Risk Stratification Using a Perioperative Nomogram for Predicting the Mortality of Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients Selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Pathological Features
3.3. Treatment and Surgical Details
3.4. Complications and Recurrence
3.5. Factors Associated with the Progression-Free and Overall Survival of Bladder Cancer Patients
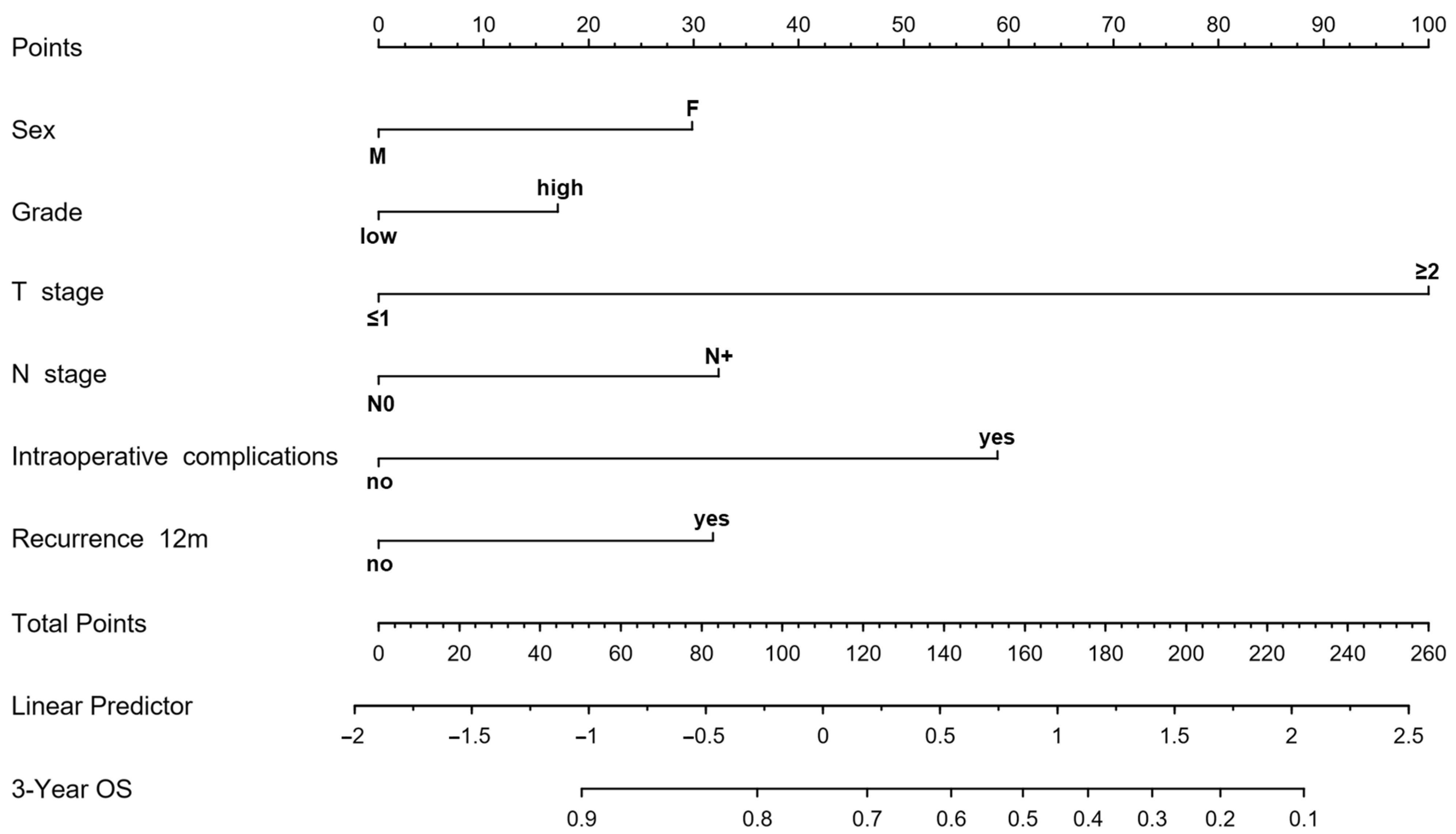
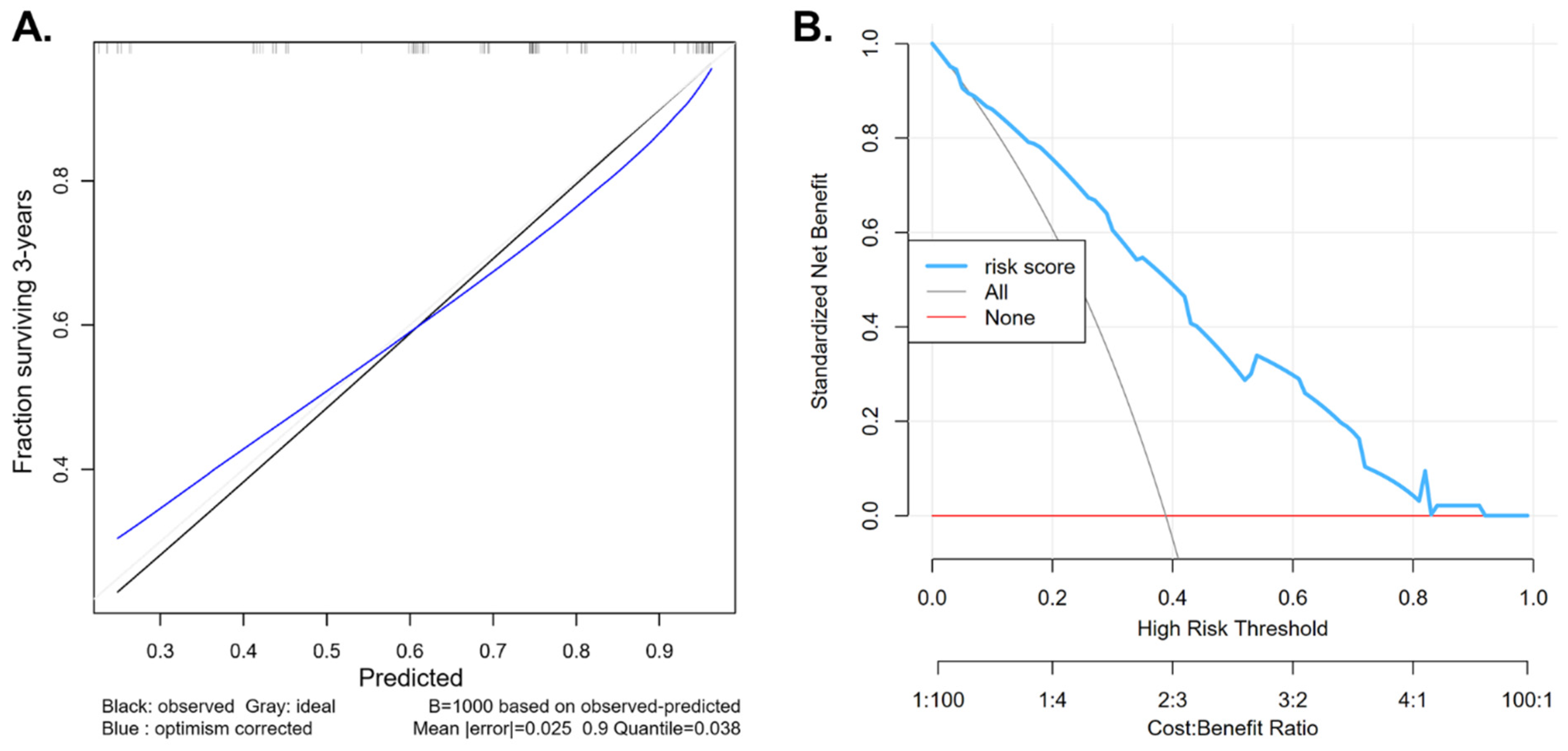
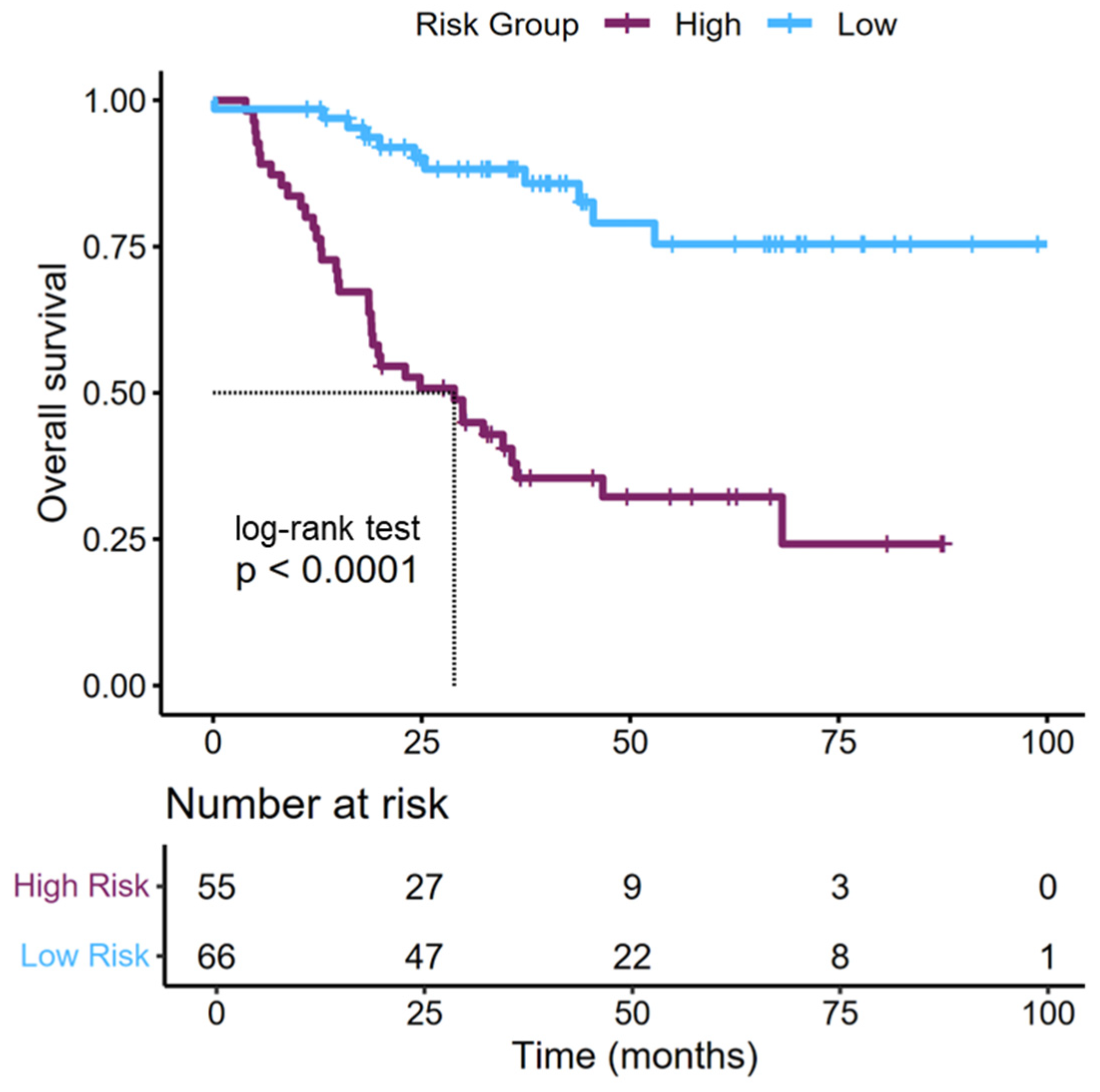
3.6. Risk Stratification of Patients Based on Perioperative and Pathological Features
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Results in the Context of the Published Literature
4.2. Nomograms from the Published Literature
4.3. Future Research Directions
4.4. Study Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- van der Heijden, A.G.; Bruins, H.M.; Carrion, A.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Fietkau, R.; Kailavasan, M.; Lorch, A.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2025 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2025, 87, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, A.; Di Maida, F.; Tasso, G.; Mari, A.; Bossa, R.; Sforza, S.; Grosso, A.A.; Tellini, R.; Vittori, G.; Siena, G.; et al. Robot Assisted Radical Cystectomy with Florence Robotic Intracorporeal Neobladder (FloRIN): Analysis of Survival and Functional Outcomes after First 100 Consecutive Patients upon Accomplishment of Phase 3 IDEAL Framework. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2651–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraich, T.A.; Khalid, S.Y.; Ali, A.; Kathia, U.M. Comparative Outcomes of Radical Cystectomy in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e50646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Zha, Z.; Qu, W.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, J. Clinicopathological Factors in Bladder Cancer for Cancer-Specific Survival Outcomes Following Radical Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cookson, M.S.; Guercio, B.J.; Cheng, L. Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Bladder Cancer. BMJ 2024, 384, e076743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Villarrubia, J.; Torres-Jiménez, J.; Bueno-Bravo, C.; García-Mondaray, R.; Subiela, J.D.; Gajate, P. Current and Future Landscape of Perioperative Treatment for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrió-Sanz, P.; Martinez-Cayuelas, L.; Lumbreras, B.; Sánchez-Caballero, L.; Palazón-Bru, A.; Gil-Guillén, V.F.; Gómez-Pérez, L. Mortality Prediction Models after Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Tumour: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Bladder Cancer Nomogram Consortium; Bochner, B.H.; Kattan, M.W.; Vora, K.C. Postoperative Nomogram Predicting Risk of Recurrence After Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3967–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook: From the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7th ed.; Edge, S.B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-0-387-88442-4. [Google Scholar]
- American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Amin, M.B., Greene, F.L., Edge, S.B., Eds.; corrected at 3rd printing; AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-40617-6. [Google Scholar]
- Eble, J.N.; Sauter, G.; Epstein, J.; Sesterhenn, I. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2004; ISBN 978-92-832-2415-0. [Google Scholar]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.; Ulbright, T.; Reuter, V. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2016; ISBN 978-92-832-2437-2. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. Rms: Regression Modeling Strategies. R Package Version 8.0. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rms/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Tay, J.K.; Narasimhan, B.; Hastie, T. Elastic Net Regularization Paths for All Generalized Linear Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2023, 106, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Jacobus, S.; Bellmunt, J.; Qu, A.; Appleman, L.J.; Tretter, C.; Bubley, G.J.; Stack, E.C.; Signoretti, S.; Walsh, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant Dose-Dense Methotrexate, Vinblastine, Doxorubicin, and Cisplatin With Pegfilgrastim Support in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Cancer: Pathologic, Radiologic, and Biomarker Correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, V.; Magno, C.; Spitaleri, G.; Garipoli, C.; Maisano, C.; Alafaci, E.; Adamo, B.; Rossello, R.; Scandurra, G.; Scimone, A. Phase II Study of Gemcitabine and Cisplatin in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Long-Term Follow-up of a 3-Week Regimen. Oncology 2005, 69, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, A.; Kimura, S.; Foerster, B.; Abufaraj, M.; D’Andrea, D.; Gust, K.M.; Shariat, S.F. