Efficacy and Safety of Esaxerenone for Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Extraction and Analysis
3. Results
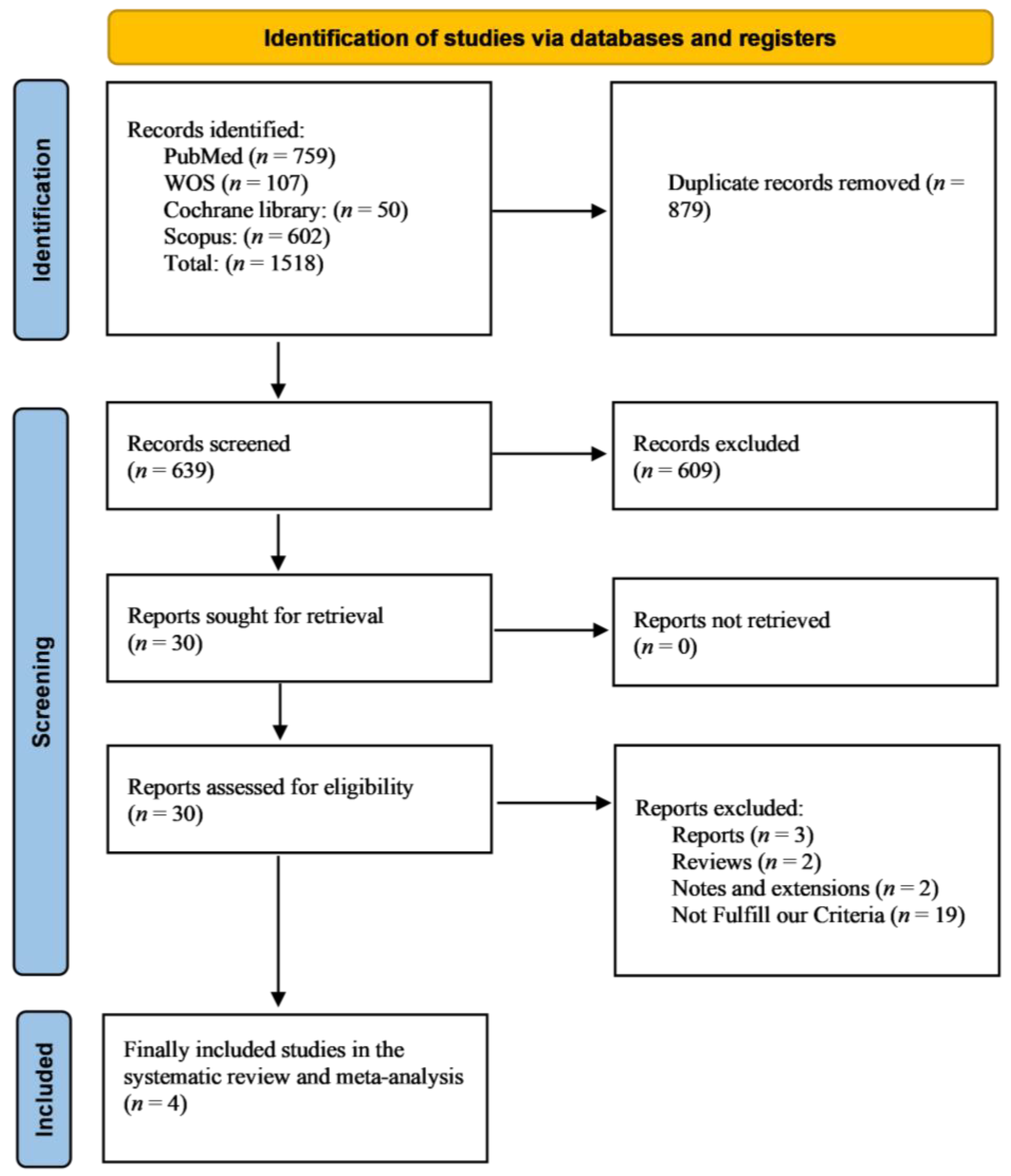
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics
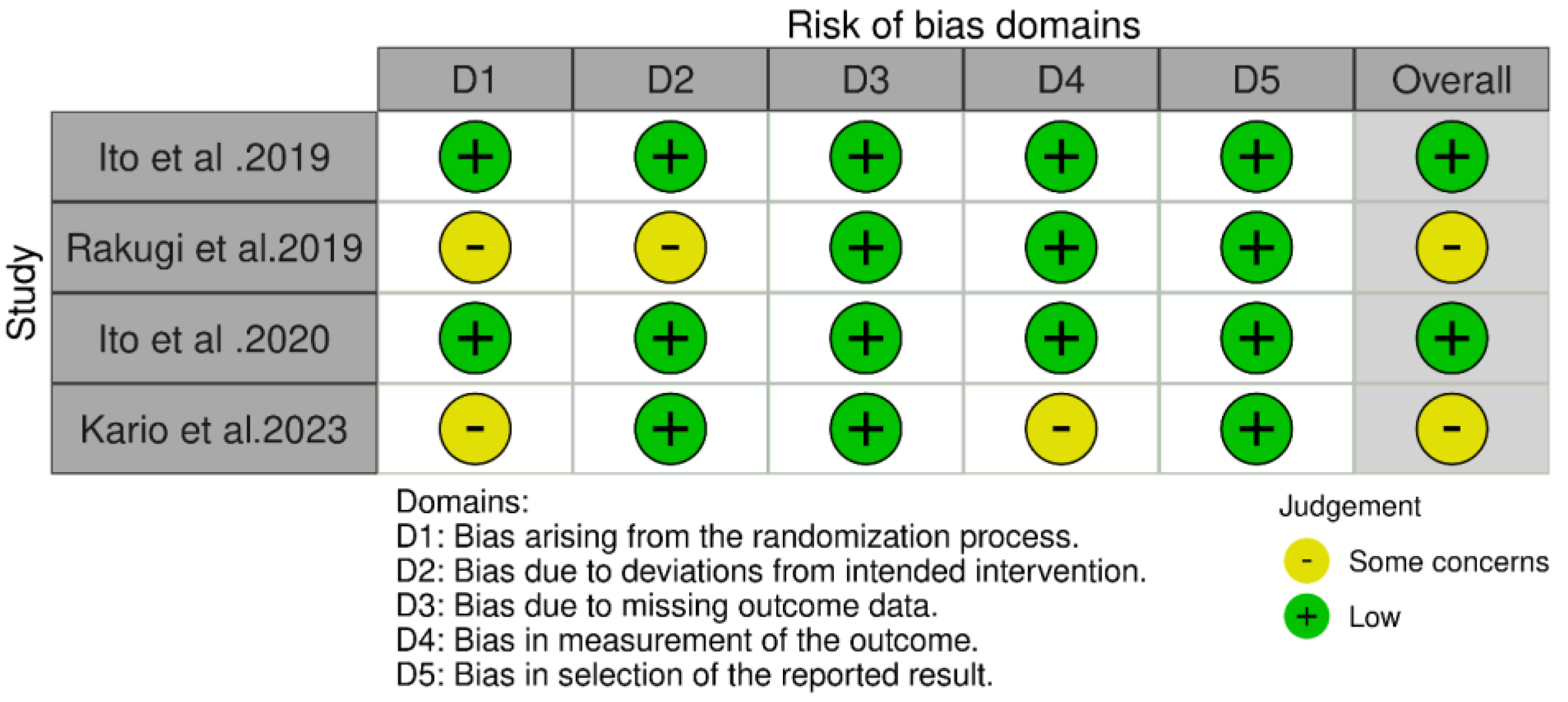
3.3. Quality Assessment
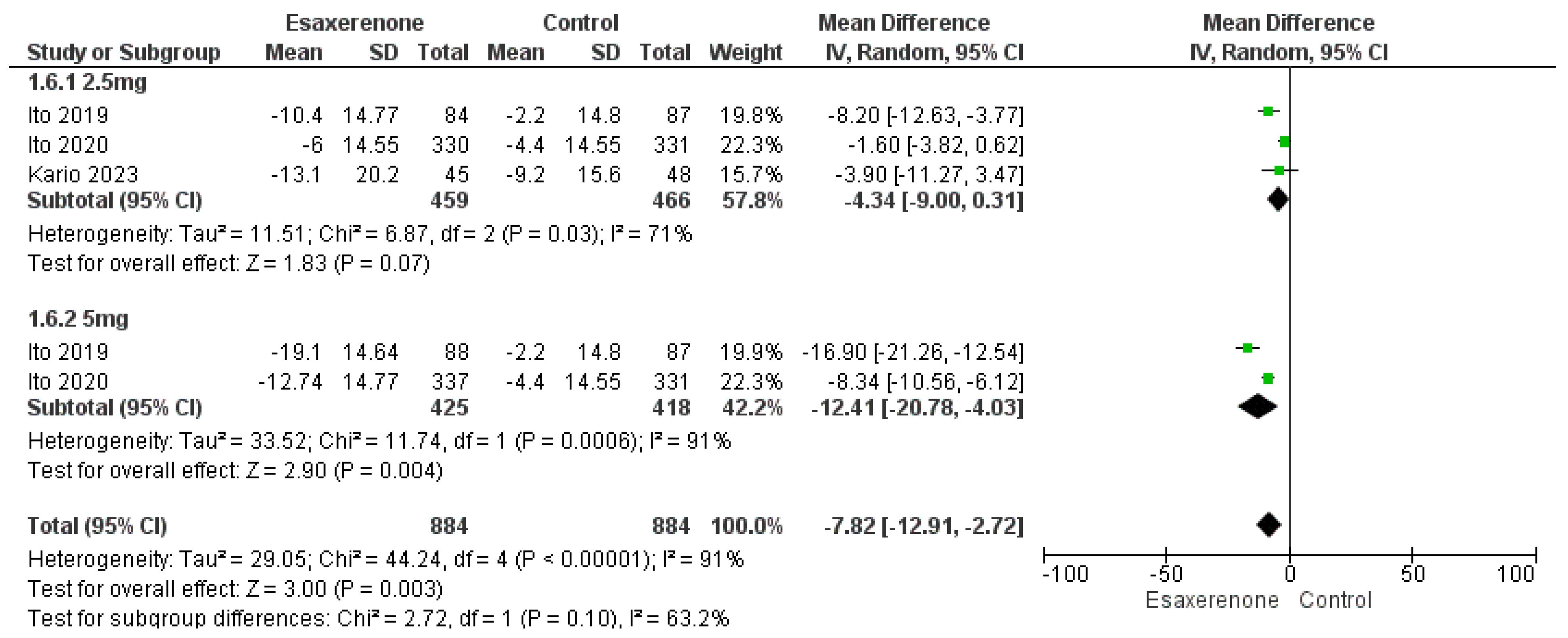
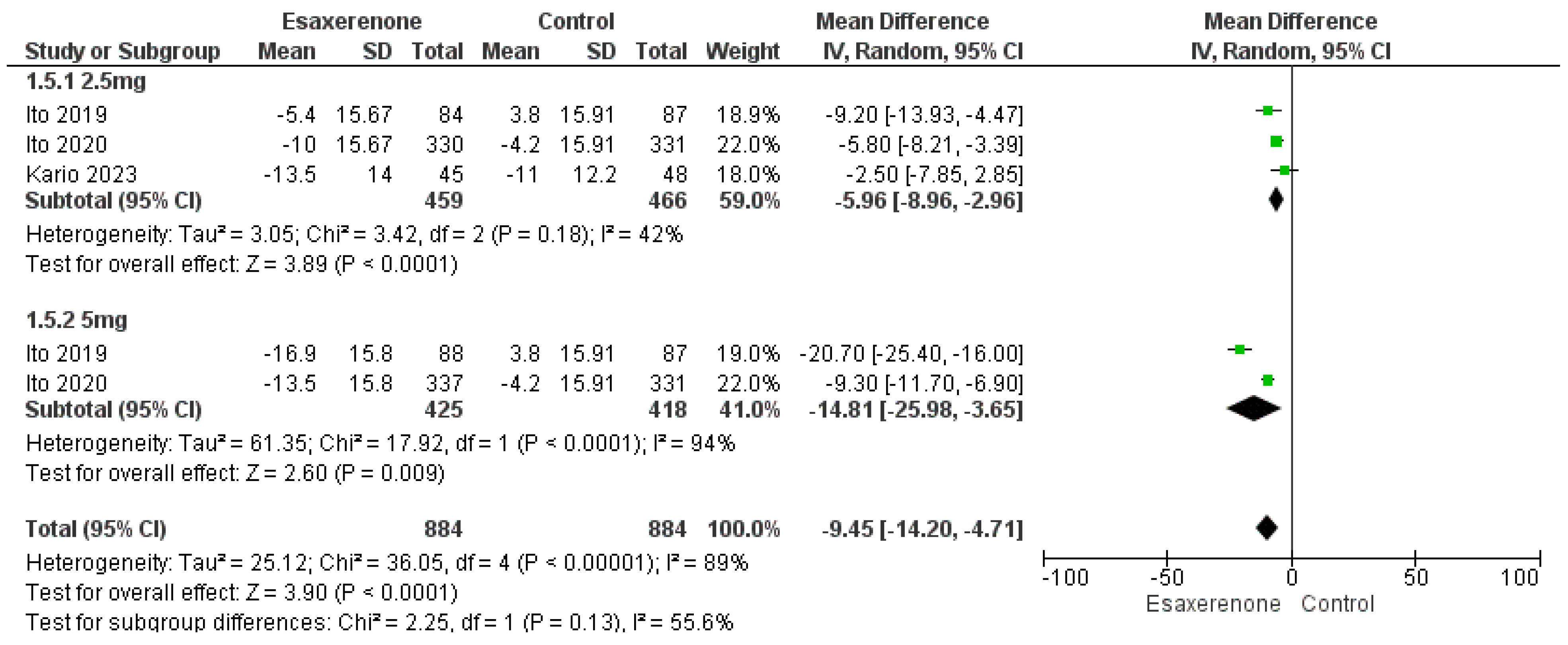
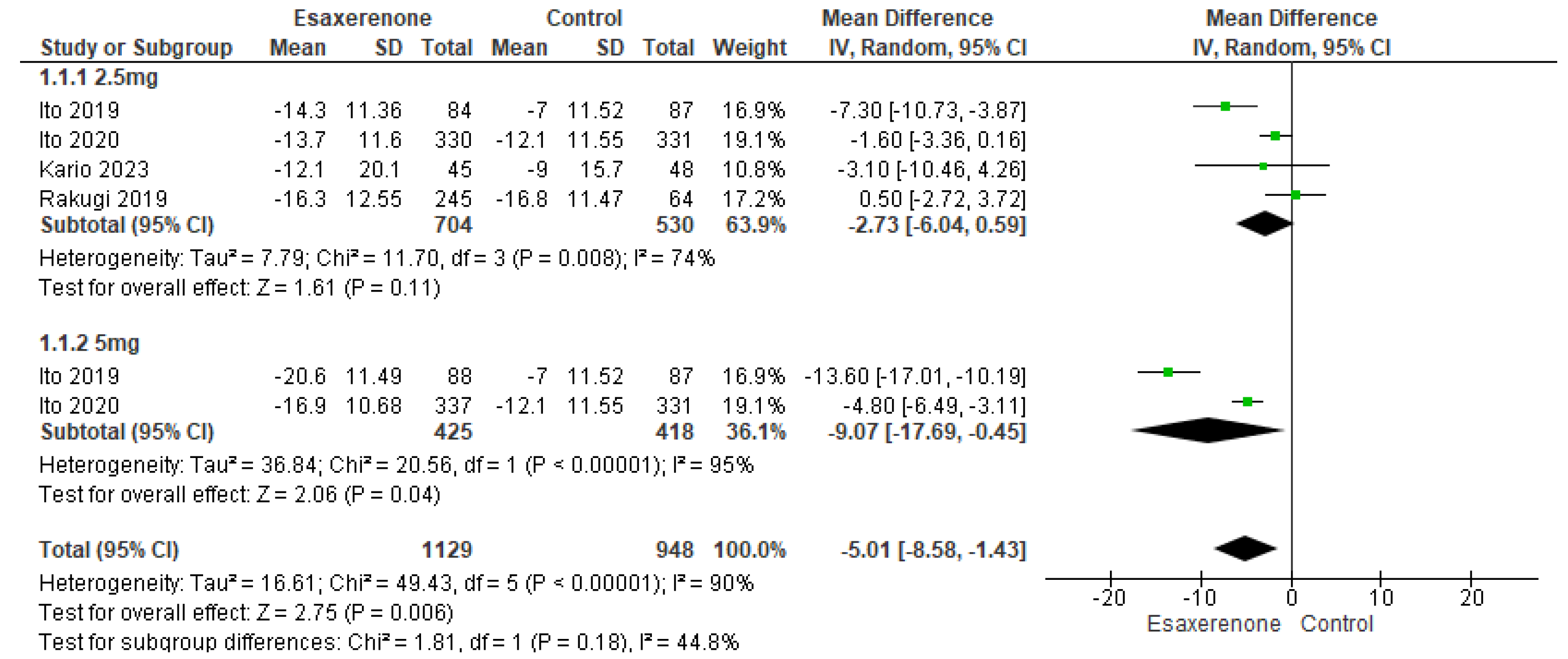
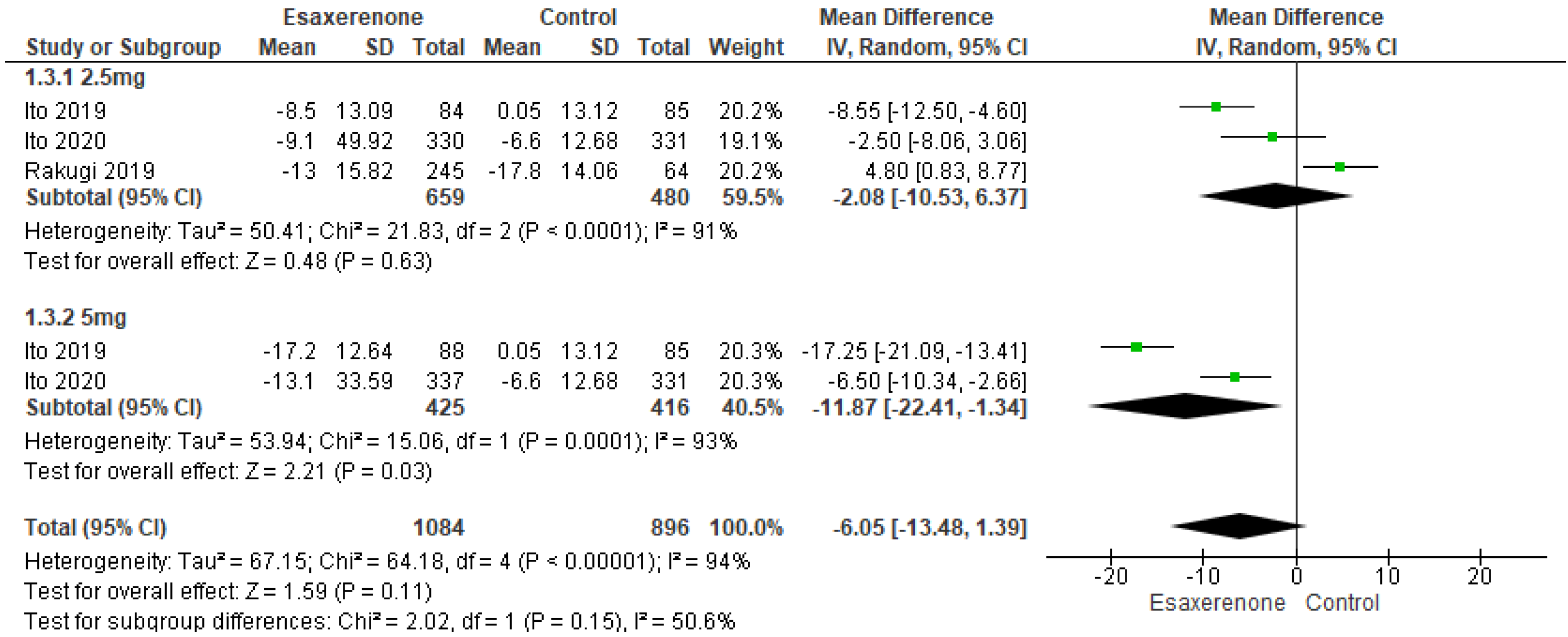
3.4. Primary Efficacy Outcomes
Sitting BP
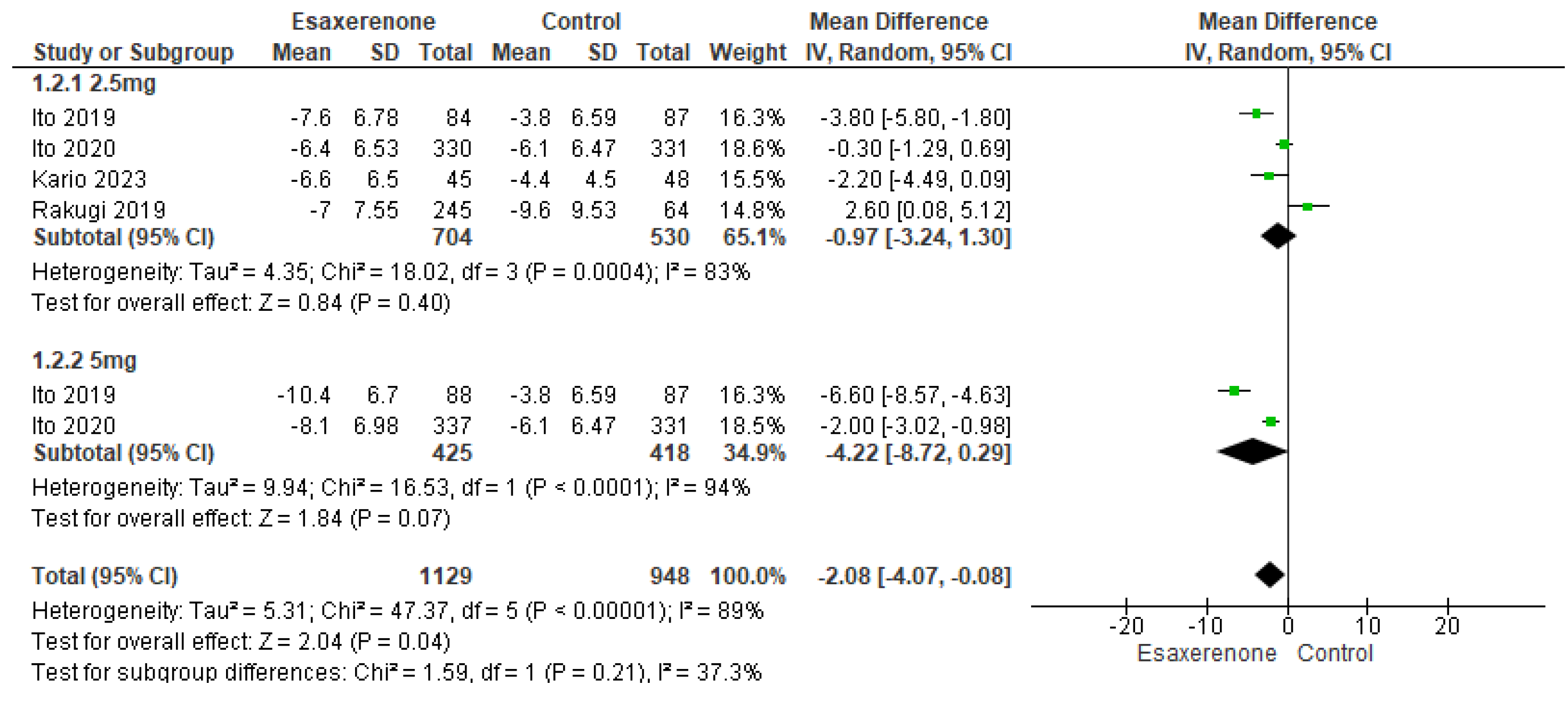
3.5. Secondary Efficacy Outcomes
3.5.1. Twenty-Four h BP
3.5.2. Target BP Achievement
3.5.3. BP During Different Times Measurements
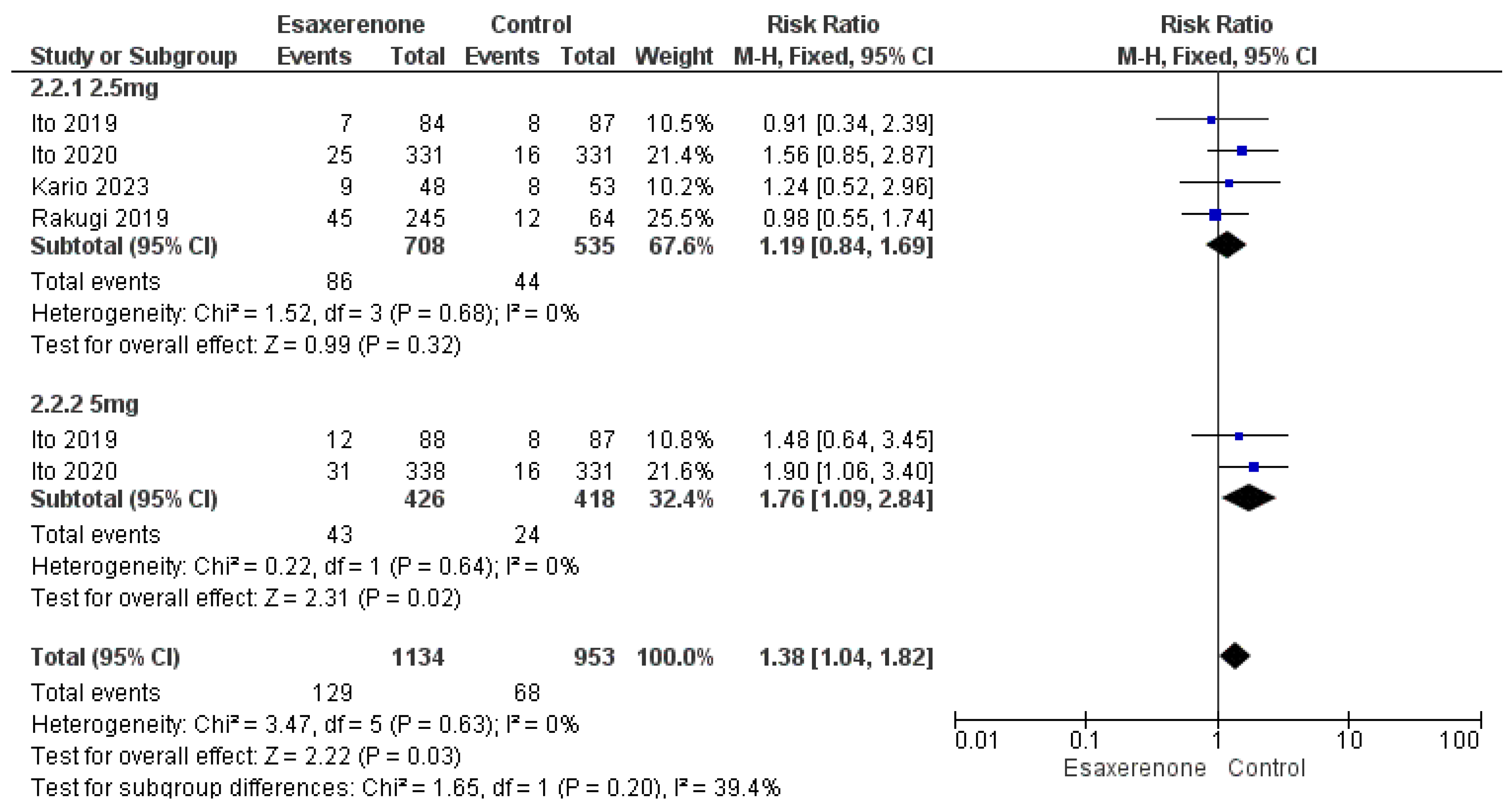
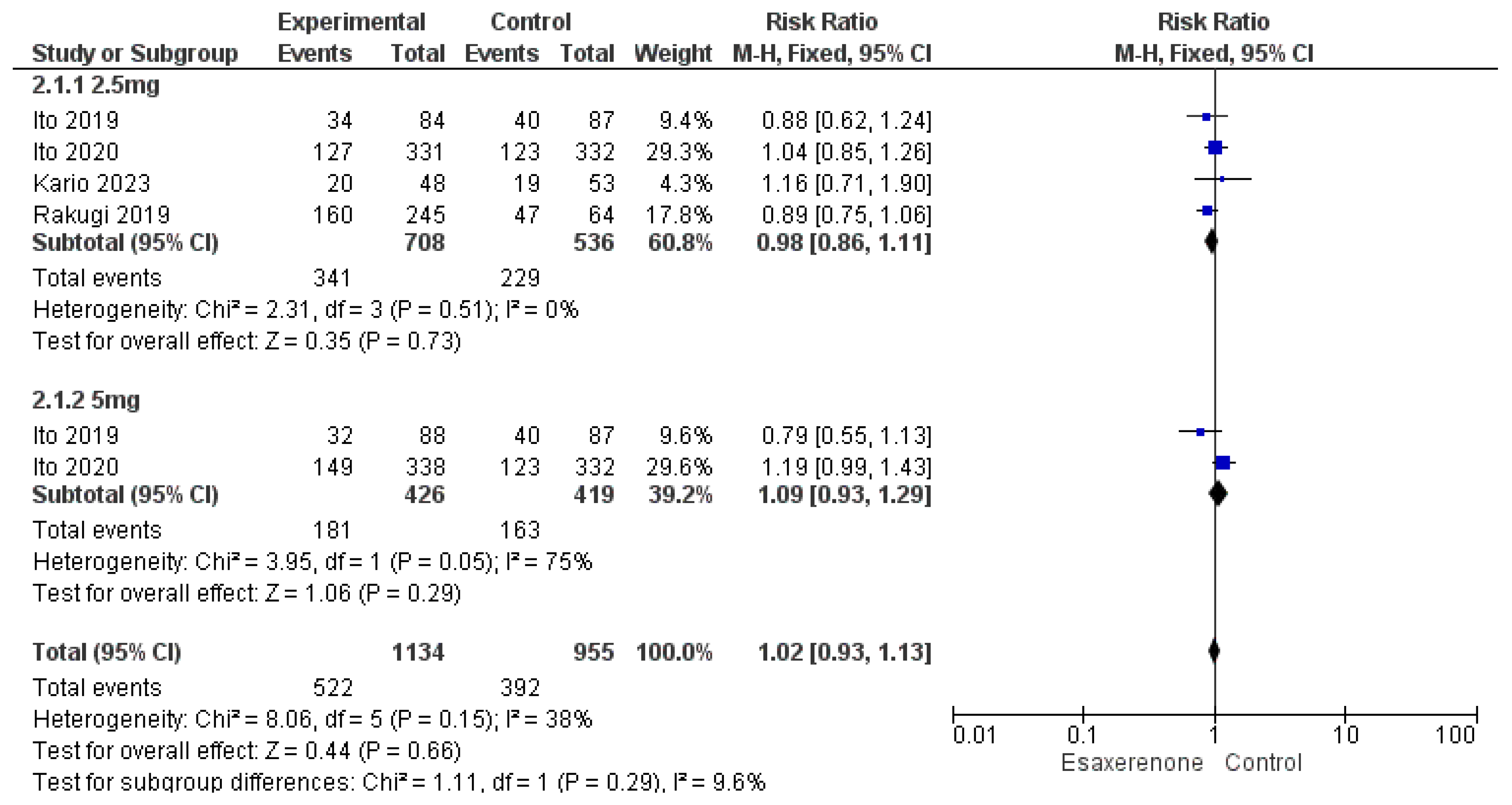
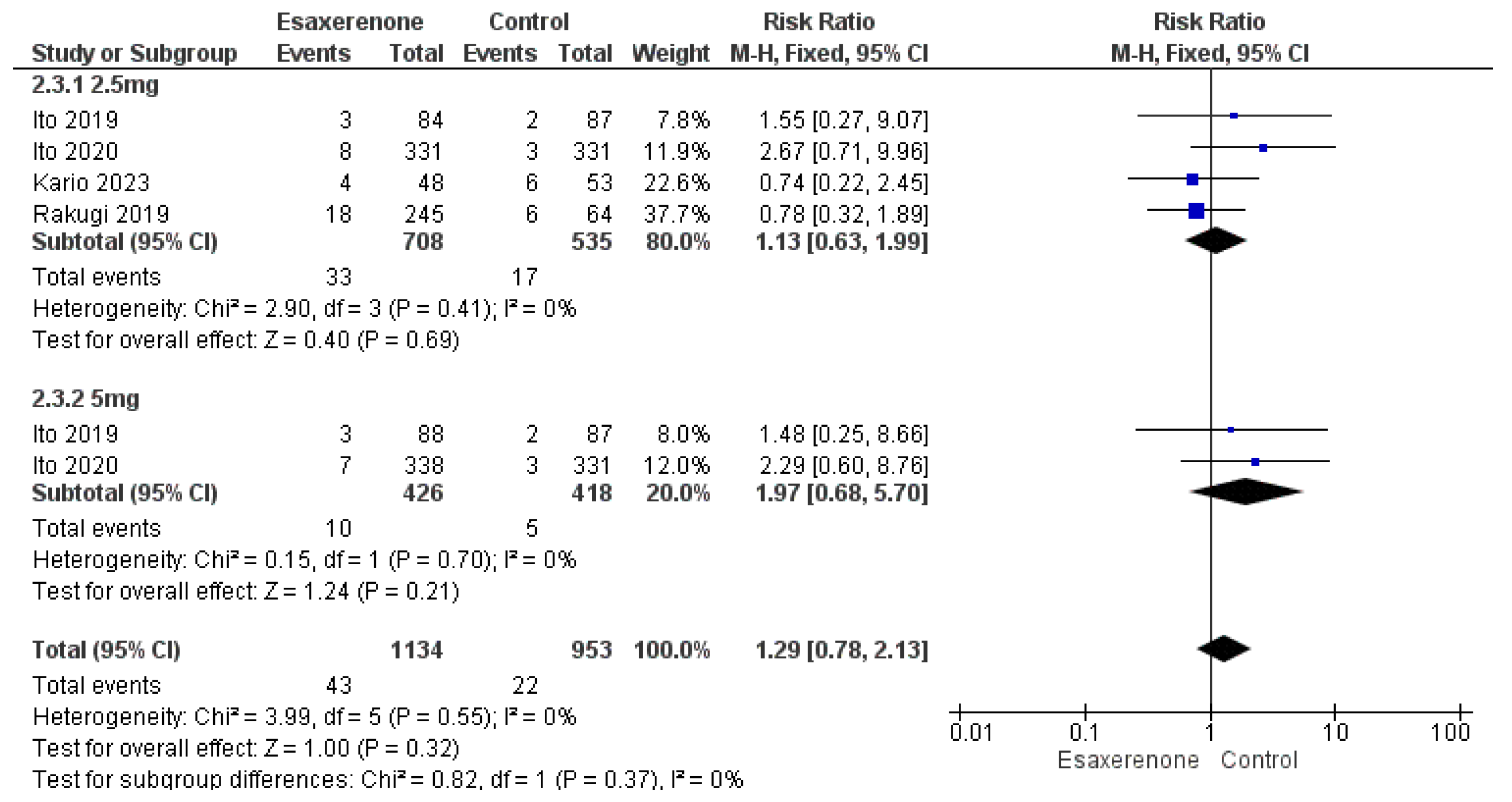
3.6. Safety Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRs | Mineralocorticoid receptors |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
| SBP | Sitting systolic BP |
| PRA | Plasma renin activity |
| PAC | Plasma aldosterone concentration |
Appendix A
| Database | Search Strategy | No |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (Esaxerenone [Title/Abstract] OR CS-3150 [Title/Abstract] OR Minnebro [Title/Abstract] OR “mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist” [Title/Abstract] OR “MR antagonist” [Title/Abstract] OR “MR blocker” [Title/Abstract]) AND (Hypertension The bold text and background color in the table footer were not essential, so I have removed them. [MeSH] OR Hypertension [Title/Abstract] OR “high blood pressure” [Title/Abstract] OR “elevated blood pressure” [Title/Abstract] OR HTN [Title/Abstract] OR “blood pressure” [Title/Abstract] OR antihypertensive [Title/Abstract]) | 759 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY((Esaxerenone OR CS-3150 OR Minnebro OR “mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist” OR “MR antagonist” OR “MR blocker”) AND (Hypertension OR “high blood pressure” OR “elevated blood pressure” OR HTN OR “blood pressure” OR antihypertensive)) | 802 |
