Advancements in Inlay Glenoid Components for Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
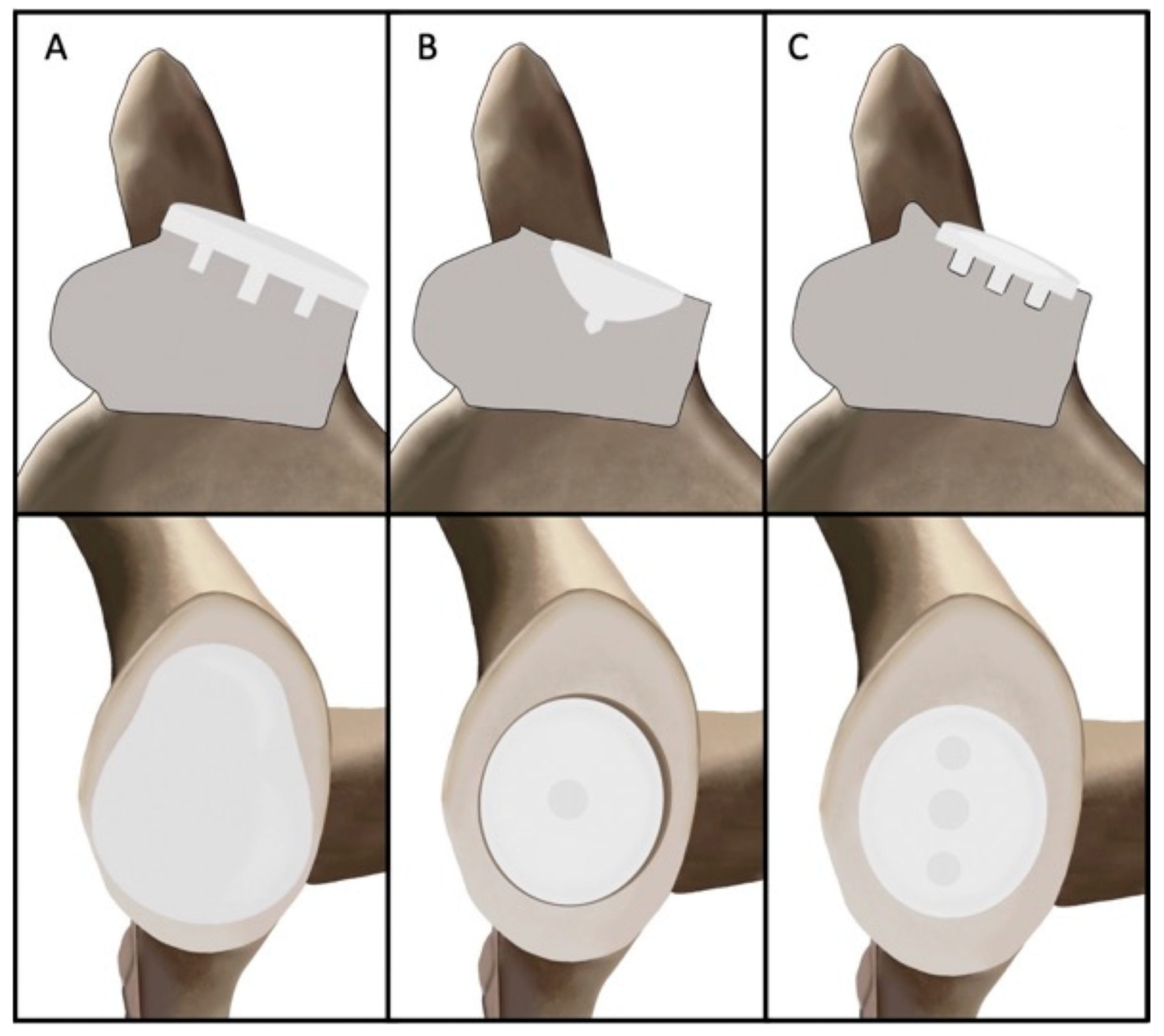
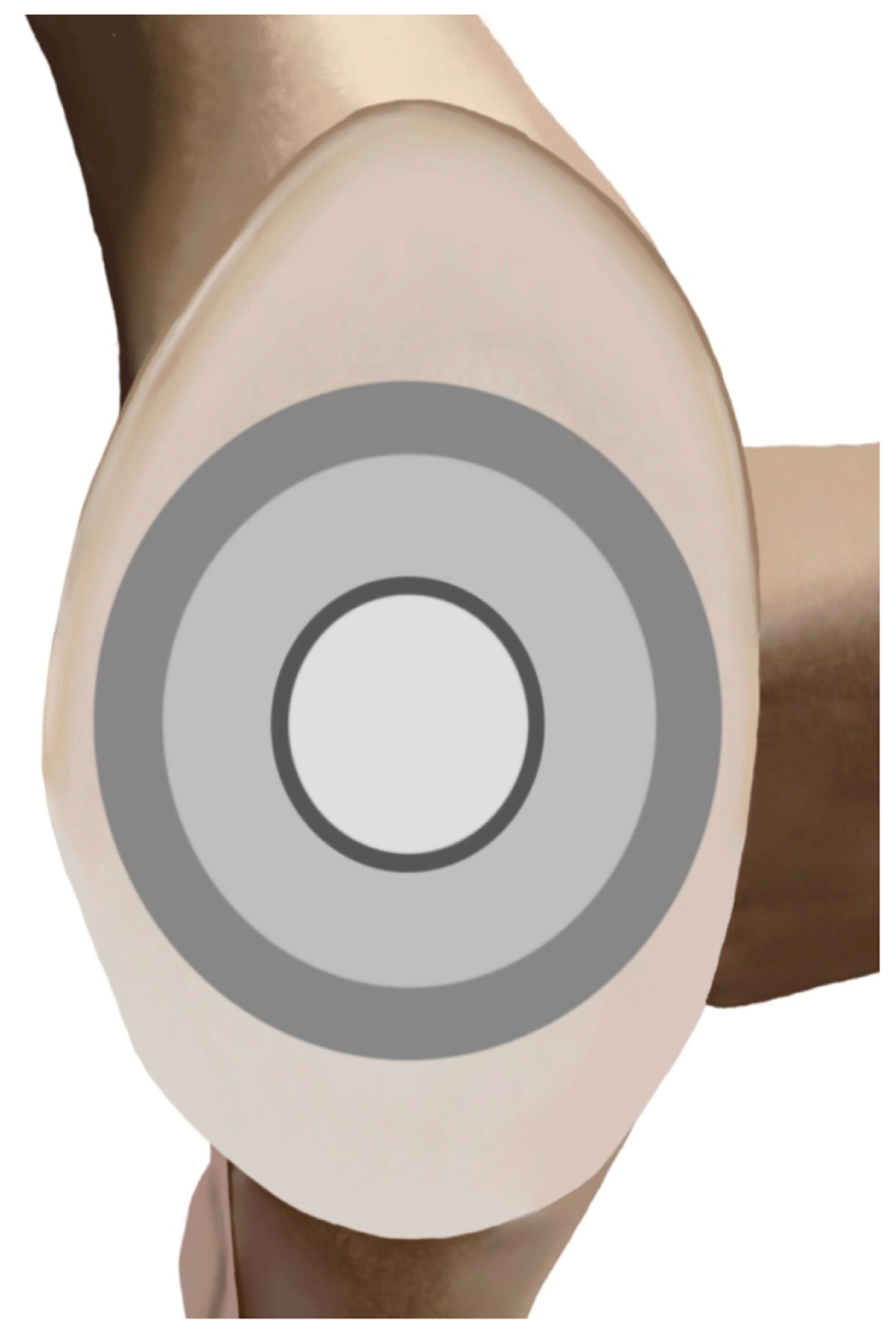
2. Design Philosophy
3. Biomechanics Evidence
4. Clinical Evidence
| Study | Study Design | Implant | N (Shoulders) | Follow-Up (Mean, Minimum, Range) | Pre- to Postoperative Improvement in Outcomes (Mean ± SD Unless Otherwise Specified) | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gunther et al. (2012) [38] | Retro | Custom implants manufactured by Biomet, Inc. (Warsaw, IN, USA) | 7 | 52 months, 36 months, 44–60 months |
|
|
| Davis et al. (2016) [39] | Retro | Ascension Orthopaedics [Austin, TX, USA] Shoulder Innovations [Ada, MI, USA] Arthrosurface [Franklin, MA, USA]) | 9 | 34 months, 36 months, 25–43 |
|
|
| Gunther et al. (2019) [54] | Retro | Custom implants manufactured by Biomet, Inc. (Warsaw, IN, USA) | 24 | 104 months, 72 months, 76–142 months |
|
|
| Johnston et al. (2023) [50] | Retro | InSet glenoid implant (Shoulder Innovations, Grand Rapids, MI, USA) | 75 | 28.7 months, 24 months, 24–42 months |
|
|
5. Special Considerations
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matache, B.A.; Lapner, P. Anatomic Shoulder Arthroplasty: Technical Considerations. Open Orthop. J. 2017, 11, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occhiboi, E.P.; Clement, R.D. Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Indications, Outcomes, and Complications. JBJS J. Orthop. Physician Assist. 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorica, Z.; McFarland, K.; O’Neill, C.N.; Vanderbeck, J.; Vap, A.R. Anatomic Shoulder Arthroplasty in the Setting of Concurrent or Prior Rotator Cuff Repair: A Systematic Review. J. Shoulder Elb. Arthroplast. 2023, 7, 247154922311527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilber, S. Shoulder Arthroplasty: Historical Considerations. Open Orthop. J. 2017, 11, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, R.; Borroni, M.; Delle Rose, G.; Conti, M.; Garofalo, R.; Castagna, A. Convertible metal-backed glenoid in total shoulder arthroplasty: A single-centre case series with minimum 15 years’ follow-up. Bone Jt. Open 2025, 6, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, M.; Lee, W.; Jeon, I.-H.; Lee, K.W.; Koh, K.H. Is reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (rTSA) more advantageous than anatomic TSA (aTSA) for osteoarthritis with intact cuff tendon? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2022, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, S.A.; Flurin, P.-H.; Wright, T.W.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Elwell, J.A.; Roche, C.P.; Friedman, R.J. Comparison of complication types and rates associated with anatomic and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, J.R.; Helms, S.M.; Colbath, G.P.; Przestrzelski, B.T.; Hawkins, R.J.; DesJardins, J.D. A comparison of onlay versus inlay glenoid component loosening in total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2017, 26, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, S.B.; Lynch, T.L.; O’Farrell, D.; Calyore, C.; Rodenhouse, A. Finite element analysis and physiologic testing of a novel, inset glenoid fixation technique. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2012, 21, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, A.J.; Williams, A.A.; Tzeuton, S.; Gutman, M.; Davis, D.E.; Harding, M.; Williams, G.R.; Cronin, K.J. Total shoulder arthroplasty using an inlay glenoid component for glenoid deficiency: Mid- to long-term follow-up of a previously published cohort. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Amirouche, F. Glenoid Prosthesis Design Considerations in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Arthroplast. 2022, 6, 247154922211428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, S.B.; Bervell, J.A. Inset Glenoid Technology: A Paradigm Shift in Shoulder Replacement Surgery. J. Orthop. Exp. Innov. 2020, 1, 13447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsen, F.A.; Clinton, J.; Lynch, J.; Bertelsen, A.; Richardson, M.L. Glenoid Component Failure in Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Am. Vol. 2008, 90, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotti, J.P.; Gabriel, J.P.; Schneck, S.L.; Evans, B.G.; Misra, S. The normal glenohumeral relationships. An anatomical study of one hundred and forty shoulders. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1992, 74, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumstein, V.; Kraljević, M.; Hoechel, S.; Conzen, A.; Nowakowski, A.M.; Müller-Gerbl, M. The glenohumeral joint—A mismatching system? A morphological analysis of the cartilaginous and osseous curvature of the humeral head and the glenoid cavity. J. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, B.D.; Garrigues, G.E. How should I be putting my anatomic glenoids in? What we know and what we don’t know. Semin. Arthroplast. JSES 2023, 33, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muench, L.N.; Slater, M.; Archambault, S.; Berthold, D.P.; Rupp, M.-C.; Obopilwe, E.; Cote, M.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Contact Mechanics of Elliptical and Spherical Head Implants during Axial Rotation in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Biomechanical Comparison. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muench, L.N.; Kia, C.; Murphey, M.; Obopilwe, E.; Cote, M.P.; Imhoff, A.B.; Mazzocca, A.D.; Berthold, D.P. Elliptical heads result in increased glenohumeral translation along with micro-motion of the glenoid component during axial rotation in total shoulder arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2021, 143, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, I.; Buscayret, F.; Edwards, T.B.; Nemoz, C.; Boileau, P.; Walch, G. Radiographic comparison of flat-back and convex-back glenoid components in total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2005, 14, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, M.D.; Jensen, K.L.; Southworth, C.; Matsen, F.A. The Radiographic Evaluation of Keeled and Pegged Glenoid Component Insertion. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2002, 84, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglin, C.; Wyss, U.P.; Nyffeler, R.W.; Gerber, C. Loosening performance of cemented glenoid prosthesis design pairs. Clin. Biomech. 2001, 16, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsher, A.; Gohal, C.; Madden, K.; Miller, B.; Bedi, A.; Alolabi, B.; Khan, M. A comparison of pegged vs. keeled glenoid components regarding functional and radiographic outcomes in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JSES Open Access 2019, 3, 136–144.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLendon, P.B.; Schoch, B.S.; Sperling, J.W.; Sánchez-Sotelo, J.; Schleck, C.D.; Cofield, R.H. Survival of the pegged glenoid component in shoulder arthroplasty: Part II. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2017, 26, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.J.; Cil, A.; Sperling, J.W.; Sanchez-Sotelo, J.; Schleck, C.D.; Cofield, R.H. Survival of the glenoid component in shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2009, 18, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, M.T.; Chan, P.H.; Prentice, H.A.; Burfeind, W.E.; Yian, E.H.; Singh, A.; Paxton, E.W.; Navarro, R.A. The association between glenoid component design and revision risk in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.S.; Alder-Price, A.C.; Rainbird, S.; Graves, S.E.; De Steiger, R.N.; Peng, Y.; Holder, C.; Lorimer, M.F.; Gill, S.D. Reduced Revision Rates in Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with Crosslinked Polyethylene: Results From the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Clin. Orthop. 2022, 480, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadonikolakis, A.; Neradilek, M.B.; Matsen, F.A. Failure of the Glenoid Component in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of the English-Language Literature Between 2006 and 2012. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 95, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endrizzi, D.P.; Henry, P.; Mackenzie, J.A. Early Metallic Debris Formation with a Porous Tantalum Glenoid Component: A Radiographic Analysis with 2 Year Minimum Follow-Up. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, e115–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucentese, S.F.; Costouros, J.G.; Kühnel, S.-P.; Gerber, C. Total shoulder arthroplasty with an uncemented soft-metal-backed glenoid component. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2010, 19, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.J.; Cheung, E.; Grey, S.G.; Flurin, P.-H.; Wright, T.W.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Roche, C.P. Clinical and radiographic comparison of a hybrid cage glenoid to a cemented polyethylene glenoid in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 2308–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulotta, L.V.; Chambers, K.L.; Warren, R.F.; Dines, D.M.; Craig, E.V. No differences in early results of a hybrid glenoid compared with a pegged implant. Clin. Orthop. 