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Lymphovascular Invasion in Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2018, 36, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T. Lymph Node Dissection for Bladder Cancer: Current Standards and the Latest Evidence. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppie, T.M.; Vickers, A.J.; Vora, K.; Dalbagni, G.; Bochner, B.H. Standardization of Pelvic Lymphadenectomy Performed at Radical Cystectomy: Can We Establish a Minimum Number of Lymph Nodes That Should Be Removed? Cancer 2006, 107, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packiam, V.T.; Tsivian, M.; Boorjian, S.A. The Evolving Role of Lymphadenectomy for Bladder Cancer: Why, When, and How. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 3082093–3083093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, R.; Shrivastava, N.; Sharma, A.P.; Choudhary, G.R.; Srivastava, A. The Adequacy of Pelvic Lymphadenectomy During Radical Cystectomy for Carcinoma Urinary Bladder: A Narrative Review of Literature. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 687636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissner, J.; Koeppen, C.; Wolf, H.K. Prognostic Significance of Vascular and Perineural Invasion in Urothelial Bladder Cancer Treated with Radical Cystectomy. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.K.; Abol-Enein, H.; Artibani, W.; Bochner, B.; Dalbagni, G.; Daneshmand, S.; Fradet, Y.; Hautmann, R.E.; Lee, C.T.; Lerner, S.P.; et al. Urinary Diversion after Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer: Options, Patient Selection, and Outcomes. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, M. Comparison of Extracorporeal and Intracorporeal Urinary Diversion after Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Mens. Health 2024, 18, 15579883241274866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razdan, S.; Sljivich, M.; Pfail, J.; Wiklund, P.K.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Waingankar, N. Predicting Morbidity and Mortality after Radical Cystectomy Using Risk Calculators: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Qi, W.; Lv, G.; Zhong, M.; Liu, X.