| Web of Science | TS = ((Esaxerenone OR CS-3150 OR Minnebro OR “mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist” OR “MR antagonist” OR “MR blocker”) AND (Hypertension OR “high blood pressure” OR “elevated blood pressure” OR HTN OR “blood pressure” OR antihypertensive)) | 907 |
| Cochrane Library | ((Esaxerenone OR CS-3150 OR Minnebro OR “mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist” OR “MR antagonist” OR “MR blocker”)) AND ((MeSH descriptor: [Hypertension] explode all trees) OR hypertension OR “high blood pressure” OR “elevated blood pressure” OR HTN OR “blood pressure” OR antihypertensive) | 211 |
References
- Pimenta, E.; Calhoun, D.A. Treatment of resistant hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 2194–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calhoun, D.A.; Jones, D.; Textor, S.; Goff, D.C.; Murphy, T.P.; Toto, R.D.; White, A.; Cushman, W.C.; White, W.; Sica, D.; et al. Resistant hypertension: Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 2008, 117, e510–e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, S.L.; Powers, J.D.; Magid, D.J.; Tavel, H.M.; Masoudi, F.A.; Margolis, K.L.; O’COnnor, P.J.; Selby, J.V.; Ho, P.M. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2012, 125, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshahawey, M.; Jafari, E.; Smith, S.M.; McDonough, C.W. Characterizing apparent treatment resistant hypertension in the United States: Insights from the All of Us Research Program. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2024, 31, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champaneria, M.K.; Patel, R.S.; Oroszi, T.L. When blood pressure refuses to budge: Exploring the complexity of resistant hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1211199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasan, R.S.; Evans, J.C.; Larson, M.G.; Wilson, P.W.; Meigs, J.B.; Rifai, N.; Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D. Serum aldosterone and the incidence of hypertension in nonhypertensive persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneton, P.; Galan, P.; Bertrais, S.; Heudes, D.; Hercberg, S.; Ménard, J. High plasma aldosterone and low renin predict blood pressure increase and hypertension in middle-aged Caucasian populations. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 22, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Katada, J.; Daida, H.; Kitamura, F.; Yokoyama, K. Effects of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.; Duprez, D.A. Resistant Hypertension and the Pivotal Role for Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists: A Clinical Update 2016. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshahat, A.; Mansour, A.; Ellabban, M.; Diaa, A.; Hassan, A.; Fawzy, A.; Saad, O.A.; Abouelmagd, M.; Eid, M.; Elaraby, A.; et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of eplerenone and spironolactone in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Tsuruoka, H.; Homma, T. CS-3150, a novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, prevents hypertension and cardiorenal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Furuie, H.; Shimizu, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Kobayashi, F.; Ishizuka, H. Single- and multiple-dose escalation study to assess pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of oral esaxerenone in healthy Japanese subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yamakawa, S. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone (CS-3150) for the treatment of essential hypertension: A phase 2 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamakawa, S. Double-Blind Randomized Phase 3 Study Comparing Esaxerenone (CS-3150) and Eplerenone in Patients with Essential Hypertension (ESAX-HTN Study). Hypertension 2020, 75, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakugi, H.; Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yamakawa, S. Long-term phase 3 study of esaxerenone as mono or combination therapy with other antihypertensive drugs in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Kato, M.; Ishii, H.; Uchiyama, K.; Nagai, M.; Takahashi, N.; Asakura, T.; Shiraiwa, T.; Yoshida, T.; et al. Nighttime home blood pressure lowering effect of esaxerenone in patients with uncontrolled nocturnal hypertension: The EARLY-NH study. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Li, Y.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone (CS-3150) in primary hypertension: A meta-analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2024, 38, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Eitner, F. Nonsteroidal antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yamakawa, S. Effect of esaxerenone on nocturnal blood pressure and natriuretic peptide in different dipping phenotypes. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, H.; Itoh, H. Mineralocorticoid Receptor-Associated Hypertension and Its Organ Damage: Clinical Relevance for Resistant Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2012, 25, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, N.; Rahman, A.; Nishiyama, A. Esaxerenone, a novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker (MRB) in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithas, P.A.; Supiano, M.A. Spironolactone and Hydrochlorothiazide Decrease Vascular Stiffness and Blood Pressure in Geriatric Hypertension. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasińska, B.; Cofta, S.; Szczepaniak-Chicheł, L.; Rzymski, P.; Trafas, T.; Paluszkiewicz, L.; Tykarski, A.; Krasiński, Z. The Effects of Eplerenone on the Circadian Blood Pressure Pattern and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Resistant Hypertension—A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Hoshide, S.; Tamaki, N.; Nagata, M.; Sasaki, K.; Kanemaru, Y.; Shimada, K.; Kario, K. Efficacy of eplerenone added to renin-angiotensin blockade in elderly hypertensive patients: The Jichi-Eplerenone Treatment (JET) study. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2011, 12, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, D.A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2010, 12, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukri, M.Z.; Tan, J.W.; Manosroi, W.; Pojoga, L.H.; Rivera, A.; Williams, J.S.; Seely, E.W.; Adler, G.K.; Jaffe, I.Z.; Karas, R.H.; et al. Biological Sex Modulates the Adrenal and Blood Pressure Responses to Angiotensin II. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, F.C. Salt, Blood Pressure, and Aldosterone in Women and Men. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1026–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Morikawa, Y.; Ubukata, N.; Tsuruoka, H.; Homma, T. CS-3150, a Novel Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Shows Preventive and Therapeutic Effects On Renal Injury in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate/Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 358, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaraby, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Ellabban, M.; Bakr, A.; Atta, K.; Elkasaby, M.H.; Atia, A.; Suppah, M.; Abdelaziz, M.; Ali, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone for essential hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83 (Suppl. S13), 