Malignancies After Renal Transplantation: Frequency, Etiology, and Prognosis—A Single Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Malignancy Assessment
2.4. Treatment Modalities
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Malignancy Profile
3.3. Comparison of Malignancy Types
3.4. Mortality Analysis
3.5. HLA Compatibility and Malignancy
3.6. Independent Risk Factors of Mortality in Post-Transplant Malignancy Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flythe, J.E.; Karlsson, N.; Sundgren, A.; Cordero, P.; Grandinetti, A.; Cremisi, H.; Rydén, A. Development of a preliminary conceptual model of the patient experience of chronic kidney disease: A targeted literature review and analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttarajappa, C.M.; Schinstock, C.A.; Wu, C.M.; Leca, N.; Kumar, V.; Vasudev, B.S.; Hariharan, S. KDOQI US Commentary on the 2020 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Candidates for Kidney Transplantation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 833–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbrook, K.; Gauntt, K.; Klassen, D. Renal transplantation: The last iteration of the rest of the world. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2023, 28, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GODT. Global Observatory on Donations and Transplantation. Available online: https://www.transplant-observatory.org/ (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- ANZDATA. Australia and New Zealand Dialysis and Transplant. Available online: http://www.anzdata.org.au (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Lentine, K.L.; Smith, J.M.; Lyden, G.R.; Miller, J.M.; Booker, S.E.; Dolan, T.G.; Temple, K.R.; Weiss, S.; Handarova, D.; Israni, A.K.; et al. OPTN/SRTR 2023 Annual Data Report: Kidney. Am. J. Transplant. 2025, 25, S22–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adra, D.; Al-Qaoud, T.; Fowler, K.; Wong, G. De Novo Malignancies after Kidney Transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; Dong, H.; Bai, H.; Chen, L. Current Trends and Future Directions of Malignancy After kidney Transplantation: A 1970–2022 Bibliometric Analysis. Ann. Transplant. 2024, 29, e942074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arican, A.; Karakayali, H.; Coşkun, M.; Colak, T.; Erdal, R.; Haberal, M. Incidence and clinical characteristics of malignancies after renal transplantation: One center's experience. Transplant. Proc. 2001, 33, 2809–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, G.S.; Jhala, M. Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciesielski, W.; Frąk, W.; Gmitrzuk, J.; Kuczyński, P.; Klimczak, T.; Durczyński, A.; Strzelczyk, J.; Hogendorf, P. The assesement of the long-term effects of kidney transplantation, including the incidence of malignant tumors, in recipients operated on between 2006 and 2015—A cohort study and literature review. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2025, 97, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Matsumura, S.; Imanaka, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Kishikawa, H.; Nishimura, K. Malignancy With Immunosuppression After Renal Transplantation: A Competing Risk Analysis. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, C.A.; Wu, H.H.L.; Pullerits, K.; Garland, S.; Middleton, R.; Chinnadurai, R.; Kalra, P.A. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of De Novo Malignancy following Kidney Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, T.; Teng, C.C.; Inker, L.A.; Redd, A.; Ying, J.; Woodward, M.; Coresh, J.; Levey, A.S. Utility and validity of estimated GFR-based surrogate time-to-event end points in CKD: A simulation study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Snyder, J.J.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Wang, C. Cancer after kidney transplantation in the United States. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massicotte-Azarniouch, D.; Noel, J.A.; Knoll, G.A. Epidemiology of Cancer in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Semin. Nephrol. 2024, 44, 151494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, E.A.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr.; Kasiske, B.L.; Israni, A.K.; Snyder, J.J.; Wolfe, R.A.; Goodrich, N.P.; Bayakly, A.R.; Clarke, C.A.; et al. Spectrum of cancer risk among US solid organ transplant recipients. JAMA 2011, 306, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, F.A.; Halleck, F.; Lehner, L.; Schrezenmeier, E.V.; Naik, M.; Schmidt, D.; Khadzhynov, D.; Kast, K.; Budde, K.; Staeck, O. De-novo malignancies after kidney transplantation: A long-term observational study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwarn, P.; Sutharattanapong, N.; Disthabanchong, S.; Kantachuvesiri, S.; Kitiyakara, C.; Phakdeekitcharoen, B.; Ingsathit, A.; Sumethkul, V. Incidence of De Novo Post-Transplant Malignancies in Thai Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center, Population-Controlled, Retrospective Cohort Study at the Highest Volume Kidney Transplant Center in Thailand. Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 11614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedotti, P.; Cardillo, M.; Rossini, G.; Arcuri, V.; Boschiero, L.; Caldara, R.; Cannella, G.; Dissegna, D.; Gotti, E.; Marchini, F.; et al. Incidence of cancer after kidney transplant: Results from the North Italy transplant program. Transplantation 2003, 76, 1448–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E. Human papillomaviruses and non-melanoma skin cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saowapa, S.; Polpichai, N.; Siladech, P.; Wannaphut, C.; Tanariyakul, M.; Wattanachayakul, P.; Lalitnithi, P. Evaluating Kaposi Sarcoma in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e52527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mallawany, N.K.; Rouce, R.H. EBV and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder: A complex relationship. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2024, 2024, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulovski, R.; Møller, D.L.; Knudsen, A.D.; Sørensen, S.S.; Rasmussen, A.; Nielsen, S.D.; Wareham, N.E. Early- and late-onset posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders among adult kidney and liver transplant recipients. Eur. J. Haematol. 2022, 109, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Ruzinova, M.B.; Marks, L.J. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Semin. Nephrol. 2024, 44, 151503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.; Othman, J.; Heldman, M.R.; Slavin, M.A. Epstein-Barr virus posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: Update on management and outcomes. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 34, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kriesche, H.U.; Schold, J.D.; Srinivas, T.R.; Kaplan, B. Lack of improvement in renal allograft survival despite a marked decrease in acute rejection rates over the most recent era. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.M.; Lee, M.; Hyun, J.; Lim, S.; Kang, J.M.; Ahn, J.G.; Joo, D.J.; Jung, I.; Ihn, K. Incidence and Features of Lymphoid Proliferation and Lymphomas after Solid Organ or Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in a National Database Cohort. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 56, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.S.; Vautier, M.; Allenbach, Y.; Zahr, N.; Benveniste, O.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Salem, J.E. Sirolimus and mTOR Inhibitors: A Review of Side Effects and Specific Management in Solid Organ Transplantation. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçer Vural, A.; Karataş Toğral, A.; Güleç, A.T.; Haberal, M. Kaposi Sarcoma in the Era of Rapamycin Remains a Therapeutic Challenge in Organ Transplant Recipients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 16, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewska, B.; Imko-Walczuk, B.; Dębska-Ślizień, A. Non-melanoma skin cancer outcomes in kidney transplant recipients converted from calcineurin inhibitors to mTOR inhibitors: A systematic review. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2023, 40, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuna, S.A.; Lam, W.; Daly, C.; Kim, S.J.; Baxter, N.N. Cancer evaluation in the assessment of solid organ transplant candidates: A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines. Transplant. Rev. 2018, 32, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collett, D.; Mumford, L.; Banner, N.R.; Neuberger, J.; Watson, C. Comparison of the incidence of malignancy in recipients of different types of organ: A UK Registry audit. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.A.; Wen, M.C.; Tsai, S.F.; Wu, M.J.; Yu, T.M.; Chuang, Y.W.; Huang, S.T.; Chen, C.H. Outcome of Brain Lymphoma in a High Epstein-Barr Virus-Prevalence Country After Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2023, 55, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watschinger, B.; Budde, K.; Crespo, M.; Heemann, U.; Hilbrands, L.; Maggiore, U.; Mariat, C.; Oberbauer, R.; Oniscu, G.C.; Peruzzi, L.; et al. Pre-existing malignancies in renal transplant candidates-time to reconsider waiting times. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total (n = 163), n (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex (F/M) | 56 (34.4)/107 (65.5) |
| Follow-up Time (months) * | 157 (7–531) |
| Duration of Renal Replacement Therapy (months) * | 84 (13–156) |
| Age of TX * | 40.0 (13.0–72.0) |
| Age of Malignancy Diagnosis * | 50 (23.0–78.0) |
| Smoking status | 28 (23.7) |
| eGFR at Diagnosis (mL/min) * | 59.0 (8.0–117.0) |
| ESRD etiology | |
| Chronic GN | 29 (17.8) |
| CAKUT | 13 (8.0) |
| HT | 10 (6.1) |
| PRD | 10 (6.1) |
| Amyloidosis | 8 (4.9) |
| VUR nephropathy | 7 (4.2) |
| DM | 5 (3.1) |
| Others | 5 (3.1) |
| Unknown | 76 (46.6) |
| Donor type | |
| Deceased | 53 (32.5) |
| Living | 110 (67.5) |
| HLA histocompatibility *** | |
| 0 | 6 (4.9) |
| I | 5 (4.1) |
| II | 13 (10.7) |
| III | 74 (60.7) |
| IV | 11 (9.0) |
| V | 5 (4.1) |
| VI | 8 (4.8) |
| DM-Post-TX | 42 (26.6) |
| History of acute rejection | 13 (7.7) |
| Acute Rejection Period | |
| Within first year | 12 (92.3) |
| After first year | 1 (7.6) |
| Graft loss | 20 (12.3) |
| Causes of Graft Loss | |
| Chronic Allograft Nephropathy | 16 (9.3) |
| Chronic AMR | 2 (1.3) |
| TCMR + AMR | 1 (0.6) |
| AA Amyloidosis | 1 (0.6) |
| EBV Serology | 38 (23.3) |
| CMV Serology | 82 (50.3) |
| HBV Serology | 10 (6.1) |
| HCV Serology | 35 (21.5) |
| BKV Serology | 12 (7.4) |
| Pre-TX Dialysis Duration * | 22.0 (1.0–185.0) |
| Pre-TX Dialysis | 143 (87.7) |
| Pre-TX Dialysis Type | |
| HD | 121 (76.5) |
| PD | 12 (7.6) |
| PD + HD | 6 (3.8) |
| Retransplantation | 4 (2.5) |
| Unknown | 5 (3.2) |
| Induction Regimen ** | |
| ATG/ALG | 47 (28.8) |
| Anti-IL-2 | 4 (2.5) |
| HLA histocompatibility *** | |