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, S.; et al. The Effect of the Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Program on Radical Cystectomy: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Godoy, G.; Lerner, S.P. Use of Nomograms for Predictions of Outcome in Patients with Advanced Bladder Cancer. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2009, 1, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Xiao, B.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, H.; Peng, C.; Liang, B.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, M. Integrated Multicenter Deep Learning System for Prognostic Prediction in Bladder Cancer. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Osman, M.; Brendel, M.; Tangen, C.M.; Flaig, T.W.; Thompson, I.M.; Plets, M.; Scott Lucia, M.; Theodorescu, D.; Gustafson, D.; et al. Predicting Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer via Interpretable Multimodal Deep Learning. npj Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Seigne, J.D.; Schned, A.R.; Kelsey, K.T.; Karagas, M.R.; Hassanpour, S. A Machine Learning Approach for Long-Term Prognosis of Bladder Cancer Based on Clinical and Molecular Features. AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2020, 2020, 607–616. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Jiang, R. The Role of Perioperative Factors in the Prognosis of Cancer Patients: A Coin Has Two Sides. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 39, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, F.; Krabbe, L.-M.; Todenhöfer, T.; Dobruch, J.; Mitra, A.P.; Inman, B.A.; Gust, K.M.; Lotan, Y.; Shariat, S.F. Molecular Markers in Bladder Cancer. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Sheybaee Moghaddam, F.; Ghoreifi, A.; Ladi-Seyedian, S.; Cai, J.; Miranda, G.; Aron, M.; Schuckman, A.; Desai, M.; Gill, I.; et al. The Effect of Enhanced Recovery after Surgery on Oncologic Outcome Following Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 54, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, L.H.; Yuk, H.D. Enhanced Recovery after Surgery of Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Summary Statistics n = 121 | |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic Characteristics and Risk Factors | ||
