Phenotyping Fatigue Profiles in Marfan Syndrome Through Cluster Analysis: A Cross-Sectional Study of Psychosocial and Clinical Correlates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Sample Size
2.3. Setting and Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Measures
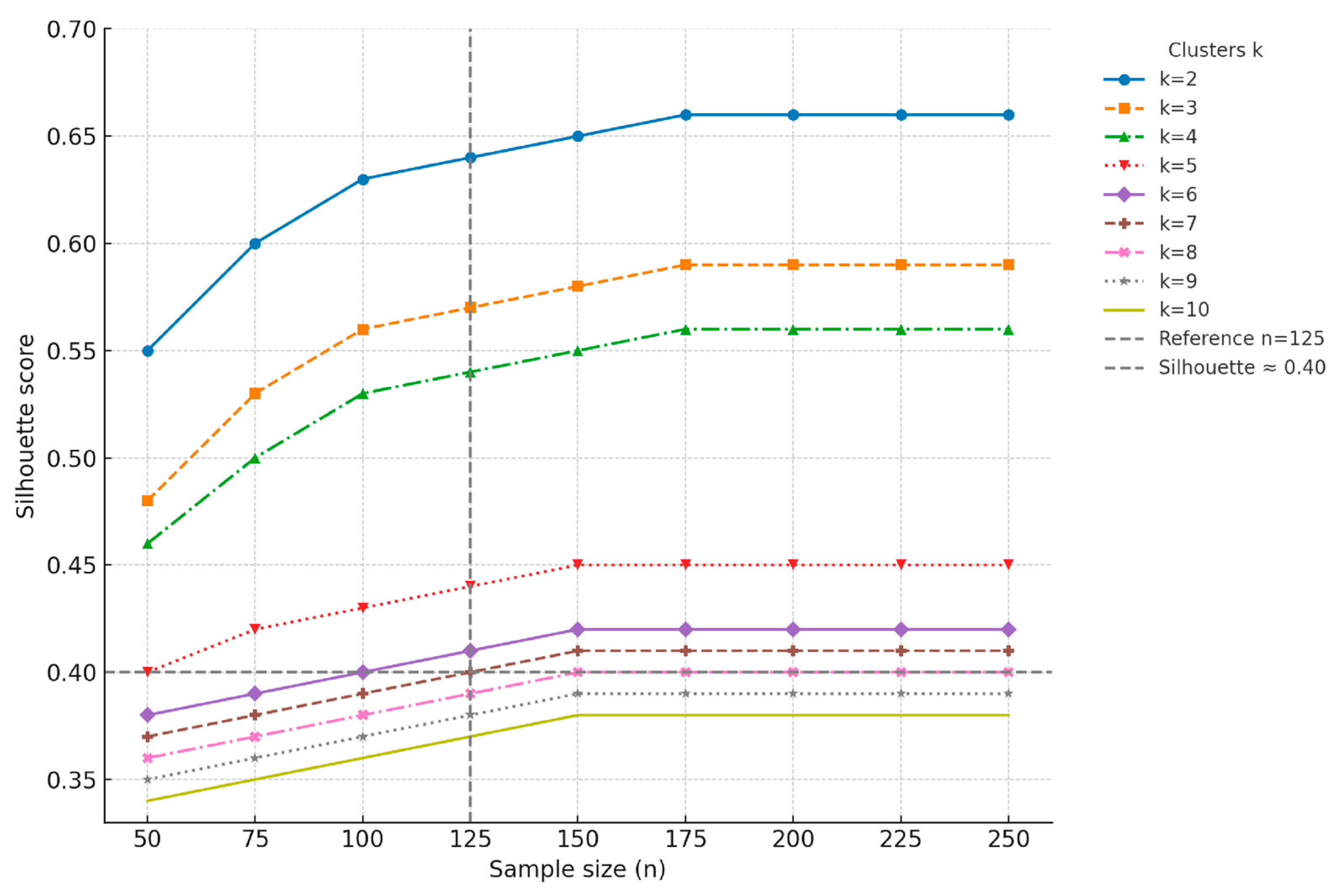
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
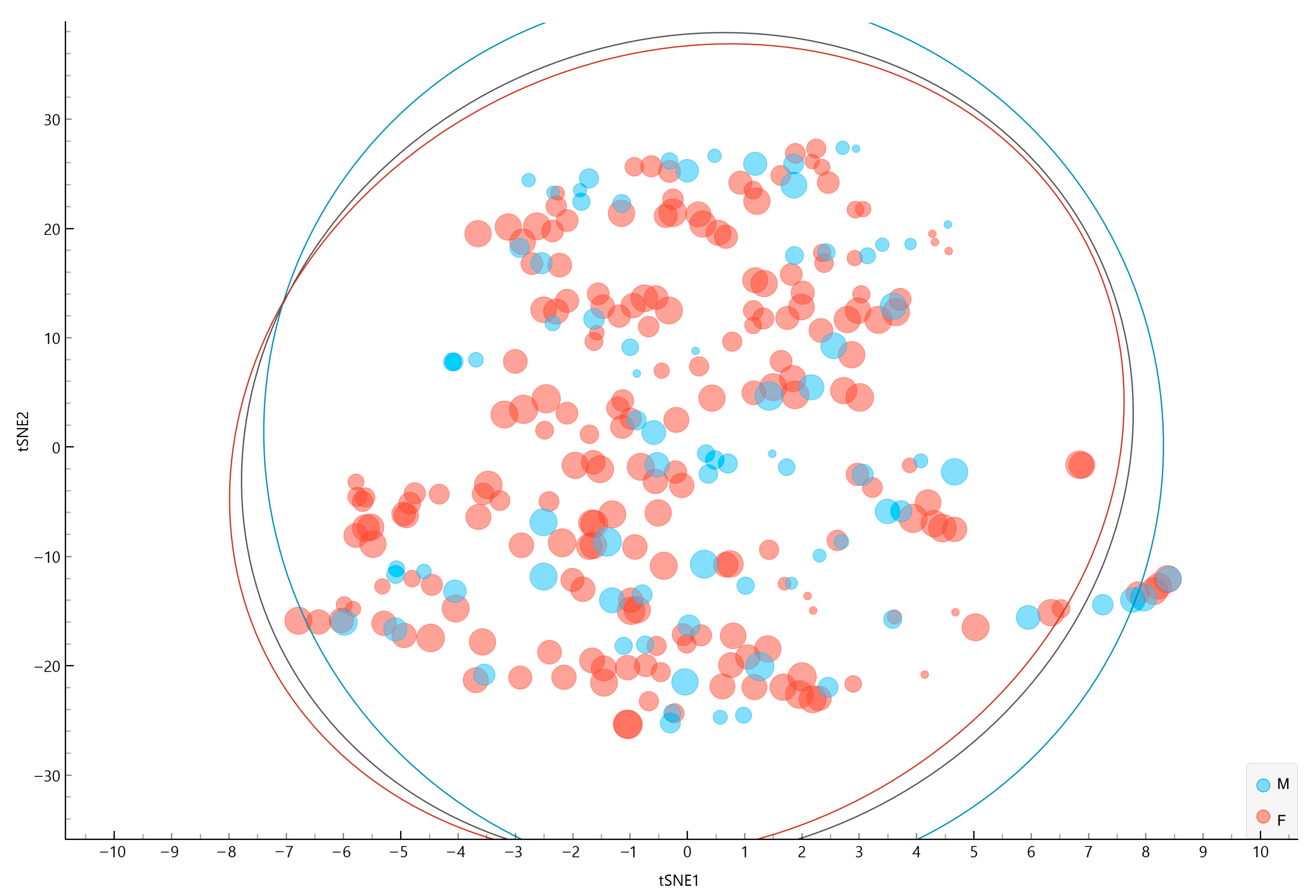
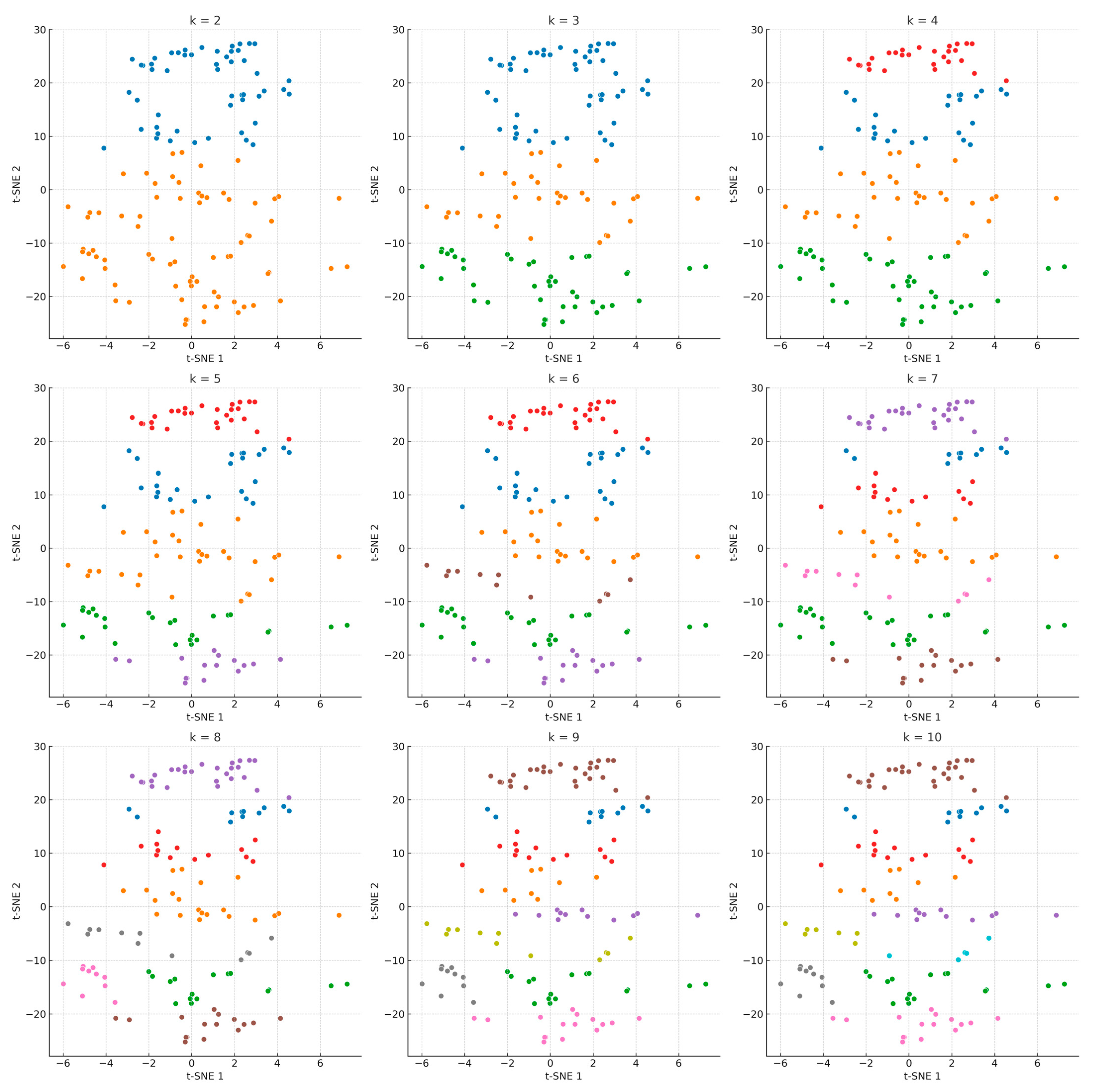
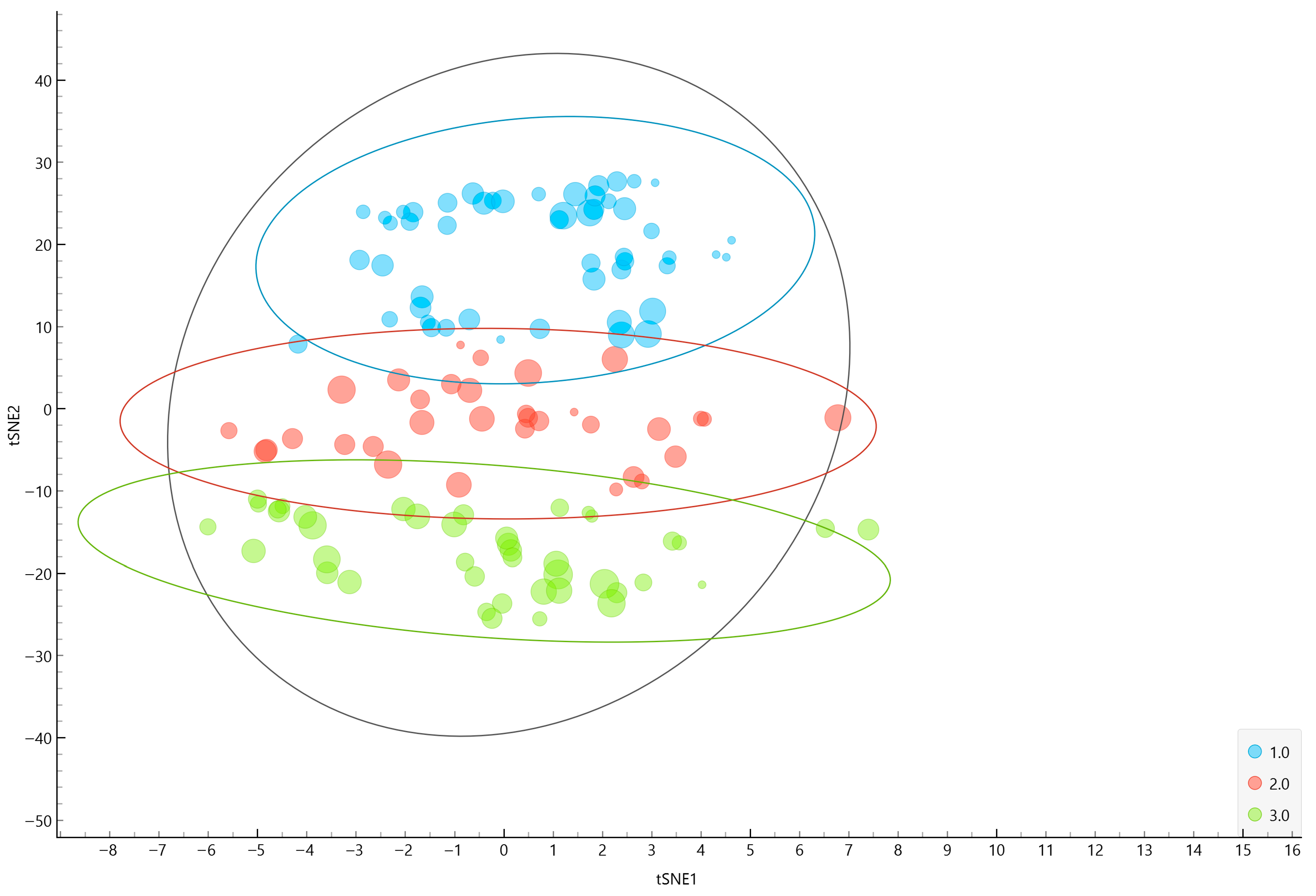
3.2. t-SNE
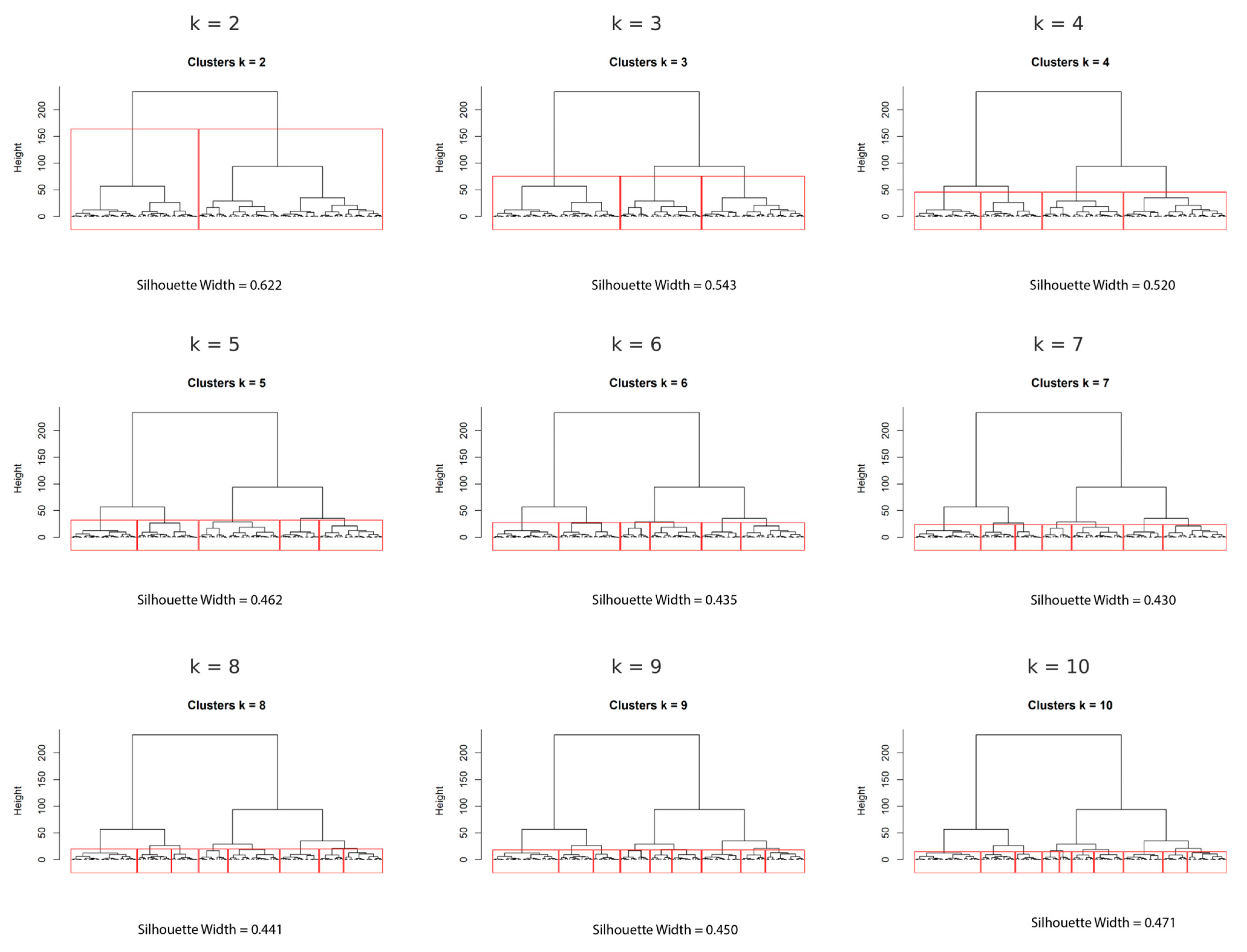
3.3. Hierarchical Clustering
Optimal Cluster Solution
3.4. Exploratory Associations Between Age, Psychosocial Factors, and Fatigue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MFS | Marfan Syndrome |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| FSS | Fatigue Severity Scale |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
| ISI | Insomnia Severity Index |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| t-SNE | t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding |
References
- Warnink-Kavelaars, J.; De Koning, L.; Rombaut, L.; Alsem, M.; Menke, L.; Oosterlaan, J.; Buizer, A.; Engelbert, R.; on behalf of the Pediatric Heritable Connective Tissue Disorders Study Group. Heritable Connective Tissue Disorders in Childhood: Increased Fatigue, Pain, Disability and Decreased General Health. Genes 2021, 12, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnink-Kavelaars, J.; De Koning, L.E.; Rombaut, L.; Menke, L.A.; Alsem, M.W.; Van Oers, H.A.; Buizer, A.I.; Engelbert, R.H.H.; Oosterlaan, J.; Pediatric Heritable Connective Tissue Disorder study group. Heritable Connective Tissue Disorders in Childhood: Decreased Health-related Quality of Life and Mental Health. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 2096–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, S.; Micaglio, E.; Taurino, J.; Salvi, P.; Rurali, E.; Perrucci, G.L.; Dolci, C.; Udugampolage, N.S.; Caruso, R.; Gentilini, D.; et al. Marfan Syndrome: Enhanced Diagnostic Tools and Follow-up Management Strategies. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeys, B.L.; Dietz, H.C.; Braverman, A.C.; Callewaert, B.L.; De Backer, J.; Devereux, R.B.; Hilhorst-Hofstee, Y.; Jondeau, G.; Faivre, L.; Milewicz, D.M.; et al. The Revised Ghent Nosology for the Marfan Syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.-H. An Update of Medical Care in Marfan Syndrome. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2022, 34, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, C.; Fongwen, N.T.; Chobufo, M.D.; Ajibade, A.; Roberts, M.; Greathouse, M.; Ngonge, A.L.; Adekolu, A.; Hamirani, Y.S. Frequency of Cardiac Valvulopathies in Patients With Marfan Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e54141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, S.; Lew, A.; Sokol, S.; Jalali, P.; Andres, U.; Olski, D. Early Cardiac Intervention Decreases the Mortality Risk Linked With Marfan Syndrome. Cureus 2025, 17, e82910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugampolage, N.; Taurino, J.; Bassotti, A.; Pini, A.; Caruso, R.; Callus, E.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; De Angeli, G.; Paglione, G.; et al. Exploring Fatigue in Marfan and Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study in Two Italian Healthcare Centres. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e087298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugampolage, N.; Caruso, R.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; Callus, E.; Dellafiore, F.; Pittella, F.; Arrigoni, C.; Taurino, J.; Pini, A. Self-Care Behaviors and Their Individual-Level Determinants in Italian Adults with Marfan Syndrome: A Single-Center Cross-Sectional Study. Appl. Nurs. Res. ANR 2024, 78, 151821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, N.L.; Kainth, G.S.; Johnson, M.; Rangan, A.; Kottam, L.; Swainston, K. Psychological Interventions to Improve Pain, Fatigue, Anxiety, Depression, and Quality of Life in Children and Adults with Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 44, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Kong, F.; Horne, R.; Francomano, C.; Biesecker, B. Living with Marfan Syndrome I. Perceptions of the Condition. Clin. Genet. 2001, 60, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.-M.; Jing, H. Marfan’s Syndrome: An Overview. Sao Paulo Med. J. (Rev. Paul. Med.) 2010, 128, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, S.M.; Sloan, B.; Jones, J.A. Pathophysiology and Pathogenesis of Marfan Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1348, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, H.M.; Niaz, T.; Bowen, J.M. What Is Marfan Syndrome? JAMA 2023, 329, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M. Marfan Syndrome. Nursing 2024, 54, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugampolage, N.; Caruso, R.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; Callus, E.; Taurino, J.; Pini, A. Describing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Its Associations with Depression, Anxiety and Insomnia: A Descriptive Study in Italian Adults with Marfan Syndrome during the COVID-19 Third Wave. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e067024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanem, T.T.; Rand-Hendriksen, S.; Brunborg, C.; Geiran, O.R.; Røe, C. Health-Related Quality of Life in Marfan Syndrome: A 10-Year Follow-Up. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugampolage, N.; Caruso, R.; Panetta, M.; Callus, E.; Dellafiore, F.; Magon, A.; Marelli, S.; Pini, A. Is SF-12 a Valid and Reliable Measurement of Health-Related Quality of Life among Adults with Marfan Syndrome? A Confirmatory Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, M.; Bianchetti, A.; Udugampolage, N.S.; Taurino, J.; Caruso, R.; Pini, A.; Callus, E. Discussing Psychological and Psychotherapeutic Support for Patients with Marfan Syndrome (MFS) and Their Family: An Example of a Structured Program in Italy. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1176692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathen, T.; Velvin, G.; Rand-Hendriksen, S.; Robinson, H.S. Fatigue in Adults with Marfan Syndrome, Occurrence and Associations to Pain and Other Factors. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.; Crettenden, A.; Evans, K.; Thiessen, M.; Toohey, M.; Watson, A.; Dollman, J. Fatigue Is a Major Issue for Children and Adolescents with Physical Disabilities. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velvin, G.; Johansen, H.; Østertun-Geirdal, A.; Bathen, T. Fatigue in Patients with Syndromic Heritable Thoracic Aortic Disease: A Systematic Review of the Literature and a Qualitative Study of Patients’ Experiences and Perceptions. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voermans, N.C.; Knoop, H.; Bleijenberg, G.; Van Engelen, B.G. Fatigue Is Associated with Muscle Weakness in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: An Explorative Study. Physiotherapy 2011, 97, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylow, H.E.; Esfandiarei, M.; Ratiu, I. Voice Symptoms and Quality of Life in Individuals With Marfan Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Voice Off. J. Voice Found. 2024, 38, 1254.e1–1254.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voermans, N.C.; Knoop, H.; van de Kamp, N.; Hamel, B.C.; Bleijenberg, G.; van Engelen, B.G. Fatigue Is a Frequent and Clinically Relevant Problem in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 40, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy For Insomnia (CBT-I) Across The Life Span: Guidelines and Clinical Protocols for Health Professionals, 1st ed.; Baglioni, C., Espie, C.A., Riemann, D., European Sleep Research Society, European Insomnia Network, European Academy for Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Insomnia, Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-119-78513-2. [Google Scholar]
