaili et al. (2020) [50] | Iran | N = 74 B-ALL T-ALL | BFM-2009 | Cons | miR-24 | Expression ↓ | ↑ (II–IV) | FAF1 APAF1 MYC E2F2 CCNB1 CDC2 |
| Research | Country | Study Group | Treatment | Phase | miRNA | Changes | Risk | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leger et al. (2017) [58] | USA | N = 37 ALL | anthracyclines | Cons | miR-29b miR-499 miR-1 | Expression ↑ | ↑ | PI3K mTOR HIF1α VEGF |
| Cheung et al. (2014) [61] | China | N = 40 ALL AML | anthracyclines | - | miR-1 | Expression ↑ | ↑ | IRX5 KCNE1 SLC8A1 B56A ACTA2 MYH11 |
| Oatmen et al. (2020) [65] | USA | N = 20 | anthracyclines | - | miR-181-5p miR-199a-5p miR-107 miR-499-5p miR-145-5p miR-100-5p miR-103a-3p miR-142-3p | Expression ↓ | ↑ | - |
| Research | Country | Study Group | Treatment | Phase | miRNA | Changes | Risk | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| da Silva Menezes et al. (2022) [35] | Brazil | N = 77 B-ALL | ALL IC-BFM 2002 | - | miR-200c | SNP rs12904 | ↑ | ABCA2 ABCA3 |
| miR-499a | SNP rs3746444 | FOXO1A PBX1 | ||||||
| let-7a-1 | SNP rs10739971 | NRAS MYC | ||||||
| Zhan et al. (2023) [30] | China | N = 181 ALL | GD-2008-ALL SCCLG-2016-ALL | Cons | miR-1206 | SNP rs2114358 | ↑ | SLCO1A2 ABCC2 ABCG2 TYMS FPGS |
| miR-323b | SNP rs56103835 | ABCC1/2/4 SHTM1 |
| Research | Country | Study Group | Treatment | Phase | miRNA | Changes | Risk | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| da Silva Menezes et al. (2022) [35] | Brazil | N = 77 B-ALL | ALL IC-BFM 2002 | - | miR-149 | SNP rs2292832 | ↑ | CDC42 BCL2 SIRT1 |
| miR-2053 | SNP rs10505168 | ↑ | KIF3C PI3K/Akt | |||||
| miR-605 | SNP rs2043556 | ↑ | MDM2 | |||||
| miR-938 | SNP rs2505901 | ↓ | RBM5 SMAD3 | |||||
| Gutierrez-Camino et al. (2018) [94] | Spain | N = 179 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-3117 | SNP rs12402181 | ↓ | ABCC1 RALBP1 |
| miR-4881 | SNP rs7896283 | ↑ | Axon guidance pathway | |||||
| Martin-Guerrero et al. (2019) [96] | Spain | N = 152 B-ALL | LAL-SHOP 94/99/2005 | Ind | miR-202 | SNP rs12355840 | ↑ (I–II) | TUBB2B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitura-Lesiuk, M.M.; Dubaj, M.; Bigosiński, K.; Raniewicz, M. The Role of miRNAs as Predictors of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy Toxicity in Children: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165869
Mitura-Lesiuk MM, Dubaj M, Bigosiński K, Raniewicz M. The Role of miRNAs as Predictors of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy Toxicity in Children: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165869
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitura-Lesiuk, Małgorzata M., Maciej Dubaj, Karol Bigosiński, and Mateusz Raniewicz. 2025. "The Role of miRNAs as Predictors of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy Toxicity in Children: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165869
APA StyleMitura-Lesiuk, M. M., Dubaj, M., Bigosiński, K., & Raniewicz, M. (2025). The Role of miRNAs as Predictors of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy Toxicity in Children: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165869






