Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) with Expandable Banana-Shaped Interbody Spacers—Institutional 5-Year Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Hospital Setting
2.2. Patient Identification
2.3. Data Collection and Variables
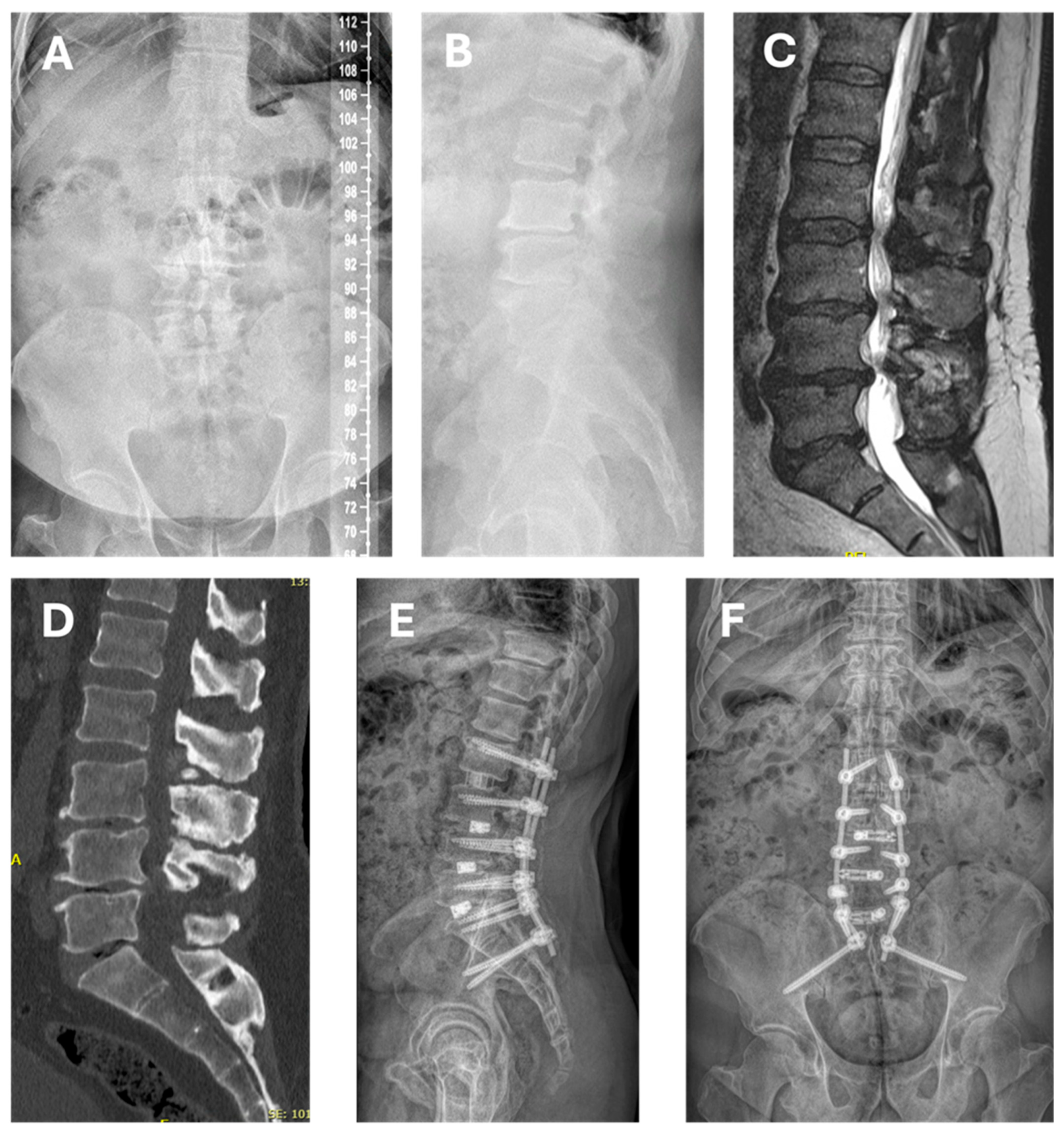
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort
3.2. Follow-Up and Reasons for Missing Data
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
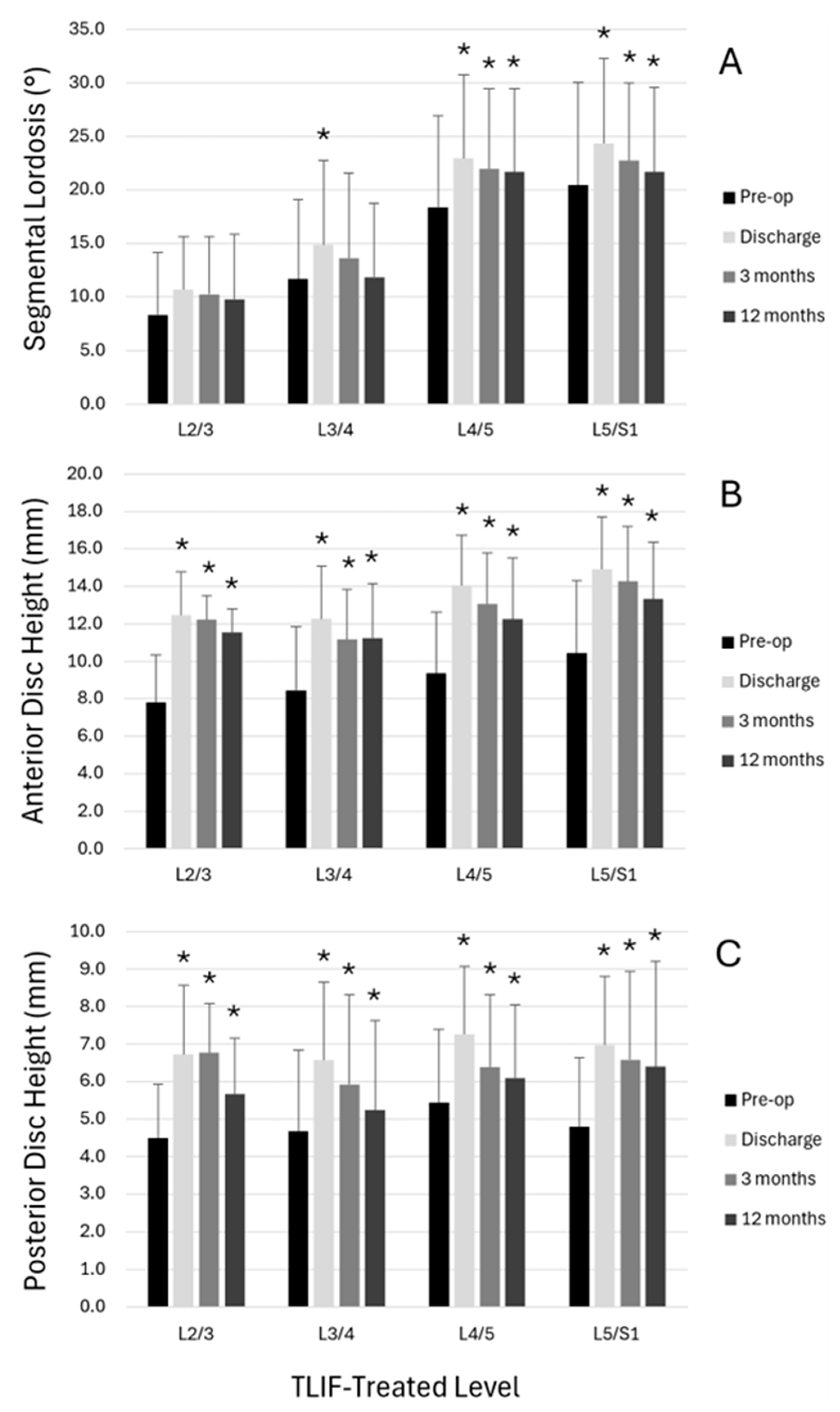
3.4. Radiological Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Practice
4.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Simone, M.; Choucha, A.; Ciaglia, E.; Conti, V.; Pecoraro, G.; Santurro, A.; Puca, A.A.; Cascella, M.; Iaconetta, G. Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomic and Pathophysiologic Characterization, Clinical Evaluation, Biomarkers, AI, and Treatment Options. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautschi, O.P.; Stienen, M.N.; Corniola, M.V.; Schaller, K. Minimal invasive surgery: Historical review, current status and perspective. Praxis 2014, 103, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, J.G.; Jeszenszky, D. Die posteriore, lumbale, interkorporelle Fusion in unilateraler transforaminaler Technik. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 1998, 10, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, D.K.; Choudhri, T.F.; Dailey, A.T.; Groff, M.W.; Khoo, L.; Matz, P.G.; Mummaneni, P.; Watters, W.C., 3rd; Wang, J.; Walters, B.C.; et al. Guidelines for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 7: Intractable low-back pain without stenosis or spondylolisthesis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2005, 2, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, J.A.; Lambrechts, M.J.; Dees, A.; Thomas, T.; Hiranaka, C.G.; Kurd, M.F.; Radcliff, K.E.; Anderson, D.G. Static versus Expandable Interbody Fusion Devices: A Comparison of 1-Year Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2023, 17, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowin, S.C. Wolff’s law of trabecular architecture at remodeling equilibrium. J. Biomech. Eng. 1986, 108, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, S.D.; Bridwell, K.; Dimar, J.R.; Horton, W.; Berven, S.; Schwab, F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine 2005, 30, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisien, A.; Wai, E.K.; ElSayed, M.S.A.; Frei, H. Subsidence of Spinal Fusion Cages: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2022, 16, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawasli, A.H.; Khalifeh, J.M.; Chatrath, A.; Yarbrough, C.K.; Ray, W.Z. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with expandable versus static interbody devices: Radiographic assessment of sagittal segmental and pelvic parameters. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.X.; Kim, J.S.; Kotheeranurak, V.; Chen, C.M.; Hu, B.S.; Rui, G. Does the application of expandable cages in TLIF provide improved clinical and radiological results compared to static cages? A meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 949938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnav, A.S.; Saville, P.; McAnany, S.; Kirnaz, S.; Wipplinger, C.; Navarro-Ramirez, R.; Hartl, R.; Yang, J.; Gang, C.H.; Qureshi, S.A. Retrospective Review of Immediate Restoration of Lordosis in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Comparison of Static and Expandable Interbody Cages. Oper. Neurosurg. 