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 69 (65;73) | |
| Sex, n (%) | F | 25 (20.66) |
| M | 96 (79.34) | |
| BMI, median (IQR) | 26.42 (22.8;29.1) | |
| Area of Residence, n (%) | rural | 42 (34.71) |
| urban | 79 (65.29) | |
| Smoker Status, n (%) | no | 31 (25.62) |
| yes | 90 (74.38) | |
| Number of Cigarettes, median (IQR) | 20 (20;25) | |
| Number of Years Smoking, median (IQR) | 21 (20;30) | |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | no | 40 (33.06) |
| yes | 81 (66.94) | |
| Blood Hypertension, n (%) | no | 80 (66.12) |
| yes | 41 (33.88) | |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | no | 88 (72.73) |
| yes | 33 (27.27) | |
| Pathological Characteristics | ||
| Histotype, n (%) | urothelial | 113 (93.39) |
| squamous | 4 (3.31) | |
| neuroendocrine | 2 (1.65) | |
| other | 2 (1.65) | |
| Grade, n (%) | low | 23 (20) |
| high | 92 (80) | |
| T, n (%) | T0 | 12 (9.92) |
| T1 | 27 (22.31) | |
| T2 | 33 (27.27) | |
| T3 | 31 (25.62) | |
| T4 | 18 (14.88) | |
| N, n (%) | N0 | 87 (71.9) |
| N1 | 10 (8.26) | |
| N2 | 11 (9.09) | |
| N3 | 1 (0.83) | |
| Nx | 12 (9.92) | |
| Pn, n (%) | absent | 12 (44.44) |
| present | 15 (55.56) | |
| Surgical Procedures and Treatment | ||
| Time from Diagnosis to Cystectomy (months), median (IQR) | 3 (2;5) | |
| Lymph Node Dissection, n (%) | no | 14 (11.57) |
| yes | 107 (88.43) | |
| Nerve Sparing, n (%) | none | 78 (82.98) |
| Unilateral | 5 (5.32) | |
| Bilateral | 11 (11.7) | |
| Type of Diversion, n (%) | Ureterostomy | 58 (47.93) |
| Ileal Conduit | 53 (43.8) | |
| Neobladder | 10 (8.26) | |
| Intra/Extracorporeal Diversion, n (%) | Intracorporeal | 57 (47.11) |
| Extracorporeal | 64 (52.89) | |
| Treatment, n (%) | NAC | 51 (42.86) |
| AC | 21 (17.65) | |
| Surgery only | 47 (39.5) | |
| Number of NAC Cycles, median (IQR) | 4 (3;4) | |
| Toxicity, n (%) | no | 76 (89.41) |
| yes | 9 (10.59) | |
| Need for Dose Reduction, n (%) | no | 57 (96.61) |
| yes | 2 (3.39) | |
| Total Operative Time (minutes), median (IQR) | 305 (200;370) | |
| Cystectomy Operative Time (minutes), median (IQR) | 150 (130;170) | |
| Lymphadenectomy Operative Time (minutes), median (IQR) | 50 (50;60) | |
| Urinary Diversion Operative Time (minutes), median (IQR) | 180 (160;200) | |
| Day of Mobilization, median (IQR) | 2 (1;2) | |
