Pars Plana Vitrectomy Combined with Anti-VEGF Injections as an Approach to Treat Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
Therapy
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
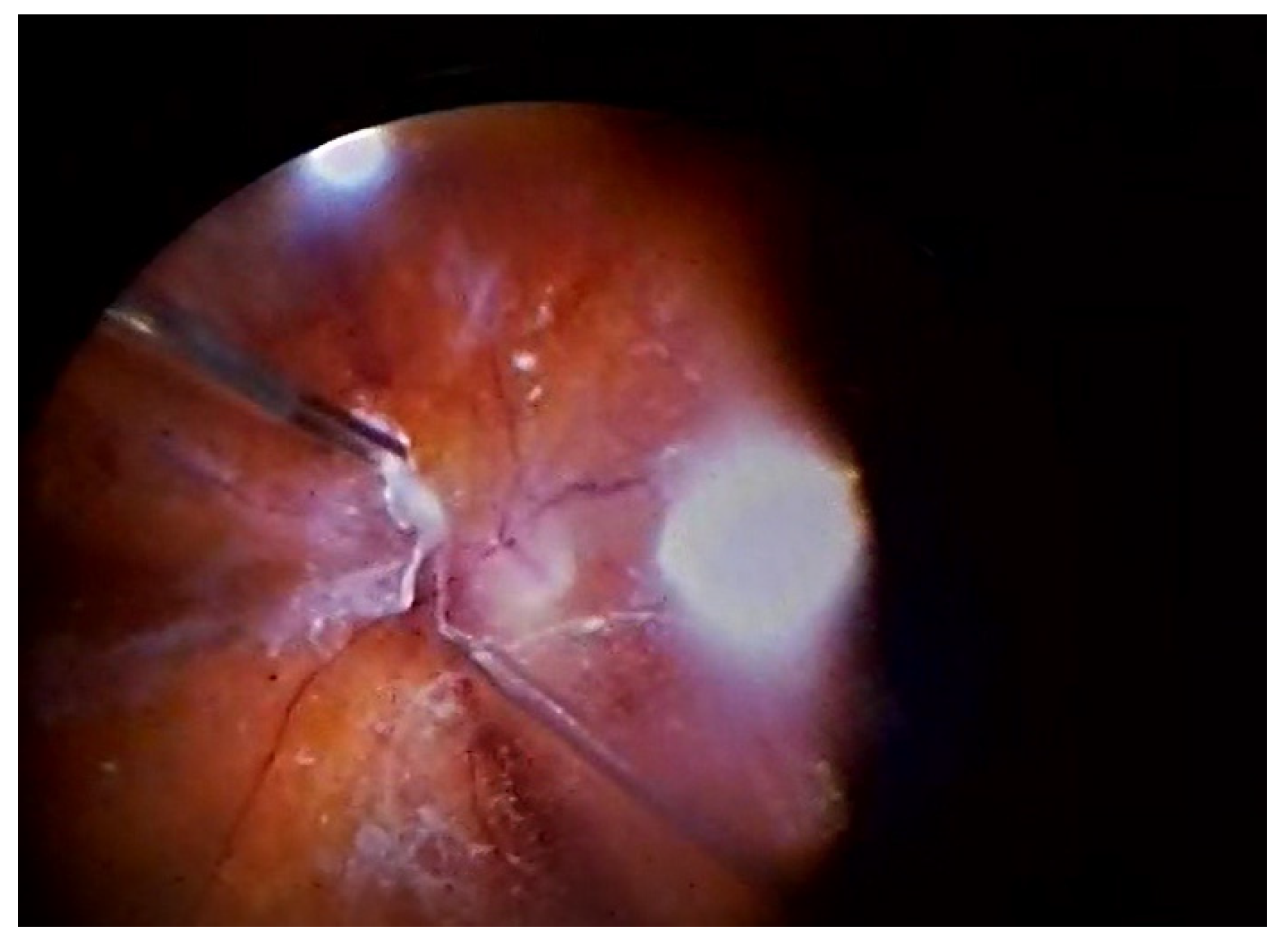
2.3. Surgery
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Course of the Procedure
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDR | Proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| RD | Diabetic retinopathy |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| DME | Diabetic macular oedema |
| NPDR | Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| NCVH | Non-clearing vitreous haemorrhage |
| CMT | Central macular thickness |
| FVM | Fibrovascular membranes |
| VH | Vitreous haemorrhage |
| RNFL | Retinal nerve fibre layer |
| NVG | Neovascular glaucoma |
| TRD | Tractional retinal detachment |
| POVCH | Postoperative vitreous cavity haemorrhage |
| TSCPC | Transscleral Cyclophotocoagulation |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani, M.; Eviatar, T.; Komaneshter, D.; Vinker, S. Diabetic retinopathy-incidence and risk factors in a community setting—A longitudinal study. Scand. J. Prim. Healthcare 2018, 36, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, V.; Eigentler, T.K. Pathogenesis of diabetic macro- and microangiopathy. Clin. Nephrol. 2008, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.E.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: Looking forward to 2030. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1077669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reddy, S.K.; Devi, V.; Seetharaman, A.T.M.; Shailaja, S.; Bhat, K.M.R.; Gangaraju, R.; Upadhya, D. Cell and molecular targeted therapies for diabetic retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1416668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bressler, N.M.; Beaulieu, W.T.; Glassman, A.R.; Blinder, K.J.; Bressler, S.B.; Jampol, L.M.; Melia, M.; Wells, J.A.; Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network. Persistent macular thickening following intravitreous aflibercept, bevacizumab, or ranibizumab for central-involved diabetic macular edema with vision impairment: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Cortes, J.H.; Martinez-Pacheco, V.A.; Gonzalez-Cantu, J.E.; Bilgic, A.; De Ribot, F.M.; Sudhalkar, A.; Mohamed-Hamsho, J.; Kodjikian, L.; Mathis, T. Current treatments and innovations in diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatziralli, I.; Touhami, S.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Agapitou, C.; Dimitriou, E.; Theodossiadis, G.; Theodossiadis, P. Disentangling the association between retinal non-perfusion and anti-VEGF agents in diabetic retinopathy. Eye 2022, 36, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.H.; Roberts, G.E.; Liu, G.S. Updates on gene therapy for diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, S. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: What can we learn at 14 years? Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 1799–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M.; Chen, M.; Medina, R.J.; McKay, G.J.; Jenkins, A.; Gardiner, T.A.; Lyons, T.J.; Hammes, H.P.; Simo, R.; et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 51, 156–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadakar, K.; Rahmani, S.; Tedeschi, T.; Lavine, J.A.; Fawzi, A.A. Short Term Effect of Pre-Operative Anti-VEGF on Angiogenic and Fibrotic Profile of Fibrovascular Membranes of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dervenis, P.; Dervenis, N.; Smith, J.M.; Steel, D.H. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factors in combination with vitrectomy for complications of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 5, CD008214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- The Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Photocoagulation treatment of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Clinical application of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (DRS) findings, DRS Report Number 8. Ophthalmology 1981, 88, 583–600. [Google Scholar]
- Bromeo, A.J.; Veloso, A.; Lerit, S.J.; Gomez, M.C. Tractional retinal detachment (‘crunch’ phenomenon) from intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injection in central retinal vein occlusion. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e240506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schreur, V.; Brouwers, J.; Van Huet, R.A.; Smeets, S.; Phan, M.; Hoyng, C.B.; de Jong, E.K.; Klevering, B.J. Long-term outcomes of vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, P.; Mohite, A.; Virgili, G.; Lois, N. Outcomes and complications of pars plana vitrectomy for tractional retinal detachment in people with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023, 141, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, C.; Fang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qiu, C. Optimal timing of preoperative intravitreal anti-VEGF injection for proliferative diabetic retinopathy patients. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 15, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koca, S.; Kılıç, D. Long-term longitudinal retinal changes after conventional and pattern scan laser panretinal photocoagulation in diabetic retinopathy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 44, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Fukutomi, A.; Sun, M.T.; Durkin, S.; Gilhotra, J.; Chan, W.O. Anti-VEGF crunch syndrome in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2021, 66, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Wang, C.G.; Dou, H.L.; Feng, X.F.; Xu, Y.M.; Ma, Z.Z. Effect of intravitreal ranibizumab pretreatment on vitrectomy in young patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Zou, J.; Zeng, J.; Ding, C. The efficacy and safety of intravitreal injection of Ranibizumab as pre-treatment for vitrectomy in proliferative diabetic retinopathy with vitreous hemorrhage. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pérez-Argandoña, E.; Verdaguer, J.; Zacharías, S.; González, R. Preoperative intravitreal bevacizumab for proliferative diabetic retinopathy patients undergoing vitrectomy—First update. Medwave 2019, 19, e7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M.; Steel, D.H. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for prevention of postoperative vitreous cavity haemorrhage after vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD008214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Groups | Study Parameters | Age—Years | Visual Acuity logMAR (Operated Eyes) | Intraocular Pressure (Operated Eye) | Visual Acuity (Non-Operated Eye) | Intraocular Pressure (Non-Operated Eye) | Rubeosis | Proliferations | Tractions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Group (anti-VEGF) | Mean and Standard deviation | 57.18 ± 14.33 | 0.14 ± 0.14 | 17.37 ± 3.39 | 0.40 ± 0.31 | 16.49 ± 4.09 | 0.14 ± 0.35 | 0.84 ± 0.37 | 0.26 ± 0.44 |