2020, 18, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armocida, D.; Pesce, A.; Cimatti, M.; Proietti, L.; Santoro, A.; Frati, A. Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Expandable Cages: Increased Risk of Late Postoperative Subsidence Without a Real Improvement of Perioperative Outcomes: A Clinical Monocentric Study. World Neurosurg. 2021, 156, e57–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, C.F.; Zhang, J.K.; Greenberg, J.K.; Javeed, S.; Khalifeh, J.M.; Jain, D.; Dorward, I.; Santiago, P.; Molina, C.; Pennicooke, B.; et al. Comparison of local and regional radiographic outcomes in minimally invasive and open TLIF: A propensity score-matched cohort. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2022, 37, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khechen, B.; Haws, B.E.; Patel, D.V.; Yoo, J.S.; Guntin, J.A.; Cardinal, K.L.; Iyer, S.; Singh, K. Static Versus Expandable Devices Provide Similar Clinical Outcomes Following Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. HSS J. 2020, 16, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickley, C.; Philipp, T.; Wang, E.; Zhong, J.; Balouch, E.; O’Malley, N.; Leon, C.; Maglaras, C.; Manning, J.; Varlotta, C.; et al. Expandable cages increase the risk of intraoperative subsidence but do not improve perioperative outcomes in single level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2021, 21, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, T.J.; Joseph, J.R.; Terman, S.W.; Park, P. Expandable vs. Static Cages in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Radiographic Comparison of Segmental and Lumbar Sagittal Angles. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chou, D.; Pennicooke, B.; Rivera, J.; Tan, L.A.; Berven, S.; Mummaneni, P.V. Long-term radiographic outcomes of expandable versus static cages in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2020, 34, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.W.; Doerr, T.M.; Luna, I.Y.; Joshua, G.; Shen, S.R.; Fu, X.; Wu, A.M. Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Expandable Technology: A Clinical and Radiographic Analysis of 50 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2016, 90, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, I.C.; Than, K.D.; Chen, K.S.; Wang, A.C.; Park, P. Failure of a polyether-ether-ketone expandable interbody cage following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24 (Suppl. 4), S555–S559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, J.; Koro, L.; Richards, D.; Keegan, C.; Fessler, R.D.; Fessler, R.G. Expandable versus Static Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cages: 1-year Radiographic Parameters and Patient-Reported Outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2022, 159, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejrati, N.; Martens, B.; Jost, B.; Bozinov, O.; Stienen, M.N. Failure of an expandable lumbar interbody spacer–a critical analysis of secondary collapse, pseudoarthrosis and revision rates after thoracolumbar fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2025, 34, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boktor, J.G.; Pockett, R.D.; Verghese, N. The expandable transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion—Two years follow-up. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2018, 9, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco, J.A.; Karamian, B.A.; DiMaria, S.L.; Patel, P.D.; Divi, S.N.; Chang, M.; Timmons, T.; Grewal, L.; Hallman, H.; Lee, J.K.; et al. Static Versus Expandable Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) Interbody Cages: A Comparison of One-Year Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes for One-Level Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2021, 152, e492–e501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Ji, C.; Kang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.; Feng, H.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy of expandable interbody fusion cage (EXP-IFC) and non-expandable interbody fusion cage (NE-IFC) in MIS-TLIF for lumbar degenerative diseases: A systematic retrospective study on 62 patients. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1008171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelfand, Y.; Benton, J.; De la Garza-Ramos, R.; Yanamadala, V.; Yassari, R.; Kinon, M.D. Effect of Cage Type on Short-Term Radiographic Outcomes in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, e953–e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jitpakdee, K.; Sommer, F.; Gouveia, E.; Mykolajtchuk, C.; Boadi, B.; Berger, J.; Hussain, I.; Hartl, R. Expandable cages that expand both height and lordosis provide improved immediate effect on sagittal alignment and short-term clinical outcomes following minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS TLIF). J. Spine Surg. 2024, 10, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassemeier, T.; Haversath, M.; Jager, M. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with expandable cages: Radiological and clinical results of banana-shaped and straight implants. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2018, 9, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, S.; Vaishnav, A.S.; Sheha, E.; Urakawa, H.; Sato, K.; Othman, Y.; Chaudhary, C.; Lee, R.; Cong, G.T.; Chaudhary, S.; et al. Combining Expandable Interbody Cage Technology with a Minimally Invasive Technique to Harvest Iliac Crest Autograft Bone to Optimize Fusion Outcomes in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery. Clin. Spine Surg. 2021, 34, E522–E530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, J.; Malone, H.; Witiw, C.D.; Kolcun, J.P.G.; Koro, L.; Keegan, K.C.; Ahmad, S.; Kerolus, M.G.; David, B.T.; Fessler, R.D.; et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using a novel minimally invasive expandable interbody cage: Patient-reported outcomes and radiographic parameters. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 35, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yearley, A.G.; Chalif, J.I.; Zaidi, H.A. Utility of Expandable Interbody Cages in Open Transforaminal Interbody Fusions: A Comparison With Static Cages. Cureus 2023, 15, e40262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stienen, M.N.; Joswig, H.; Smoll, N.R.; Corniola, M.V.; Schaller, K.; Hildebrandt, G.; Gautschi, O.P. Influence of Body Mass Index on Subjective and Objective Measures of Pain, Functional Impairment, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease. World Neurosurg. 2016, 96, 570–577.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stienen, M.N.; Smoll, N.R.; Hildebrandt, G.; Schaller, K.; Gautschi, O.P. Influence of smoking status at time of surgery for herniated lumbar disk on postoperative pain and health-related quality of life. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 122, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joswig, H.; Stienen, M.N.; Smoll, N.R.; Corniola, M.V.; Chau, I.; Schaller, K.; Hildebrandt, G.; Gautschi, O.P. Effects of Smoking on Subjective and Objective Measures of Pain Intensity, Functional Impairment, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Lumbar Degenerative Disk Disease. World Neurosurg. 2017, 99, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, K.; Schmitt, V.; Espinola-Klein, C.; Munzel, T.; Konstantinides, S.; Hobohm, L. Comorbidity burden assessed by the charlson comorbidity index and its influence on prognosis of patients with pulmonary embolism. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44 (Suppl. 2), ehad655.2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrapon, A.P.R.; Zattra, C.M.; Voglis, S.; Velz, J.; Vasella, F.; Akeret, K.; Held, U.; Schiavolin, S.; Bozinov, O.; Ferroli, P.; et al. Adverse Events in Neurosurgery: The Novel Therapy-Disability-Neurology Grade. Neurosurgery 2021, 89, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joswig, H.; Hock, C.; Hildebrandt, G.; Schaller, K.; Stienen, M.N. Microscopic lumbar spinal stenosis decompression: Is surgical education safe? Acta Neurochir. 2016, 158, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnab, I. Negative disc exploration. An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1971, 53, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafazal, S.I.; Sell, P.J. Outcome scores in spinal surgery quantified: Excellent, good, fair and poor in terms of patient-completed tools. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantigan, J.W.; Steffee, A.D. A carbon fiber implant to aid interbody lumbar fusion. Two-year clinical results in the first 26 patients. Spine 1993, 18, 2106–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenke, L.G.; Bridwell, K.H.; Bullis, D.; Betz, R.R.; Baldus, C.; Schoenecker, P.L. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J. Spinal Disord. 1992, 5, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizman, N.M.; O’Brien, J.R.; Poehling-Monaghan, K.L.; Yu, W.D. Pseudarthrosis of the spine. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2009, 17, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laouissat, F.; Sebaaly, A.; Gehrchen, M.; Roussouly, P. Classification of normal sagittal spine alignment: Refounding the Roussouly classification. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizones, J.; Moreno-Manzanaro, L.; Sanchez Perez-Grueso, F.J.; Vila-Casademunt, A.; Yilgor, C.; Obeid, I.; Alanay, A.; Kleinstuck, F.; Acaroglu, E.R.; Pellise, F.; et al. Restoring the ideal Roussouly sagittal profile in adult scoliosis surgery decreases the risk of mechanical complications. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebaaly, A.; Grobost, P.; Mallam, L.; Roussouly, P. Description of the sagittal alignment of the degenerative human spine. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.D.; Baron, E.M.; Levesque, M. Extrusion of expandable stacked interbody device for lumbar fusion: Case report of a complication. Spine 2012, 37, E1155–E1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveque, J.A.; Segebarth, B.; Schroerlucke, S.R.; Khanna, N.; Pollina, J., Jr.; Youssef, J.A.; Tohmeh, A.G.; Uribe, J.S. A Multicenter Radiographic Evaluation of the Rates of Preoperative and Postoperative Malalignment in Degenerative Spinal Fusions. Spine 2018, 43, E782–E789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.X.; He, L.R.; Nan, J.N.; Xu, W.B.; Xiao, K.; Que, Z.; Jhang, S.W.; Chen, C.M.; Zhu, M.T.; Rui, G. Comparing Outcomes of Banana-Shaped and Straight Cages in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurospine 2024, 21, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, R.; Chin, C.T.; Rajagopalan, P.; Duan, P.G.; Li, B.; Burch, S.; Berven, S.H.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Chou, D. Comparison of Lumbosacral Fusion Grade in Patients after Transforaminal and Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.; Kurian, S.J.; Wahood, W.; Goyal, A.; Elder, B.D.; Bydon, M. Assessing the Difference in Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes Between Expandable Cage and Nonexpandable Cage Among Patients Undergoing Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, 596–606.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macki, M.; Hamilton, T.; Haddad, Y.W.; Chang, V. Expandable Cage Technology-Transforaminal, Anterior, and Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Oper. Neurosurg. 2021, 21 (Suppl. 1), S69–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, T.; Merrill, R.K.; Shahi, P.; Pathania, S.; Araghi, K.; Maayan, O.; Zhao, E.; Shinn, D.; Kim, Y.E.; Kamil, R.; et al. Predictors of Subsidence and its Clinical Impact After Expandable Cage Insertion in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion. Spine 2023, 48, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.A.; Ayala, G.A.; Roura, R.; Christmas, K.N.; Warren, D.H.; Simon, P. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with an expandable interbody device: Two-year clinical and radiographic outcomes. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2023, 16, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldaner, N.; Stienen, M.N. Subjective and Objective Measures of Symptoms, Function, and Outcome in Patients with Degenerative Spine Disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72 (Suppl. 10), 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.6 (SD 12.4) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 136 (50.4%) |
| Male | 134 (49.6%) |
| BMI categories, according to the WHO | |
