Evaluating the Efficacy of a Novel Titanium Cage System in ALIF and LLIF: A Retrospective Clinical and Radiographic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Sample Selection
- Adults aged 18 to 80 years, with lumbar degenerative spine disease requiring interbody fusion at one or more levels between L2 and S1.
- Patients treated with either an LLIF, an ALIF, or a combination of LLIF and ALIF devices, with supplemental fixation as necessary.
- Patients under 18 years or over 80 years of age at the time of surgery.
- Patients with lumbar disease from infections (e.g., tuberculosis) or of neoplastic, traumatic, or congenital etiology.
- Patients necessitating deformity correction.
- Patients with severe osteoporosis.
2.4. Preoperative and Procedural Characteristics
2.5. Clinical Outcomes
2.6. Radiographic Outcomes
2.7. Adverse Events and Complications
2.8. Missing Data
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
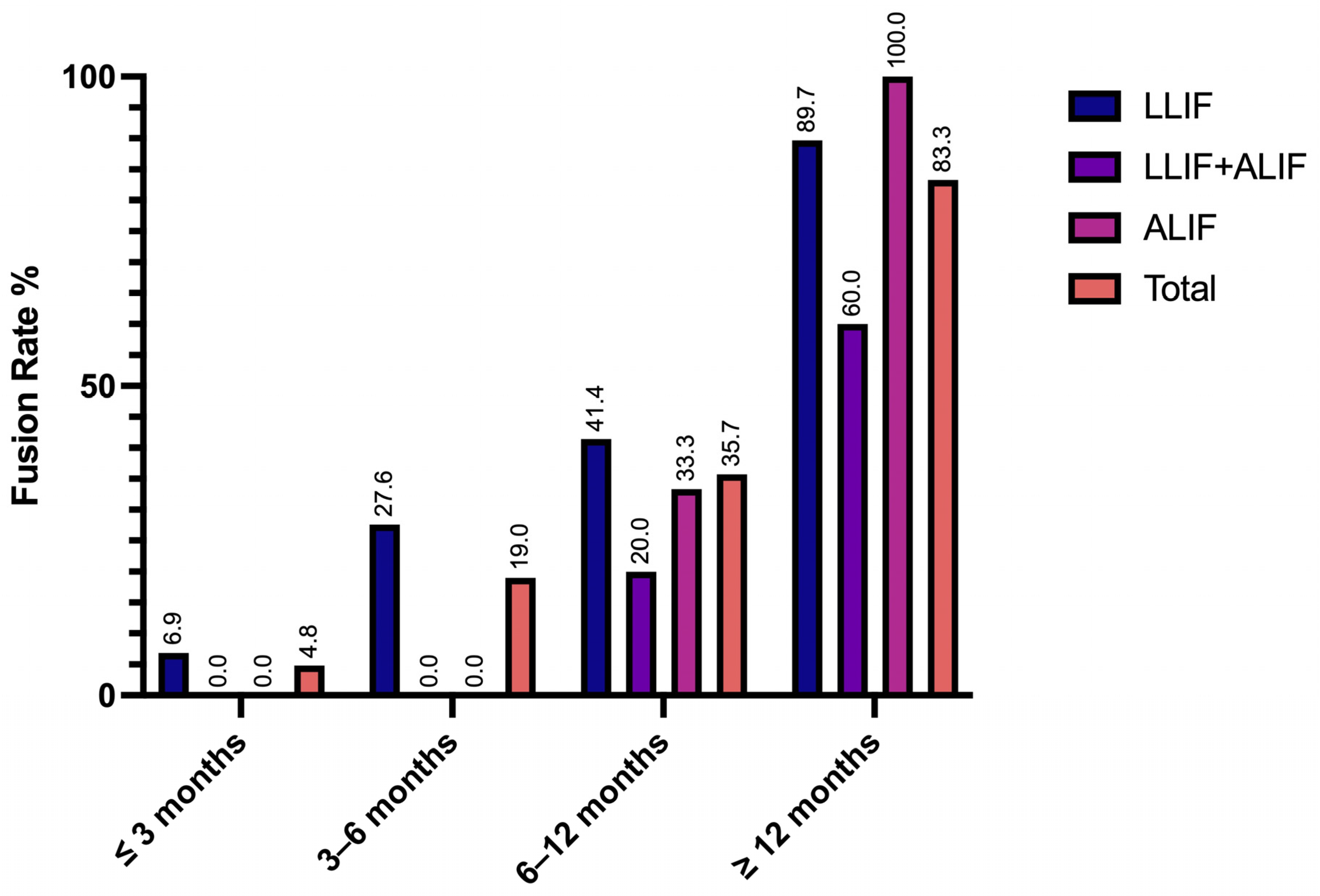
3.2. Radiographic Outcomes and Adverse Events
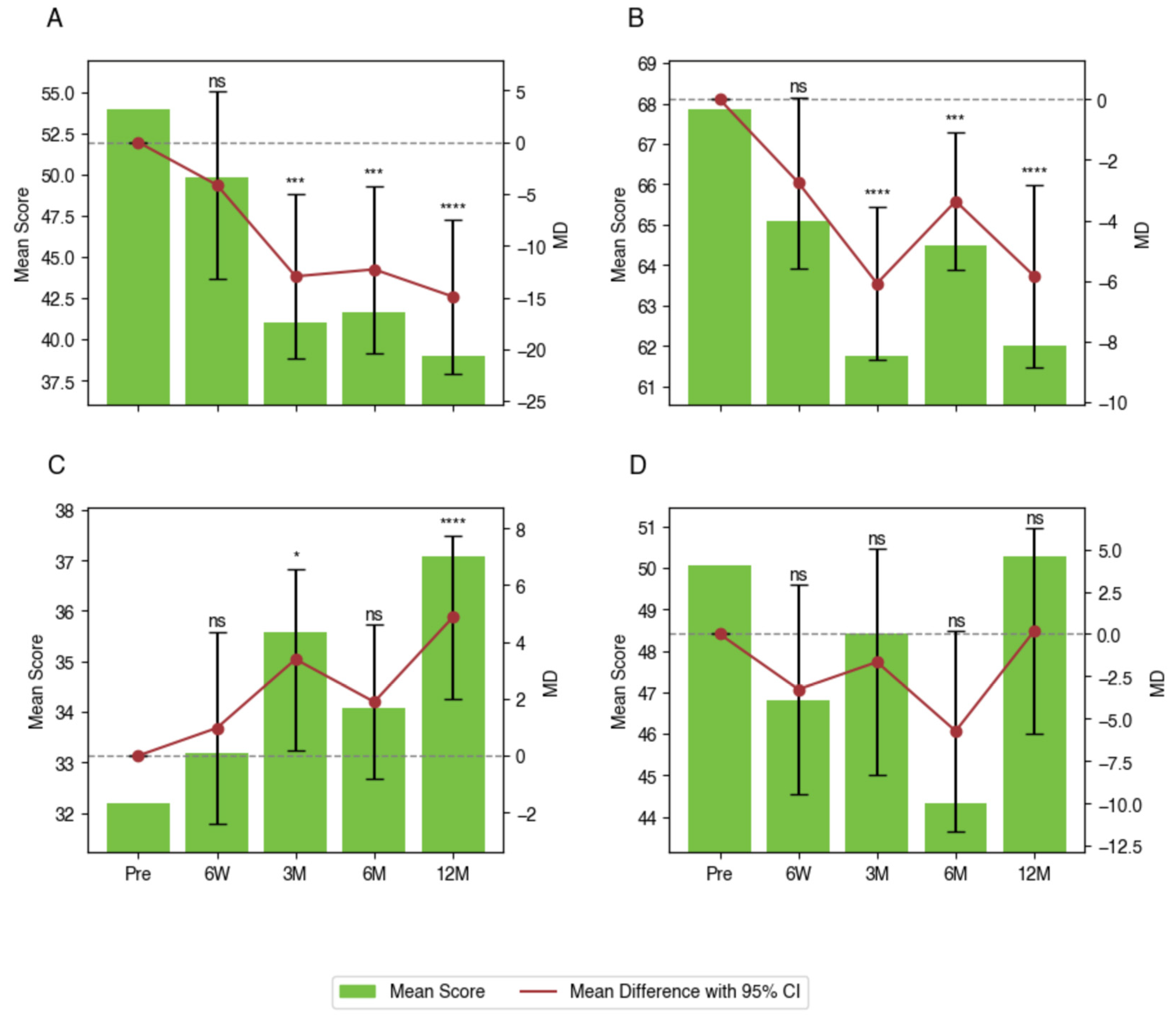
3.3. Within-Group Differences in PROMs
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LLIF | Lateral lumbar interbody fusion |
| ALIF | Anterior lumbar interbody fusion |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| PROMIS | Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System |
| DSD | Degenerative spine disease |
| PEEK | Polyether ether ketone |
| PROMs | Patient-reported outcome measures |
| STROBE | Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology |
| TRIPOD+AI | Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis + artificial intelligence |
| AE | Adverse events |
| LMM | Linear mixed-effects model |
References
- Teng, I.; Han, J.; Phan, K.; Mobbs, R. A meta-analysis comparing ALIF, PLIF, TLIF and LLIF. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 44, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Virk, S.; Qureshi, S. Interbody Fusions in the Lumbar Spine: A Review. HSS J. 2020, 16, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.J.; Phan, K.; Giang, G.; Maharaj, M.M.; Phan, S.; Mobbs, R.J. Subsidence following anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF): A prospective study. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobbs, R.J.; Phan, K.; Malham, G.; Seex, K.; Rao, P.J. Lumbar interbody fusion: Techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. J. Spine Surg. 2015, 1, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, K.K.; Tseng, W.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, K.H.; Pan, C.C.; Lu, W.X.; Shih, C.M.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of radiographic and clinical outcomes between ALIF, OLIF, and TLIF over 2-year follow-up: A comparative study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, G.; Martin, N.; Williams, G.M.; Unger, J.; Yee-Yanagishita, C.; Pelletier, M.; Walsh, W.; Peng, Y.; Jekir, M. Choice of Spinal Interbody Fusion Cage Material and Design Influences Subsidence and Osseointegration Performance. World Neurosurg. 