- van Andel, M.M.; Graaumans, K.; Groenink, M.; Zwinderman, A.H.; van Kimmenade, R.R.J.; Scholte, A.J.H.A.; van den Berg, M.P.; Dickinson, M.G.; Knoop, H.; Bosch, J.A.; et al. A Cross-Sectional Study on Fatigue, Anxiety, and Symptoms of Depression and Their Relation with Medical Status in Adult Patients with Marfan Syndrome. Psychological Consequences in Marfan Syndrome. Clin. Genet. 2022, 102, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonian, C.; Freilinger, S.; Achenbach, S.; Ewert, P.; Gundlach, U.; Kaemmerer, H.; Nagdyman, N.; Neidenbach, R.C.; Pieper, L.; Schelling, J.; et al. Quality of Life in Patients with Marfan Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study of 102 Adult Patients. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 11, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, H.E.C.; Critchley, H.D.; Eccles, J.A. Connecting Brain and Body: Transdiagnostic Relevance of Connective Tissue Variants to Neuropsychiatric Symptom Expression. World J. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, E.K.S.; Fischer, A.L.; Manocha, R.H.K. Depressive Symptoms Are Highly Prevalent and Associated with Fatigue and Pain Catastrophizing in the Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders and Hypermobile Ehlers Danlos Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2025, 45, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieste, L.; Cannizzo, S.; Palla, I.; Triulzi, I.; Turchetti, G. State of the Art and Future Directions in Assessing the Quality of Life in Rare and Complex Connective Tissue and Musculoskeletal Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 986218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier, I.; Kamga, L.T.; Morin, L.; Bal, L.; Faivre, L.; Jondeau, G.; Tran, V.-T.; Milleron, O. Determinants of Fatigue in Patients with Marfan Syndrome: A Study Using PROMS. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2025, 20, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Gube, M.; Chaabene, H.; Prieske, O.; Zenon, A.; Broscheid, K.-C.; Schega, L.; Husmann, F.; Weippert, M. Fatigue and Human Performance: An Updated Framework. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G.W. A Review Of Monte Carlo Tests Of Cluster Analysis. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1981, 16, 379–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervan, D.; Coronado, A.M.; Luyo, J.E. Cluster-Based Stratified Sampling for Fast Reliability Evaluation of Composite Power Systems Based on Sequential Monte Carlo Simulation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 147, 108813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugampolage, N.S.; Pini, A.