| Day of First Bowel Movement, median (IQR) | 3 (3;5) | |
| Number of Postoperative Hospital Days, median (IQR) | 8 (6;11) | |
| Days to Catheter Removal in Patients with Neobladder, median (IQR) | 27 (21;33) | |
| Days to Ureteral Stents Removal in Patients with Ileal Conduit, median (IQR) | 28 (23;30) | |
| Complications | ||
| Estimated Blood Loss (ml), median (IQR) | 250 (200;400) | |
| Intraoperative Transfusion, n (%) | no | 119 (98.35) |
| yes | 2 (1.65) | |
| Preoperative Transfusions, n (%) | no | 94 (77.69) |
| yes | 27 (22.31) | |
| Postoperative Transfusions, n (%) | no | 90 (74.38) |
| yes | 31 (25.62) | |
| Intraoperative Complications, n (%) | no | 108 (89.26) |
| yes | 13 (10.74) | |
| Postsurgical Complications, n (%) | no | 110 (90.91) |
| yes | 11 (9.09) | |
| Clavien Classification, n (%) | 1 | 18 (22.78) |
| 2 | 42 (53.16) | |
| 3 | 15 (18.99) | |
| >3 | 4 (5.06) | |
| Rehospitalization, n (%) | no | 76 (62.81) |
| yes | 45 (37.19) | |
| Need for Surgical Reintervention, n (%) | no | 117 (96.69) |
| yes | 4 (3.31) | |
| Follow-up | ||
| Recurrence Site, n (%) | none | 77 (64.16) |
| local | 11 (9.17) | |
| distant | 26 (21.67) | |
| local and distant | 6 (5) | |
| OS | PFS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Demographic characteristics and risk factors | |||||
| Age | 1.03 (0.99;1.07) | 0.140 | 1.03 (1;1.07) | 0.056 | |
| Sex, M vs. F | 0.41 (0.23;0.76) | 0.004 | 0.6 (0.32;1.12) | 0.111 | |
| BMI | 1 (1;1) | 0.136 | 1 (1;1) | 0.415 | |
| Smoker status, yes vs. no | 0.72 (0.39;1.32) | 0.285 | 1.27 (0.65;2.49) | 0.483 | |
| Number of cigarettes | 1 (0.97;1.04) | 0.868 | 1 (0.97;1.03) | 0.942 | |
| Number of years smoking | 0.99 (0.95;1.03) | 0.684 | 0.98 (0.94;1.02) | 0.374 | |
| Comorbidities, present vs. absent | 0.74 (0.41;1.32) | 0.305 | 0.51 (0.29;0.89) | 0.018 | |
| Blood hypertension, present vs. absent | 0.92 (0.5;1.7) | 0.790 | 1.3 (0.71;2.37) | 0.389 | |
| Diabetes mellitus, present vs. absent | 0.92 (0.48;1.74) | 0.788 | 0.95 (0.5;1.8) | 0.880 | |
| Pathological characteristics | |||||
| Grade, high vs. low | 2.14 (0.90;5.05) | 0.082 | 1.70 (0.72;4) | 0.225 | |
| LVI, present vs. absent | 2.22 (1.25;3.94) | 0.006 | 1.8 (1.03;3.14) | 0.038 | |
| T stage, 2+ vs. <2 | 8.75 (2.72;28.22) | <0.001 | 5.4 (2.13;13.71) | <0.001 | |
| N stage, N+ vs. N0 | 1.1 (1.01;1.2) | 0.030 | 1.07 (0.99;1.17) | 0.099 | |