2022, 162, e626–e634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, A.J.; Chanbour, H.; Chen, J.W.; Young, M.W.; Stephens, B.F. Implant Surface Technologies to Promote Spinal Fusion: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2023, 17, S35–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adl Amini, D.; Okano, I.; Oezel, L.; Zhu, J.; Chiapparelli, E.; Shue, J.; Sama, A.A.; Cammisa, F.P.; Girardi, F.P.; Hughes, A.P. Evaluation of cage subsidence in standalone lateral lumbar interbody fusion: Novel 3D-printed titanium versus polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heary, R.F.; Parvathreddy, N.; Sampath, S.; Agarwal, N. Elastic modulus in the selection of interbody implants. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.; Cheong, C.K.; Hey, H.W.D. Titanium (Ti) cages may be superior to polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages in lumbar interbody fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical and radiological outcomes of spinal interbody fusions using Ti versus PEEK cages. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhatanadgige, W.; Tangchitcharoen, N.; Kerr, S.J.; Tanasansomboon, T.; Yingsakmongkol, W.; Kotheeranurak, V.; Limthongkul, W. A Comparison of Polyetheretherketone and Titanium-Coated Polyetheretherketone in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Randomized Clinical Trial. World Neurosurg. 2022, 168, e471–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, M.; Fleege, C.; Tarhan, T.; Schreiner, S.; Makowski, M.R.; Rauschmann, M.; Arabmotlagh, M. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using polyetheretherketone oblique cages with and without a titanium coating: A randomised clinical pilot study. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99-b, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuura, Y.; Wright-Chisem, J.; Wright-Chisem, A.; Virk, S.; McAnany, S. The Importance of Surface Technology in Spinal Fusion. HSS J. 2020, 16, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandrovcová, M.; Bačáková, L. Adhesion, growth and differentiation of osteoblasts on surface-modified materials developed for bone implants. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittens, R.A.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. Implant osseointegration and the role of microroughness and nanostructures: Lessons for spine implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laratta, J.L.; Vivace, B.J.; López-Peña, M.; Guzón, F.M.; Gonzalez-Cantalpeidra, A.; Jorge-Mora, A.; Villar-Liste, R.M.; Pino-Lopez, L.; Lukyanchuk, A.; Taghizadeh, E.A.; et al. 3D-printed titanium cages without bone graft outperform PEEK cages with autograft in an animal model. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittens, R.A.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Cheng, A.; Anderson, D.M.; McLachlan, T.; Stephan, I.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Sandhage, K.H.; Fedorov, A.G.; Rupp, F.; et al. The roles of titanium surface micro/nanotopography and wettability on the differential response of human osteoblast lineage cells. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6268–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; An, J.; Zhao, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, W.