| Low | 92 (79.3) |
| High | 24 (20.7) |
| DM-Pre-TX | 12 (7.3) |
| Maintenance treatment | |
| Steroids | 161 (98.8) |
| CsA | 113 (69.3) |
| MMF-MYF | 80 (49.1) |
| AZA | 78 (47.9) |
| FK | 44 (27.0) |
| EVO | 2 (1.2) |
| RAPA | 2 (1.2) |
| Number of rejections | |
| I | 11 (84.6) |
| II | 2 (15.4) |
| Rejection treatment | |
| Pulse steroid | 8 (61.5) |
| Pulse steroid + ATG | 4 (30.8) |
| IVIG | 1 (7.7) |
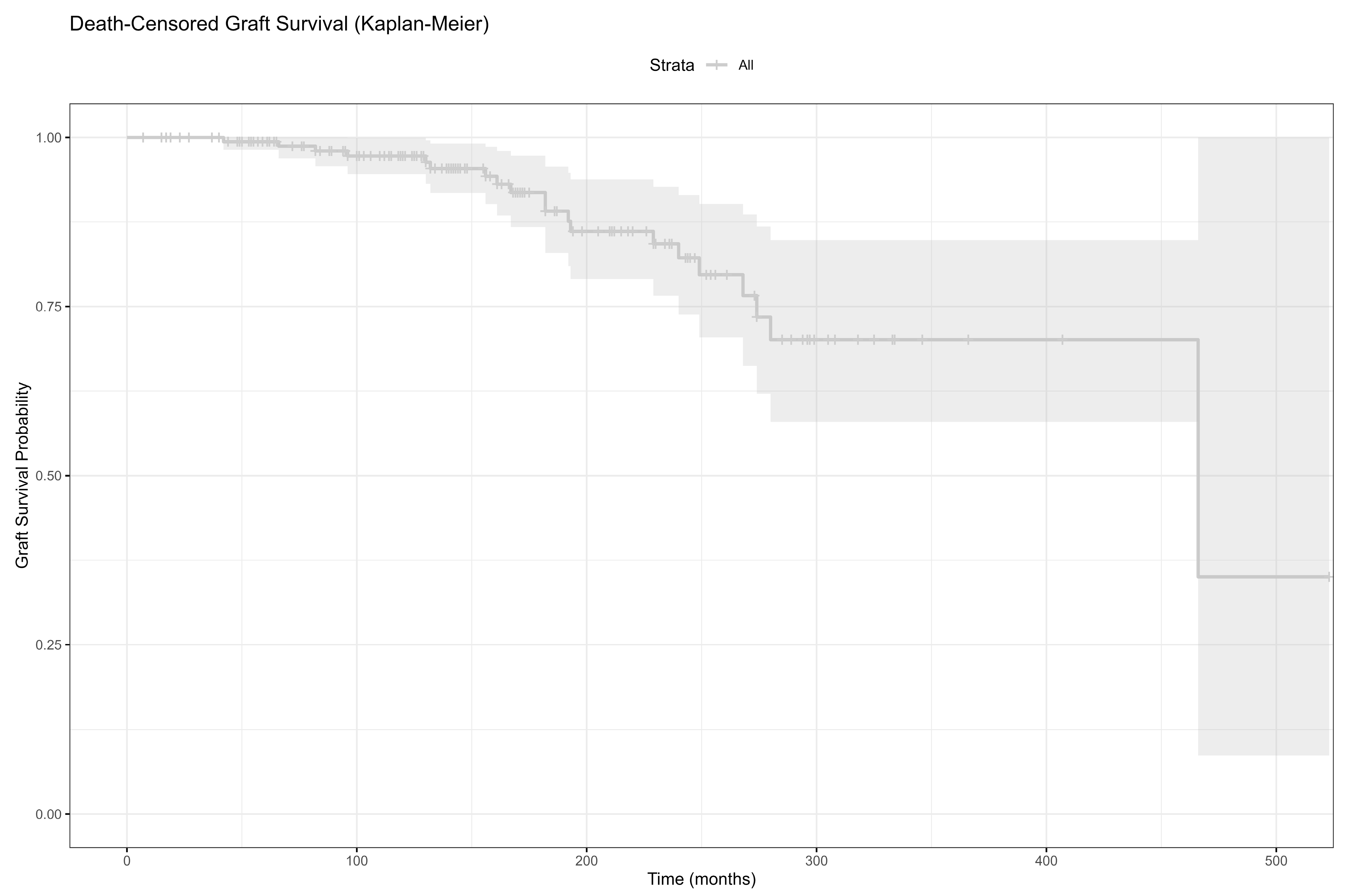
| Death-censored graft survival | |
| Actual Graft Loss | 20 (12.0) |
| Death-Censored | 51 (30.5) |
| Mortality | 93 (57.1) |
| Variables | Total (n = 163), n (%) |
|---|---|
| Presence of Pre-TX Malignancy * | 11 (6.8) |
| Type of Pre-TX malignancy | |
| Non-melanoma Skin Tumor | 1 (9.1) |
| Breast | 2 (18.2) |
| Colon | 1 (9.1) |
| RCC | 1 (9.1) |
| Bladder | 1 (9.1) |
| Intracranial | 2 (18.2) |
| Others | 3 (27.3) |
| Organ Dysfunction at diagnosis in those with PTLD | 9 (52.9) |
| Post-Diagnosis IS Regimen | |
| Same | 29 (17.7) |
| Combination with mTOR | 97 (59.5) |
| Combination Without mTOR | 34 (20.9) |
| Post-TX malignancy * | 160 (95.8) |
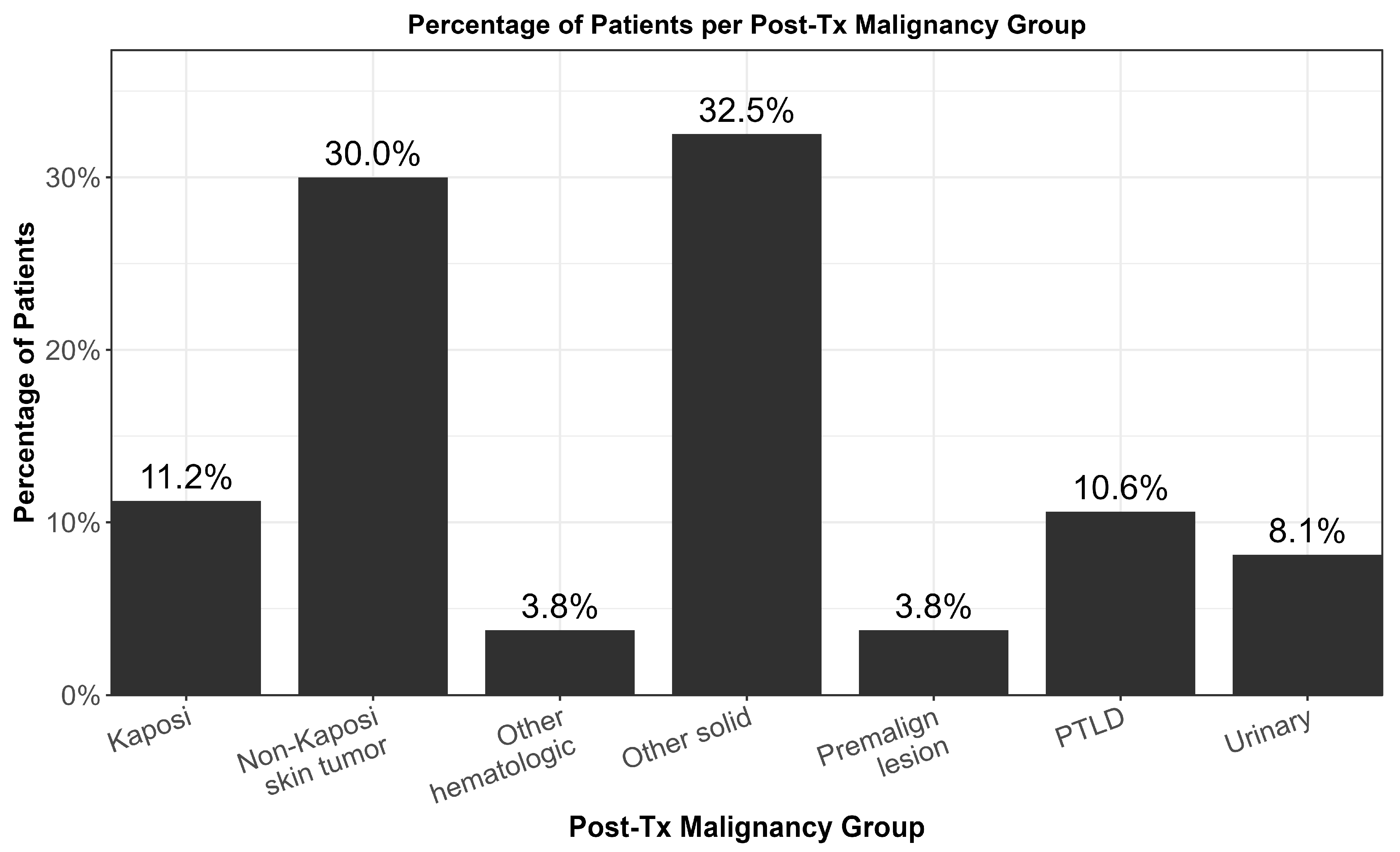
| Type of Post-TX malignancy | |
| Non-Kaposi Sarcoma Skin Tumor | 48 (30.0) |
| Kaposi Sarcoma | 18 (11.1) |
| PTLD | 17 (10.5) |
| Urinary | 13 (8.0) |
| Other Solid Tumor | 52 (31.9) |
| Other Hematological Tumor | 6 (3.7) |
| Premalignant lesions | 6 (3.7) |
| CNS involvement in patients with PTLD | 4 (23.5) |
| Treatment for Malignancy | |
| Surgery + CT/RT | 30 (18.4) |
| Surgery | 78 (47.8) |
| CT | 12 (7.4) |
| CT + RT | 5 (3.1) |
| Reduction of immunosuppression | 14 (8.6) |
| Surgery + RAI | 4 (2.4) |
| RT | 2 (1.5) |
| Follow-up without treatment | 18 (11.0) |
| Kaposi Sarcoma n = 18, n (%) | Non-Kaposi Sarcoma Skin Tumor n = 48, n (%) | PTLD n = 17, n (%) | Urinary n = 13, n (%) | Other Solid Tumor n = 52, n (%) | Other Hematological Tumor n = 6, n (%) | Premalignant Lesions n = 6, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age * | 59.3 ± 12.8 | 62.0 ± 8.8 | 55.6 ± 10.2 | 66.2 ± 12.5 | 56.2 ± 12.0 | 54.2 ± 13.7 | 47.3 ± 7.7 |
| Sex (F/M) | 3 (16.7)/15 (83.3) | 9 (18.8)/39 (81.3) | 6 (35.3)/11 (64.7) | 2 (15.4)/11 (84.6) | 25 (48.1)/27 (51.9) | 2 (33.3)/4 (66.7) | 5 (83.3)/1 (16.7) |
| Induction Regimen ** | |||||||
| ATG/ALG | 3 (16.7) | 8 (16.7) | 9 (52.9) | 3 (23.1) | 8 (34.6) | 2 (33.3) | 1 (16.7) |
| Anti-IL-2 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (16.7) |
| History of acute rejection | 3 (16.7) | 4 (8.3) | 1 (5.9) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (9.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (16.7) |
| Survivors, n = 70, n (%) | Non-Survivors, n = 93, n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age of Malignancy Diagnosis | 45.6 ± 10.5 | 52.6 ± 12.1 | <0.001 |