2015, 473, 3918–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Sedrak, P.; Gohal, C.; Athwal, G.S.; Khan, M.; Alolabi, B. Hybrid Glenoid Designs in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. HSS J. 2022, 18, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.N.; Cregar, W.M.; Rao, A.J.; Trofa, D.P.; Schiffern, S.C.; Hamid, N.; Saltzman, B.M. Anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty with inlay glenoid component: A systematic review. Shoulder Elb. 2023, 16, 175857322311548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Todd, E.; Wright, M.A.; Murthi, A.M. Evaluation of clinical and radiographic outcomes after total shoulder arthroplasty with inset Trabecular Metal-backed glenoid. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karademir, G.; Aslan, Ö. Glenoid Morphology and Related Parameters in Turkish Society. Cureus 2022, 14, e27959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.M.; Galvin, J.W.; Bozoghlian, M.F.; Glass, N.; Wright, M. Gender bias in glenosphere size selection in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: Glenoid size correlates with height and weight, not just gender. JSES Int. 2025, 9, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piponov, H.I.; Savin, D.; Shah, N.; Esposito, D.; Schwartz, B.; Moretti, V.; Goldberg, B. Glenoid version and size: Does gender, ethnicity, or body size play a role? Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 2347–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, S.B.; Lynch, T.L. Total shoulder replacement surgery with custom glenoid implants for severe bone deficiency. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2012, 21, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E.; Acevedo, D.; Williams, A.; Williams, G. Total shoulder arthroplasty using an inlay mini-glenoid component for glenoid deficiency: A 2-year follow-up of 9 shoulders in 7 patients. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://shoulderinnovations.com/inset-glenoid/ (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Burr, D.B.; Gallant, M.A. Bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Gupta, A.; Pappou, I.; Hussey, M.M.; Santoni, B.G.; Inoue, N.; Frankle, M.A. Glenoid subchondral bone density distribution in male total shoulder arthroplasty subjects with eccentric and concentric wear. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglin, C.; Wyss, U.P.; Pichora, D.R. Mechanical testing of shoulder prostheses and recommendations for glenoid design. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2000, 9, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.Z.; Jawa, A.; Wiater, J.M.; Cuff, D.J.; Murthi, A.M.; Smith, M.J.; Miller, D.; Vasconcellos, D.; Riebesell, S.; Austin, L.S. Biomechanical comparison of a novel circular glenoid with peripheral ring fixation to a standard anchor pegged glenoid in total shoulder arthroplasty. Semin. Arthroplast. JSES 2023, 34, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, S.; Scarcella, M.; Everhart, J.; Samuel, L.; Miniaci, A. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with a Nonspherical Humeral Head and Inlay Glenoid in Elite Weight Lifters: A Prospective Case Series. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2021, 9, 23259671211021055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetanovich, G.L.; Naylor, A.J.; O’Brien, M.C.; Waterman, B.R.; Garcia, G.H.; Nicholson, G.P. Anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty with an inlay glenoid component: Clinical outcomes and return to activity. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, A.C.; Peterson, J.; Jones, M.H.; Miniaci, A. Total shoulder arthroplasty with nonspherical humeral head and inlay glenoid replacement: Clinical results comparing concentric and nonconcentric glenoid stages in primary shoulder arthritis. JSES Open Access 2019, 3, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, J.W.; Zvijac, J.E.; Porter, D.A.; Saxena, A.; Vargas, L.A. Inlay total shoulder arthroplasty for primary glenohumeral arthritis. JSES Int. 2021, 5, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, E.J.; Roche, C.; Flurin, P.-H.; Wright, T.; Zuckerman, J.D. The glenoid in shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2009, 18, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, P.S.; Strony, J.T.; Churchill, J.L.; Kankaria, R.; Sears, B.W.; Garrigues, G.E.; Gillespie, R.J. Clinical and radiographic outcomes following anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty utilizing an inset glenoid component at 2-year minimum follow-up: A dual center study. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2023, 32, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cofield, R.H. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1984, 66, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, J.W.; Cofield, R.H.; O’Driscoll, S.W.; Torchia, M.E.; Rowland, C.M. Radiographic assessment of ingrowth total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2000, 9, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.J.; Hawthorne, K.B.; Genez, B.M. The use of computerized tomography in the measurement of glenoid version. JBJS 1992, 74, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, S.B.; Tran, S.K. Long-term follow-up of total shoulder replacement surgery with inset glenoid implants for arthritis with deficient bone. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsen, F.A. The ream and run: Not for every patient, every surgeon or every problem. Int. Orthop. 2015, 39, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reddy, A.R.; Hones, K.M.; Rakauskas, T.R.; King, J.J.; Wright, T.W.; Schoch, B.S.; Hao, K.A. Advancements in Inlay Glenoid Components for Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165820
Reddy AR, Hones KM, Rakauskas TR, King JJ, Wright TW, Schoch BS, Hao KA. Advancements in Inlay Glenoid Components for Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165820
Chicago/Turabian StyleReddy, Akshay R., Keegan M. Hones, Taylor R. Rakauskas, Joseph J. King, Thomas W. Wright, Bradley S. Schoch, and Kevin A. Hao. 2025. "Advancements in Inlay Glenoid Components for Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165820
APA StyleReddy, A. R., Hones, K. M., Rakauskas, T. R., King, J. J., Wright, T. W., Schoch, B. S., & Hao, K. A. (2025). Advancements in Inlay Glenoid Components for Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165820