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, F. Surface Modification Techniques to Produce Micro/Nano-scale Topographies on Ti-Based Implant Surfaces for Improved Osseointegration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 835008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, N.; Fujibayashi, S.; Takemoto, M.; Sasaki, K.; Otsuki, B.; Nakamura, T.; Matsushita, T.; Kokubo, T.; Matsuda, S. Effect of pore size on bone ingrowth into porous titanium implants fabricated by additive manufacturing: An in vivo experiment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 59, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2008, 82, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.S.; Moons, K.G.; Dhiman, P.; Riley, R.D.; Beam, A.L.; Van Calster, B.; Ghassemi, M.; Liu, X.; Reitsma, J.B.; van Smeden, M. TRIPOD+ AI statement: Updated guidance for reporting clinical prediction models that use regression or machine learning methods. BMJ 2024, 385, q902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridwell, K.H.; Lenke, L.G.; McEnery, K.W.; Baldus, C.; Blanke, K. Anterior fresh frozen structural allografts in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Do they work if combined with posterior fusion and instrumentation in adult patients with kyphosis or anterior column defects? Spine 1995, 20, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Abdala, N.; Oliveira, L.; Amaral, R.; Coutinho, E.; Pimenta, L. Radiographic and clinical evaluation of cage subsidence after stand-alone lateral interbody fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 19, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, S.; Albers, C.E.; Elfiky, T.; Deml, M.C.; Milavec, H.; Bigdon, S.F.; Benneker, L.M. First Results of a New Vacuum Plasma Sprayed (VPS) Titanium-Coated Carbon/PEEK Composite Cage for Lumbar Interbody Fusion. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazierhan, S.; Li, C.; Guo, R.; Lu, L.; Aikeremu, D.; Xu, K.; Wang, H. MIS-TLIF or CLIF for single segmental lumbar degenerative disease. Medicine 2022, 101, e31534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velluto, C.; Mundis, G., Jr.; Scaramuzzo, L.; Perna, A.; Capece, G.; Cruciani, A.; Inverso, M.; Borruto, M.I.; Proietti, L. Radiological evaluation of fusion patterns after Lateral Lumbar Interbody fusion with 3D-printed porous titanium cages vs. conventional titanium cages. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1446792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, N.; Vodovotz, L.; Muthiah, N.; Deng, H.; Guha, D.; Agarwal, N.; Ozpinar, A.; Mushlin, H.M.; Puccio, L.; Hamilton, D.K.; et al. Subsidence after lateral lumbar interbody fusion using a 3D-printed porous titanium interbody cage: Single-institution case series. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2022, 37, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Kim, D.M.; Park, S. Comparison of Fusion, Subsidence, and Clinical Results Between 3D-Printed Porous Titanium Cage and Polyetheretherketone Cage in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Minimum of 2 Years Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2023, 177, e732–e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segi, N.; Nakashima, H.; Ito, S.; Ouchida, J.; Oishi, R.; Yamauchi, I.; Miyairi, Y.; Morita, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Kanbara, S.; et al. Trabecular Bone Remodeling after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Comparison of the Osseointegration in Three-Dimensional Porous Titanium Cages and Polyether-Ether-Ketone Cages. Glob. Spine J. 2025, 15, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, N.; Deng, H.; Muthiah, N.; Vodovotz, L.; Dembinski, R.; Guha, D.; Agarwal, N.; Ozpinar, A.; Hamilton, D.K.; Kanter, A.S.; et al. Graft subsidence and reoperation after lateral lumbar interbody fusion: A propensity score-matched and cost analysis of polyetheretherketone versus 3D-printed porous titanium interbodies. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2023, 39, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, C.; Santro, T.; Awad, M.; Morokoff, A. 3D-printed titanium alloy cage in anterior and lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spine disease. J. Spine Surg. 2024, 10, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, J.P.; Williams, G.P.; Zomaya, M.P.; Choy, W.; Turner, J.D.; Snyder, L.A.; Uribe, J.S. Enhancing the Technical Pearls for L5-S1 Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Patients with Body Mass Index More Than 30: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes at 1-Year Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2024, 194, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamdouhi, T.; Wang, V.; Echevarria, A.C.; Katz, A.; Morris, M.; Zavurov, G.; Verma, R. A Comprehensive Review of the Historical Description of Spine Surgery and Its Evolution. Cureus 2024, 16, e54461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.L.; Gornet, M.F.; Burkus, J.K. CT evaluation of lumbar interbody fusion: Current concepts. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, J.; Ma, L.; Meng, X. Unilateral Endoscopic and Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2025, 12, 1585783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, R. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS TLIF) in treatment of degenerative diseases of lumbosacral spine compared to modified open TLIF: A prospective randomised controlled study. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2024, 58, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Jia, D.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, C.; Ning, Y.; Leng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, B. Comparison of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (Mis-TLIF) with bilateral decompression via unilateral approach and open-TLIF with bilateral decompression for degenerative lumbar diseases: A retrospective cohort study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossopoulos, P.N.; Bardeesi, A.; Wang, T.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Ononogbu-Uche, F.C.; Than, K.D.; Crutcher, C.; Pokorny, G.