| Range | 23.0–90.00 | 0.01–0.60 | 7.00–28.0 | 0.01–1.04 | 5.00–40.0 | 0.0–1.00 | 0.0–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | |
| Control Group (no anti-VEGF) | Mean and Standard deviation | 62.35 ± 12.98 | 0.10 ± 0.20 | 17.33 ± 4.06 | 0.30 ± 0.34 | 16.34 ± 2.98 | 0.08 ± 0.27 | 0.83 ± 0.38 | 0.23 ± 0.42 |
| Range | 23.0–90.0 | 0.00–1.00 | 5.00–37.00 | 0.00–1.81 | 6.00–25.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | |
| p | 0.0064 | 0.0001 | 0.89 | 0.0001 | 0.97 | 0.15 | 0.86 | 0.65 |
| Group | Study Parameters | Intraoperative Haemorrhage | Retinl Breaks | Visual Acuity (Operated Eye) | IOP—(Operated Eyes) | Visual Acuity (Non-Operated Eyes | IOP—(Non-Operated Eyes) | Anterior Chamber Hyphema | Retinal Detachment | Ocular Hypotony | Glaucoma | Surgery Duration | Repeat Surgery | Number of Anti-Glaucoma Drugs | TSCPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study group (anti-VEGF) | Mean and SD | 0.97 ± 0.86 | 0.34 ± 0.56 | 0.24 ± 0.27 | 16.84 ± 6.25 | 0.26 ± 0.35 | 17.65 ± 4.42 | 0.12 ± 0.33 | 0.05 ± 0.22 | 0.08 ± 0.27 | 0.26 ± 0.44 | 47.62 ± 9.87 | 0.23 ± 0.46 | 0.48 ± 1.11 | 0.25 ± 0.49 |
| Range | 0.00–4.00 | 0.00–2.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 4.00–40.00 | 0.00–3.00 | 5.00–30.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 30.00–95.00 | 0.00–2.00 | 0.00–4.00 | 0.00–2.00 | |
| Contro group (no anti- VEGF) | Mean and SD | 1.51 ± 1.22 | 0.56 ± 0.76 | 0.37 ± 0.45 | 17.78 ± 6.22 | 0.31 ± 0.24 | 18.79 ± 3.88 | 0.28 ± 0.45 | 0.10 ± 0.31 | 0.10 ± 0.31 | 0.47 ± 0.5 | 50.05 ± 9.41 | 0.12 ± 0.33 | 0.67 ± 1.22 | 0.30 ± 0.52 |
| Range | 0.00–4.00 | 0.00–3.00 | 0.01–4.00 | 4.00–33.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 11.00–26.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 1.00–70.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–4.00 | 0.00–2.00 | |
| p | 0.003 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.147 | 0.49 | 0.0006 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leszczyński, R.; Olszowski, W.; Jaworski, M.; Górska, A.; Lorenc, A.; Jastrzębska-Miazga, I.; Pawlicki, K. Pars Plana Vitrectomy Combined with Anti-VEGF Injections as an Approach to Treat Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155349
Leszczyński R, Olszowski W, Jaworski M, Górska A, Lorenc A, Jastrzębska-Miazga I, Pawlicki K. Pars Plana Vitrectomy Combined with Anti-VEGF Injections as an Approach to Treat Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155349
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeszczyński, Rafał, Wojciech Olszowski, Marcin Jaworski, Aleksandra Górska, Anna Lorenc, Irmina Jastrzębska-Miazga, and Krzysztof Pawlicki. 2025. "Pars Plana Vitrectomy Combined with Anti-VEGF Injections as an Approach to Treat Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155349
APA StyleLeszczyński, R., Olszowski, W., Jaworski, M., Górska, A., Lorenc, A., Jastrzębska-Miazga, I., & Pawlicki, K. (2025). Pars Plana Vitrectomy Combined with Anti-VEGF Injections as an Approach to Treat Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155349