| Sex (F/M) | 34 (48.6)/36 (51.4) | 22 (23.7)/71 (76.4) | 0.001 |
| Follow-up Time (months) | 162.5 (15/561) | 150 (7–473) | 0.299 |
| Age of TX | 37.3 ± 10.8 | 43.7 ± 12.2 | <0.001 |
| Duration of Renal Replacement Therapy (months) | 84 (13–156) | 36 (13–36) | 0.018 |
| Smoking status | 11 (22.9) | 17 (24.3) | >0.999 |
| Donor type | 0.930 | ||
| Deceased | 22 (31.4) | 31 (33.3) | |
| Living | 48 (68.6) | 62 (66.7) | |
| HLA histocompatibility | 0.030 | ||
| 0 | 5 (8.8) | 1 (1.5) | |
| I | 3 (5.3) | 2 (3.2) | |
| II | 2 (3.5) | 11 (16.3) | |
| III | 34 (59.7) | 40 (61.5) | |
| IV | 8 (14.0) | 3 (4.6) | |
| V | 3 (5.3) | 2 (3.1) | |
| VI | 2 (3.5) | 6 (9.2) | |
| HLA histocompatibility | 0.422 | ||
| Low | 39 (75.0) | 53 (82.8) | |
| High | 13 (25.0) | 11 (17.2) | |
| EBV Serology | 23 (32.9) | 15 (16.1) | 0.026 |
| CMV Serology | 39 (55.7) | 43 (46.2) | 0.460 |
| HBV Serology | 3 (4.3) | 7 (7.5) | 0.285 |
| HCV Serology | 12 (17.1) | 23 (24.7) | 0.076 |
| BKV Serology | 8 (11.4) | 4 (4.3) | 0.092 |
| ATG/ALG | 20 (28.6) | 27 (29.0) | 0.281 |
| Anti-IL2 | 3 (4.3) | 1 (1.2) | 0.161 |
| CNI drugs | 0.017 | ||
| FK | 27 (38.6) | 17 (18.3) | |
| CsA | 41 (58.6) | 72 (77.4) | |
| Antimetabolite drugs | 0.006 | ||
| MMF-MYF | 43 (61.4) | 37 (39.8) | |
| AZA | 27 (38.6) | 51 (54.8) | |
| mTOR drugs | >0.999 | ||
| EVO | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.1) | |
| RAPA | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Steroid | 70 (100.0) | 91 (97.9) | 0.507 |
| History of acute rejection | 7 (10.0) | 6 (6.5) | 0.592 |
| Within first year acute rejection | 7 (100.0) | 5 (83.3) | 0.462 |
| Number of rejections | 0.462 | ||
| I | 5 (71.4) | 6 (100.0) | |
| II | 2 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Rejection treatment | 0.414 | ||
| Pulse steroid | 5 (71.4) | 3 (50.0) | |
| Pulse steroid + ATG | 1 (14.3) | 3 (50.0) | |
| IVIG | 1 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Presence of Pre-TX Malignancy | 7 (10.0) | 4 (4.3) | 0.209 |
| Type of Pre-TX malignancy | 0.050 | ||
| Non-melanoma Skin Tumor | 1 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Breast | 0 (0.0) | 2 (50.0) | |
| Colon | 0 (0.0) | 1 (25.0) | |
| RCC | 0 (0.0) | 1 (25.0) | |
| Bladder | 1 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Intracranial | 2 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Others | 3 (42.9) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Graft loss | 7 (10.0) | 10 (10.8) | >0.999 |
| Type of Post-TX malignancy | 0.005 | ||
| Non-Kaposi Sarcoma Skin Tumor | 7 (11.1) | 9 (9.9) | |
| Kaposi Sarcoma | 16 (25.4) | 30 (33.0) | |
| PTLD | 6 (9.5) | 11 (12.1) | |
| Urinary | 2 (3.2) | 10 (11.0) | |