| Underweight (<18.5 kg/m2) | 2 (0.7%) |
| Healthy (18.5–24.9 kg/m2) | 89 (33.0%) |
| Overweight (25–30 kg/m2) | 100 (37.0%) |
| Obese (>30 kg/m2) | 79 (29.3%) |
| Smoking status | |
| Nonsmoker | 157 (58.1%) |
| Smoker | 85 (31.5%) |
| Former smoker | 28 (10.4%) |
| ASA grade | |
| I | 7 (2.6%) |
| II | 169 (62.6%) |
| III | 90 (33.3%) |
| IV | 4 (1.5%) |
| CCI severity | |
| Very low | 113 (41.9%) |
| Mild | 103 (38.1%) |
| Moderate | 37 (13.7%) |
| Severe | 17 (6.3%) |
| CFI severity | |
| Very fit | 22 (8.1%) |
| Well | 82 (30.4%) |
| Managing well | 97 (35.9%) |
| Vulnerable | 57 (21.1%) |
| Mildly frail | 8 (3.0%) |
| Moderately frail | 3 (1.1%) |
| Severely frail | 1 (0.4%) |
| Degenerative disease type | |
| (Recurrent) disc herniation | 42 (15.6%) |
| Spinal stenosis with instability | 62 (23.0%) |
| Degenerative spondylolisthesis | 75 (27.8%) |
| Isthmic spondylolisthesis | 38 (14.1%) |
| Other | 53 (19.6%) |
| Total | n = 270 (100%) |
| Variable | |
|---|---|
| TLIF segment ** | |
| L2/3 | 11 (3.4%) |
| L3/4 | 44 (13.6%) |
| L4/5 | 164 (50.6%) |
| L5/S1 | 105 (32.4%) |
| Number of operated segments * | 1.5 (SD 0.7, range: 1–4) |
| Type of interbody spacer ** | |
| 8° lordotic | 161 (49.7%) |
| 15° lordotic | 163 (50.3%) |
| Other types of interbody fusion employed * | |
| None | 234 (86.7%) |
| XLIF/LLIF | 7 (2.6%) |
| ALIF | 14 (5.2%) |
| PLIF | 12 (4.4%) |
| Other | 3 (1.1%) |
| Type of laminectomy ** | |
| Partial | 231 (71.3%) |
| Complete | 93 (28.7%) |
| Length of surgery, in minutes * | 263 (SD 89, range: 124–725) |
| Estimated blood loss, in milliliters * | 556 (SD 446, range: 50–3600) |
| Intraoperative AE * | |
| No | 239 (88.5%) |
| Yes | 31 (11.5%) |
| Type of intraoperative AE *** | |
| Dural lesion | 23 (74.2%) |
| Hardware-related | 5 (16.1%) |
| Osseous injury | 2 (6.5%) |
| Excessive bleeding | 1 (3.2%) |
| Variable | Discharge | 90 Days | 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|
| AE | |||
| No | 217 (80.4%) | 227 (84.1%) | 185 (68.5%) |
| Yes | 53 (19.6%) | 27 (10.0%) | 25 (9.3%) |
| Missing data | 0 (0%) | 16 (5.9%) | 60 (22.2%) |
| Type of AE # | |||
| Medical | 36 (67.9%) | 1 (3.7%) | 0 (0%) |
| Surgical | 17 (33.1%) | 26 (96.3%) | 25 (100%) |
| TDN grade of AE | |||
| 1 (mild AE) | 7 (13.2%) | 1 (3.7%) | 0 (0%) |
| 2 (mild to moderate AE) | 22 (41.5%) | 2 (7.4%) | 5 (20.0%) |
| 3 (moderate AE) | 19 (35.8%) | 22 (81.5%) | 18 (72.0%) |
| 4 (severe AE) | 5 (9.4%) | 2 (7.4%) | 1 (4.0%) |
| 5 (death) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.0%) |
| Clinical outcome | n/a | ||
| Excellent | 92 (34.1%) | 93 (34.5%) | |
| Good | 97 (35.9%) | 55 (20.4%) | |
| Fair | 42 (15.6%) | 44 (16.3%) | |
| Poor | 24 (8.9) | 14 (5.2%) | |
| Missing data | 15 (5.6%) | 64 (23.7%) | |
| Posterolateral fusion | n/a | Assessable levels n = 220 | Assessable levels n = 209 |
| Definitively not solid | 11 (5.0%) | 17 (8.1%) | |
| Probably not solid | 138 (62.7%) | 51 (24.4%) | |
| Possibly solid | 55 (25.0%) | 83 (39.7%) | |
| Definitively solid | 16 (7.3%) | 58 (27.8%) | |
| Intersomatic fusion | n/a | Assessable levels n = 221 | Assessable levels n = 216 |
| Fusion | 10 (4.5%) | 95 (44.0%) | |
| Intermediate type | 183 (82.8%) | 90 (41.7%) | |