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study ID | Study Arms (%) | Site | Trial Registration | Age, (Mean ± SD) y | Male, n (%) | BMI, (Mean ± SD) (kg/m2) | Follow-Up Duration (Months) | Daily Dose (mg) | Hypertension Grade, n (%) | Prior Treatment of HTN, n (%) | Duration of HTN, Months | Past History, n (%) | Inclusion Criteria | Primary Endpoints | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ito, 2019 [13] | Esaxerenone (1.25, 2.5, or 5 mg/day), placebo, or eplerenone (50–100 mg/day) | Japan | NR | 57.0 ± 9.3 | 295 (69.7) | 25.5 ± 4.0 | 12 weeks | Esaxerenone (1.25, 2.5, or 5 mg/day), eplerenone (50–100 mg/day) | Grade I or II | 221 (52.2) | NR | Diabetes 58 (13.7), LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) 129.3 ± 31.8 | Inclusion criteria: aged ≥ 20 years at time of informed consent; sitting systolic BP (SBP) of ≥140 to <180 mmHg and diastolic BP (DBP) ≥90 to <110 mmHg; and 24 h BP by ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM) of ≥130/80 mmHg. | Change from baseline in sitting BP (SBP and DBP) at the end of the treatment period, defined as the average sitting BP of week 10 and week 12 after last observation carried forward (LOCF) imputation of missing values. | The incidence of adverse events was similar in all treatment groups. Serum K+ levels initially increased in proportion to esaxerenone dose but were stable from week 2 until week 12. Plasma esaxerenone concentration increased in proportion to the dose. In conclusion, esaxerenone is an effective and tolerable treatment option for patients with essential hypertension. |
| Ito, 2020 [14] | Esaxerenone 2.5 or 5 mg/day or eplerenone 50 mg/day | Japan | NCT02890173 | 55.5 ± 9.6 | 721 (72.2) | 25.7 ± 4.1 | 12 weeks | Esaxerenone 2.5 or 5 mg/day or eplerenone 50 mg/day | Grade I: 454 (45.5) or II: 544 (54.5) | 514 (51.5) | NR | Comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus 156 (15.6), Triglycerides, mg/dL 138.1 ± 115.1 | Included patients who provided informed consent, received ≥1 dose of study drug, and had at least one efficacy measurement. The per-protocol set (PPS) included patients who completed study treatments without major protocol deviations or missing primary end point data and had study drug compliance of ≥75%. The safety analysis set included all those who received ≥1 dose of the study drug. | Changes in sitting SBP and DBP from baseline until the end of treatment (defined as mean BP calculated using values from weeks 10 and 12). | These results indicate that esaxerenone is an effective and well-tolerated MR blocker in Japanese patients with essential hypertension, with BP-lowering activity at least equivalent to eplerenone. |
| Kario, 2023 [16] | Angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium-channel blocker | Japan | NR | 67.6 ± 11.6 | 47 (50.5) | 25.5 ± 4.3 | 12 weeks | The starting dose was 2.5 mg, which could be titrated to 5 mg if the response was inadequate | NR | NR | 140.2 ± 122.1 | Type 2 DM 33 (35.5), diabetic retinopathy 8 (8.6), dyslipidemia 52 (55.9), hyperuricemia 17 (18.3), heart failure 1 (1.1), smoking 14 (15.1) | Received at least one dose of esaxerenone, and had at least one efficacy endpoint evaluation. The per-protocol set (PPS) was defined as FAS patients who adhered to the package insert of esaxerenone. | The change in nighttime home SBP and DBP measured with the brachial device from baseline to the end of treatment (EOT). | Esaxerenone was effective in lowering nighttime home BP as well as morning and bedtime home BP and office BP, was safe, and showed organ-protective effects in patients with uncontrolled nocturnal hypertension. Caution is warranted regarding elevated serum potassium levels. |