| Other Solid Tumor | 24 (38.1) | 27 (29.7) | |
| Other Hematological Tumor | 4 (6.4) | 2 (2.2) | |
| Premalignant lesions | 4 (6.4) | 2 (2.2) |
| Low HLA Histocompatibility, n = 94, n (%) | High HLA Histocompatibility, n = 24, n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Pre-TX malignancy | >0.999 | ||
| Non-melanoma Skin Tumor | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Breast | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Colon | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| RCC | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Bladder | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Intracranial | 2 (25.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Others | 2 (25.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Type of Post-TX malignancy | 0.408 | ||
| Non-Kaposi Sarcoma Skin Tumor | 12 (13.5) | 3 (12.5) | |
| Kaposi Sarcoma | 27 (30.3) | 7 (29.2) | |
| PTLD | 10 (11.2) | 2 (8.3) | |
| Urinary | 3 (3.4) | 3 (12.5) | |
| Other Solid Tumor | 31 (34.8) | 7 (29.2) | |
| Other Hematological Tumor | 2 (2.3) | 2 (8.3) | |
| Premalignant lesions | 4 (4.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| p-Value | OR | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Age at Transplantation | 0.678 | 1.026 | 0.910 | 1.156 |
| EBV Serostatus | 0.383 | 0.260 | 0.013 | 5.356 |
| Maintenance Therapy (Calcineurin Inhibitor) | 0.111 | 0.132 | 0.011 | 1.591 |
| Maintenance Therapy (Antimetabolite) | 0.404 | 3.207 | 0.208 | 49.434 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atalah, F.; Acarbay, A.; Karakök, A.; Beşiroğlu, M.; Kuş, F.; Arıcı, H.; Dirim, A.B.; Suleymanova, V.; Türkmen, A.; Yazıcı, H. Malignancies After Renal Transplantation: Frequency, Etiology, and Prognosis—A Single Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165858
Atalah F, Acarbay A, Karakök A, Beşiroğlu M, Kuş F, Arıcı H, Dirim AB, Suleymanova V, Türkmen A, Yazıcı H. Malignancies After Renal Transplantation: Frequency, Etiology, and Prognosis—A Single Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165858
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtalah, Fatih, Aydın Acarbay, Akgün Karakök, Mehmet Beşiroğlu, Fatih Kuş, Huzeyfe Arıcı, Ahmet Burak Dirim, Vafa Suleymanova, Aydın Türkmen, and Halil Yazıcı. 2025. "Malignancies After Renal Transplantation: Frequency, Etiology, and Prognosis—A Single Center Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165858
APA StyleAtalah, F., Acarbay, A., Karakök, A., Beşiroğlu, M., Kuş, F., Arıcı, H., Dirim, A. B., Suleymanova, V., Türkmen, A., & Yazıcı, H. (2025). Malignancies After Renal Transplantation: Frequency, Etiology, and Prognosis—A Single Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165858