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; Callus, E.; Taurino, J.; Caruso, R. COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy in Italian Adults with Marfan Syndrome: Insights from a Secondary Analysis of a Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Minor, B.L.; Elliott, V.; Fernandez, M.; O’Neal, L.; McLeod, L.; Delacqua, G.; Delacqua, F.; Kirby, J.; et al. The REDCap Consortium: Building an International Community of Software Platform Partners. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 95, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janßen, R.; Kesler, R.; Kummer, M.; Waldfogel, J. GDPR and the Lost Generation of Innovative Apps; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; p. w30028. [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano, M.; Chiorri, C.; De Micco, R.; Russo, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Trojano, L.; Tessitore, A. Fatigue in Parkinson’s Disease: Italian Validation of the Parkinson Fatigue Scale and the Fatigue Severity Scale Using a Rasch Analysis Approach. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 65, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Pasquarella, C.; Odone, A.; Colucci, M.E.; Costanza, A.; Serafini, G.; Aguglia, A.; Belvederi Murri, M.; Brakoulias, V.; Amore, M.; et al. Screening for Depression in Primary Care with Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9): A Systematic Review. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 279, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castronovo, V.; Galbiati, A.; Marelli, S.; Brombin, C.; Cugnata, F.; Giarolli, L.; Anelli, M.M.; Rinaldi, F.; Ferini-Strambi, L. Validation Study of the Italian Version of the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI). Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlits, J.; McAfee, S.; Taylor, J.-A.; Shum, E.; Yang, Q.; Nunez, E.; Kameron, K.; Fenech, K.; Rodriguez, J.; Torri, A.; et al. Statistical Approaches for Establishing Appropriate Immunogenicity Assay Cut Points: Impact of Sample Distribution, Sample Size, and Outlier Removal. AAPS J. 2023, 25, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anowar, F.; Sadaoui, S.; Selim, B. Conceptual and Empirical Comparison of Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms (PCA, KPCA, LDA, MDS, SVD, LLE, ISOMAP, LE, ICA, t-SNE). Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajal, E.; Katara, V.; Bhatia, M.; Hooda, M. A Review of Clustering Algorithms: Comparison of DBSCAN and K-Meanwith Oversampling and t-SNE. Recent Pat. Eng. 2022, 16, e180122191239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Xi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Comprehensive Survey on Hierarchical Clustering Algorithms and the Recent Developments. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 8219–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, F.; Caruso, R.; Notarnicola, I.; Belloni, S.; De Maria, M.