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Pollina, J.; et al. Advancing Prone-Transpsoas Spine Surgery: A Narrative Review and Evolution of Indications with Representative Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnake, K.J.; Rappert, D.; Storzer, B.; Schreyer, S.; Hilber, F.; Mehren, C. Lumbar fusion-Indications and techniques. Orthopade 2019, 48, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitouni, D.; Pfortmiller, D.; Coric, D.; Kim, P.K.; Smith, M.D.; Dyer, E.H.; Adamson, T.E.; McGirt, M.J.; Rossi, V.J. Does type of bone graft matter? A retrospective review of the use of biological bone grafts in patients undergoing elective 1-3 level spinal interbody fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chan, J.L.; Eleanore, A.; DeCost, K.; Luk, J.; Neukam, L.C.; Rizvi, T.Z.; Lin, Z.; Ghogawala, Z.; Magge, S.N.; et al. Radiographic and Clinical Comparison of Polyetheretherketone Versus 3D-Printed Titanium Cages in Lumbar Interbody Fusion-A Single Institution’s Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Zou, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Xiu, P.; Feng, G.; Song, Y.; Yang, X. Comparison between Three-Dimensional Printed Titanium and PEEK Cages for Cervical and Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Prospective Controlled Trial. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, K.; Qi, L. Clinical and radiological outcomes of titanium cage versus polyetheretherketone cage in lumbar interbody fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2025, 48, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corso, K.A.; Teferra, A.A.; Michielli, A.; Corrado, K.; Marcini, A.; Lotito, M.; Smith, C.; Costa, M.; Ruppenkamp, J.; Wallace, A. Evaluation of Healthcare Outcomes of Patients Treated with 3D-Printed-Titanium and PEEK Cages During Fusion Procedures in the Lumbar Spine. Med. Devices 2025, 18, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic a | LLIF (n = 32) | LLIF + ALIF (n = 12) | ALIF (n = 4) | Total (n = 48) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall N patients (%) | 32 (66.7) | 12 (25) | 4 (8.3) | 48 (100) |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Female | 20 (62.5) | 7 (58.3) | 3 (75.0) | 30 (62.5) |
| Male | 12 (37.5) | 5 (41.7) | 1 (25.0) | 18 (37.5) |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 60.3 ± 10.5 | 62.3 ± 12.4 | 42.8 ± 10.9 | 59.4 ± 12.0 |
| Median | 61 | 65 | 47 | 60.5 |
| Range (Min, Max) | 35, 79 | 36, 80 | 27, 50 | 27, 80 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 29.6 ± 4.5 | 29.9 ± 4.8 | 32.1 ± 9.3 | 29.9 ± 5.0 |
| Median | 29.0 | 28.4 | 32.4 | 29.0 |
| Range (Min, Max) | 20.9, 39.3 | 21.6, 37.0 | 20.4, 43.2 | 20.4, 43.2 |
| Preop. Smoking History, n (%) | ||||
| Current smoker | 3 (9.4) | 1 (8.3) | 2 (50.0) | 6 (12.5) |
| Previous smoker | 6 (18.8) | 6 (50.0) | - | 12 (25.0) |
| Never smoker | 23 (71.9) | 5 (41.7) | 2 (50.0) | 30 (62.5) |
| Comorbidities at Time of Surgery, n (%) | ||||
| COPD | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Diabetes | 8 (25.0) | 2 (16.7) | - | 10 (20.8) |
| Obesity | 4 (12.5) | 3 (25.0) | 3 (75.0) | 10 (20.8) |
| Osteoporosis b | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Steroid Usage | - | 1 (8.3) | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Previous Spine Surgery | ||||