| Incidental prostate cancer, present vs. absent | 0.64 (0.29;1.43) | 0.273 | 0.73 (0.35;1.5) | 0.388 | |
| Surgical procedures and treatment | |||||
| Lymph node dissection, yes vs. no | 0.4 (0.19;0.83) | 0.013 | 0.64 (0.3;1.37) | 0.249 | |
| Nerve sparing, yes vs. no | 0.24 (0.06;0.99) | 0.049 | 0.27 (0.08;0.88) | 0.03 | |
| Urinary diversion type (ref = ureterostomy) | Ileal Conduit | 0.3 (0.15;0.6) | 0.001 | 0.42 (0.22;0.77) | 0.005 |
| Neobladder | 0.43 (0.1;1.78) | 0.243 | 0.56 (0.17;1.82) | 0.334 | |
| Urinary diversion intra/extracorporeal, yes vs. no | 0.36 (0.19;0.66) | 0.001 | 0.43 (0.24;0.77) | 0.005 | |
| Total surgery duration | 1 (0.99;1) | 0.002 | 1 (0.99;1) | 0.105 | |
| Cystectomy duration | 1 (0.99;1.01) | 0.663 | 1.01 (1;1.02) | 0.038 | |
| PLND duration | 0.98 (0.96;1) | 0.105 | 1.01 (0.99;1.03) | 0.203 | |
| Urinary diversion duration | 1 (0.98;1.01) | 0.655 | 1.01 (1;1.02) | 0.265 | |
| Number of days in hospital | 0.98 (0.92;1.04) | 0.445 | 1.02 (0.97;1.08) | 0.337 | |
| Days to Catheter removal (patients with neobladder) | 1 (0.95;1.06) | 0.983 | 1.04 (1;1.1) | 0.071 | |
| Days to Urinary catheter removal (patients with ileal conduit) | 1.03 (0.79;1.33) | 0.845 | 0.89 (0.76;1.05) | 0.167 | |
| Received CHT, yes vs. no | 1.15 (0.63;2.09) | 0.640 | 0.53 (0.3;0.94) | 0.030 | |
| Complications | |||||
| Quantity of blood lost | 1 (1;1) | 0.226 | 1 (1;1) | 0.561 | |
| Transfusion—during surgery, received vs. no | 20.75 (4.17;103.39) | <0.001 | 3.13 (0.42;23.58) | 0.268 | |
| Transfusion—after surgery, received vs. no | 1.26 (0.64;2.48) | 0.499 | 1.48 (0.8;2.76) | 0.211 | |
| Number of days to mobilization | 1.12 (0.8;1.57) | 0.519 | 0.9 (0.65;1.25) | 0.545 | |
| Number of days to bowel movement | 1.03 (0.8;1.33) | 0.811 | 1.09 (0.87;1.38) | 0.445 | |
| Intraoperative complications, present vs. absent | 3.04 (1.46;6.34) | 0.003 | 1.11 (0.44;2.82) | 0.818 | |
| Postsurgical complications, present vs. absent | 1.79 (0.76;4.23) | 0.183 | 0.9 (0.32;2.51) | 0.844 | |
| Clavien classification (ref = no complication) | 1 | 0.97 (0.4;2.34) | 0.948 | 1.43 (0.66;3.11) | 0.369 |
| 2 | 1.25 (0.64;2.43) | 0.509 | 1.02 (0.52;2) | 0.958 | |
| ≥3 | 0.54 (0.2;1.46) | 0.222 | 0.63 (0.24;1.61) | 0.333 | |
| Rehospitalization, yes vs. no | 1.23 (0.69;2.2) | 0.475 | 1.57 (0.9;2.75) | 0.112 | |