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; Prendi, E.; Pata, X.; Duka, B.; et al. Analyzing Readiness for Interprofessional Education among Health Program Students Using Hierarchical Clustering. J. Interprof. Care 2025, 39, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aert, R.C.M. Meta-Analyzing Partial Correlation Coefficients Using Fisher’s z Transformation. Res. Synth. Methods 2023, 14, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanidis, Z.; Kotsiou, O.S. The Impact of Chronic Fatigue on Psychopathology in Outpatient Physiotherapy Patients. Musculoskeletal Care 2025, 23, e70116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, C.; Schlueter, A. Review of Data-Driven Energy Modelling Techniques for Building Retrofit. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahe, A.M.; Adams, R.D.; Nicholson, L.L. Features That Exacerbate Fatigue Severity in Joint Hypermobility Syndrome/Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome—Hypermobility Type. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Kartoun, U.; Stavropoulos, H.; Zambrano, J.A.; Tang, P.C. Personalized Treatment Options for Chronic Diseases Using Precision Cohort Analytics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.T.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Heitkemper, E.M.; Choi, E.; Burgermaster, M. Psychosocial Phenotyping as a Personalization Strategy for Chronic Disease Self-Management Interventions. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 1617–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Zein Abdin, Z.; Yin, H.; Giannis, C.; Hsieh, R.; Pickering, J.G.; Chandy, M. Harnessing iPSCs to Model Marfan Syndrome: Advancing Clinical Diagnosis and Drug Discovery. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouini, S.; Milleron, O.; Eliahou, L.; Jondeau, G.; Vitiello, D. Is Physical Activity a Future Therapy for Patients with Marfan Syndrome? Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouini, S.; Milleron, O.; Eliahou, L.; Jondeau, G.; Vitiello, D. Effects of a Personalized Home-Based Training Program among Patients Suffering from Marfan Syndrome: A Pilot Randomized and Controlled Study. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2021, 10, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öcalan, S.; Üzar-Özçetin, Y.S. The Relationship between Rumination, Fatigue and Psychological Resilience among Cancer Survivors. J. Clin. Nurs. 2022, 31, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, F. Accounting for Research Fatigue in Research Ethics. Bioethics 2021, 35, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaes, A.W.; Goërtz, Y.M.J.; Van Herck, M.; Beijers, R.J.H.C.G.; Van Beers, M.; Burtin, C.; Janssen, D.J.A.