| Lumbar Fusion | 7 (21.9) | 1 (8.3) | 1 (25.0) | 9 (18.8) |
| Lumbar Other | 5 (15.6) | 3 (25.0) | - | 8 (16.7) |
| Cervical Spine | - | 3 (25.0) | - | 3 (6.3) |
| Length of Follow-up Time (months) | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 11.0 ± 5.7 | 15.4 ± 4.9 | 10.0 ± 6.4 | 12.0 ± 5.8 |
| Median | 11.0 | 13.0 | 11.5 | 12.0 |
| Range (Min, Max) | 2.0, 25.0 | 11.0, 24.0 | 1.0, 16.0 | 1.0, 25.0 |
| Patient Diagnosis, n (%) c | ||||
| Disc degeneration | 11 (34.4) | 4 (33.3) | 2 (50.0) | 17 (35.4) |
| Radiculopathy | 3 (9.4) | 1 (8.3) | - | 4 (8.3) |
| Stenosis | 12 (37.5) | 7 (58.3) | 1 (25.0) | 20 (41.7) |
| Neurogenic claudication | 4 (12.5) | 5 (41.7) | 1 (25.0) | 10 (20.8) |
| Lumbar spondylosis | 9 (28.1) | 7 (58.3) | - | 16 (33.3) |
| Spondylolisthesis | 21 (65.6) | 4 (33.3) | 2 (50.0) | 27 (56.3) |
| Pseudarthrosis | 2 (6.3) | - | - | 2 (4.2) |
| Adjacent segment disease | 3 (9.4) | 1 (8.3) | - | 4 (8.3) |
| Off-label: Osteomyelitis d | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Characteristic | LLIF (n = 32) | LLIF + ALIF (n = 12) | ALIF (n = 4) | Total (n = 48) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retroperitoneal Surgical Approach, n (%) | ||||
| Anterior to Psoas (ATP) | 6 (18.8) | 6 (50.0) | - | 12 (25.0) |
| Transpsoas | 26 (81.3) | 6 (50.0) | 4 (100.0) | 36 (75.0) |
| Operation Duration, n (%) | ||||
| ≤2 h | 5 (15.6) | - | - | 5 (10.4) |
| 2–3 h | 8 (25.0) | 1 (8.3) | - | 9 (18.8) |
| 3–4 h | 6 (18.8) | - | - | 6 (12.5) |
| >4 h | 13 (40.6) | 11 (91.7) | 3 (75.0) | 27 (56.3) |
| Estimated Blood Loss (cc) | ||||
| Mean | 210.9 | 420.8 | 175.0 | 260.4 |
| SD | 225.8 | 229.1 | 86.6 | 235.0 |
| Median | 150.0 | 425.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 |
| Min, Max | 0.0, 850.0 | 50.0, 900.0 | 50.0, 250.0 | 0.0, 900.0 |
| Length of Hospital Stay, n (%) | ||||
| 1 day | 3 (9.4) | - | - | 3 (6.3) |
| ≤5 days | 23 (71.9) | 9 (75.0) | 3 (75.0) | 35 (72.9) |
| 6–10 days | 6 (18.8) | 2 (16.7) | 1 (25.0) | 9 (18.8) |
| >10 days | - | 1 (8.3) | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Number of Levels Cages Implanted, n (%) | ||||
| 1 | 24 (75.0) | - | 4 (100.0) | 28 (58.3) |
| 2 | 5 (15.6) | 6 (50.0) | - | 11 (22.9) |
| 3 | 3 (9.4) | 5 (41.7) | - | 8 (16.7) |
| 4 | - | 1 (8.3) | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Vertebral Levels Implanted a, n (%) | ||||
| L1/L2 | - | 1 (8.3) | - | 1 (2.1) |
| L2/L3 | 7 (21.9) | 2 (16.7) | - | 9 (18.8) |
| L3/L4 | 15 (46.9) | 6 (50.0) | - | 21 (43.8) |
| L4/L5 | 20 (62.5) | 10 (83.3) | - | 30 (62.5) |
| L5/S1 | 1 (3.1) | 12 (100.0) | 4 (100.0) | 17 (35.4) |
| Supplemental Fixation Used, n (%) | ||||
| Pedicle screws | 28 (87.5) | 9 (75.0) | 4 (100.0) | 41 (85.4) |
| None | 3 (9.4) | 1 (8.3) | - | 4 (8.3) |
| Missing | 1 (3.1) | 2 (16.7) | - | 3 (6.3) |
| Graft Material b, n (%) | ||||
| Autograft (local bone) | 4 (12.5) | 3 (25.0) | - | 7 (14.6) |
| Autograft (iliac crest) | 13 (40.6) | 8 (66.7) | 2 (50.0) | 23 (47.9) |
| Allograft | 30 (93.8) | 12 (100.0) | 4 (100.0) | 46 (95.8) |
| BMA | 30 (93.8) | 12 (100.0) | 2 (50.0) | 44 (91.7) |