| Rakugi, 2019 [15] | Patients received esaxerenone monotherapy or esaxerenone in combination with a CCB or RAS inhibitor. | Japan | NR | 56.2 ± 9.2 | 286 (77.7) | 25.7 ± 3.6 | 28, 52 weeks | Patients were treated with esaxerenone starting at 2.5 mg/day, increasing to 5 mg/day if required to achieve blood pressure (BP) targets. | Grade I: 176 (47.8) or II: 192 (52.2) | 244 (66.3) | NR | Diabetes 67 (18.2) | Received the study drug at least once, and had efficacy endpoint data measured at least once during the treatment period. | The primary endpoint was a change from baseline in sitting BP | Esaxerenone was also well-tolerated with a rate of hyperkalemia at 5.4% (serum potassium ≥ 5.5 mEq/L), indicating a good safety profile for treatment over the long term or in combination with a CCB or RAS inhibitor. In conclusion, esaxerenone may be a promising treatment option for patients with hypertension. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hafez, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Mansour, A.; Kamal, I.; Bakr, A.; Gadelmawla, A.F.; Elsayed, H.; Mohamed, M.R.; Ali, K.; Elhelw, M. Efficacy and Safety of Esaxerenone for Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165663
Hafez A, Abdelaziz A, Mansour A, Kamal I, Bakr A, Gadelmawla AF, Elsayed H, Mohamed MR, Ali K, Elhelw M. Efficacy and Safety of Esaxerenone for Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165663
Chicago/Turabian StyleHafez, Abdelrahman, Ahmed Abdelaziz, Ahmed Mansour, Ibrahim Kamal, Ali Bakr, Ahmed Farid Gadelmawla, Hanaa Elsayed, Mohamed Reyad Mohamed, Karim Ali, and Mohamed Elhelw. 2025. "Efficacy and Safety of Esaxerenone for Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165663
APA StyleHafez, A., Abdelaziz, A., Mansour, A., Kamal, I., Bakr, A., Gadelmawla, A. F., Elsayed, H., Mohamed, M. R., Ali, K., & Elhelw, M. (2025). Efficacy and Safety of Esaxerenone for Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165663