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Spruit, M.A. Physical and Mental Fatigue in People with Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbitan, L.; Alzraikat, N.; Tanous, H.; Saad, A.M.; Odeh, M. From One Size Fits All to a Tailored Approach: Integrating Precision Medicine into Medical Education. BMC Med. Educ. 2025, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, P.V. Beyond One Size Fits All—Personalised Prevention Strategies Using Physical Activity: Editorial. Eur. J. Physiother. 2024, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purgato, M.; Singh, R.; Acarturk, C.; Cuijpers, P. Moving beyond a ‘One-Size-Fits-All’ Rationale in Global Mental Health: Prospects of a Precision Psychology Paradigm. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2021, 30, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 61 (48%) | |
| Female | 66 (52%) | |
| Age | ||
| Years (mean ± SD) | 38.75 ± 14.06 | |
| Primary school | 2 (1.6%) | |
| Lower secondary school | 30 (23.6%) | |
| Higher secondary school | 48 (37.8%) | |
| University | 47 (37.0%) | |
| Years since diagnosis, median (IQR) | 13 (7–23) | |
| Profession | ||
| Active worker—office | 71 (55.9%) | |
| Active worker—home | 8 (6.3%) | |
| Occasional worker | 3 (2.4%) | |
| Retired | 3 (2.4%) | |
| Unemployed | 42 (33.1%) | |
| Cardiovascular comorbidities | 102 (80.3%) | |
| Hypertension | 11 (8.7%) | |
| Cardiovascular medications | 97 (76.4%) | |
| Respiratory diseases | 18 (14.2%) | |
| Other diseases | 104 (81.9%) | |
| Visual impairments | 56 (44.1%) | |
| Thyroid dysfunction | 12 (11.5%) | |
| Neuropathies | 3 (2.9%) | |
| Joint diseases | 8 (7.7%) | |
| Scoliosis | 71 (68.3%) | |
| Multiple conditions | 1 (0.96%) | |
| BMI | ||
| kg/m2 (median; IQR) | 21.33 (19.11–23.41) | |
| PHQ-9 | ||
| Score (mean ± SD) | 6.01 ± 4.51 | |
| No depressive symptoms | 52 (40.9%) | |
| Minimal depressive symptoms | 54 (42.5%) | |
| Minor depression | 15 (11.8%) | |
| Moderate major depression | 4 (3.1%) | |
| Severe major depression | 2 (1.6%) | |
| ISI | ||
| Score (mean ± SD) | 7.02 ± 4.13 | |
| No clinically significant insomnia | 78 (61.4%) | |
| Subthreshold insomnia | 43 (33.9%) | |
| Clinical insomnia (moderate) | 6 (4.7%) | |
| FSS | ||
| Score (mean ± SD) | 3.88 ± 1.68 | |
| Clinically relevant fatigue | 40 (31.5%) | |
| Fatigue in the last two weeks | ||
| Never | 9 (7.6%) | |
| Sometimes | 80 (67.2%) | |
| Every day | 30 (25.2%) | |
| Fatigue pattern | ||
| In the morning | 25 (21.0%) | |
| In the afternoon | 78 (65.5%) | |
| All day | 16 (13.4%) | |
| Characteristic | Cluster 1 (N = 49) | Cluster 2 (N = 32) | Cluster 3 (N = 46) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 22.6 ± 3.1 | 36.4 ± 5.9 | 53.5 ± 6.1 | <0.001 |