| chronOS | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| ViviGen | 1 (3.1) | - | 1 (25.0) | 2 (4.2) |
| Hydroxyapatite synthetic graft | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Characteristic | Preop. Baseline | 6 Weeks Change | 3 Months Change | 6 Months Change | 12 Months Change | 24 Months Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLIF 1 (n, n missing) | 60, 2 | 46, 16 | 49, 13 | 42, 20 | 42, 20 | 23, 39 |
| Global Lumbar Lordosis (°) | 43.52 ± 13.19 | −0.49 ± 7.82 | 0.55 ± 13.30 | 1.73 ± 7.56 | 1.31 ± 10.49 | 0.20 ± 8.08 |
| Segmental Lumbar Lordosis (°) | 31.42 ± 16.52 | −0.82 ± 12.23 | 0.37 ± 12.25 | 2.21 ± 7.45 | 1.50 ± 12.57 | −4.08 ± 14.96 |
| Anterior Disc Space Height (mm) | 8.15 ± 3.66 | 3.96 ± 3.60 | 4.75 ± 4.29 | 4.08 ± 4.33 | 4.16 ± 3.70 | 3.85 ± 4.23 |
| Posterior Disc Space Height (mm) | 4.78 ± 2.15 | 2.79 ± 2.78 | 3.33 ± 2.49 | 3.01 ± 2.09 | 2.74 ± 2.75 | 2.95 ± 2.56 |
| Mean Disc Space Height (mm) | 6.16 ± 2.61 | 3.37 ± 2.70 | 4.04 ± 3.08 | 3.54 ± 2.90 | 3.45 ± 2.95 | 3.40 ± 3.15 |
| Foraminal Height (mm) | 16.53 ± 4.83 | 2.64 ± 4.73 | 2.71 ± 4.45 | 2.47 ± 5.69 | 2.44 ± 3.82 | 2.86 ± 4.36 |
| ALIF 1 (n, n missing) | 16, 0 | 12, 4 | 13, 3 | 11, 5 | 9, 7 | 4, 12 |
| Global Lumbar Lordosis (°) | 42.19 ± 15.10 | 0.66 ± 9.14 | 1.53 ± 13.77 | 3.21 ± 5.41 | 8.06 ± 12.06 | 0.78 ± 2.72 |
| Segmental Lumbar Lordosis (°) | 24.38 ± 12.48 | 4.93 ± 8.58 | 6.24 ± 6.30 | 4.34 ± 5.67 | 8.20 ± 10.80 | 4.40 ± 4.77 |
| Anterior Disc Space Height (mm) | 8.23 ± 3.97 | 8.38 ± 3.79 | 8.50 ± 3.29 | 8.34 ± 3.78 | 8.72 ± 2.11 | 9.20 ± 4.10 |
| Posterior Disc Space Height (mm) | 4.10 ± 1.61 | 3.84 ± 1.99 | 3.95 ± 1.50 | 3.80 ± 1.93 | 3.81 ± 1.56 | 4.83 ± 1.56 |
| Mean Disc Space Height (mm) | 6.16 ± 2.61 | 6.11 ± 2.37 | 6.22 ± 1.90 | 6.07 ± 2.33 | 6.27 ± 1.47 | 7.01 ± 2.17 |
| Foraminal Height (mm) | 12.14 ± 4.43 | 3.89 ± 3.67 | 2.76 ± 4.22 | 4.00 ± 3.37 | 4.42 ± 3.41 | 7.10 ± 2.63 |
| Characteristic | LLIF (n = 32) | LLIF+ALIF (n = 12) | ALIF (n = 4) | Total (n = 48) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE Severity a, n (%) | ||||
| Mild | 34 (106.3) | 17 (141.7) | 5 (125.0) | 56 (116.7) |
| Moderate | 10 (31.3) | 5 (41.7) | 2 (50.0) | 17 (35.4) |
| Serious (SAE) | - | - | - | - |
| n missing | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| AE Relatedness to Device (Cage), n (%) | ||||
| Not Related | 40 (125.0) | 16 (133.3) | 4 (100.0) | 60 (125.0) |
| Probably Related | - | 2 (16.7) | - | 2 (4.2) |
| Possibly Related | 1 (3.1) | 2 (16.7) | 3 (75.0) | 6 (12.5) |
| Definitely Related | 3 (9.4) | 2 (16.7) | - | 5 (10.4) |
| n missing | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| AE Relatedness to Procedure, n (%) | ||||
| Not Related | 14 (43.8) | 3 (25.0) | - | 17 (35.4) |
| Probably Related | 3 (9.4) | 3 (25.0) | 1 (25.0) | 7 (14.6) |
| Possibly Related | 23 (71.9) | 14 (116.7) | 6 (150.0) | 43 (89.6) |
| Definitely Related | 3 (9.4) | 2 (16.7) | - | 5 (10.4) |
| n missing | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Revision/Reoperation Summary, n (%) | ||||
| Reoperation– Right L5 Nerve Decompression by Transforaminal Approach for Restenosis | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Revision– L5/S1 ALIF Cage Replaced by Same 3D-printed titanium ALIF Cage for Cage Migration | - | 1 (8.3) b | - | 1 (2.1) |