| Pseudarthrosis | 28 (12.7%) | 31 (14.4%) | |
| Any radiographic fusion | n/a | Assessable levels n = 222 | Assessable levels n = 216 |
| Fused | 71 (32.0%) | 158 (73.1%) | |
| Not fused | 151 (68.0%) | 58 (26.9%) | |
| Clinical non-union | n/a | Assessable levels n = 279 | Assessable levels n = 249 |
| No | 258 (92.5%) | 219 (88.0%) | |
| Yes | 21 (7.5%) | 30 (12.0%) | |
| Cage collapse | n/a | n/a | Assessable levels n = 250 |
| No | 250 (100%) | ||
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) |
| Spinopelvic Parameters | Preoperative | Discharge | 90 Days Postoperative | 12 Months Postoperative | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI, in ° | 57.1 (12.1) | ||||||
| Total LL, in ° | 51.6 (14.2) | 49.8 (12.7) | 0.003 | 53.6 (12.5) | 0.025 | 53.8 (12.3) | 0.004 |
| SS, in ° | 38.0 (9.7) | 37.0 (8.8) | 0.030 | 38.5 (9.0) | 0.816 | 39.1 (8.6) | 0.030 |
| PT, in ° | 19.0 (8.4) | 19.9 (8.9) | 0.037 | 18.8 (8.6) | 0.850 | 18.1 (9.1) | 0.072 |
| Segmental lordosis, in ° | 17.8 (9.3) | 21.9 (8.6) | <0.001 | 20.8 (8.2) | <0.001 | 20.0 (8.6) | <0.001 |
| C7 SVA, in cm | 4.2 (3.9) | 4.1 (3.3) | 0.173 | 5.0 (3.5) | 0.468 | 5.8 (4.6) | 0.514 |
| Ideal LL, in ° | 58.0 (7.4) | ||||||
| Ideal-actual LL mismatch, in ° | 6.4 (12.2) | 8.2 (11.1) | 0.003 | 4.5 (11.2) | 0.025 | 4.0 (11.4) | 0.004 |
| PI-LL mismatch, in ° | 5.5 (11.9) | 7.2 (11.8) | 0.003 | 3.7 (11.7) | 0.032 | 3.3 (12.4) | 0.004 |
| Intervertebral distance, in mm | |||||||
| Anterior disc space | 9.6 (3.5) | 14.0 (2.9) | <0.001 | 13.2 (2.9) | <0.001 | 12.5 (3.2) | <0.001 |
| Middle disc space | 8.2 (2.8) | 11.8 (2.3) | <0.001 | 11.0 (2.2) | <0.001 | 10.5 (2.4) | <0.001 |
| Posterior disc space | 5.1 (1.9) | 7.1 (1.9) | <0.001 | 6.4 (2.1) | <0.001 | 6.1 (2.3) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stienen, M.N.; Bertulli, L.; Fischer, G.; Bättig, L.; Yildiz, Y.; Feuerstein, L.; Kissling, F.; Schöfl, T.; Stengel, F.C.; Gianoli, D.; et al. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) with Expandable Banana-Shaped Interbody Spacers—Institutional 5-Year Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155402
Stienen MN, Bertulli L, Fischer G, Bättig L, Yildiz Y, Feuerstein L, Kissling F, Schöfl T, Stengel FC, Gianoli D, et al. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) with Expandable Banana-Shaped Interbody Spacers—Institutional 5-Year Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155402
Chicago/Turabian StyleStienen, Martin N., Lorenzo Bertulli, Gregor Fischer, Linda Bättig, Yesim Yildiz, Laurin Feuerstein, Francis Kissling, Thomas Schöfl, Felix C. Stengel, Daniele Gianoli, and et al. 2025. "Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) with Expandable Banana-Shaped Interbody Spacers—Institutional 5-Year Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155402
APA StyleStienen, M. N., Bertulli, L., Fischer, G., Bättig, L., Yildiz, Y., Feuerstein, L., Kissling, F., Schöfl, T., Stengel, F. C., Gianoli, D., Motov, S., Schonfeld, E., Veeravagu, A., Martens, B., & Hejrati, N. (2025). Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) with Expandable Banana-Shaped Interbody Spacers—Institutional 5-Year Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155402