| Need for surgical reintervention, yes vs. no | 1.44 (0.35;5.98) | 0.611 | 0.74 (0.18;3.07) | 0.682 | |
| Follow-up | |||||
| Recurrence within the first year, yes vs. no | 2.28 (1.29;4.05) | 0.005 | |||
| Recurrence site (ref = none) | local | 2.5 (0.98;6.35) | 0.055 | ||
| distant | 3.54 (1.82;6.89) | <0.001 | |||
| local and distant | 6.62 (2.41;18.19) | <0.001 | |||
| Parameter | Original Index | Training | Test | Optimism | Corrected Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dxy. Somers’ D rank correlation | 0.533 | 0.551 | 0.501 | 0.050 | 0.483 |
| R2. Explained variation | 0.300 | 0.343 | 0.268 | 0.076 | 0.225 |
| Calibration slope | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.777 | 0.223 | 0.777 |
| D. Discrimination index | 0.098 | 0.118 | 0.086 | 0.032 | 0.066 |
| U. Unreliability index | −0.005 | −0.005 | 0.015 | −0.020 | 0.015 |
| Q. Quality index | 0.103 | 0.123 | 0.070 | 0.052 | 0.051 |
| g. Goodness-of-fit | 1.342 | 1.636 | 1.185 | 0.451 | 0.891 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulf, D.-V.; Burnar, A.L.; Dulf, P.-L.; Matei, D.-R.; Maria, H.R.; Bungărdean, C.; Buzoianu, M.; Andraș, I.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Crișan, N.; et al. Risk Stratification Using a Perioperative Nomogram for Predicting the Mortality of Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165810
Dulf D-V, Burnar AL, Dulf P-L, Matei D-R, Maria HR, Bungărdean C, Buzoianu M, Andraș I, Ciuleanu T-E, Crișan N, et al. Risk Stratification Using a Perioperative Nomogram for Predicting the Mortality of Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165810
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulf, Daniel-Vasile, Anamaria Larisa Burnar, Patricia-Lorena Dulf, Doina-Ramona Matei, Hendea Raluca Maria, Cătălina Bungărdean, Maximilian Buzoianu, Iulia Andraș, Tudor-Eliade Ciuleanu, Nicolae Crișan, and et al. 2025. "Risk Stratification Using a Perioperative Nomogram for Predicting the Mortality of Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165810
APA StyleDulf, D.-V., Burnar, A. L., Dulf, P.-L., Matei, D.-R., Maria, H. R., Bungărdean, C., Buzoianu, M., Andraș, I., Ciuleanu, T.-E., Crișan, N., & Coadă, C. A. (2025). Risk Stratification Using a Perioperative Nomogram for Predicting the Mortality of Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165810