| Radiographic Complications, n (%) | ||||
| Non-union (≥ 12 months c) | 3 (9.4) | 4 (33.3) | - | 7 (14.6) |
| Cage Subsidence (grades 1, 2, and 3) (at any timepoint) | 6 (18.8) | 2 (16.7) | - | 8 (16.7) |
| Cage Migration (at any timepoint) | 1 (3.1) | 2 (16.7) | 1 (25.0) | 4 (8.3) |
| Spondylolisthesis (at any timepoint) | 1 (3.1) | - | - | 1 (2.1) |
| PROM | Timepoint | Mean Score (95% CI) | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODI | Pre-Op | 54.0 (47.1 to 60.9) | - | - |
| 6 Weeks | 49.8 (43.6 to 56.0) | −4.1 (−13.2 to 4.9) | 1.0000 | |
| 3 Months | 41.0 (35.8 to 46.2) | −13.0 (−20.9 to −5.0) | 0.0002 | |
| 6 Months | 41.7 (36.4 to 47.0) | −12.3 (−20.4 to −4.2) | 0.0005 | |
| 12 Months | 39.0 (34.3 to 43.7) | −14.9 (−22.4 to −7.5) | <0.0001 | |
| PROMIS Pain Interference | Pre-Op | 67.9 (65.7 to 70.0) | - | - |
| 6 Weeks | 65.1 (63.0 to 67.2) | −2.8 (−5.6 to 0.1) | 0.0606 | |
| 3 Months | 61.8 (59.9 to 63.7) | −6.1 (−8.6 to −3.6) | <0.0001 | |
| 6 Months | 64.5 (62.8 to 66.2) | −3.4 (−5.6 to −1.1) | 0.0008 | |
| 12 Months | 62.0 (59.7 to 64.3) | −5.9 (−8.9 to −2.8) | <0.0001 | |
| PROMIS Physical Function | Pre-Op | 32.2 (29.8 to 34.6) | - | - |
| 6 Weeks | 33.2 (30.7 to 35.6) | 1.0 (−2.4 to 4.4) | 1.0000 | |
| 3 Months | 35.6 (33.3 to 37.9) | 3.4 (0.2 to 6.6) | 0.0317 | |
| 6 Months | 34.1 (32.2 to 35.9) | 1.9 (−0.8 to 4.6) | 0.3617 | |
| 12 Months | 37.1 (35.1 to 39.1) | 4.9 (2.0 to 7.8) | 0.0001 | |
| PROMIS Depression | Pre-Op | 50.1 (46.2 to 53.9) | - | - |
| 6 Weeks | 46.8 (43.8 to 49.8) | −3.3 (−9.5 to 3.0) | 0.8641 | |
| 3 Months | 48.4 (44.8 to 52.0) | −1.7 (−8.3 to 5.0) | 1.0000 | |
| 6 Months | 44.3 (41.7 to 47.0) | −5.7 (−11.7 to 0.2) | 0.0653 | |
| 12 Months | 50.3 (47.4 to 53.1) | 0.2 (−5.9 to 6.3) | 1.0000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turlip, R.W.; Dagli, M.M.; Chung, R.J.; Chauhan, D.; Kim, R.J.; Kincaid, J.; Ahmad, H.S.; Ghenbot, Y.; Yoon, J.W. Evaluating the Efficacy of a Novel Titanium Cage System in ALIF and LLIF: A Retrospective Clinical and Radiographic Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165814
Turlip RW, Dagli MM, Chung RJ, Chauhan D, Kim RJ, Kincaid J, Ahmad HS, Ghenbot Y, Yoon JW. Evaluating the Efficacy of a Novel Titanium Cage System in ALIF and LLIF: A Retrospective Clinical and Radiographic Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165814
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurlip, Ryan W., Mert Marcel Dagli, Richard J. Chung, Daksh Chauhan, Richelle J. Kim, Julia Kincaid, Hasan S. Ahmad, Yohannes Ghenbot, and Jang Won Yoon. 2025. "Evaluating the Efficacy of a Novel Titanium Cage System in ALIF and LLIF: A Retrospective Clinical and Radiographic Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165814
APA StyleTurlip, R. W., Dagli, M. M., Chung, R. J., Chauhan, D., Kim, R. J., Kincaid, J., Ahmad, H. S., Ghenbot, Y., & Yoon, J. W. (2025). Evaluating the Efficacy of a Novel Titanium Cage System in ALIF and LLIF: A Retrospective Clinical and Radiographic Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165814