| Years since diagnosis (median, IQR) | 8.6 (6.6–10.0) | 12.1 (9.7–15.0) | 15.6 (13.7–19.0) | 0.0027 |
| BMI (median, IQR) | 20.0 (18.4–21.4) | 21.8 (19.5–23.6) | 23.9 (22.5–25.6) | <0.001 |
| Sex: male | 20 (40.8) | 17 (53.1) | 24 (52.2) | 0.137 |
| Sex: female | 14 (59.2) | 23 (46.9) | 29 (47.8) | |
| PHQ-9 (mean ± SD) | 3.5 ± 2.6 | 5.8 ± 3.7 | 7.2 ± 3.6 | 0.016 |
| No depressive symptoms | 18 (36.7) | 15 (46.9) | 19 (41.3) | |
| Minimal depressive symptoms | 12 (24.5) | 16 (50.0) | 26 (56.5) | |
| Minor depression | 4 (8.2) | 5 (15.6) | 6 (13.0) | |
| Moderate major depression | 0 | 3 (9.4) | 1 (2.2) | |
| Severe major depression | 0 | 1 (3.1) | 1 (2.2) | |
| ISI (mean ± SD) | 4.3 ± 3.7 | 6.7 ± 4.5 | 8.8 ± 4.8 | 0.029 |
| No insomnia | 22 (44.9) | 23 (71.9) | 33 (71.79) | |
| Subthreshold insomnia | 11 (22.4) | 16 (50.0) | 17 (37.09) | |
| Clinical insomnia (moderate) | 1 (2.0) | 1 (3.1) | 3 (6.5) | |
| FSS (mean ± SD) | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 3.5 ± 1.1 | 4.9 ± 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Clinically relevant fatigue | 0 | 9 (25.1) | 31 (67.4) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Udugampolage, N.S.; Taurino, J.; Pini, A.; Callus, E.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; De Angeli, G.; Angolani, M.; Paglione, G.; Baroni, I.; et al. Phenotyping Fatigue Profiles in Marfan Syndrome Through Cluster Analysis: A Cross-Sectional Study of Psychosocial and Clinical Correlates. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165802
Udugampolage NS, Taurino J, Pini A, Callus E, Magon A, Conte G, De Angeli G, Angolani M, Paglione G, Baroni I, et al. Phenotyping Fatigue Profiles in Marfan Syndrome Through Cluster Analysis: A Cross-Sectional Study of Psychosocial and Clinical Correlates. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165802
Chicago/Turabian StyleUdugampolage, Nathasha Samali, Jacopo Taurino, Alessandro Pini, Edward Callus, Arianna Magon, Gianluca Conte, Giada De Angeli, Miriam Angolani, Giulia Paglione, Irene Baroni, and et al. 2025. "Phenotyping Fatigue Profiles in Marfan Syndrome Through Cluster Analysis: A Cross-Sectional Study of Psychosocial and Clinical Correlates" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165802
APA StyleUdugampolage, N. S., Taurino, J., Pini, A., Callus, E., Magon, A., Conte, G., De Angeli, G., Angolani, M., Paglione, G., Baroni, I., Iozzo, P., & Caruso, R. (2025). Phenotyping Fatigue Profiles in Marfan Syndrome Through Cluster Analysis: A Cross-Sectional Study of Psychosocial and Clinical Correlates. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165802






